INSERTION, CHECKS & MAINTENANCE
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what are the general categories of denture faults
patient related
laboratory related
clinician related
what are some patient related denture faults
systemic diseases: Parkinson’s, dyskinesia, hormonal
local pathology: atrophic (flat) ridges, fibrous ridges, large bulbous ridges, undercuts, anomalies such as lumps and bumps, tori
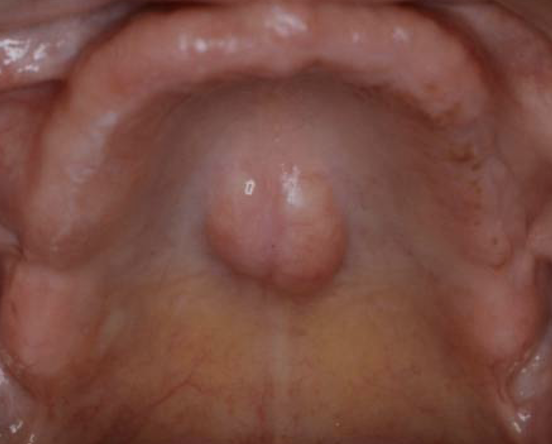
outline torus palatini and its affect on wearing dentures
torus palatini: benign bony protrusions on the roof of the mouth
difficult to place posterior border of denture
creates a rocking force on dentures
can reduce the amount of palatal coverage for dentures causing reduced retention
what are some laboratory related faults
technical errors
investment - tooth movement
processing - flash, post dam
damage to the model
outline investment
investment: covering a wax model of the denture in a special plaster material in the laboratory
what issues can there be with the investment stage
investment: covering a wax model of the denture in a special plaster material in the laboratory
there can be a small amount of tooth movement when the denture is invested
air bubbles in the plaster can cause surface defects on the denture
weak plaster can cause movement of the teeth
what issue can there be with the processing stage
‘flash’ excess acrylic can cause general defects
what are some clinical related faults
impression defects
registration errors
what is an example of an impression error
debonding of alginate at primary impressions
what anatomy can lead to inaccurate registrations and why
an atrophic ridge
difficult to get bite registration block to stay still on an atrophic ridge - can be slight movement when patient closes blocks together
what are the steps for denture placement technique
inspect fitting surface
insert - correct faults
check occlusion - correct faults
fitting surface - remove pressure spots
security - correct faults
how can the fitting surface be checked for rough areas
checking the fitting surface for rough areas
cotton wool test
run along FS, if dislodged or sticks then smooth that area before insertion
can also use a gloved hand to run along FS
—
also ask patient once they have the denture in if there is anywhere they feel uncomfortable
what tool is used to check articulation
articulating paper - can give false results
what two recorded positions need to be coincident in patients with full dentures
ICP and RCP
what is the purpose of the precentric check record
to check occlusion
outline the precentric check record process
put a small amount of wax/ silicone over the molar teeth on the right and left
get patient back into centric relation
manipulate the mouth slowly closed just before the RCP so the teeth indent the wax/ silicone but they are not coming into contact themselves
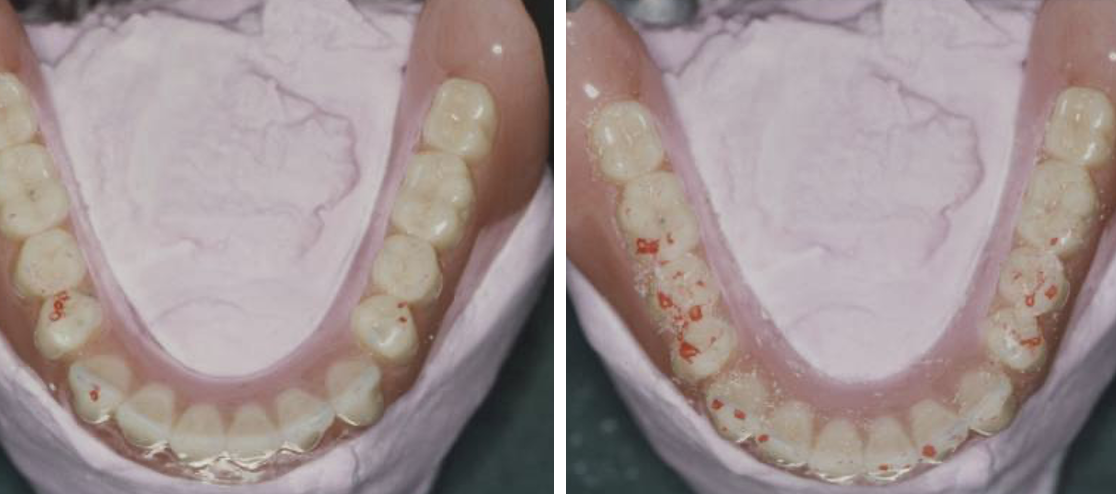
what occurs after the precentric check
teeth are sent back to the lab and remounted in plaster and put on articulator (helps stabilise the dentures so they do not rock when tapped together)
occlusion is checked on the articulator
gradually adjust and deepen the fossae to improve and increase the number of occlusal contacts - do not reduce cusp height
image of pre and post centric check record
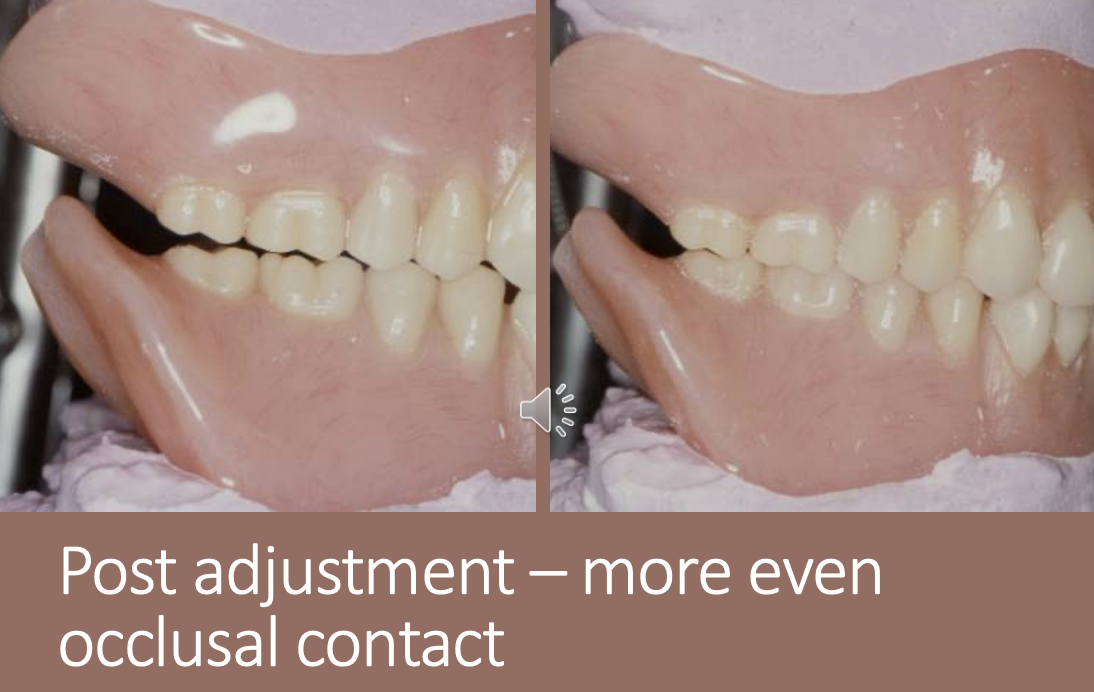
what other aspect of occlusion needs to be checked for
tooth contacts during lateral movements
how are lateral movements checked for
adjust using BULL
Buccal Upper cusps and Lingual Lower cusps
used in class I cases
how can pressure spots on the fitting surface be removed
by using Coltene PSI paste
PSI = pressure spot indicator
how should PSI paste be used
4cm of PSI paste for 1 quadrant
keep each paste at the width of the nozzle it comes in
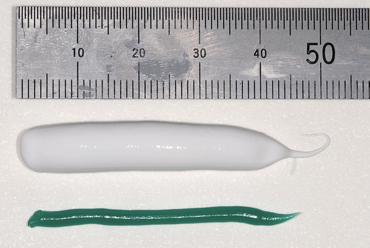
how should the PSI paste be applied
mix quickly and apply evenly - should be pale green not mint green
insert into patients mouth, press firmly and border mould well
how can you tell where the pressure spots are after using the PSI paste
where the denture shows through the PSI paste are where the pressure spots are
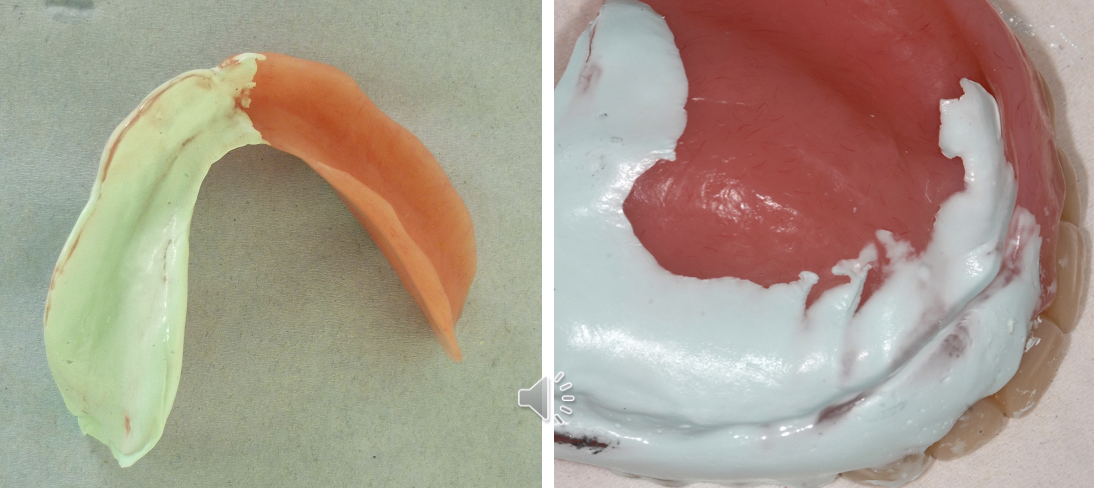
what is the pencil in the PSI kit for
marking where the denture shows through the PSI paste
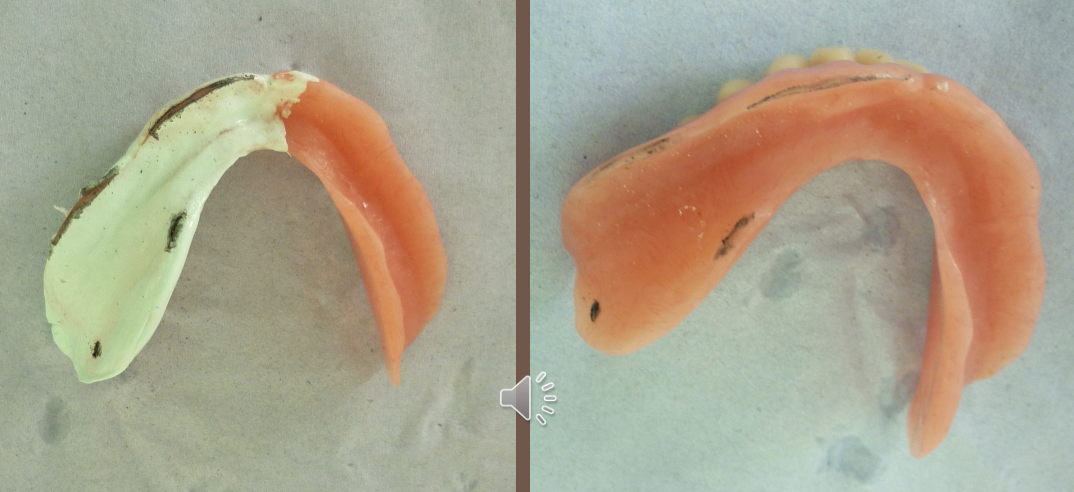
how should the denture be adjusted after marking with the PSI pencil
peel PSI paste away
use bur to adjust denture where the pencil marks have been made
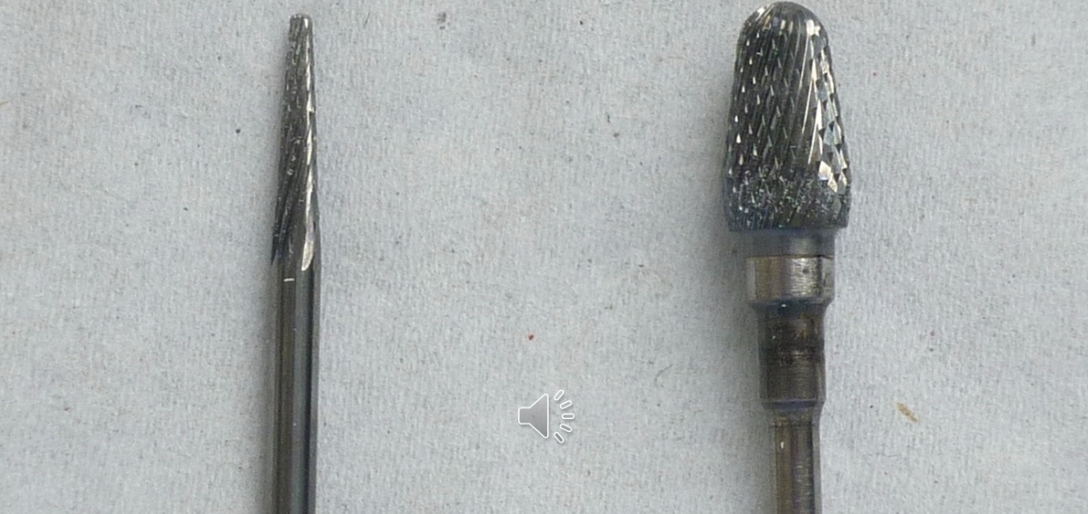
which burs should be used for denture trimming
LHS: hard to reach areas
RHS: good general purpose bur

what feature of a denture can cause denture insecurity
overextensions
how are overextensions corrected
place index finger on denture gently and pull up on cheeks and lip
if the denture pulls up, it is overextended
trim until the denture is not displaced
what is another reason for denture insecurity
inadequate post dam region
how is an inadequate post dam corrected
use autopolymerising acrylic resin to create a more functional post dam
if there is insufficient space for the midline frenum what problem can arise
the midline frenum will push the denture downwards when the patient talks or smiles if there is insufficient space for it to move
how should patients be advised on pain when wearing dentures
incredibly common in first week
reassure that you are always contactable and this is normal
if dentures must be removed due to pain, wear for 25h prior to next appt.
book patient in the week after for their review appt.
__________ plays a large part in denture success
psychology plays a large part in denture success

what is the best way to keep dentures clean
a combination of mechanical and chemical cleaning
mechanical: using a soft bristled brush
chemical: soaking
what should you ask the patient to do before their review appt.
bring the products/ equipment they used to clean their dentures to ensure they are following manufacturers instructions
what is denture stomatitis caused by
result of poor denture hygiene
also caused by patient sleeping in their dentures at night - discourage this
what should dentures not be soaked in
household bleach/ oven cleaner/ any domestic cleaners
what can be a barrier to good denture hygiene
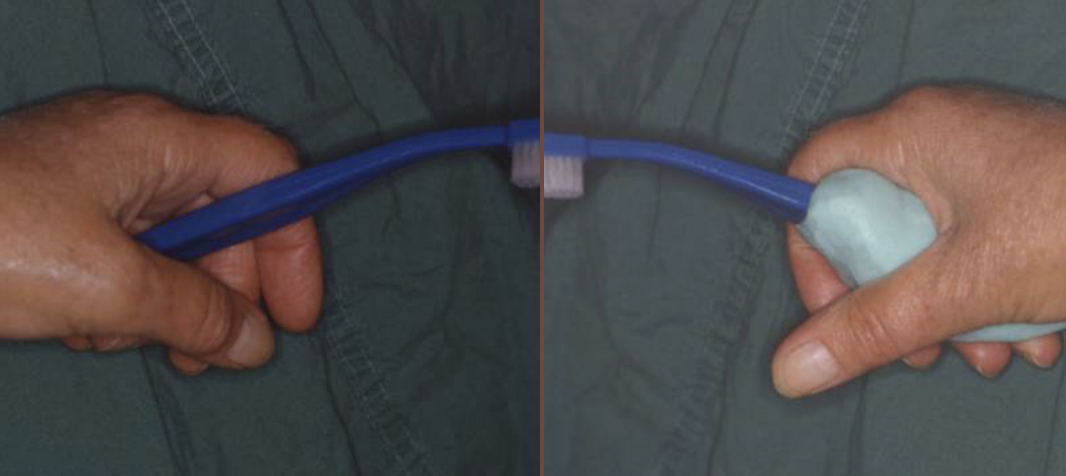
patients with arthritis/ difficulty gripping a brush
how can difficulty gripping handles be solved
silicone putty can be added to handle to give the patient a better grip
what are denture fixatives
adhesive that secures dentures to the gum
should be encouraged
what is a major cause of ulcers in denture wearers and how can this be managed
dry mouth
recommend dry mouth mouthrinse e.g. biotene
what else should you give patients at the end of their appt.
written instructions
in case they forget verbal instructions