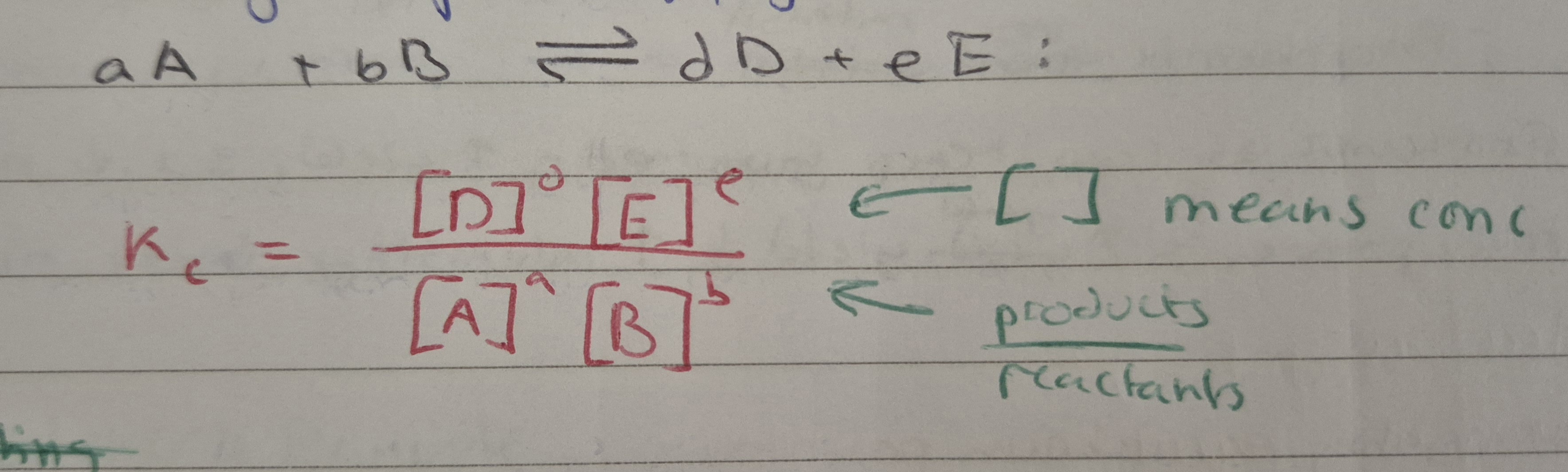M3S2: Physical Chemistry
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Standard condition
100kPa
298K
Standard enthalpy change of reaction
ΔrH
Enthalpy change when reaction occur in molar quantities shown in chemical equation, under standard conditions & standard state
Standard enthalpy change of formation
ΔfH
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of compound formed from its elements in their standard states
Standard enthalpy change of combustion
ΔcH
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of substance completely burn in oxygen under standard conditions & standard states
Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation
ΔneutH
Enthalpy change when solution of acid & alkali react = 1 mole water under standard conditions
Measuring enthalpy change equation
q = mcΔT
c = 4.18
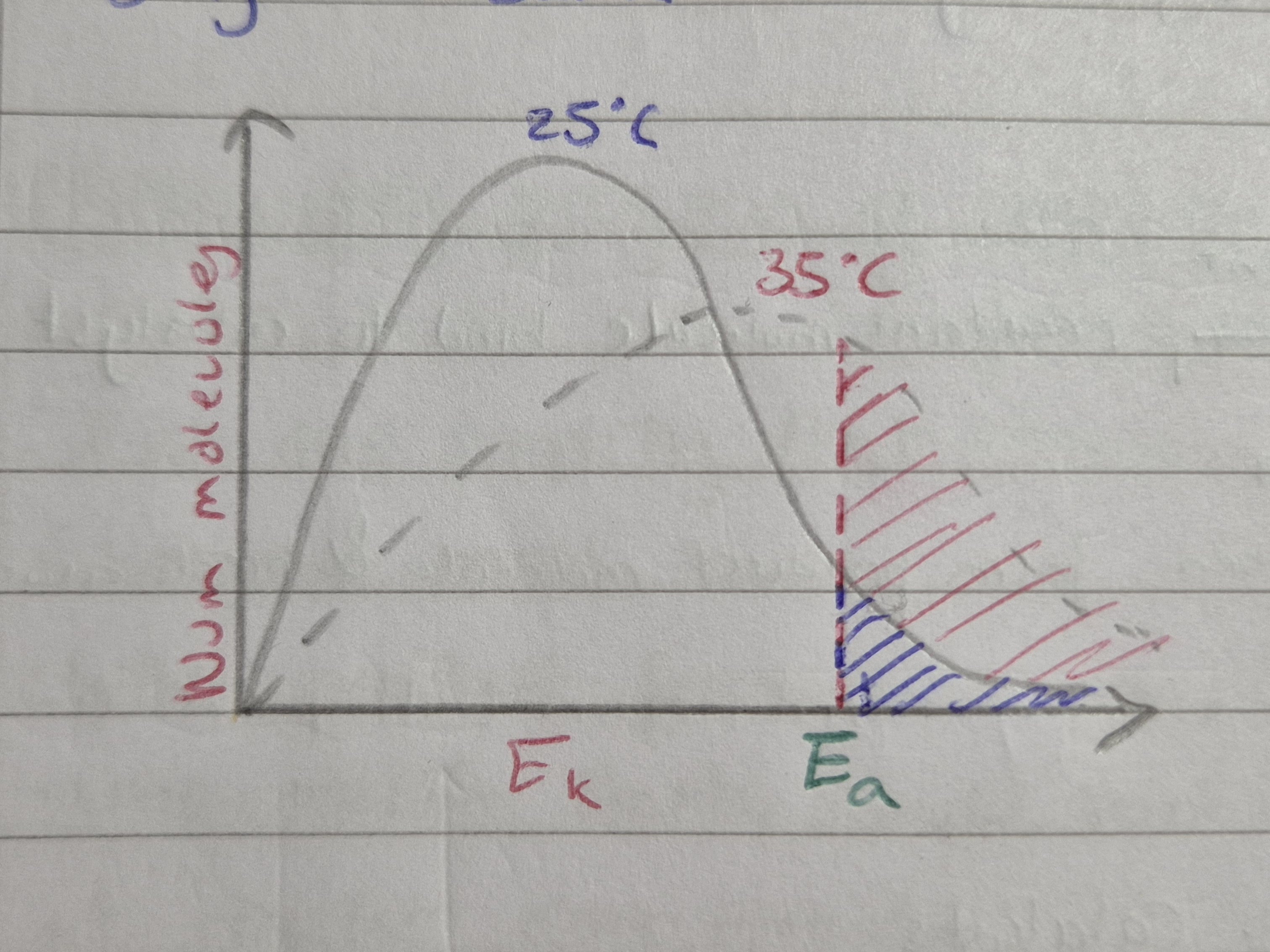
Effect of temp on reaction rate
Increase temp = molecules on average have more Ek therefore greater proportion of molecules will have at least activation energy required to react
For Boltzmann, same num molecules = area under graph same
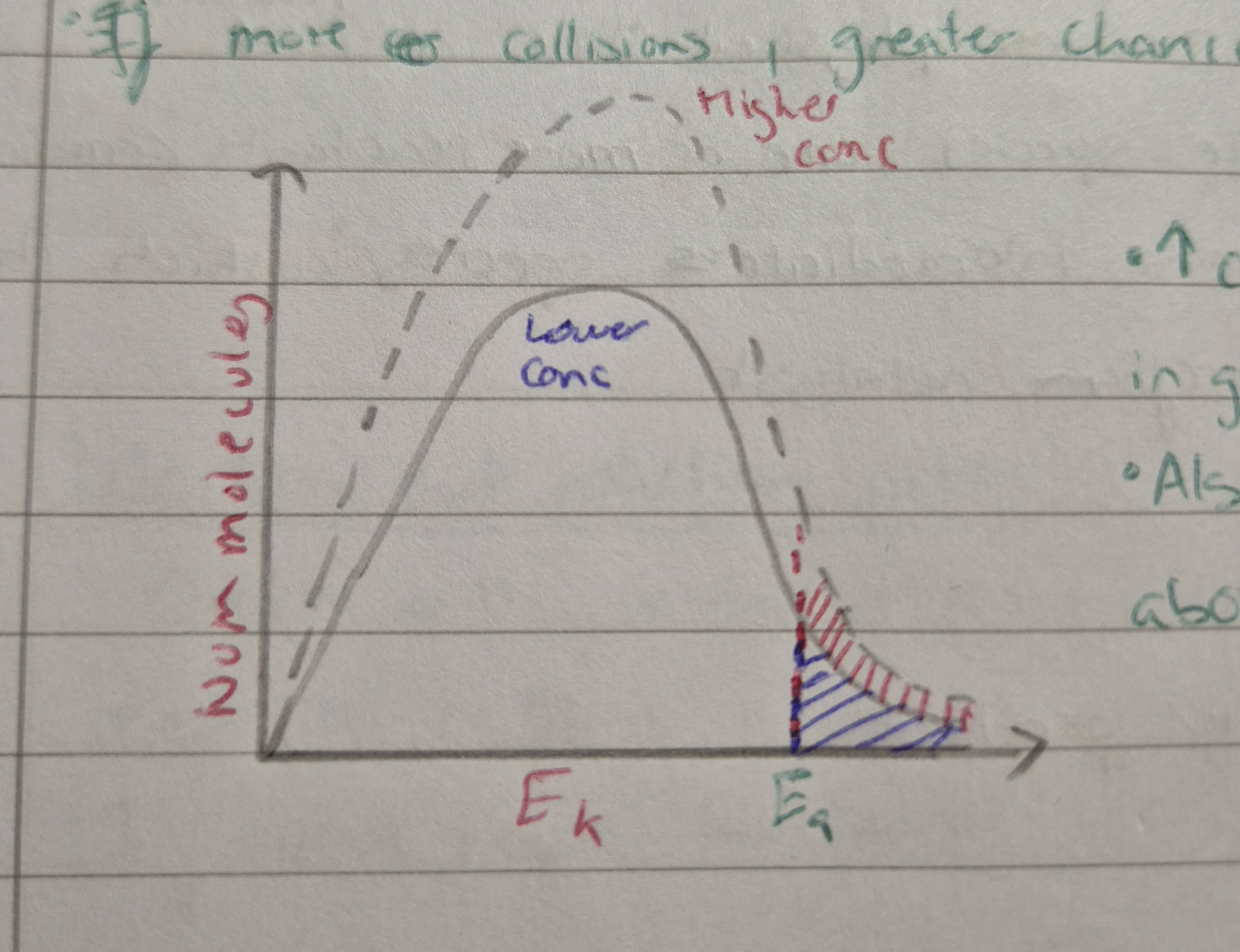
Effect of conc on reaction rate
If conc increase = increase num molecules
Also be more molecules with energies above activation energy
Catalyst
Increase rate by providing alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy
Chemically unchanged by end of reaction
Heterogenous catalyst
Catalyst different phase from reactants i.e. different physical state
Homogeneous catalyst
Catalyst in same physical state as reactants
Catalytic converters
2CO + 2NO —> 2CO2 + N2
Rate of reaction
(amount reactants used/products formed) / time
Dynamic equilibrium
Forward reaction = backward reaction
In closed system
Le Chatelier’s Principles
Increase conc of reactants = increase products
Increase pressure = shift side fewer gas moles
Increase temp = shift endothermic side
Alcohol production from alkene
60-70 atm
300 degrees Celsius
Phosphoric acid catalyst
High pressure = increase yield & rate
Exothermic so low temp favoured = increase yield but decrease rate
C2H4 (g) + H2O (g) ⇌ C2H5OH (g) ΔH = -46 KJmol-1
Kc
Kc changes with temp
If Kc increases = quantity products increases & quantities reactants decreases = equilibrium shifts right