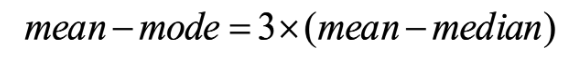CPSC 4300 Final
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
Data mining
extraction of interesting (non-trivial, implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful) patterns or knowledge from a huge amount of data
Alternative names for data mining
knowledge discovery in databases (KKD), knowledge extraction, data analysis, etc.
Data science
the analysis of data using quantitative and qualitative techniques to be able to explore trends and patterns in data
Data science turns raw data into __________ ___________ that can be used for _______ ________
meaningful information, decision making
What are the steps of the data science process?
Ask an interesting question
Get the data
Explore the data
Model the data
Communicate/visualize the results
What types of things are asked for a question to be considered interesting?
What is the scientific goal?
What would you do if you had all of the data?
What do you want to predict/estimate?
What questions are asked when getting the data?
How was the data sampled?
Which data is relevant?
Are there privacy issues?
What questions are asked when exploring the data?
How can the data be plotted?
Are there anomalies?
Are there patterns?
What questions are asked when modeling the data?
How can a model be built?
How can a model be fitted?
How can a model be validated?
What questions are asked when communicating/visualizing the results?
What was learned?
Do the results make sense?
Will storytelling be effective?
Data
observations, facts, or measurements collected about the world
Where does data come from?
internal sources (already collected organizational data), external sources (data available for free or a fee), and external sources requiring collection efforts (data from external sources that require special processing)
What are the ways to gather online data?
API (application programming interface), RSS (rich site summary), or web scraping
What is an API?
a prebuilt set of functions developed by a company to access their services, often not free
What is a RSS?
a summary of frequently updated online content in standard format for free
What is web scraping?
using software, scripts, or by hand extracting data from what is displayed on a page or what is contained in the HTML files
What should be considered when web scraping?
Is it violating terms of service?
Are there privacy concerns?
Is there an API or fee that is being bypassed?
Is the company willing to share the data?
What is the most popular data type?
tabular (rows and columns of data)
What are features?
data fields representing characteristics or features of data (each column is a feature)
Nominal feature
categories, states, or names of things (ex: hair color)
Binary feature
a nominal attribute with only 2 states (0 and 1)
Symmetric binary attribute
both outcomes are equally important (ex: left vs. right handed)
Asymmetric binary attribute
outcomes are not equally important (ex: positive vs. negative medical test)
Ordinal feature
values have a meaningful order but magnitude in between values is unknown (ex: grades)
Quantity interval attribute
measured on a scale of equal sized units where values have order (ex: calendar dates); no true 0 point
Quantity ratio attribute
has an inherent 0 point; values are in order of a magnitude larger than the previous unit (ex: temperature in K)
Is student ID nominal, ordinal, or interval?
nominal
Is eye color nominal, ordinal, or interval?
nominal
Is color in the color spectrum nominal, ordinal, or interval?
interval
Discrete attribute
has a finite or countably infinite set of values (ex: zip codes)
Continuous attribute
has real numbers as attribute values (ex: height)
Binary attributes are a special case of ______ attributes
discrete
Continuous attributes are usually represented as ________ ______ variables
floating point
What does a relational records table look like?
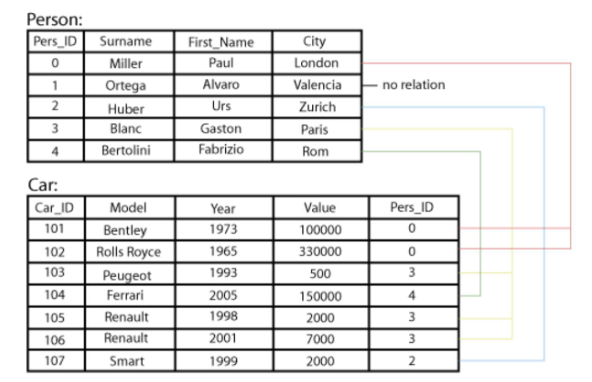
What does transaction data look like?

What is text data?
texts in various domains and languages
What is network/graph data?
information networks (ex: transportation and social networks)
What are some examples of sequential data?
video, genetic sequences, time-series data
What are some examples of spatial/image data?
maps, images
What are the 4 major tasks in data preprocessing?
cleaning, integration, reduction, transformation, and discretization
What does data cleaning do?
handle missing data, smooth noisy data, identify or remove outliers, and resolve inconsistencies
What does data integration do?
integrate multiple databases, data cubes, or files
What does data reduction do?
reduce dimensionality and numerosity, and compress data
What do data transformation and discretization do?
normalize data and generate concept hierarchy
What are the most common issues with data?
messy format, missing values, wrong values, and unusable data
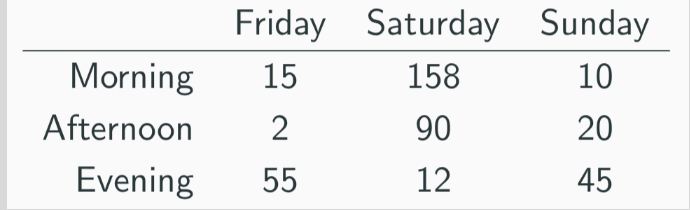
What is the best way to fix the messy data in this table? (number of produce deliveries over a weekend)
make each column represent a variable rather than a single value (ID, time, day, number), and fill in the data from there
Why might data be incomplete?
equipment malfunctions, inconsistent then deleted, misunderstood during additions, considered not important, not saved
What are the methods to handle missing data?
ignoring the tuple (done when class label is missing), filling in the missing value manually (tedious though), filling in automatically with a global constant, the mean, mean for all samples in the same class, or most probable value
When is ignoring the tuple not effective?
when the % of missing values per attribute varies considerably
When can conditional imputation be used?
if certain variables correlate with others
What is the best method for imputing data?
using predictive modeling
What is hot deck imputation?
randomly selecting a value from a record that matches with other variables
What is advanced text imputation?
using text mining/machine learning models that can predict the diagnosis based on similar records or related variables
What is noise?
random error or variance in a measured variable
Why might there be incorrect attribute values/noisy data?
faulty data collection instruments, data entry or transmission problems, technology limitations, or inconsistency in naming convention
How can noisy data be handled?
binning, regression, clustering, or semi-supervised
What is binning?
sorting data into equal frequency bins, then smoothing by each bin’s mean, median, or boundaries
What is regression?
smoothing by fitting the data into regression functions
What is clustering?
detecting and removing outliers
What is semi-supervised?
combined computer and human inspection of noisy data
What is data integration?
combining data from multiple sources
What is schema integration?
integrating metadata from different sources
What is entity identification?
identifying real world entities from multiple sources that often needs machine learning (ex: same person, different names/nicknames)
What are the possible reasons for data value conflicts?
different representations or scales
Redundant data often occurs when ________ multiple databases
integrating
What is object identification?
identifying if the same object has different names in different databases
What is derivable data?
attributes than can be derived from an attribute in another table
Redundant attributes may be detected by _________ analysis and ________ analysis
correlation, covariance
What does integrating data carefully from multiple sources help do?
reduce/avoid redundancies and improve mining speed/quality
What does the chi-square (x²) test do?
discovers the correlation relationship between 2 nominal attributes (A and B)
In the chi-square test, what does the null hypothesis say?
the 2 variables are independent
The cells that contribute the most to the chi-square value are those whose actual count is ________ from the expected count
different
The larger the chi-square value, the more likely that variables are ________
related
Correlation does not imply _______
causality
What is the correlation coefficient value range?
[-1, 1]
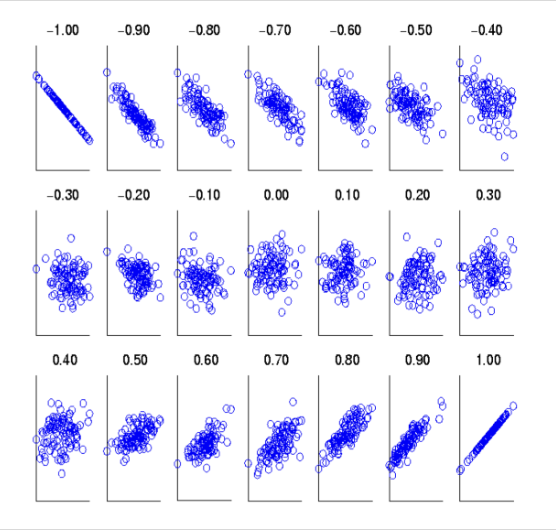
What does this graph show?
scatter plots whose correlation coefficients change from -1 to 1
After data reduction, the data set is much ______ in volume, yet produces almost the _____ analytical results
smaller, same
Why should data reduction occur?
a database may store massive amounts of data, and complex analysis may take a very long time on the complete data set
What are the methods for data reduction?
regression/log-linear models, histograms/clustering/sampling, data cube aggregation, and data compression
Simple random sampling
equal probability of selecting any particular item
Sampling without replacement
once an object is selected, it is removed from the population
Sampling with replacement
a selected object is not removed from the population
Stratified sampling
cluster the data set and draw samples from each cluster
What is data transformation?
a function that maps the entire set of values of a given attribute to a new set of replacement values (in other words each old value can be identified with one of the new values)
What are the methods for data transformation?
smoothing, attribute construction, aggregation, normalization, and discretization
What is the normalization formula?
(given number - min) / (max - min) * (new max - new min) + new min
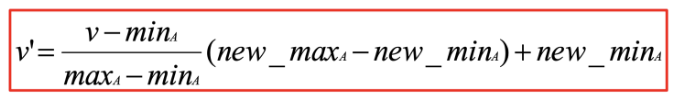
What is the z-score formula?
(number given - mean) / std dev
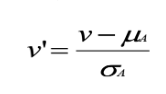
What are the 3 types of attributes in data discretization?
nominal (values from unordered set), ordinal (values from ordered set), and numeric (real numbers)
Discretization divides the range of a continuous attribute into _______
intervals
What are the data discretization methods?
binning, histogram analysis, clustering analysis, decision tree analysis, correlation (chi-square) analysis
What is equal width binning?
divides data into intervals of equal size; not helpful with skewed data
What is equal depth binning?
divides data into intervals with approximately the same number of samples; not helpful with categorical attributes

Is this equal width or equal depth binning?
equal width
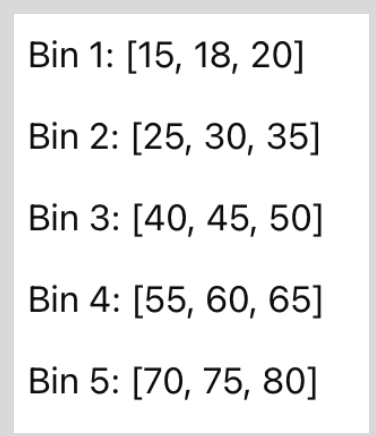
Is this equal width or equal depth binning?
equal depth
How does classification work?
class labels are given (if supervised), entropy determines split point, and it has a top-down recursive split
What is different about a trimmed mean?
extreme values are chopped
What is the median?
middle value if odd, average of 2 middle values if evens
The mean is sensitive to extreme _______
outliers
What is the mode?
value that occurs most frequently in data
What is the empirical formula in unimodal data?