IB Biology SL - Carbon, Macromolecules, Functional groups
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Carbon-based molecules make up:
all living things = organic chemistry
Which carbon molecules do not make up life?
carbon dioxides: CO, CO2
carbonates: CO32-
hydrocarbonate: HCO3-
methane: CH4
How many bonds does carbon make?
4 covalent bonds.
tetravalent
making 4 covalent bonds (e.g Carbon)
Carbon skeletons
chains of C. (can occur straight, branched, ringed, attached to other things.)
Hydrocarbons
Carbon skeleton with just hydrogens attached
non-polar → hydrophobic
hydrocarbons are seen in phospholipid layers for this reason.
Isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula, but different forms.
e.g. butane is C4H10 → isobutane has a different structure.
Geometric isomers
What is a functional group?
Things attached to C skeleton that are involved in chemical reactions.
A certain group of atoms or bonds within a molecule that determines its properties.
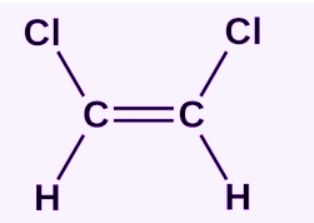
Cis isomer
note Cl is a placeholder for X
formula is C2H2X2
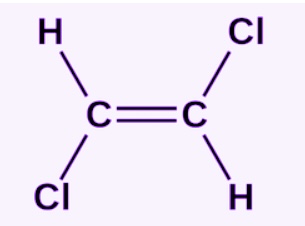
Trans isomer
note Cl is a placeholder for X
formula is C2H2X2
Enantiomers
Mirror image isomers → left / right hand
What are macromolecules?
Large molecule made of repeating identical / similar subunits (monomers).
What are polymers, what do they make up?
Large molecules made up of small repeating monomers. They make up macromolecules.
How is a polymer made?
dehydration synthesis reactions (aka condensation).
when 2 monomers are covalently bonded together through the removal of a water molecule.
anabolic reaction
costs E (ATP) + usually require enzymes
How are polymers broken apart?
hydrolysis reactions
when a covalent bond between monomers is broken by the addition of water.
catabolic reaction
Release E (e.g. digestion)
Hydroxyl
- OH → R-OH
an O bonded to C skeleton and a H.
makes up alcohols ex: ethanol, isopropyl alcohol
polar molecule + will dissolve in water
Carbonyl
CO
C double bonded to an O and single bonded to C skeleton.
ex: formaldehyde, acetone.
where the double bond occurs determines properties.
Carboxyl
-COOH
C with a double bonded O2, Sb-OH, and bonded to C skeleton.
carboxylic acids
e.g. acetic acids (vinegar)
donate H+: -COOH → COO- + H+
Amino
-NH2
N bonded to C skeleton and 2 Hs
monomers of proteins
accept H+ (base)
NH2 + H+ → NH3+
They are buffers!
NH2 and COOH
Sulfhydryl
-SH
- S bonded to C-skel and H
make up thiols
Stabilize the structure of large molecules, like proteins.
Phosphate
-PO4-
ion bonded to C skeleton
e.g. ATP and DNA
create energy transfers