histology unit 4,5,6
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hooooo boy, strap in and git 'er done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
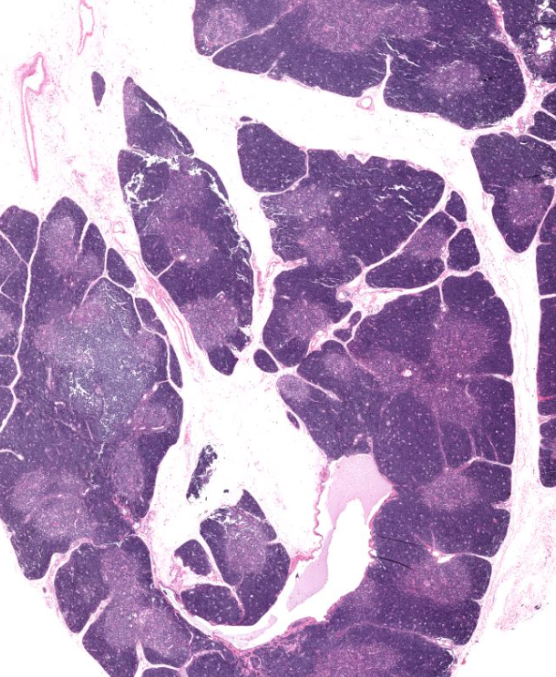
thymus
exocrine, produces T cells
not present as much in adults
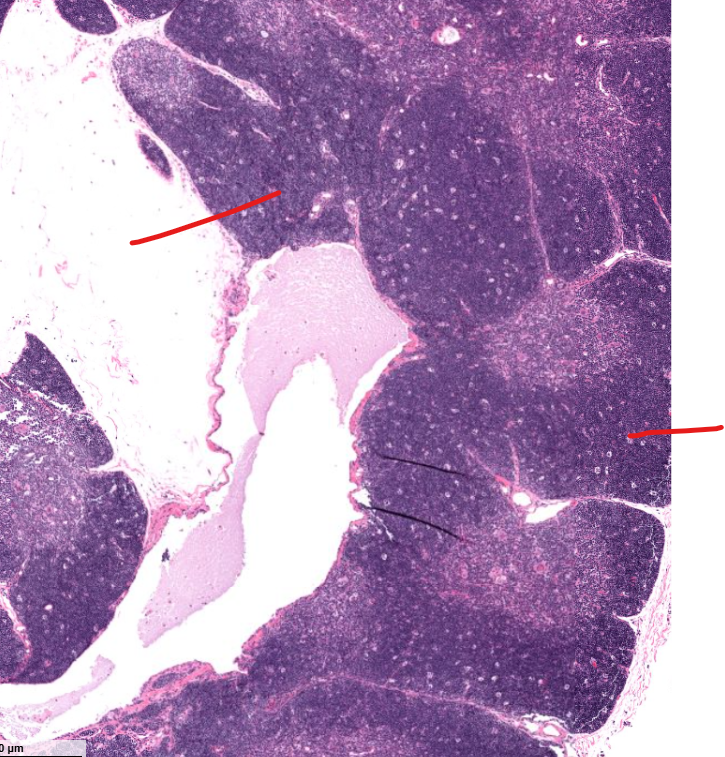
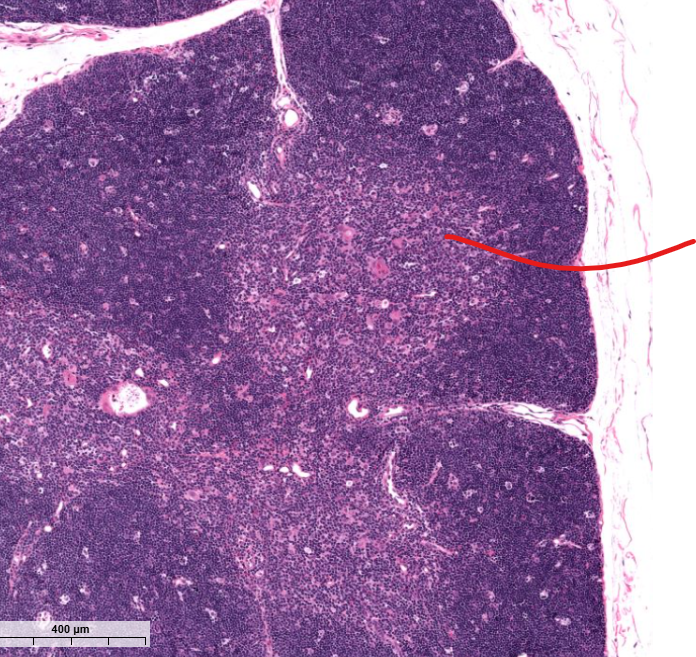
cortex of the thymus
contains t cells
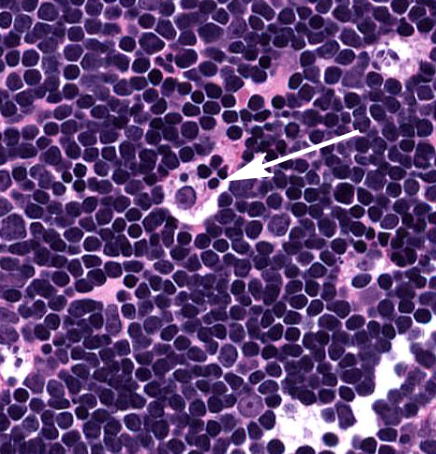
macrophage (shown in the thymus)
medulla of the thymus
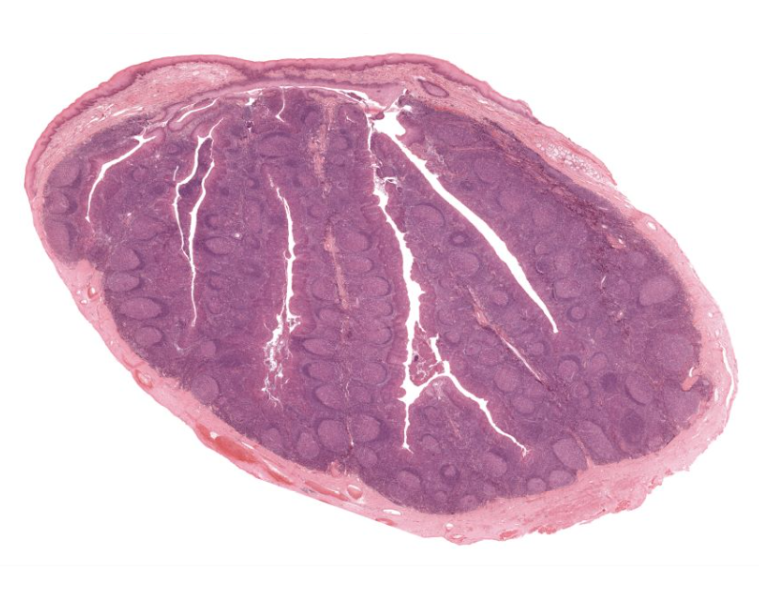
tonsil
pat of lymph system
produces WBCs
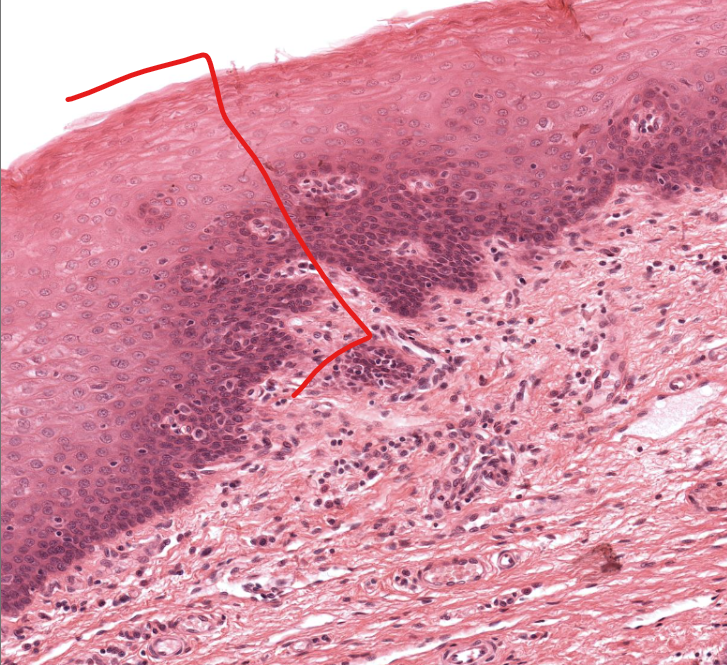
(tissue type)
stratified squamous epi
shown on the tonsil
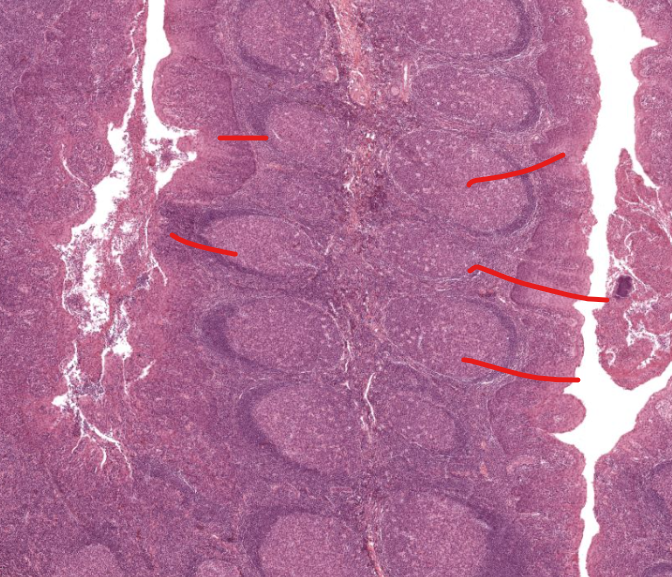
lymph nodules
aggregation of lymphocytes that have germinal centers
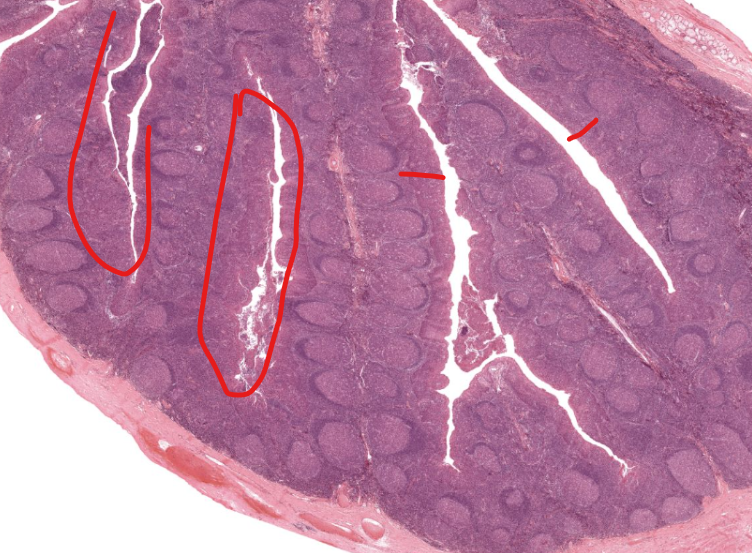
crypts of tonsils
where the food and such enters/is tested
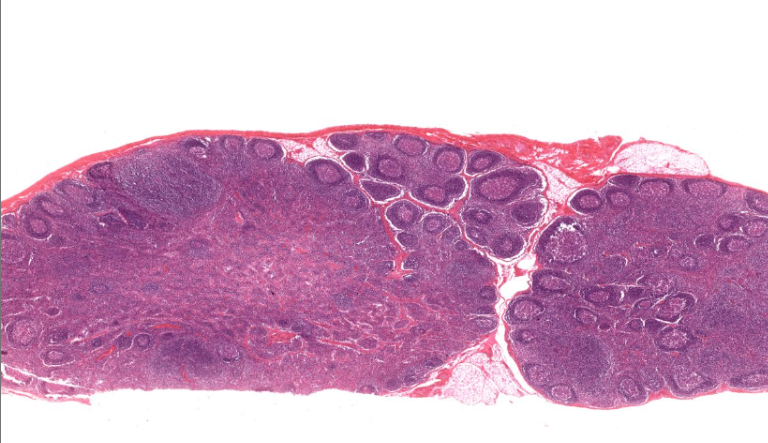
lymph node
clumps/clusters
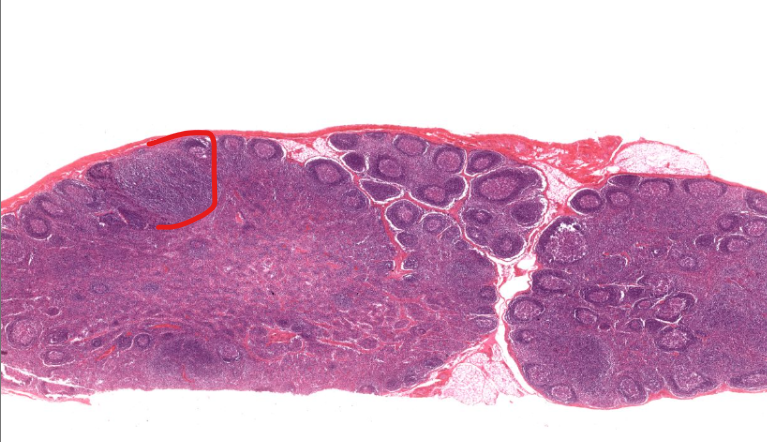
region of organ
cortex of lymph node
region of organ

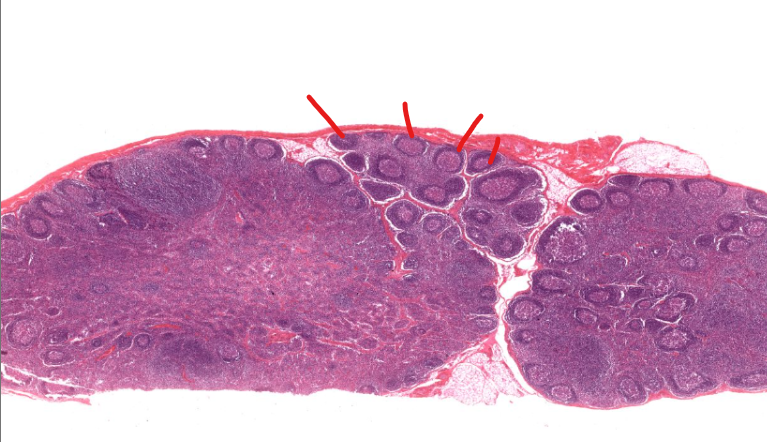
(structure)
nodules
spleen
solid organ
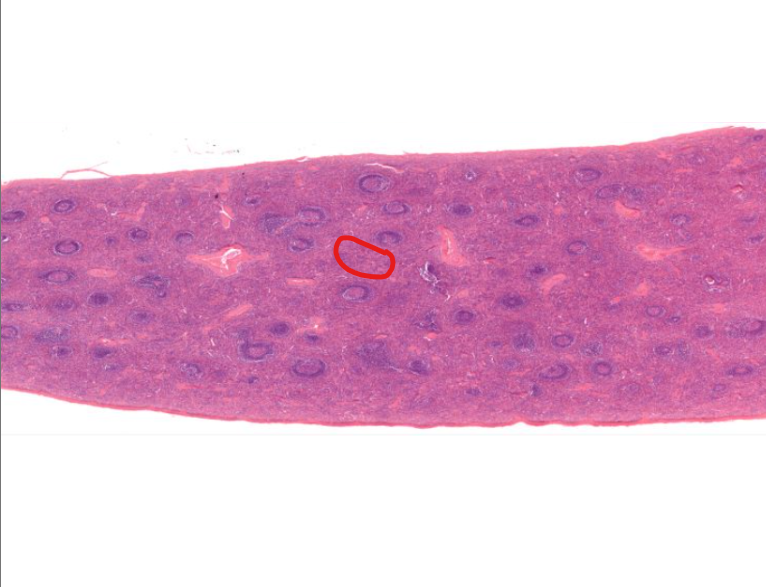
“white” pulp
made up of lymphocytes
lots of basophils
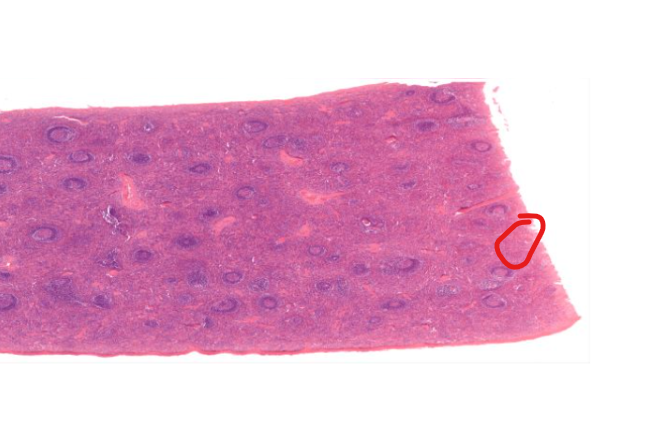
“red” pulp
filters and degrades RBCs
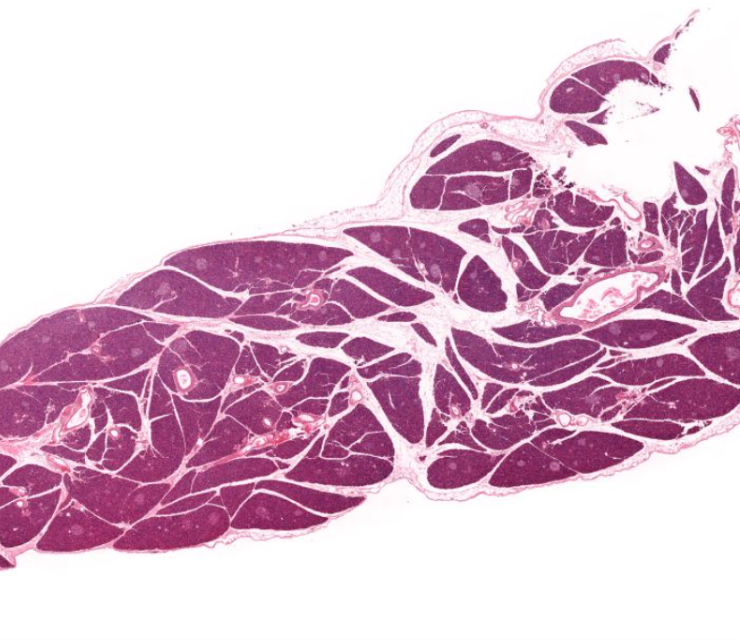
pancreas
looks like a shitty purple unicorn horn
exocrine secretes digestive enzymes
endocrine releases insulin and glucagon
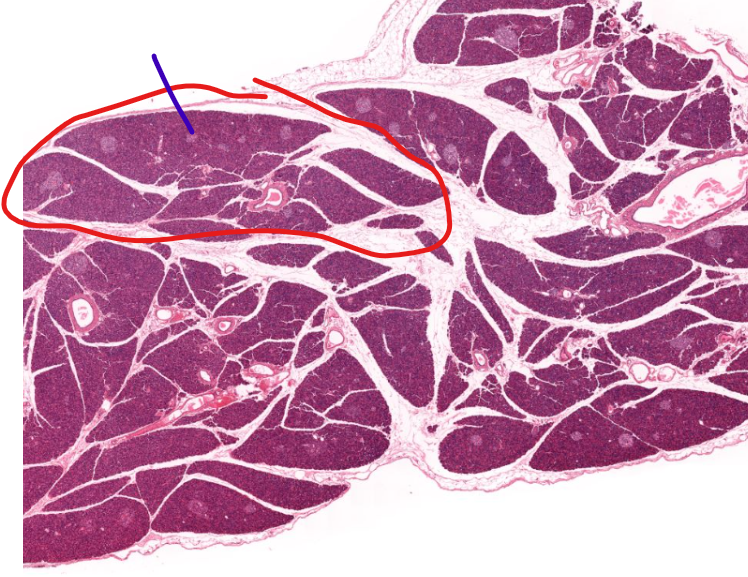
lobe (red) and lobule (blue) of the pancreas
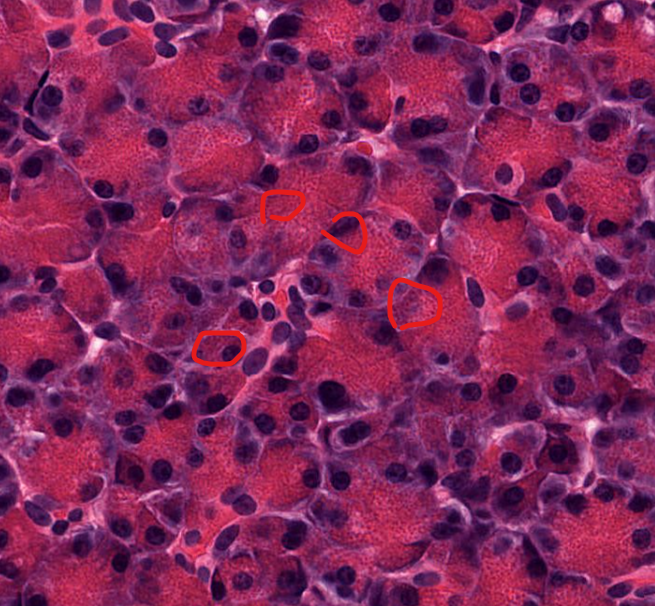
type of cell
exocrine cells of the pancreas
secrete insulin and glucagon
shaped like a slice of pie
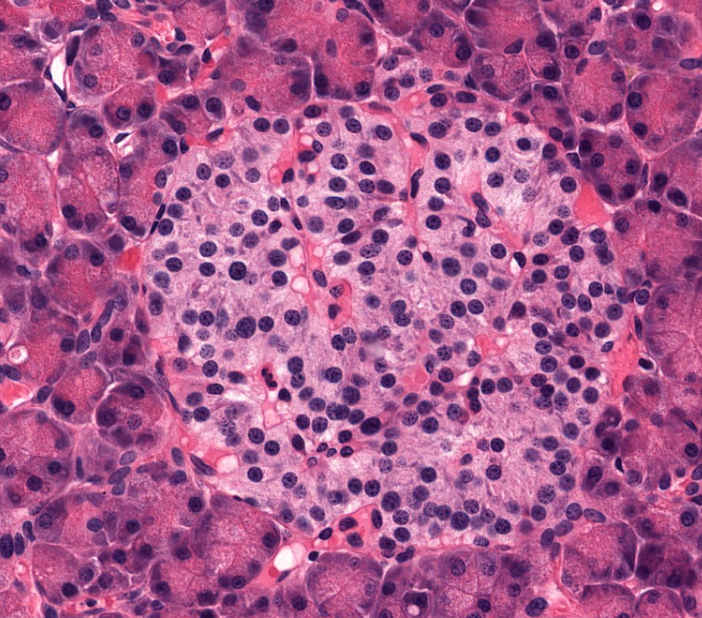
structure
islet of Langerhans of the pancreas
endocrine cell
secrete hormones for digestion
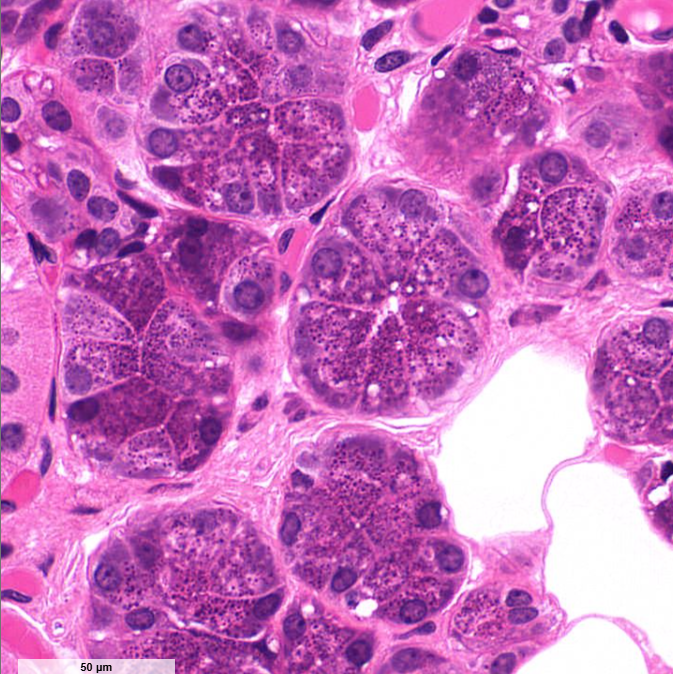
parotid gland
you can tell bc of the of the white holes
secretes mucus and watery fluid
serous cells of the salivary glands
secrete serous fluid
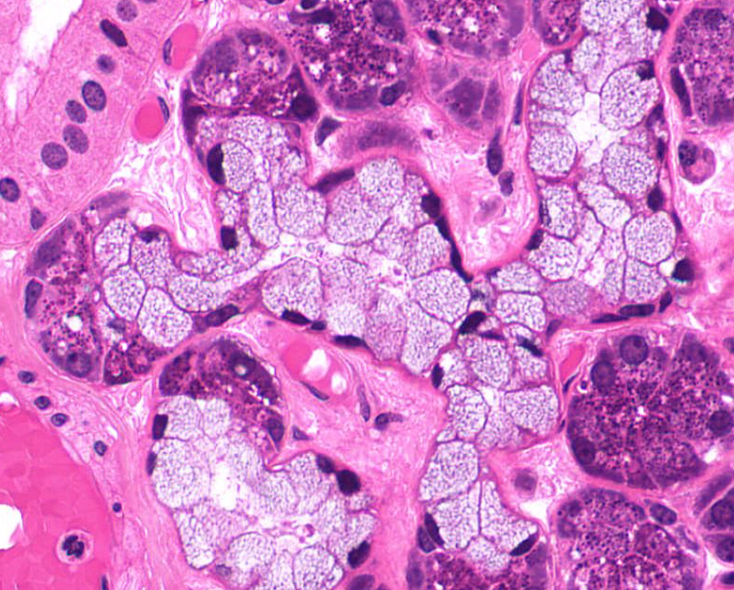
mucous cells of the salivary gland
secrete mucus
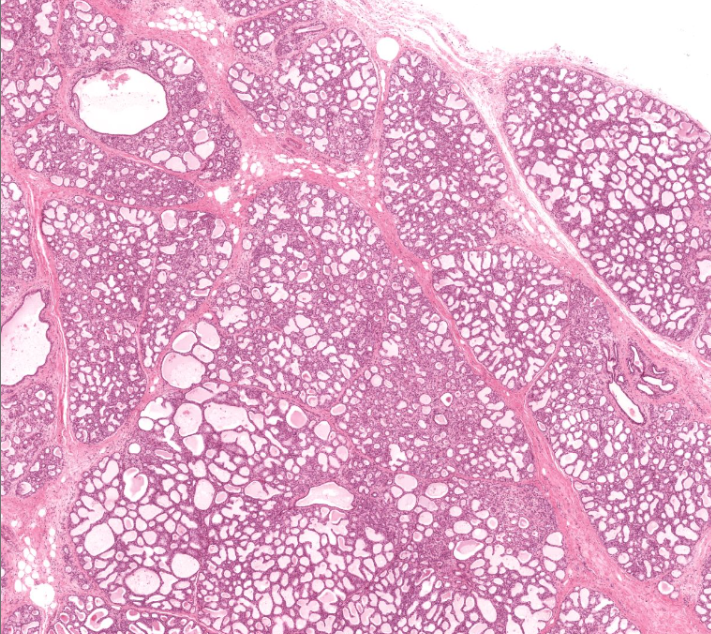
mammary gland
has many open holes, of varying sizes
has very light pink in open holes
produces milk
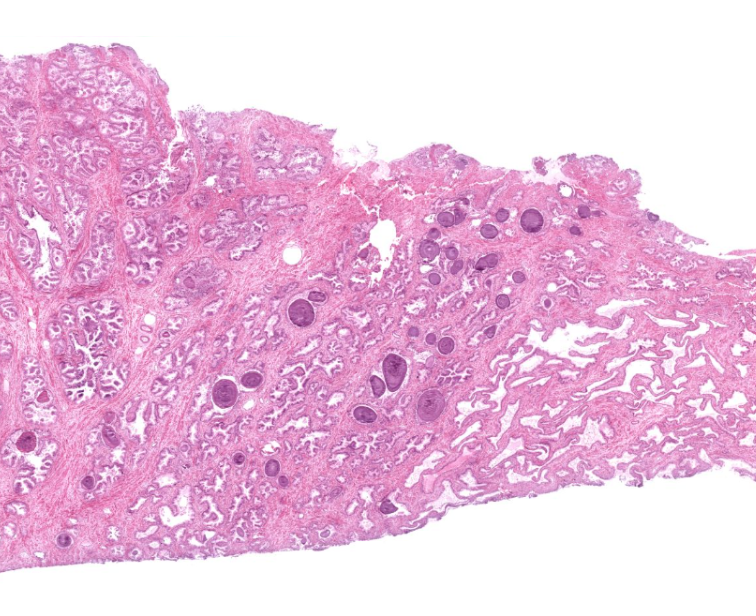
prostate gland
secretes prostatic fluid???
identifiable by the dark purple structures
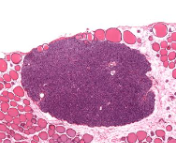
parathyroid gland
identifiable by the fact its dark purple
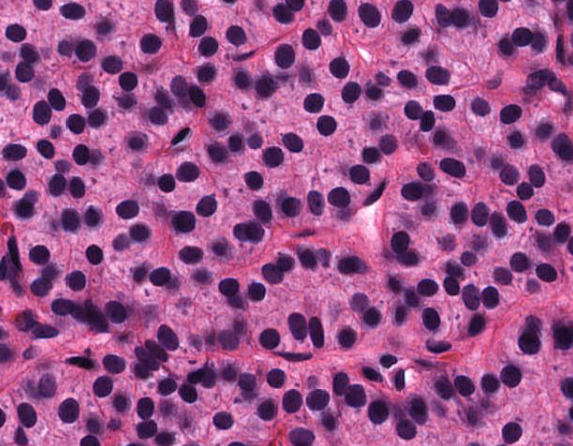
chief cells of parathyroid gland
thymus
LARGE tightly packed lymphocytes
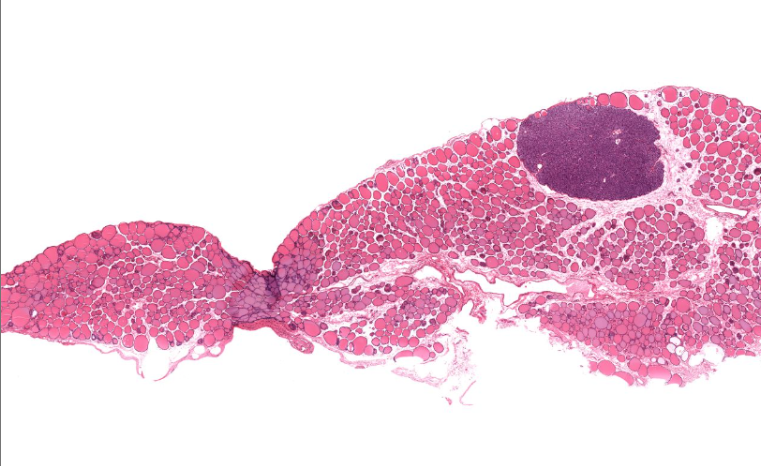
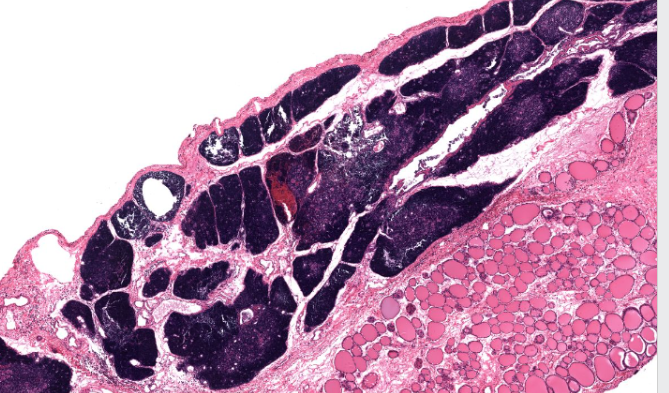
thyroid gland
pretty opaque pink colloid
identifiable by the follicles
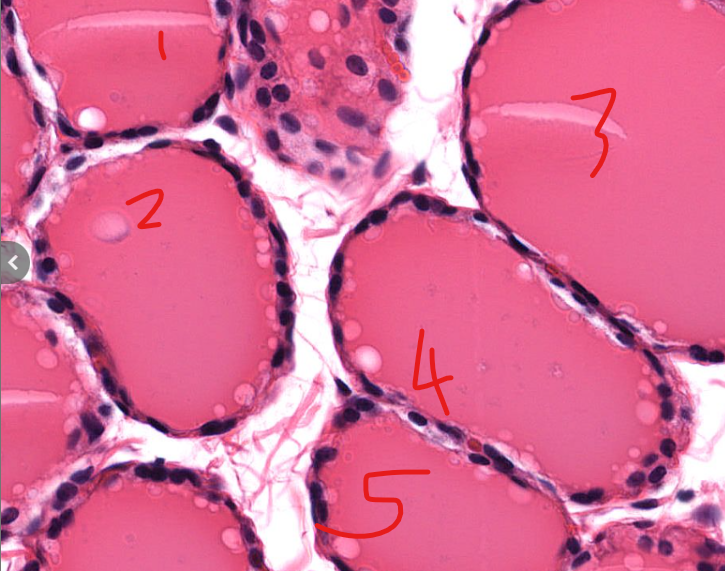
thyroid follicles
the precursor of thyroid hormones
pituitary gland

anterior pituitary
secretes GH, prolactin, ACTH, TSH, FSL, LH
chromaphils of the pituitary
secrete hormones
chromaphobes of the pituitary
do not secrete hormones
posterior pituitary
secretes ADH and oxytocin
mostly made up of neurons
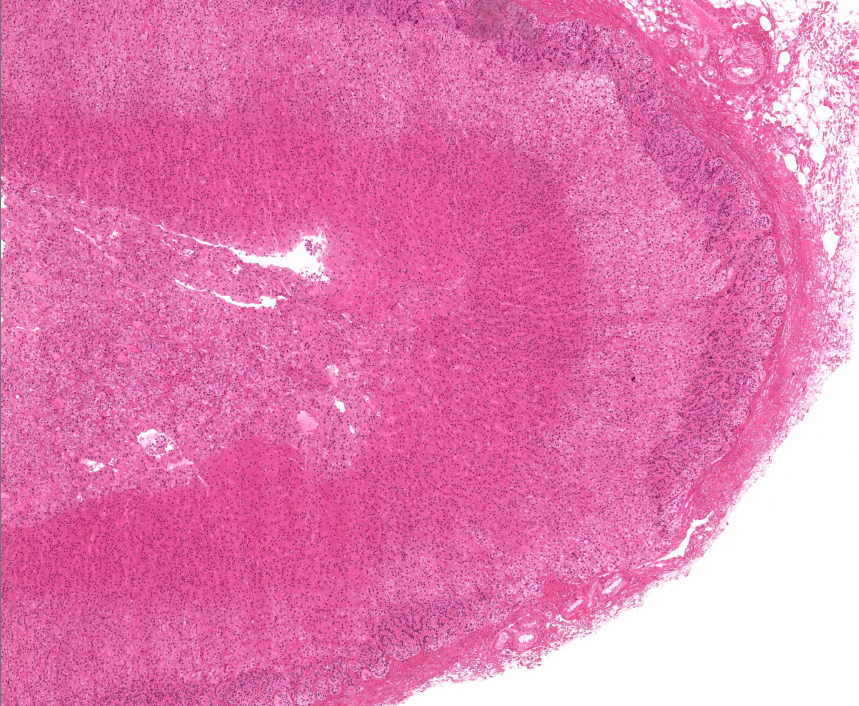
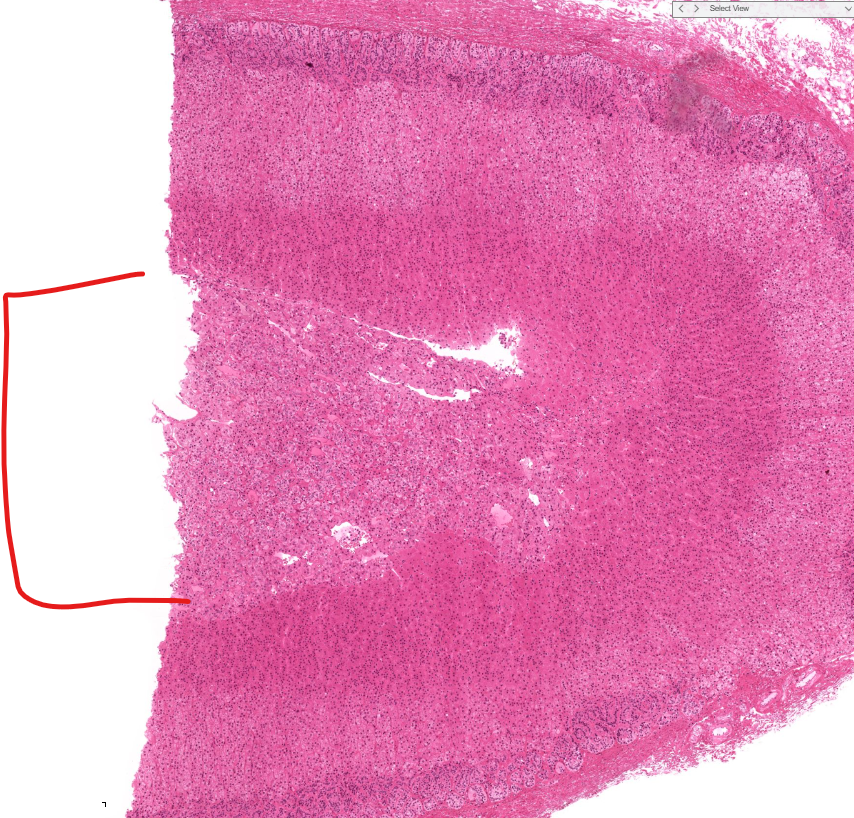
adrenal gland

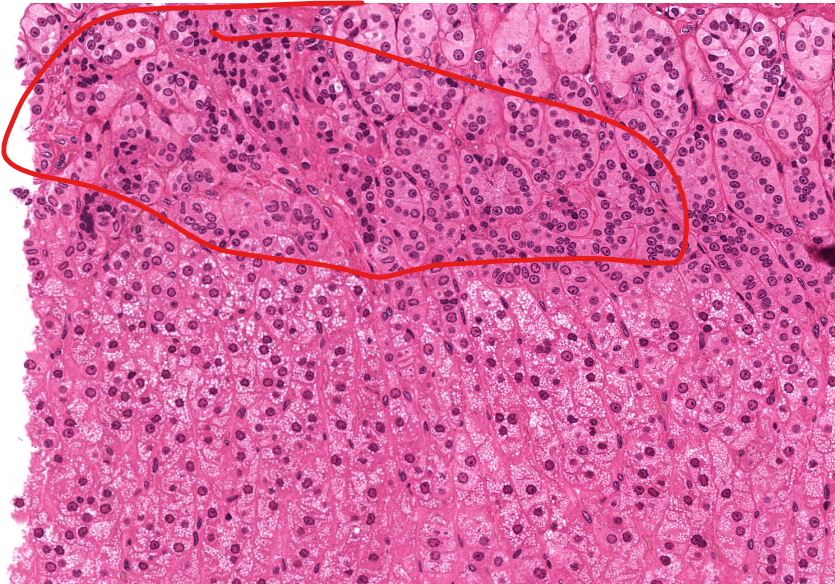
capsule of adrenal gland
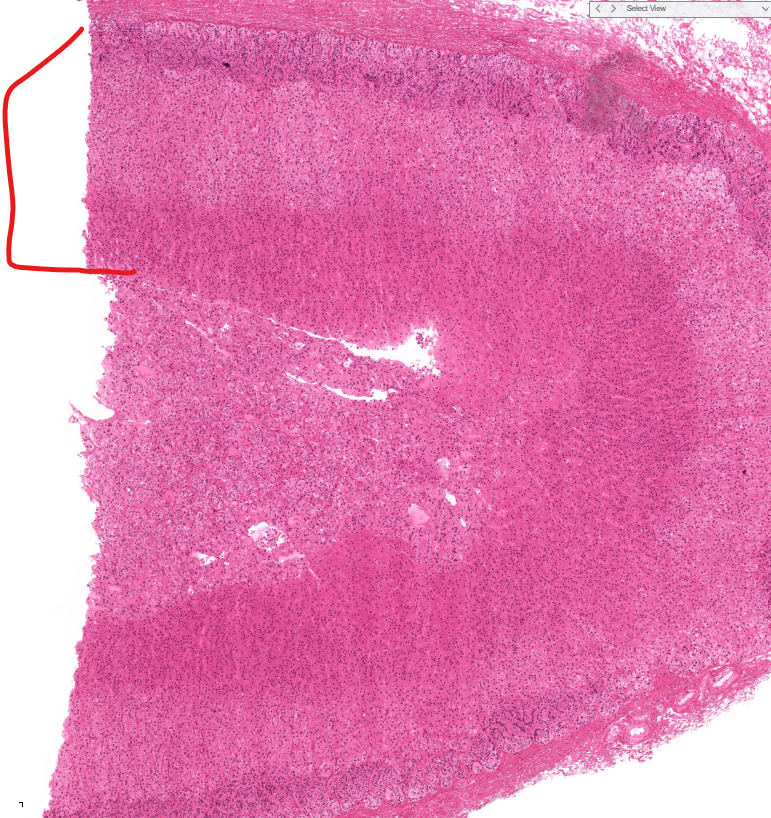
adrenal cortex
made up of zona glomerulosa (aldosterone)
zona fasiculata (cortisol)
zona reticularis (sex hormones)
adrenal medulla
secretes catecholamines
(layer)
zona glomerulosa of the adrenals
secretes aldosterone
has lots of dark spots

(layer)
zona fasiculata of the adrenals
secretes cortisol
has the trabeculae and one central nucleus
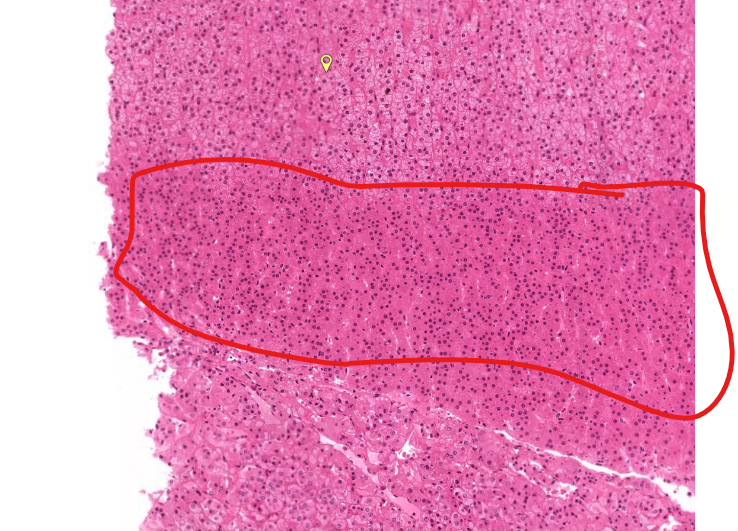
(layer)
zona reticularis
secretes precursors to testosterone
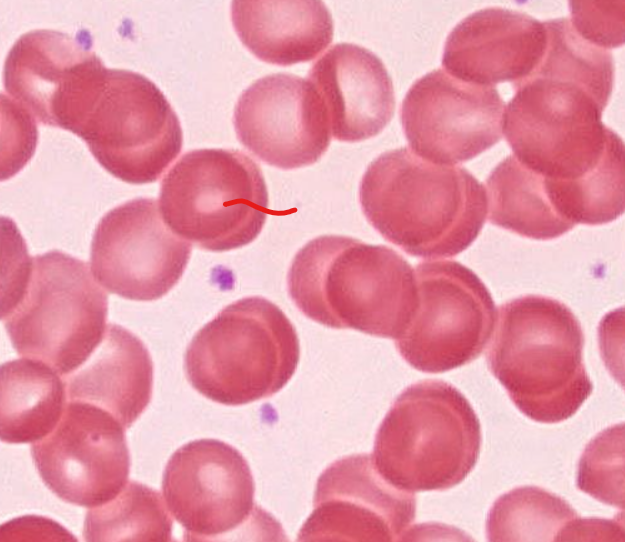
RBC
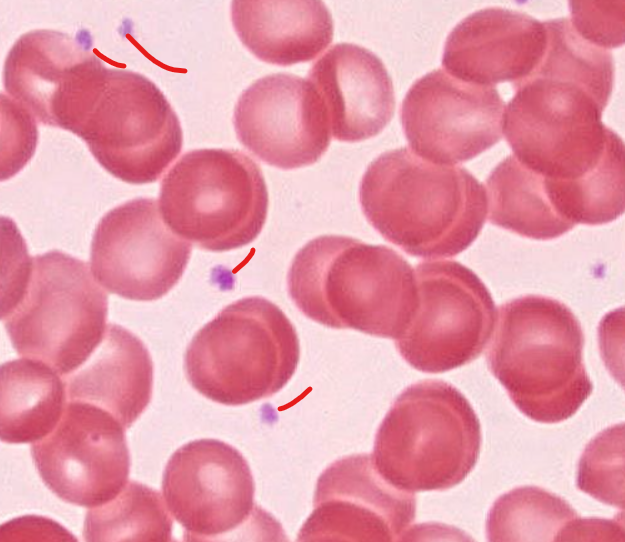
platelets

neutrophil
polymorphonucleic
lighter outside stain/granules

eosinophils
red granules
double lobed nuclei
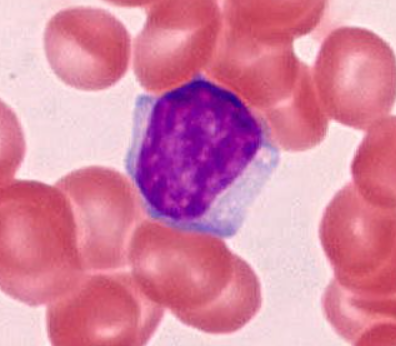
lymphocyte
purpley, not a huge amount of cell visible outside of the nucleus

monocyte
massive
usually kidney bean shaped nuclei

aorta
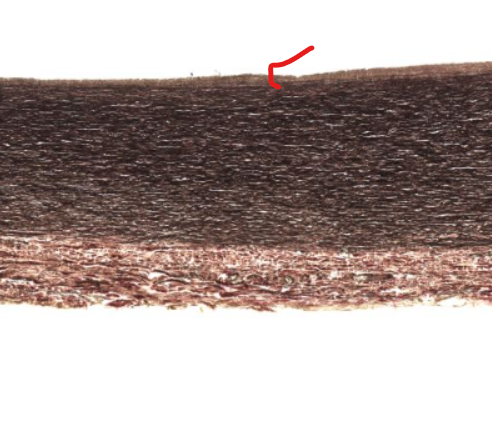

(layer)
tunica intima of the aorta
mostly elastic fibers in subendothelial CT
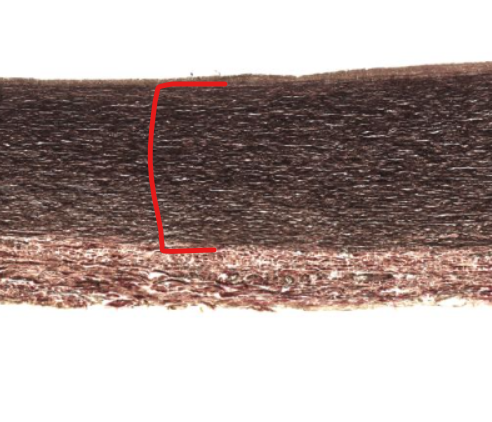

(layer)
tunica media of the aorta
contain smooth muscle and elastic fibers
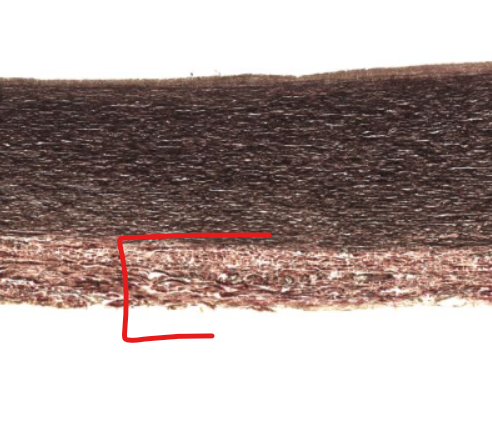

tunica adventitia of artery
outer layer
little to no elastic
muscular vs elastic artery
elastic arteries face large pressure changes and need to stretch to accommodate blood. Think of the aorta for this
muscular arteries have more muscle around them, aka can be constricted more often. Think of peripheral arteries
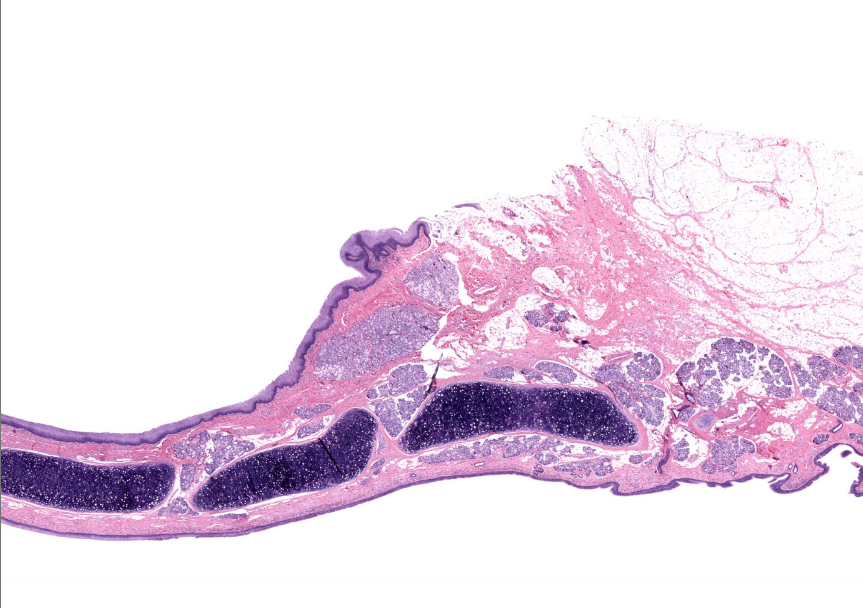
epiglottis
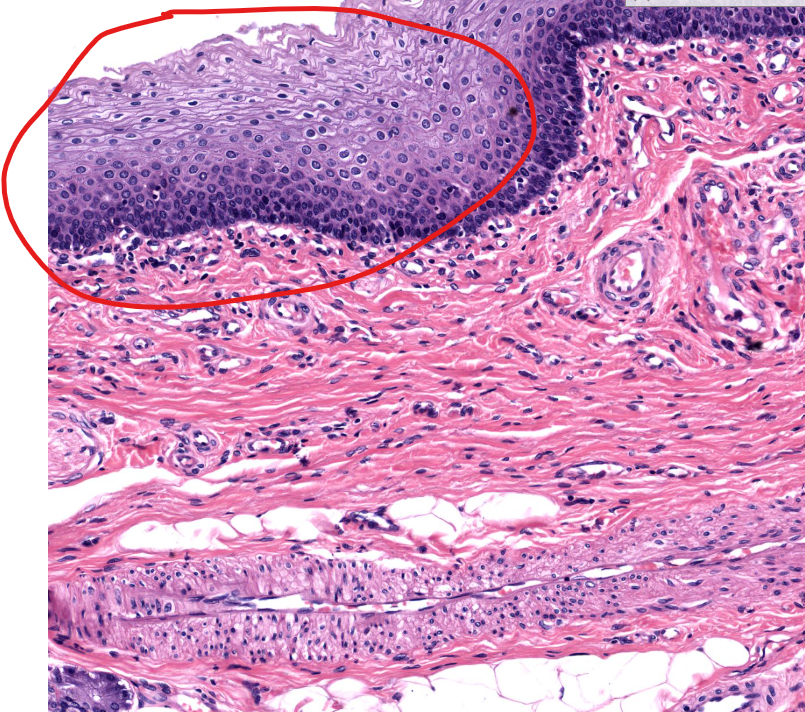
tissue type
strat. squamous non-keratinized epi
found on anterior/lingual surface of epiglottis
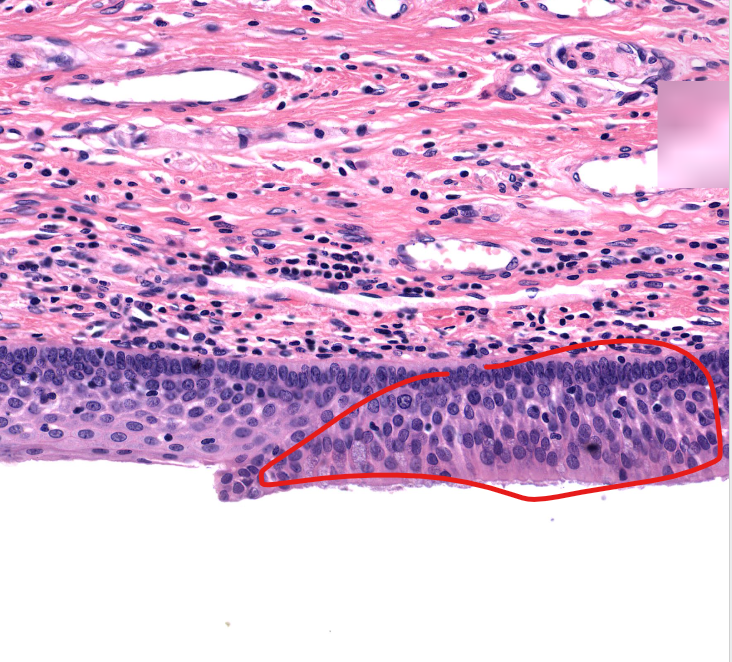
(tissue type)
respiratory epi
aka ciliated pseudostratified epithelium
found on posterior/trachea side of the epiglottis
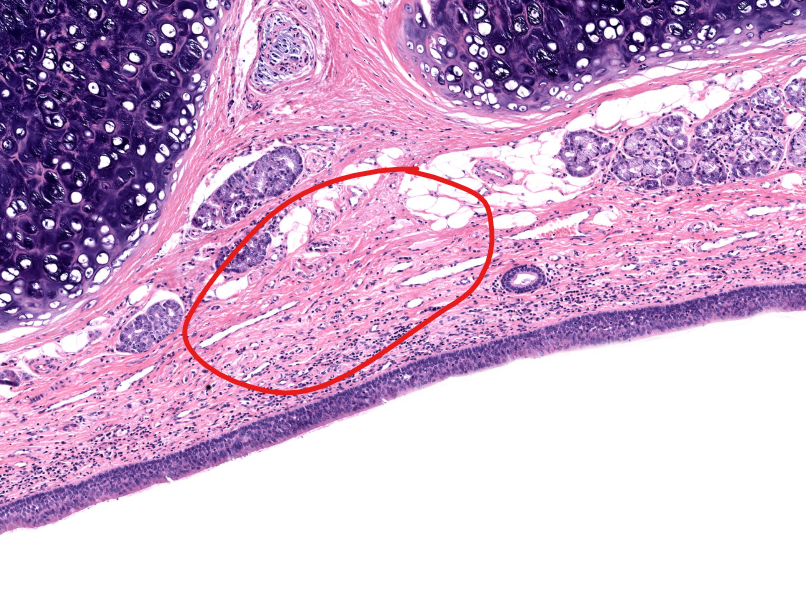
tissue type
lamina propria of the epiglottis
supports epithelium
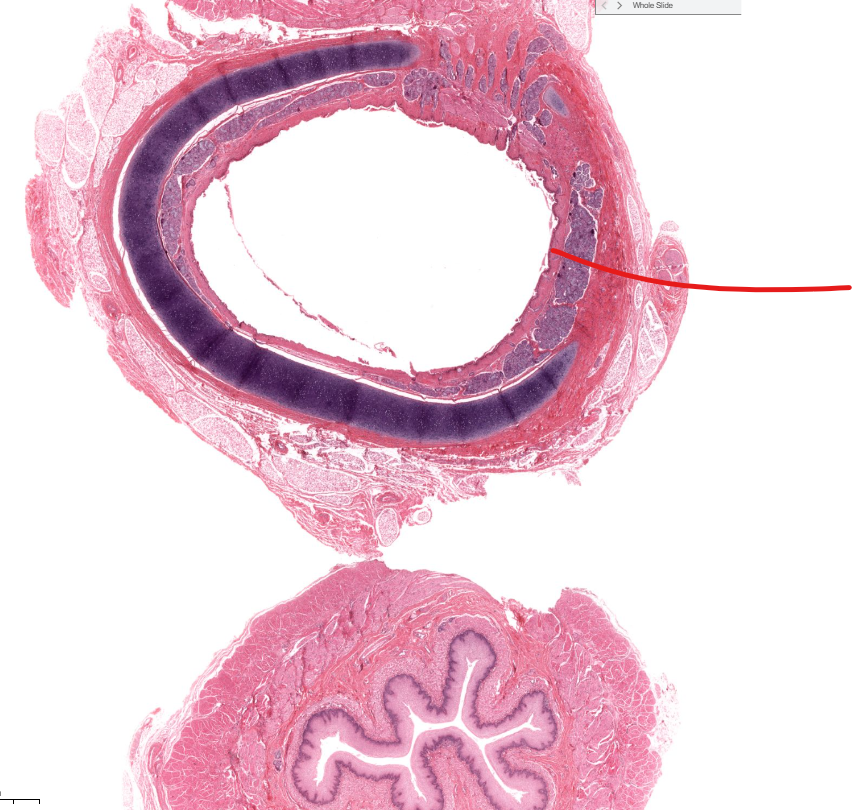
trachea
air to lungs
has respiratory epi on the lumen
C shaped cartilage with muscle to expand with swallowed food in esophagus
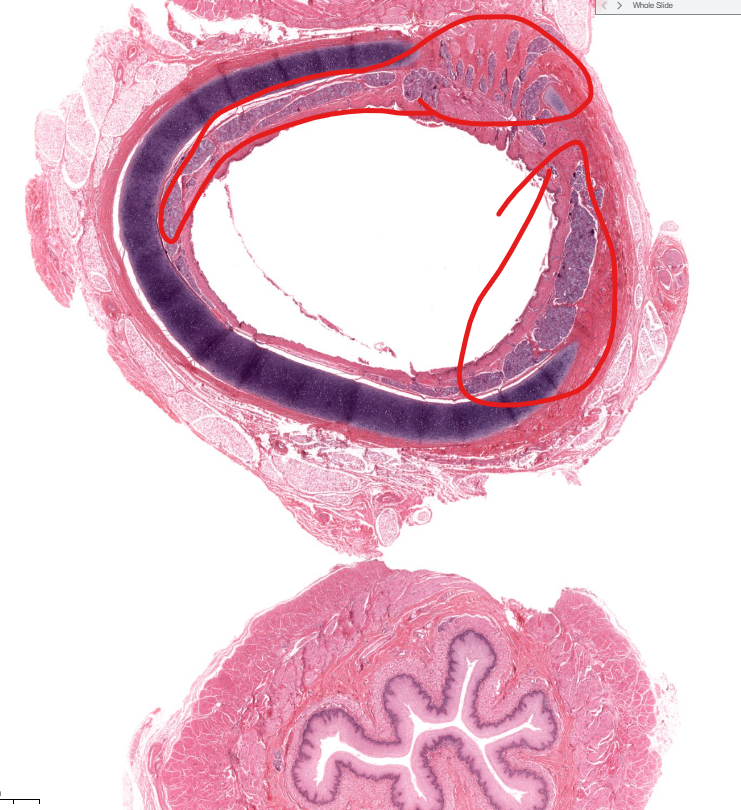
sero-mucous glands of the trachea
smooth muscle of the trachea
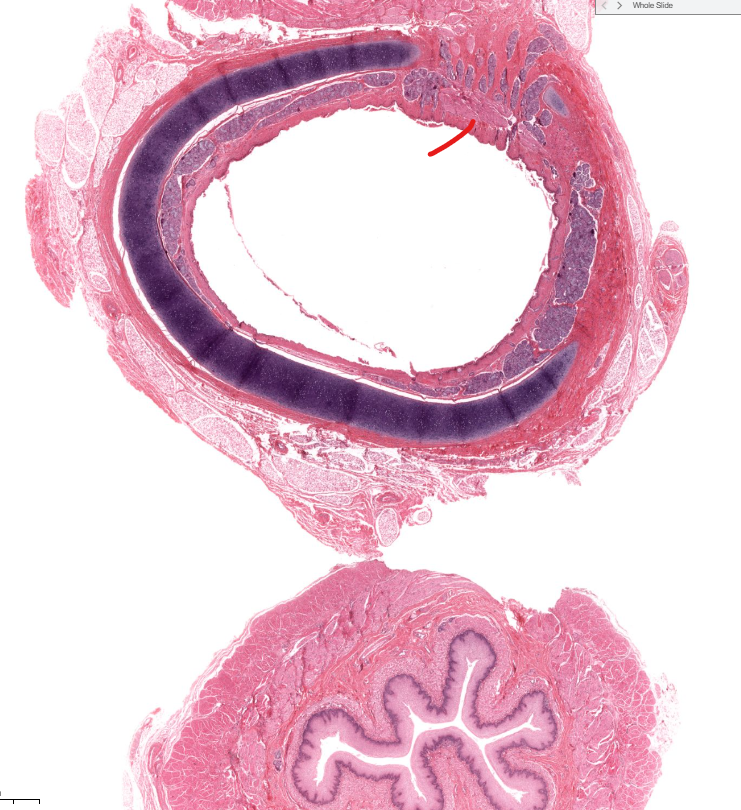
(organ)
lung
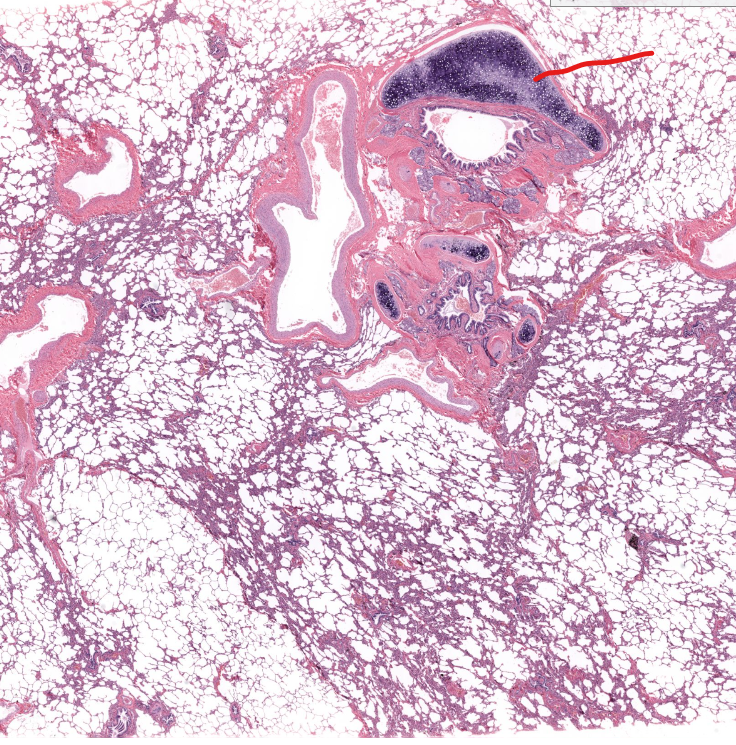
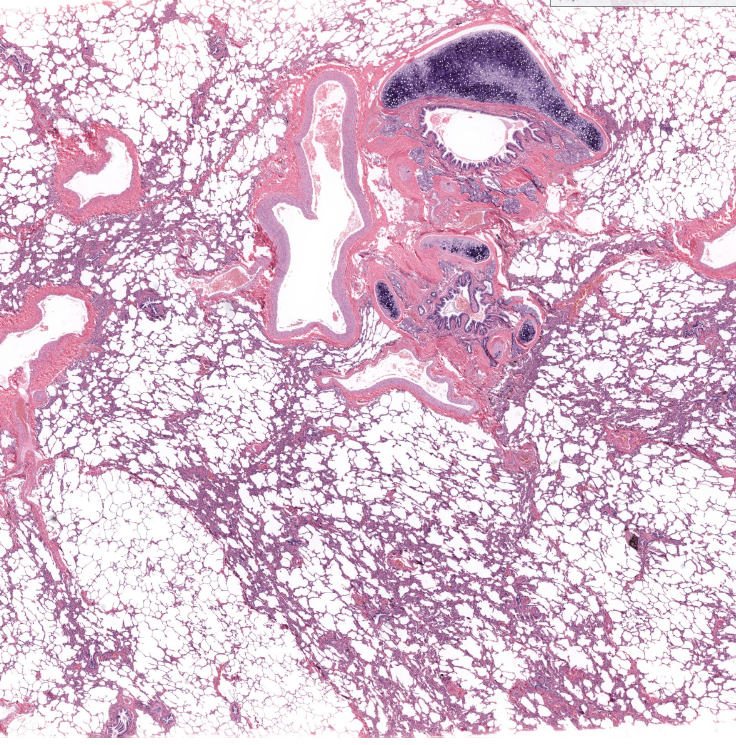
bronchiole cartilage of lung
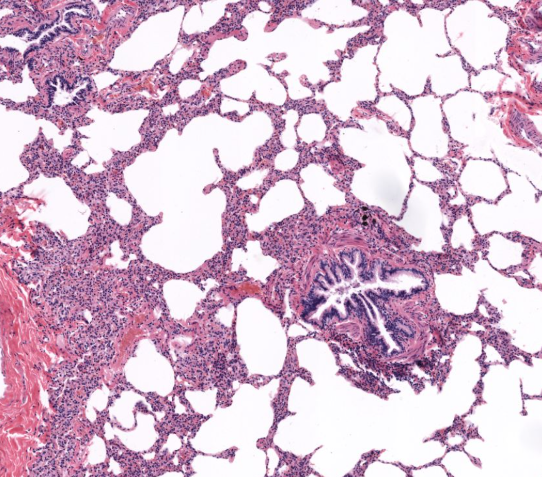
terminal bronchiole of lung
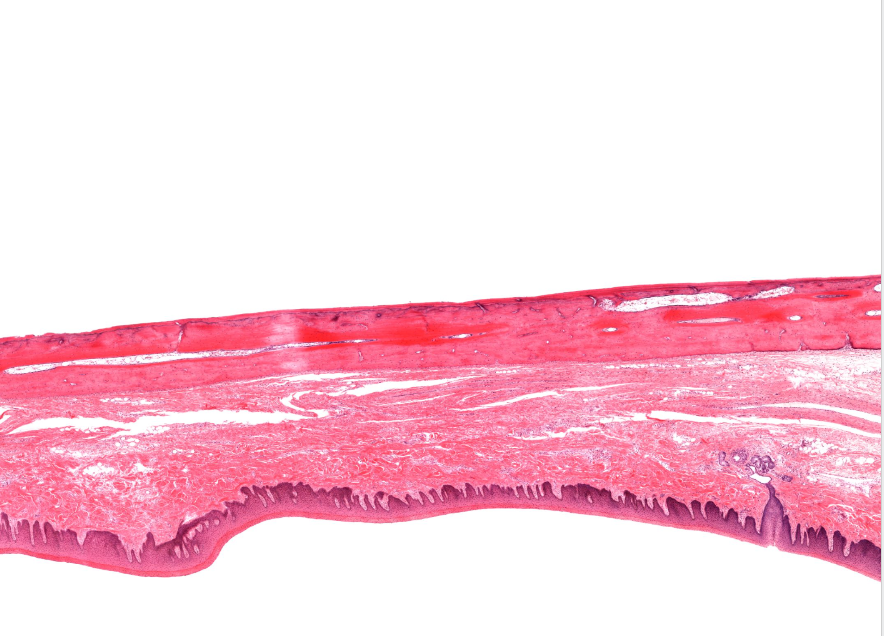

(red line)
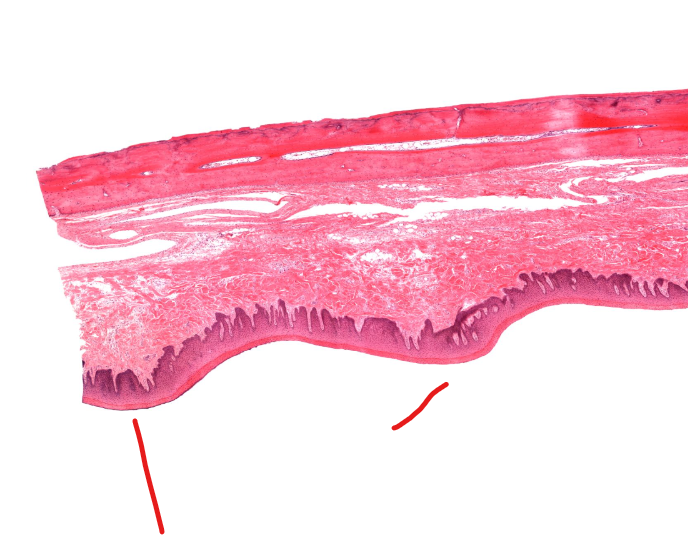
hard palate
thin red horizontal plate
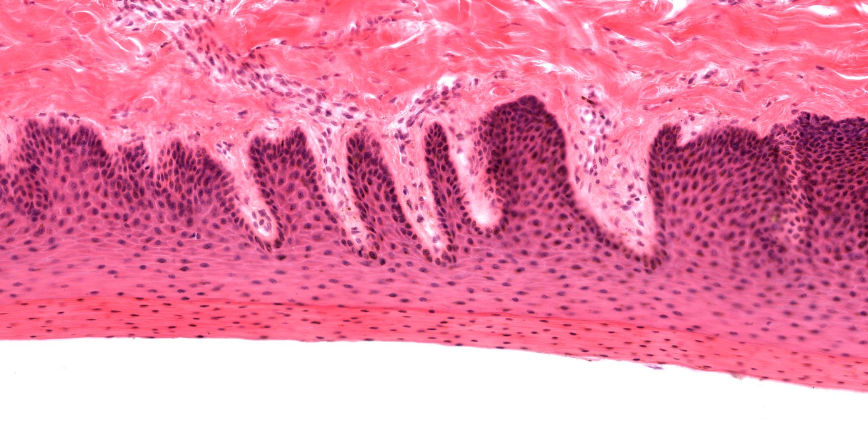
lower layer
mucous membrane of hard palate
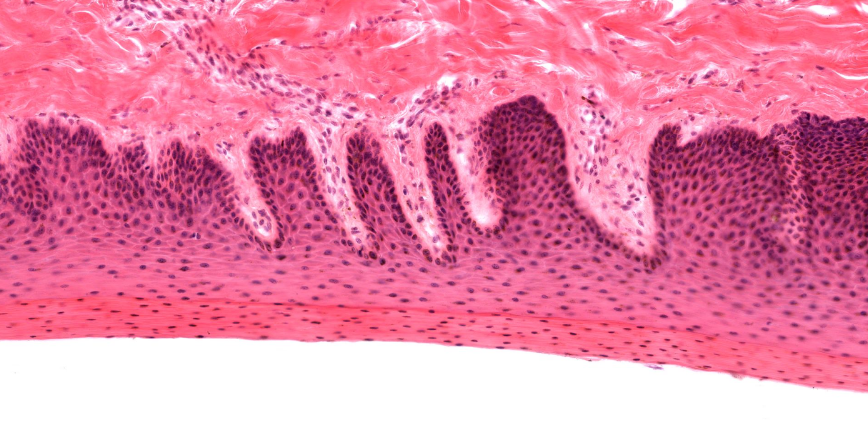
wavy lines
dermal papillaeZ
structure
rugae of soft palate
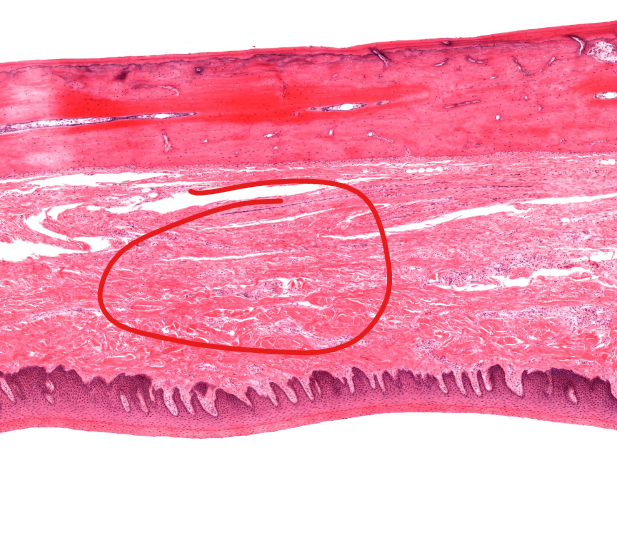
layer
submucosa
dense irregular CT
supports epi
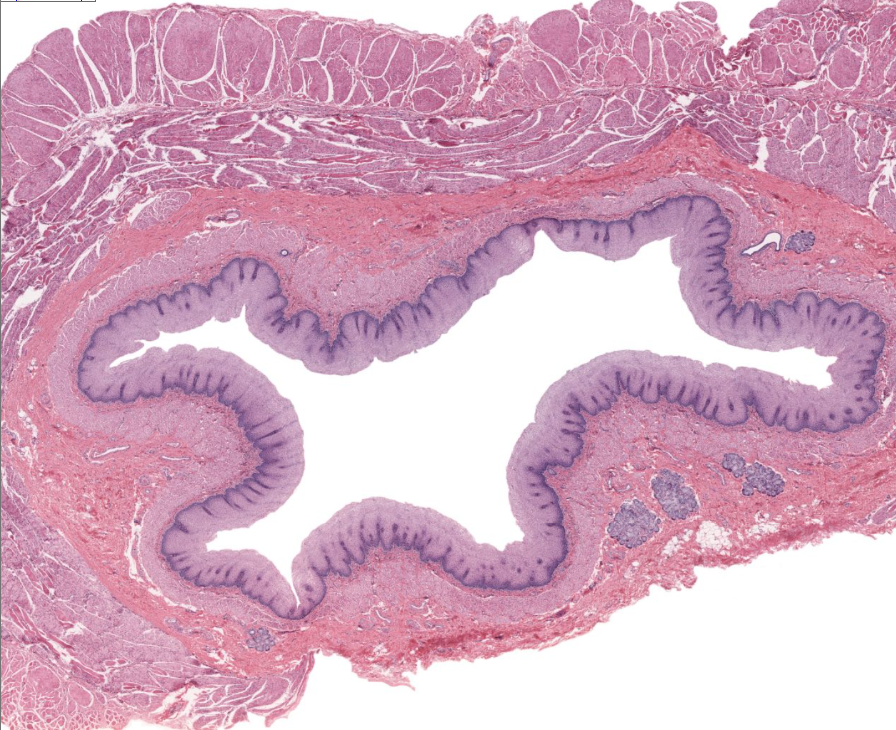
esophagus
note strat sq. epi
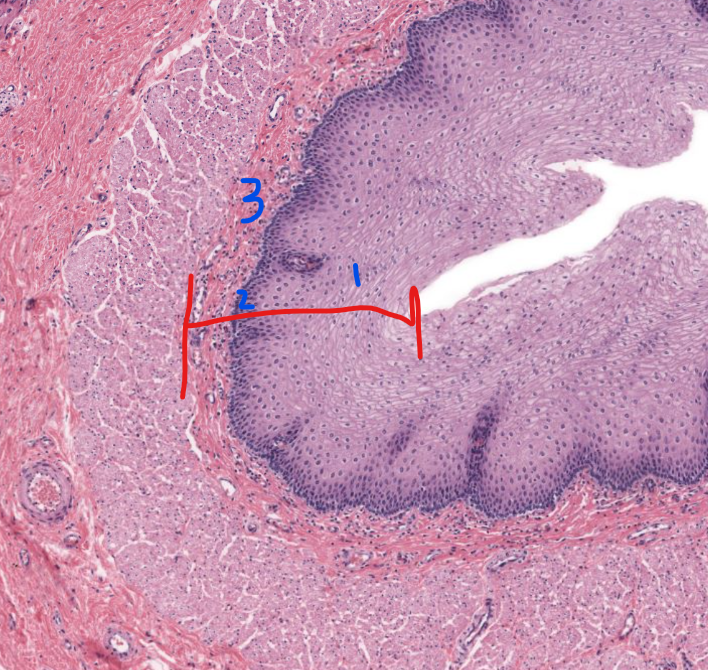
layer
mucosa of esophagus
strat.squamous n-keratineized epi
lamina propria
muscular mucosae
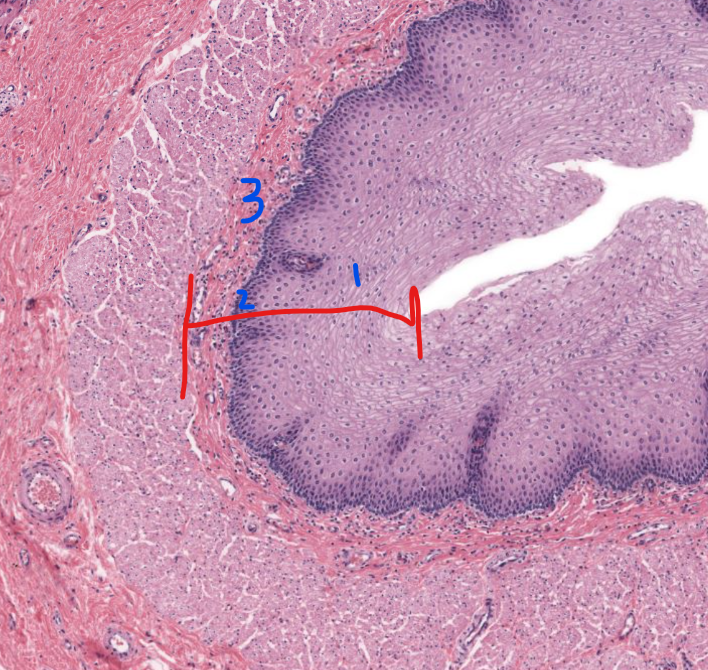
1
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium of esophagus
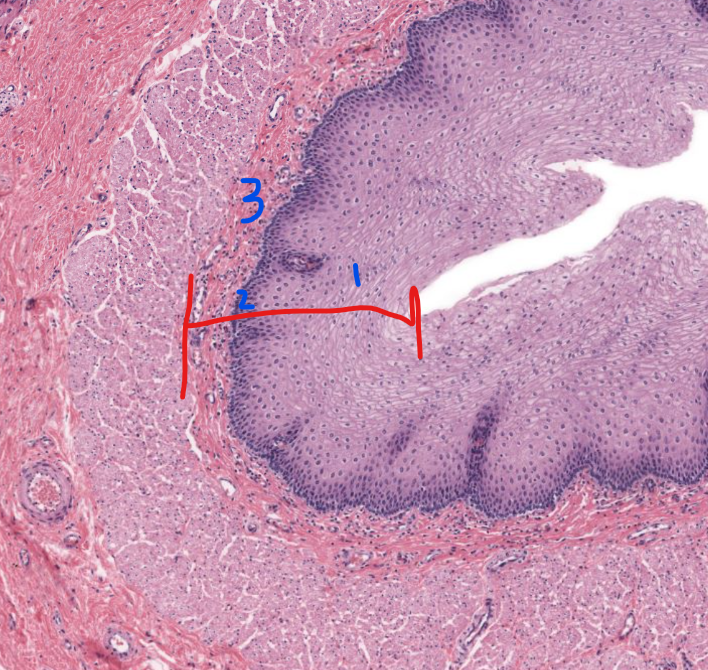
2
lamina propria of esophagus
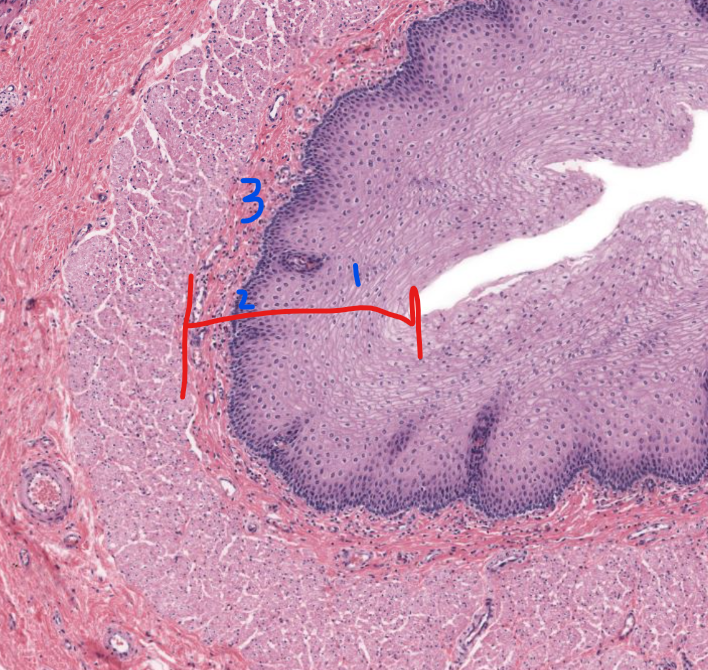
3
muscularis mucosa of the esophagus
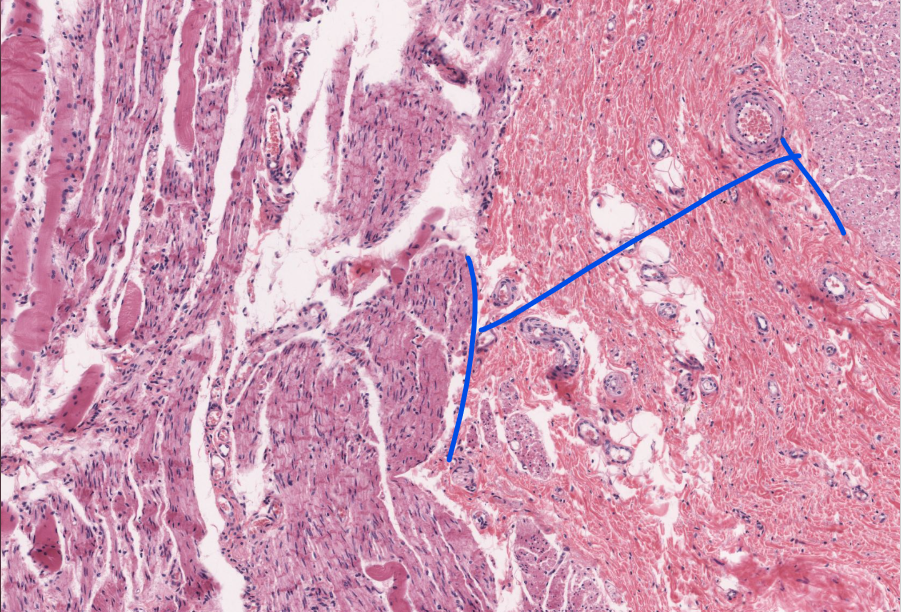
layer
submucosa of the esophagus
submucosal glands!
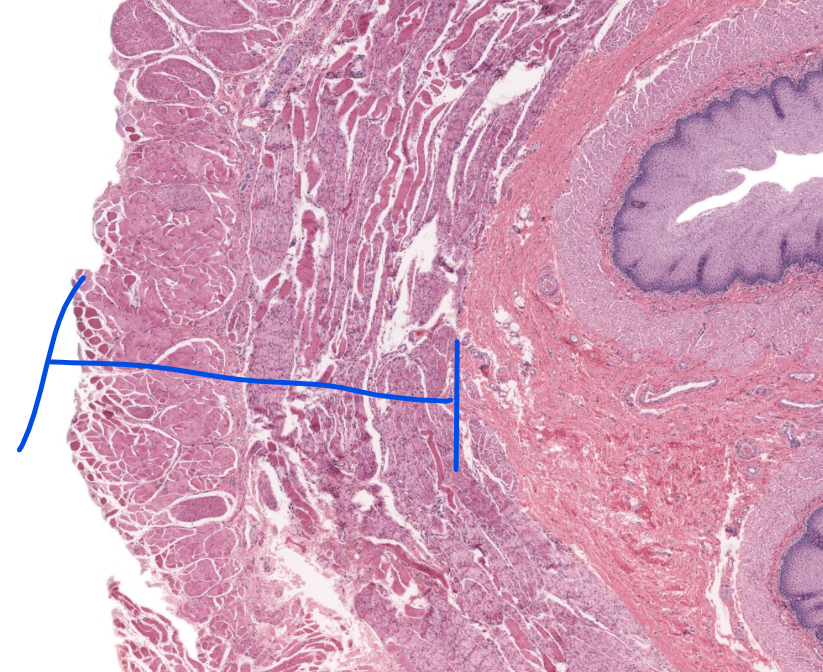
layer
muscularis externa of esophagus
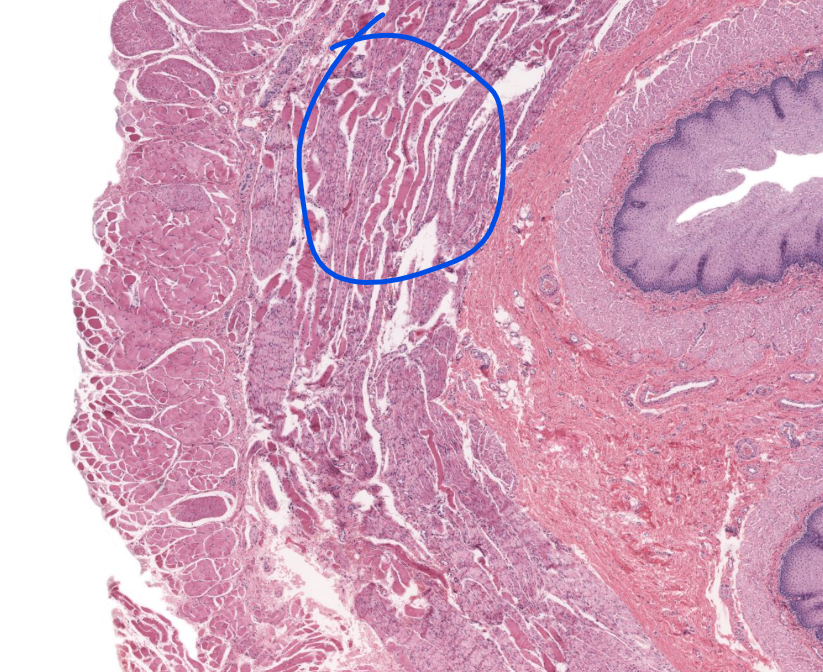
specific layer
inner layer muscularis externa of esophagus
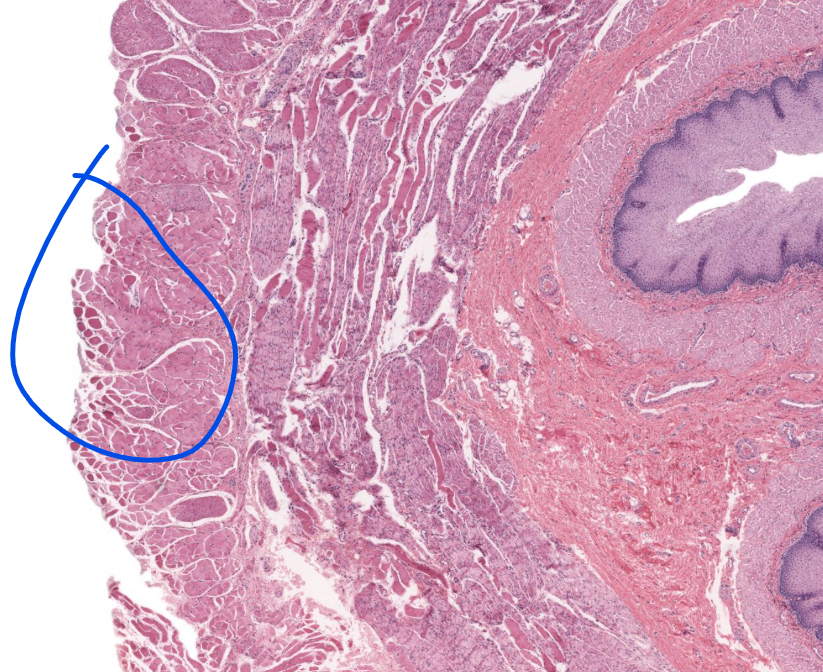
specific layer
outer layer muscularis externa of the esophagus
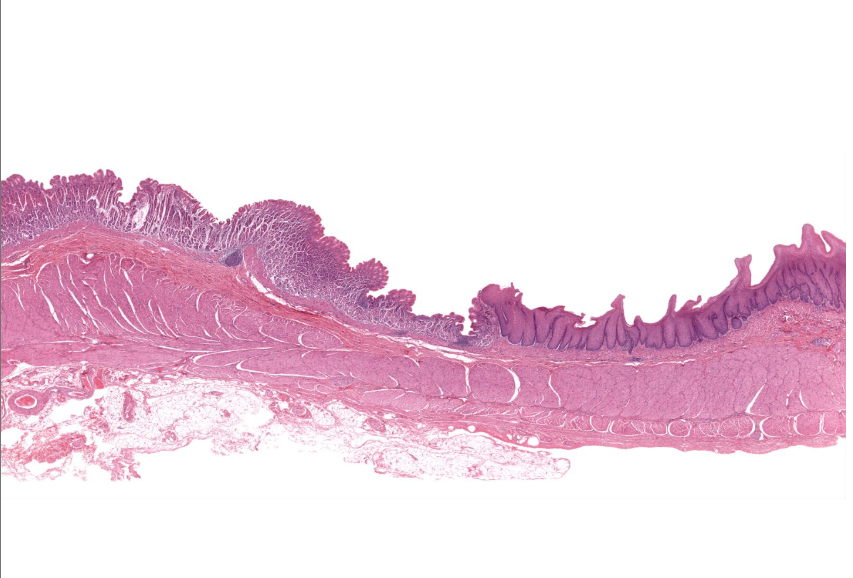
gastroesophageal junction
notice the shift from strat squamous to simple columnar (with long linear/coiled glands)
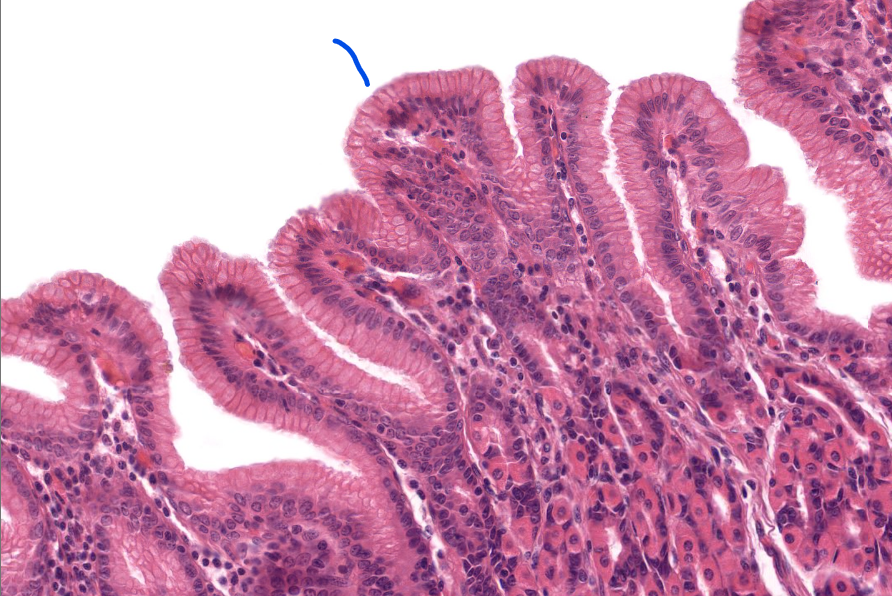
tissue type
simple columnar epi of the stomach
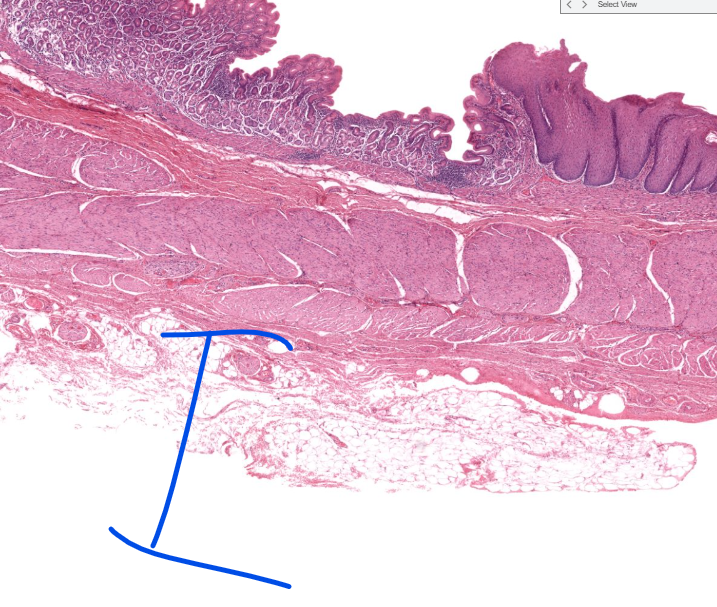
layer
adventitia

gastric rugae
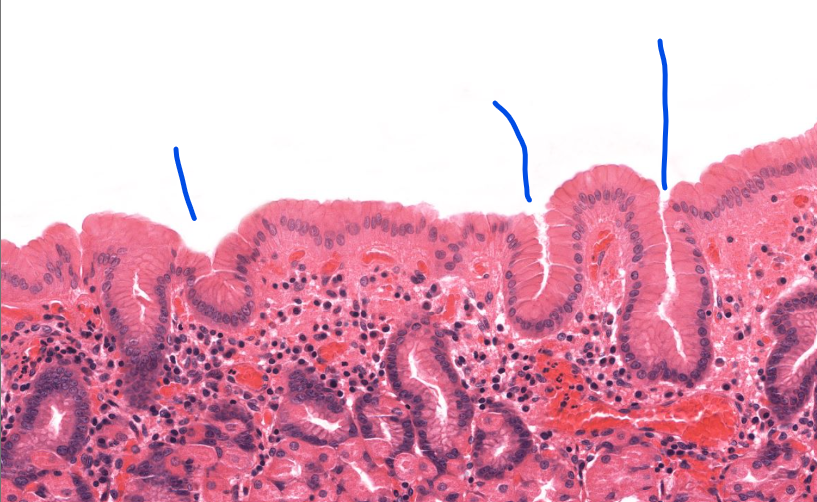
gastric pits
have mucosal cells (lighter pink/clear)
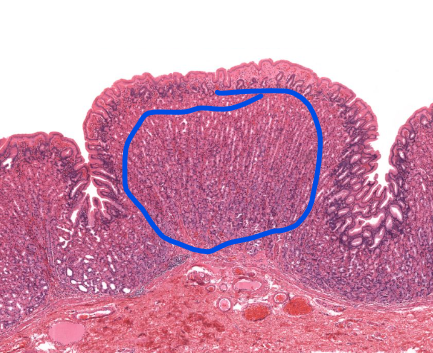
gastric glands
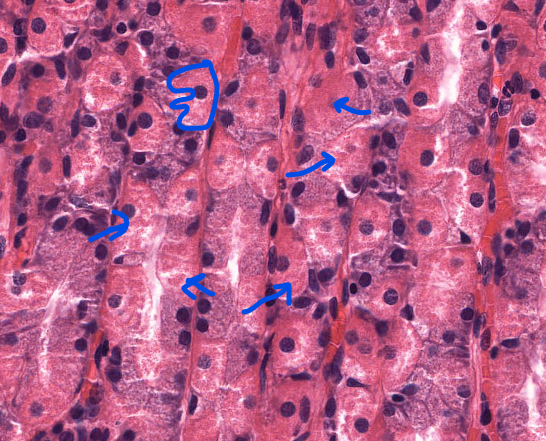
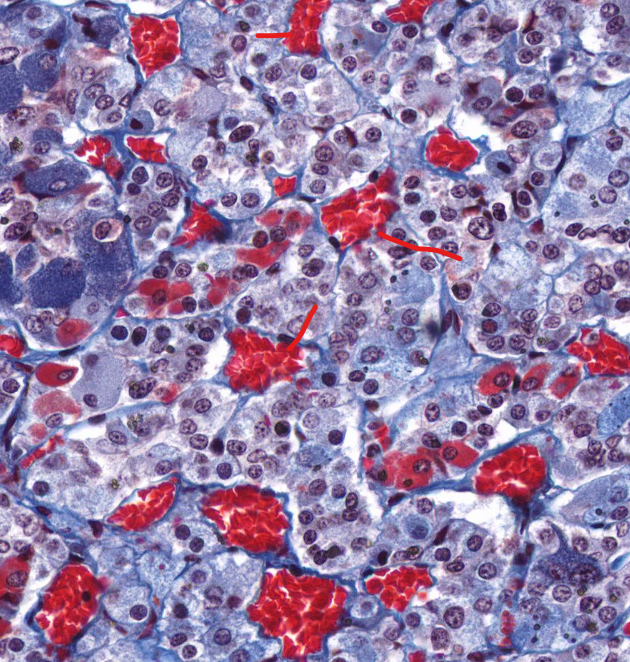
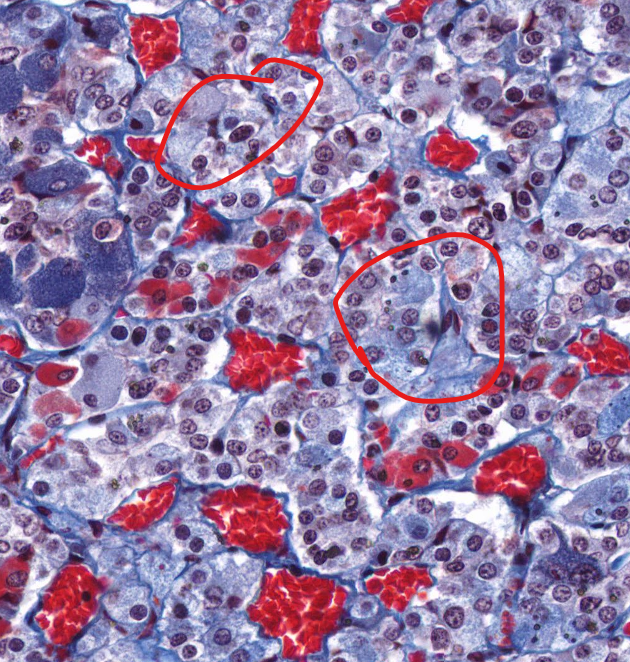
parietal cells of the stomach
secrete HCL
closer to the lumen of the stomach
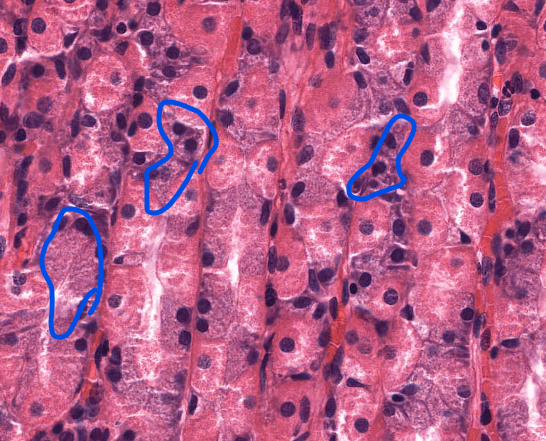
chief cells of the stomach
secrete pepsinogen
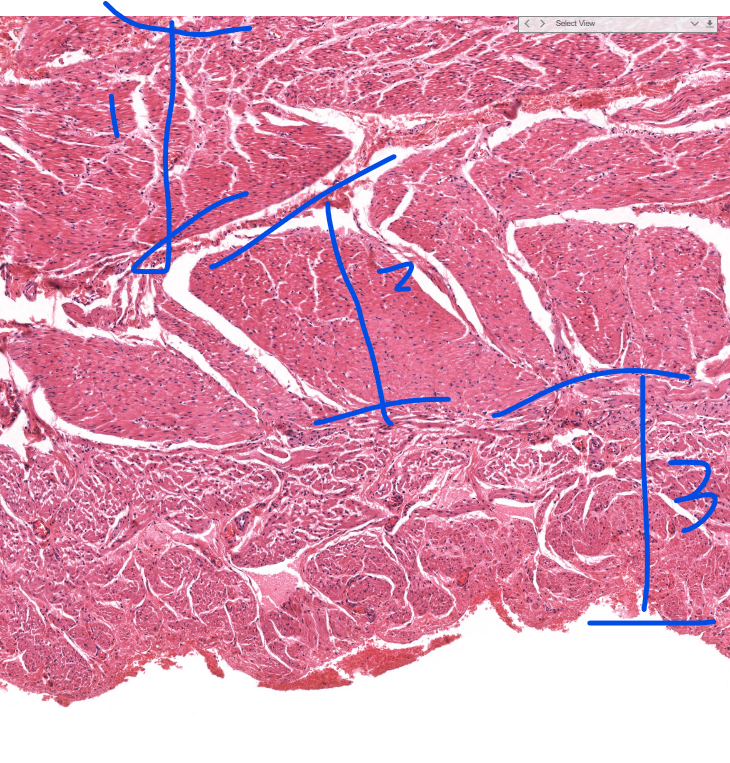
muscular layers of the stomach
inner oblique layer
middle circular layer
outer longitudinal layer

duodenum
purple “bubbles” secrete bicarbonate to neutralize
duodenum has circular folds or spiraled rings along the surface
notice the villi and microvilli
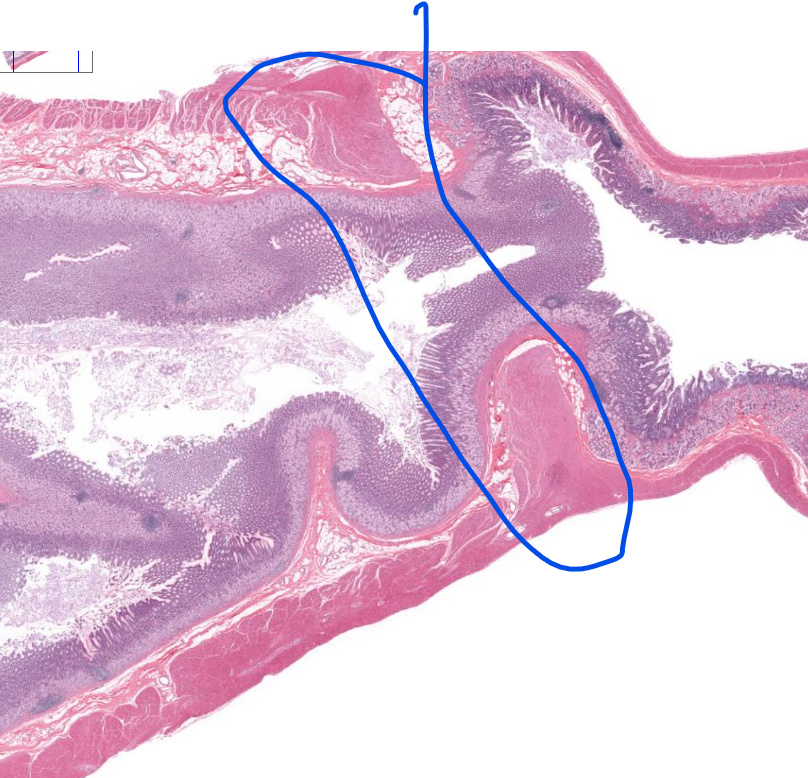
pyloric sphincter
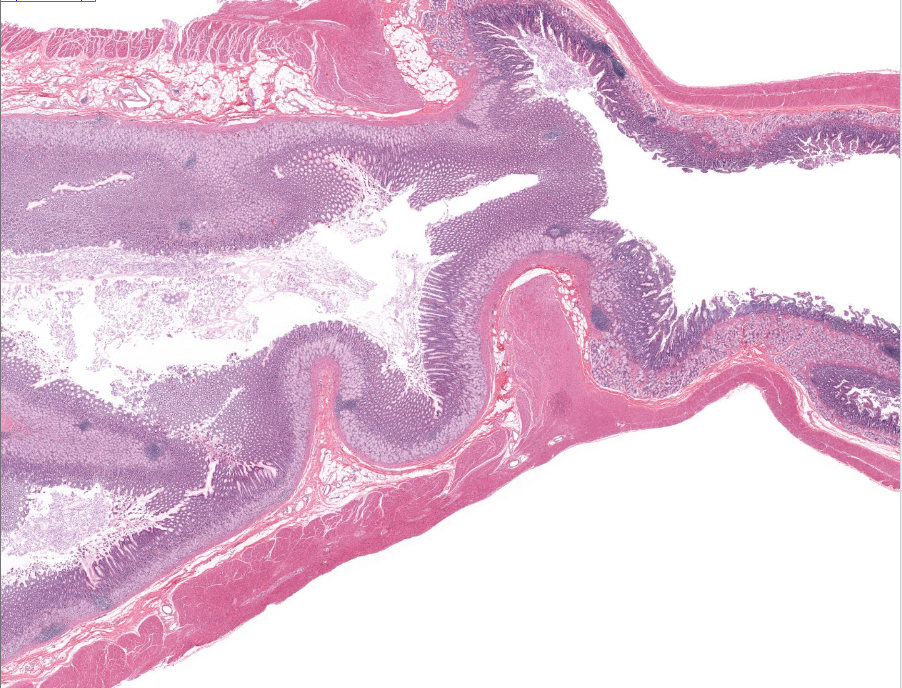
gastroduodenal junction
notice how thicky the muscle is around the stomach, as well as the rugae
notice the thicky sphincter
notice the villi or the duodenum
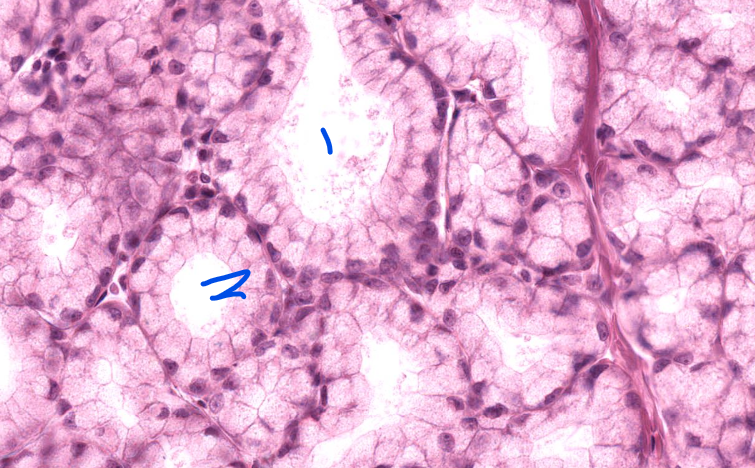
brunners gland of the duodenum
secrete bicarbonate
in the submucosa
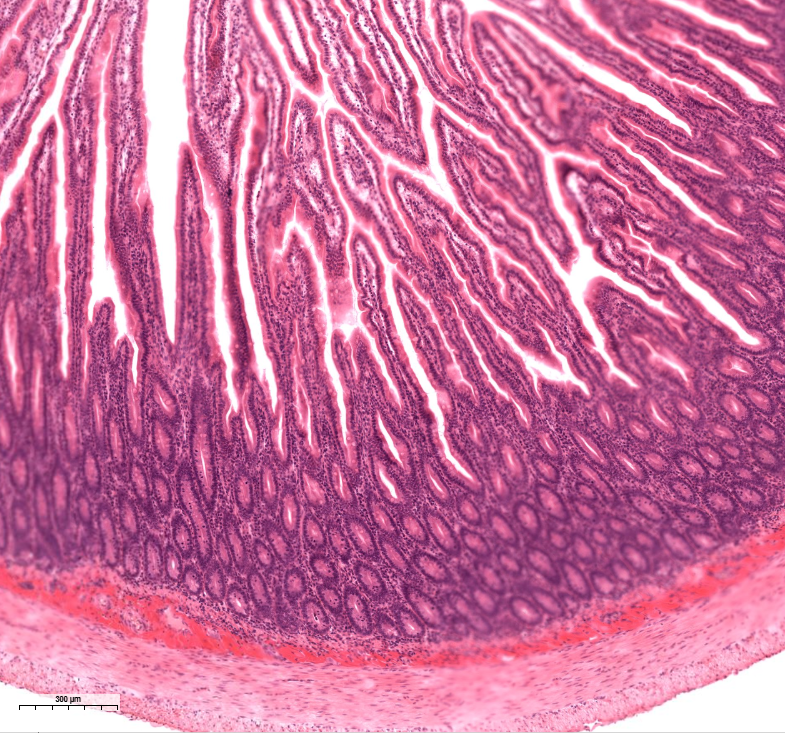
jejunum
notice the submucosa is small af
notice the intestinal crypts are very convoluted
notice a lack of modifications to the submucosa
some of this structure doesn’t have serosa
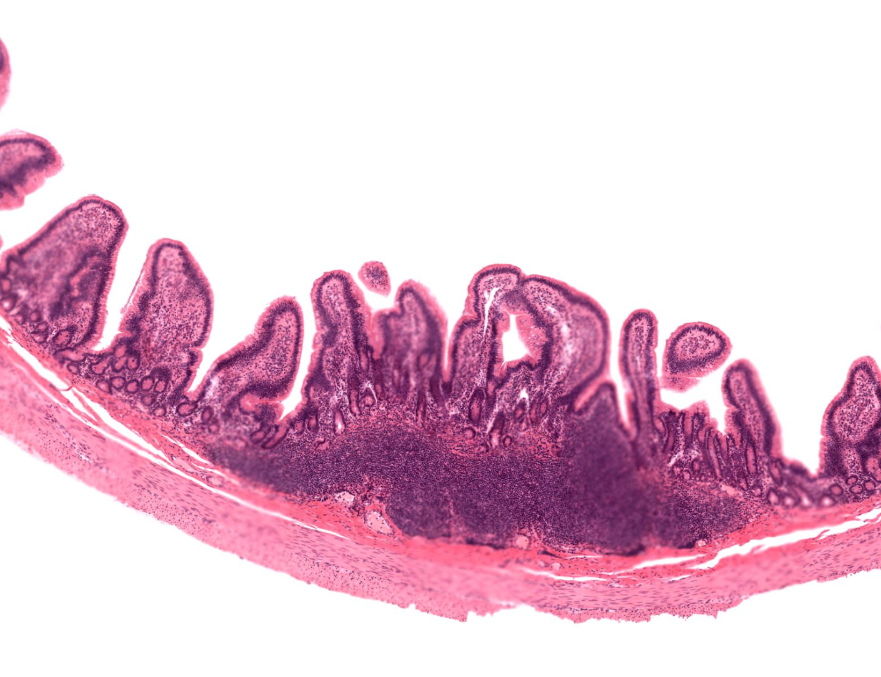
ilium
notice the short villi
notice the immune tissue in the submucosa (peyers patches)
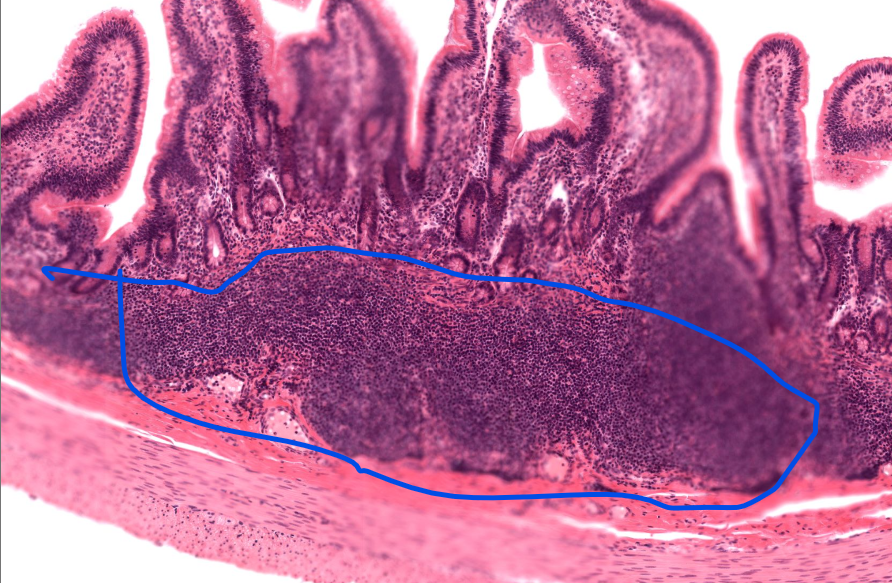
peyer’s patch
cluster of lymphocytes in the ilium
large intestine
notice the lack of villi
abundant lamina propria
areas of thick longitudinal muscle
some lymphoid tissue
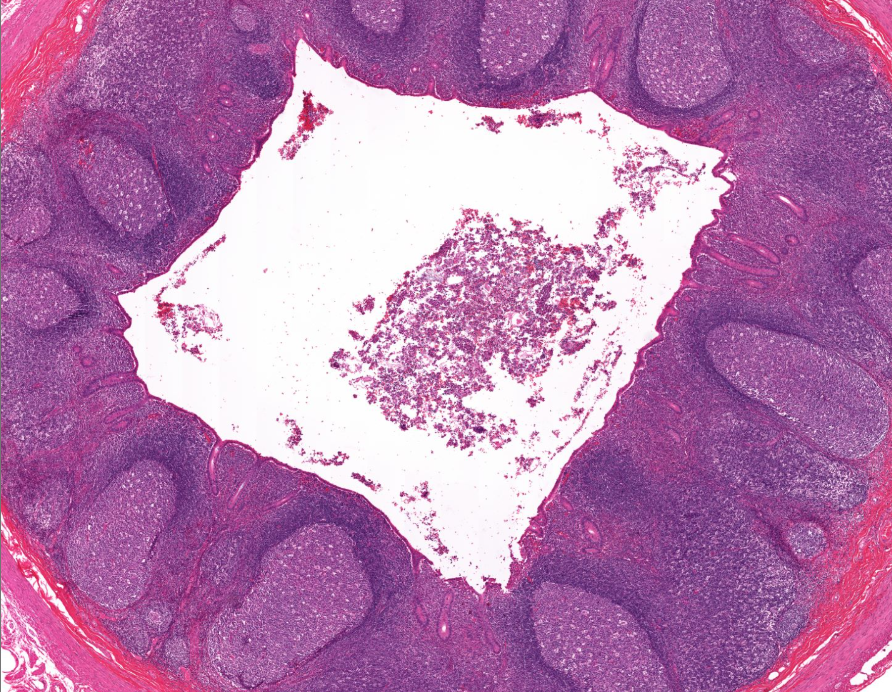
vermiform appendix
notice the absurd amount of lymphocytes
no villi
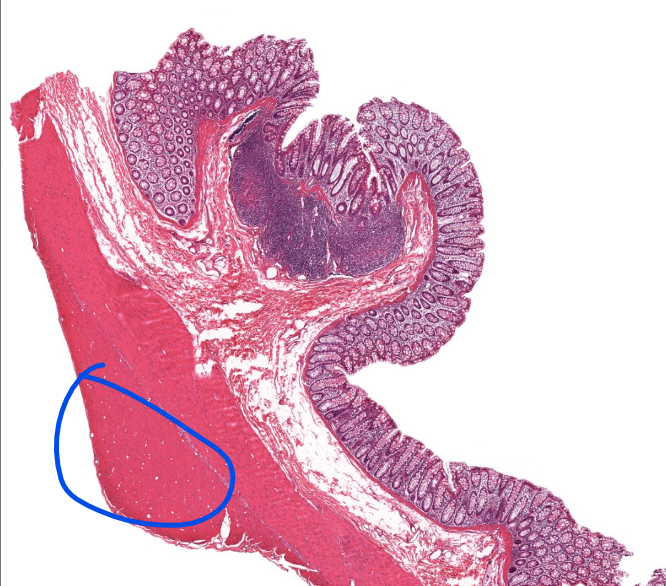
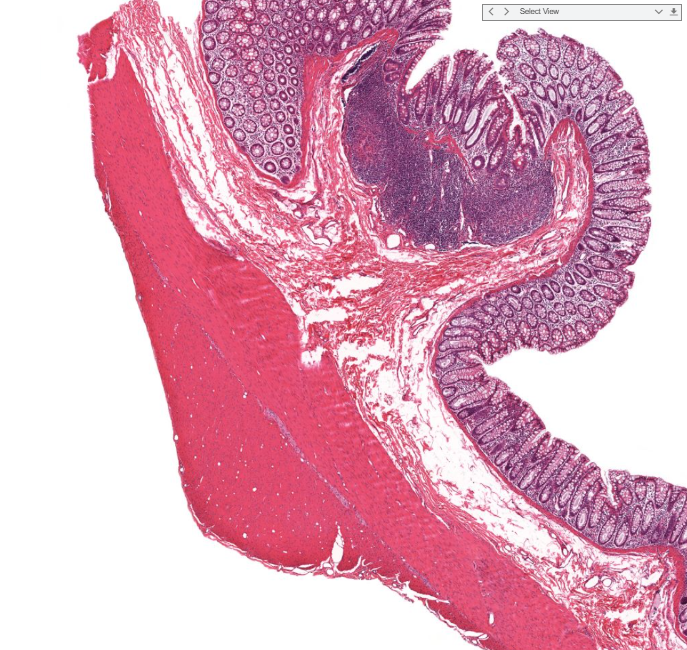
tenia coli
where the longitudinal muscle is thicky in the colon
usually three tenia coli on each cross section
causes the lumpy appearance of the lg. intestines/haustra
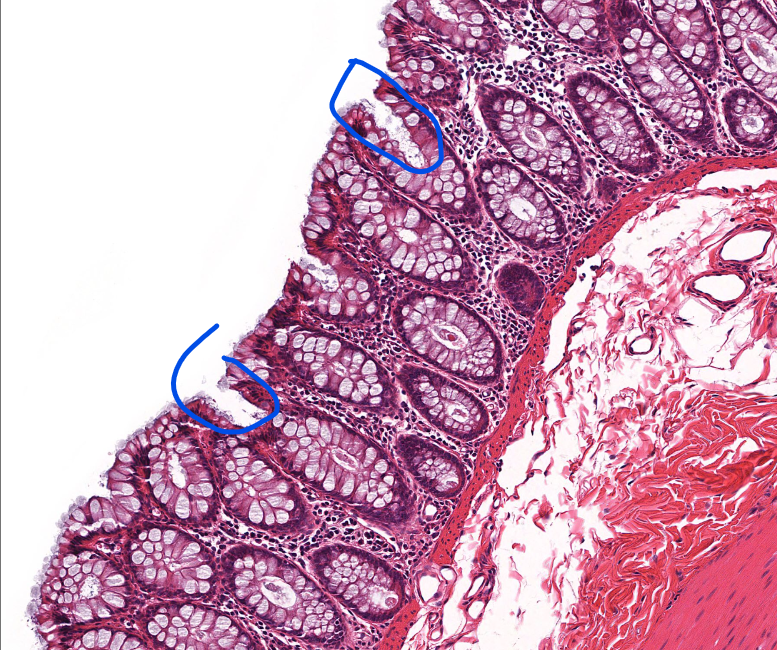
intestinal crypts of lieberkuhn
TONS of goblet cells
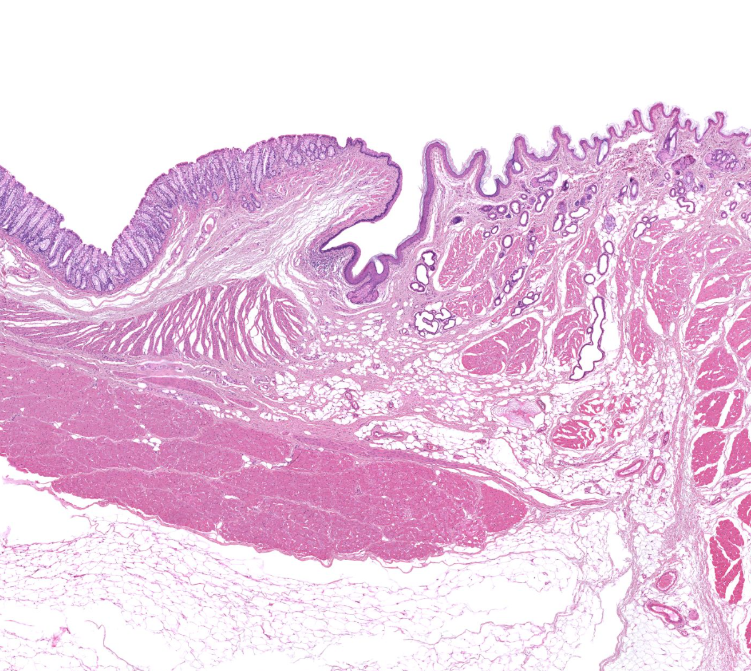
recto-anal junction
notice the goblet cells and crypts of the colon
notice the stratified squamous cells of the anus
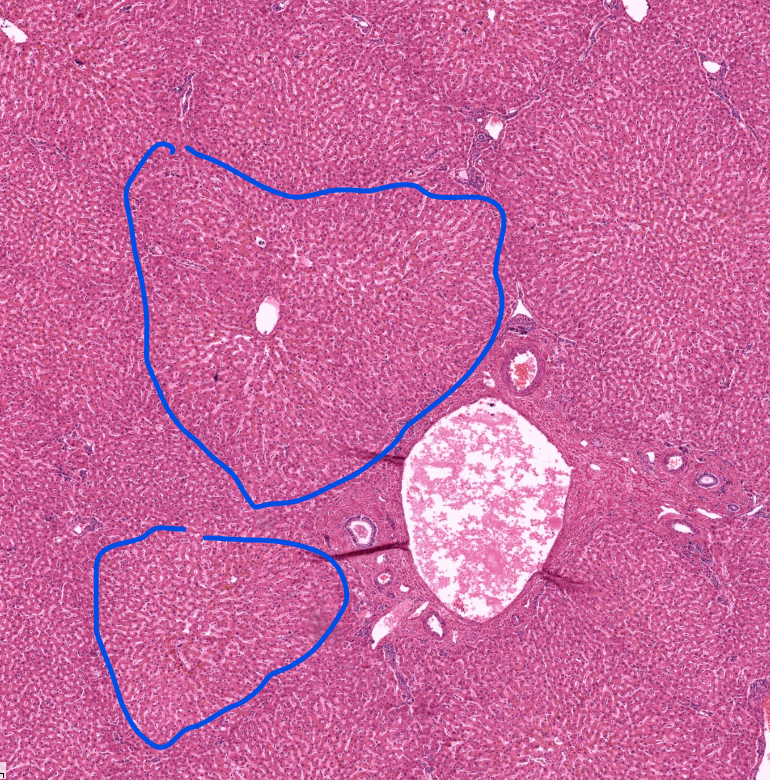
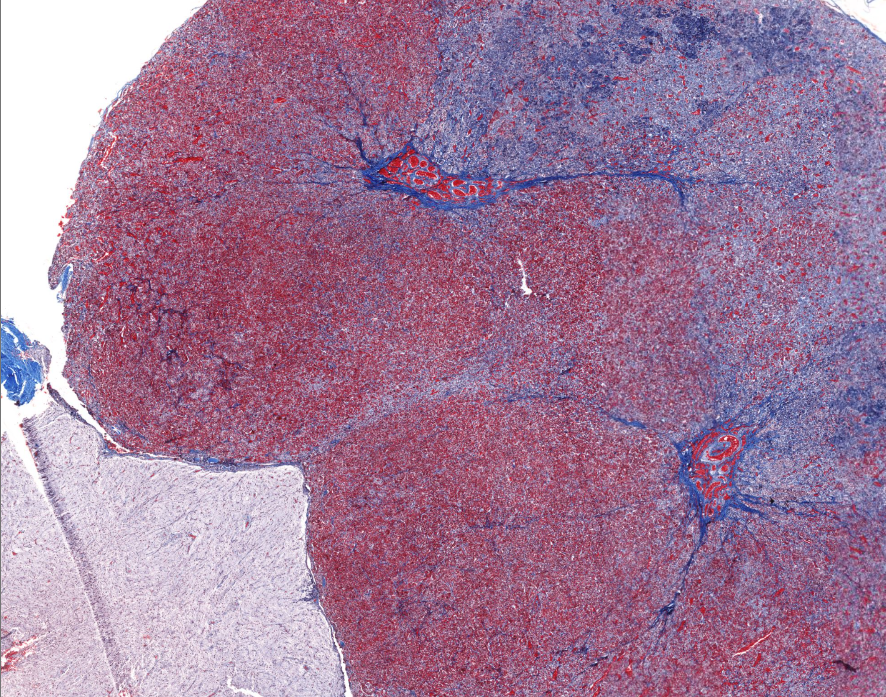
lobules of the liver
has arteries and veins and bile ducts at the “corners” aka portal triads
has a central vein for absorbed things to leave
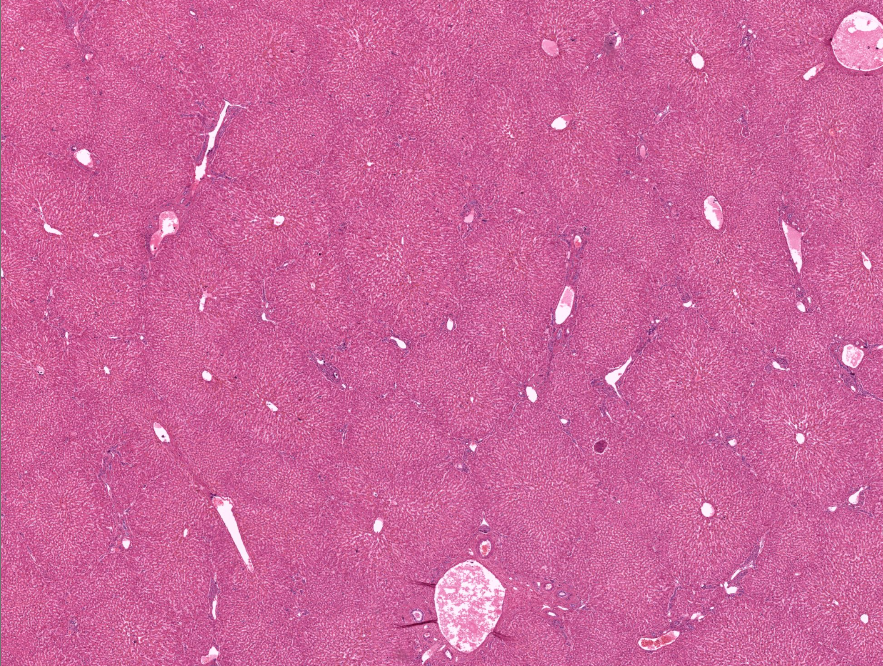
liver
“sponge” bc it processes blood/nutrients/etc
notice geometric shapes and holes
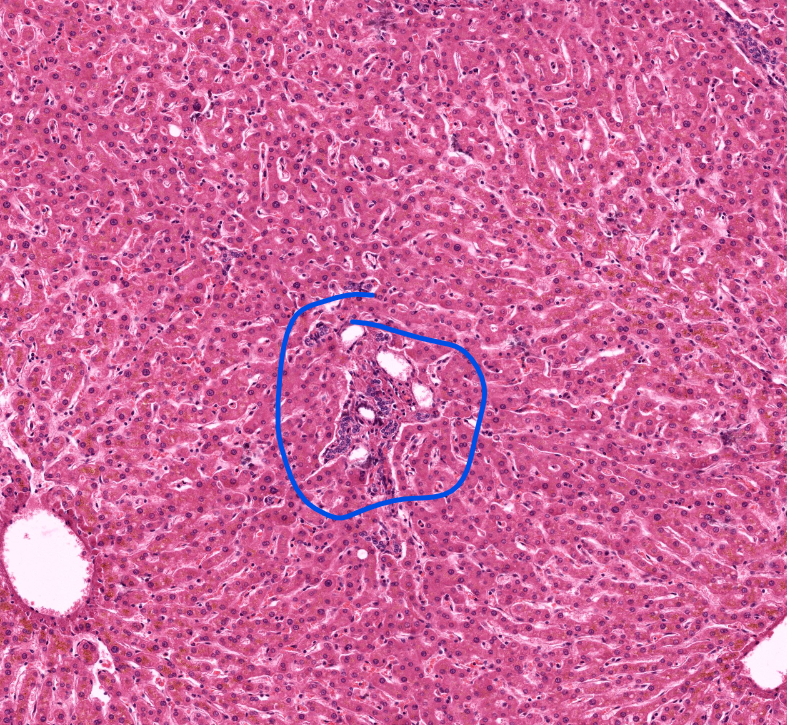
portal triad of the liver
capillary/AV and bile duct