Unit 1: The Nervouse System & Neurotransmission
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Neurons
A nerve cell, the basic building block of the nervous system
Glial Cells
The other nerve aids in the maintenance of homeostasis, and forms myelin
Action Potential
Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by our senses or by neighboring neurons. A neuron sends a message by firing an impulse, called the action potential a brief electrical charge that travels down its axon.
Threshold
-55mv
Resting State
-70mv( negative potassium inside / positive sodium outside
Depolarization
This is the phase of the action potential where the inside of the neuron becomes less negative (more positive) due to the influx of positive ions. The is positive sodium inside.
Repolarization
It is the crucial phase of an action potential where it returns to its negative resting state after firing. This means that potassium is released outside the neuron.
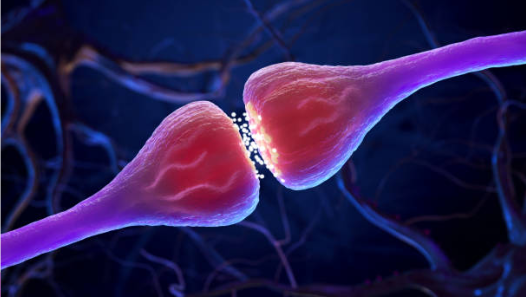
Synapse
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or synaptic cleft.
Neurotransmitters
When an action potential reaches the knob like terminals at an axon’s end, it triggers of chemical messenger
Neurogenesis
The process by which new neurons are formed in the brain ( this happens in the hippocampus)
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord( Interpret incoming sensory info and issue instructions based on past experiences and current conditions
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic and Autonomic( serves as communication lines)
Somatic
Voluntary movement of skeletal muscle
Autonomic
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
fight or flight
Parasympathetic
rest and digest
Sensory Neurons
Run from sensory receptors(eyes,ears,nose,tongue,skin) TO the spinal cord + brain
Motor Neurons
Run from the brain & spinal cord to the muscles and glands of the body
They affect ( bring about) a motor response
Carries impulses to effector organs, the muscles, and glands
The cell body is always located in the CNS
Interneurons
Go between for afferent and efferent neurons
Connect the sensory and motor in the neural pathways
Cell bodies are always located in CNS
Adrenaline
Is the release in response to stress or danger. Increases heart rate and blood flow, leading to physical boost and heightened awareness.
Noradrenaline
This is released throughout the day to help you stay alert affects attention and responding actions in the brain. Contracts blood vessels, increasing blood flow.
Leptin
A hormone that allows you to feel full
Ghrelin
Hormone that allows you to feel hungry
Melatonin
A hormone in your body that plays a role in sleep
Oxytocin
As oxytocin is associated with trust, sexual arousal and relationship building
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Encourage an action potential to occur
ex: glutamate, epinephrine and norepinephrine, acetylcholine, dopamine
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Discourage an action potential from occurring
ex: GABA, serotonin
Dopamine
Is crucial for the reward system, motivation, pleasure, and motor control.
Serotonin
This regulates mood, happiness, sleep, appetite and learning.
GABA
Calming neurotransmitter, this calms firing nerves in the central nervous system. High Levels improve focus, low levels cause anxiety. Also contributes to motor control and vision.
Acetylcholine
Learning neurotramitter involves thought, learning and memory. Activates muscle action in the body. Also deals with attention and awakening
Glutamate
Memory neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory, regulates the development and creation of nerve contacts
Endorphins
Euphoria neurotransmitter acts like a potent painkiller and induce feelings of pleasure, well-being
Acetylcholine Malfunctions
With Alzheimer’s disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate.
Dopamine Malfunctions
Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease.
Serotonin Malfunctions
Undersupply linked to depression. Some antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels.
Norepinephrine Malfunctions
Undersupply can depress mood.
GABA Malfunction
Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors and insomnia
Glutamate Malfunction
Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
Substance P
Though to have a role in the regulation of pain, asthma, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease and in the CNS, emesis, migraine, schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety.
Agonist
Bind to a neurotransmitter receptor to produce a response
Antagonist
bind receptor to prevent a response
Psychoactive drugs
SSRIs( selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors). These are drugs that prevent the reuptake of serotonin, pushing more into the system
ex: Zoloft, Lexapro, Prozac
Stimulants
Increased neural activity
ex: caffeine, cocaine
Depressants
decreased neural activity
ex: alcohol, opiates
Hallucinogens
altered state of consciousness perception
ex: LSD, Marijuana