ESCI 402 - Final Exam
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
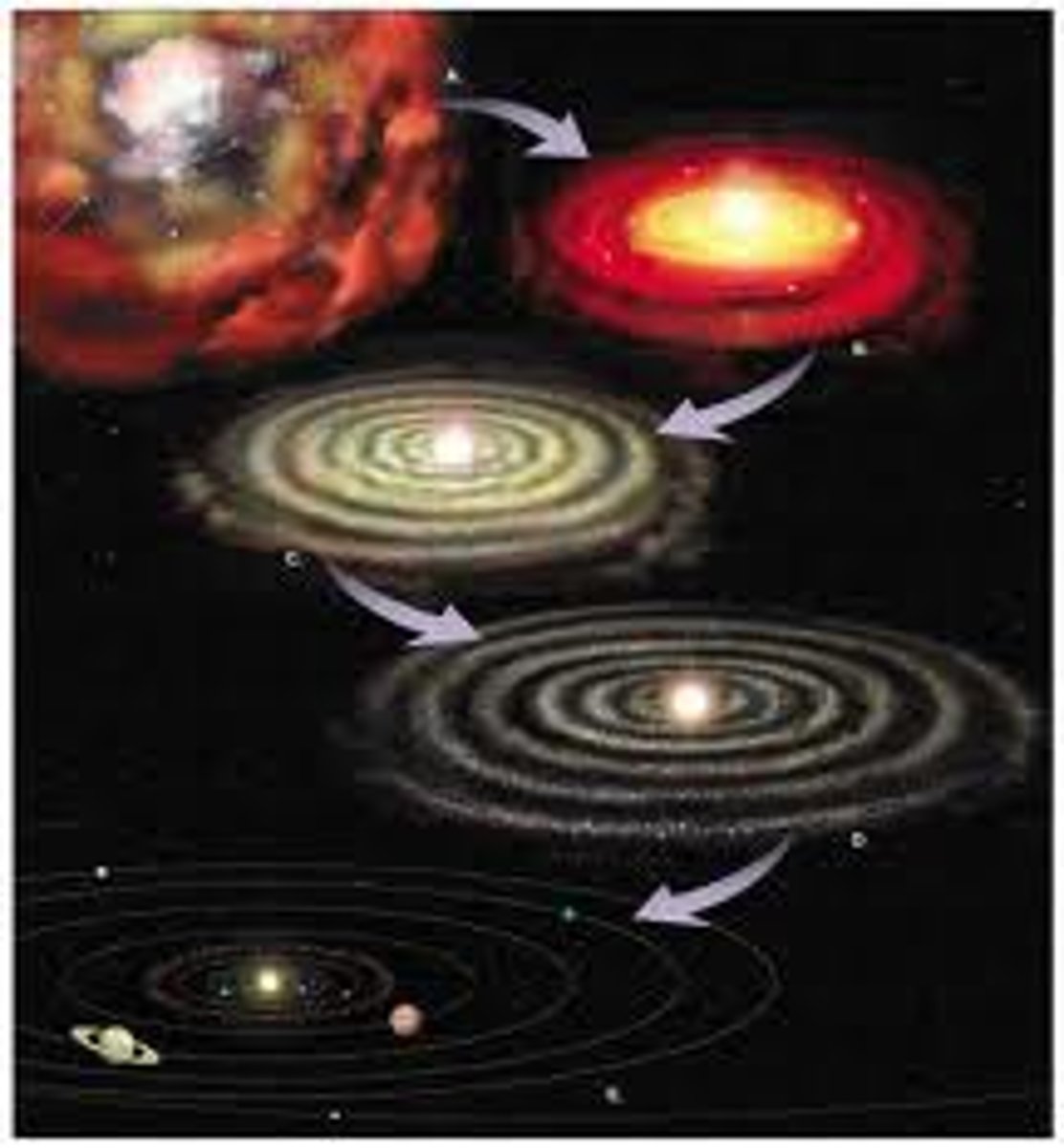
Solar Nebula Hypothesis
describes the formation of our solar system from a nebula cloud made from a collection of dust and gas
Order of the Solar Nebula Hypothesis
A. The Solar Nebula condenses and shrinks
B. Due to gravitational forces, it forms a disk and begins rotation
C. 90% of the material concentrates centrally and becomes the sun.
D. Accretion Begins
E. Solar System today
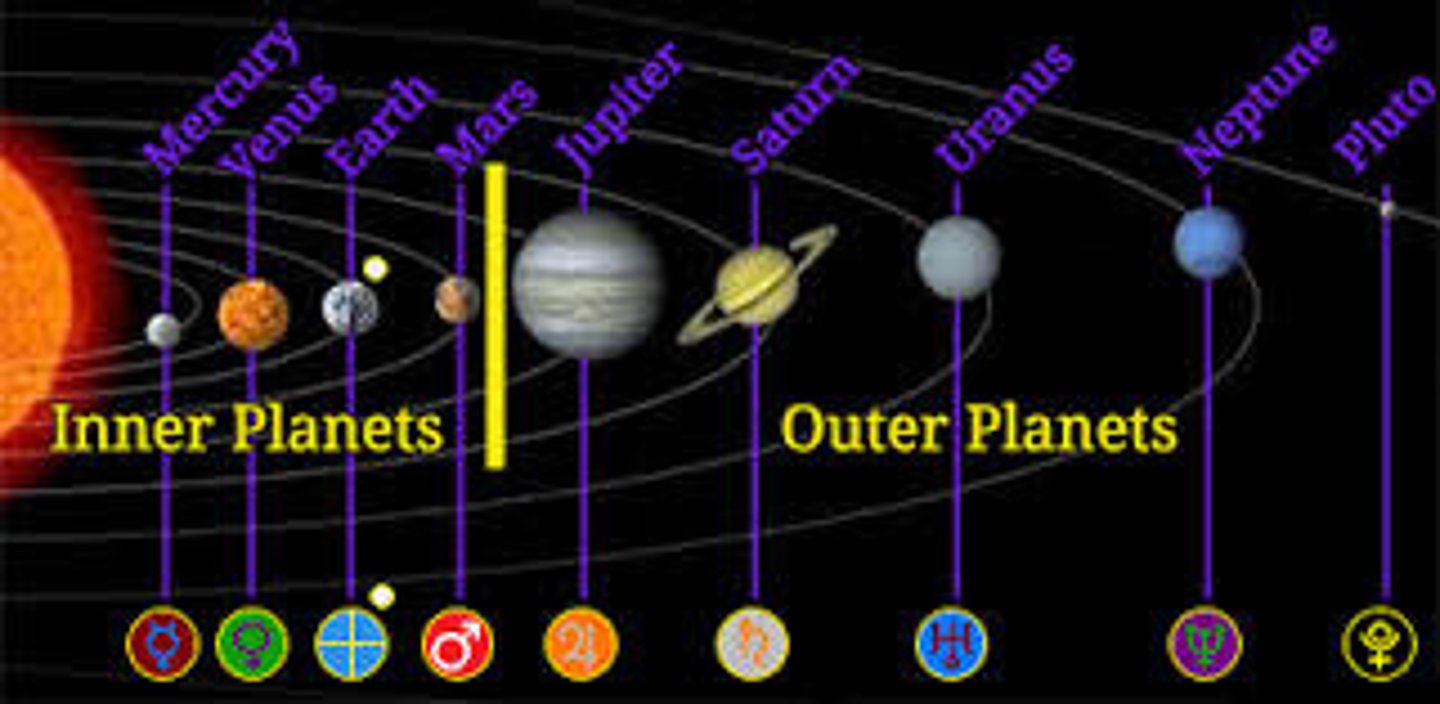
What are the terrestrial planets and what are the gas giants.
Terrestrial: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars
Gas giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
What are the differences between the terrestrial planets and gas giants?
Terrestrial Planets
-Smaller high-density
-Accreted from rock/metal planetesimals
Gas Planets
-Massive, Low density, outer planets
-Accreted from ice-rich planetesimals
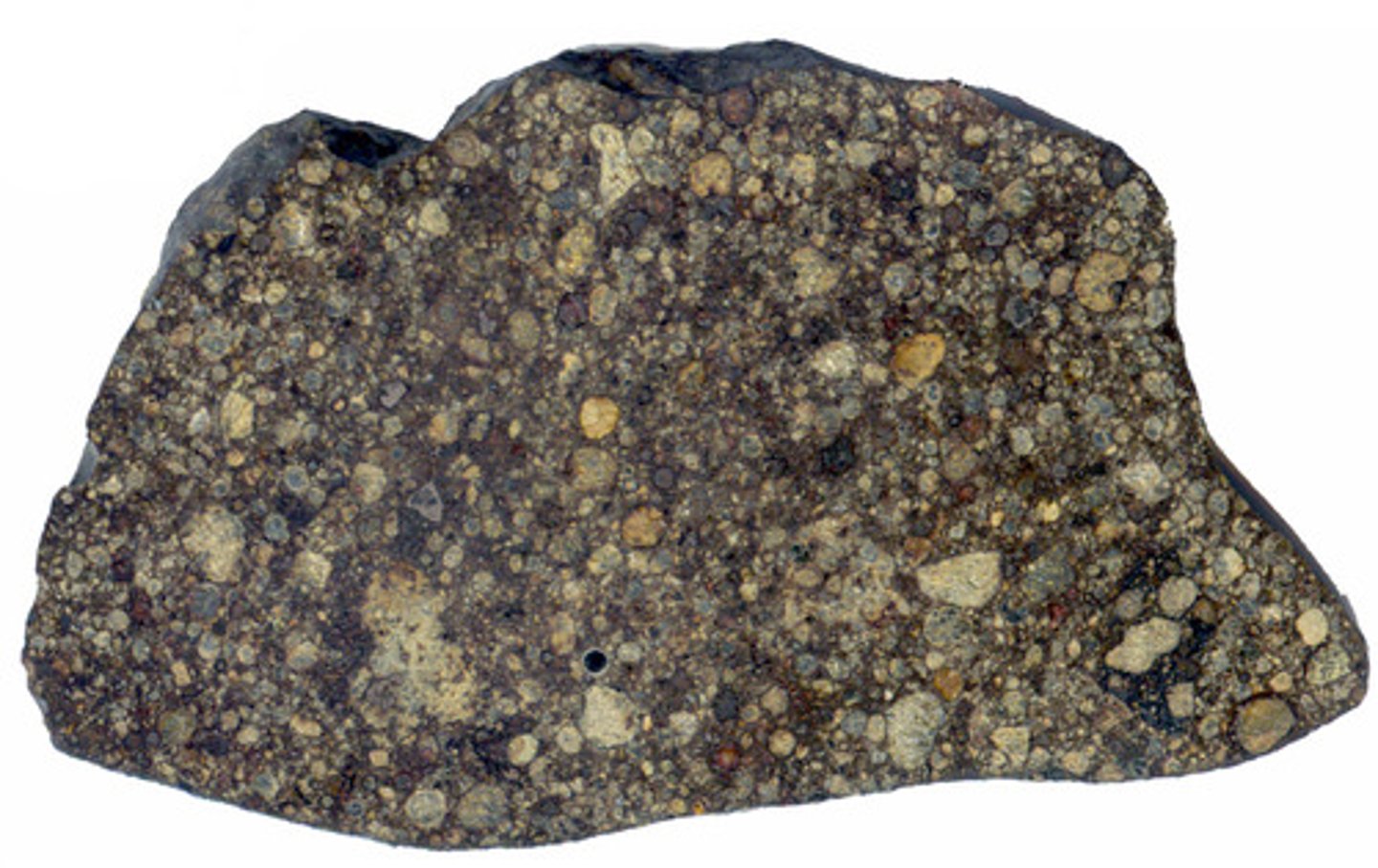
Why are Carbonaceous Chondrites (meteorites) Relevant to Earth's composition?
Earth is abundant with them; they contain Chondrules (cooled molten droplets from hot nebular gas) and have the same composition as the sun.

What is Earth most composed of?
Mg (Magnesium), Si (Silicon), Fe (Iron)
What are the theories of the creation of the moon?
Fission, Co-accretion, Capture, Giant Impact
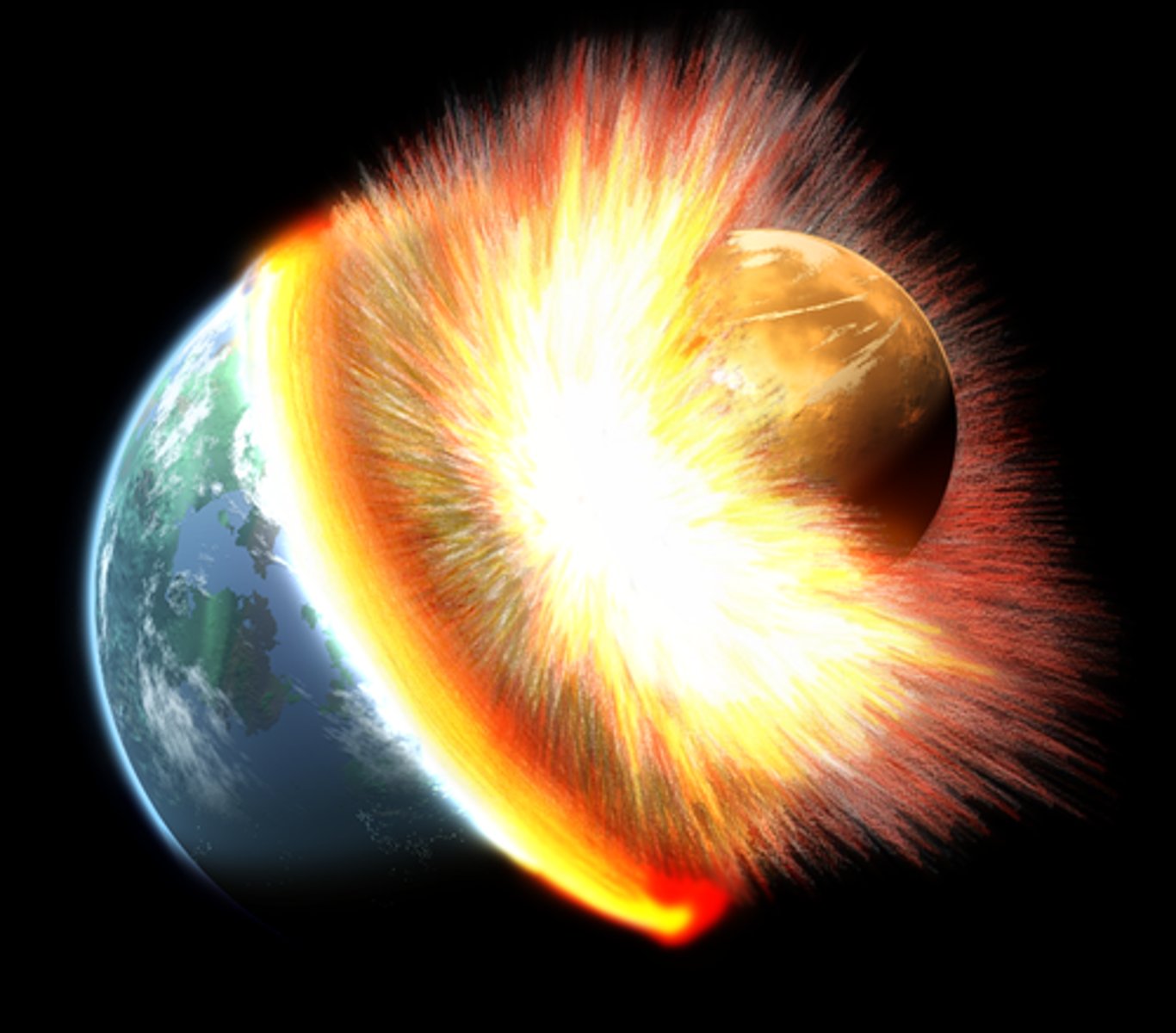
How was the moon formed?
It was formed by debris from a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized protoplanet called Theia

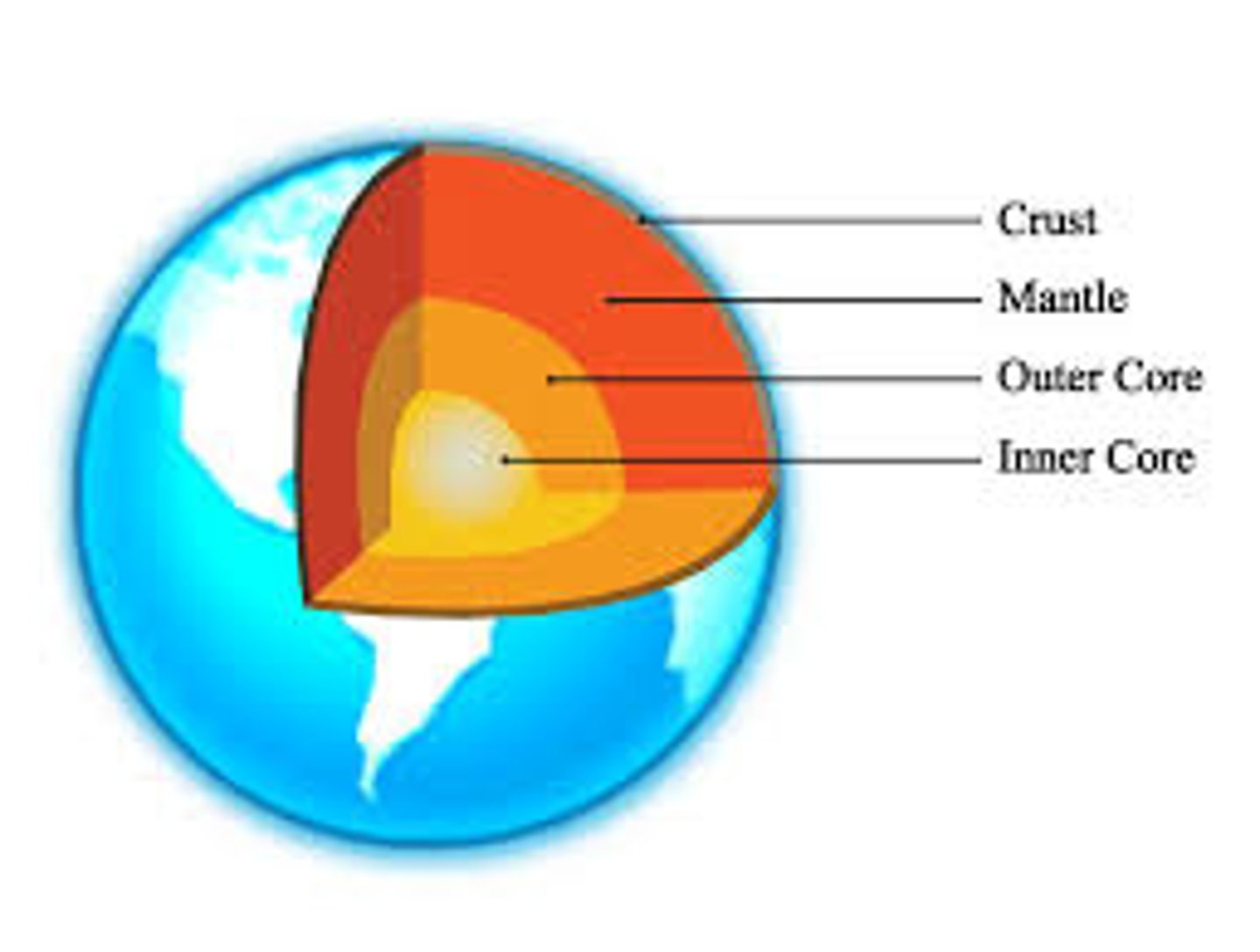
How did the Earth segregate into crust, mantle, and core?
By melting, impacts caused melting, metal from impactors sank in intact or as droplets.
What are the chemical layers of Earth?
crust, mantle, core
What evidence are there for liquid water on Hadean Earth?
Zircons (silicate minerals with gas inclusions) found in the Jack Hills, Australia
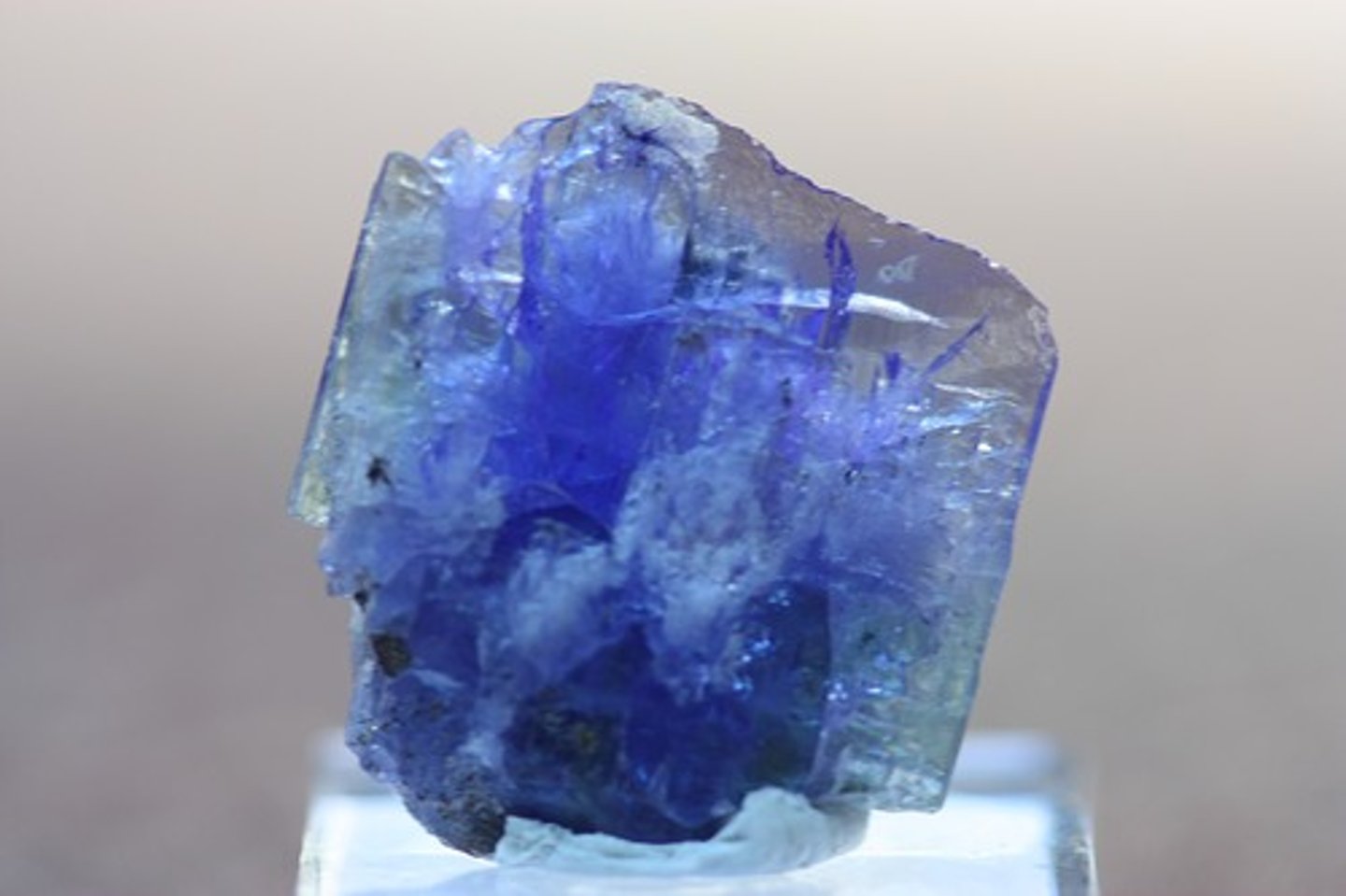

Why are Zircons Relevant?
Zircons can be dated using the lead in them to over 4.4 billion years ago, and have trace amounts of titanium, which was evidence for water at the time of the Zircons' formation.
Origin of the Ocean Argument #1: Degassing
Volcanic and general degassing from the Earth's interior slowly and steadily increased the ocean's volume over 2-3 billion years. Due to evidence provided from Zircons, this is unlikely.
Origin of the Ocean Argument #2: Comets
During Earth's formation, asteroids bombarded Earth's surface and provided the water we have today. This theory has evidence, considering there was a spike in impacts found through crater counting on the moon, and that there is a match with the water composition in nearby asteroid belts.
Origin of the Atmosphere Arguments
Impact Degassing from Meteorite impacts, Volcanism degassing, comet and meteorite delivery. Most likely a combination of all three of these.
Likely Causes of the Great Oxydation Event?
Cyanobacteria, Stromatolites (microbial mats) performing photosynthesis.
How do we know the timing of the Great Oxygenation Event?
Banded Iron Formations, Paleosols, Redbeds
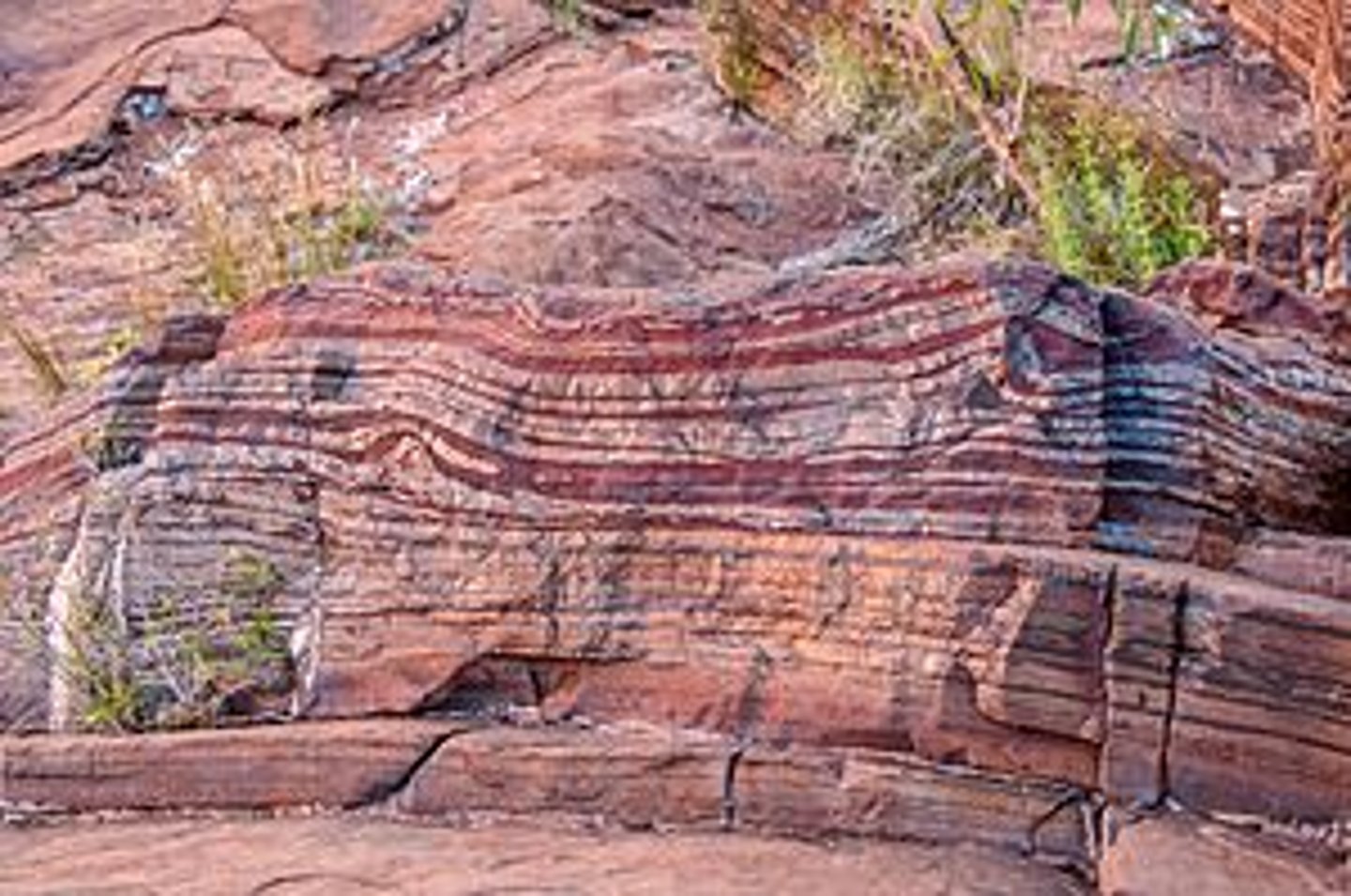
Banded Iron Formations (BIF's)
Evidence of oxygen in the atmosphere in the sediments and rocks, caused by the oxidation of Iron when exposed to oxygen. Alternating patterns might suggest seasonal deposition of oxidized and non-oxidized iron.

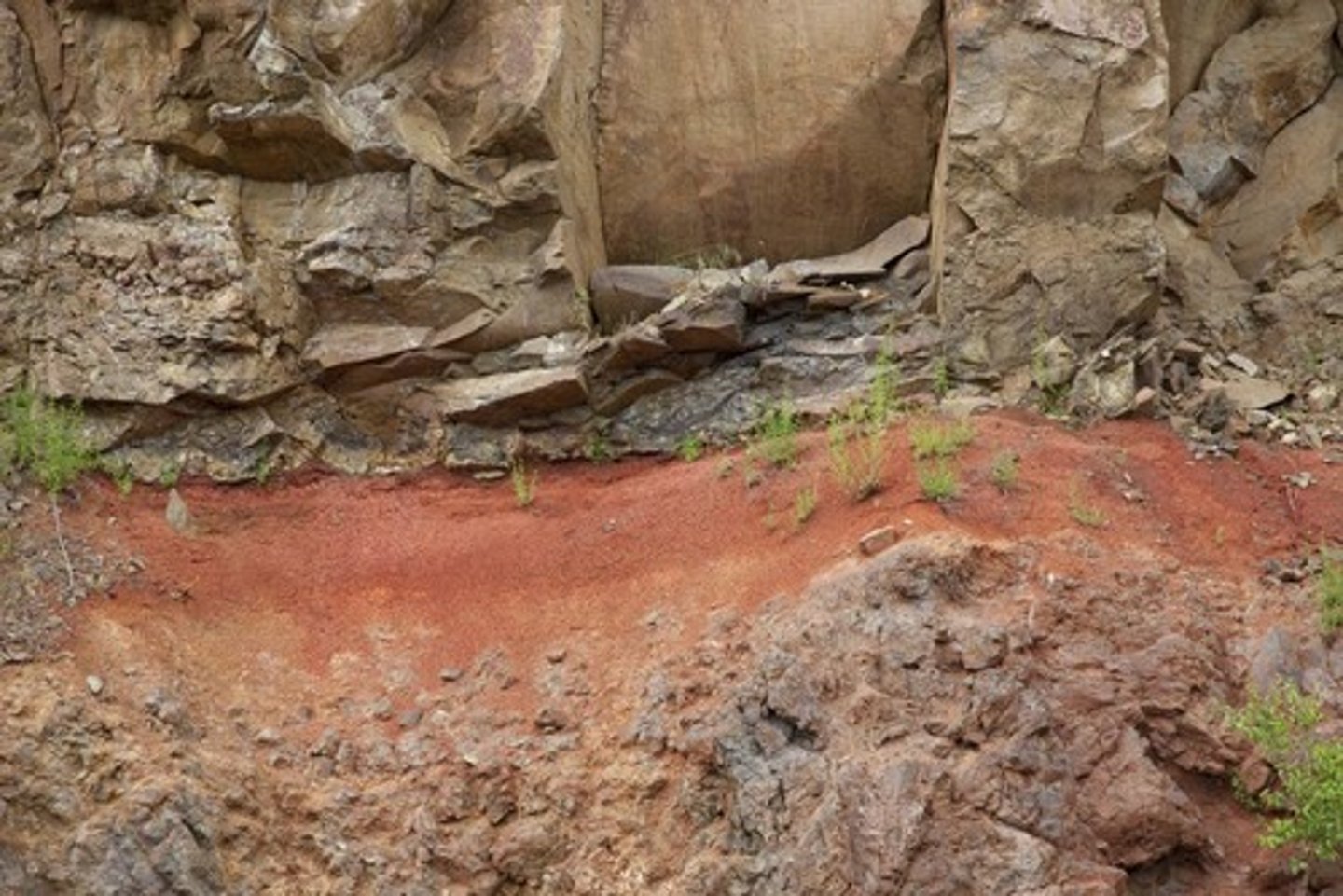
Paleosols
ancient soils that are significantly depleted in iron before 2.4 Gyr and abundant in Iron after 2.4 Gyr, due to the fact that iron is extremely soluble and able to be carried away by groundwater when not exposed to oxygen. Proving that before 2.4 Gyr, there were very low amounts of Oxygen, and after there was.

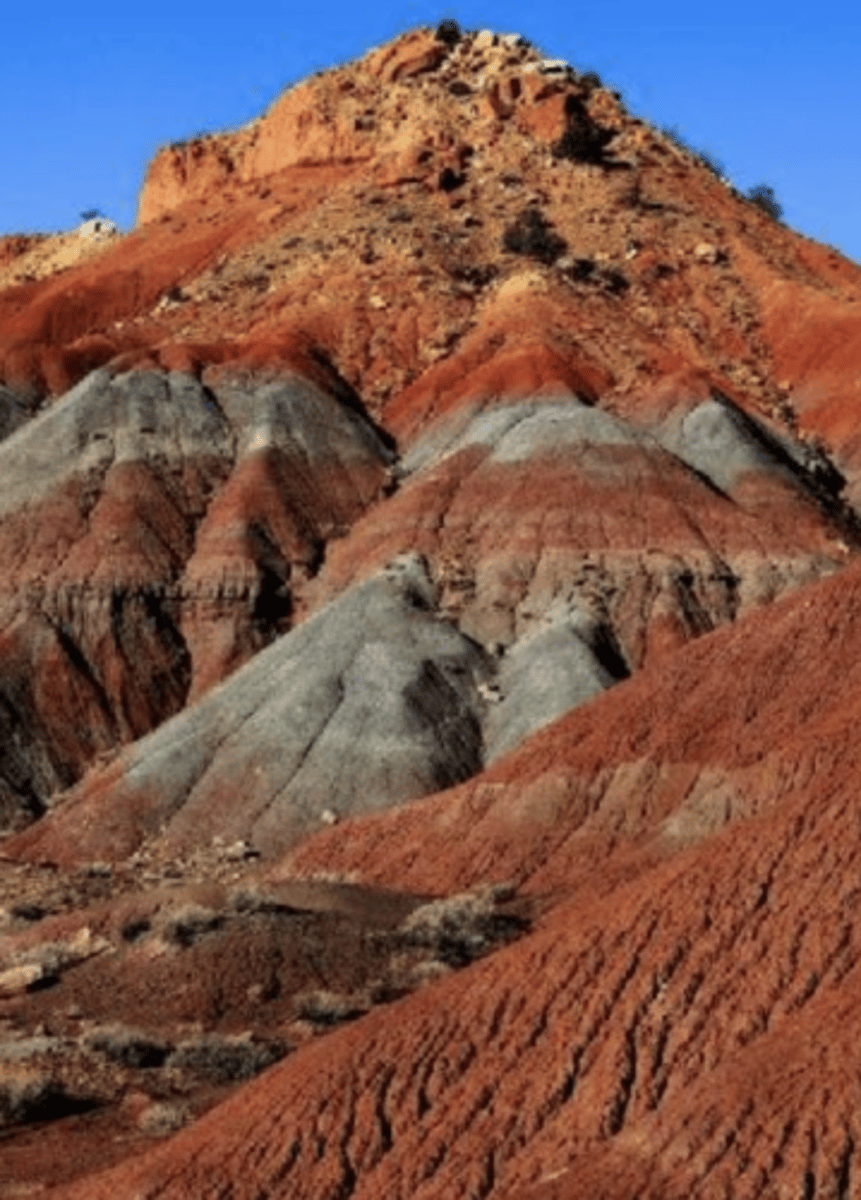
Red Beds
Sedimentary rock deposits that contain oxidized iron, provides evidence that there was oxygen present in the atmosphere when they formed. Therefore, because there are no Red Beds older than 2.2 Gyr, this proves there was little to no oxygen in the atmosphere before then.

Why is there a delay between photosynthesis and the GOE?
Possibly due to the fact that it took a long time for photosynthesis to remove all of the ferrous iron present in the atmosphere, organisms did photosynthesis but were not originally producing oxygen, reduced volcanic gases.
How did life likely form and where?
The Miller-Urey experiment proved organic amino acids could form from inorganic raw materials, and likely in Hydrothermal vents along mid-ocean ridges.
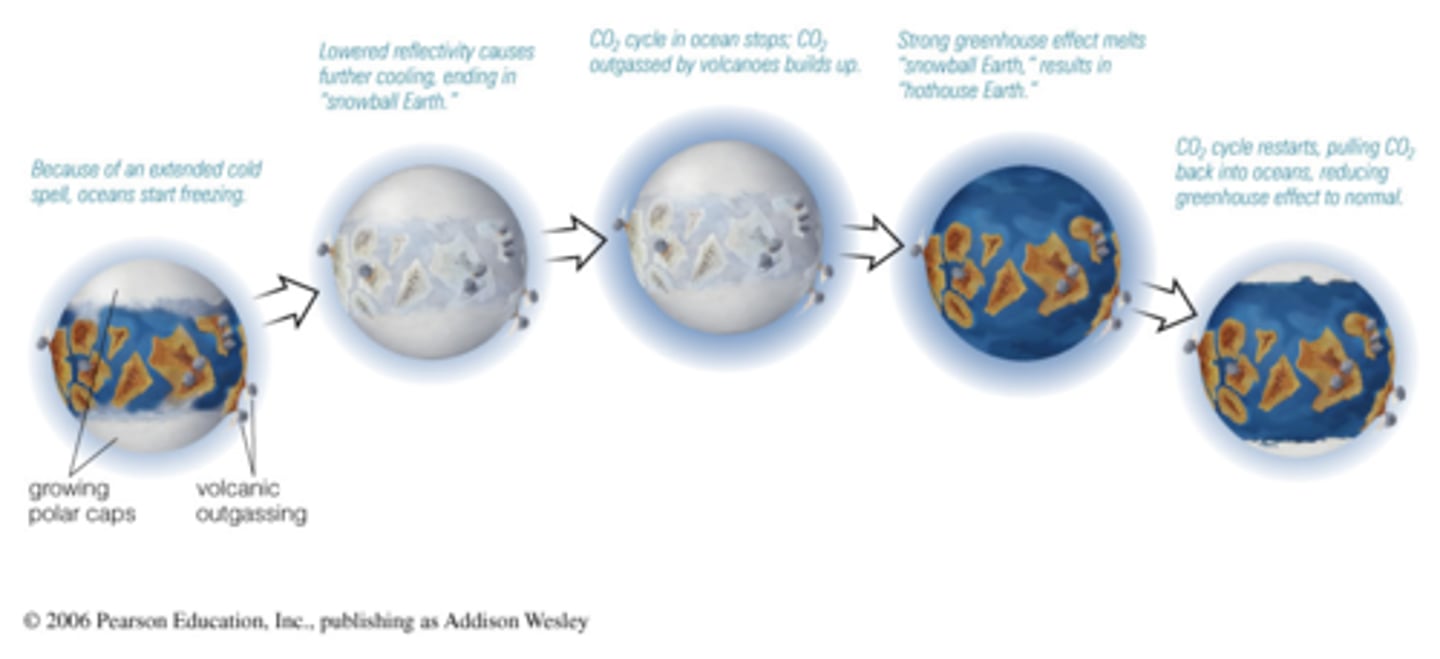
Snowball Earth Hypothesis
During one or more periods before 650 MYA, Earth was almost completely covered by glaciers. This is proved by glacial till at low latitudes.
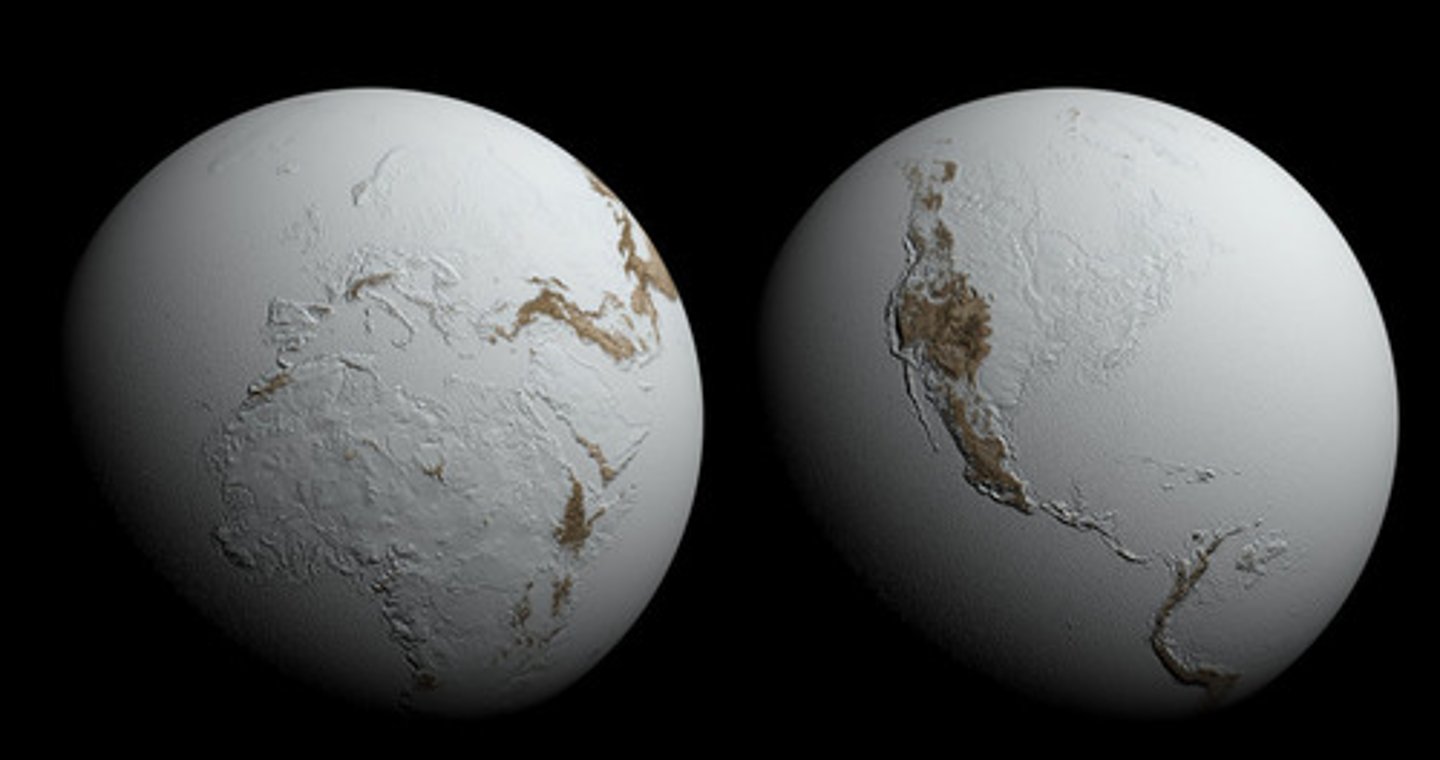
How would Snowball Earth Form?
1. An extended cold spell causes oceans to freeze
2. Earth reflects more sunlight, glaciers expand
3. CO2 cycles in oceans stop, and CO2 from volcanoes builds up in the atmosphere
4. The greenhouse effect ends "snowball Earth"
5. CO2 cycles begin again pulling CO2 back into the ocean.
Metazoan
Multicellular animal, composed of cells differentiated into tissues and organs
Edicarian life
have the first evidence of an organism with a suspended digestive tract and a Metazoan
Cambrian Explosion
A burst of evolutionary origins when most of the major body plans of animals appeared in a relatively brief time in geologic history, recorded in the fossil record about 545 to 525 million years ago.
What major evolution happened during the Cambrian Explosion?
Exoskeleton, which helped protect against UV radiation, prevented drying out, and protected vs predators.
What caused Gigantism in the Carboniferous?
Caused by a large increase of oxygen in the atmosphere, which in turn allowed creatures to be much larger then they are presently.
Supercontinent Cycle
The process of change during which supercontinents develop and later break apart, forming pieces that may merge once again in geologic time to make yet another supercontinent. Nuna, Rodinia, Gondwana, and Pangea
Order of Appalachian Orgoenies
Taconic, Acadian, Alleghenian
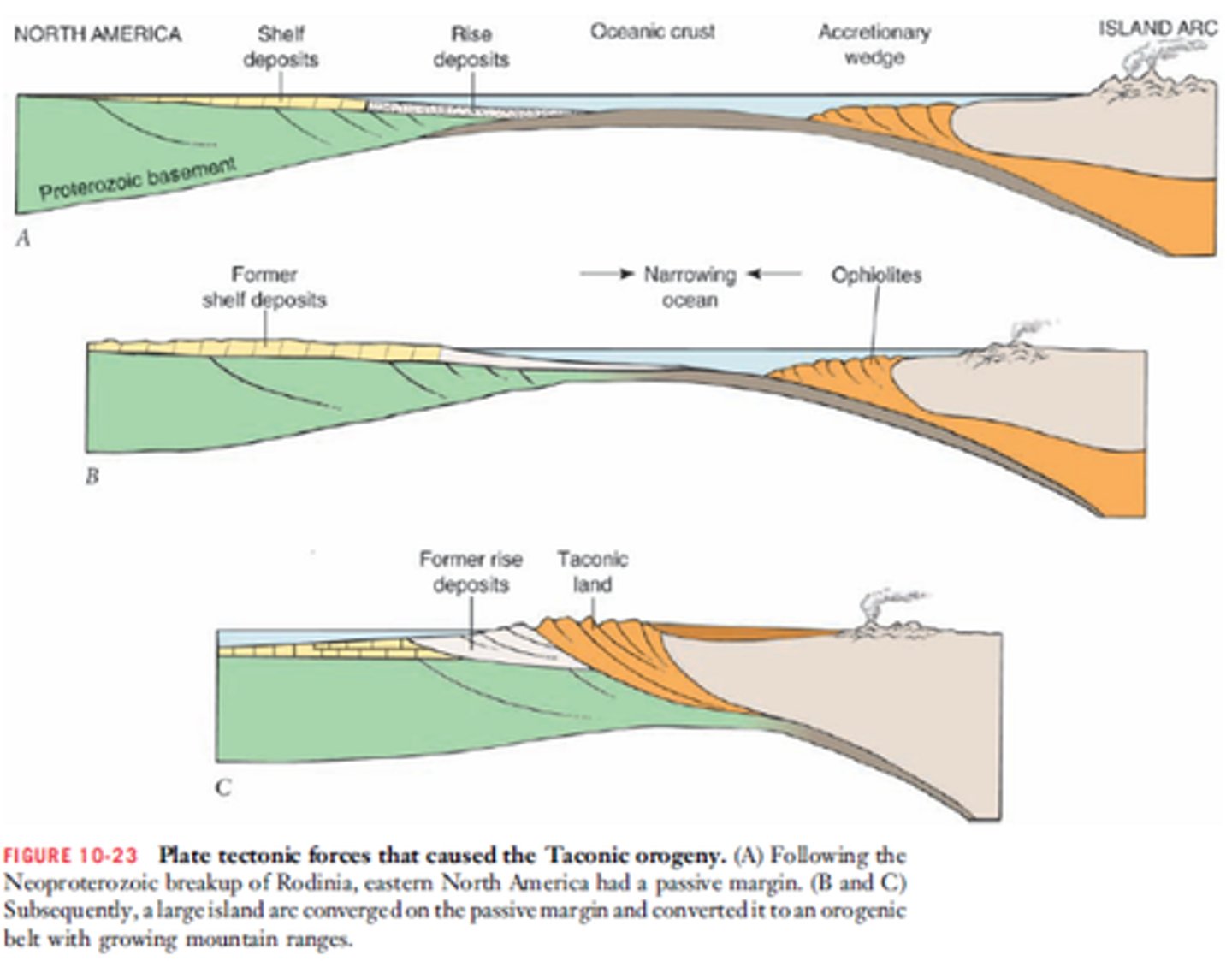
Taconic Orogeny
The Laurentian plate subducts under the island arc, creating an accretionary wedge that grows from scraping material off the subducting slab. The Island Arc and Laurentian Plate combined by the mid to late Ordovician.
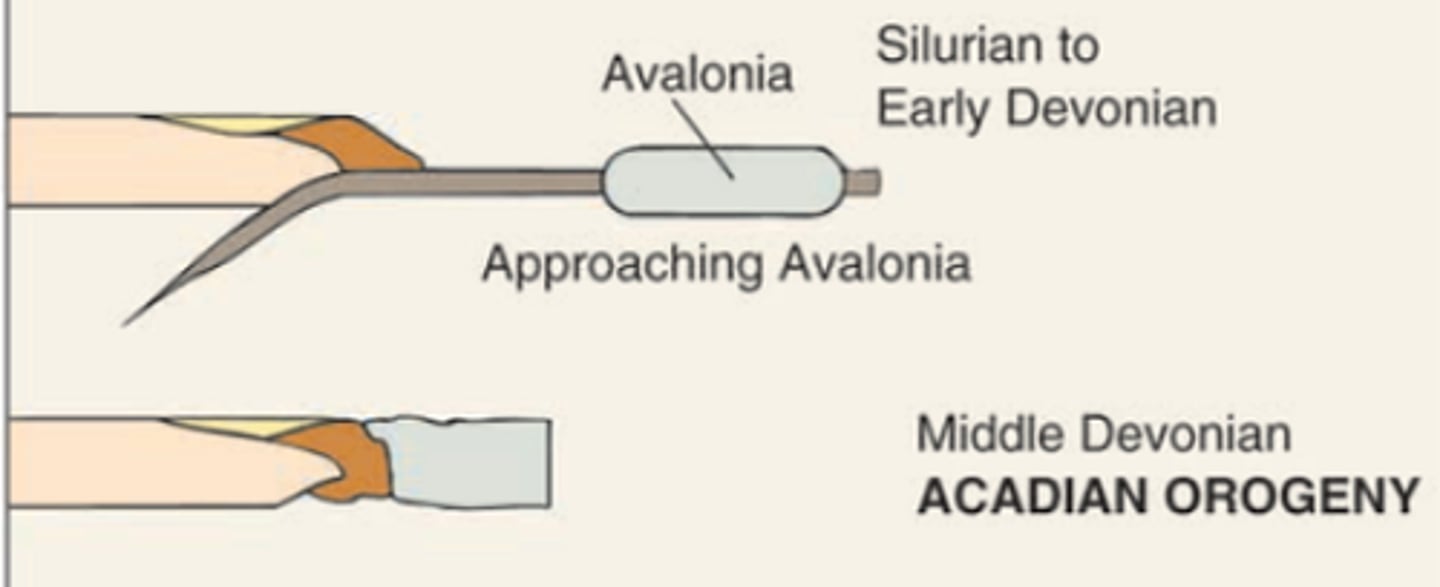
Acadian Orogeny
An episode of mountain building in the northern Appalachians during the Devonian Period where Avalonia and Laurentia collide, with Avalonia subducting.
Alleghenian Orogeny
Mountain-building event that occurred when the part of Gondwana that is now Africa began to collide with Laurasia during the Permian.
Appalachian Plateau
Broadly folded, sedimentary rocks, heavily incised by rivers
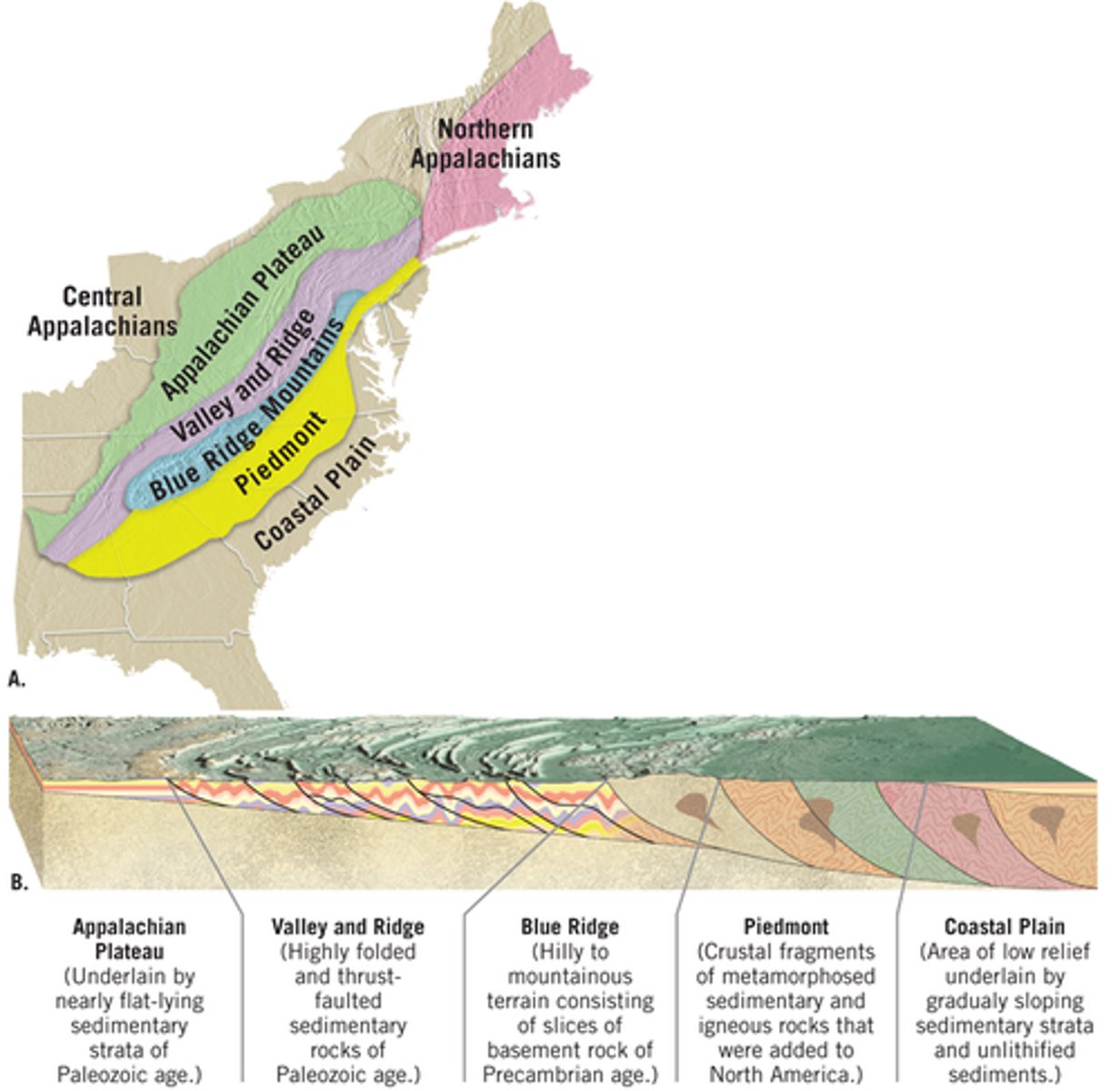
Valley and Ridge
Highly deformed sedimentary rocks, variable resistance to erosion
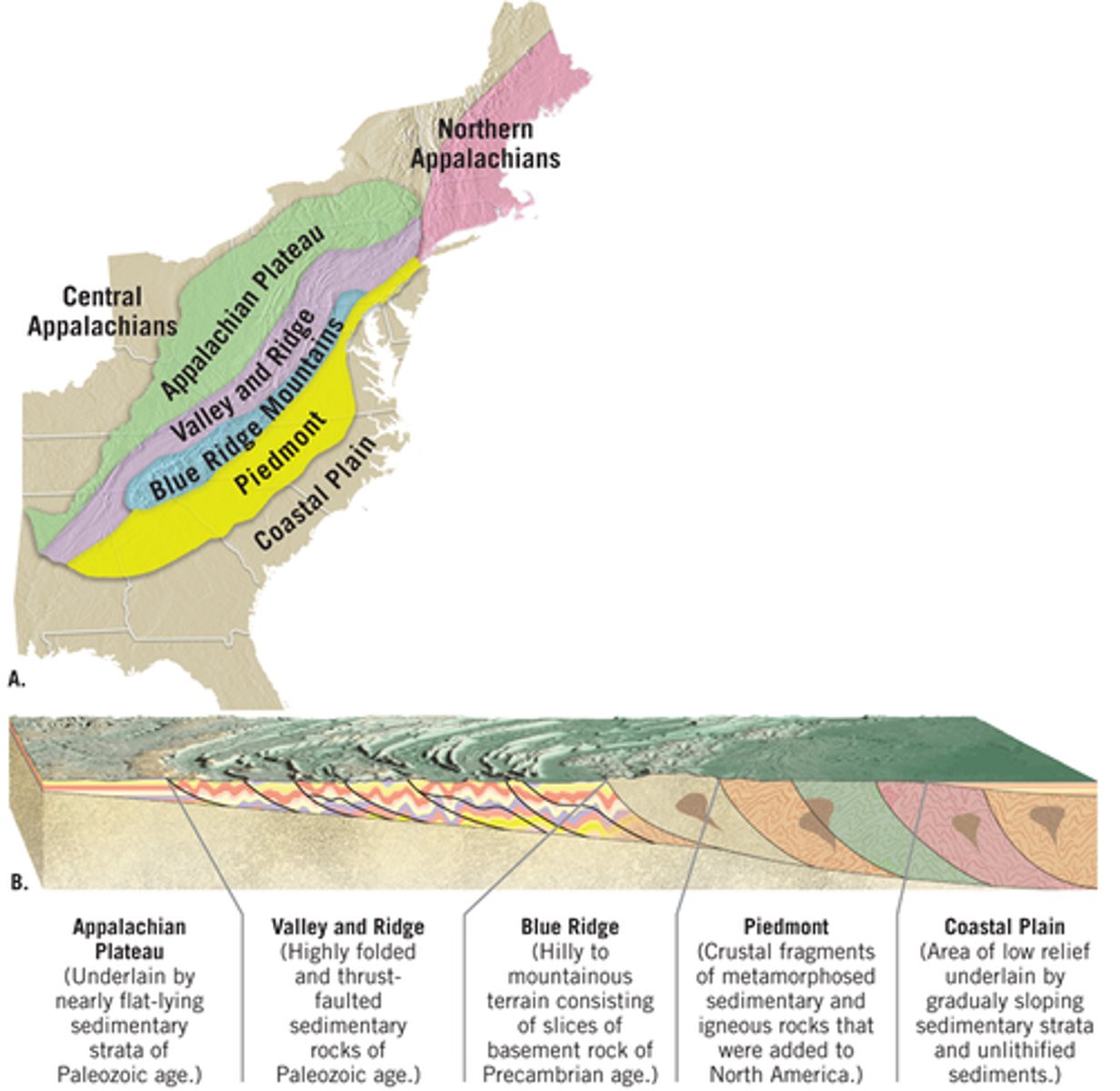
Blue Ridge Mountains
Strongly Metamorphosed rocks, intrusive igneous rocks
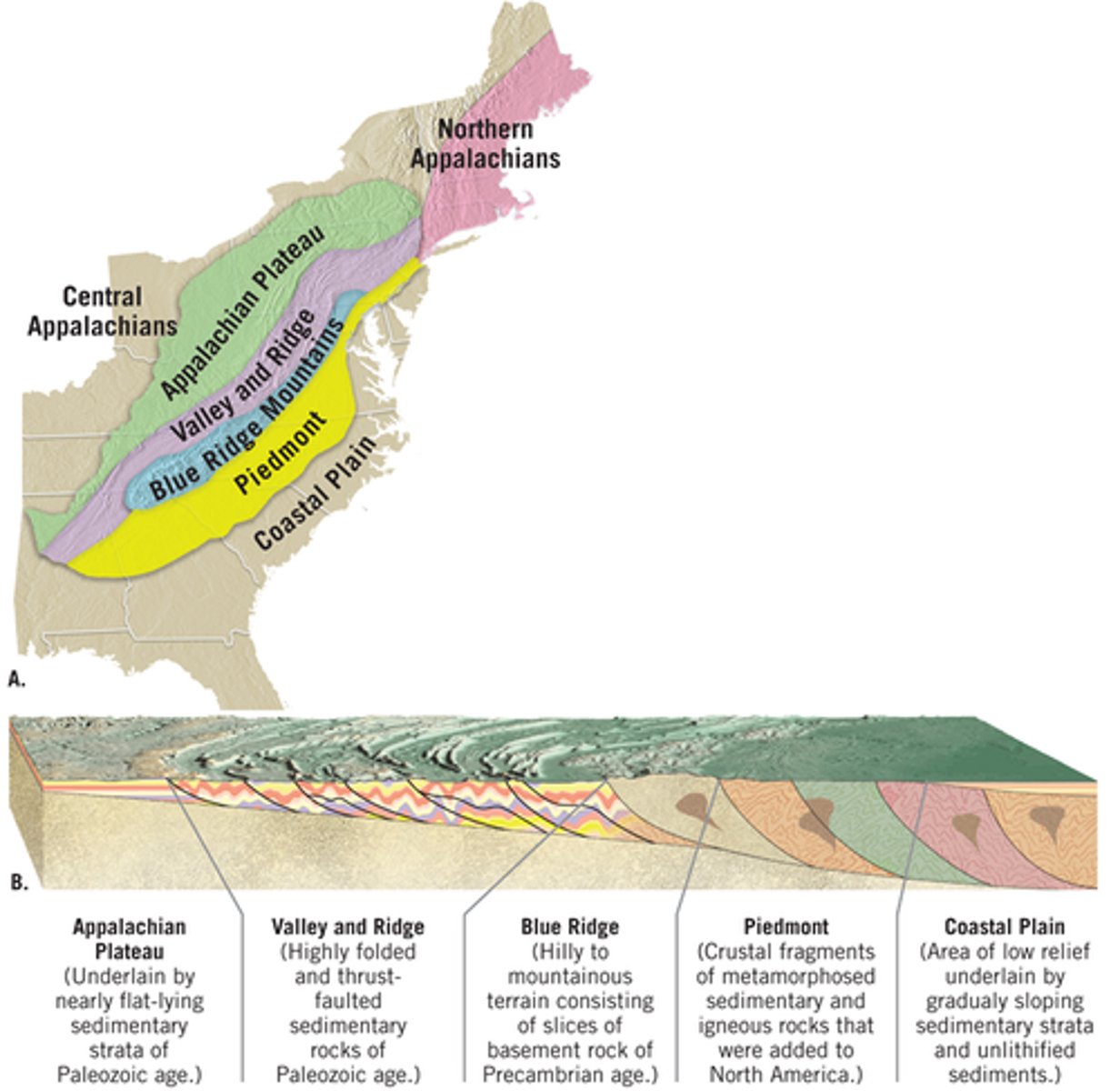
Piedmont
Slates, schists, gneisses (metamorphic) Intrusive igneous rocks
Evidence of Pangea
Puzzle-like fit of the continents, Glacial evidence, The Gondwana Succession (unique succession of rocks found on all southern continents), Paleomagnetism, Distribution of fossils
Synapsids
became more dominant in the Permian, including everything more closely related to mammals.
Therapsids
Synapsids that eventually evolved into pelycosaurs included rodent-like Cynodonts and predators like Gorgonopsids.
Plant Life on Pangea
seed-producing trees such as Glossopteris, and Gingkoes evolved during the permian.
Low Equabillity of Pangea's climate
temperatures are very different around the world, shown by coal deposits, Tillites (glaciers), and Evaporites
High Seasonality of Pangea's climate
seasonal temperature changes and precipitation are large, as shown by lungfish burrows, redbeds and evaporites, and monsoons
Cyclicty of Pangea's climate
natural variations in global climate caused changes in glacier extent and sea level, shown by Cyclothems (cyclic repetitions of marine and non-marine strata demonstrating changes in sea level)
Large Igneous Provinces
a region in which huge volumes of lava and/or ash erupted over a relatively short interval of geologic time, causes massive global warming, acid rain, ocean acidification, aerosols blocked sunlight
End Permian Mass Extinction
The largest mass extinction event of all time, resulting in the loss of 95% of marine species, was the result of a warming event brought on by the Siberian Traps volcanism.
What survived the End Permian Mass Extinction?
small mammal like synapsids like cyndonts and some diapsids that eventully became the dinosaurs
Pikaia
Thought to be one of the oldest known animals with a notochord; lived during the Cambrian.
Order of Fish class evolution
1. jawless (Agnathans), 2. spiny fishes (Acanthodians), 3. Plate-skinned fishes with jaws (placoderms), 4. cartilaginous skeletons (Chondrichthyes), 5. fishes with bony skeletons (Osteichthyes)
Lobe-finned fish
A group of fish that eventually evolved into tetrapods
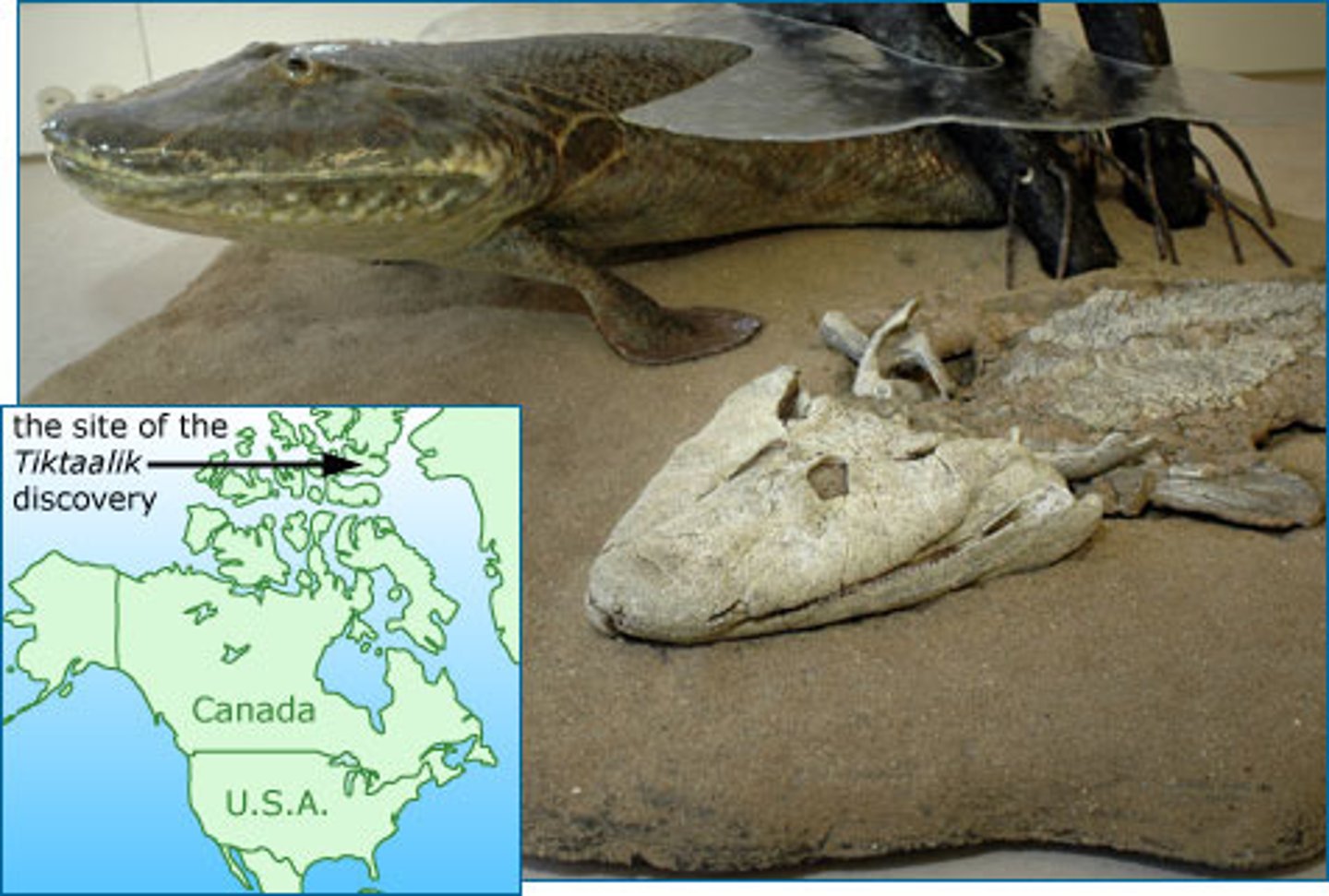
Tiktaalik Rosea
transitional fossil between fish and tetrapods, considered the "missing link"

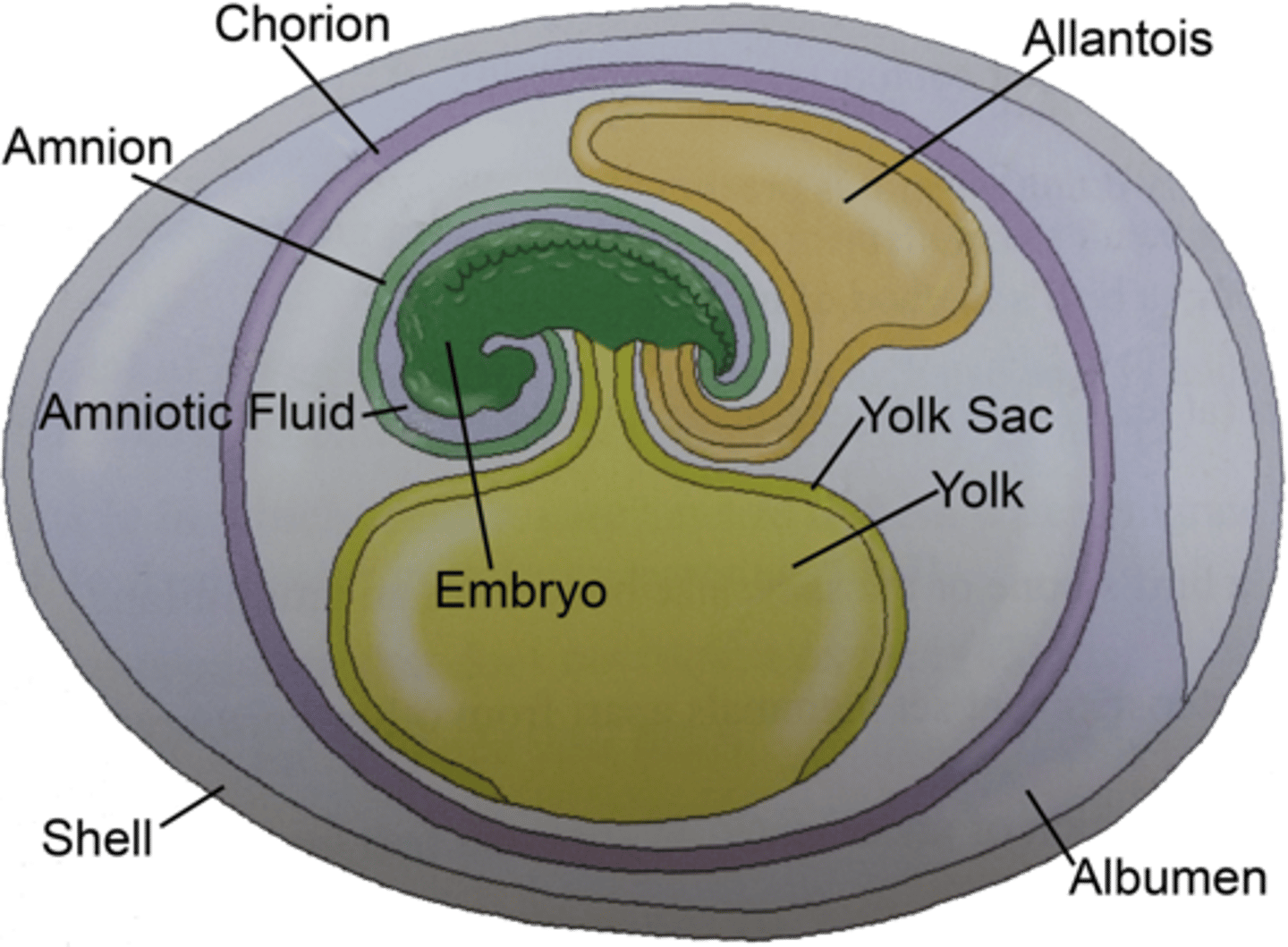
Amniotic Egg
embryo enclosed in a membrane that allows oxygen to enter but retains water, allows for animals to reproduce on land.
Archosaurs
A group of reptiles ancestral to dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and crocodilians
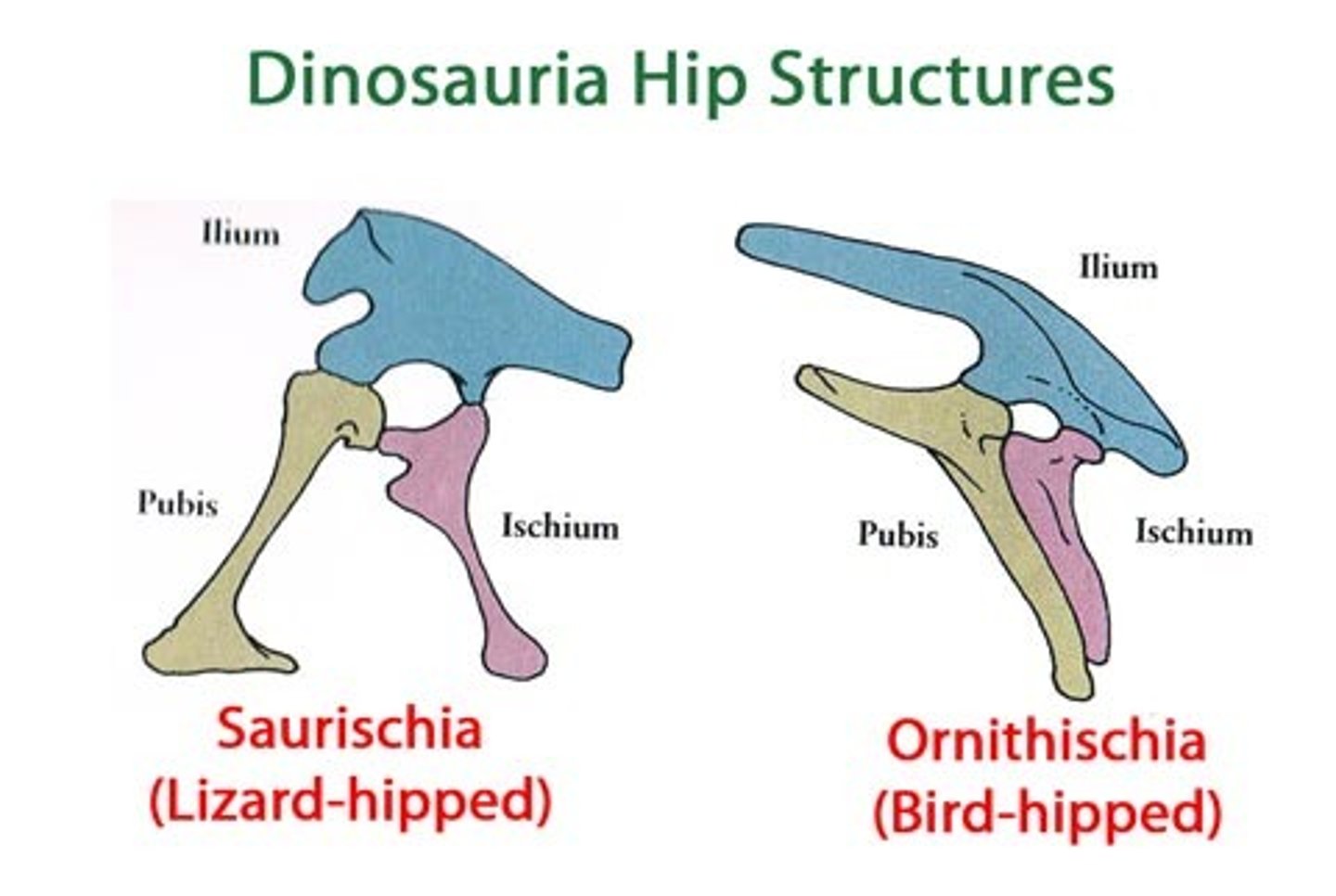
Ornithischians "bird-hipped"
herbivores, plant eaters
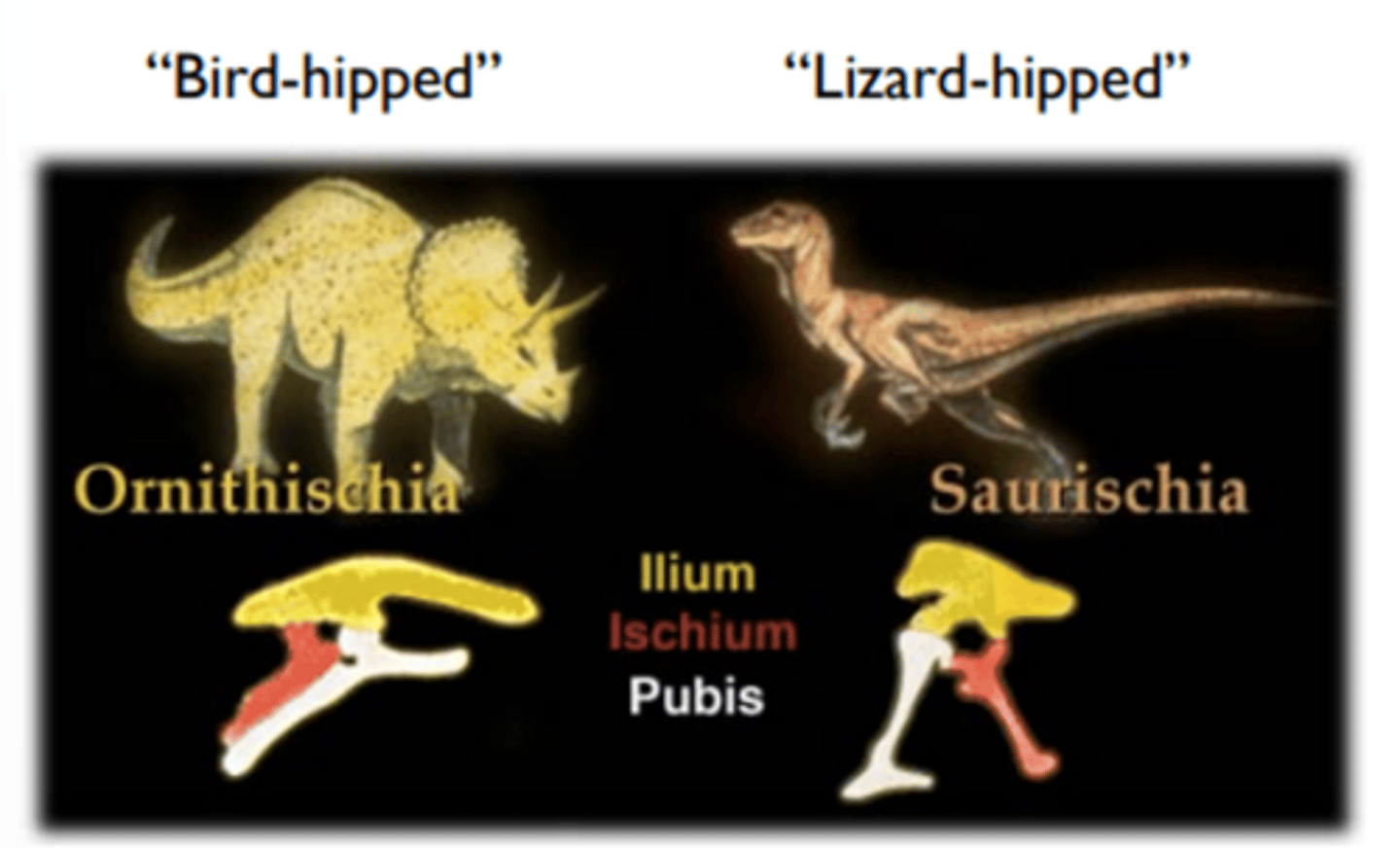
Saurischians "lizard hipped"
lizard-hipped dinosaurs, carnivorous
End-Cretaceous mass extinction
Caused by a giant asteroid impact, shown through iridium anomaly, shocked quartz, Tekites (cooled droplets of molten rock), Carbon Soot.
What were the effects of the asteroid impact that caused the end-Cretaceous mass extinction?
heating of the atmosphere, low light for weeks, impact winter, global warming, acid rain.

Order of Orogenies in the Western Cordillera
Nevadan, Sevier, Laramide
Nevadan Orogeny
The Farallon Plate subducts under the North American Plate, leading to deformation and magma generation.
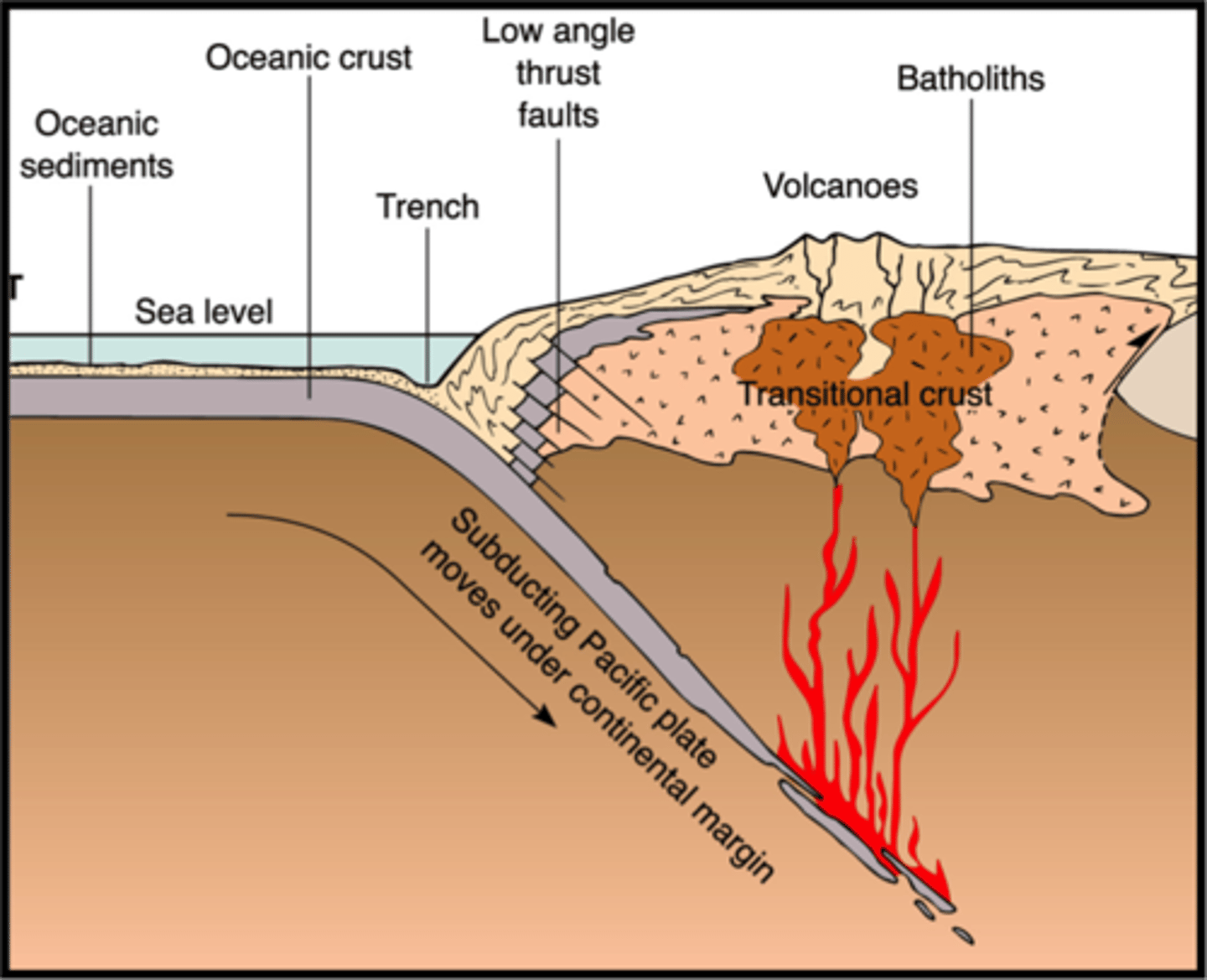
Melange
crumpled or altered rock sequence that was once trapped between converging plates.
Batholith
large mass of intrusive igneous rock believed to have solidified deep within the earth

Sevier Orogeny
The Farallon Plate subducted under the North American plate at a relatively low angle (flat-slab subduction). This leads to "thin-skinned" deformation.
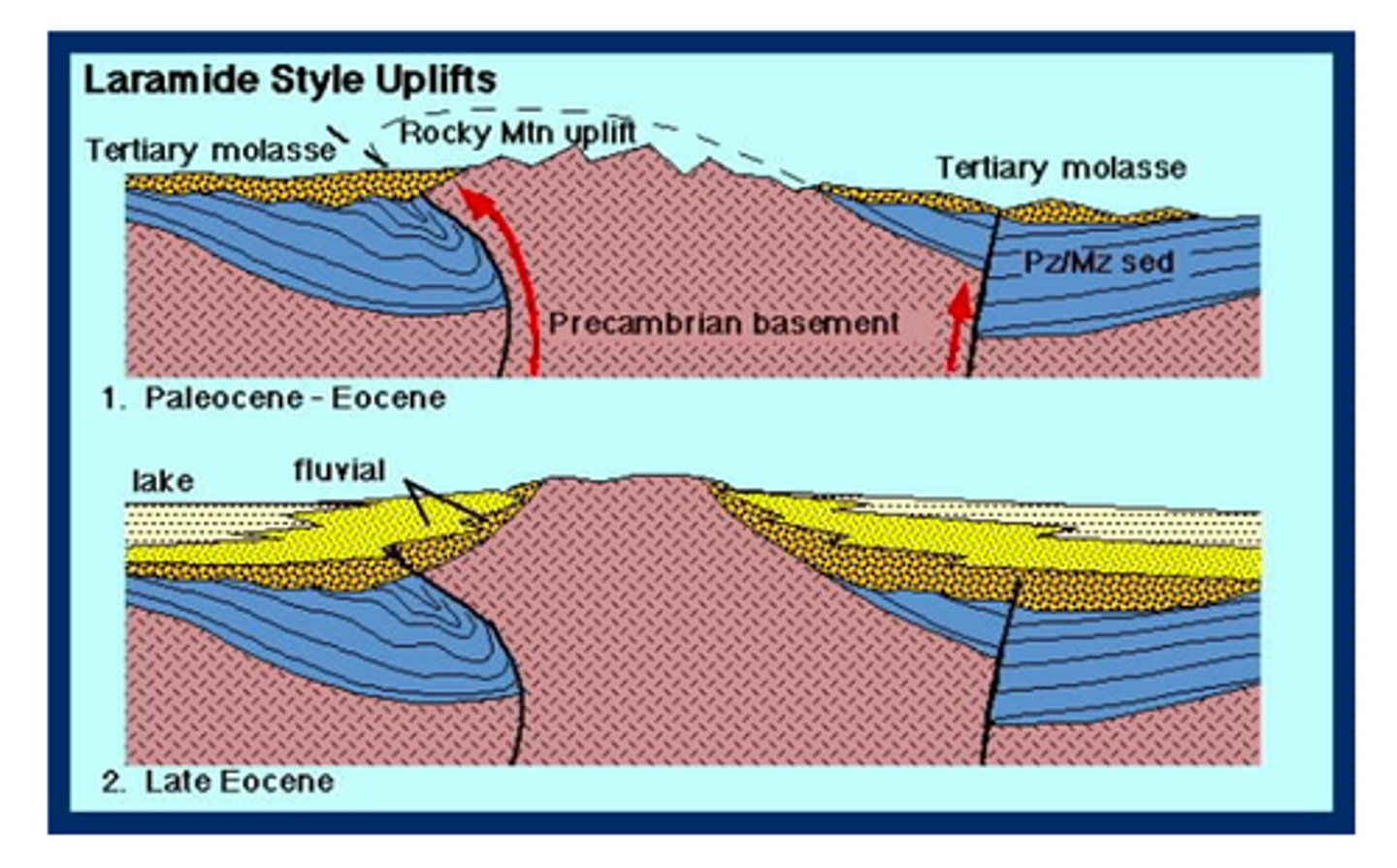
Laramide Orogeny
Reverse faults that are high-angle and involve basement rock, require much more stress. This leads to "thick-skinned" deformation.
Basin and Range Province
A large area of alternating basins and mountain ranges around Nevada
How was the basin and range province formed?
1. Whole region arched upwards, 2. Arch subsided, normal faults resulted, 3. Uplifted mountain vaults became ranges and sources of sediment to adjacent down-dropped basins.
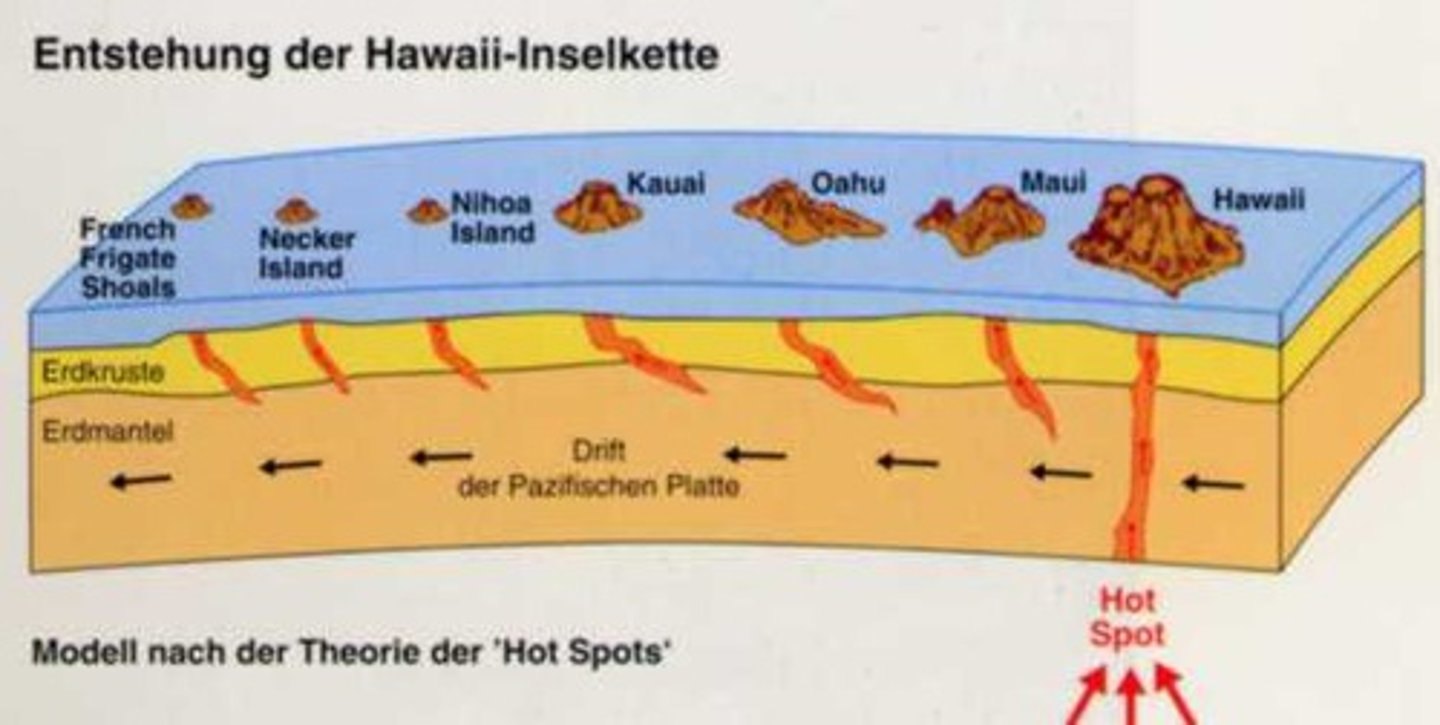
Hotspots
relatively small area of Earth's surface where a stationary, deep-seated mantle plume brings molten material up to the surface by way of melting through the lithosphere
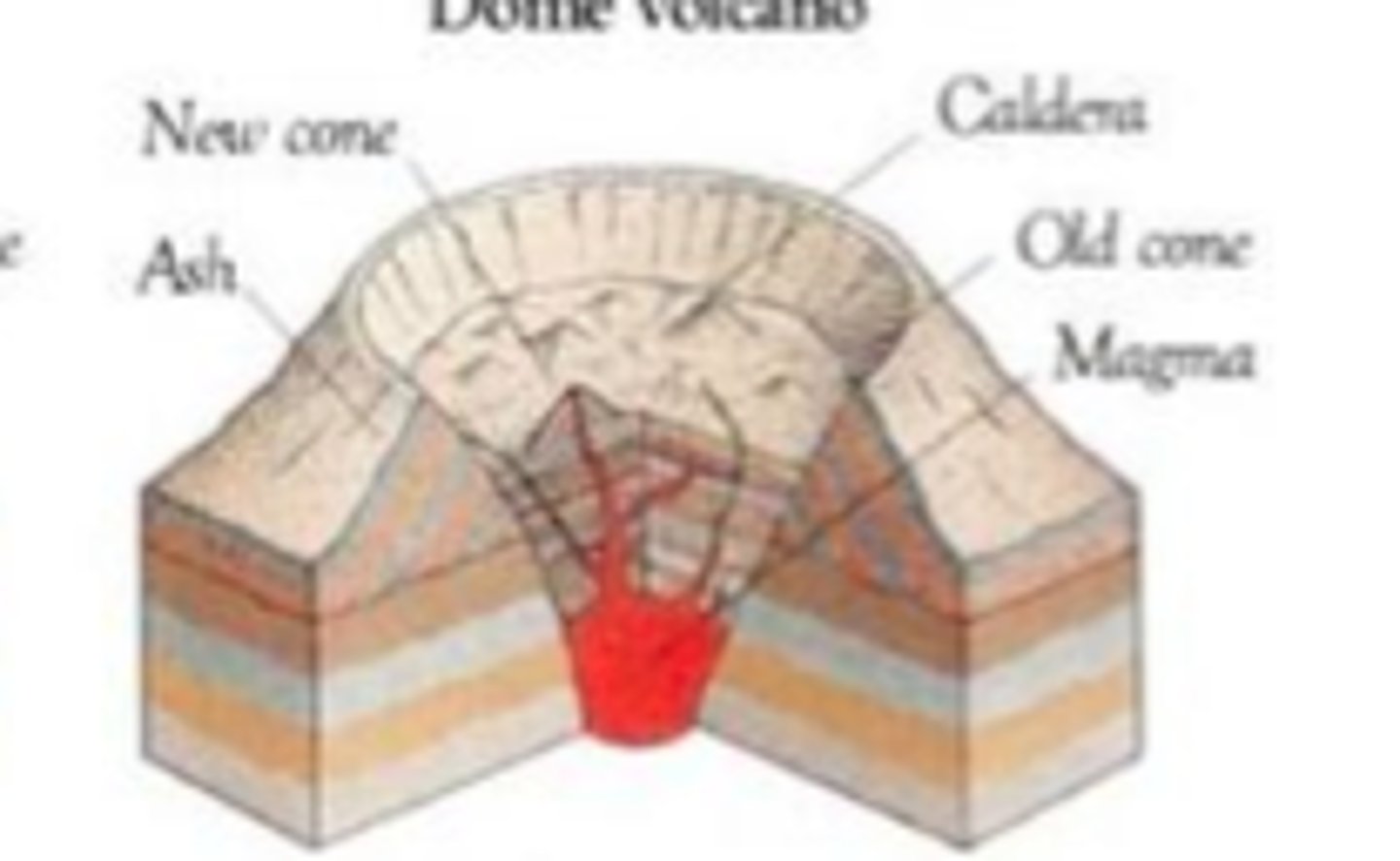
Caldera
The large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano's magma chamber collapsed.
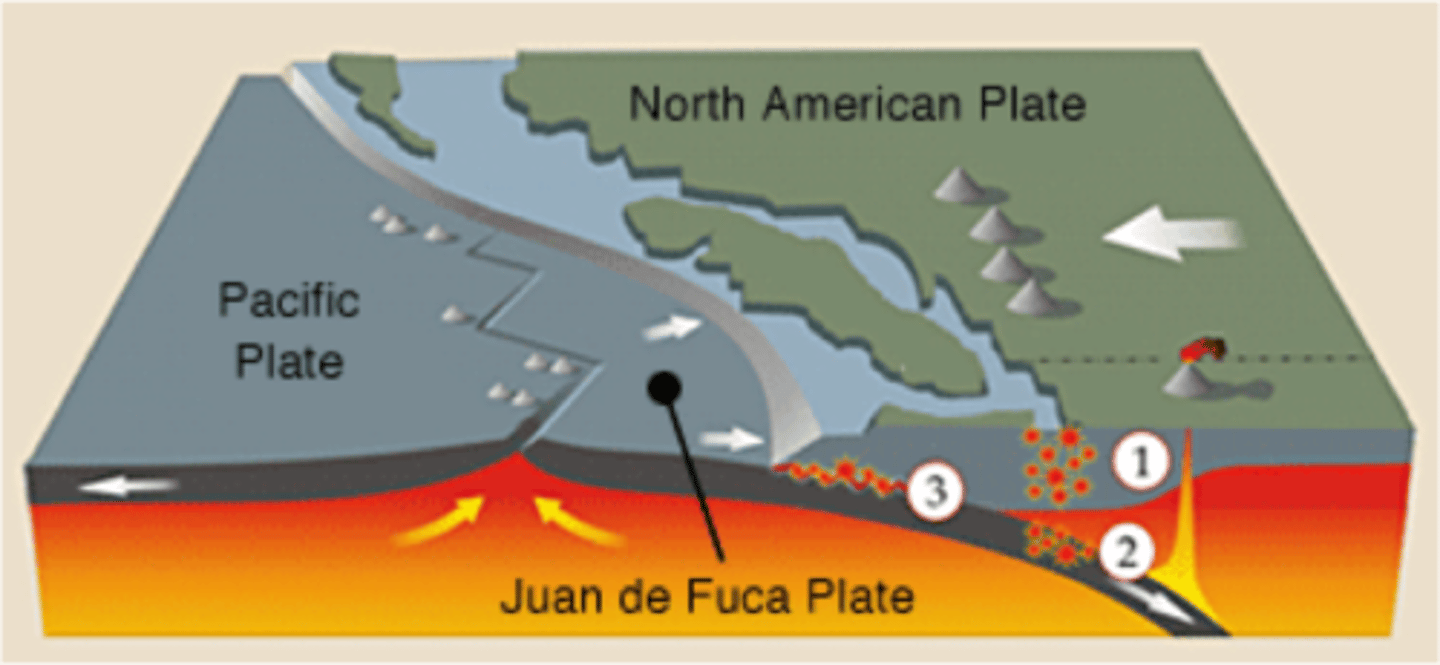
Cascadia Subduction Zone
A volcanic arc which has formed as a result of the subducting Juan DeFuca plate
Ice Age
any period of time during which glaciers covered a large part of the earth's surface
Glacial
a cold period within an ice age
Interglacial
warm period that occurs during an ice age
Glacier
A large mass of moving ice and snow on land

Glacial Till
sediment transported by flowing ice and deposited beneath a glacier; lots of poorly sorted sediments

Moraines (Terminal and Lateral)
A mound, ridge, or mass of material that was left on the ground by a receding glacier. Terminal marks the maximum limit of a glacier's advance. Lateral forms along the glacier sides.
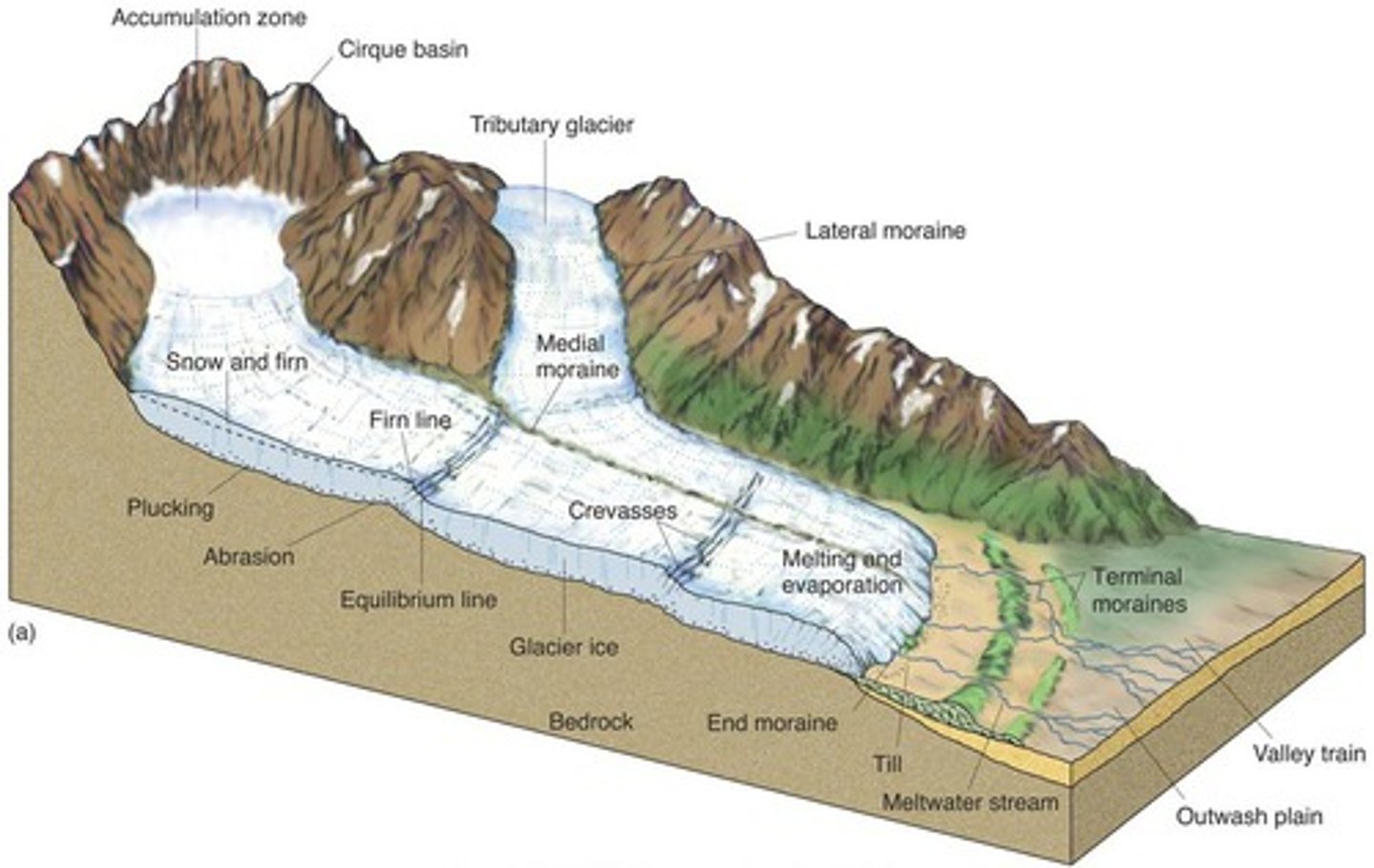
Glacial Scours/Striations
indicate past ice flow direction, scratches in the rock left behind from rocks stuck in the glacier scraping against the ground.
Glacial Erratic
An ice-transported boulder that was not derived from the bedrock near its present site.
Chemical Evidence of Glaciation
Ice sheet growth during an Ice Age locks up the 16O, making the oceans enriched in the other stable oxygen, 18O.
Milankovitch Cycles
Changes in the shape earth's orbit and tilt that cause glacial periods and interglacial periods.
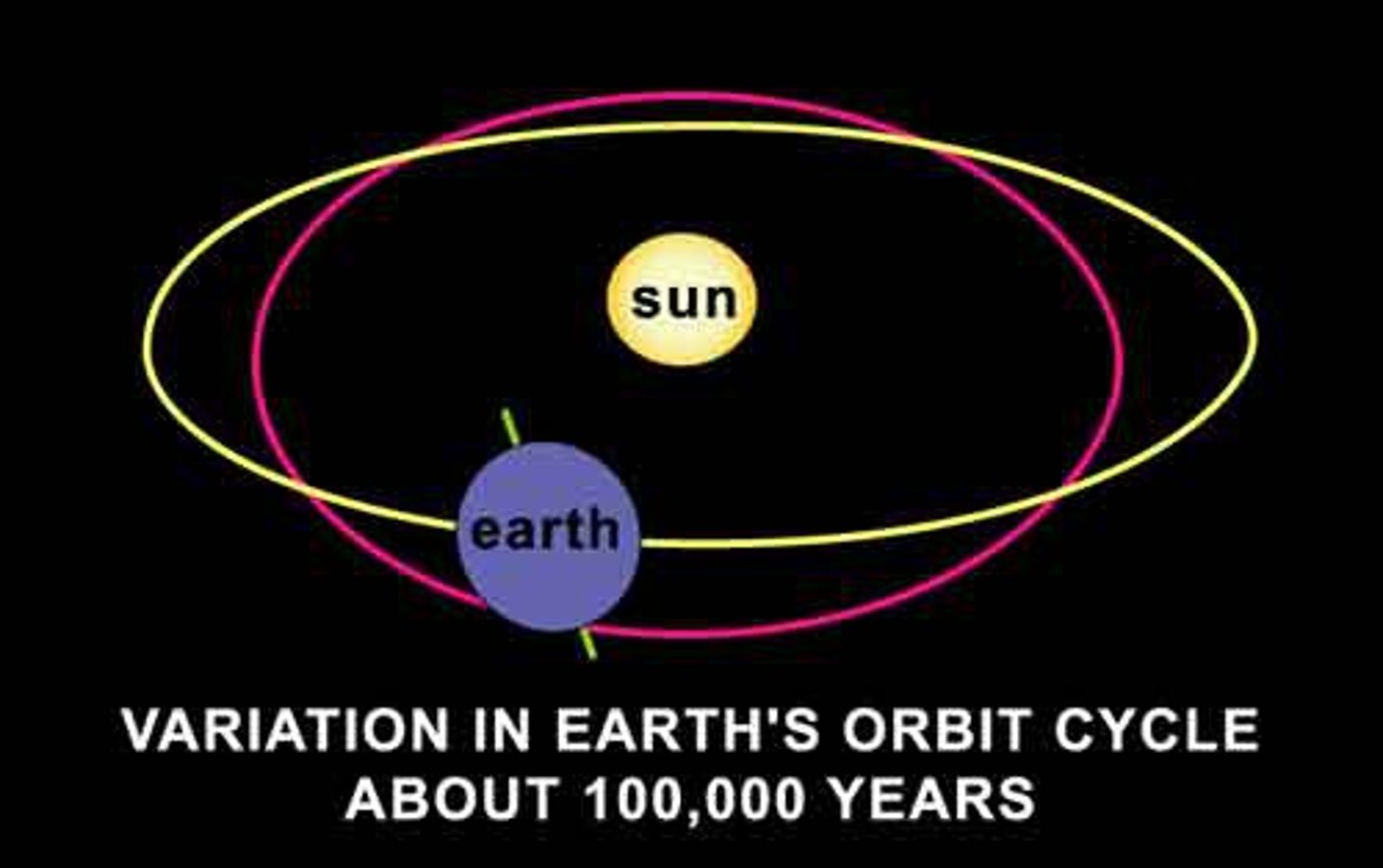
Earth Eccentricity
The elongation of Earth's orbit recieves more some the more elongated the orbit is. 100,000 year cycles
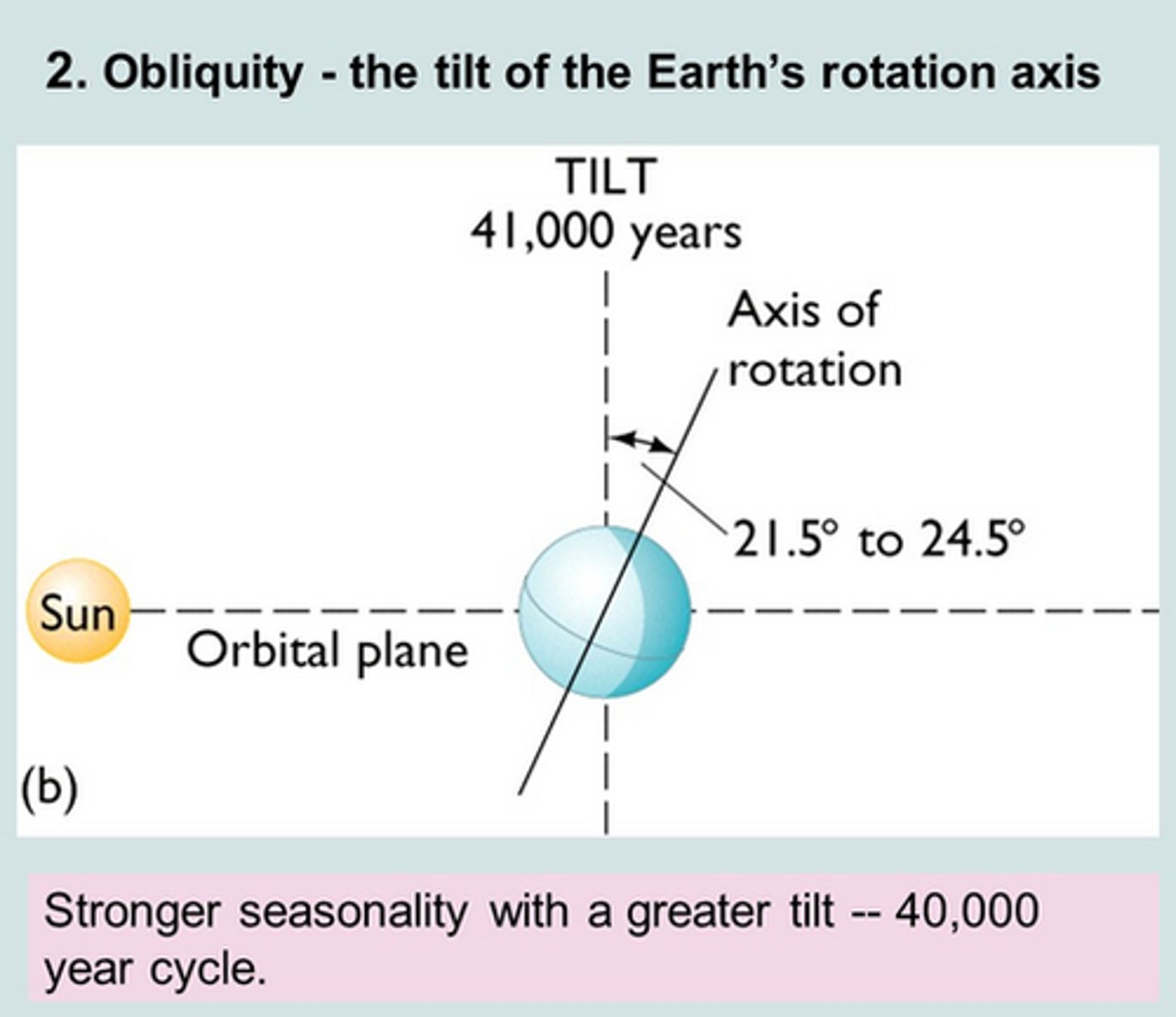
Earth Obliquity
Variation in the Earth's tilt, the greater tilt, the more solar energy the poles receive. 41,000-year cycles.
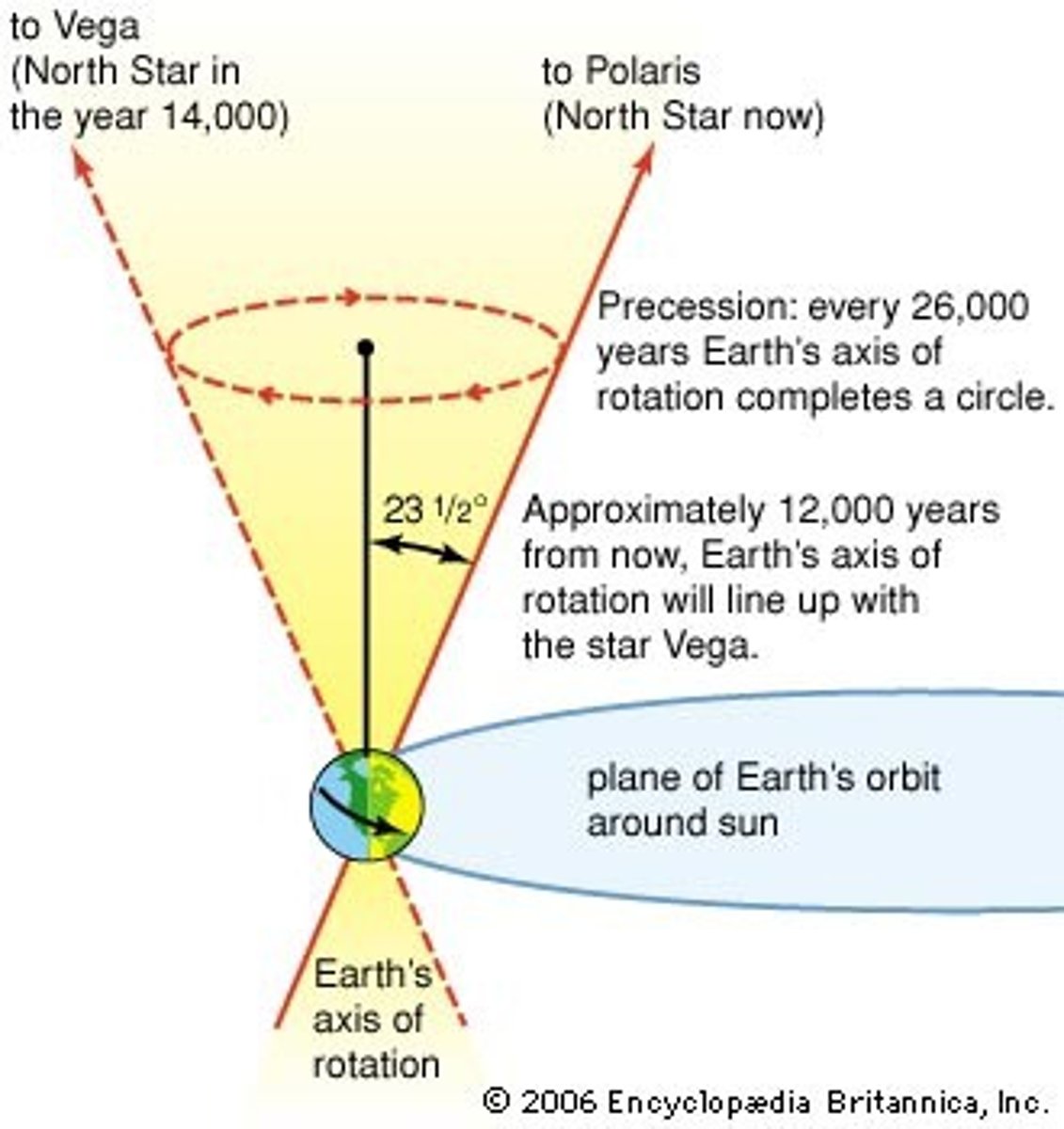
Earths Precession
The slight wobble of earth on its axis. 26,000 year cycles
Physical Evidence for Sea Level Change
Marine Terraces and Shoreline Platforms, Beach ridges, Cave deposits, corals
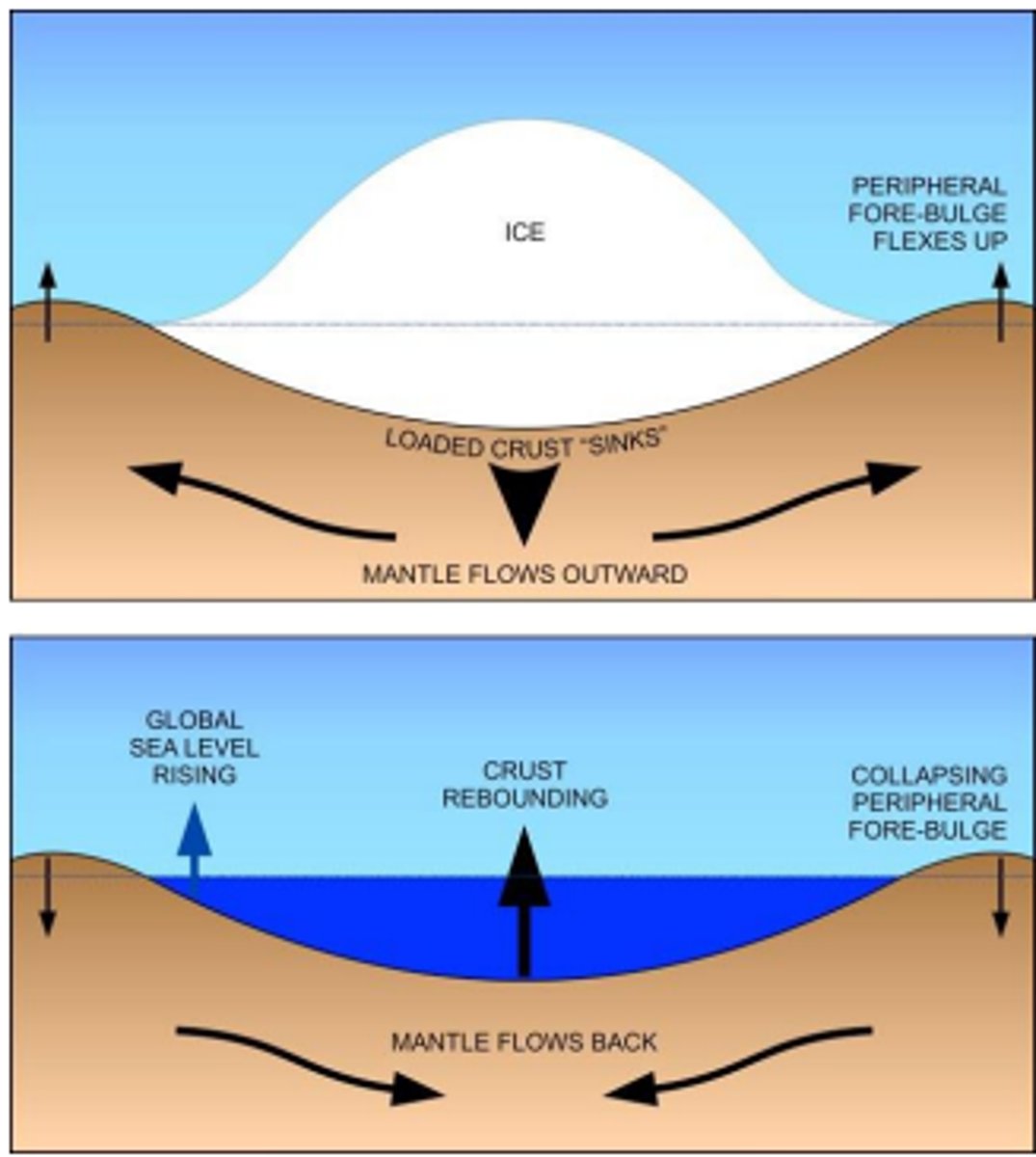
Glacial Isostatic Adjustment
Mantle flows outward when the crust sinks downward due to being crushed by a glacier, this causes peripheral bulges outside of the glacier. When the glacier recedes, the crust rebounds upward and the mantle flows back, making the sea level appear to be rising.
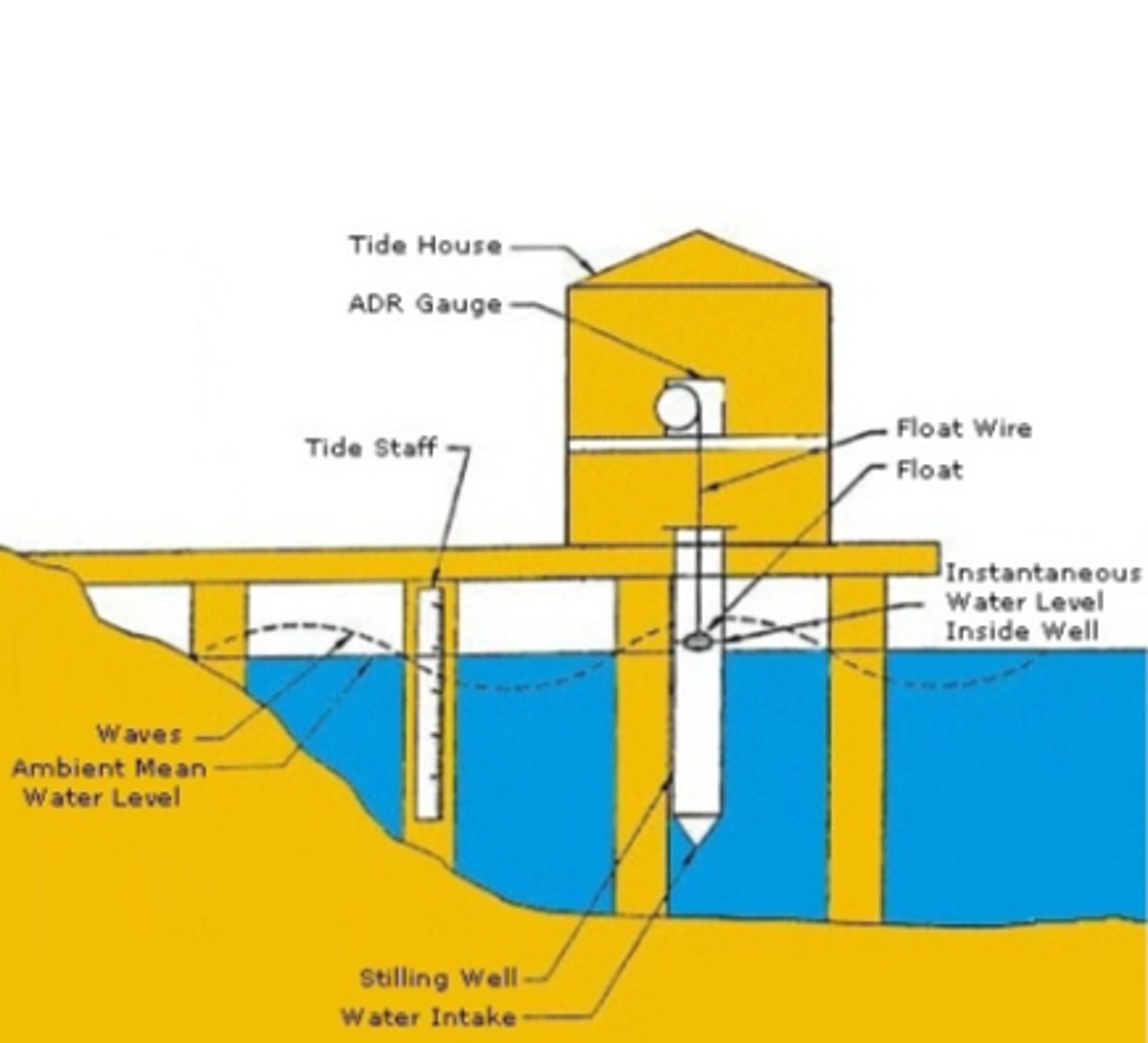
Tide gauges
mounted along the shoreline, they are used to measure the local sea level, stuck to the ocean floor, they measure from the ground to the sea surface
Causes of modern sea level change
ice melting, vertical land movement, ocean circulation, terrestrial water storage,m ocean-atmosphere interaction.