BIS 2C Lab Practical Exam
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
homology
characters present in organisms because they were inherited from a common ancestor
homoplasy
two structures with the same morphology, where this morphology was not inherited from a common ancestor (evolved multiple times independently)
Conflict vs Congruence
whether or not new data correlates with the hypothesized phylogeny (congruence) or doesn't correlate with the hypothesized phylogeny (conflict)
Cladograms
branch lengths are meaningless
Phylograms
branch lengths correspond to amount of evolution that has occurred since the last node
Chronograms
length of each branch shows absolute time (usually has a bar/scale)
What is LUCA?
Last Universal Common Ancestor. Last life form whose descendants persist today.
Major characteristics of Archaea
ether linkages, 70s ribosome, extremophiles (generally), haploid
Major characteristics of Bacteria
peptidoglycan in membranes, ester linkages, 70s ribosome, haploid
Major characteristics of Eukarya
membrane bound organelles, ester linkages, 80s ribosome, diploid
What is LGT and why is it problematic for phylogeny reconstruction?
Lateral gene transfer = transfer of genetic material between two organisms from one lineage to another
LGT is problematic for phylogeny reconstruction because distantly related species may appear more closely related than they actually are. Exchange of genes among UNRELATED organisms ERASES phylogenetic history
Transformation vs Transduction vs Conjugation
Transformation- dna brought in from environment
Transduction -virus or bacteriophage inserts new genetic material in host
Conjugation-between two bacteria via sex pili; exchange parts of genome (plasmids)
Rhizobium symbiosis
bacteria
found in roots of legumes
form round balls called nodules
plant uses ammonia created by bacteria; bacteria uses sugars from plant
mutualistic relationship (both benefit)
Anabaena (cynobacteria)
cyanobacteria can get nitrogen from the atmosphere --> plant (water fern) uses the nitrogen
cyanobacteria get shelter in plant's leaves
mutualistic relationship (both benefit)
termite hindgut
bacteria and archaea help digest cellulose (from wood diet) for the termite
bacteria and archaea get constant source of cellulose
symbiotic relationship (termite can't survive w/o bacteria and archaea) and a mutualistic relationship (both benefit)
belong in Microbial Eukaryotes and are methanogonic archaeons
What is bioremediation?
use of microbes to clean up contaminated soil and groundwater. Archaea and bacteria have very diverse metabolic capabilities, so they can metabolize contaminants cleaning up a lot of messes that would otherwise hurt the environment
energy source
light = "photo"
breaking chemical bonds = "chemo"
electron donor source
organic = "organo"
inorganic = "litho"
carbon source
organic = "hetero"
O=C=O = "auto"
ocular lens (eyepiece)
objective lens
how to calculate total magnification
capable of independent adjustment
objective lens vary in power - 5X, 10X, and 40X objectives
calculate total magnification by multiplying objective times ocular
coarse focus on microscope
the large one; typically only used at lower magnification levels; moves stage up and down
fine adjustment on microscope
the small one; makes smaller adjustments to the slide
stage clip on microscope
used to secure the slide
endosymbiont theory
Big organism engulfs small organism resulting in an additional membrane forming around it. If it is not digested it may form a symbiosis with the host and continue to live and reproduce inside the host organism
primary endosymbiosis
involves the engulfment of a bacterium by another free living organism.
Secondary endosymbiosis: occurs when the product of primary endosymbiosis is itself engulfed and retained by another free living eukaryote.
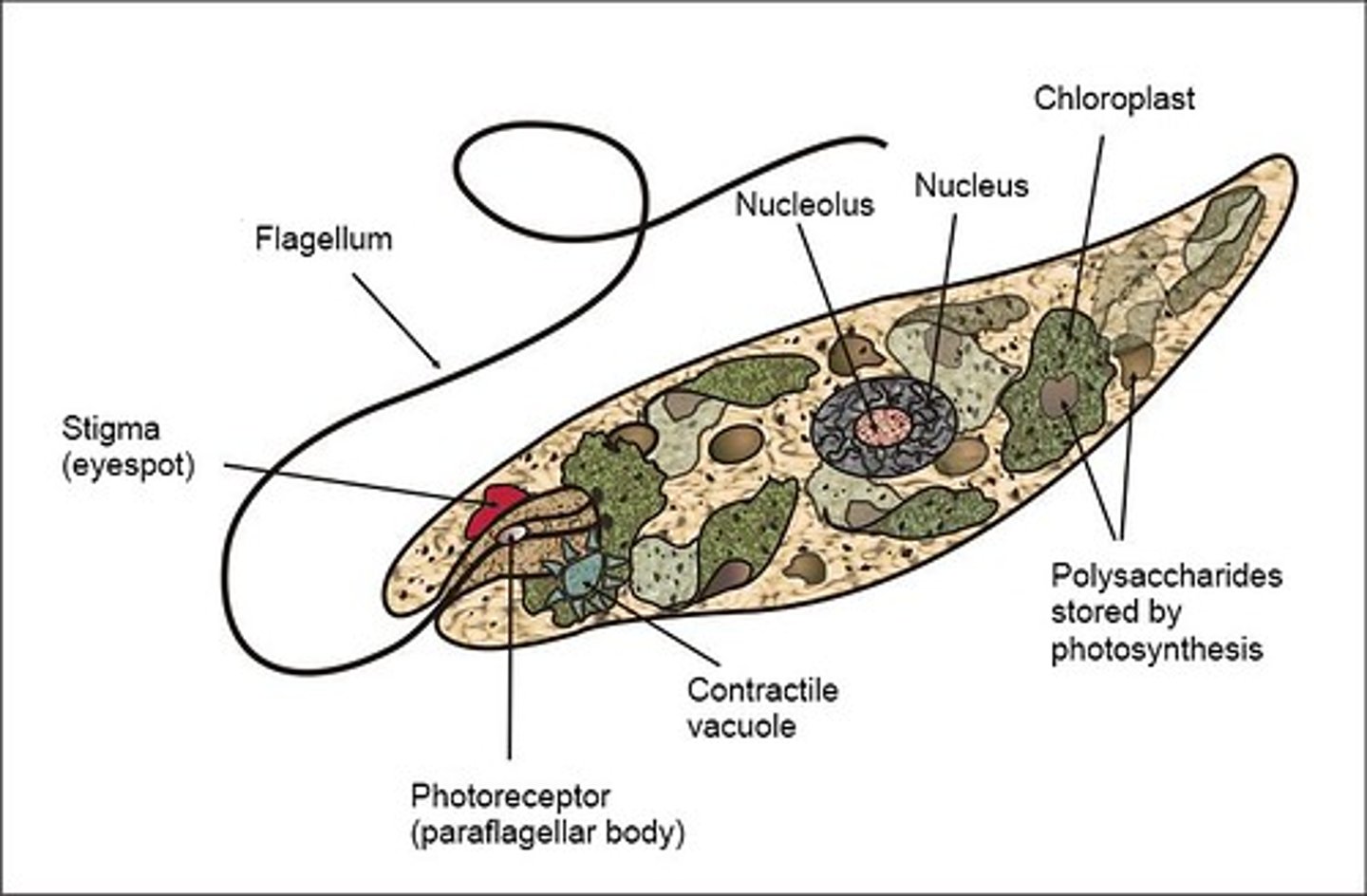
Euglena
flagella, photosynthetic (chloroplasts)
Blepharisma
cilia, not photosynthetic, eat bacteria or each other if no food source
Paramecium
cilia, not photosynthetic, food vacuole
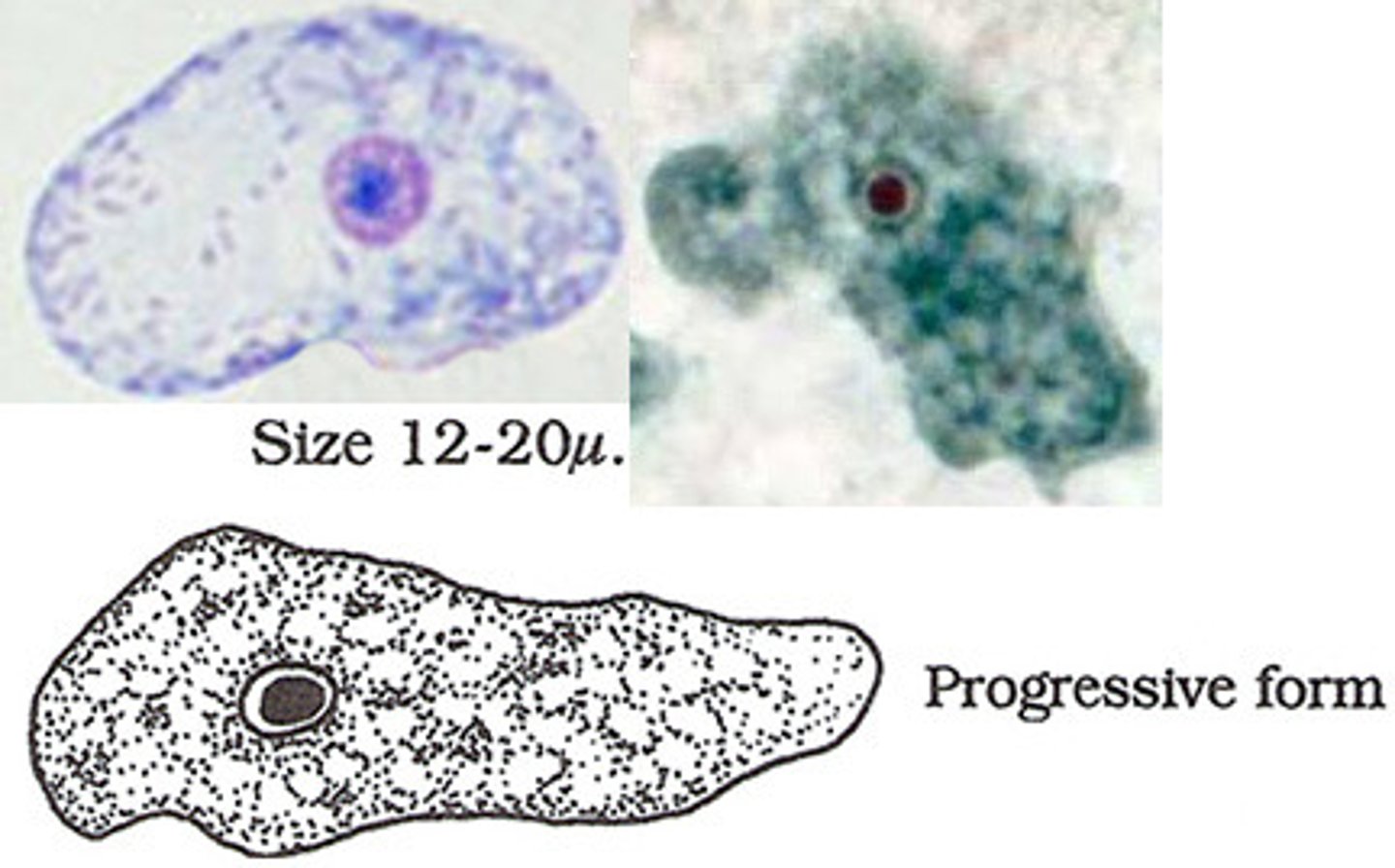
Naegleria
change body forms based on how much food is in the environment
Non-amoeboid body form (flagella) is better suited for movement so is common when food source is absent or scarce
amoeboid body form is better suited for eating and so is common when food source is present
certain genes/body forms expressed @ certain environments (nutrient level) → need to get around faster to go longer distances to find food when nutrients decrease (amoeboid form very slow compared to flagellate)
problem with phylogeny bc of this
not photosynthetic
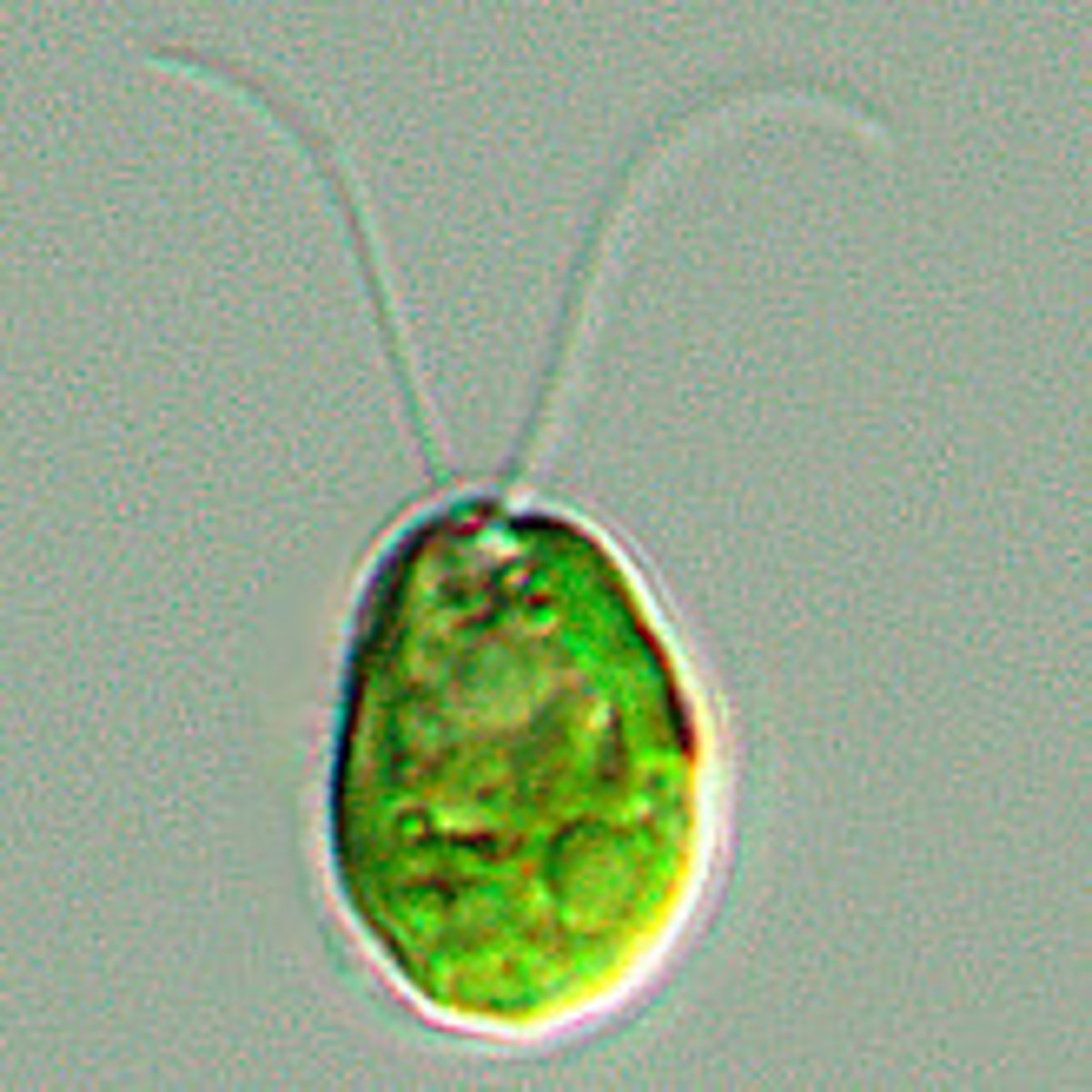
Chlamydomonas
flagella, photosynthetic
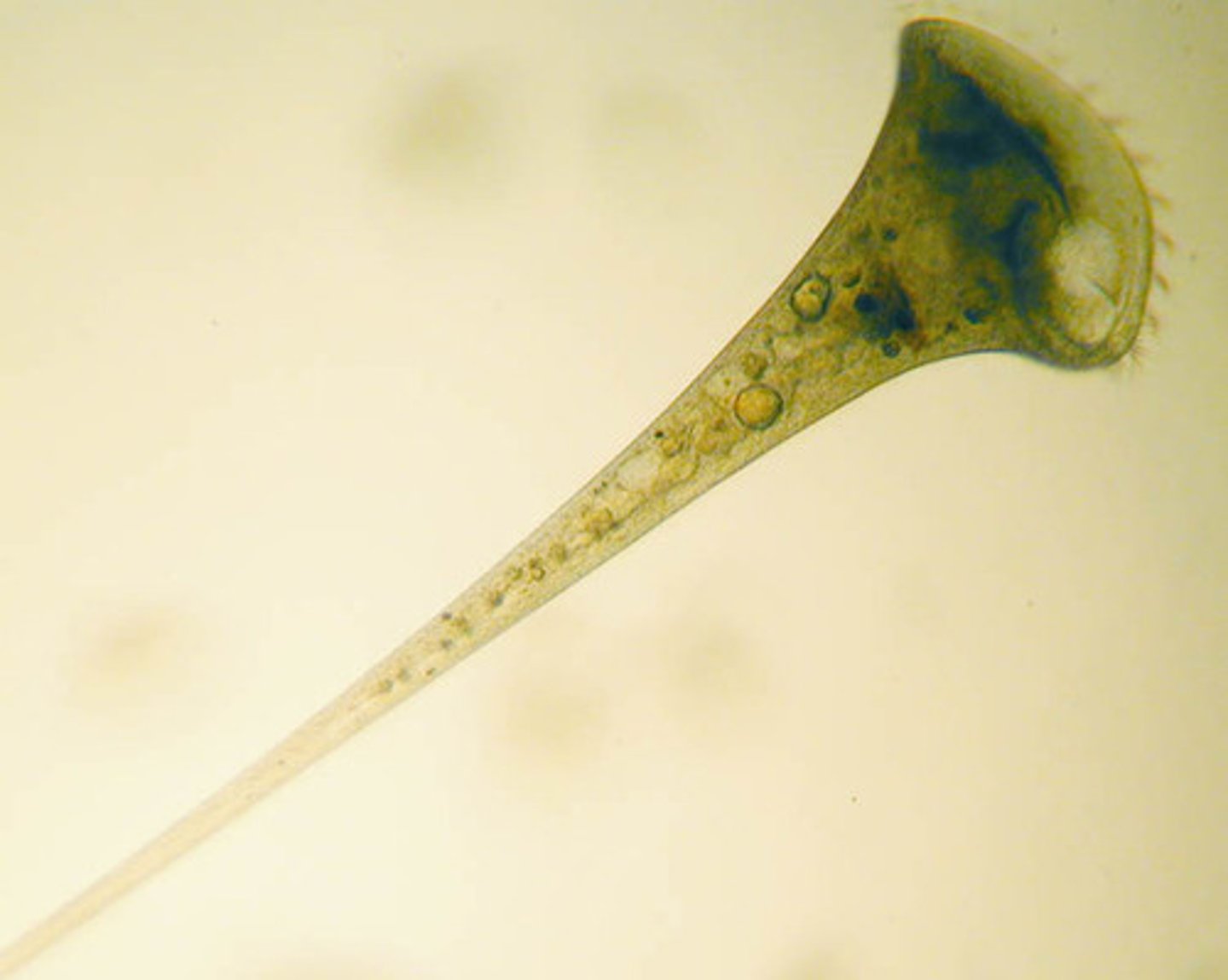
Stentor
cilia, photosynthetic (via photosynthetic relationships with algae)
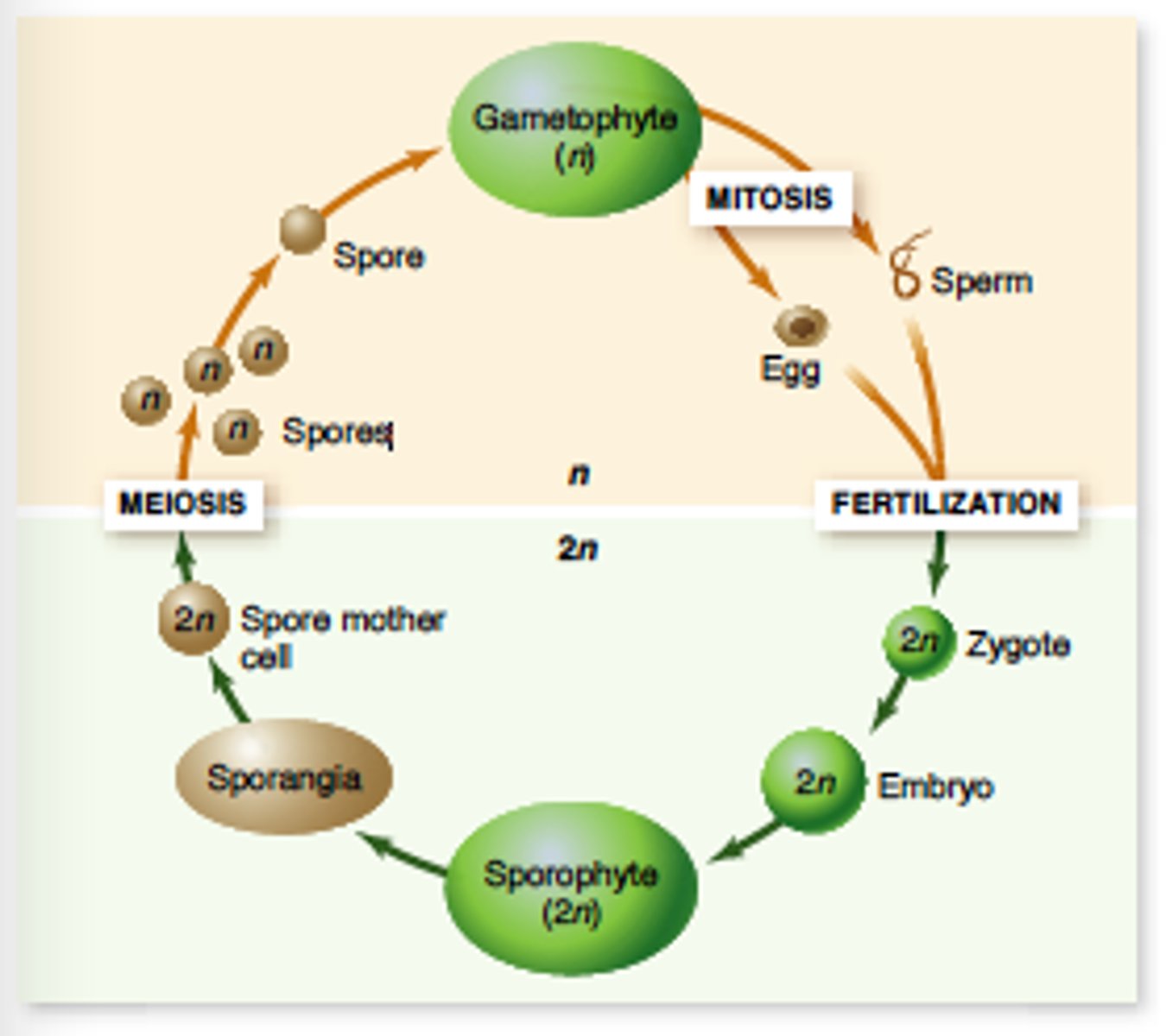
Alteration of Generations life cycle
Liverworts
Non-vascular plant
no true stomata
sporophyte doesn't function in dispersal
flat 2D growth (thallose and leafy)
bryophyte
Moss
Non-vascular plant
3D growth
cap sporangium
sporophyte (with stomata) dependent on gametophyte
meristem cells at base - form new tissues
bryophyte
Hornworts
Non-vascular plant
green sporophyte
gametophyte does photosynthesis
sporophyte dependent on gametophyte
meristem cells at base - form new tissues
bryophyte
Lycophytes
Vascular plant
microphylls
true roots
sporophyte dominant
independent gametophyte
strobili (cones)
Dichotomous branching
Ex. lycopodium and selaginella
Evolved heterospory (in Selaginella --> a homoplasy)
Monilophytes
Vascular plant
Megaphylls
DO NOT produce seeds (seedless vascular plants)
Independent gametophytes, independent sporophyte?
Most monilophytes are homosporous but some (Water Ferns) are heterosporous.
DNA chloroplast inversion
Only 1 sporangi
Ex: psilotum, equisetum [horsetail], fern
Gymnosperm
Vascular Plant
Naked seeds
Nutritive tissue (n)
Integument, ovule, pollen with pollen tube,
heterospory
BVC (bivascular cambium)
Ex: Cycad, Ginkgo, Conifers, Gnetophytes
Angiosperm
Vascular Plant
flowering plants
seeds
Double fertilization results in nutritive tissue (3n)
endosperm
Majority of plants
Reduced gametophyte- only 7 cells
Phloem with companion cells - sieve element
Reproduction involves flowers and pollinators
Are both tracheids and vessel elements
Basal Angiosperms vs Monocot vs Eudicot
Basal Angiosperms = non-monophyletic group
Monocots- bifacial vascular cambium (BVC) absent; scattered vascular bundles; 1 cotyledon; flower parts in threes and multiples of three; parallel leaf veins;
Dicots- BVC present; organized vascular bundles; 2 cotyledons; leaf veins form a net pattern; flower parts in 4s or 5s and their multiples
Algal relatives of Plants
green algae (Coleochaete and Chara) have the same photosynthetic pigments, the same type of flagella, and the same fundamental process of cell division
Types and trends of growth
Filamentous growth: 1 cell is cut vertically in half, divides, then a new cell forms in between
Branched growth: cell is cut in half horizontally
Apical growth: land plants specialization; the cell at the tip; youngest cell is closest to the apex (tip/end) (like a tree, new growth on top, furthest from base which is older)
Cutting faces: # of directions in which a cell divides (flat body only 2 cutting faces, 2D; 3D growth for 3 cutting faces (upward))
Two basic types of leaves and when did they evolve?
Megaphylls- complex vasculature; evolved in the MRCA of monilophytes
Microphylls-single vein of vasculature; evolved from sterilized sporangia
Bifacial vascular cambium
Pushes new vasculature to grow out instead of up, resulting in wider plants
Separates new and old vascular tissues.
Xylem grows inwards, phloem outwards
Gymnosperm vs Angiosperm life cycle
gymnosperm life cycle: megagametophyte remains in nutritive tissue (2N) and is made even if not fertilized; m. and f. cones; both megasporangia make 4 megaspores (N), only 1 surivves
angiosperm life cycle: flowers (can be perfect or imperfect); no cones; ovary wall (2n) around seed coat (2n); nutritive tissue is result of double fertilization and is the endosperm (3n) and is only made when embryo is present
Ways flowers attract pollinators
orchids look like female bees (males try to mate with flower and get pollen on them instead)
long nectar tubes attract moths with equally/similarly long tongues
Moth: white, no landing pad, strong odor
Hummingbird: red, lots of nectar, no landing pad
Bee: nectar, landing pad
Fly: mottled color, foul odor
Simple fruit
Develops from 1 flower w/ a single carpel --> 1 fruit; have many seeds (apple, banana, mango, grapes)
Aggregate fruit
1 flower many fruit (blackberry) results from several carpels on a single flower
Multiple fruit
many flowers merge together to form a fruit (pineapples)
Accessory fruit
formed from non-ovary tissue (strawberries)
Role of secondary metabolites in plants
produces a large number of specialized compounds that do not aid in the growth and development of plants but are required for the plant to survive in its environment
secondary plant metabolites are useful in the long term, often for defense purposes, and give plants characteristics such as color
Secondary plant metabolites are also used in signalling and regulation of primary metabolic pathways
Monophyletic groups/sister taxa tend to have similar secondary metabolites (i.e. citrus and mint in lab)
Epiphytes (from Conservatory tour)
a plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant (such as a tree) and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it
not a parasite bc do not negatively affect host (just rely on them for physical support)
Ex: spanish moss

Carnivorous plants
hot, humid, wet areas, nutrients washed away, so catch insects for nutrients; leaves always catch insects
Sarraceniaceae (Pitcher plant family) N America, few in S america → pleistocene b/c continental drift (cacti more likely older b/c more widespread than sarraceniaceae)
Droseraceae (sundew family) triassic period when all continents together → now found all across the world
Nepenthaceae (tropical pitcher plant family) Malasia/Indonesia or Madagascar (Cretaceans), Jurassic period if could travel by wind dispersal (more recent if can disperse a far way)
Venus fly trap (North Carolina)

Stem modifications
water retention w/ accordian bulbous shaped stem; 2 types of stem (on 1 plant)--bulbous (stores/retains water and nutrients and starch/sugars) on bottom, and thin on top for photosynthesis; stems not as efficient at photosynthesis, but can still do it
Rhizomes, tubers
Leaf modifications
Holes in upper canopy leaves (nearer to sun) allows to stay cool easier and better for winds
Small, thin leaves that close/fold in when touched to protect against predators and strong winds (lose less moisture) - Mimosa pudica
Sweet leaves (extremely) to protect against being eaten (stevia plant)
Square shape w/ spores on edge--1 'branch' w/ lots of the square leaves is actually 1 entire leaf: very organized, with a lot more spores and easier dispersal of spores
Smaller leaves grouped to look like a flower that are fuzzy --> repels water to not be over watered and stays on surface of water
Ascomycetes
Fungi
Largest phylum of Fungi
Ex. yeast, used for beer/wine making, truffles, brewer's yeast
Shoot spores
haploid
Basidiomycetes
dykarion
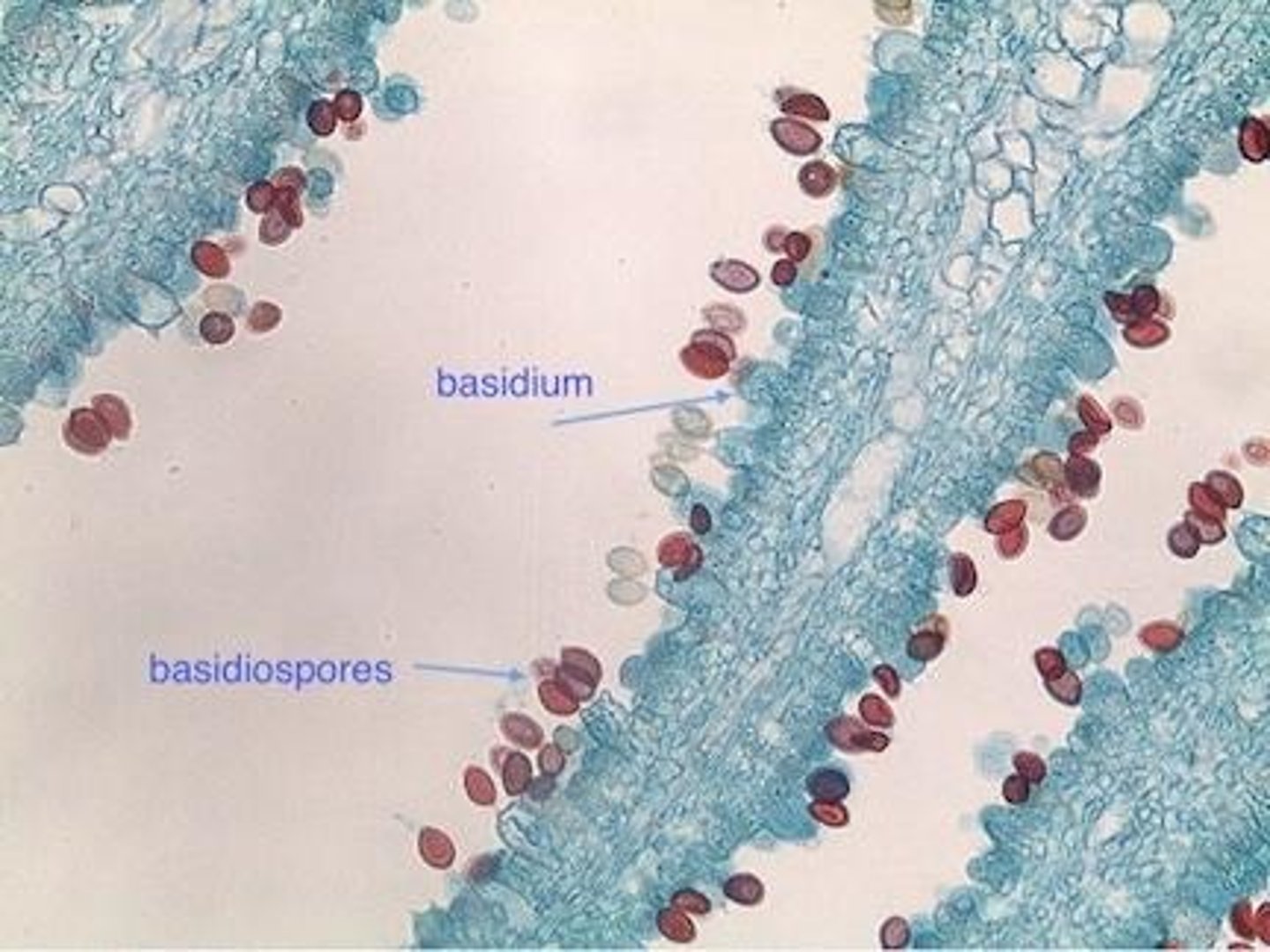
Lichens and their symbiosis
Lichen are the result of a symbiosis between ascomycota + (algae or cyanobacteria) + yeast
Fungi provide shelter, algae or cyanobacteria produces food from photosynthesis, yeast protects by producing toxic vulpinic acid
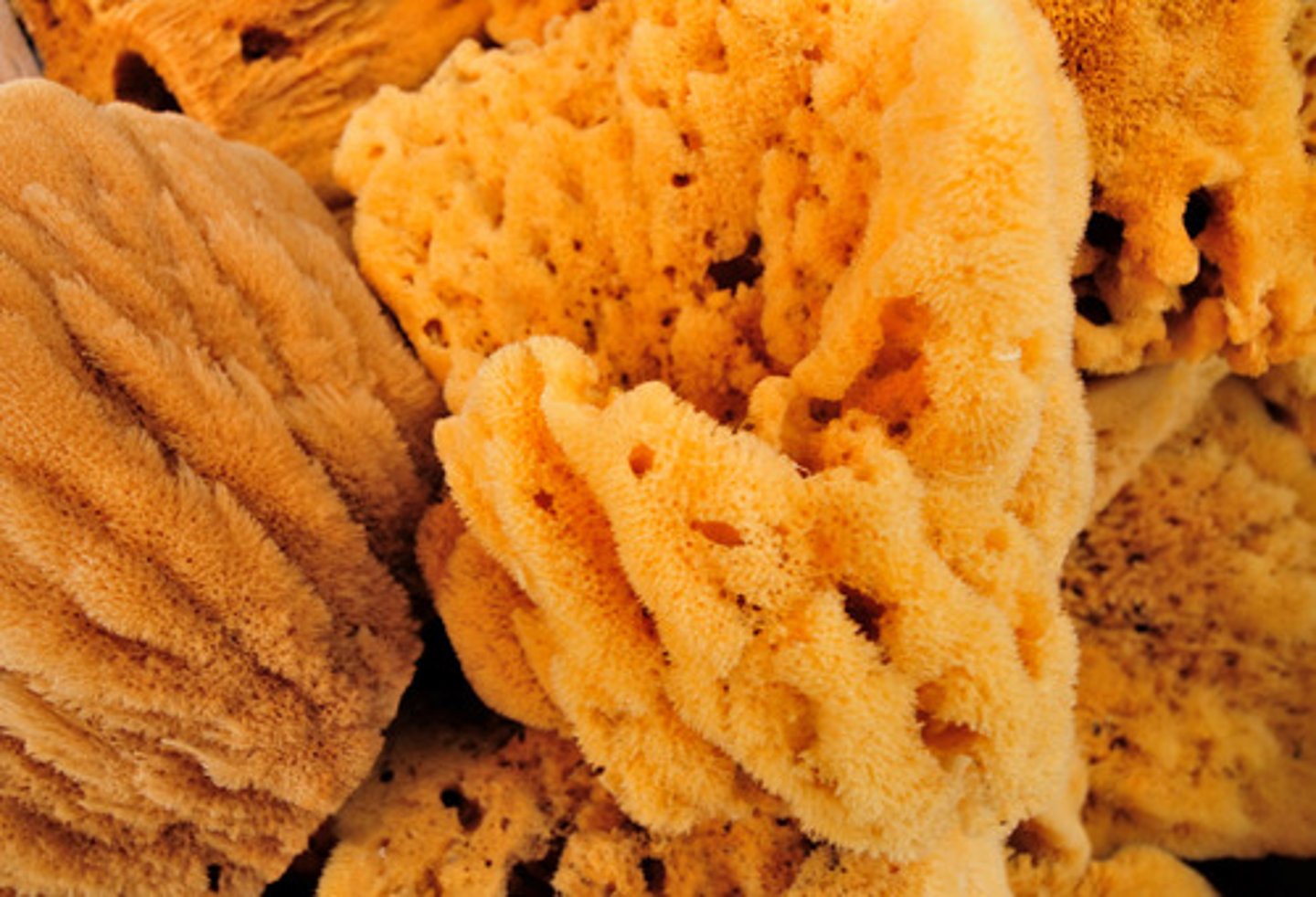
Porifera
spicules (silica/calcium)
networks of collagen
choanocytes = filter water and capture food
asymetrical
no gut
Ex: sponges

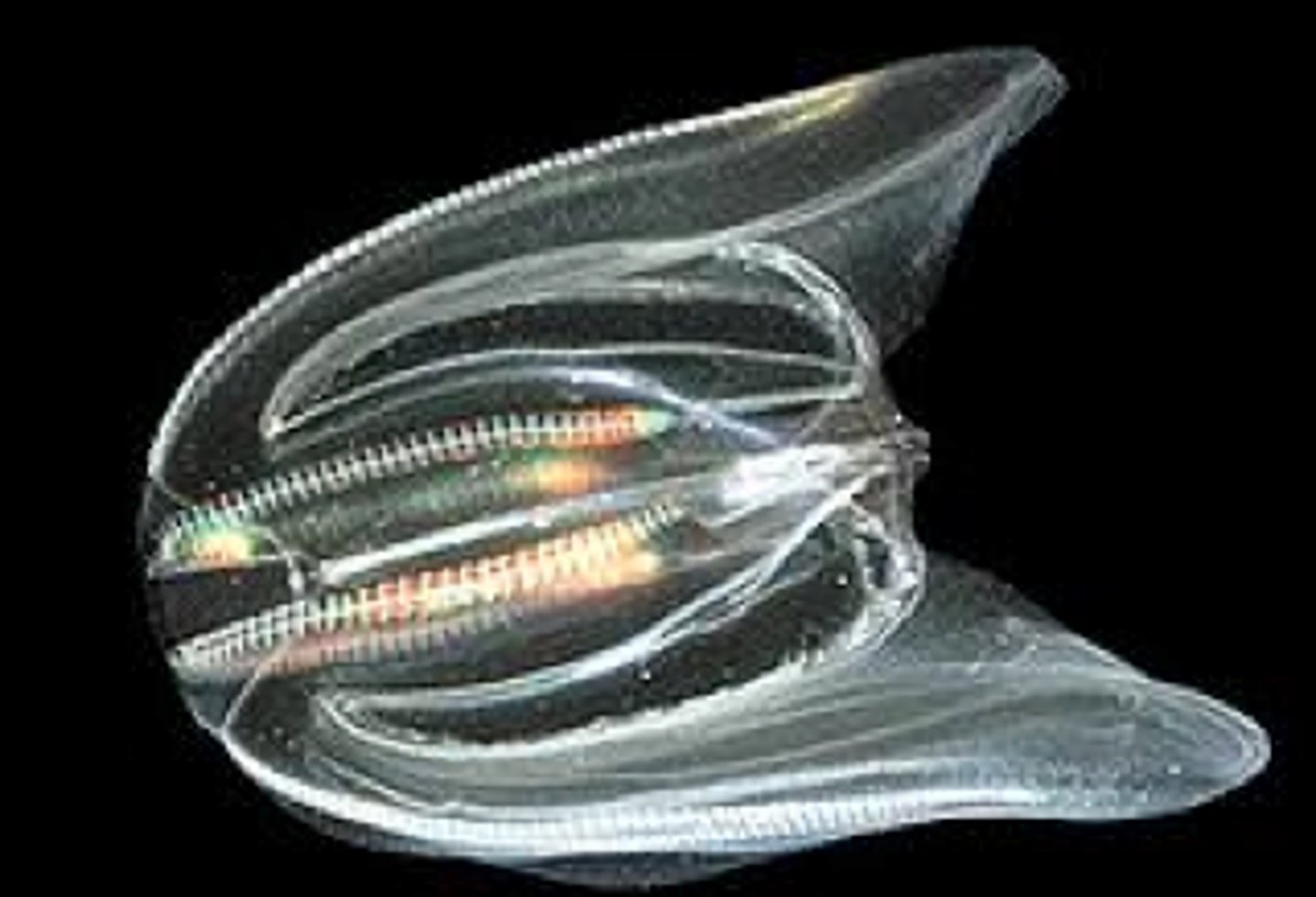
Ctenaphora
use rows of cilia to move themselves (cilia in rows called combs/ctenes)
radial symmetry
diploblastic development
complete gut
Ex: comb jellies (not related to jellies!)

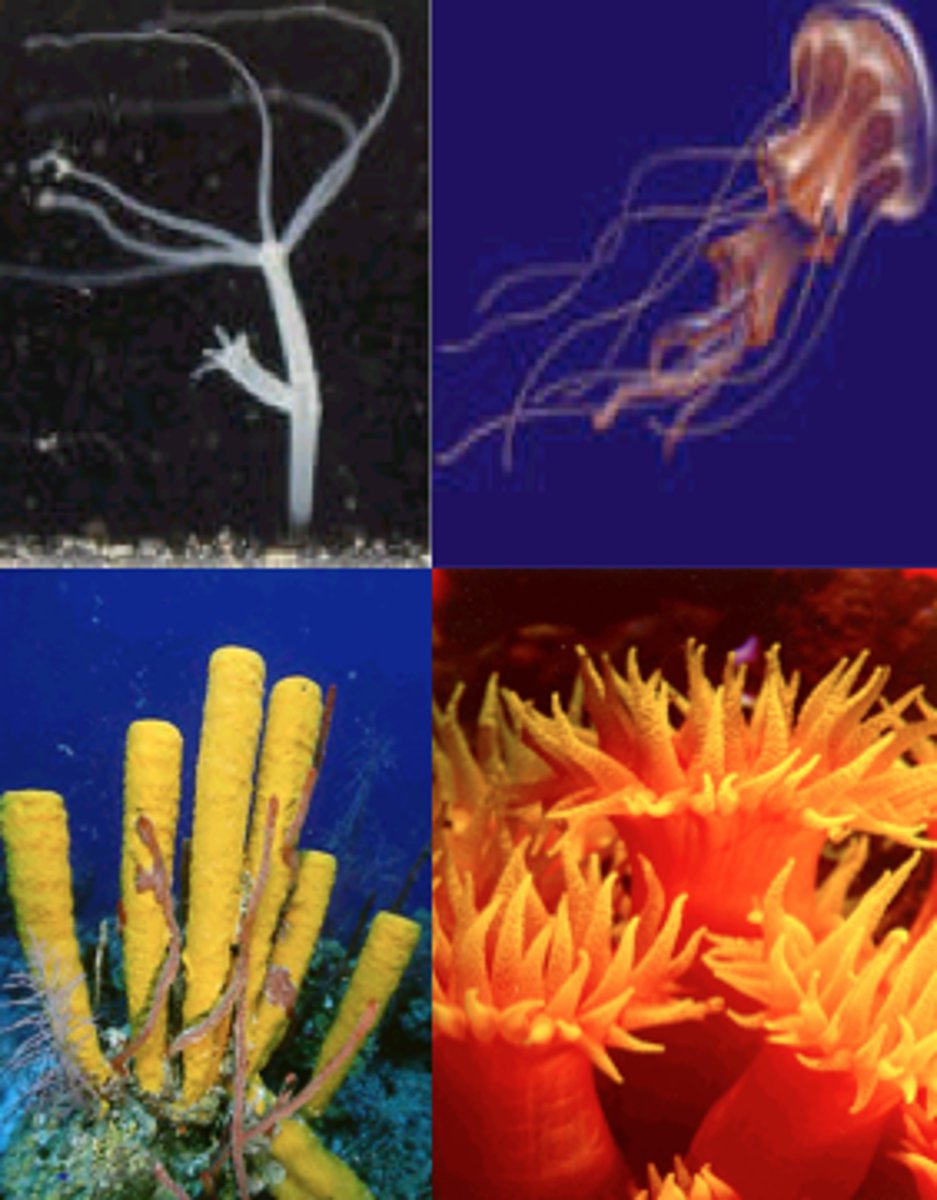
Cnidaria
sting-bearing nematocysts/cnidocytes for protection and capture of prey
polyp reproduces by budding or fission
can be colony or medusa forms
2 way gut
radial symmetry
Ex: Corals, sea anemones, box jellies, true jellies (jellyfish), Portugese Man o'War, etc.

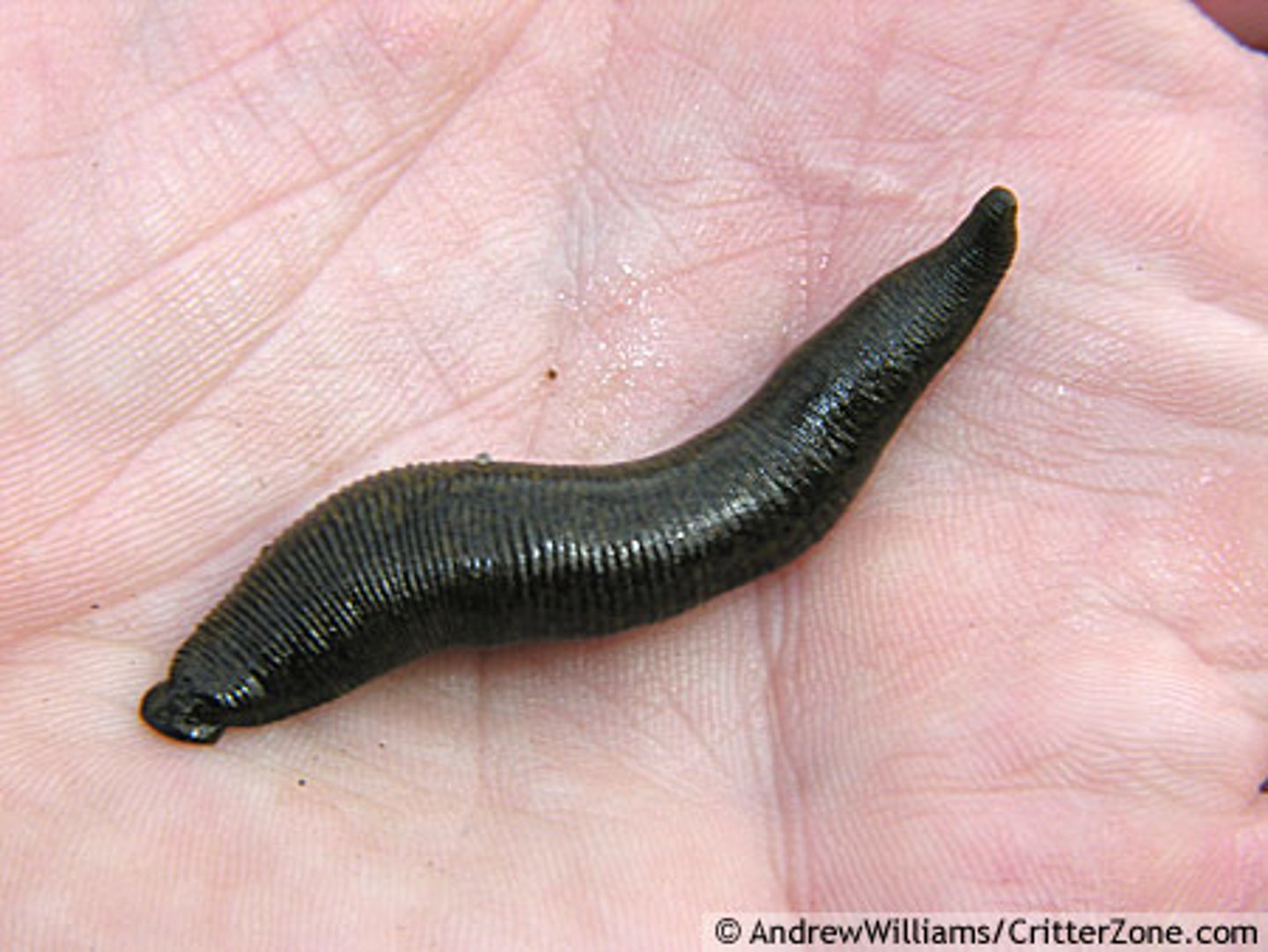
Annelida
Bilaterally symmetrical coelomate protostomes with segmented (metameric) body
each segment with paired bundles of chitinous setae, and parapodia (polychaetes only)
body wall with inner longitudinal and outer circular muscles
each segment the same
each unit contains locomotory, reproduction, excretory, and respiratory structures
Triploblastic (mesoderm)
complete 1 way gut
cephalized
spiral, mosaic cleavage
trochophore larvae
Ex: leeches, earthworms, bristleworms

Mollusca
Bilaterally symmetrical (secondarily asymmetrical)
coelomate protostomes with: complete gut,reduced coelom open circulatory system
in most, well developed nervous system (especially in cephalopods)
trocophore larva
synapomorphies: mantle (4 functions), foot, radula(inside mouth); spiral, mosaic cleavage; cephalization
Ex: chitons, bivalves, gastropods (snails and limpets), and cephalopods (squid)
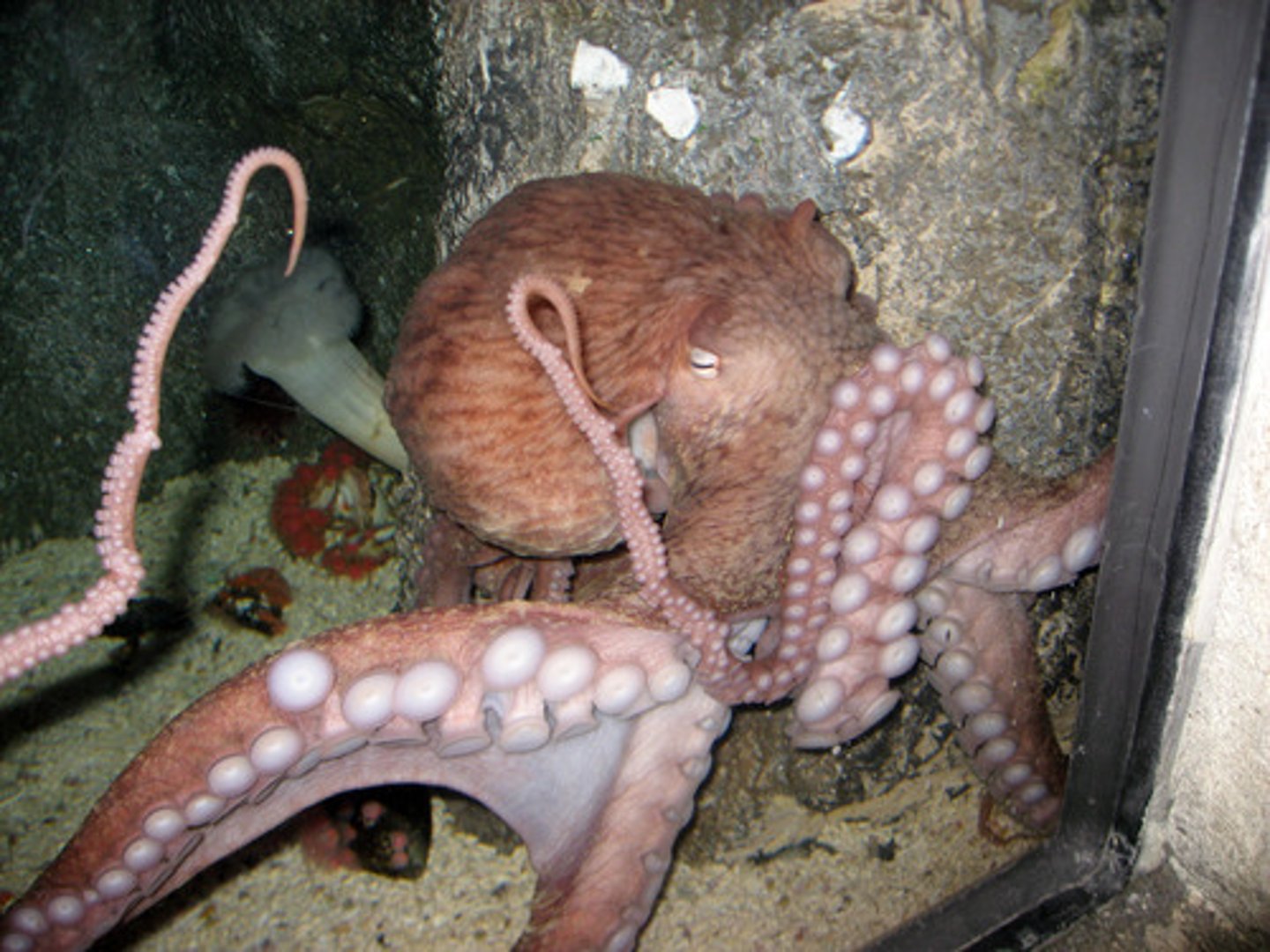

Arthropoda
protostomes
bilateral symmetry
exoskeleton (more energy required to shed and secrete new exoskeleton regularly, and they are vulnerable before new one hardens; grow in size by molting exoskeleton; reabsorb nutrients before completely shed old exoskeleton; muscles are attached to basement cuticle, under the layer that sheds)
segmentation
ecdysis
triploblastic
1 way complete gut
cephalization
horseshoe crabs and insects = 3 tagmata; jointed appendages (crustaceans have specialized appendages for feeding, walking, and swimming)
insects are hemimetabolous (make small increases in body size w/ each molt and juvenile resembles adult) or holometabolous (dramatic changes in form during their life, i.e. caterpillar to butterfly)
Ex: spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs (living fossil), centipeeds, crustaceans, insects
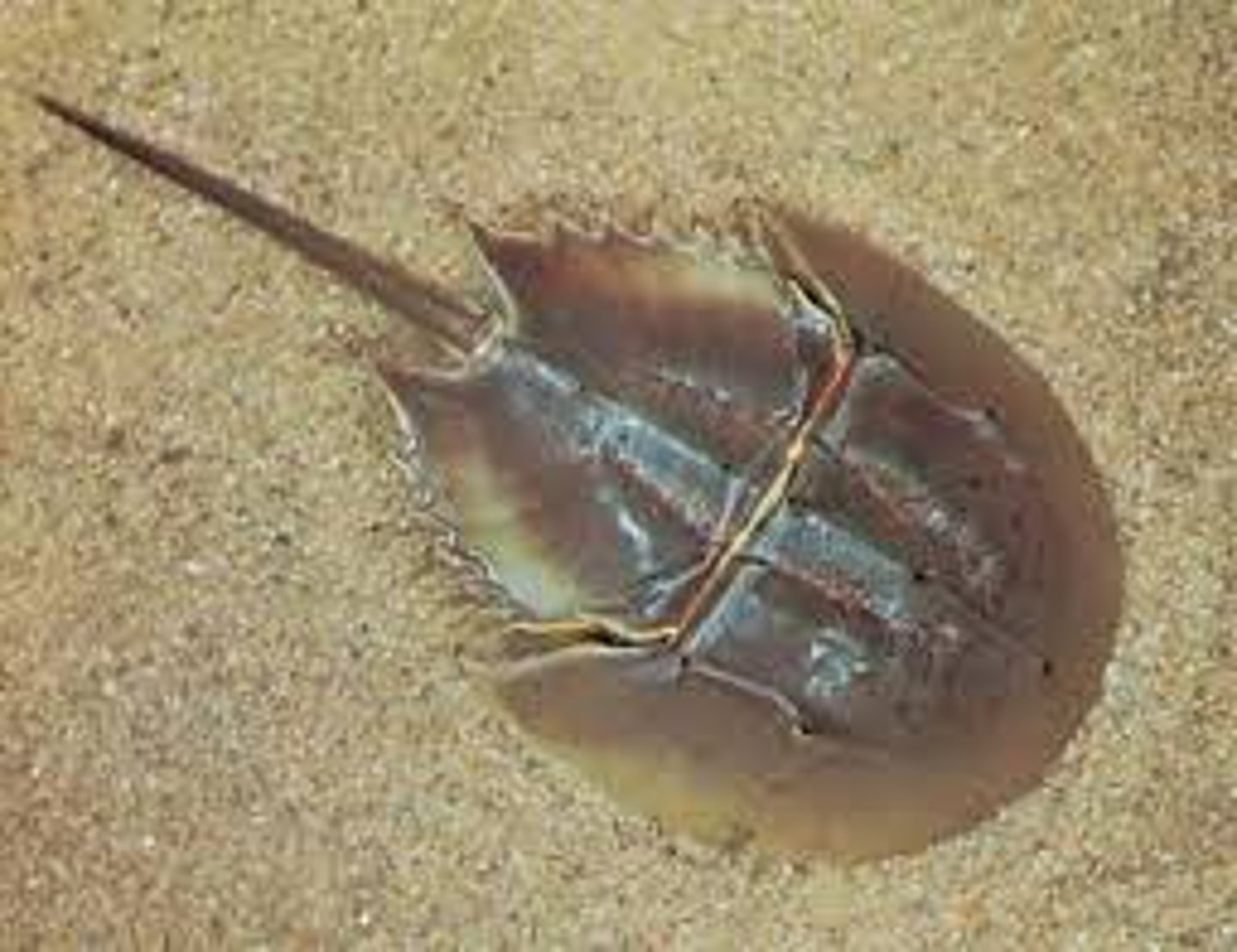

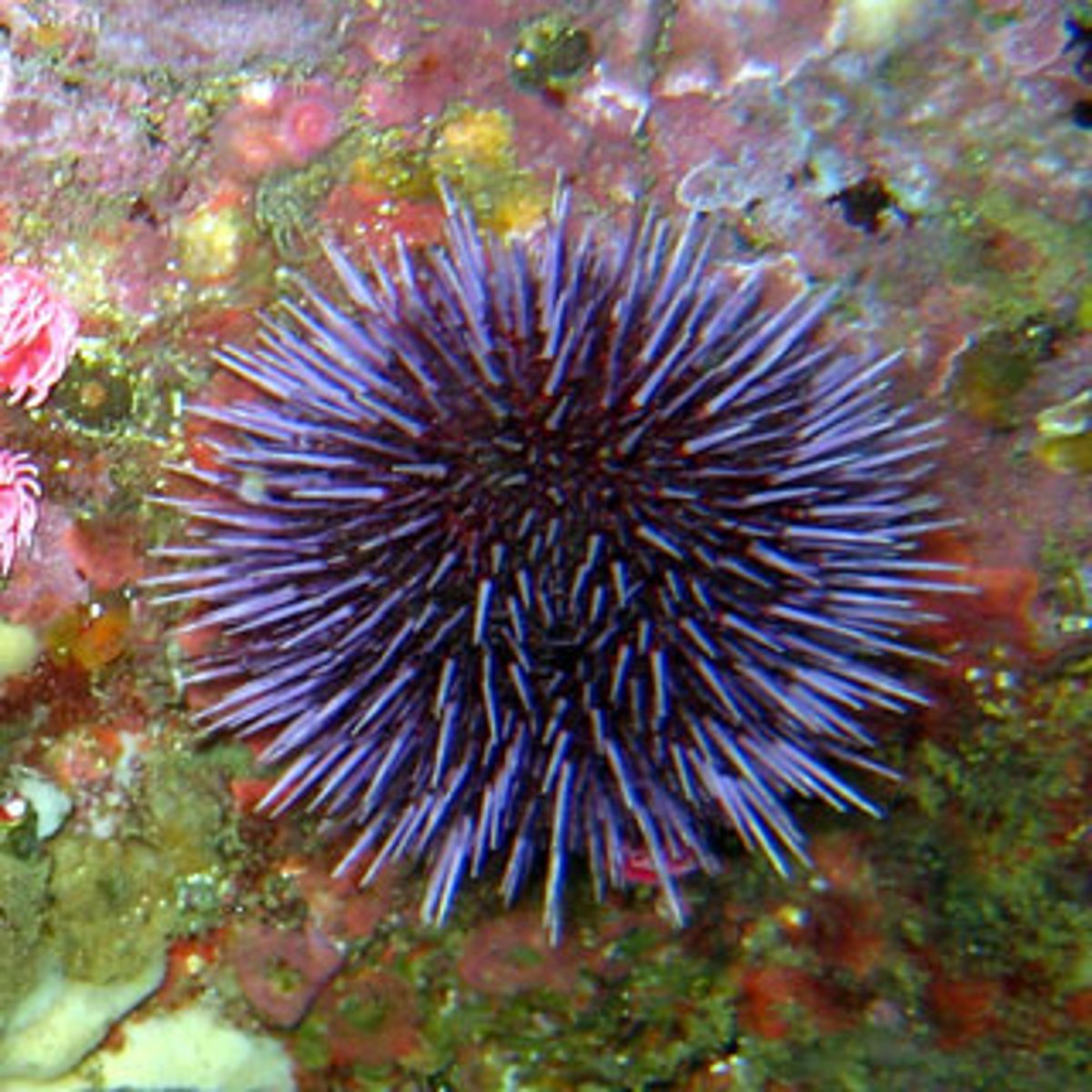
Echinodermata
Adults = radial symmetry (usually pentaradial) Deuterostomes
able to regenerate tissue, organs, limbs, and reproduce asexually
ossicles
calcite endoskeleton
water vascular system
tube feet
radial, regulative cleavage
Ex: sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea lillies, and sea cucumbers

Chordata
have notochord
bilaterally symmetrical
deuterostome coelomates
Vertebrate chordates can have body plans organized via segmentation
Postanal tail
endostyle
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
triploblastic
complete 1 way gutf
Ex: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals, sea squirts, and lancelets

Types of symmetry
radial = many axis of symmetry
Ex: sea anemone
bilateral = one cut of symmetry separating organism into a left and right half
Ex: humans
Usually tied to cephalization and a complete gut
pentaradial = 5 pt symmetry
Ex: sea star
asymmetrical = not symmetrical
Ex: sponge
Types of digestive systems
Complete gut (one way)-mouth and anus
Incomplete gut (two way gut)-blind gut, food and waste exit same hole
Cephalization
head vs no head
(involves concentrating neural cells and morphologies in one area to form a central control area)
Associated with bilateral symmetry with exceptions in bivalves and echinoderms (echinoderms are not cephalized; lost this when they 'changed' symmetry from bilateral to pentaradial)
Metazoan development
zygote (2N) --> radial/spiral cleavage --> blastula --> gastrula
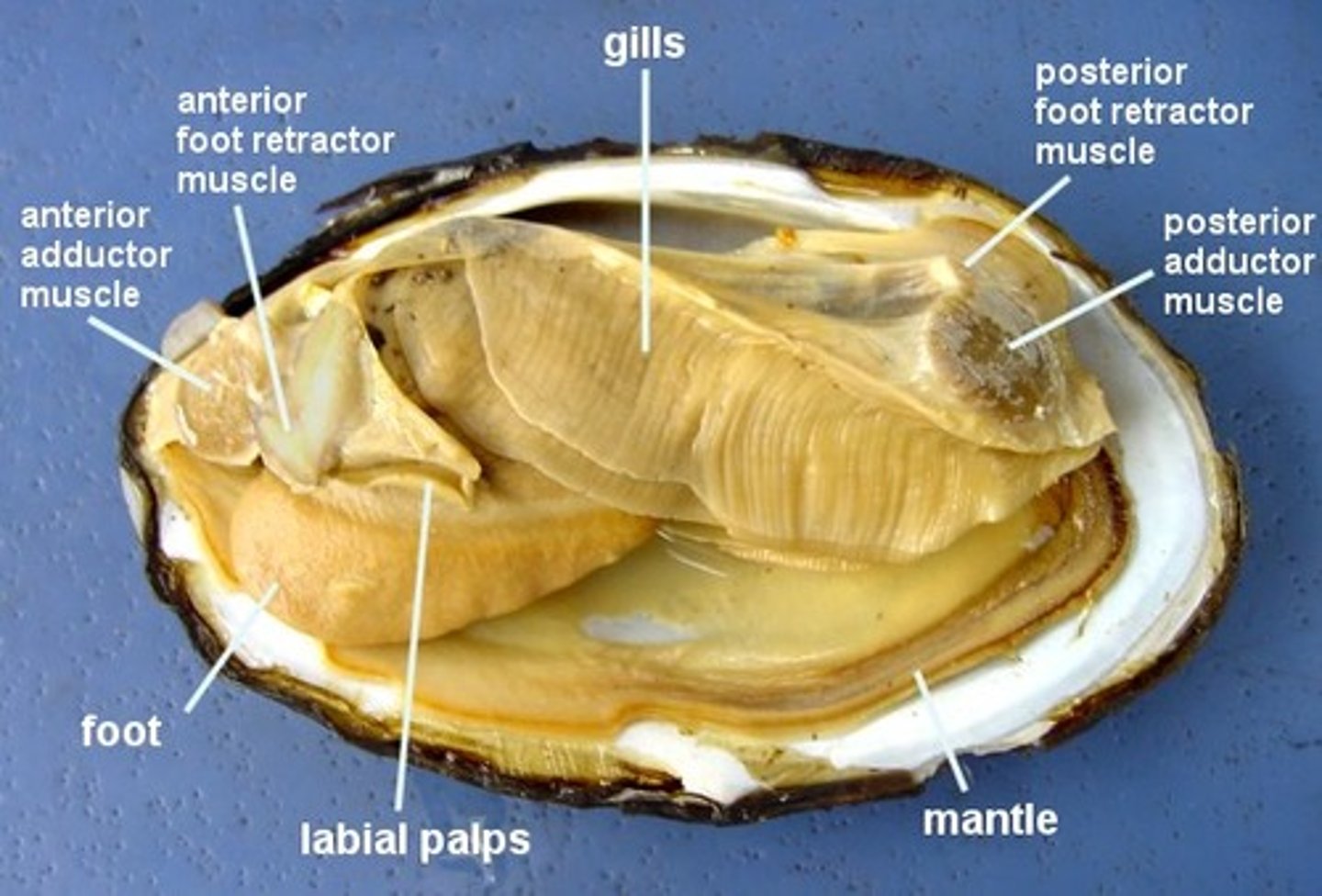
Identify key features on a dissected bivalve (i.e. mussel)
Know where the foot, radula, mantle, shell, gills, etc. are located
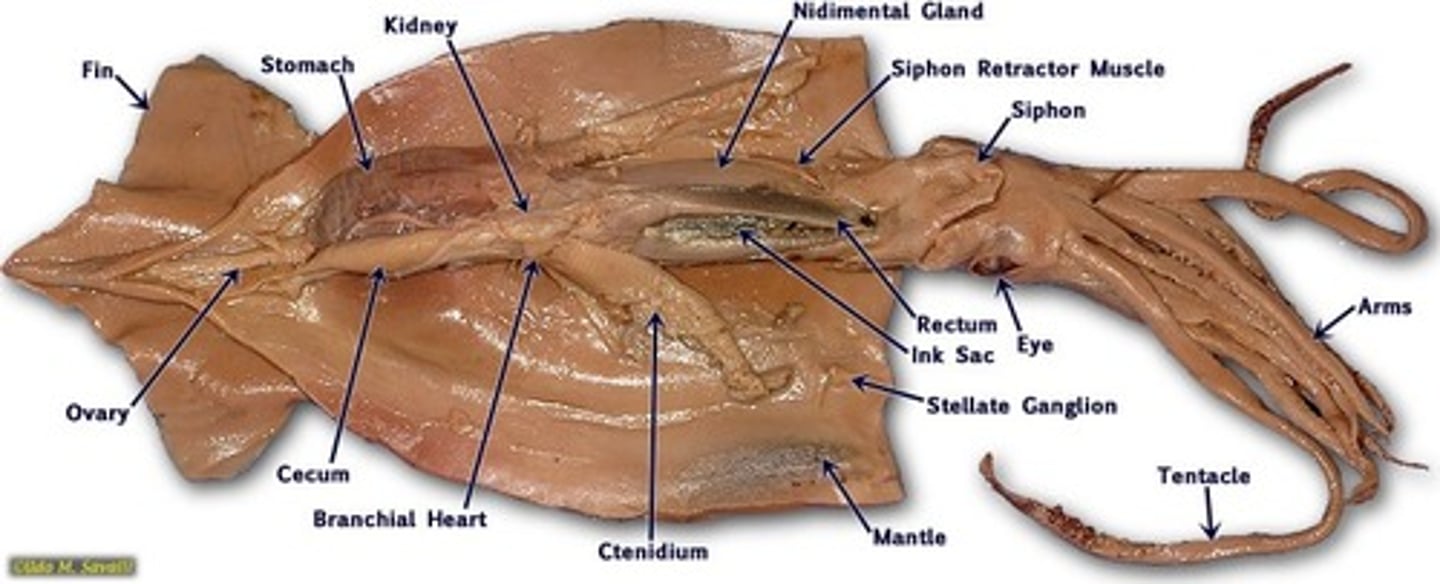
Identify key features on a dissected squid
Know where the inc sac, pen, siphon, mantle, tentacle, etc. are located
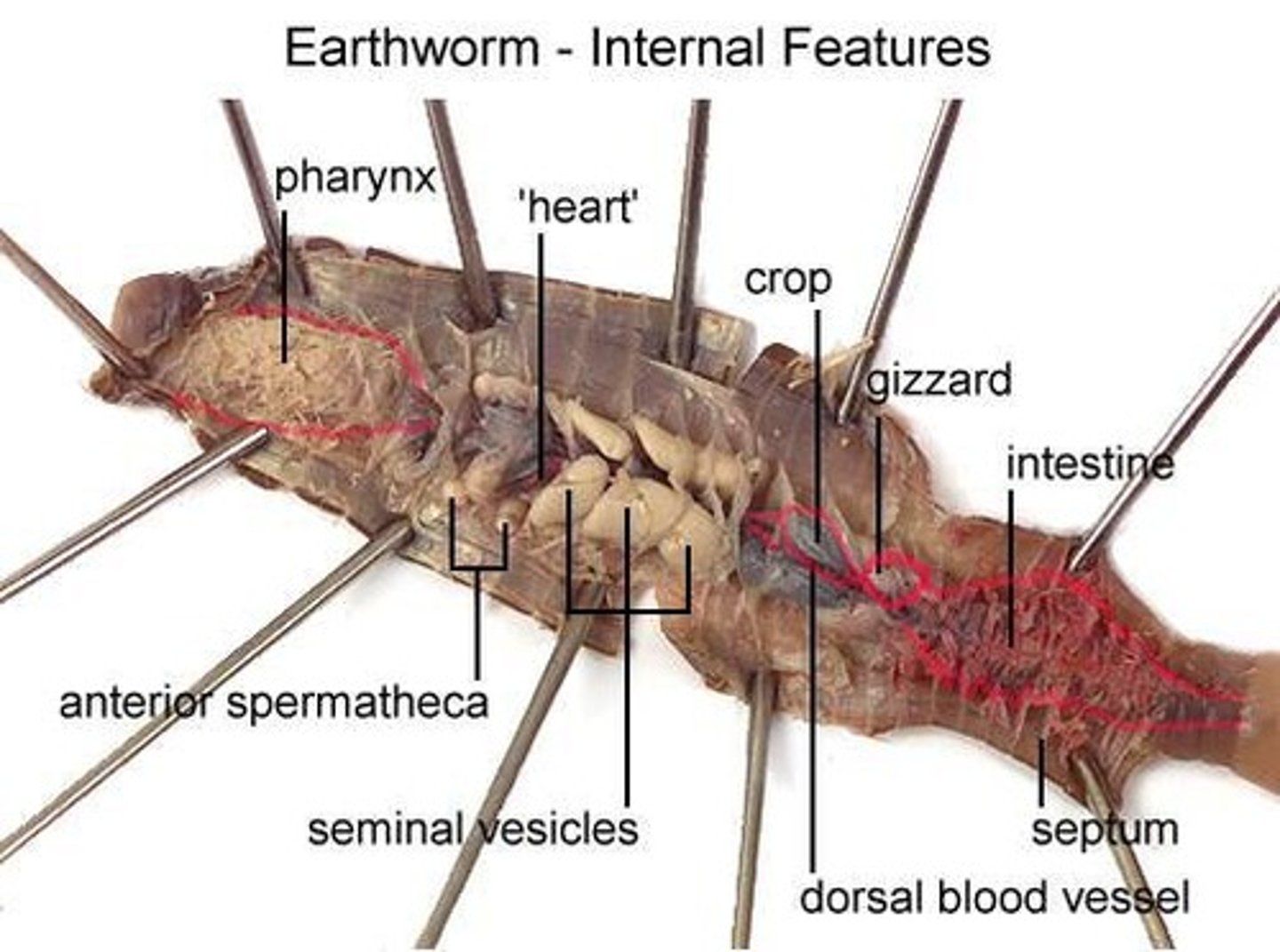
Identify key features on a dissected earthworm
Know where the crop, nerve cord, clitellum, etc. are located