MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATION OF THE CERVICAL SPINE (P2; Objective assesment)
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
If the patient is supporting the head and neck during the history and observation and is afraid to move the head what sign does this indicate?
Rust’s Sign
indication of cervical instability dt fracture or ligamentous injury
OI GUIDELINES: (skim thru)
Manner of arrival
Mental status (lethargic, alert, coherence)
Facial expression/wincing (indication of irritable pain)
Protective posturing
Rust’s Sign
Attachments and assistive devices
Cervical collar (can be hard or soft; for fx, instability, sprain, strains)
Signs of inflammation
Trophic skin changes
Especially on the distal extremity if myotomes and dermatomes are affected
Deformities, asymmetries, deviation
Cervical Lordosis = poor postural habits (PA)
True or False
Abnormalities in one area frequently affect another area. For example, excessive thoracic kyphosis may cause a “poking” chin (cervical spine is in extension) to compensate for the thoracic deformity and to maintain the body’s center of gravity centered beneath the base of support.
FALSE:
Abnormalities in one area frequently affect another area. For example, excessive lumbar lordosis may cause a “poking” chin (cervical spine is in extension) to compensate for the lumbar deformity and to maintain the body’s center of gravity centered beneath the base of support.
Normal Value for cervical lordosis
30° to 40°
Stiff neck; muscle spasm, tightness, or prominence of the sternocleidomastoid muscle causing lateral flexion to affected side and opposite side rotation; can be congenital or acquired
Torticollis
In Klippel-Feil syndrome which cervical vertebra are most commonly affected by congenital fusion?
C3-5
Acute torticollis can also be caused by what type of neck problem?
head is laterally flexed away from painful side
Disc problems can cause acute torticollis
A habitual poking chin can result in adaptive shortening of what muscles?
Occipital muscles
True or False:
A poking chin causes the cervical spine to change alignment resulting in increased comprehensive stress of the facet joints and anterior discs and other anterior elements
False:
A poking chin or military posture causes the cervical spine to change alignment resulting in increased comprehensive stress of the facet joints and posterior discs and other posterior elements
A poking chin may also lead to weaknesses in what group of muscles?
Deep neck flexors
What muscles are weak in an upper crossed syndrome?
deep neck flexors
rhomboids
serratus anterior
lower trapezius.
What muscles are tight in an upper crossed syndrome?
pectoralis major and minor
upper trapezius
levator scapulae
True or False:
Torticollis may be habitual, in other words, the patient always goes back to this posture.
True
Habitual posture may result from postural compensation, weak muscles, hearing loss, temporomandibular joint problems, or wearing of bifocals or trifocals.
Which shoulder is lower, dominant side or non dominant side?
Dominant side should be slightly lower
emphasis on slightly
Which shoulder is lower, injured side or non non-injured side?
Non-injured side is lower
the injured side may be elevated to provide protection or because of muscle spasm
Rounded shoulders may be the result of or the cause of a poking chin, also causes the:
scapulae to protract or retract?
humerus to laterally or medially rotate?
Anterior/Posterior structures to lengthen?
Anterior/Posterior structures to tighten?
Rounded shoulders may be the result of or the cause of a poking chin, also causes the:
scapulae to protract
humerus to medially rotate
Posterior structures to lengthen
Anterior structures to tighten
Atrophy of the deltoid is caused by which nerve palsy?
Axillary nerve palsy (C5, C6 nerve root)
True or False:
Observing patient facial expression is important to give the examiner an idea on how much the patient is objectively suffering.
FALSE:
Observing patient facial expression is important to give the examiner an idea on how much the patient is subjectively suffering.
Patient with cervical spine injury describe findings:
Head tilted towards pain or away from pain?
Head rotated towards pain or away from pain?
Face tilted upward or downward?
Patient with cervical spine injury describe findings:
Head tilted away from pain
Head rotated away from pain
Face tilted upward
hysterical patient describe findings:
Head tilted towards pain or away from pain?
Head rotated towards pain or away from pain?
Face tilted upward or downward?
hysterical patient describe findings:
Head tilted towards pain
Head rotated towards pain
Face tilted downward
True or False:
Referred pain from conditions, such as spondylosis, tends to occur in the shoulder and arm rather than the neck.
True:
Common areas for spondylosis are c4-5, c5-6 and c6-7
nerve roots c5, 6 and 7 have dermatome distributions to the shoulder and arm
True or False:
when examining the cervical spine it must include the neck, upper thoracic spine, upper ribs, and both upper limbs.
True:
Many of the symptoms that occur in an upper limb originate from the neck. Unless there is a history of definite trauma to a peripheral joint, an upper limb scanning examination must be performed to rule out problems within the neck.
If the patients movement is aberrant or uncontrolled during AROM examination, what is this called?
Cervical movement control dysfunction
Female patients tend to have a greater cervical active ROM than males, except in what movement?
Flexion
True or False:
ALL cervical motion available range decreases with age.
False:
All except rotation at C1-C2 decreases, rotation may increase.
True or False:
The movements should be done in a particular order so that the most painful movements are done first, so the painful portion of the examination finishes faster.
False:
The movements should be done in a particular order so that the most painful movements are done last, and no residual pain is carried over from the previous movement.
True or False:
In the very acute cervical, only movements that give the most information are done in order to prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
True
If the symptoms are relieved in neutral position, is the condition irritable or nonirritable?
nonirritable
If the symptoms are not relieved in neutral position, is the condition irritable or nonirritable?
Irritable
movements may be restricted depending on the intensity of the symptoms.
True or False:
In AROM and PROM, if the patient is able to hold the end range position, the symptoms would not be considered severe
True
True or False:
If patient cannot hold end range position, we can apply overpressure to determine what causes this.
False:
If the patient cannot hold the end range position, any symptoms would be considered more severe and overpressure should not be applied
Which combination of movements can cause the vertebral artery to be compressed ?
rotation, side flexion, and extension
Rotation alone can also cause compression
During flexion, _______ occurs in the upper cervical spine, whereas _______ occurs in the lower cervical spine.
During flexion, nodding occurs in the upper cervical spine, whereas flexion occurs in the lower cervical spine
True or False:
Movement can occur between C2 and C7 without affecting the other vertebrae
False:
Movement can occur between C1 and C2 without affecting the other vertebrae
for C2 to C7, if one vertebra moves, the ones adjacent to it will also move.
ROM values for cervical spine (follow AAOS):
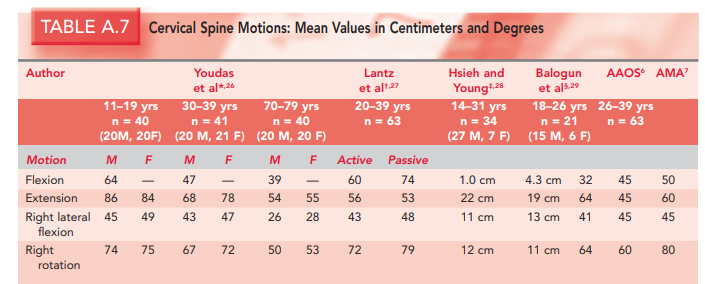
You ask a patient to nod to test the upper cervical spine (C0-C2), electric shock sensation down the neck, what sign is this called?
Lhermitte sign
indicates severe pathology
Maximum ROM for forward flexion of the lower cervical spine is?
80° to 90°
True or False:
For flexion the extreme of ROM is normally found when the chin is able to reach the chest with the mouth closed; up to two finger-widths between chin and chest is considered abnormal.
False
For flexion the extreme of ROM is normally found when the chin is able to reach the chest with the mouth closed; up to two finger-widths between chin and chest is considered normal.
If the deep neck flexors are weak what muscle initiates flexion?
Sternocleidomastoid
causing the jaw to lead the movement, not the nose, because the SCM causes the chin to initially elevate before flexion occurs
In flexion, the intervertebral disc _______ posteriorly and _______ anteriorly
In flexion, the intervertebral disc widens posteriorly and narrows anteriorly
The intervertebral foramen is how many percent larger on flexion than on extension?
20% to 30% larger
The vertebrae shift ________ in flexion and ________ in extension
The vertebrae shift forward in flexion and backward in extension
True or False:
the mastoid process moves away from the C1 transverse process on flexion and moves toward it on extension.
False:
the mastoid process moves away from the C1 transverse process on flexion and extension.
If there is a prominent spinous process of the axis on flexion, what does this indicate?
Forward subluxation of the atlas
Sharp-Purser test to test for that
If serious symptoms arise (e.g., tingling in the feet, loss of balance, drop attack) during upper cervical extension, this indicates what?
Spinal cord compression or Vertebrobasilar dysfunction.
Extension, or backward bending of the cervical spine, is normally limited to how many degrees
70°
Side, or lateral, flexion is approximately how many degrees to the right and left
45° (AAOS)
Normally, rotation is __________ right and left, and the chin does not quite reach the plane of the shoulder
Normally, rotation is 60° right and left, and the chin does not quite reach the plane of the shoulder
True or False:
Rotation and side flexion always occur together (coupled movement) but not necessarily in the same direction.
True
refresher: C0-2 & C7-T1 opposite directions; C2-7 same directions
Most of the rotation occurs between C1 and C2 If the patient can rotate _____________, then it is unlikely that the C1/C2 articulation is at fault
40° to 50°
If, however, side flexion occurs early to allow full motion, C1–C2 is probably involved
True or False
If, in the history, the patient has complained that repetitive movements or sustained postures have caused problems, not only should the specific movements be performed, but they should be either repeated several times or sustained to see if the symptoms are exacerbated.
True:
movement restrictions and possible causes:
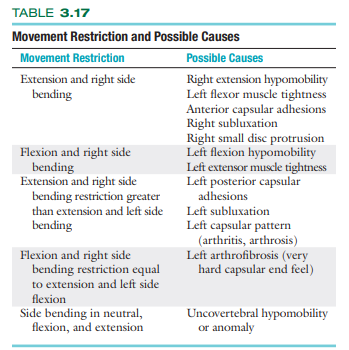
True or False:
If patient cannot complete AROM, and no overpressure can be tested, PROM can be done in supine
True
True or False:
The passive ROM with the patient supine is normally greater than the active and passive ROM with the patient sitting
True
When doing passive flexion with overpressure, if pain is felt in the lower extremities, it may indicate a lower-extremity radiculopathy of one of the lower limb peripheral nerves as the movement stretches the dura
What test is this?
Lindner test
passive flexion + overpressure + second hand on sternum to prevent thoracic flexion.
What test is this?
Soto-Hall test
basically linder test + second hand on sternum to prevent thoracic flexion.
Normal endfeel of all cervical spine movements
Tissue stretch
Resisted Isoms (MMT) basically know ur moina 😅
Whole pic wont fit so go to the next card
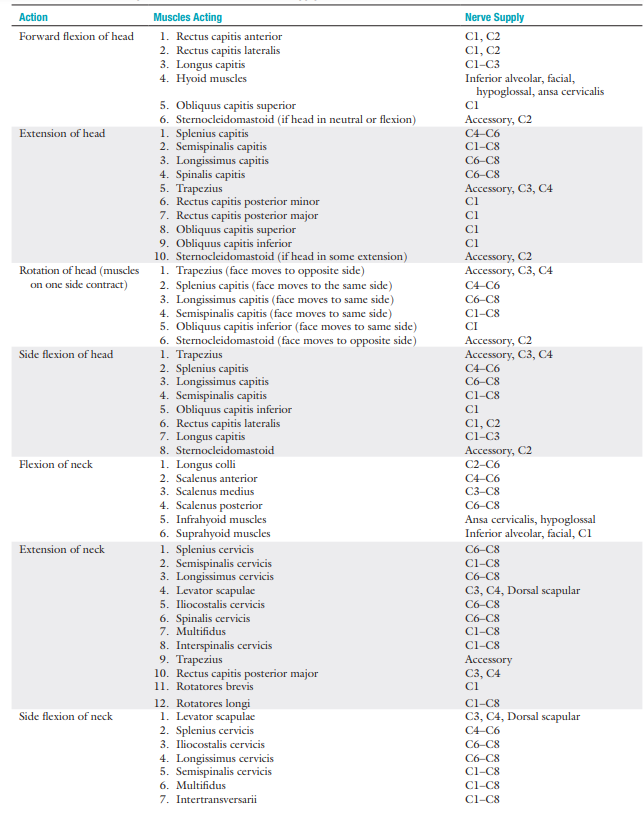
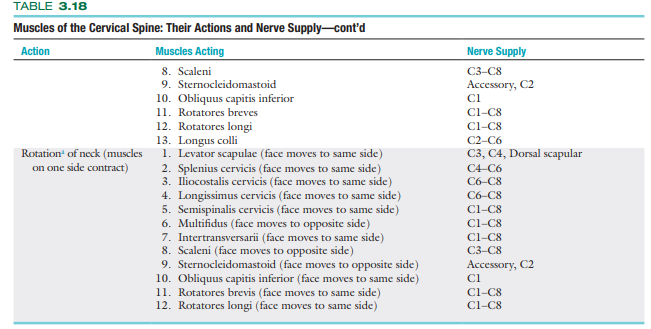
After the resisted isometric movements to the cervical spine have been completed, what is performed to rule out obvious pathology in the extremities?
Peripheral joint scanning
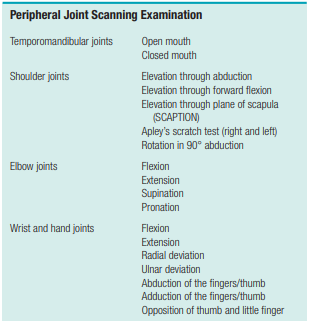
TMJ examination:
Pain or tenderness, especially on closing the mandible, usually indicates?
Posterior Capsulitis
Myotomes (lite version)
Myotomes Pro Max
When testing myotomes the contraction should be held for at least how many seconds?
5 seconds
SENSORY ASSESSMENT overview
sensory scanning examination → gross sensory assessment
% sensory deficit as to what senses in what areas
indicate devices used during testing
Done on the pt’s head and face
Instruments for sensory testing (Superficial senses)
pinwheel
pin
cotton batting
brush
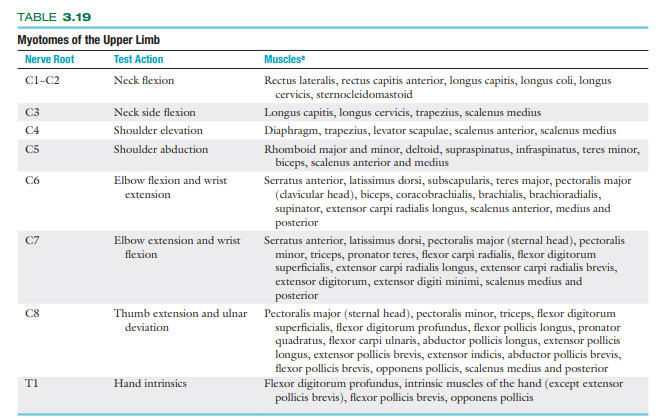
Reflex testing to test for UMN / LMN lesion:
Biceps (C5-C6)
Triceps (C7-C8)
Brachioradialis (C5- C6)
UMN lesion = Hyperreflexia
LMN lesion = Hyporeflexia
Identify the sign:
PT holds pt’s middle finger and briskly flicks the distal phalanx
(+) if IP joint of the thumb of same hand flexes or abducts
Hoffman Sign (UMN Lesion)
Identify the sign:
Pathological reflex
PT rapidly taps near the styloid process at the wrist
(+) finger flexion and slight elbow extension
Inverted Supinator Sign (Inverted Brachioradialis Jerk) (UMN Lesion)
Multiplanar Activities of Neck (Functional Assessment):
Breathing
Swallowing
Looking up to the ceiling
Looking down at the belt buckle or shoes
Shoulder check
Tuck chin in
Poke chin out
Neck Strength
True or False:
Normally when breathing, gulping or gasping can be occasionally heard.
False:
unlabored breathing should be seen with the mouth closed. There should be no gulping or gasping.
At least how many degrees of neck extension is usually necessary for everyday activities.
40° to 50°
If this range is not available, the patient will bend the back or the knees, or both, to obtain the desired range.
when looking down at belt buckle or shoe laces at least how many degrees of neck flexion is necessary?
60° to 70°
If this range is not available, the patient will flex the back to complete the task.
At least how many degrees of neck rotation is needed for shoulder checking?
60° to 70°
If this range is not available, the patient will rotate the trunk to accomplish this task
When you ask the patient to tuck their chin, what are the respective movements of the upper and lower cervical spine?
Upper cervical flexion
Lower cervical extension
When you ask the patient to poke their chin out, what are the respective movements of the upper and lower cervical spine?
Upper cervical extension
Lower cervical flexion
A male football player, who plays as an offensive lineman and weighs 120 kg, is concerned about the risk of neck injury. How much force (in kg) does his neck need to generate to minimize the risk of injury?
36 kg of force
In athletes, neck strength should be approximately equivalent to 30% of body weight to decrease chance of injury
SPECIAL TESTS For Neurological Sx
Foraminal Compression (Spurling’s) Test
Maximum Cervical Compression Test
Jackson’s Compression Test
Distraction Test
Bakody’s Test (C4-C5 affectation)
Upper Limb Tension Test / Elvey Test
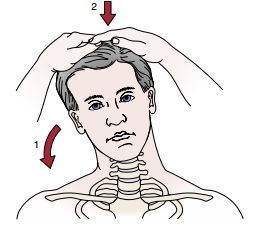
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Foraminal Compression (Spurling) Test
Pt side flexes neck on affected side
PT pushes straight down
3 Stages:
Head in neutral
Head in extension
Head in ext and rotation
(+) replication of sx
If during the spurling test:
If pain is felt on opposite side
(+) muscle spasm (tension myalgia or whiplash)
What sign is this?
Reverse Spurling Sign

Identify the test and what it’s for:
Jackson Compression Test (testing nerve root compression)
Pt rotates head to one side
PT punishes straight down
(+) radiation of pain to the arm
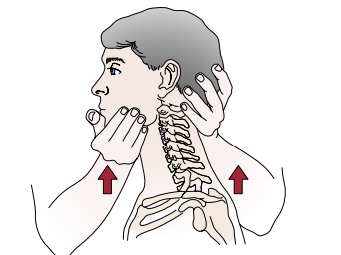
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Cervical Distraction Test (relieve sx of nerve root compression)
Pt in sitting/supine position
Place one hand around the occiput and one hand under the chin
Slowly lift pt’s head
(+) relief or reduction of pain
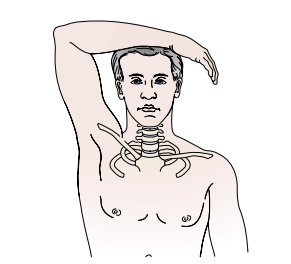
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Shoulder abduction / Bakody’s Test (C4-C5 affectation)
Pt is sitting or supine
PT passively or pt actively elevates arm through abduction until it rests on top of head
(+) Bakody’s Sign if relief occurs
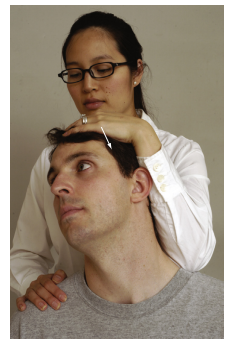
wat dis
Maximum Cervical Compression Test (nerve root/VBI)
Pt in sitting position, laterally flex and rotate head to same side (add extension for more compression)
(+) if pain radiates to arm (on compressed side)
pain on the convex side indicates muscle strain
held for 20 to 30 seconds to elicit symptoms of VBI
Upper Limb Neurodynamic / Tension Test 1-4 or Elvey Test:
ULTT A / ULNT 1 nerve bias = ?
ULTT B/ ULNT 2 nerve bias = ?
ULTT C/ ULNT 3 nerve bias = ?
ULTT D/ ULNT 4 nerve bias = ?
ULTT A / ULNT 1 nerve bias = Median nerve, anterior interosseous nerve, C5, C6, C7
ULTT B/ ULNT 2 nerve bias = Median nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, axillary nerve
ULTT C/ ULNT 3 nerve bias = Radial nerve
ULTT D/ ULNT 4 nerve bias = Ulnar nerve, C8 and T1
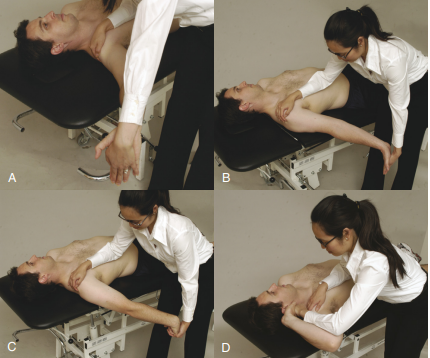
Identify which ULNT/ULTT is which:
A. ULTT A / ULNT 1
B. ULTT B/ ULNT 2
C. ULTT C/ ULNT 3
D. ULTT D/ ULNT 4
ehhh watch the vid for procedure so long eh.
Special Tests for Instability
Sharp-Purser Test
Transverse Ligament Stress Test
Lateral Shear Test
Alar Ligament Stress Test
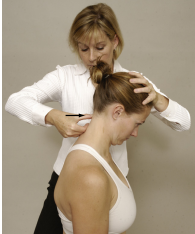
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Sharp-Purser Test (Atlanto-axial instability)
Extreme caution is required
PT places one hand on forehead, and one on spinous process of C2
Pt flexes the head while PT applies posterior pressure on forehead
(+) sliding back of the head (sublaxation)
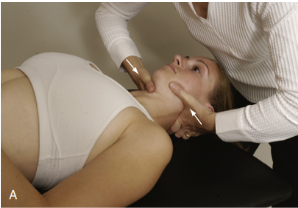
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Lateral (Transverse) Shear Ligament Test
Instability of atlanto-axial articulation (odontoid dysplasia)
Pt in supine
PT puts radial side of 2nd MCP joint to transverse process of atlas and othe MCP joint on opposite transverse process
PT pushes it together
Normally painful
The test can also be used to test other levels of the cervical spine
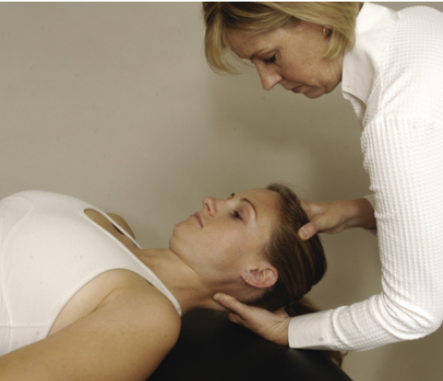
Identify the test and what it’s for:
Lateral Flexion Alar Ligament Stress Test (Alar ligament instability)
Pt in supine with head in neutral position
PT stabilizes axis with wide pinch grip around spinous process and lamina
PT side flexes the head and axis
(+) if abnormal side flexion occurs
Special Test for Vascular Problems
Vertebral Artery (Cervical Quadrant Test)
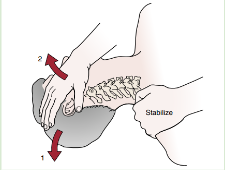
Test? wat for?
VBI Test or Cervical Quadrant Test
Pt in supine
PT extends and side flexes pt’s head, then rotate to same side hold for 30 secs
(+) provoking referred sx if opposite artery is affected
(+) dizziness or nystagmus (nerve compression)
Upper brachial plexus injury (C5-C6); Muscles of the shoulder region and elbow are affected; sensation of the radial surface of forearm, arm, and deltoid are affected
What palsy?
Erb-Duchenne Paralysis / Palsy
Atrophy and weakness of muscles of forearm, hand, and triceps (distal extremity changes)
Functionless hand
sensory loss on ulnar side of forearm and hand
What palsy?
Klumpke (Dejerine- Klumpke) Paralysis / Palsy
Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy is present in how many percent of births?
0.1 to 0.4%
Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy usually fully recovers by how many months?
2 months
Uncured until 3 months:
Decreased strength and ROM in UE
Palpation is usually done in what position?
Supine/Prone
Take not of these things in Palpation:
Skin temp and texture
Muscle tone, spasm, guarding, flaccid paralysis
Tenderness
Mobility of the spinous process
tightness/contracture = stretching
Taut bands, nodules, trigger points = massage
If I missed something u think is important message me nlng thru Rhyan Chua on fb messenger
From the screen 💻 to the ring 💍 to the PEN 🖊to the king 🤴 wheres my crown 👑 thats my bling 💎 always trouble when i reign 😈
