Psychology 1 Midterm/Final
1/242
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-4: -1.1 -Why Study Psychology? -1.2 - What Psychologists Do? -1.3 - A History of Psychology), -1.4 - (Contemporary Perspectives -2.1 - Conducting Research -2.2 - Surveys, Samples, and Populations - 2.3 - Using Observations for Research - 2.4 - Experimental & Ethical Issues - 3.1 - The Nervous System - 3.2 - The Brain: Our Control Center - 3.3 - The Endocrine System - 3.4 - Heredity: Our Genetic Background - 4.1 - Understanding Sensation/Perception - 4.2 - Vision - 4.3 - Hearing - 4.4 - Other Senses - 4.5 - Perception
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
Psychology (definition)
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Theory
A statement that attempts to explain why things are the way they are and why they happen the way they do
Principle
A basic truth or law
Morality
The concept of good/right conduct
Behavior
Any action that other people can observe and measure
Social Science
A science that deals with and tries to explain the social aspects of the world around us
Example: Psychology
Natural Science
A science that deals with and tries to explain the natural aspects of the world around us
Examples: Chemistry, Biology, etc.
Goals of Psychology
Seeks to observe, describe, predict, and modify behaviors and mental processes
Cognitive Activities
Mental processes (can't be observed/measured)
Examples: Dreaming, Thoughts, etc.
Emotions
Feelings that can affect how someone's behavior and mental processes
Psychological Constructs
What psychologists use to help them study what we can't see (mental processes)
Surveys
A type of research method where psychologists collect data through questions asked of a particular group
Experimentation
A type of research method where psychologists collect data through running physical tests on humans/animals
Cognitive
The study of mental processes and mental disorders
Clinical Psychologist
-Makes up the majority of psychologists-Concerned with child/adult mental health, learning disabilities, geriatrics, and general health
-Treat people with problems like anxiety, depression, and other more serious conditions
-Cannot prescribe medication to patients
Psychiatrist
A medical doctor who treats psychological conditions and can prescribe medication for those conditions
Counseling Psychologist
-Treats people with adjustment problems
-Employed in businesses or higher educational institutions
School Psychologist
-Identify and help students who have problems that interfere with learning
-Use interviews, tests, and observation to help students
Educational Psychologist
-Focus on course planning and instructional methods for an entire school system (not concerned with individual problems)
-Study how learning is affected by psychological, cultural, economic, and instructional methods
-Some aid in standardized testing and issue various tests to determine college success
Developmental Psychologist
-Study changes (physical, cognitive, social, etc.) that occur throughout an individual's lifespan
-Some are especially interested in the struggles that adolescents face
Personality Psychologist
-Identify and study human characteristics/traits
-Interested in the origins of psychological problems
-Concerned with issues like anxiety, aggression, and gender roles
Social Psychologist
-Concerned with people's social behavior
-Focus on external rather than internal influences
Experimental Psychologist
-Conduct research into basic processes such as the functions of the nervous system, sensation, perception, learning, memory, thinking, and motivation
-Study reasons for psychological and biological reasons for cognitive behavior
-Most likely to perform basic research
Biological Psychologist
-Study the relationship between biological changes and psychological events
Basic Research
Research that has no immediate application and that's done for its own sake
Specialized Fields
Fields of psychology that focus on one specific aspect of behavior/mental processes
Environmental Psychologist
-Studies how people are influenced and influenced by the environment
Comparative Psychologist
-Studies animal behavior across different species
Consumer Psychologist
-Studies people and their work
-Employed by corporations to improve working conditions and increase output
-Also trained in organizational psychology
Organizational Psychologist
-Studies how people behave in organizations
-Employed by corporations to improve working conditions and increase output
-Also trained in industrial psychology
Human Factors Psychologist
-Try to find the best ways to design products for people to use
-Consider how a product will be used, affect people, look, feel, and how the product will be engineered so it's safe, durable, and comfortable to use
Community Psychologist
-Study and help create social systems (hospitals, mental health centers, school programs) that promote and foster individual well-being
-Focus on promoting change in social environments, helping powerless people, preventing threats to mental health in social environments
Forensic Psychology
-Work in the criminal justice system
-Determine psychological competence of defendants
-Try to explain how psychological problems can lead to criminal behavior
-Work with police departments to help secret police officers, help officers cope with stress, train officers in handling dangerous situations (family violence, suicide, hostage crisis)
Health Psychologist
-Study of how behavior and mental processes relate to physical health
-Try to find correlations between stress/anxiety and health problems
-Also focus on disease prevention
Cross-Culture Psychologist
-Study behavior and mental processes under different cultural conditions
7 Psychological Approaches
1.) Evolutionary (epigenetic)
2.) Biological (homeostasis)
3.) Behavioral
4.) Cognitive
5.) Humanistic
6.) Psychodynamic (Freud)
7.) Sociocultural
Biological Approach
Focuses on the nervous system, brain, hormones, and genetics (epigenetics)
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on genes
Psychodynamic Approach
Emphasizes internal/unconscious conflicts and focuses on sexual and aggressive instincts that collide with what is socially acceptable
Behavioral Approach
Examines the learning process and influence of rewards and punishments on behavior
Evolutionary Approach
Investigates how primal survival instincts can influence behaviors
Cognitive Approach
Focuses on methods people receive, store, and process information (signals sent/received by the brain through senses and physical stimuli)
Humanistic Approach
Emphasizes an individual's potential for growth and the role of perception in guiding behavior and mental processes
Sociocultural Approach
Explores how behavior is shaped by society, culture, history, and etc.
William James
-Founder of functionalism
-Early psychologist (~1842-1910)
-Influenced by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution
-Considered the founder of American Psychology
Natural Selection
Process where individuals that are best adapted to their environment will survive longer and have a higher chance to pass on their genes to offspring
Howard Gardner
-Believed/created the theory of multiple intelligences
-Functionalist
Theory of Multiple Intelligences
The theory created by Gardner that believes that some people are more naturally gifted in certain areas than others
Rehabilitation Psychology
A branch of psychology that works with patients who are challenged with disabilities
Ancient Egypt
Where documented accounts of people's actions, motives, etc. date back to
Introspection
-Created by Socrates
-Encourages people to carefully examine their own thoughts/feelings
Socrates
The Ancient Greek philosopher that developed introspection
Aristotle
The Ancient Greek philosopher that created associationism based on Socrates' teachings/introspection
Associationism
-Created by Aristotle
-The theory that association with past experiences is a basic principle and affects our current behaviors
Possession
What people from the Middle Ages believed was the source behind psychological problems/issues
Water-Float Test
What people from the Middle Ages would use to test if one was possessed or not (sank and drowned = pure, floated and lived = impure/possessed)
1879
The year considered the beginning of psychology as a modern laboratory science
Wilhelm Wundt
-Founded structuralism
-Considered the founder of modern psychology
-Established the first psychology lab in Leipzig (1879)
Structuralism
A field of psychology that focuses on the basic elements of consciousness
Sigmund Freud
-Most famous of early psychologists
-Developed psychoanalysis/psychodynamic ways of thinking
-Founded the school of psychoanalysis
-Id, Ego, Superego
Psychodynamic
Assumes that most of someone's mind is unconscious
Psychoanalysis
Emphasizes unconscious motives and internal conflicts in behavior
Id
-Like a devil
-Operates on immediate gratification and selfish desires
Ego
-Like a referee or mediator
-Executive part of our personality that we have control over (conscious)
Superego
-Like an angel
-Represents internalized ideals and provides standards for what's socially acceptable
John B. Watson
-Founder of behaviorism
-Believes that people can be totally conditioned by external events and that personal choice doesn't exist
-Did an experiment on his own son to prove his theory
B.F. Skinner
-Founded reinforcement
-Believed people learn the same way animals do
-Experimented with Skinner's Box
Gestalt Psychology
-Developed by Max Wertheimer, Kurt Koffka, and Wolfgang Kohler
-An alternative to behaviorism and structuralism that's based on the idea that your brain always wants to fill in the gap (examples on pg. 17)
Biopsychosocial
Emphasizes the affects of biological, mental, and social factors on behavior
Contemporary
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes, which was influenced by early pioneers of psychology
Gate Theory
How much information the brain can handle at once
Social Learning Theory
Suggests people can change their environments or create new ones
Learning Perspective
-Emphasizes the effects of experience on behavior
-Believes that behavior is learned either from direct experience or by observing other people
Kenneth Bancroft
A famous psychologist that studied the effects of segregation on people's behaviors
Scientific Research Procedure (5 steps)
1.) Forming a Research Question
2.) Forming a Hypothesis
3.) Testing the Hypothesis
4.) Analyzing Results
5.) Drawing Conclusions
Construct
Something that can be assumed to be present but cannot be seen/measured directly
Ex: Aggressiveness & Anxiety
Hypothesis
An educated guess that attempts to answer a research question
Replicate
-To repeat and produce the same result
-In research, this must be performed so theories and studies can be proven as fact
Survey
A technique for gathering data where people are asked to respond to a series of questions about a particular subject
Target Population
The whole group an individual wants to study or describe
Random Sample
A sample that is selected by chance from the target population
Stratified Sample
A sample where subgroups in the population are represented proportionally in the sample
Bias
A predisposition to a certain point of view
Volunteer Bias
The concept that people who volunteer for research studies have a different outlook from people who don't volunteer for research studies
Methods of Observation (6)
1.) Case Study
2.) Longitudinal
3.) Cross-Sectional
4.) Naturalistic
5.) Laboratory-Observation
6.) Testing
Case Study
An in-depth investigation of an individual or a small group
Longitudinal Method
The method where researchers select a group of participants and then observe those participants over a period of time (usually years/decades)
Cross-Sectional Method
The method where researchers select a sample that includes people of different ages
Naturalistic-Observation Method
Also known as a field study, it's where researchers observe other people or animals in their natural habitats/settings
Laboratory-Observation Method
A research method where researchers observe behavior in a laboratory rather than something's natural habitat
Testing Method
Where psychologists give people psychological tests to measure someone's behavior, personality, aptitudes, etc.
Positive Correlation
A relationship between data whereas one part rises so does the other
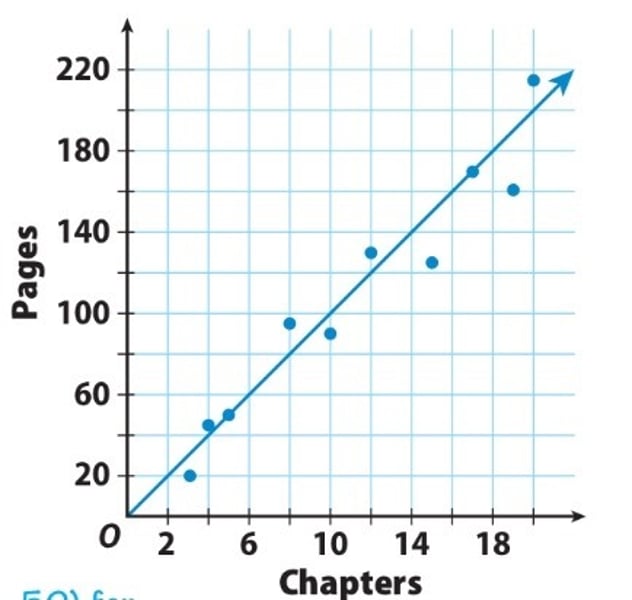
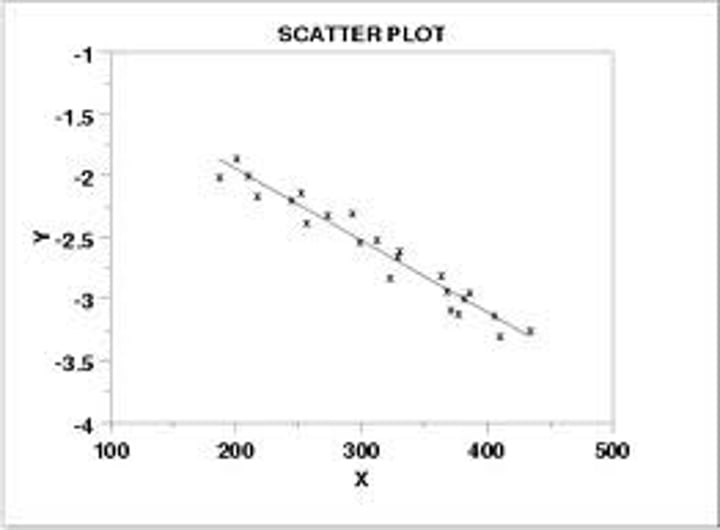
Negative Correlation
A relationship between data where one part falls and so does the other
Experiment
A method used to answer questions about cause and effect, where participants receive a treatment (a change) and their reactions are observed
Variables
Factors that can vary or change
Independent Variable
The factor that researchers manipulate so that they can determine its effect
Dependent Variable
The factor that depends on something and changes as the independent variable is changed
Experimental Group
A group in an experiment that receives the treatment
Control Group
A group in an experiment that doesn't receive the treatment
Controlled Experiment
An experiment that uses both a control group and experimental group