Biochem II Exam IV (Part 1)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
1
New cards
What are the steps of triacylglycerol synthesis from phosphatidate?
phosphatidate, phosphatidic acid phosphatase, DAG, diglyceride acyltransferase, triacylglycerol
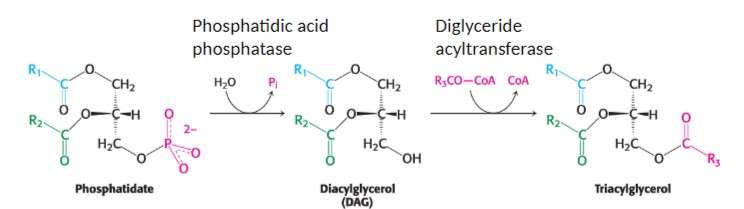
2
New cards
What is the initial product of sphingolipid synthesis?
ceramide
3
New cards
What are the steps in the synthesis of ceramide?
palmitoyl CoA + serine, (bunch of rxns), dihydroceramide, ceramide
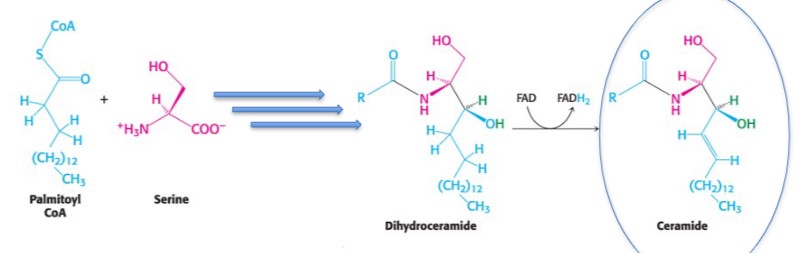
4
New cards
Which lipids function as second messengers in a variety of signal pathway?
ceramide, sphingosine, sphingosine 1-phosphate
5
New cards
What is the key regulatory enzyme in lipid metabolism?
Phosphatidic Acid Phosphatase
6
New cards
Phosphatidic acid phosphatase catalyzes the conversion of…
phosphatidate to DAG
7
New cards
In lipid metabolism, different lipids are synthesized depending on…
whether phosphatidic acid phosphatase is active or not
8
New cards
Loss of phosphatase activity in mice results in…
loss of body fat and the development of insulin resistance
9
New cards
What is the starting compound of cholesterol synthesis?
acetyl CoA
10
New cards
What are the 3 stages of cholesterol synthesis?
1. The synthesis of Isopentenyl pyrophosphate from mevalonate (cytoplasm)
2. Condensing of 6 molecules of isopentyl pyrophosphate to form squalene (ER)
3. The cyclization of squalene which is then converted into cholesterol (ER)
11
New cards
cytochrome P450 monooxygenases also functions _______ foreign substances
detoxify
12
New cards
Class of membrane-anchored enzymes that use heme as a prosthetic group and catalyze the hydroxylation of cholesterol
cytochrome P450 monooxygenases
13
New cards
What are the fates of the O2 substrate used in cytochrome P450 monooxygenases?
one is used to yield the hydroxylated product and the other is reduced to form H2O
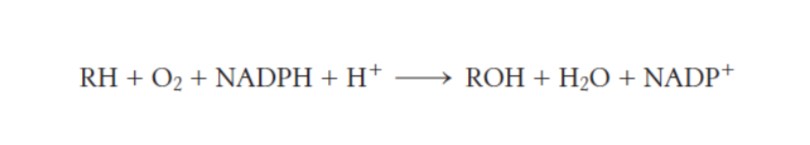
14
New cards
15
New cards
SREBP stands for…
sterol regulatory element binding protein
16
New cards
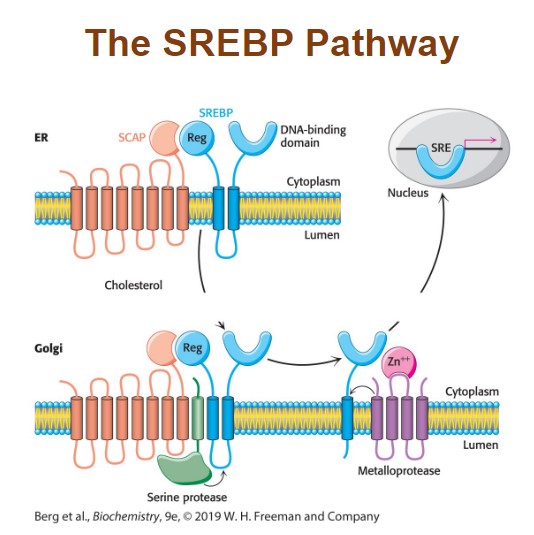
When cholesterol levels fall SCAP…
escorts SREBP to the Golgi complex where it is proteolytically processed and activated. There, the activated SREBP moves to the nucleus to stimulate reductase mRNA synthesis. (transcription factor)
17
New cards
When cholesterol levels are adequate, SCAP binds to cholesterol, which causes a structural change in SCAP that allows SCAP to bind to…
Insig (insulin induced gene)
18
New cards
What prevents the HMG CoA reductase gene from NOT being transcribed?
The interaction between SCAP and Insig. It traps SCAP and SREBP in the ER mem
19
New cards
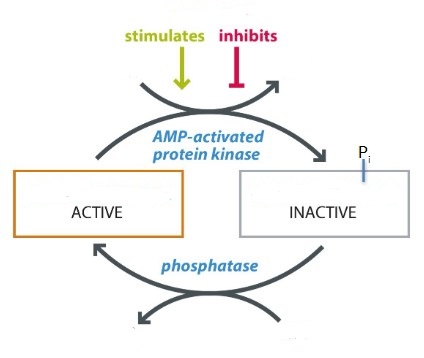
Additional regulatory strategies for cholesterol biosynthesis:
1) Rate of translation of reductase mRNA being inhibited by nonsterol metabolites of mevalonate.
2) Increase in cholesterol resulting in the proteolytic degradation of the reductase. (leads to the reductase being tagged for degradation by ubiquitin/proteasome)
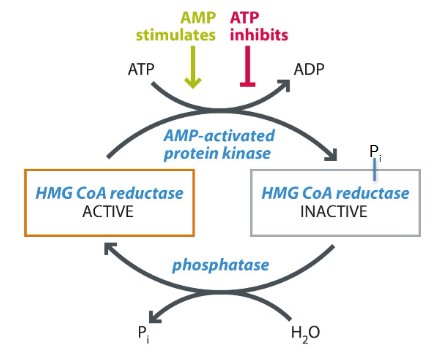
3) Phosphorylation of reductase by AMP-activated protein kinase inactivates enzyme (allows cholesterol synthesis to cease when the ATP level is low)
2) Increase in cholesterol resulting in the proteolytic degradation of the reductase. (leads to the reductase being tagged for degradation by ubiquitin/proteasome)
3) Phosphorylation of reductase by AMP-activated protein kinase inactivates enzyme (allows cholesterol synthesis to cease when the ATP level is low)
20
New cards
Cholesterol and triacylglycerols are transported in the blood in the form of …
lipoprotein particles
21
New cards
Cholesterol and triacylglycerols serve to _______ lipids and to direct ____________________
solubilize; lipoprotein particles to specific targets
22
New cards
major transporter of cholesterol in the blood to peripheral tissues
Low-density lipoprotein, LDL
23
New cards
carries cholesterol released from dying cells and membranes undergoing turnover and brings it back to the liver for excretion (reverse cholesteroltransport)
High-density lipoprotein, HDL
24
New cards
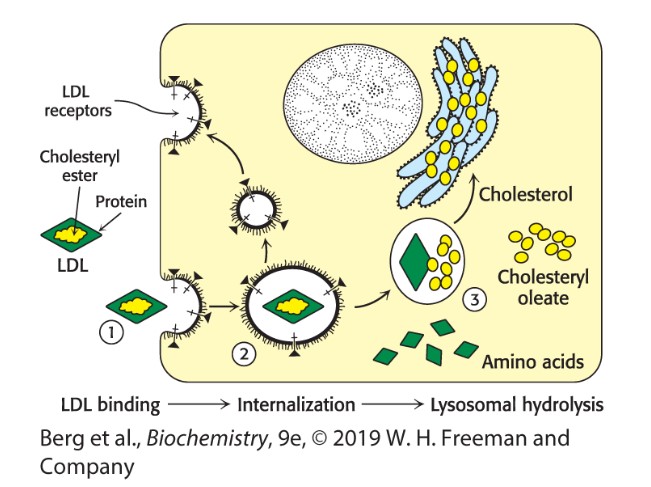
The 3 steps of receptor-mediated endocytosis:
1) LDL binds to LDL receptor
2) LDL-receptor complex is internalizedendocytosis.
3) LDL is hydrolyzed in lysosomes, and the LDL receptor is returned to the cell surface to bind another LDL particle.
2) LDL-receptor complex is internalizedendocytosis.
3) LDL is hydrolyzed in lysosomes, and the LDL receptor is returned to the cell surface to bind another LDL particle.
25
New cards
In the process of reverse cholesterol transport, HDL removes…
cholesterol from macrophages and returns it to the liver for use as bile salts or excretion
26
New cards
Competitive Inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase
Lovastatin
27
New cards
Bile salts are synthesized in the _____ and stored in the _________ until secreted into the ________________
liver; gallbladder; small intestines
28
New cards
Cholesterol is a precursor to…
steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile salts
29
New cards
detergents that render dietary lipids more accessible (due to having both a polar and nonpolar region) for digestion by lipases and thus facilitate the formation of fatty acid products
bile salts
30
New cards
What are the 5 major classes of steroid hormones?
progesterone, testosterone, estradiol, cortisol, aldosterone
31
New cards
prepares the uterus for implantation and supports pregnancy
progesterone (a progestogen)
32
New cards
promotes development of male sexual behavior and lean muscle mass
testosterone (an androgen)
33
New cards
promotes the development of female sex characteristics
estradiol (an estrogen)
34
New cards
stimulates glucose and glycogen synthesis and inhibits the inflammatory response
cortisol (a glucocorticoid)
35
New cards
regulates salt balance and the volume and pressure of blood
aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid)
36
New cards
a metabolite of testosterone, supports the embryonic development of the male phenotype
dihydrotestosterone
37
New cards
All of the steroid hormones operate in a similar fashion, in that they…
bind to and activate receptor molecules that subsequently regulate gene expression
38
New cards
Vitamin D is formed from cholesterol by the ___________ of UV-light
ring-splitting
39
New cards
In what cellular location does the synthesis of phosphatidate occur?
ER and outer mitochondrial membrane
40
New cards
Primary site of triacylglycerol synthesis
Liver
41
New cards
Phospholipid synthesis requires the combination of a(n) ________ with an _______. As in most anabolic reactions, one of the components must be activated. Which will depend on the source of the reactants.
CDP-diacylglycerol ; alcohol
42
New cards
The degradation of PHE requires oxygen. Where does the oxygen come from?
molecular oxygen
43
New cards
Amino transferases require PLP for activity. Which of the following is true concerning PLP?
a) The mechanism is very much like a protease breaking a peptide bond.
b) PLP donates high energy electrons to the reaction
c) PLP is covalently attached to the substrate by a Schiff-base linkage
d) PLP is attracted to the substrate by hydrophobic interactions
e) none of the choices
a) The mechanism is very much like a protease breaking a peptide bond.
b) PLP donates high energy electrons to the reaction
c) PLP is covalently attached to the substrate by a Schiff-base linkage
d) PLP is attracted to the substrate by hydrophobic interactions
e) none of the choices
c
44
New cards
The carbon skeletons of *___* directly enter metabloism at the level of pyruvate.
a) TYR and TRP
b) VAL and ILE
c) ALA and SER
d) THR and GLY
e) none of the choices
a) TYR and TRP
b) VAL and ILE
c) ALA and SER
d) THR and GLY
e) none of the choices
c
45
New cards
What is the activated diacylglycerol in the synthesis of some phospholipids?
cytidine diphosphodiacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol)
46
New cards
The reaction of phosphatidate with cytidine triphosphate (CTP) to form the activated diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) is driven forward by what?
by the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate.
47
New cards
The hydroxyl group on cholesterol and the subsequent hydroxyl groups added in the synthesis of steroid hormones are derived from…
a) water
b) hydroxide
c) carbon dioxide
d) molecular oxygen
e) none of the choices
a) water
b) hydroxide
c) carbon dioxide
d) molecular oxygen
e) none of the choices
d
48
New cards
In the synthesis of TAG and phospholipids, fatty acids are first attached to glycerol 3-phosphate . Which molecule is a source of glycerol 3-phosphate?
a) phosphorylation of glycerol
b) pyruvate
c) acetyl CoA
d) malonyl CoA
e) none of the choices
a) phosphorylation of glycerol
b) pyruvate
c) acetyl CoA
d) malonyl CoA
e) none of the choices
a
49
New cards
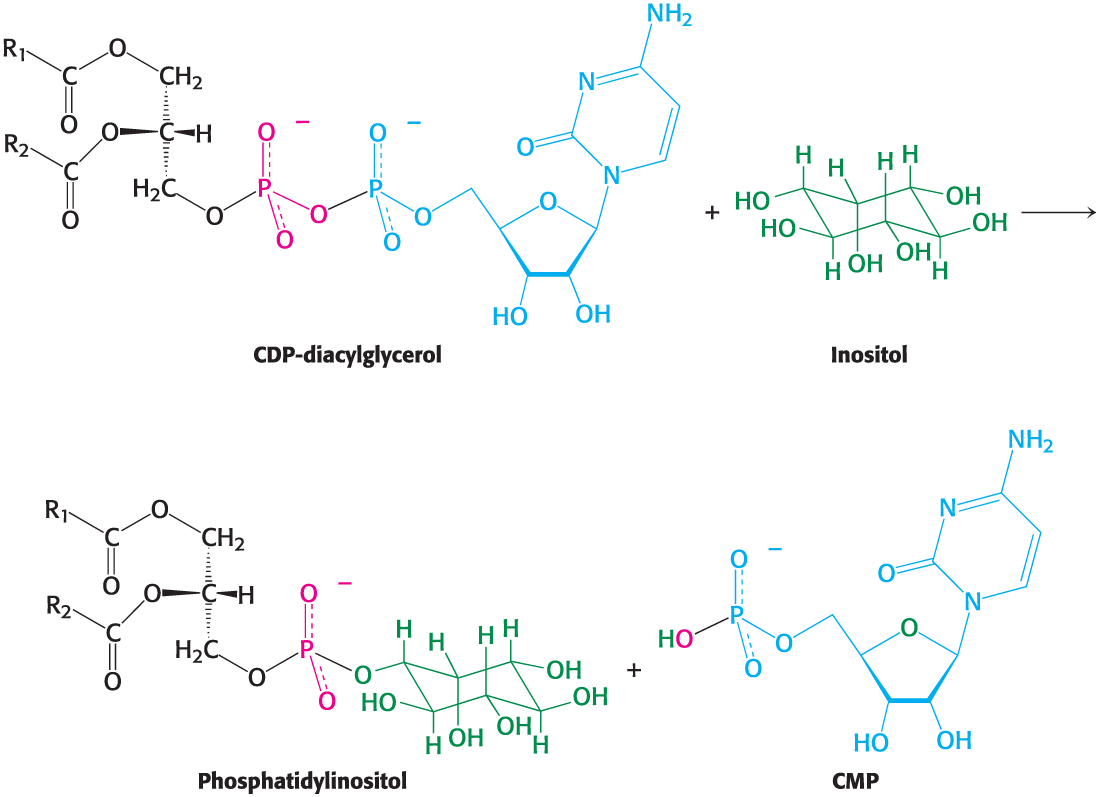
The activated phosphatidyl unit (CDP-DAG) reacts with the hydroxyl group of an alcohol to form a phosphodiester linkage. If the alcohol is **inositol**, the products are __________ and ________
phosphatidylinositol ; cytidine monophosphate (CMP)
50
New cards
*phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate* is the precursor of what two intracellular messengers?
DAG and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
51
New cards
If the alcohol CDP-DAG reacts with is phosphatidylglycerol what are the products?
diphosphatidylglycerol (cardiolipin) ; CMP
52
New cards
In eukaryotes, cardiolipin is synthesized in the __________ and is located exclusively in the ____________.
mitochondria ; inner mitochondrial membranes
53
New cards
Plays an important role in the organization of the protein components of oxidative phosphorylation
cardiolipin
54
New cards
required for the full activity of cytochrome *c* oxidase
cardiolipin
55
New cards
another word for cardiolipin
diphosphatidylglycerol
56
New cards
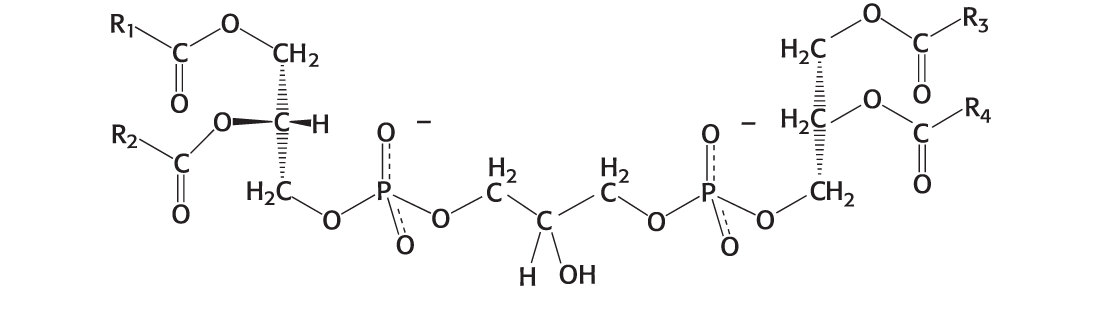
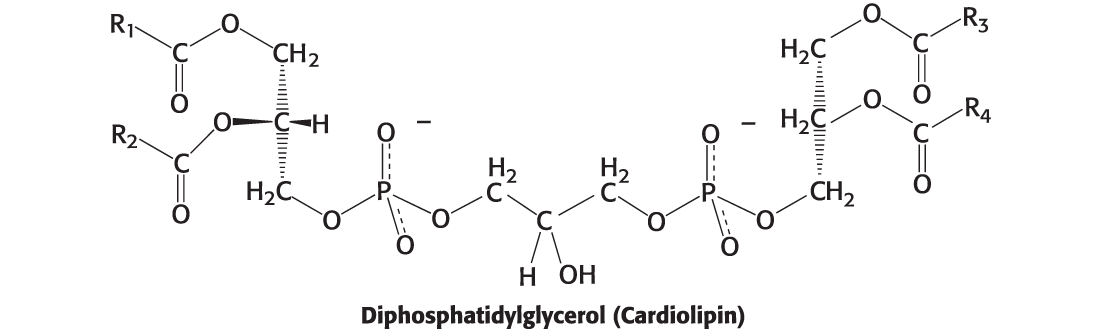
Identify the compound
Cardiolipin
57
New cards
Phosphatidylinositol is unusual in that it…….. Stearic acid usually occupies the C-1 position and arachidonic acid the C-2 position.
has a nearly fixed fatty acid composition
58
New cards
most common phospholipid in mammals comprising approximately 50% of the membrane mass
phosphatidylcholine
59
New cards
this compound is the starting point for the formation of sphingomyelin and gangliosides.
ceramide
60
New cards
the most complex sphingolipids
gangliosides
61
New cards
induces apoptosis
ceramide
62
New cards
What are the signal molecules that stimulate phosphatidic acid phosphatase?
CDP-DAG, phosphatidylinositol, and cardiolipin
63
New cards
What are the signal molecules that inhibit phosphatidic acid phosphatase?
sphingosine and dihydrosphingosine
64
New cards
When PAP is ___________it resides in the cytoplasm
phosphorylated
65
New cards
When PAP is ___________it resides in the endoplasmic reticulum
dephosphorylated
66
New cards
modulates the fluidity of animal cell membranes
cholesterol
67
New cards
the committed step in cholesterol formation
the synthesis of mevalonate
68
New cards
The synthesis of cholesterol involves the condensation of C5 units from isopentyl pyrophosphate . Which statement best summarizes the sequence of condensation that produce cholesterol?
a) Three C5 units are condensed to form a C15 unit followed by two C15 units combining to form a C30 unit that is cyclized and has carbons removed to make cholesterol (C27)
b) Nine C5 units combine together and then C3 units are removed until cholesterol (C27) is formed
c)Six C5 units are combined sequentially to make a C30 molecule that has 3C removed before it is cyclized into cholesterol (C27)
d) Two C5 units are combined to make C10. Three of the C10 units combined to make a C30 which is cyclized to form cholesterol
e) none of the above
a) Three C5 units are condensed to form a C15 unit followed by two C15 units combining to form a C30 unit that is cyclized and has carbons removed to make cholesterol (C27)
b) Nine C5 units combine together and then C3 units are removed until cholesterol (C27) is formed
c)Six C5 units are combined sequentially to make a C30 molecule that has 3C removed before it is cyclized into cholesterol (C27)
d) Two C5 units are combined to make C10. Three of the C10 units combined to make a C30 which is cyclized to form cholesterol
e) none of the above
a
69
New cards
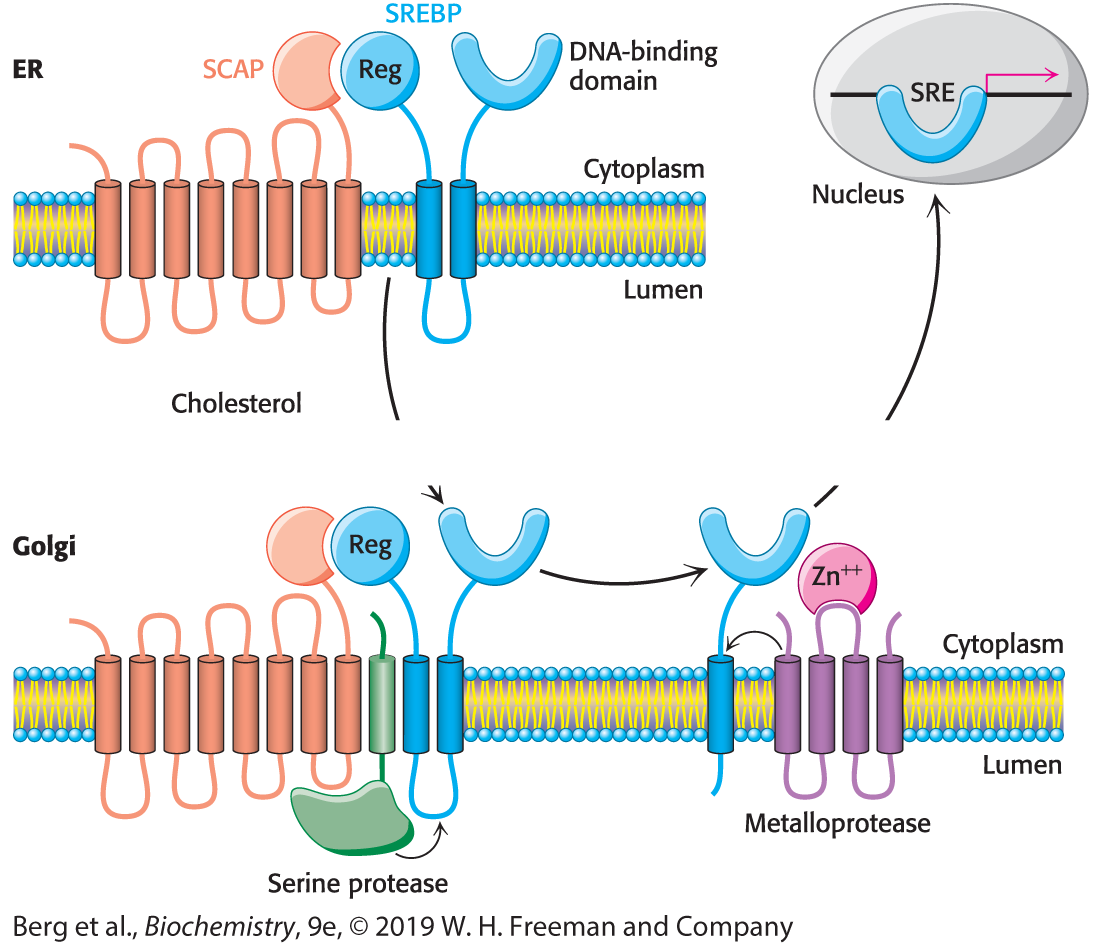
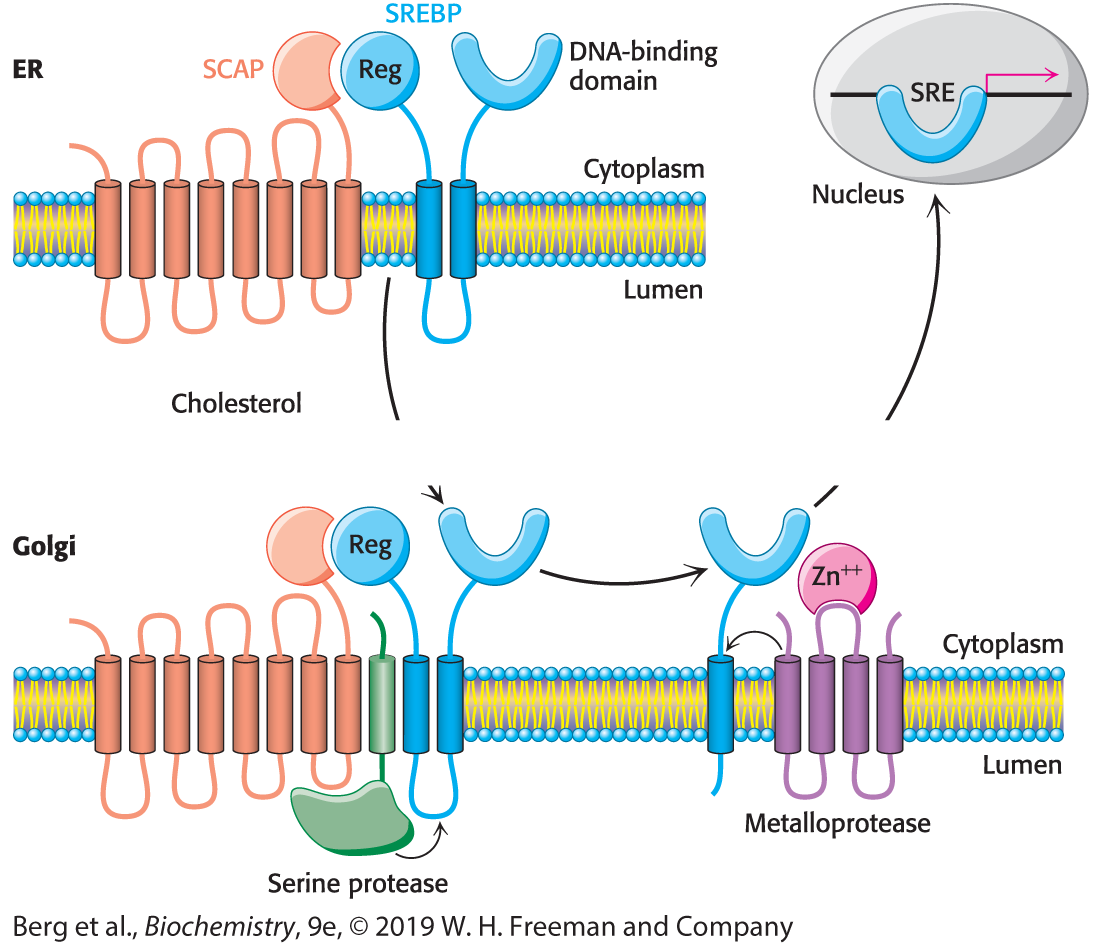
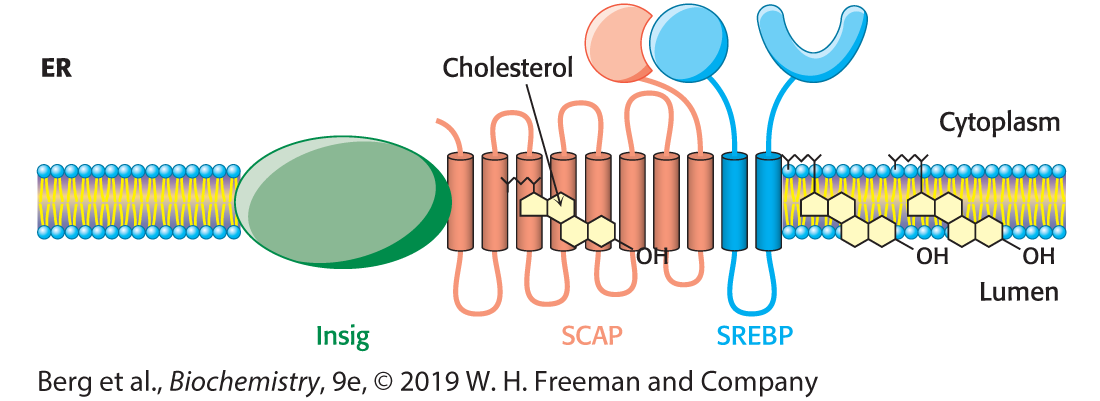
Explain each step in the picture
The SREBP pathway. SREBP resides in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it is bound to SCAP by its regulatory (Reg) domain. When cholesterol levels fall, SCAP and SREBP move to the Golgi complex, where SREBP undergoes successive proteolytic cleavages by a serine protease and a metalloprotease. The released DNA-binding domain moves to the nucleus to alter gene expression.
70
New cards
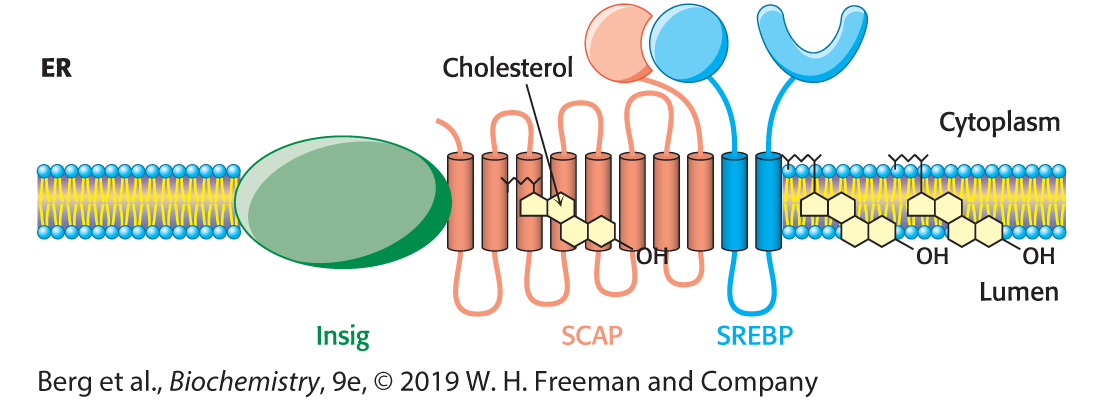
Explain what is occuring in the picture
In the presence of sterols, a subclass of Insig associated with ubiquitinating enzymes binds HMG-CoA reductase. This interaction results in the ubiquitination of the enzyme. This modification and the presence of geranylgeraniol results in extraction of the enzyme from the membrane and degradation by the proteasome.
71
New cards
Triacylglycerols, cholesterol, and other lipids obtained from the diet are carried away from the intestine in the form of large …
chylomicrons
72
New cards
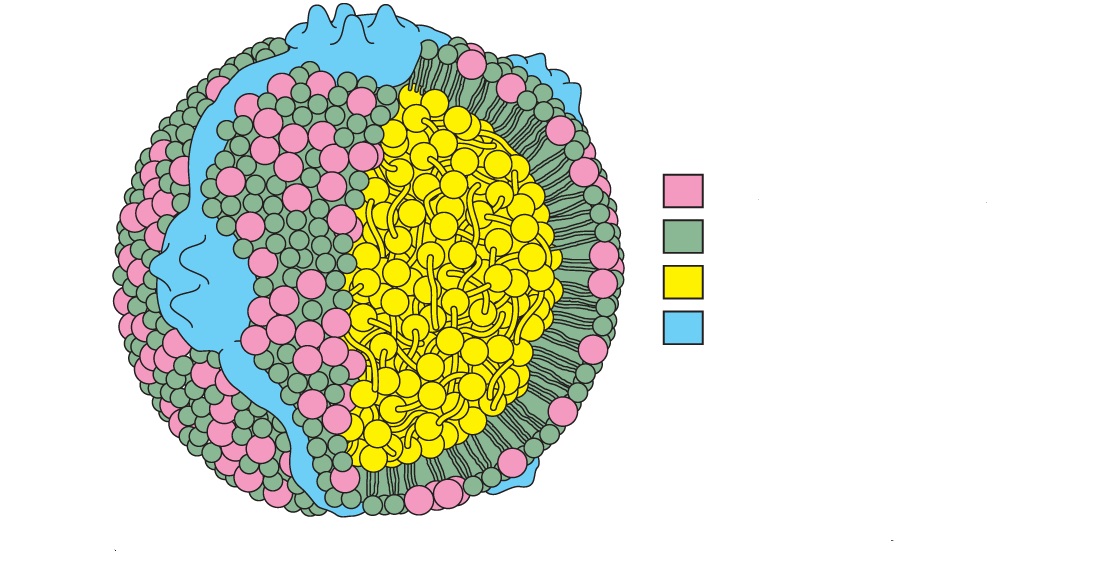
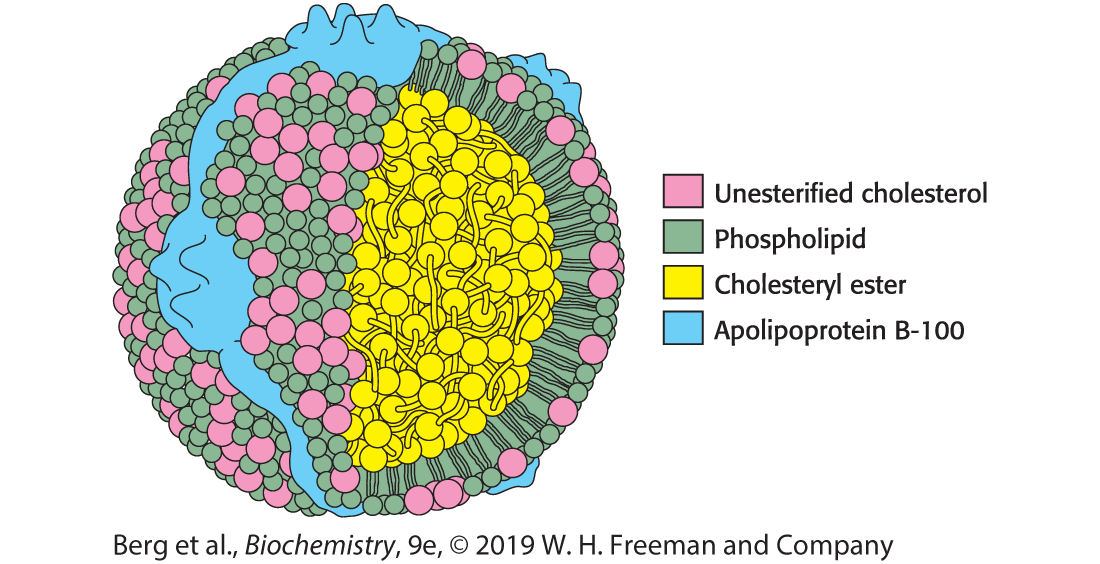
Identify the structure and the color-coded regions
low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
73
New cards
the polar derivatives of cholesterol
bile salts
74
New cards
major sites of synthesis for progestogens
corpus luteum
75
New cards
major sites of synthesis for androgens
testes
76
New cards
major sites of synthesis for estrogens
ovaries
77
New cards
major sites of synthesis for glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
adrenal cortex
78
New cards
Give examples of the wide variety of compounds formed from the C5 isopentenyl pyrophosphate
terpenes, natural rubber, carotenoids, and the side chains of": CoQ, chlorophyll, and Vit K
79
New cards
an isoprenoid
farnesene
80
New cards
All glycerol-containing phospholipids are derived from:
a) Ceramide
b) Ganglioside
c) Mevalonate
d) Phosphatidate
a) Ceramide
b) Ganglioside
c) Mevalonate
d) Phosphatidate
d
81
New cards
Sphingolipids are synthesized from:
a) Ceramide
b) Phosphatidylserine
c) Diacylglycerol
d) Isoprene
a) Ceramide
b) Phosphatidylserine
c) Diacylglycerol
d) Isoprene
a
82
New cards
The synthesis of phosphatidylcholine from phosphatidylethanolamine requires:
a) Tetrahydrofolate
b) Glycine
c) Choline
d) *S*-Adenosylmethionine
a) Tetrahydrofolate
b) Glycine
c) Choline
d) *S*-Adenosylmethionine
c
83
New cards
Cholesterol is synthesized entirely from:
a) Oxaloacetate
b) Glycerol 3-phosphate
c) Acetyl CoA
d) Serine
a) Oxaloacetate
b) Glycerol 3-phosphate
c) Acetyl CoA
d) Serine
c
84
New cards
Bile salts are synthesized from:
a) Cholesterol
b) Prostaglandin
c) Triacylglycerol
d) Ceramide
a) Cholesterol
b) Prostaglandin
c) Triacylglycerol
d) Ceramide
a
85
New cards
Describe the roles of glycerol 3-phosphate, phosphatidate, and diacylglycerol in triacylglycerol and phospholipid synthesis.
G3P is the foundation for both TAG and phospholipid synthesis. G3P is acylated twice to form phosphatidate. In TAG synthesis, the phosphoryl group is removed from G3P to form DAG, which is then acylated to form TAG. In phospholipid synthesis, phosphatidate commonly reacts with CTP to form CDP-DAG, which then reacts with an alcohol to form a phospholipid. Alternatively, DAG may react with a CDP-alcohol to form a phospholipid
86
New cards
How is the glycerol 3-phosphate required for phosphatidate synthesis generated?
G3P is formed primarily by the reduction of DHAP and to a lesser extent by the phosphorylation of glycerol.
87
New cards
Differentiate among sphingomyelin, a cerebroside, and a ganglioside.
All are synthesized from ceramide.
In sphingomyelin, the terminal hydroxyl group of ceramide is modified with phosphorylcholine.
In a cerebroside, the hydroxyl group has a glucose or galactose attached.
In a ganglioside, oligosacc. chains are attached to the hydroxyl group.
In sphingomyelin, the terminal hydroxyl group of ceramide is modified with phosphorylcholine.
In a cerebroside, the hydroxyl group has a glucose or galactose attached.
In a ganglioside, oligosacc. chains are attached to the hydroxyl group.
88
New cards
There are only 3 ways to make glycerol-based phosholipid. Describe the 3 pathways....
Activate the diacylglycerol as CDP-DAG.
Activate the alcohol as CDP-alcohol.
Use the base-exchange reaction.
Activate the alcohol as CDP-alcohol.
Use the base-exchange reaction.
89
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol from inositol?
CDP-DAG
90
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine from ethanolamine?
CDP-ethanolamine
91
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of sphingomyelin from ceramide?
phosphatidylcholine
92
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of ceramide from sphingosine?
acyl CoA
93
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of cerebroside from ceramide?
UDP-glucose/galactose
94
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of Ganglioside GM1 from ganglioside GM2?
UDP-galactose
95
New cards
What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate from geranyl pyrophosphate?
geranyl pyrophoshate
96
New cards
What would be the effect of a mutation that decreased the activity of phosphatidic acid phosphatase?
The amount of adipose tissue would decrease severely because DAG is acylated to form TAG. If there were deficient phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity, no TAGs would form.
97
New cards
Would the development of a "super statin" that inhibited all HMG CoA reductase activity be a useful drug? Explain.
No. Cholesterol is essential for membrane function and as a precursor for bile salts and steroid hormones. The complete lack of cholesterol would be lethal.
98
New cards
Glycerol-based membrane lipid
phospholipid
99
New cards
Product of the committed step in cholesterol synthesis
mevalonate
100
New cards
Ceramide with either glucose or galactose attached
sphingolipid