bio120 - final exam - SS
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
evade stress; moving
plants can’t _____ by ______
daughters; net reproductive rate
average (expected) # of _____ a female has in her lifetime = ______
own food, photosynthesis
plants can make their _____ through ____
flowers, angiosperms
_____are defining feature of _____
angiosperms
largest and most diverse group of land plants
anthers
Male reproductive structures produce pollen in structures known as ____ ; purple


stigma
Female reproductive parts receive pollen that lands on what's known as _____


autotrophic
plants are ______; make their own food through photosynthesis
light, CO2, water and soil nutrients (NPK)
all plants need the same few things to grow: _______ NPK = NITROGEN, PHOSPHOROUS & POTASSIUM
NPP
carbon gained via photosynthesis - carbon lost via respiration = net primary productivity
high NPP
north america has _____ in the summer vs winter bc thats when plants are growing the most
stomata, stomata
plants take in co2 through their ____, they lose water and oxygen out of _____
benefit : large lead size
good for harvesting light and co2, has lots of stomata
overheating
cost of large leaf size : as external temp of env incr, plant does its best it can to avoid heating up too much, large SA = can gait heat via solar radiation - bad for hot places
water loss by transpiration
cost of large leaf size: also have lot of stomata where they can lose water, bad for plants that live in dry places
population
collection of individuals of the same species living in an area
differential equation model ; instant ; reproduce continuously
time steps are going to be infinitesimally small, size of population can change in an ____, population is going to tend to be smooth over time, best for animals that _______throughout the year
difference equations
bad ; over the long term
simple exponential growth is a ____ model of reality ________
λ > 1.0 ; λ<1.0
no species has ever sustained ____ for a long period of time and no extant species has maintained ___ for long
density dependent regulation : 1st factor that can regulate growth of real populations
populations start growing more slowly when population size gets large, growth rate of the population is dependent on population size
density independent regulation : 2nd factor that can regulate growth of real populations
don’t depend on how big the population is (ex. when severe weather produces a hurricane & kills off a lot of individuals in the population)
fastest; small
in logistic growth model, population grows _____ when population size is ____
allele effects: low population density (size)
refers to negative effects of ____ on population growth rates
depend on age
another feature not captured by exponential & logistic models of population growth is how birth & death rates _______
fecundity & survivorship
_____ depend on age of the individual
life history strategies ; life events
species have different ________; which are the sequence of an organism’s ______ & what age or stage those events occur at
life history
typically _____for many plants and animals
small size
typically life history for many plants and animals start life at ______
grow; resource accumulation
typically life history for many plants and animals start life at small size, ____ for a period without reproducing
this period is for ___________
sexually mature ; reproducing
when they have enough resources, organisms become _____& start spending resources they acquire on ____
life table
Variation in fecundity & survivorship across age classes is summarized in a________
age class intervals
In models of population that incorporate age structure, time is now measured in ________
Arbitrary units of time; 20 age classes
_______ that we choose in order to have them give a reasonable number of age classes for the organism in question.
For microbes; minutes to hours
Most insects : weeks
Mammals and birds : years
Humans, typically 5 year intervals - about ______
metapopulation
a ______ is a set of local populations linked by dispersal
metacommunity
a _____is. a set of local communities linked by the disperdal of one or more of their constituent species
probability ; being alive
Lx is for survivorship ;_______of _____ at age x
semelparity ; reproductive output is increased; satiate
______ is favoured when __________ by accumulating resources for longer for ex. if reproductive output depends strongly on size (in plants if : massive flower or fruit displays attract more benefical animals or massive seed crops ____ seed predator populations allowing more seeds to go uneaten)
reproductive value , Vx ; future
expected number of _____ daughters left to an individual of age x
outcome (+ or - )
interactions between species are often classified by their ______
intra-specific competition ; conspecifics
______: competition among members of the same species (among ____) for resources
inter-specific competition ; heterospecifics
______: competition among members of the different species (among ____) for resources
scramble/exploitative competition ; depletion
Individuals of the same or different species compete via the ___ of a shared resource
As one individual consumes a resource, it leaves less of that resource available for other individuals to consume ; therefore they compete (squirrel & birds and bird feeders example )
contest/interference competition ; direct interactions
happens a result of ________ between individuals, when individuals fight over territory (ants - very territorial, invasive ones are superior competitors that drive down populations of native ants)
both species to inhibit their own growth
coexistence requires ______more than they inhibit each other’s (i.e ; intraspecific competition has to be stronger than interspecific competition)
stability ;return
____: ability of a system to _____ to equilibrium following a perturbation or disturbance (wildfire or hurricane)
coexistence; nonzero
_____: occurs when 2 or more species have ____population sizes at equilibrium
predation; consumes
______: interactions in which one organism ____all or part of another
inducible ; threats
some defences are ____, turned on in response to _____
two or more host species ; complex life cycle
many parasites require_________to complete their life cycle = __________
vectors ; transport
_______ are hosts that _____ parasites to their next host
zoonotic; reservoirs
for human ____ diseases (diseases transferred between animals and humans) we often refer to other host species as
symbiosis
living together
mutualism
beneficial interaction for both species
mutualism ≠ symbiosis
true
disperse
individuals can move from one population to another; they can _______
patch
we call each spatially distinct population a ______
sinks ; migrants; source
are populations in small habitat patches that would go extinct except ______ from _____ populations rescue these populations
locally unstable
a group of weakly coupled, ________systems can be
semelparity ; last
postpone reproduction until very last year of life
iteroparity ; multiple
reproduce in multiple years of their lives
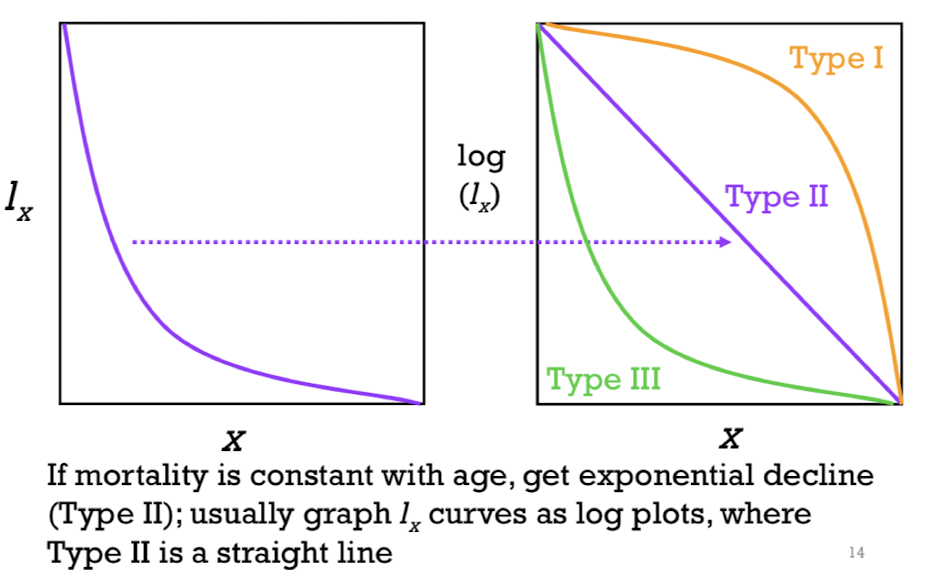
type 1 survivorship curve ; early age classes ; mortality
______: high survivorship through ________but then survivorship declines rapidly and ______ picks up fast late in life
Expected for human population
Individuals survive rlly well until middle or late years of life
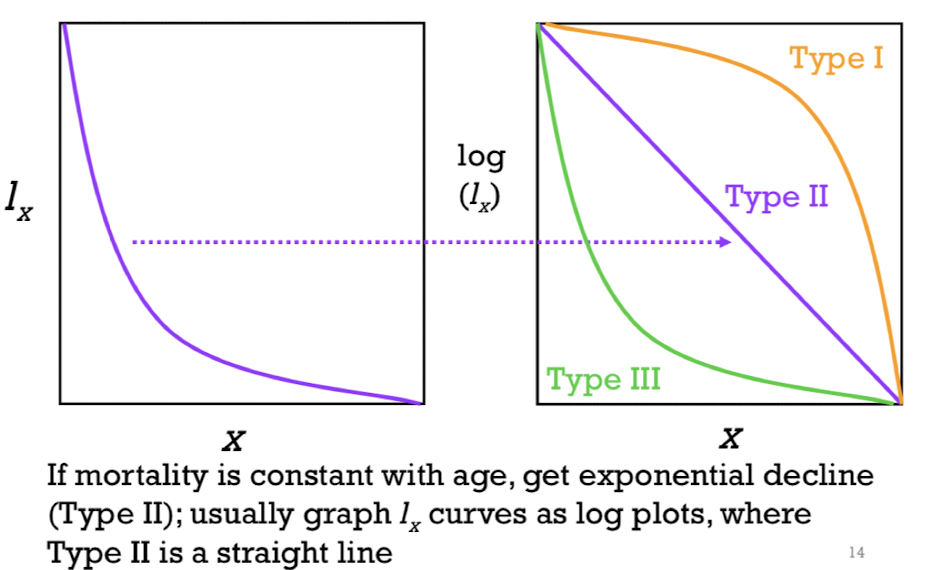
type 2 survivorship curve
Constant mortality with age is called ________; occurs in some animals where there is constant mortality risk out in the world
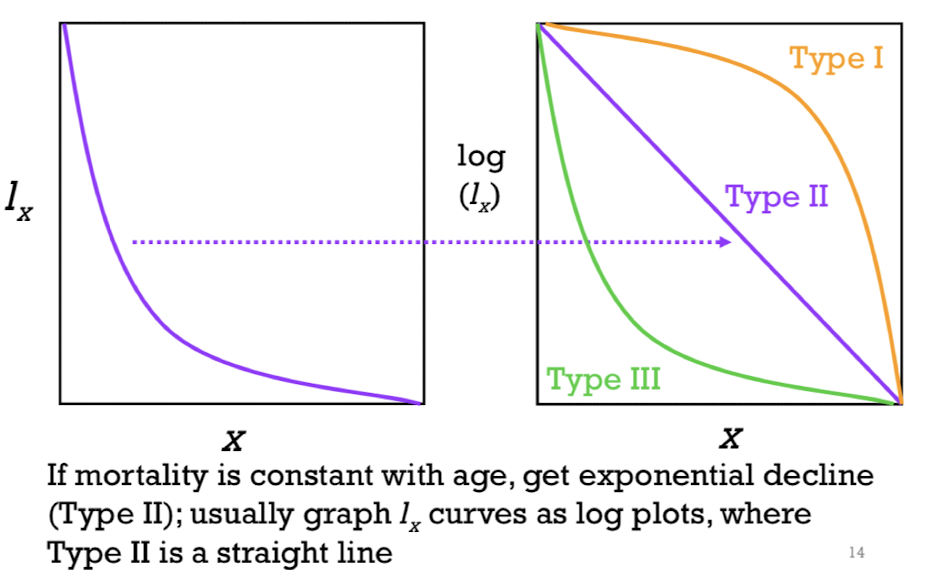
Type 3 survivorship curve; high mortality
________: means_______early in life BIT if u make it into adulthood= good chance of living for a long time - common in plants & invertebrates that makes large number of offspring but vast majority of offspring won't survive into adulthood (trees : unlikely that a seed is going to become a big tree ,but if u make it to being a tree - may live long)