Chapter 33A: Introduction to Invertebrates
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Invertebrate are…
…animals that lack a backbone
Eumetazoa characteristics
true animals with tissues
exception = Porifera
Bilateria characteristics
animals with two-sided (bilateral) symmetry and three tissue layers
most animals
Invertebrate characteristics
no backbone
97% of all animal species
morphologically diverse
occupy almost every habitat on earth

Phylum Porifera
Metazoan
closest living species = choanoflagellates (protists)
basal animals
sessile
filter feeders
Ex: sponges

Filter Feeders
Phylum Porifera;
filter out food particles from the water for nutrition as they draw it through epidermal pores and then pump out the water
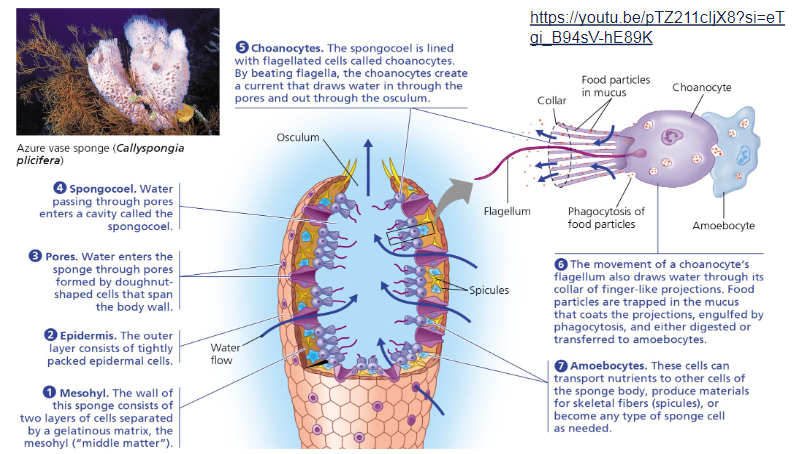
Spongocoel
filter feeders;
central cavity
Osculum
filter feeders;
large opening in the top where filtered water exits
more complex = have branched corals and several osculum
Basal animals
Phylum Porifera;
most basic
lack tissues but still have different types of cells
Mesohyl
Phylum Porifera;
two layers of cells separated by a gelatinous matrix
“middle matter”
amoebocytes and spicules found here
Epidermis
Phylum Porifera;
outer layer of tightly packed epidermal cells
Pores
Phylum Porifera;
water enters through here
formed via doughnut-shaped cells spanning the body wall
Choanocytes
Phylum Porifera;
lines Spongocoel with flagellated cells
beats to create currents that draws water in through pores and out the osculum
Amoebocytes
Phylum Porifera;
cells that transport nutrients to other cells of the sponge body
produce materials for skeletal fibers (spicules)
can become any sponge cell needed
Phylum Cnidaria
Eumetazoa;
oldest Eumetazoans = true animals
radial symmetry
gastrovascular cavity
two body plans/forms
Ex: jellyfish, corals, hydras, sea anemones, stinging-celled animals
Radial symmetry of Phylum Cnidaria
Phylum Cnidaria;
no head or brain, but have a “nerve net” that respond to stimuli
Gastrovascular cavity
Phylum Cnidaria;
Stomach: digestion, one opening, food enter→feces leave
opening surrounded by crown of tentacles (contains stinging cells)
Two body plans/forms of Phylum Cnidaria are…
Polyp and Medusa
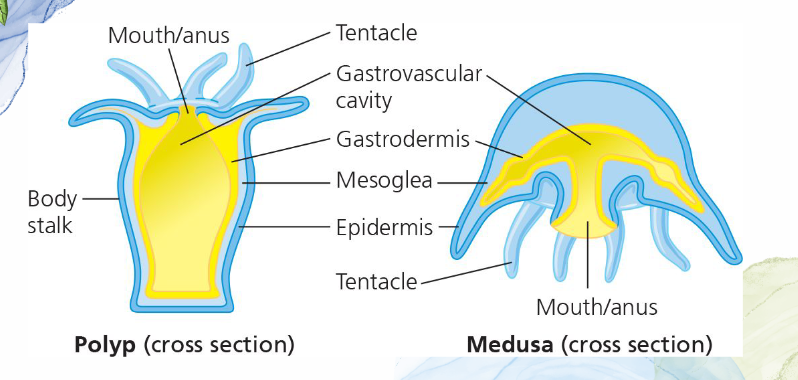
Polyp
body plan/form of Cnidaria;
usually asexual
mostly sessile
Ex: corals, sea anemone, hydra
Medusa
body plan/form of Cnidaria;
motile
sexual reproduction
medusa release egg/sperm into water→mix and fertilize→Planula larva
Ex: jellyfish, sea wasp
Nematocysts
Phylum Cnidaria;
found in cnidocytes
harpoon-like structures used for prey capture and defense
allows these animals to paralyze and kill prey much larger than them
Cnidocytes
Phylum Cnidaria;
cells unique to Cnidarians
contain "explosive" organelles called cnidocysts, used for prey capture and defense
Process of feeding for Cnidarians
prey hits “trigger” on tentacles →
coiled thread inside nematocysts release sting and can kill →
tentacles bring prey to mouth/anus
Hydrozoa
Phylum Cnidaria;
colonial
Ex: Hydra
Scyphozoa
Phylum Cnidaria;
cup animals
Ex: jellyfish

Cubozoa
Phylum Cnidaria;
highly toxic cnidocytes
respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and death within minutes if stung
Ex: sea wasp

Anthozoans
Phylum Cnidaria;
sessile
secrete and hard exoskeleton
contain zooxanthellae (photosynthetic algae)
produce colorful proteins
Ex: sea anemone, corals (coral reefs)
