Orgo chapter 10-12
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:10 PM on 4/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
1 eq of Cl2 and heat
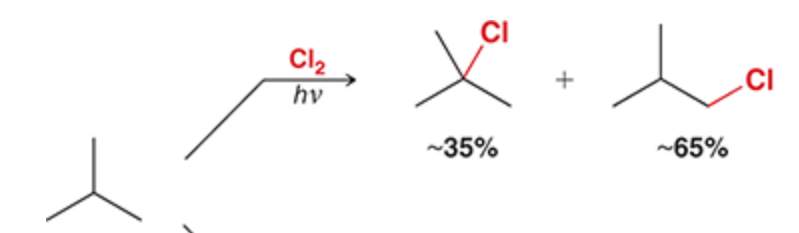
2
New cards
1 eq of Br2 and heat
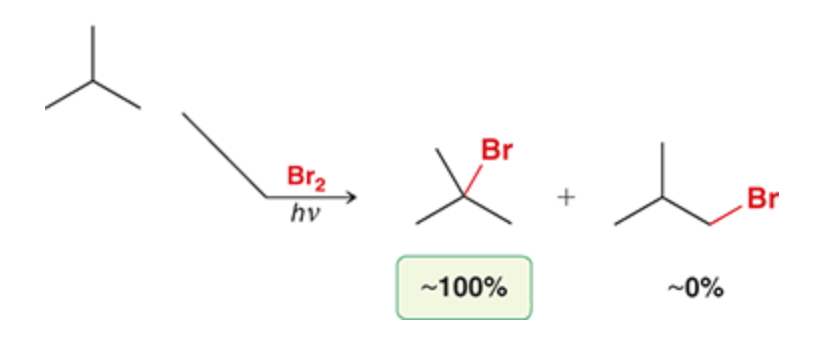
3
New cards
major monobromination (1 eq of br2)
Br is favored to attach to the tertiary position, then secondary, then primary. NEVER quaternary
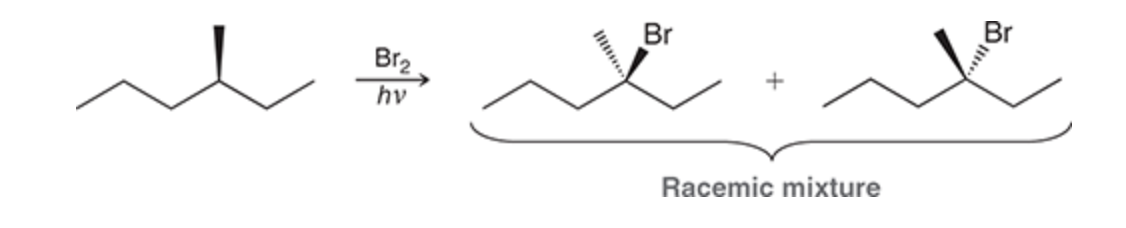
4
New cards
Radical Br2 with an existing chiral center
5
New cards
allylic bromination
Bromine is added at allylic position
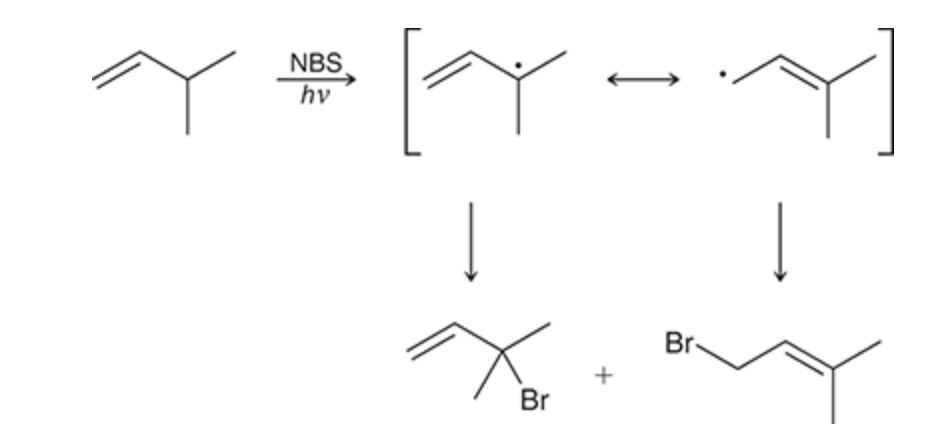
6
New cards
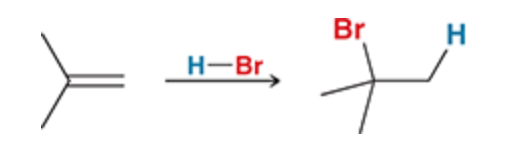
Addition of HBr
Since Br is at the most substituted carbon this is markonikov addition
7
New cards
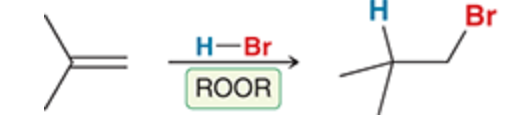
HBr and ROOR (peroxide)
This is the anti markonikov addition of HBr due to the addition of peroxide
8
New cards
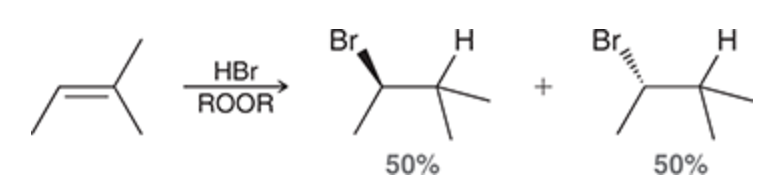
Radical addition of HBr that forms a chiral center
9
New cards
Br versus Cl
Br is slower and more selective than Cl, Br avoids mixtures
10
New cards
Halogenation at a chiral center
racemic mixture is always obtained
11
New cards
New chiral center created
both stereoisomers are produced
12
New cards
For allylic bromination NBS is used instead of Br2…
To avoid competing ionic addition reactions
13
New cards
Two step synthesis to change position of a halogen
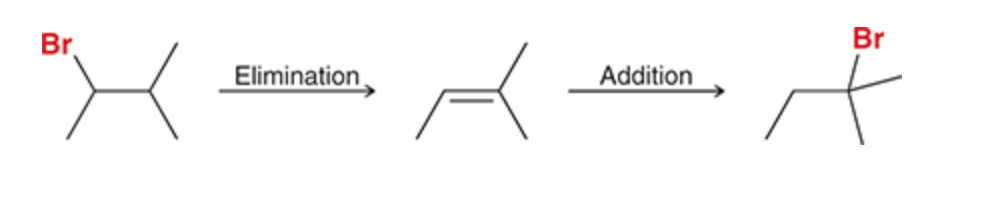
14
New cards
ozonolysis of a terminal alkyne
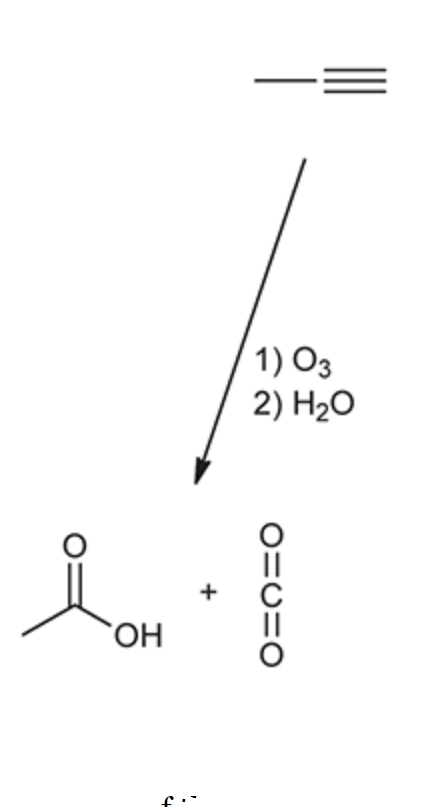
15
New cards
hydrohalogenation of an alkyne (h-x)
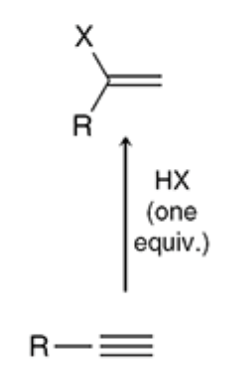
16
New cards
Formation of an Alkyne
xs NaNh2 adds a triple bond
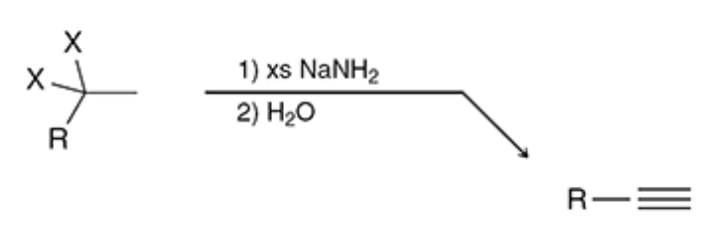
17
New cards
Hydrohalogenation of an Alkyne
xs Hx breaks a triple bond allowing more than one halogen to bond (xs br2 would add 4 br, xs hbr will add 2)
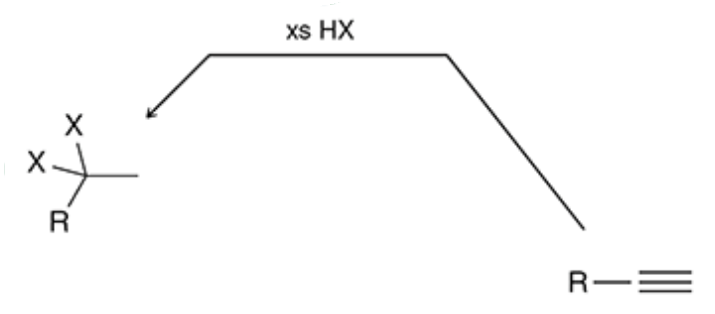
18
New cards
acid catalyzed hydration
alkyne reacts with the mercury of HgsO4, H2SO4 is the acid (h3o can also be used) and the h2o is the hydration
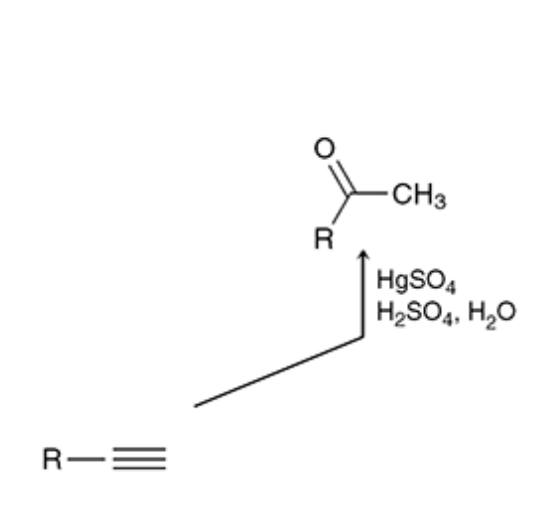
19
New cards
hydroboration oxidation
R2BH can be used for alkynes to prevent a second addition
first step generates a leaving group the second step can convert to an alcohol (enol for alkynes which then becomes a ketone)
first step generates a leaving group the second step can convert to an alcohol (enol for alkynes which then becomes a ketone)
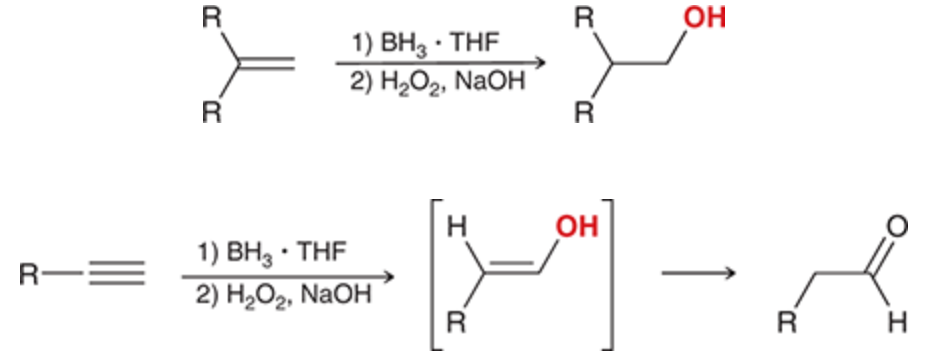
20
New cards
Halogenation (1 eq)
CCl4 is a solvent so only the x2 gets added and halogens tend to add in the anti formation rather than syn
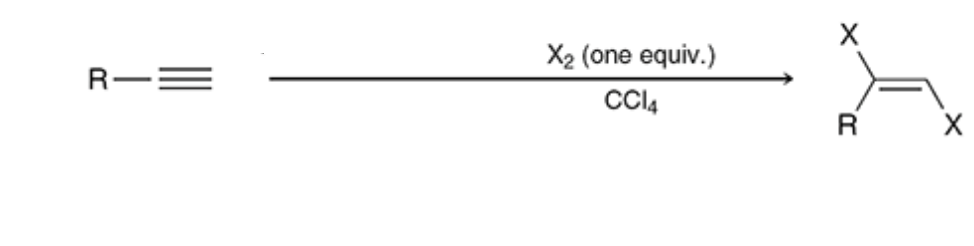
21
New cards
Halogenation ( 2 eq)
CCl4 is a solvent and with xs x2 now 4 of the halogens are added (disregard the red dot)
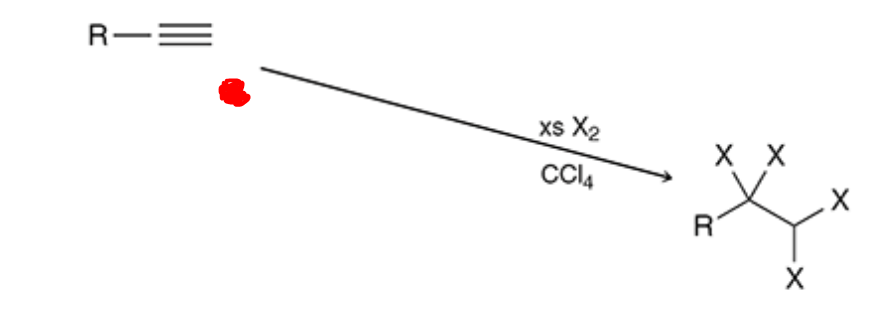
22
New cards
Alkylation
NaNH2 keeps the triple bond, the halogen gives a space for the R group to be added to deprotonate the H
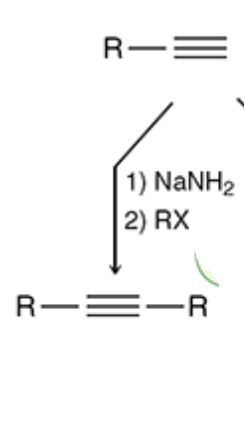
23
New cards
Hydrogenation with poisoned catalyst
H2 and Lindlars transforms alkyne to an alkene
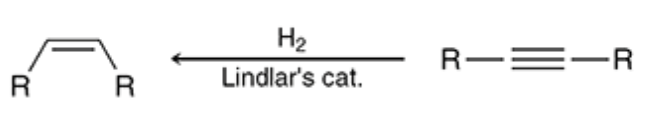
24
New cards
Hydrogenation
H2 and a metal (pt,pd etc) will turn both alkynes and alkenes to alkanes
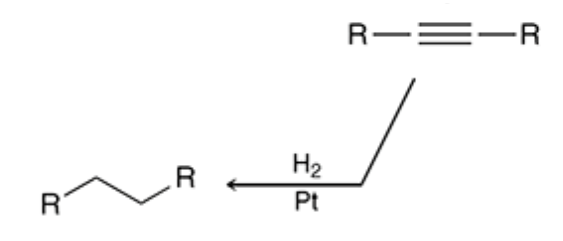
25
New cards
Dissolving metal reduction
Converts internal alkynes to trans alkenes
Na creates a radical anion intermediate then the ammonia donates a proton creating the trans alkene
Na creates a radical anion intermediate then the ammonia donates a proton creating the trans alkene
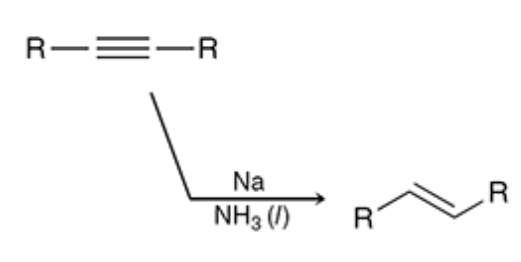
26
New cards
Alkyl halide transformations
1) NaOEt major product is a double bond
2)HBr adds Br at most subbed carbon (unless peroxide is present)
3)t-BuOK forms the hoffman product so double bond is added to the least subbed carbon
2)HBr adds Br at most subbed carbon (unless peroxide is present)
3)t-BuOK forms the hoffman product so double bond is added to the least subbed carbon
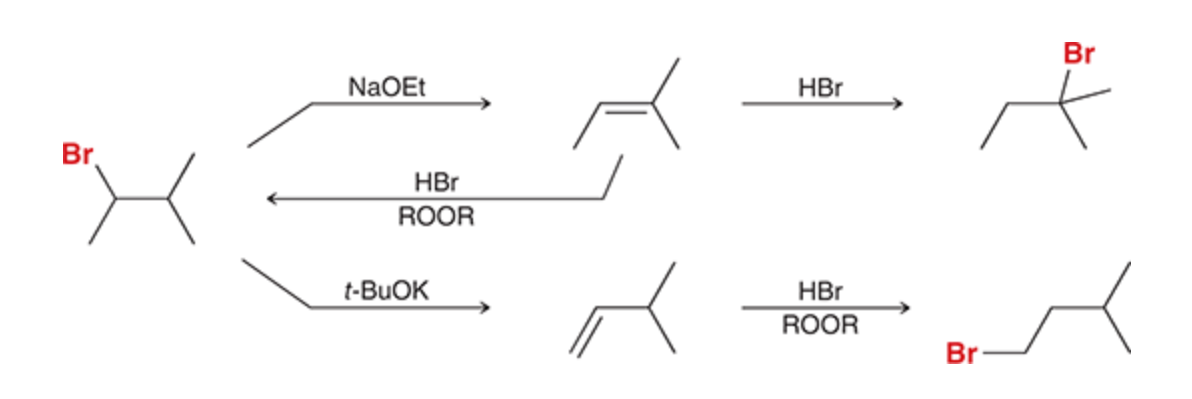
27
New cards
Use of TsCl, py
OH→OTs

28
New cards
Alkane to alkene
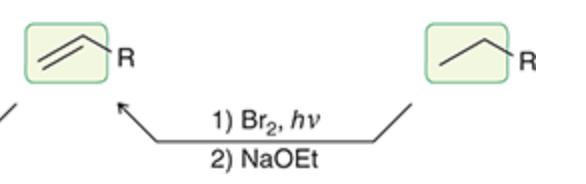
29
New cards
Alkene to alkyne
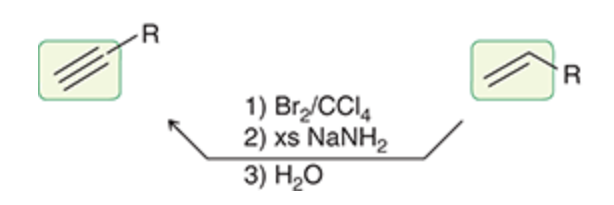
30
New cards
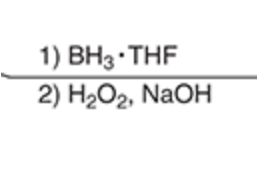
\
Convert an alkene to an alcohol
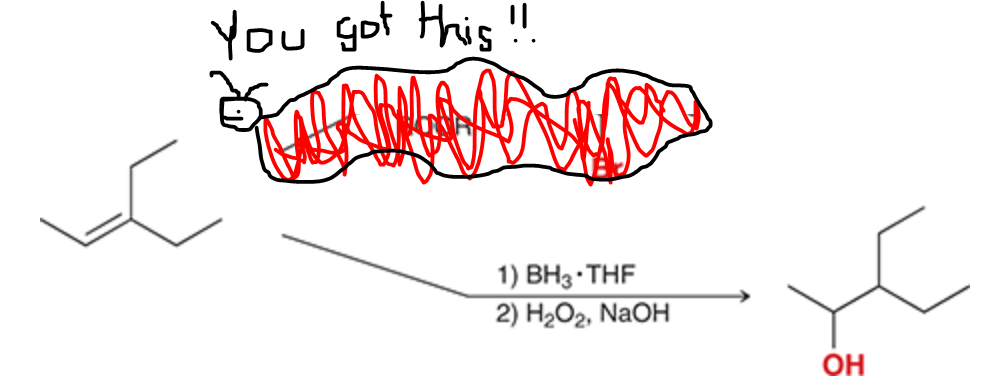
31
New cards
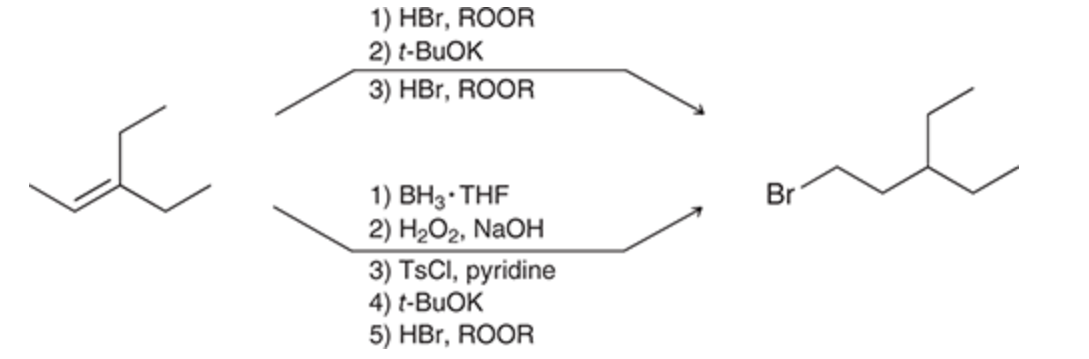
Can more than one set of reagents provide the same outcome?
Yes! orgo loves making life hard
32
New cards
How to change carbon skeleton?
React with a nucleophile with carbons to add to the carbon chain or to reduce it use ozonlysis to cleave bonds
33
New cards
Adding to carbon chain
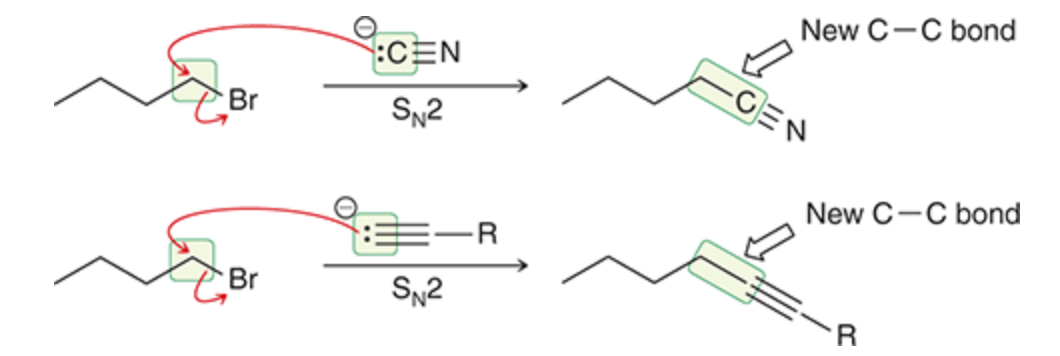
34
New cards
Reduce carbon chain
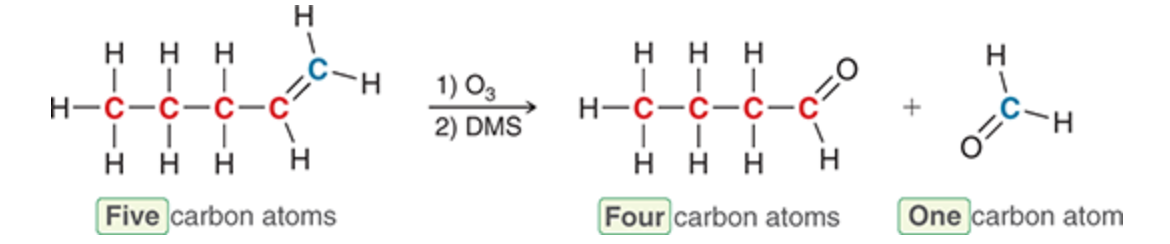
35
New cards
Creating an internal alkyne
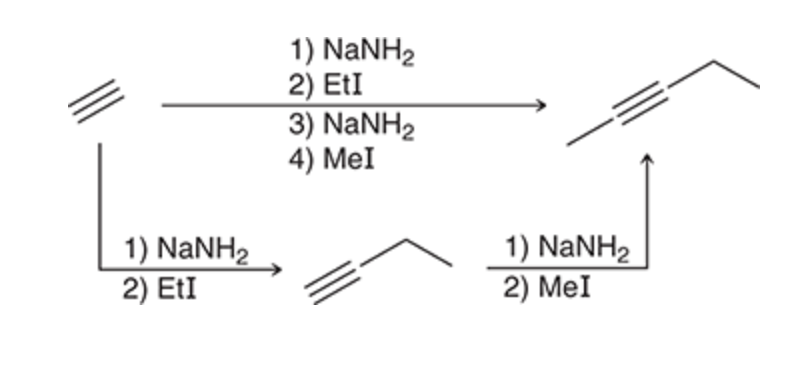
36
New cards
Target: Alkane
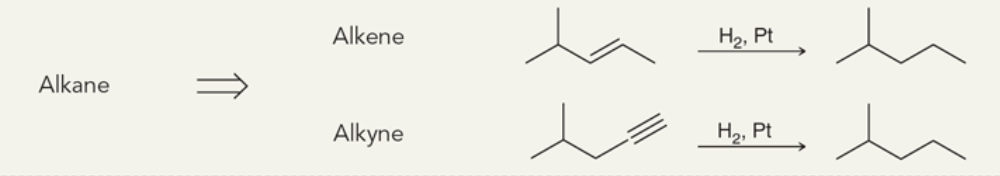
37
New cards
Target: Alkyl Halide
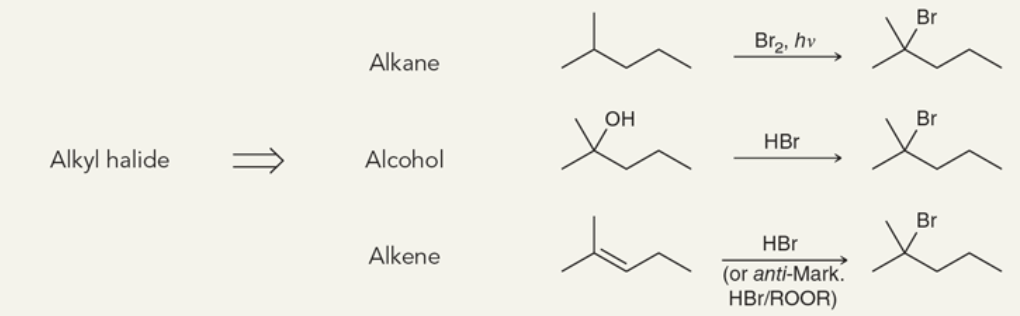
38
New cards
Target: alcohol
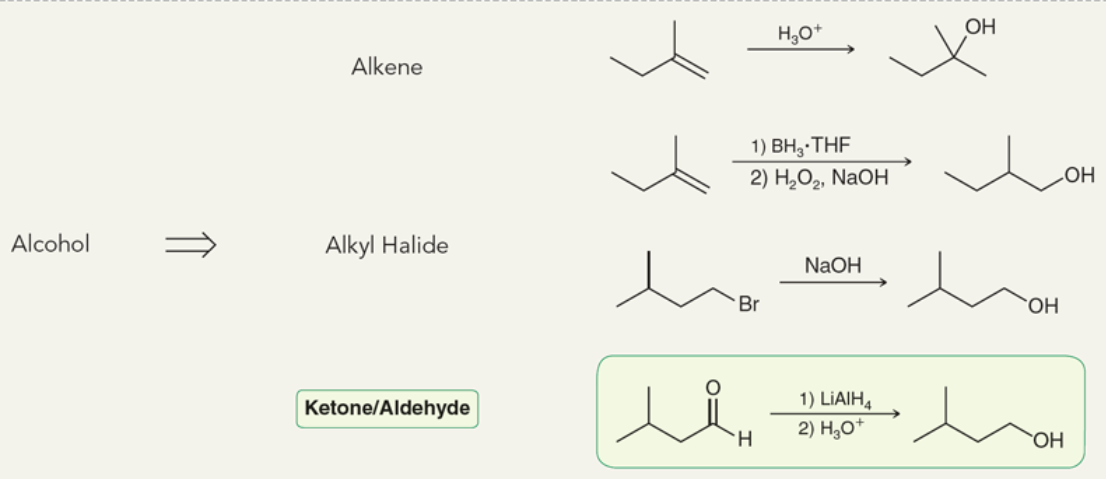
39
New cards
Target: Nucleophiles
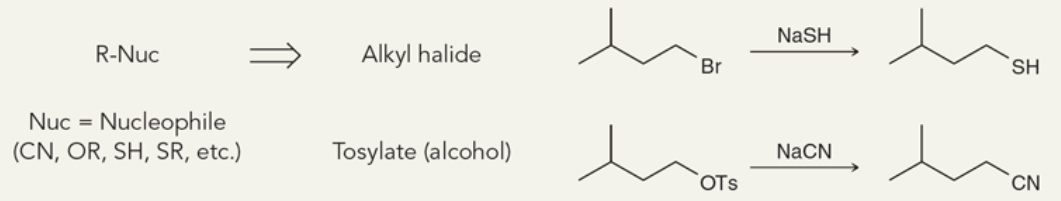
40
New cards
Target: Alkene
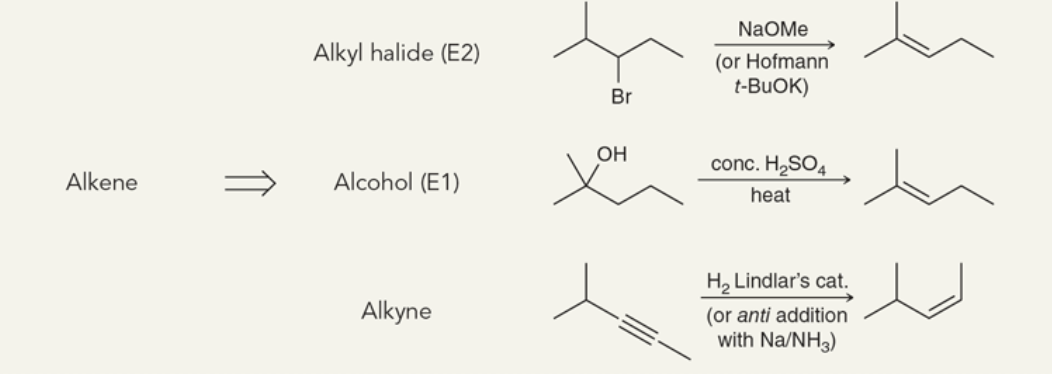
41
New cards
Target: Alkyne
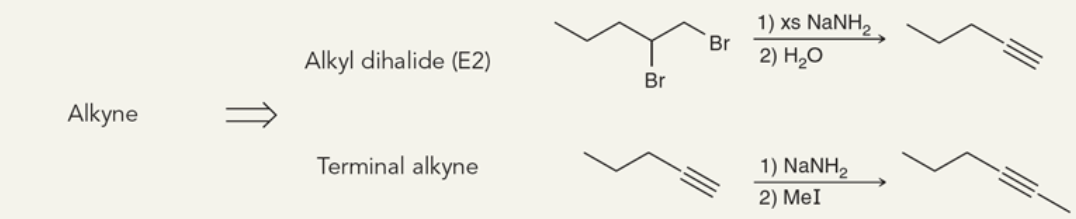
42
New cards
Target: Ketones and Aldehydes
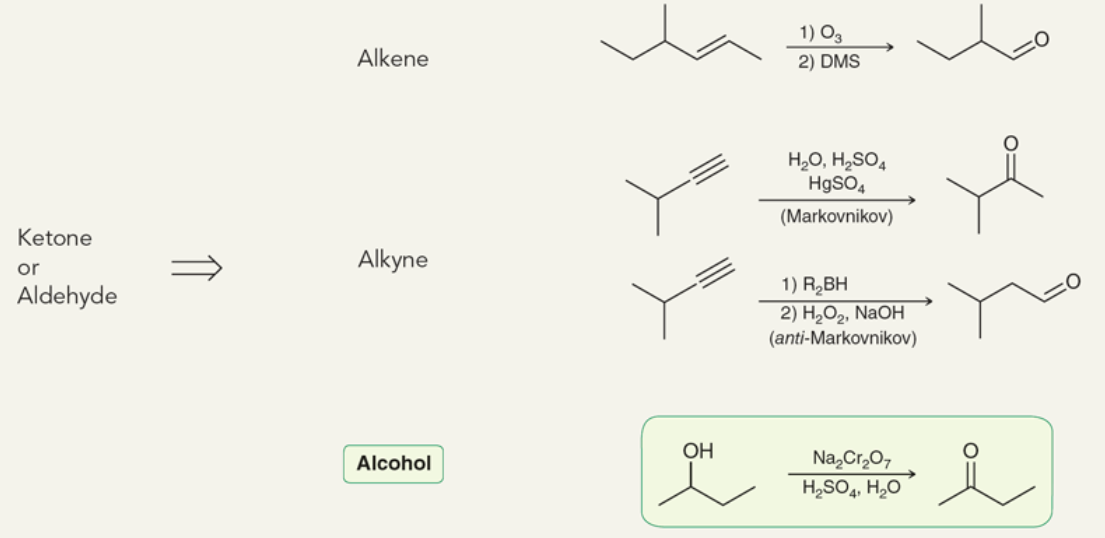
43
New cards
Target: Carboxylic Acid
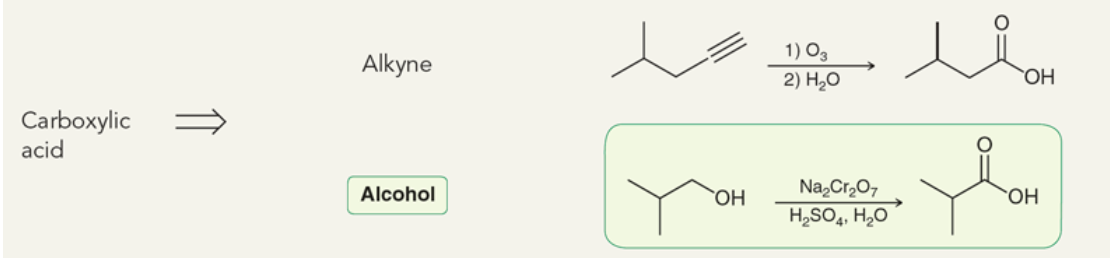
44
New cards
Na, NH3 (l)
Reduce a triple bond to a doube
45
New cards
Adding Carbons and forming an alkene
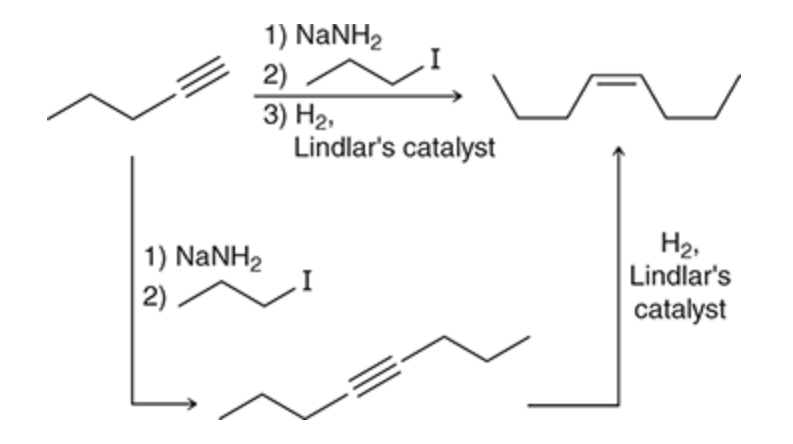
46
New cards
t-BuOK
Form a double bond
47
New cards
OsO4, NMO
Creates a diol and is steriospecific
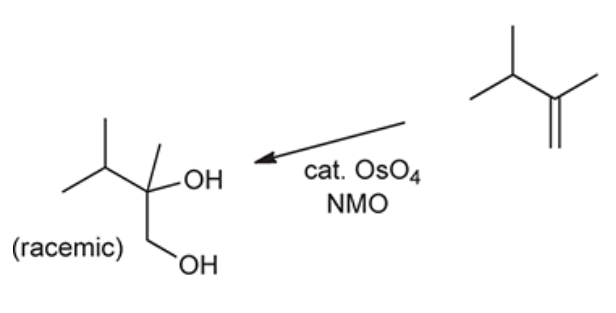
48
New cards
Charge Stability
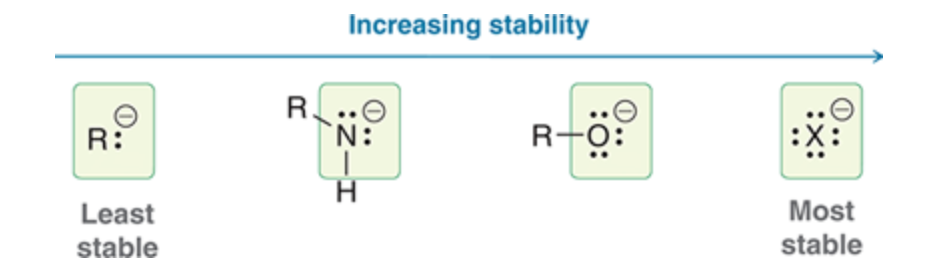
49
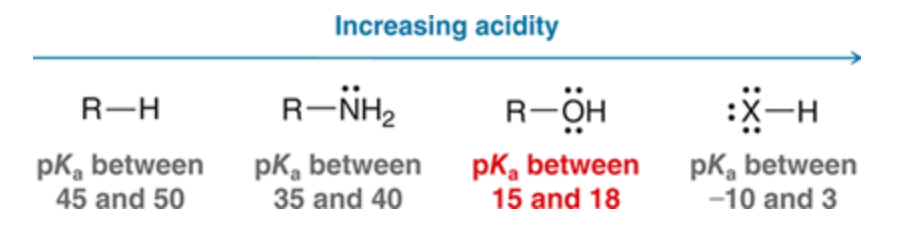
New cards
Acidity
50
New cards
Deprotonate an alcohol
1) a strong base like NaH
2) Li, Na, or K
These will produce the alkoxide ion (conj base of alcohol) and release hydrogen gas
2) Li, Na, or K
These will produce the alkoxide ion (conj base of alcohol) and release hydrogen gas
51
New cards
To convert alkoxide into corresponding alcohol
treat with H3o
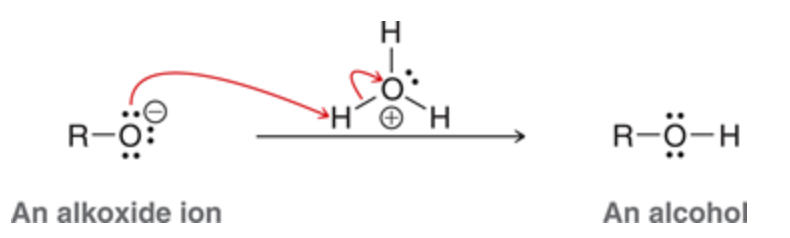
52
New cards
What impacts acidity
1) resonance more stable more resonance stronger acid
2) Induction is there another atom drawing electron density (like Cl) if so its stabilized and a stronger acid
3) Solvation effects if a compound is not sterically hindered its more solvated (stabilized) so a stronger acid (less substituents stronger acid)
2) Induction is there another atom drawing electron density (like Cl) if so its stabilized and a stronger acid
3) Solvation effects if a compound is not sterically hindered its more solvated (stabilized) so a stronger acid (less substituents stronger acid)
53
New cards
Preparing alcohols
Primary needs sn2 and a strong nucleophile while tertiary needs sn1 and a weak nucleophile
secondary alcohols cannot be prepared with sn1 as it would be too slow and it cannot use sn2 as it will favor elimination so substitution wont occur
secondary alcohols cannot be prepared with sn1 as it would be too slow and it cannot use sn2 as it will favor elimination so substitution wont occur
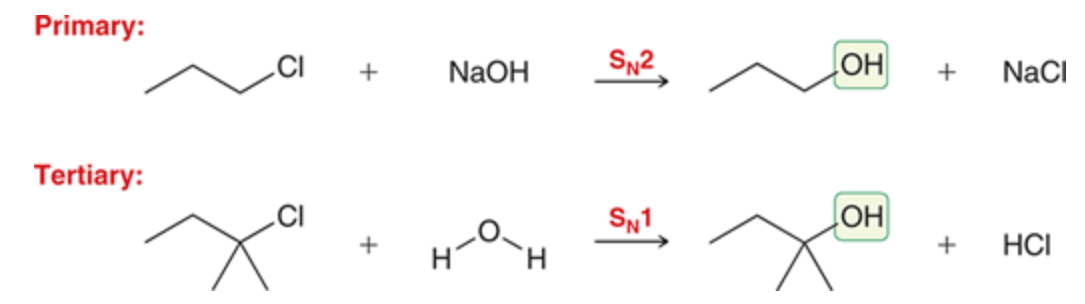
54
New cards
Produce alcohol from alkene
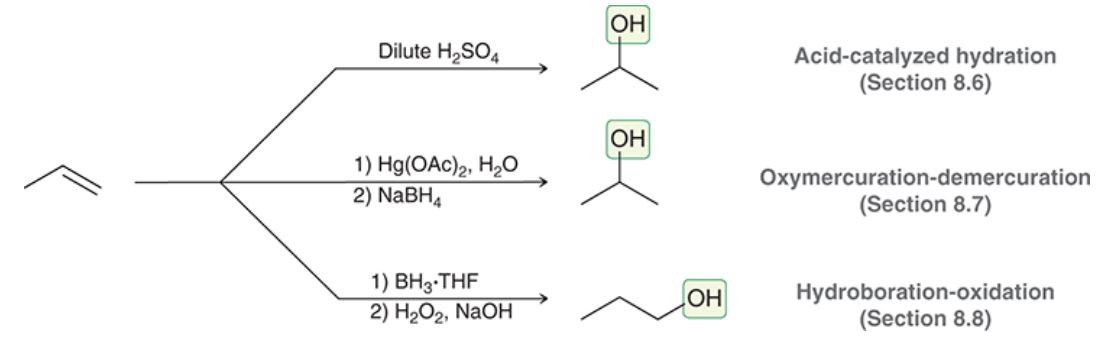
55
New cards
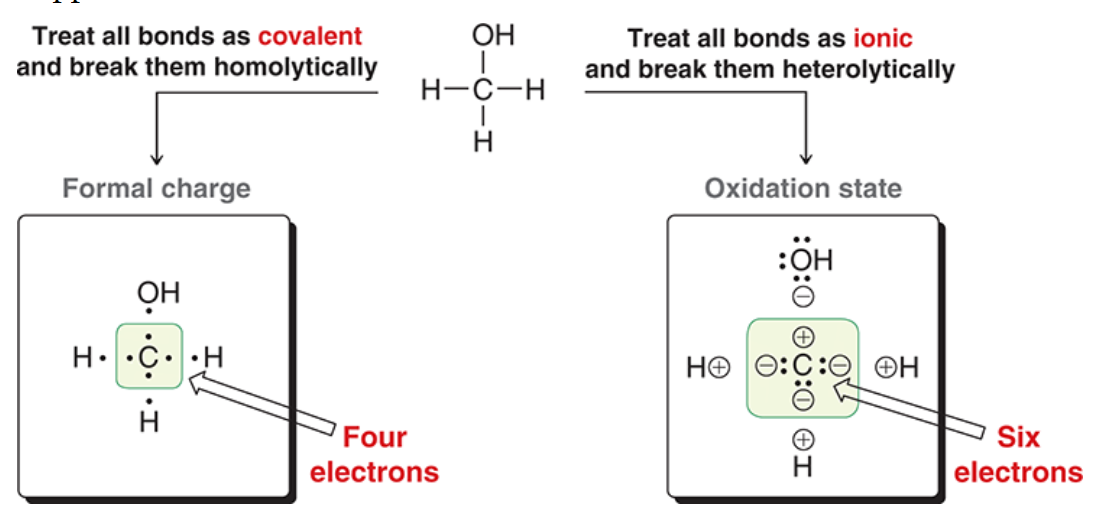
Oxidation states
If each electron goes to the more electronegative atom how many electrons will it have? bonds-electrons=oxidation state
56
New cards
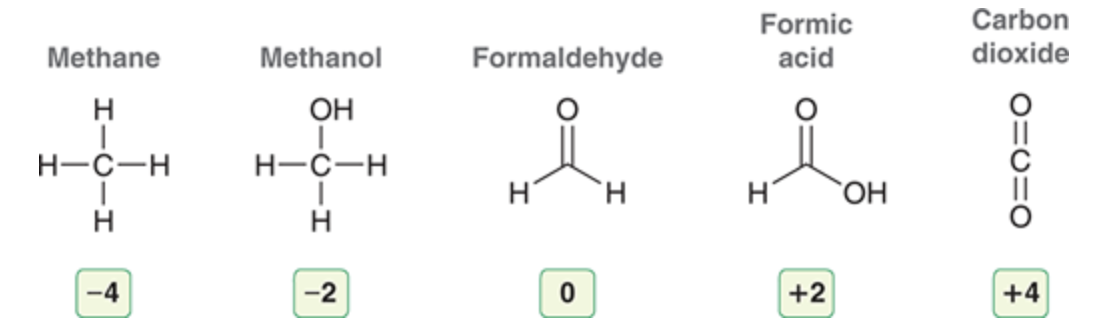
oxidation/reduction
an increase in oxidation state means the atom was oxidized while a decrease in oxidation state means it was reduced formic acid → methane is a reduction
57
New cards
Reducing agents that can be used to convert ketones/aldehydes into alcohols
1) Metal catalysts like pt, pd, ni but need high temps and high pressure rarely used
2)NaBH4 very commonly used
3)LiAlH4 (LAH) stronger reagent still commonly used BUT too reactive with protic solvents like water so the ketone/aldehyde must be treated with LAH then separately treated with H2o or H3o
2)NaBH4 very commonly used
3)LiAlH4 (LAH) stronger reagent still commonly used BUT too reactive with protic solvents like water so the ketone/aldehyde must be treated with LAH then separately treated with H2o or H3o
58
New cards
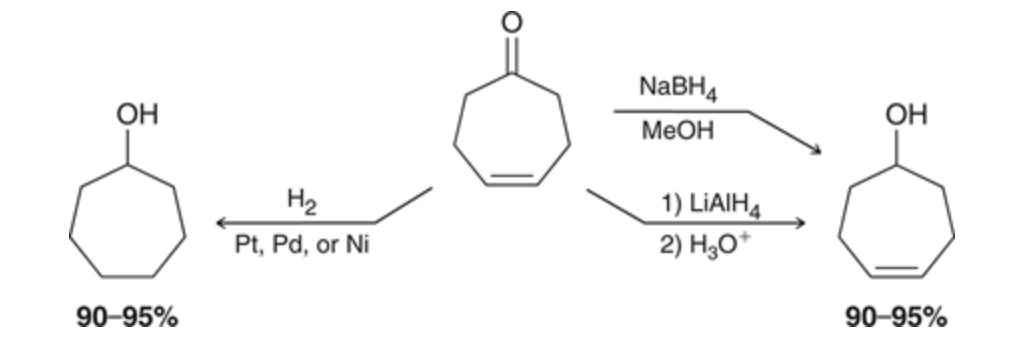
Selectively reducing carbonyl groups
NaBH4 and LAH can select only to reduce the carbonyl group while the metals will get rid of the double bond as well
59
New cards
LAH versus NaBH4
LAH can reduce a carboxylic acid or an ester to produce an alcohol due to it being more reactive than NaBH4
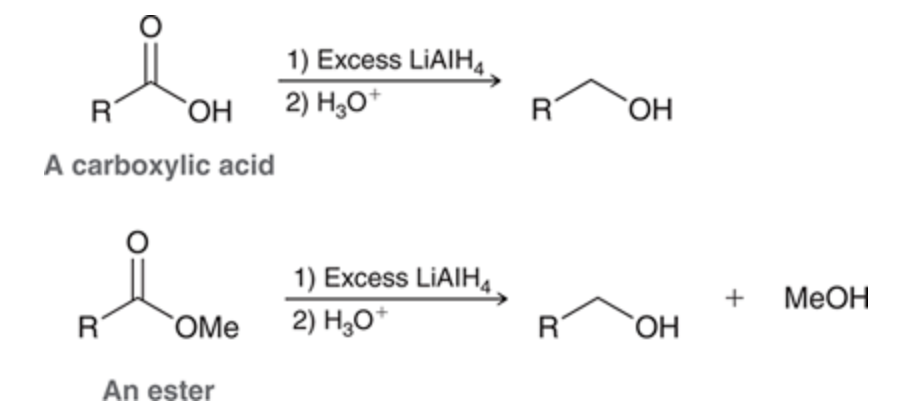
60
New cards
Formation of diols via reduction
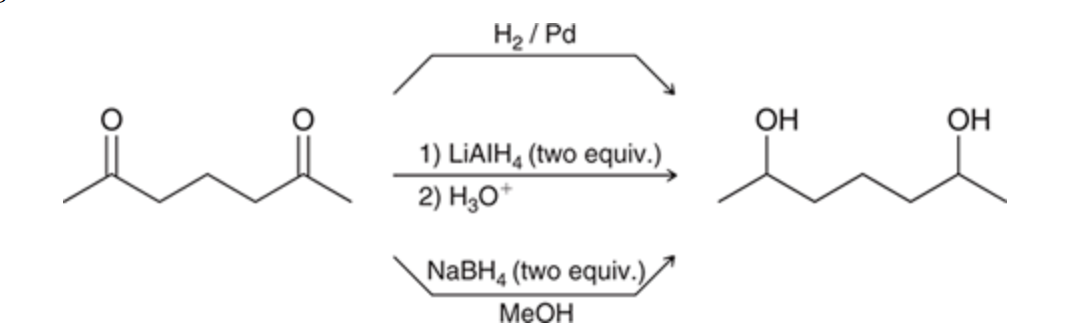
61
New cards
Diols formed via dihydroxylation
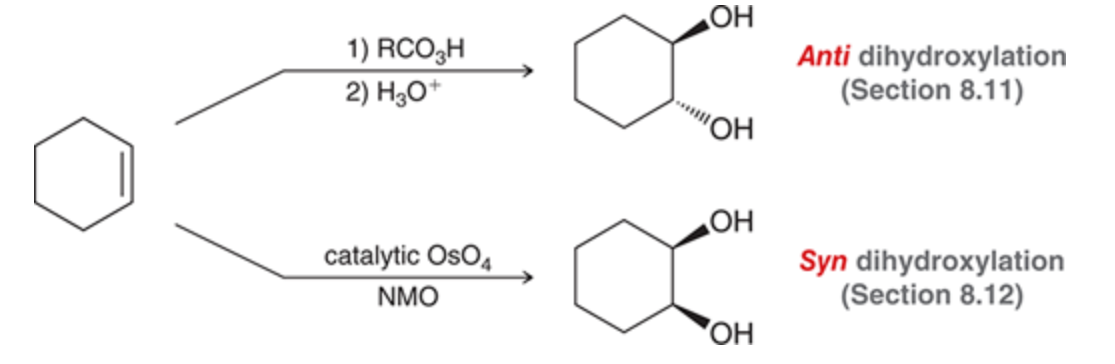
62
New cards
Grignard Reagents
Carbon nucleophiles that can attack a large range of electrophiles R-Mg-x
63
New cards
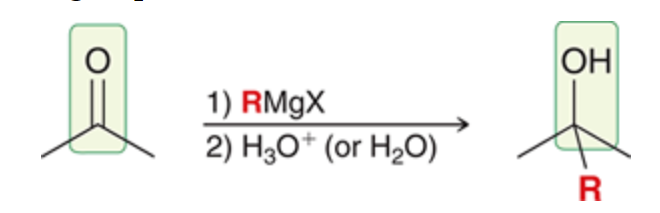
Stepwise
Proton source needs to be added separately since Grignard is a strong base it will deprotonate water
64
New cards
Grignard producing an alcohol
The second reaction forms a chiral center so there is a racemic mix of enantiomers
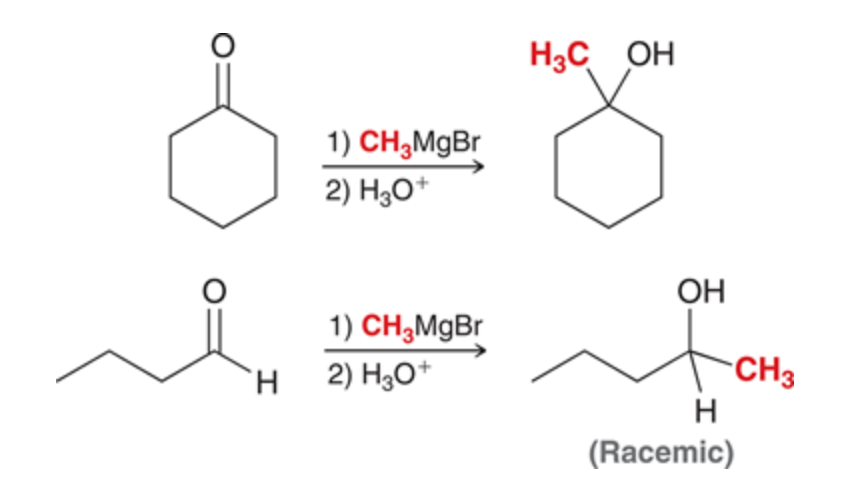
65
New cards
Grignards reacting with esters
Adds two R groups and produces an alcohol
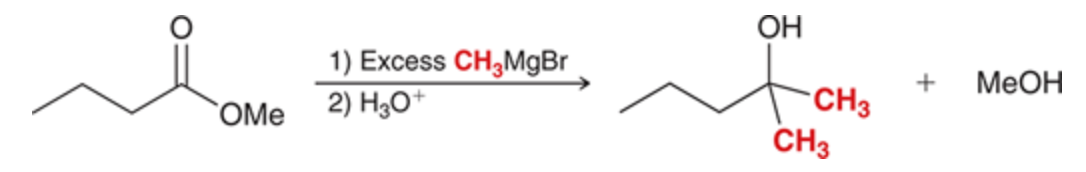
66
New cards
Grignard and carboxylic acid issues
They are not compatible as it would deprotonate and the grignard reagent couldnt form
67
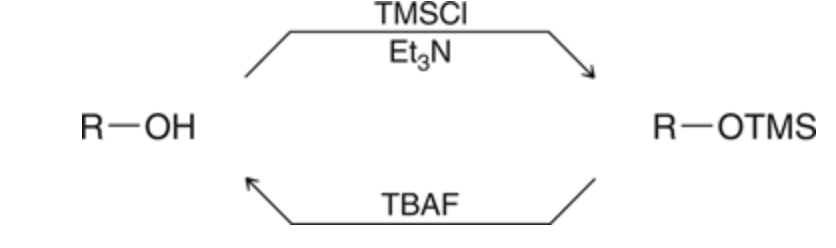
New cards
Protection of Alcohols
Protecting groups are used to prevent the grignard reagent from interacting with an OH group
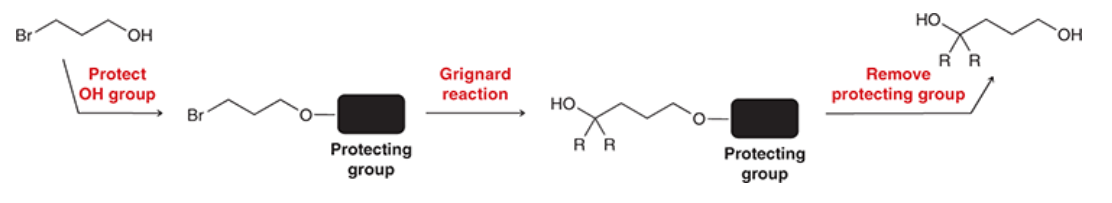
68
New cards
TBAF
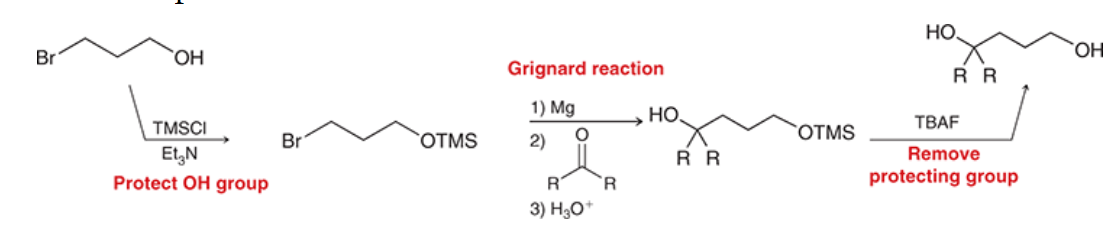
69
New cards
Sn1 rxn with tertiary alcohols
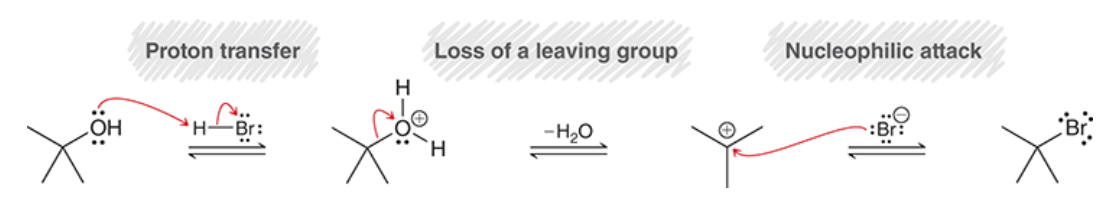
70
New cards
Sn2 rxn with primary alcohols
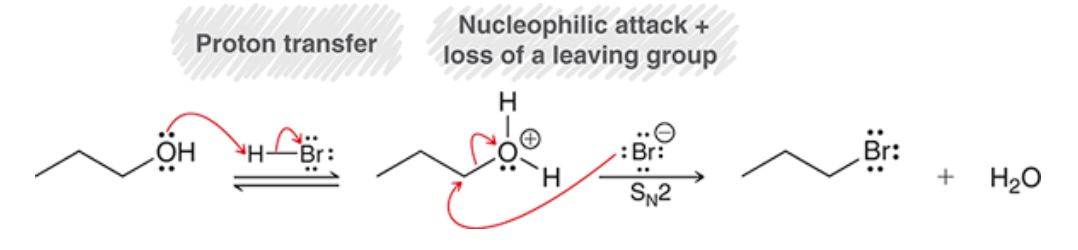
71
New cards
Primary or Secondary alcohols reacting with an Sn2 process
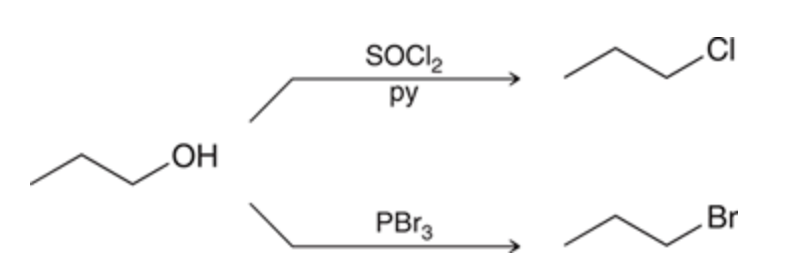
72
New cards
Tertiary alcohols E1
elimination favors more subbed alkene
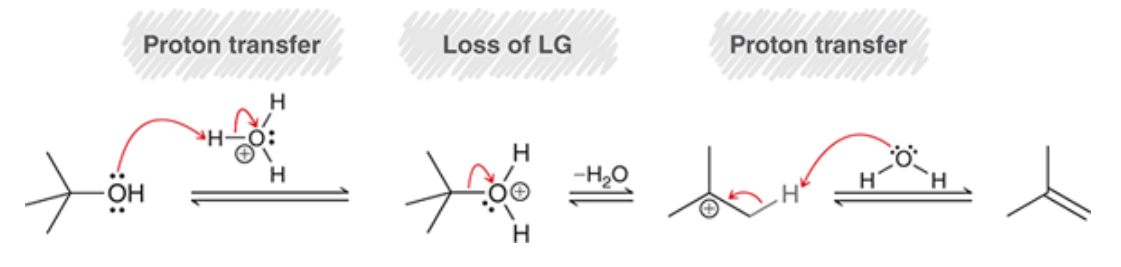
73
New cards
Tertiary alcohols E2
To use E2 the hydroxyl group must first be converted and then a strong base can be employed
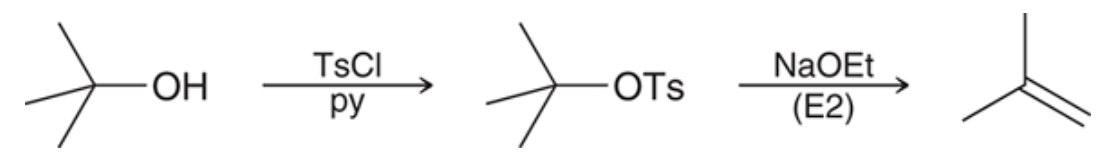
74
New cards
Alcohols during the oxidation process
Primary alcohol: can be oxidized twice first it produces an aldehyde and then the second produces a carboxylic acid
Secondary alcohol: can only be oxidized once since it only has one proton on the alpha carbon and it forms a ketone
Tertiary alcohol: Has no protons on the alpha carbon so they will not undergo oxidation
Secondary alcohol: can only be oxidized once since it only has one proton on the alpha carbon and it forms a ketone
Tertiary alcohol: Has no protons on the alpha carbon so they will not undergo oxidation
75
New cards
Chromic acid oxidations
first stage: formation of chromate ester
second stage: E2 process that forms a carbon oxygen pi bond
second stage: E2 process that forms a carbon oxygen pi bond
76
New cards
Primary Alcohol oxidized with Chromic acid
forms a carboxylic acid since its hard to stop it at the aldehyde
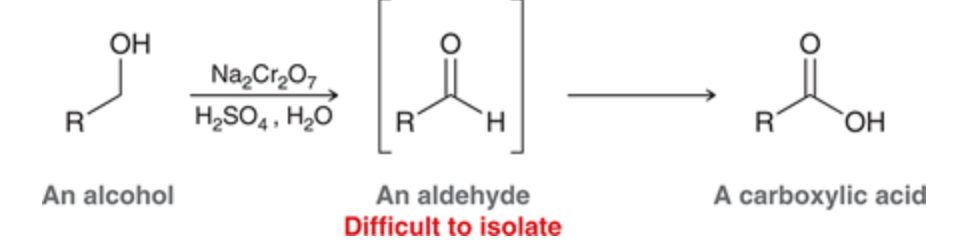
77
New cards
Primary Alcohol → aldehyde
need a selective oxidizing reagent that wont react with the aldehyde only the alcohol like PCC
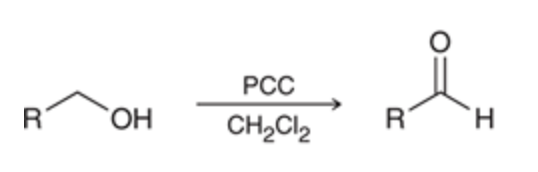
78
New cards
Secondary Alcohol to ketone
treated with a chromium oxidizing agent like chromic acid or PCC
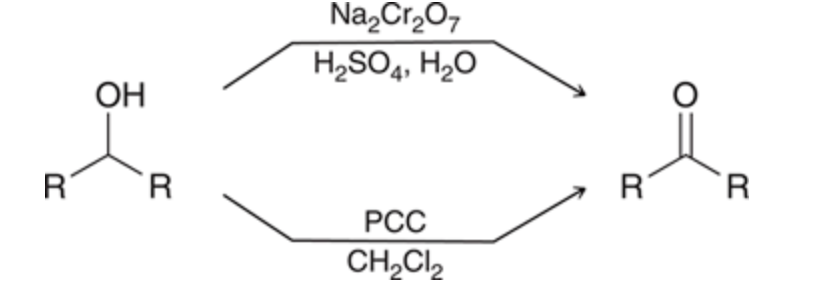
79
New cards
Swern oxidations
stage 1 DMSO reacts with (COCl)2 to convert into chlorodimethysulfonium ion which is meant to function as the active oxidizing agent stage 2 the carbon atom undergoes oxidation to make a ketone
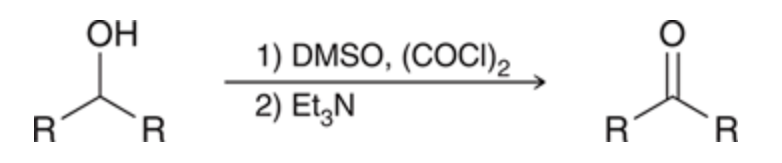
80
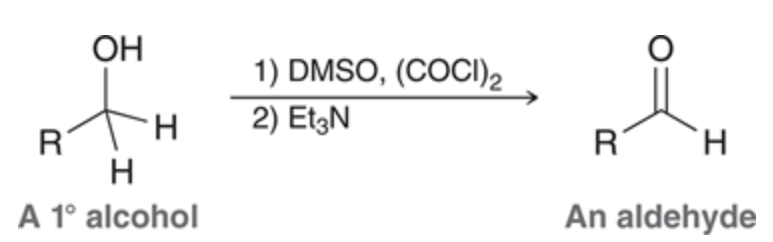
New cards
Swern oxidation can convert primary alcohols into aldehydes
these conditions lead primary alcohols converting to an aldehyde
81
New cards
Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP) oxidation
converts primary alcohols into aldehydes and secondary alcohols into ketones
DMP oxidations employ nonacidic conditions and can occur at room temp
DMP oxidations employ nonacidic conditions and can occur at room temp
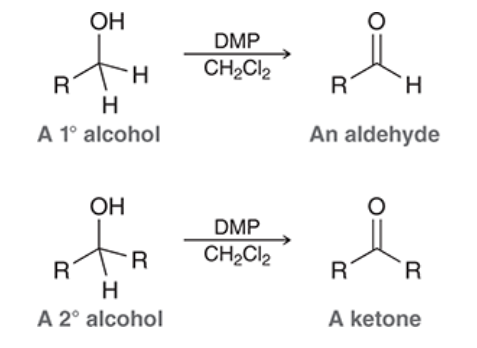
82
New cards
Chromium-based oxidations
require acidic conditions and high temps
83
New cards
NADH
Important reducing agent its less reactive than NaBH4 and LAH so it requires a catalyst
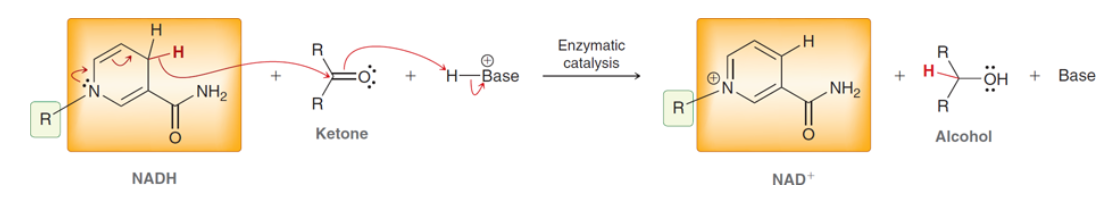
84
New cards
NAD+
Oxidized form of NADH it can act as an oxidazing agent and can accept a hydride from an alcohol so NAD+ can be reduced to produce NADH
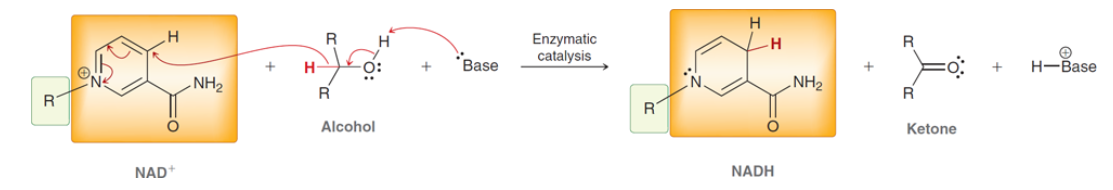
85
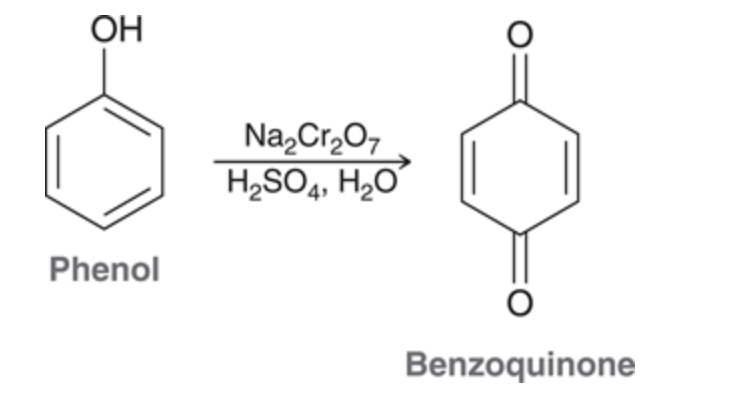
New cards
Phenol oxidation
phenol can undergo oxidation more readily than primary and secondary alcohols
86
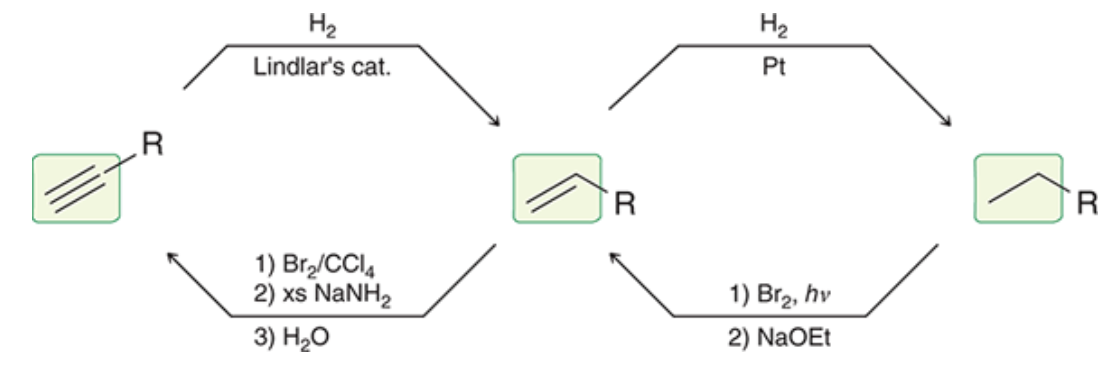
New cards
interconversions of bonds
87
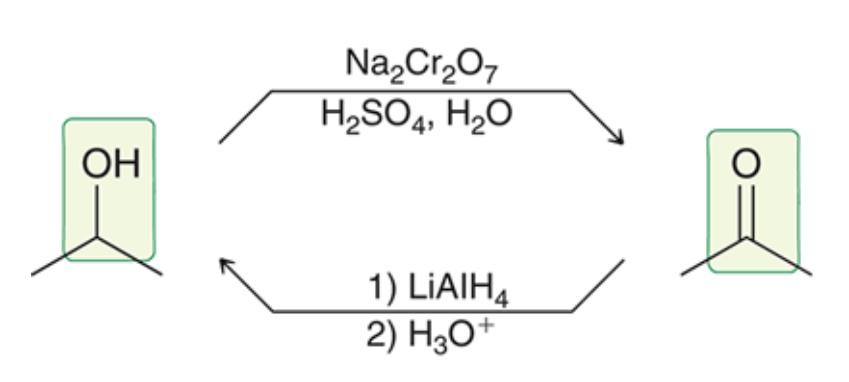
New cards
Secondary alcohols
88
New cards
Primary alcohols
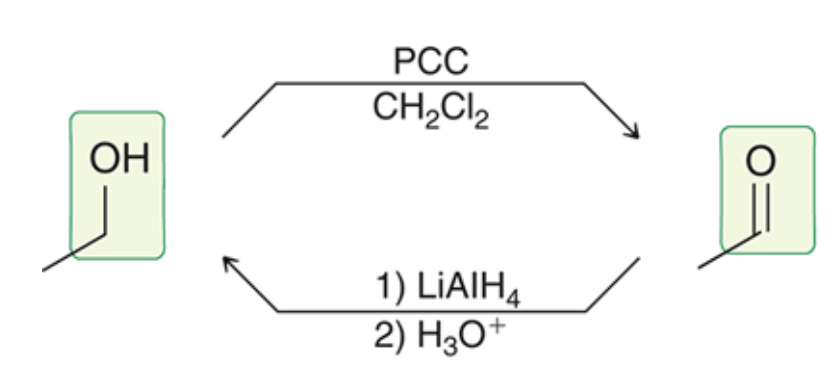
89
New cards
Oxidation states conversions
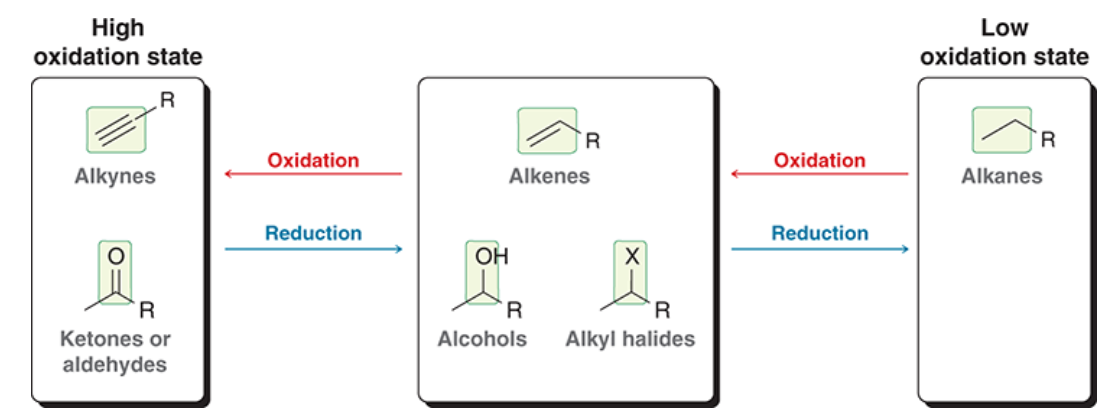
90
New cards
Conversions of chap 12 summary
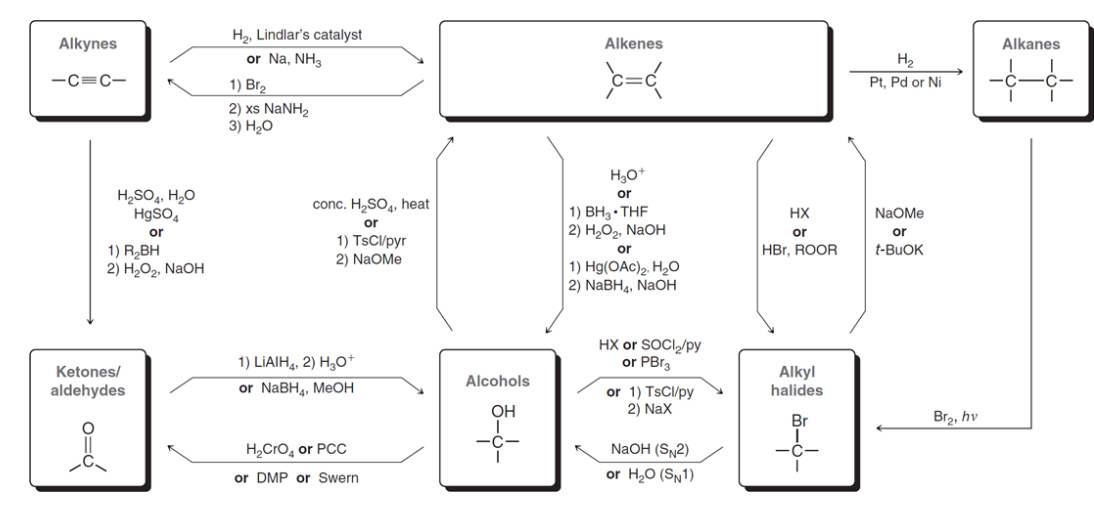
91
New cards
c-c Bond formation
can use grignard reagent and a ketone or aldehyde
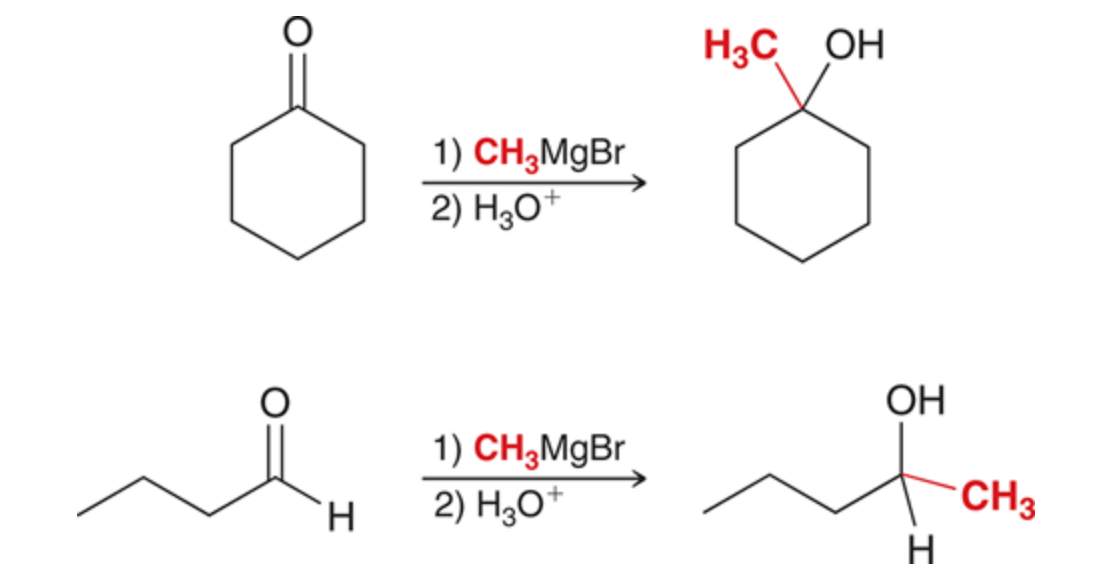
92
New cards
Ester and grignard reagent
2 new c-c bonds formed
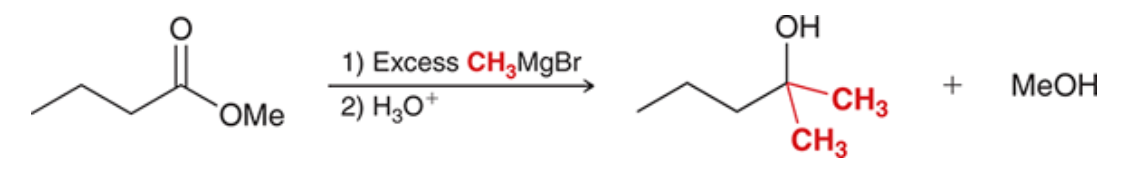
93
New cards
Addition of carbon-carbon bond summary
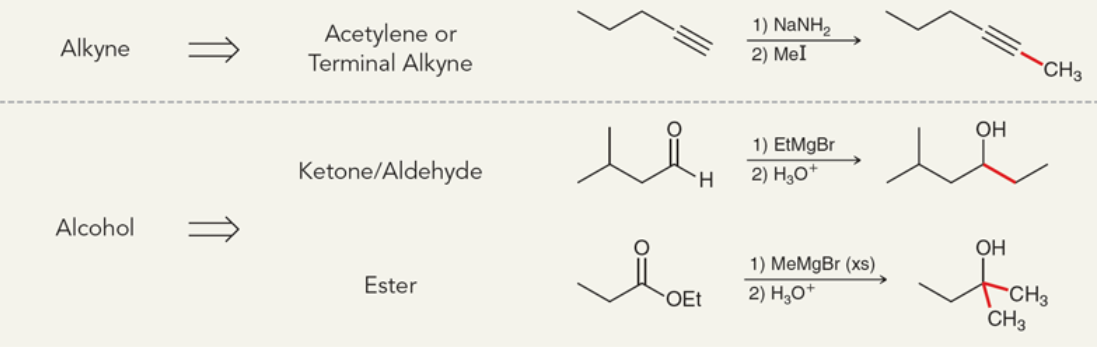
94
New cards
Aldehyde → ketone
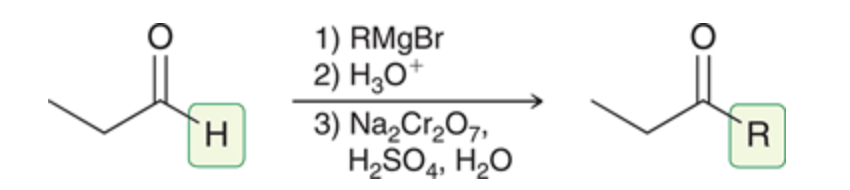
95
New cards
Conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde with an addition to carbon chain
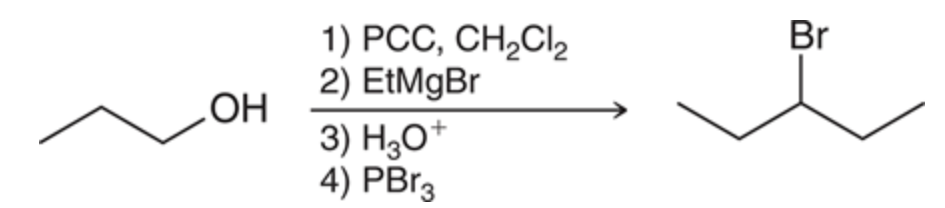
96
New cards
Secondary alcohol → tertiary alcohol
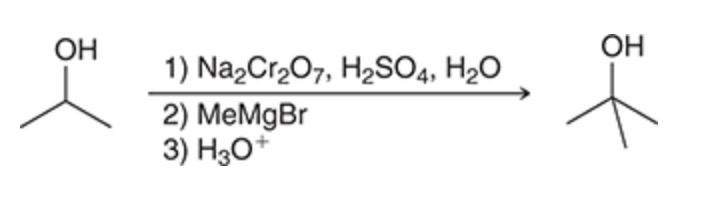
97
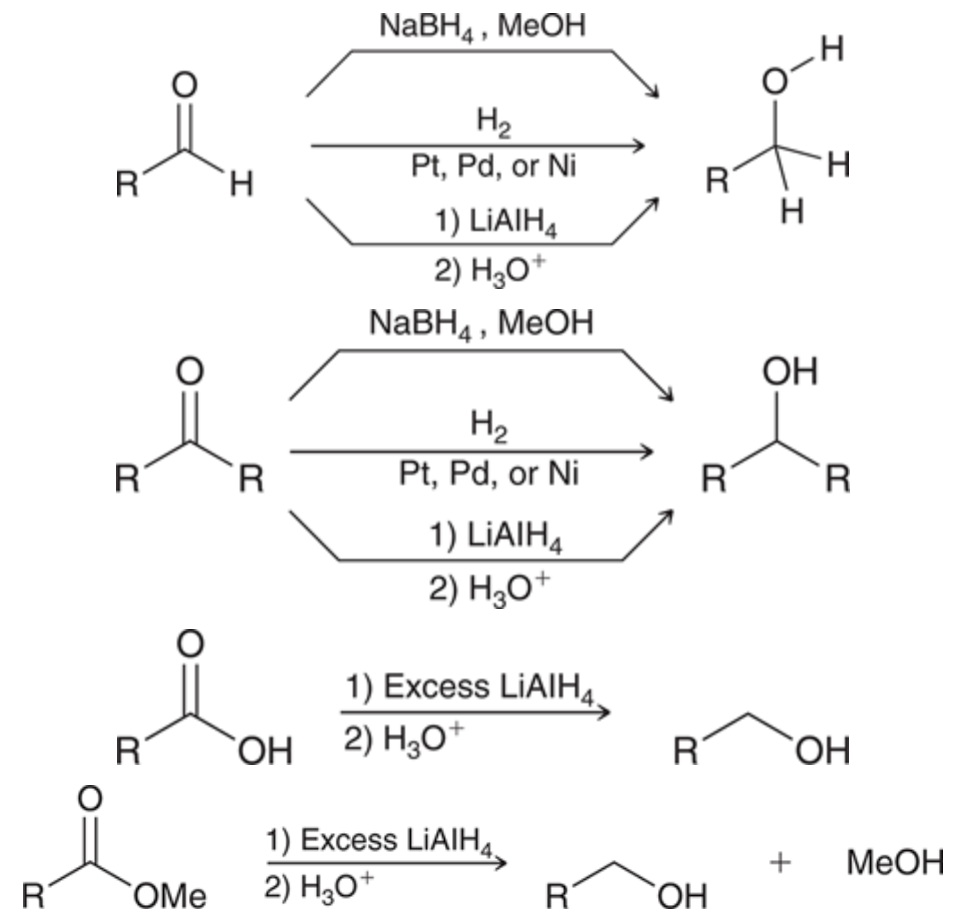
New cards
Preparation of alcohols using reduction
98
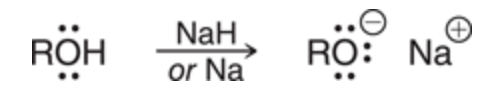
New cards
Preparation of alkoxides
Na will deprotonate
99
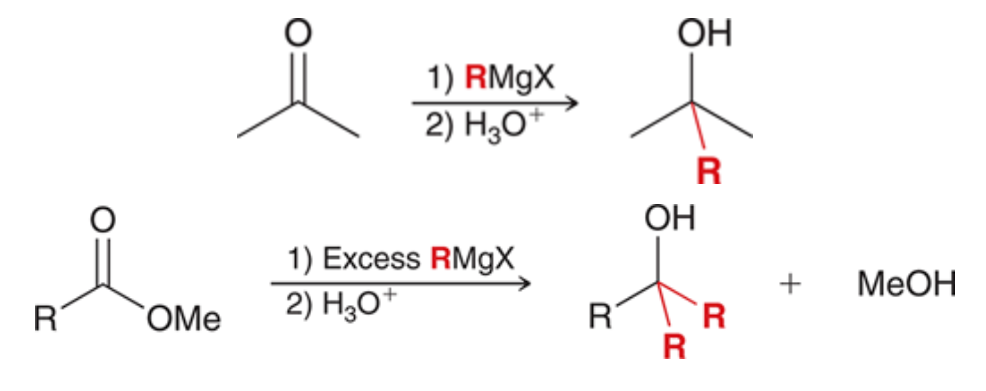
New cards
Using grignard to prepare alcohols
100
New cards
Protection and deprotection of alcohols
The addition of a protecting group and the removal