Module 3, Course 1 Carnegie Math MSMB Glossary
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 3, Course 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

30 Terms
Addition Property of Equality
States that if two values a and b are equal, adding the same value c to each will keep the sums equal. Ex: If a = b, a+c = b+c
algebraic expression
A mathematical phrase that has at least one variable, and can contain numbers and operation symbols. (no equal sign)
coefficient
A number multiplied by a variable in an algebraic expression. Ex: in the expression 3x, 3 is the coefficient
continuous graph
A graph with no breaks in it.
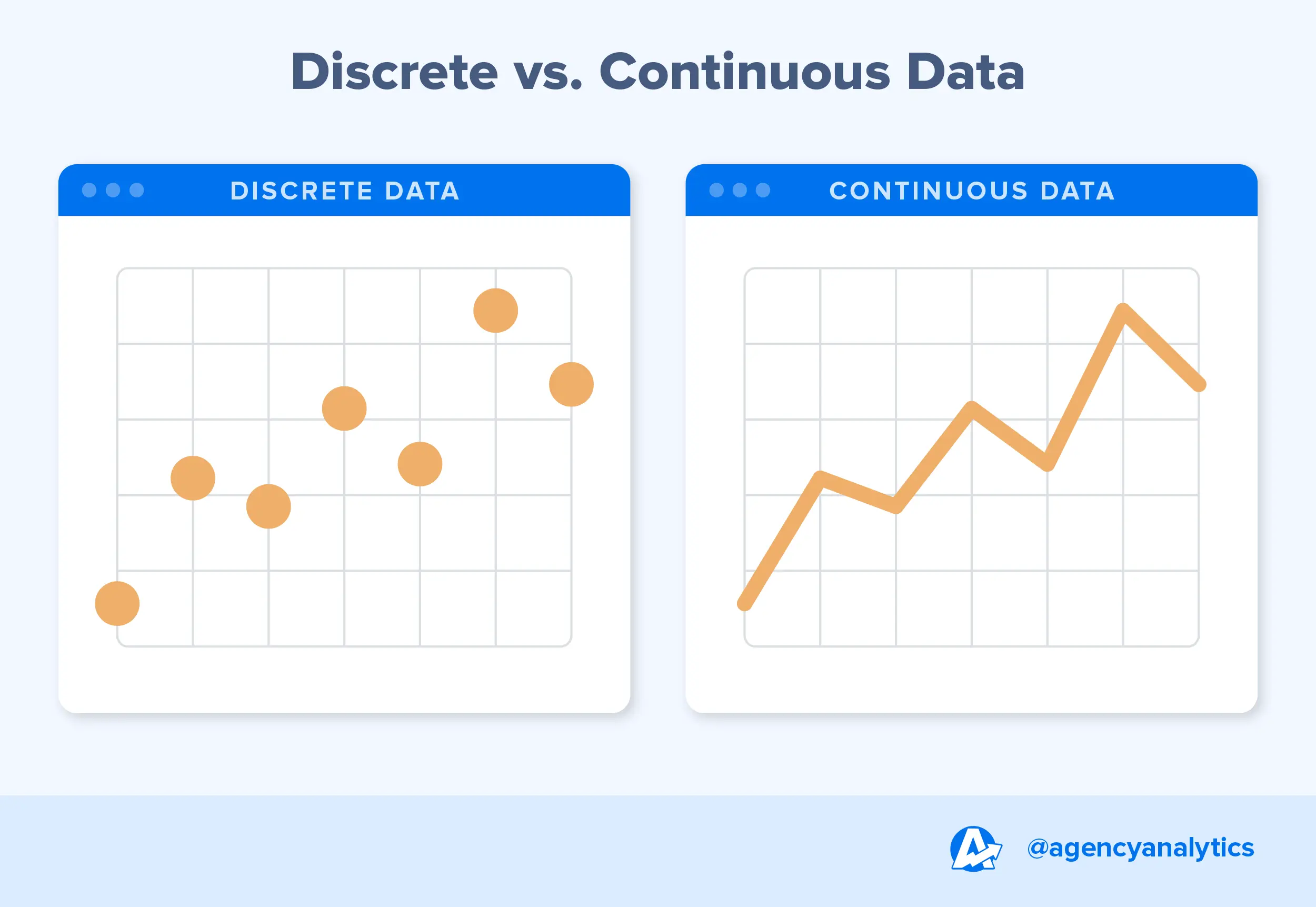
dependent quantity
The quantity that depends on another in a problem situation.
dependent variable
The variable that represents the dependent quantity.
discrete graph
A graph of isolated points.
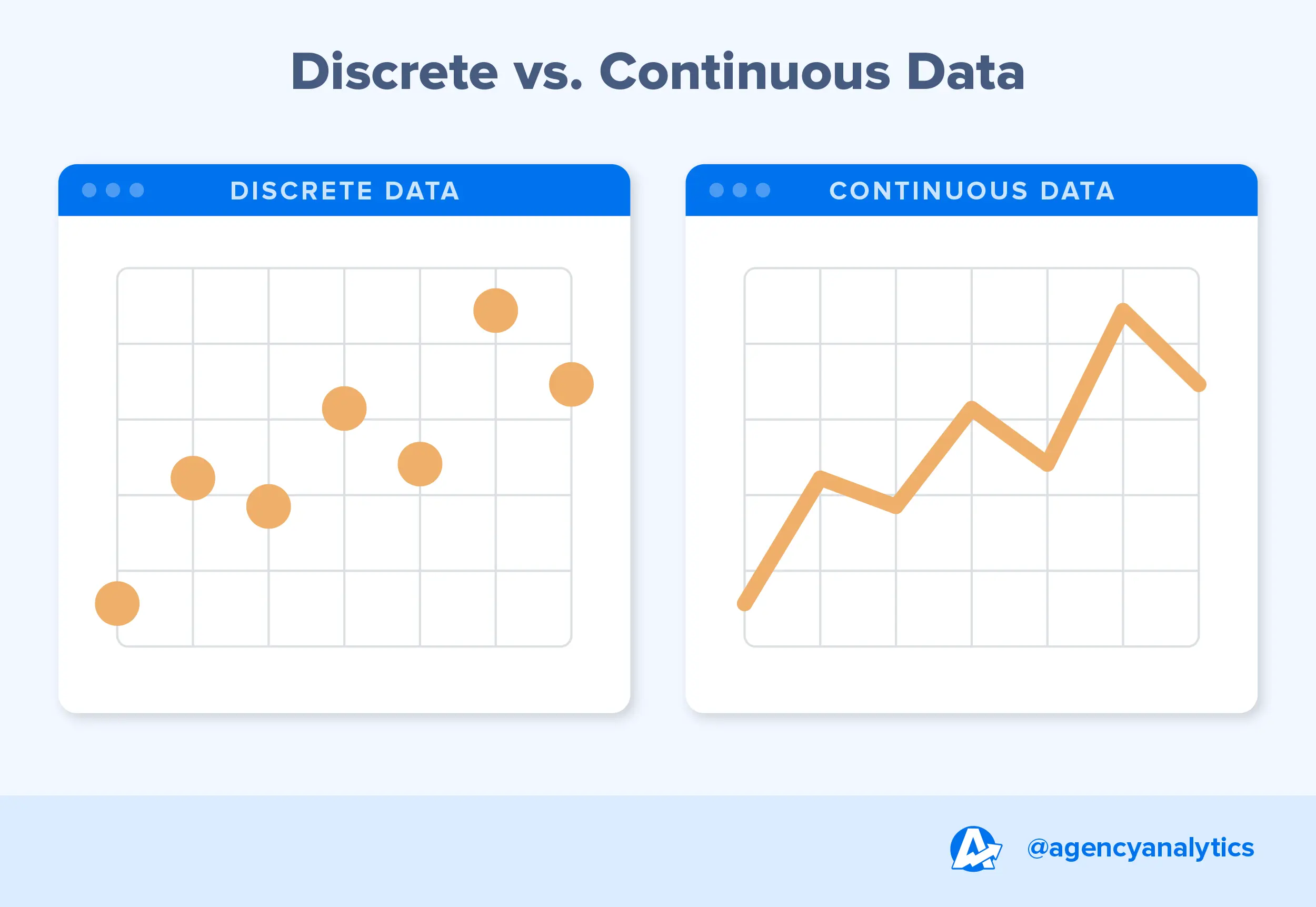
Division Property of Equality
States that when you divide equal values by the same value (c ≠ 0), the quotients are equal.
evaluate an algebraic expression
To determine the value of the expression for given values of each variable.
evaluate a numeric expression
To rewrite the expression as a single numeric value.
graph of an inequality
A set of points on a number line that makes the inequality true.
Identity Property of Addition
The sum of any number and 0 is the number itself.
Identity Property of Multiplication
The product of any number and 1 is the number itself.
independent quantity
The quantity that the dependent quantity depends on.
independent variable
The variable representing the independent quantity.
inverse operations
Operations that reverse the effects of each other.
like terms
Two or more terms that have the same variable raised to the same power.
literal equation
An equation in which the variables represent specific measures.
Multiplication Property of Equality
States that if two values are equal, multiplying each by the same value keeps them equal.
one-step equation
An equation that can be solved using only one operation.
Order of Operations
A set of rules that ensures the same result when evaluating an expression.
perfect cube
The product of three equal whole numbers.
perfect square
The product of two equal whole numbers.
Reflexive Property of Equality
A number is always equal to itself.
solution
Any value for a variable that makes an equation true.
solution set of an inequality
The set of all points that make an inequality true.
Subtraction Property of Equality
States that when subtracting the same value from equal values, the differences are equal.
Symmetric Property of Equality
If a = b, then b = a.
term
A number, variable, or product of numbers and variables in an algebraic expression.
Zero Property of Multiplication
The product of any number and 0 is 0.