Osteoarthritis and AVN
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Osteoarthritis (OA)
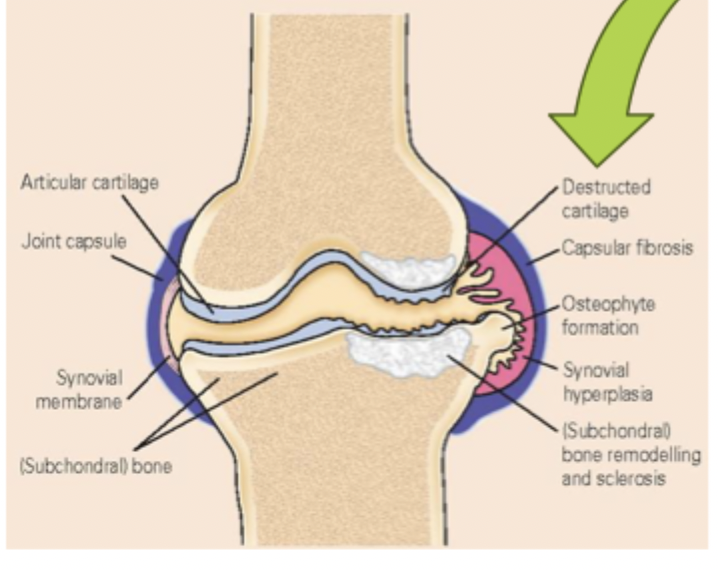
The most common cause of chronic disability due to pain and altered joint function that mostly affects middle-age or elderly people (40+) due to the “wear and tear” of the joints
Subchondral bone, cartilage, ligaments, capsule, synovial membrane, and surrounding muscle
OA involves what parts of the joint
osteophytes (making joints swollen, painful, and stiff)
Breakdown of cartilage in joint causes bone-on-bone action and may lead to
neck, hands, shoulders, lower back, hips, knees
Common sites of primary OA
increasing age, genetics, obesity, joint deformities, repetitive stress of the joint, manual labor, high impact sports
Risk factors for primary OA
primary, Secondary (caused by something else - disease, trauma, infection, etc)
Types of OA
Congenital hip dislocation, hip dysplasia, joint hypermobility, gout, hemochromatosis, bone fractures (near a joint), joint dislocation, ligament injuries, inflammatory or infectious arthropathy, AVN
Risk factors for Secondary OA
pro-inflammatory mediators (macrophage 1 - joint destruction), Anti-inflammatory cytokines (macrophage 2 - repair damage)
OA is characterized by the presence of ______________ and __________________
arthralgia, stiffness in the morning or after inactivity, tender to palpation, decreased ROM, crepitus, swelling of the joint, effusion, limb discrepancy, valgus/varus knees, Kyphosis
Common symptoms of OA
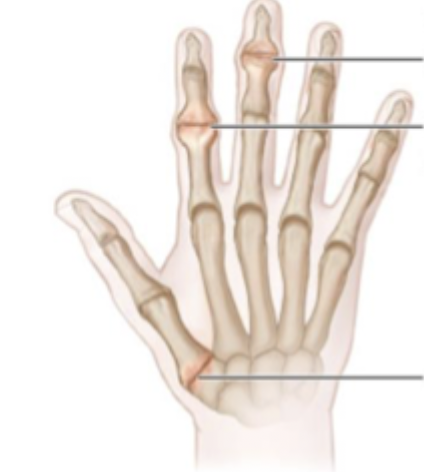
Heberden’s node
Appear on the DIP joint - may be associated with a digital myxoid pseudocyst
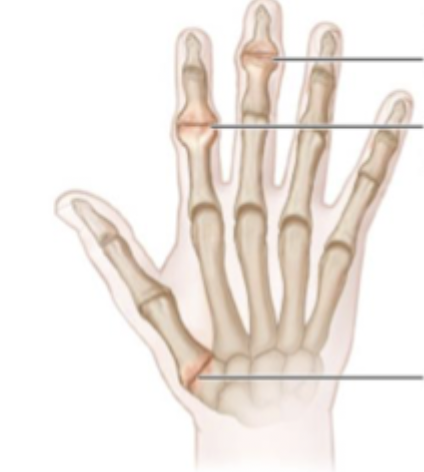
Bouchard’s nodes
Appear on the PIP joints
Weightbearing x-rays (abnormal in moderate to late OA), labs or joint arthrocentesis if you need to r/o any
Diagnostic techniques for OA
Grade 0
Which stage of OA is characterized by NO joint space narrowing (JSN)
grade 1
Which stage of OA is characterized by possible osteophytic lipping and doubtful JSN
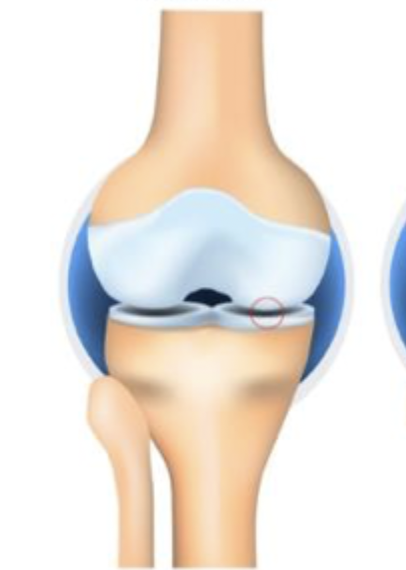
grade 2
Which stage of OA is characterized by definite osteophytes and possible JSN
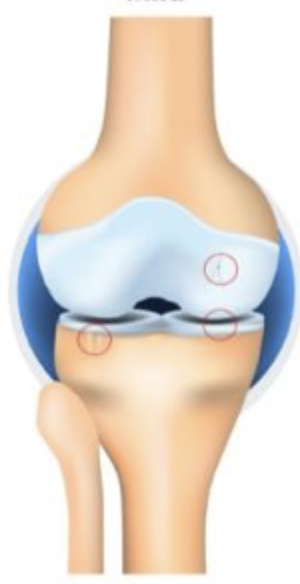
Grade 3
Which stage of OA is characterized by moderate osteophytes, definite JSN, sclerosis, possible bone end deformity
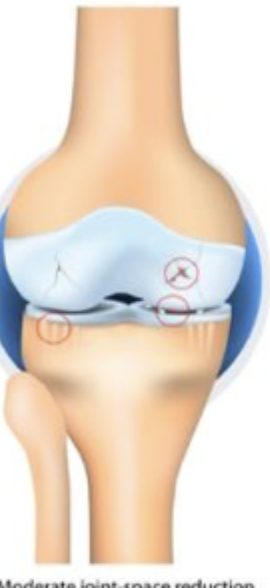
Grade 4
Which stage of OA is characterized by large osteophytes, marked JSN, severe sclerosis, and definite bone end deformity
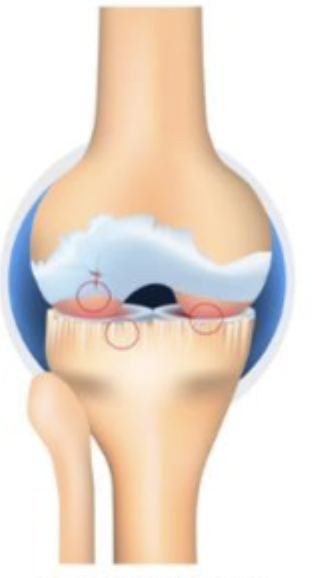
NSAIDs (topical/oral), rehab, weight loss, bracing (short term), joint injections (steroids, hyaluronic acid, platelet rich plasma), foot wedge insoles, glucosamine, chondroitin (maybe)
Non-operative management for OA
Tylenol, oral NSAIDs, topical (diclofenac), tramadol (avoid)
Analgesics for OA
ROM exercises, strengthening, non-impact (3x a week)
PT measures for OA - preserves and builds strength (improves post-op outcomes as well)
knee, ankle feet (losing weight will slow progression and keep other systems healthy)
BMI is directly correlated to progression of what types of OA
deteriorate bone, progressive cartilage damage, weakened bone/ligaments/tendone
Why can we only do 3 steroid injections per year in a joint (doesn’t cure just improves function)?
Hyaluronic acid (NO WEIGHT BEARING FOR 24 HOURS)
What type of injection can be done q 6 months and increases the viscoelasticity of synovial fluid for patients who have failure corticosteroid injection?
Platelet-Rich Plasma
What type of injection is prepared via venous blood draw which is then centrifuged to separate the plasma from RBCs usually done every 3-6 weeks - NOT FDA approved
4x
Losing 1 lb results in __ reduction in knee joint load in the obese
Glucosamine
An amino sugar required for the synthesis of glycoprotein found in the synovial fluid, ligaments, and other joint structures
Chondroitin
A building block for the formation of the joint matrix structure and is usually combined with another supplement
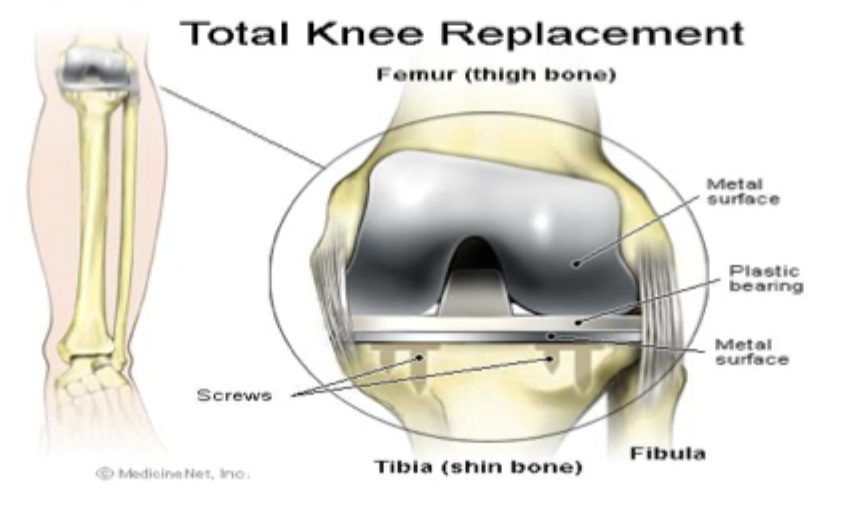
High-tibial osteotomy, joint arthroplasty, arthroscopic debridement
Operative management of OA
Avascular necrosis (AVN, osteonecrosis)
A disruption to the subchondral blood supply causing the death of cellular bony components (which can lead to the collapse of the bone)
femoral head (most common), knee, humeral head
Common sites of AVN
talus, wrist (scaphoid, lunate)
Less common sites of AVN
cellular toxicity (chemo, radiation, excessive EtOH and tobacco), trauma, long-term steroid use, vascular (arterial abnormalities, venous abnormalities, coag disorders, sickle cell crisis)
Risk factors for AVN
Xrays, MRI (early diagnosis)
78 y/o female presents to the clinic for hip pain that worsens with weight bearing. She is currently on chemo for breast cancer. She notes that her hips have been stiff and that it has been getting worse over the last few months. What diagnostics do you want?
sclerosis in later stages → subchondral collapse
Signs of AVN on x-ray
normal xrays but MRI reveals death of the bone
Stage I of AVN is characterized by
Can be seen more on regular x-rays without collapse of the femoral head
Stage II of AVN is characterized by
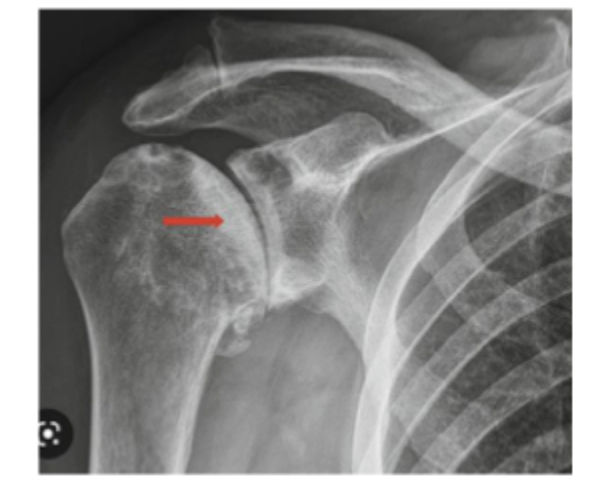
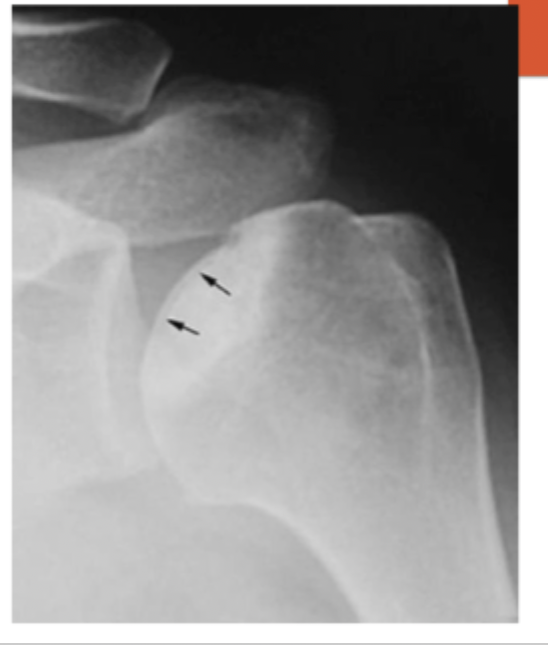
xrays show signs of collapse “crescent signs”
Stage III of AVN is characterized by
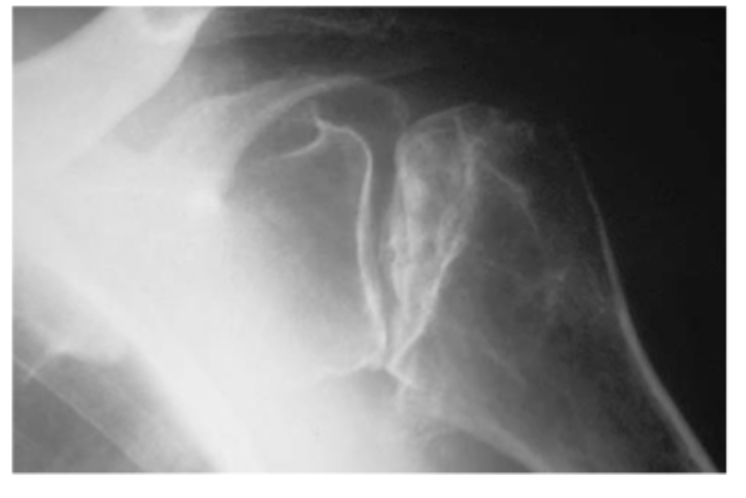
x-ray has collapse and signs of cartilage damage (arthritis)
Stage IV of AVN is characterized by
NSAIDs or Tylenol for symptomatic relief, therapy to maintain joint ROM and strengthening, Activity modification
Conservative management of AVN
Core decompression (very early stages), vascularized bone grafting, osteotomy, joint replacement
Surgical management of AVN (depends on stage and joint)
will worsen with time if left untreated, bone collapses leading to severe arthritis
Complications of AVN
limit alcohol intake, keep cholesterol levels low, monitor steroid use, avoid tobacco
Prevention of AVN