2.1 Individuals, Population, Communities, and Ecosystems
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Biosphere
an ecological system composed of individuals, populations, communities, and ecosystems, it represents the parts of the earth where life exists
Individual organism
a member of a species
Population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, which are capable of interbreeding
Community
a collection of interacting populations within the ecoysytem
Habitat
the location in which a community, species, population, or organism lives
Ecosystem
open systems in which both energy and matter can enter and exit
Binomial name
first part: genus, second part: name of species
Classification of animals
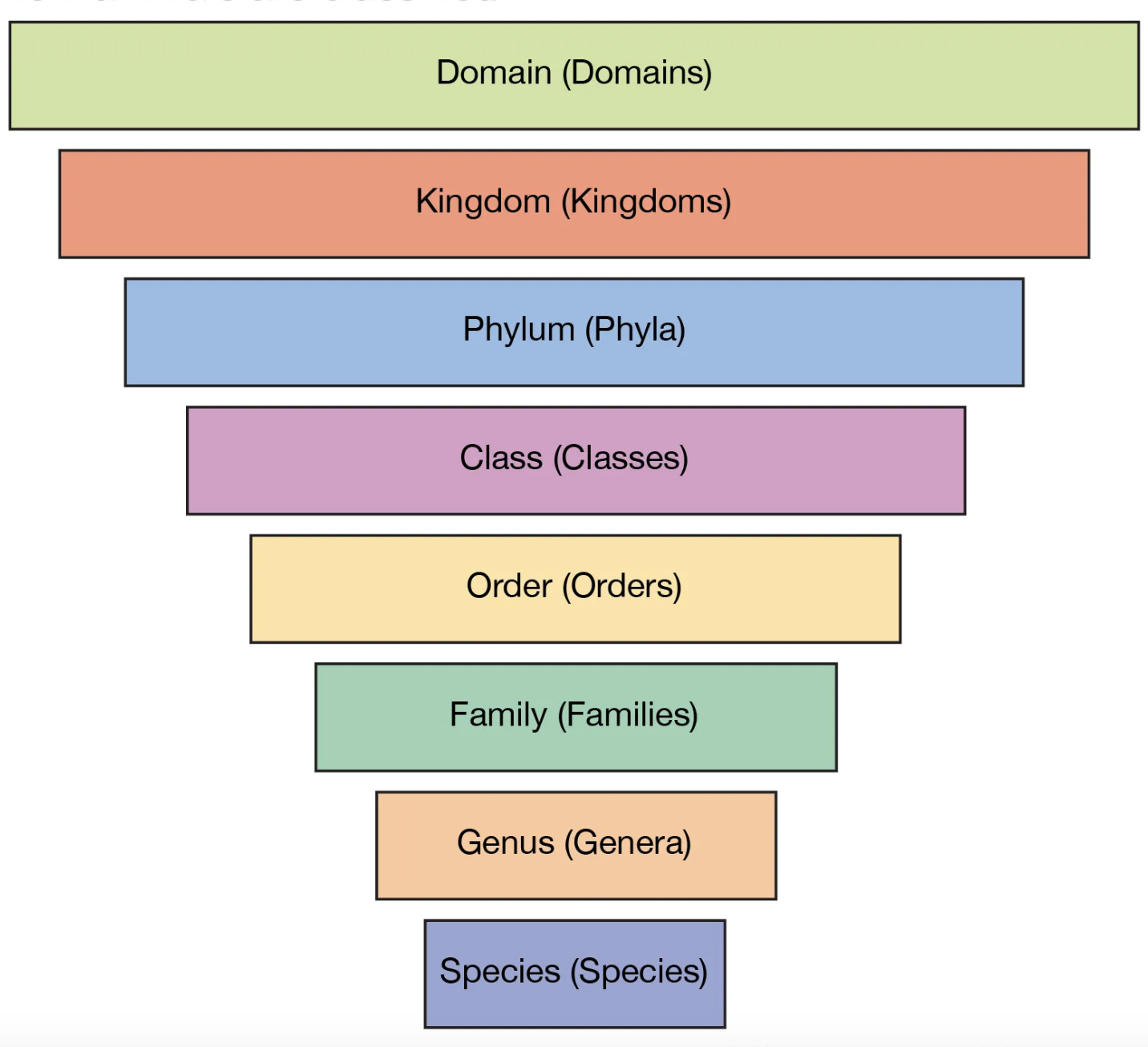
Dichotomous Key
consists of a series of paired statements/clues that provide aa guide to identifying each entity
Factors that determine the distribution of populations can be..
abiotic or biotic
Abiotic factors
non-living physical factors
Biotic factors
living, biological factors
Niche
the particular abiotic and biotic conditions and resources to which an organism or population responds
Species interactions
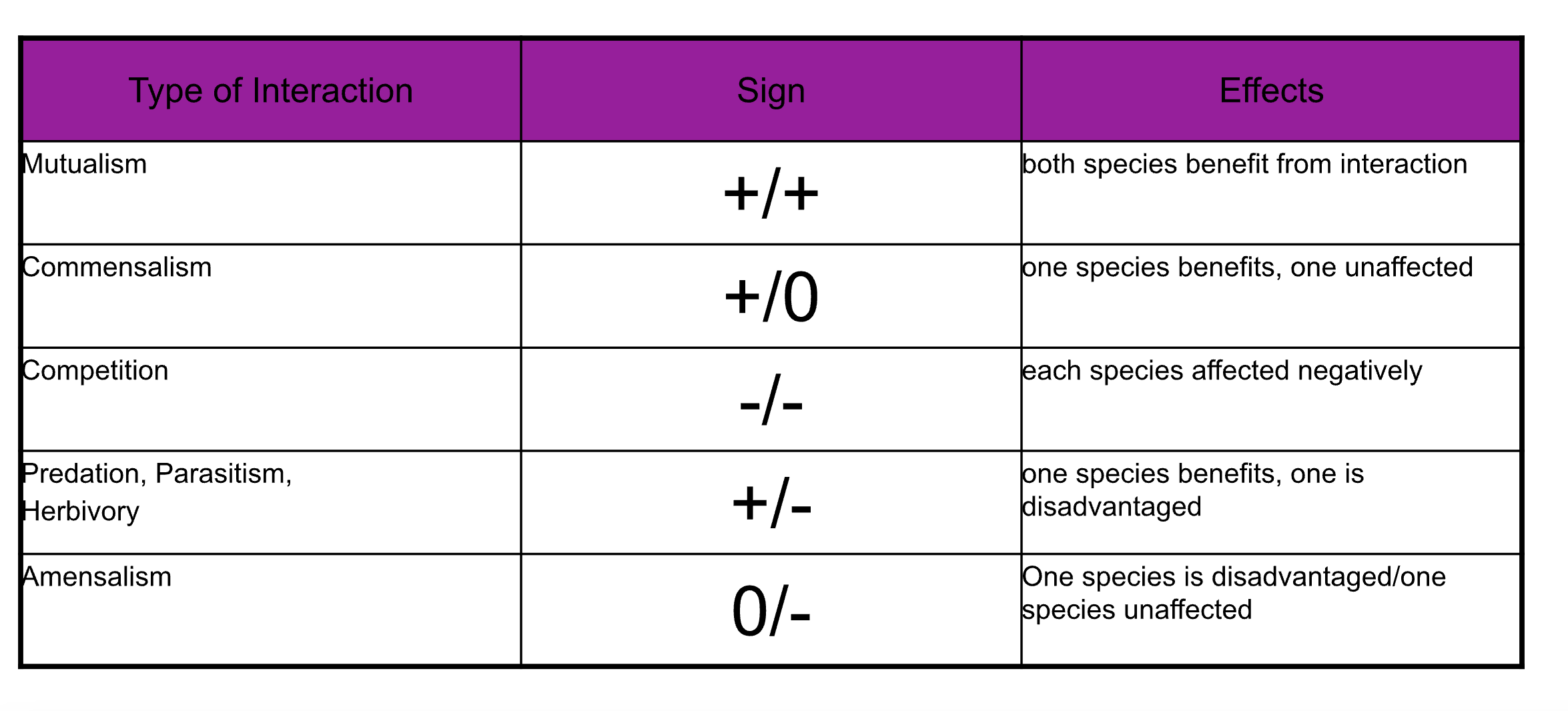
Herbivory
consumption of plant species by an animal
Predation
consumption of one species (prey) by another
Parasitism
symbiotic relationship; one species is benefitted and the other is adversely affected
Mutualism
symbiotic relationship where both partners benefit
Disease
caused by pathogens like viruses, bacteria, or fungi
Competition
interaction between organisms trying to both get a resource
Sustainability is..
a natural property of ecosystems
Human activity can lead to…
tipping points in ecosystem stability
Keystones
a single species in an ecosystem that maintains the structure + function
Biosphere integrity
encompasses species and genetic diversity as well as ecosystem function
compromising biosphere integrity will lead to..
reduction in ecosystem services, cascading effects, loss of reslience
To avoid tipping points..
the loss of biosphere integrity needs to be reversed
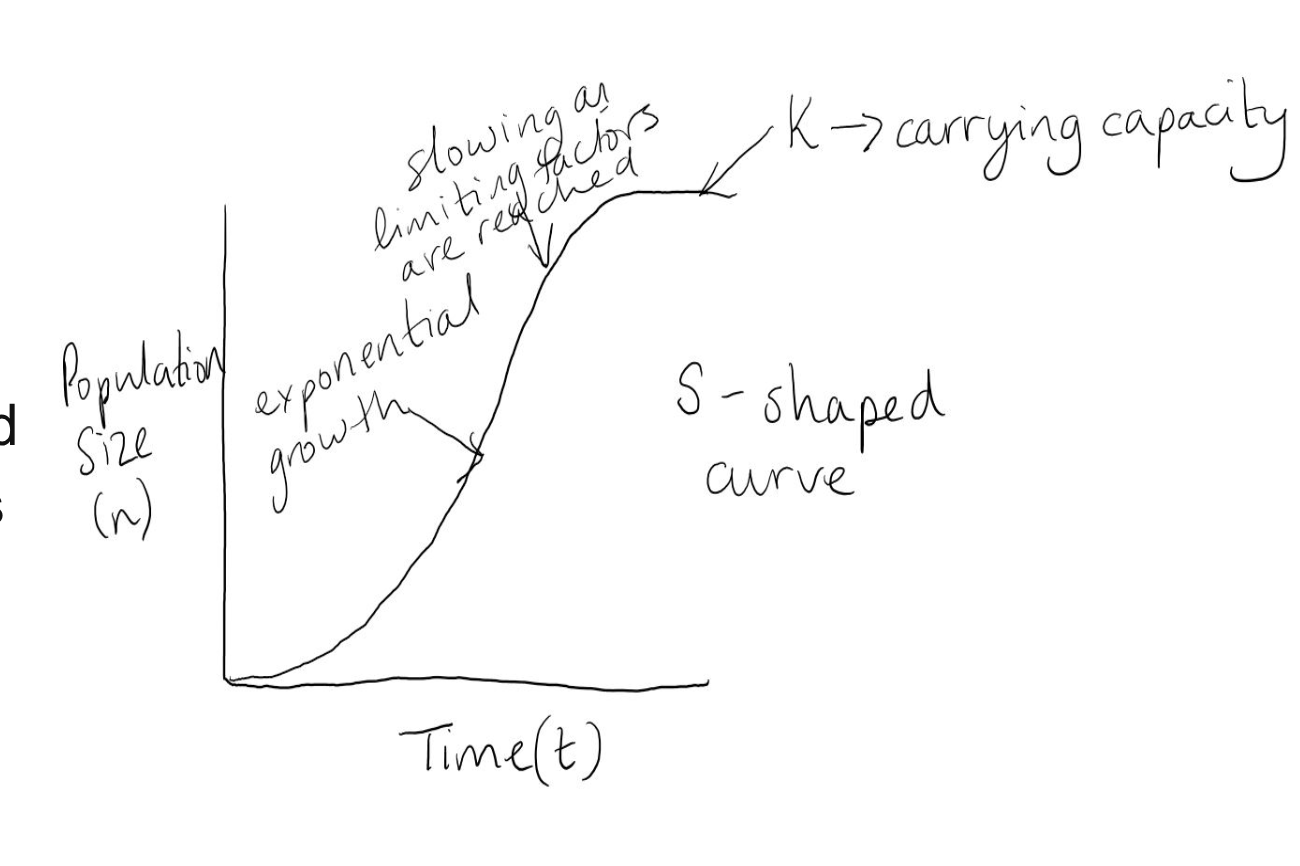
Carrying capacity
the maximum size of a population, determined by competition for resources
Carrying capacity is affected by
human activity, and biotic/abiotic factors
Population size is regulated by
density dependent factors
Density dependent factors
limiting factors that tend to regulate population size around carrying capacity (eg. competition, predation, and disease)
Density independent factors
limiting factors that will have an affect on population regardless of the size and abundance (eg. natural disasters or human activity)
Population growth can be either
exponential or limited by carrying capacity
S Curve
J Curve
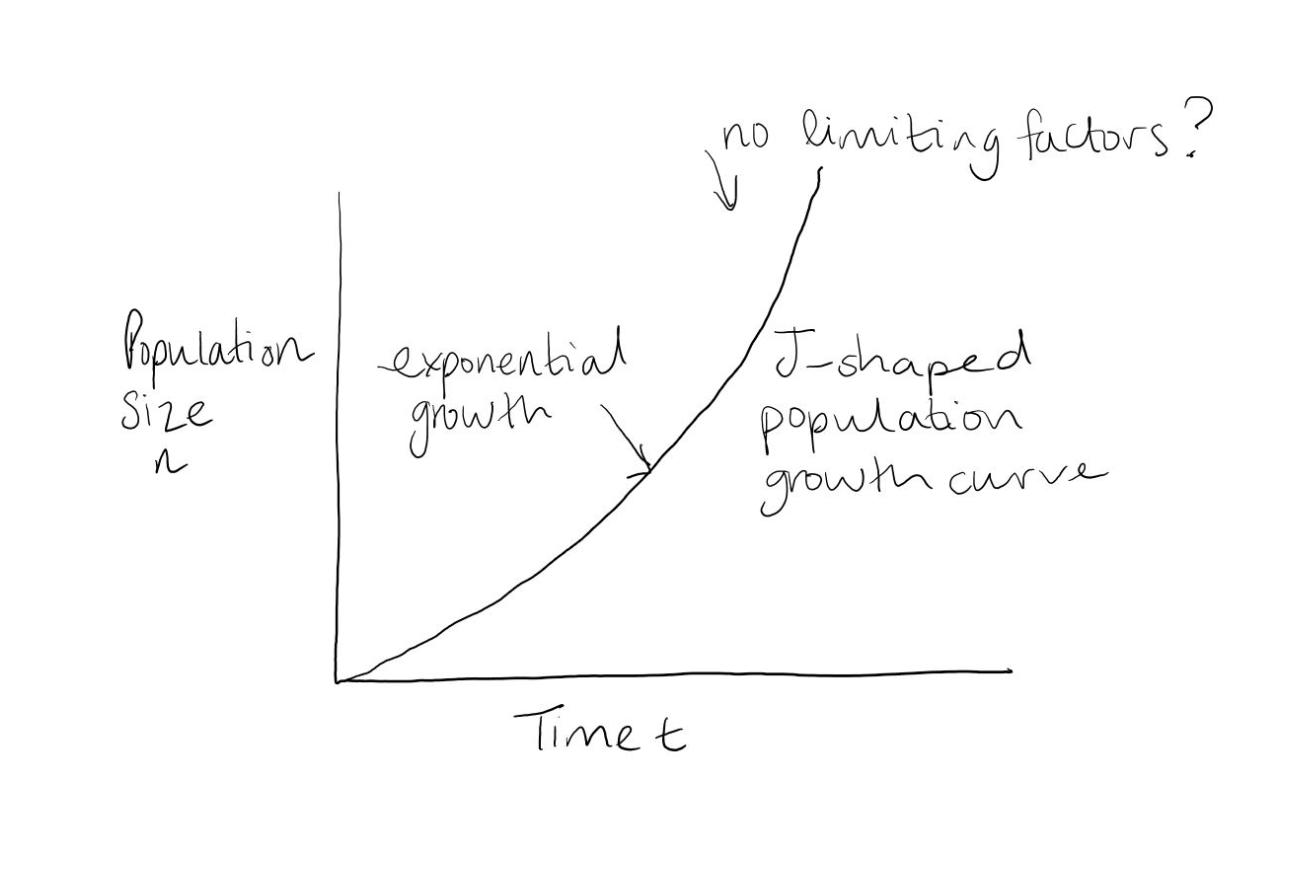
In reality…
combination of S and J
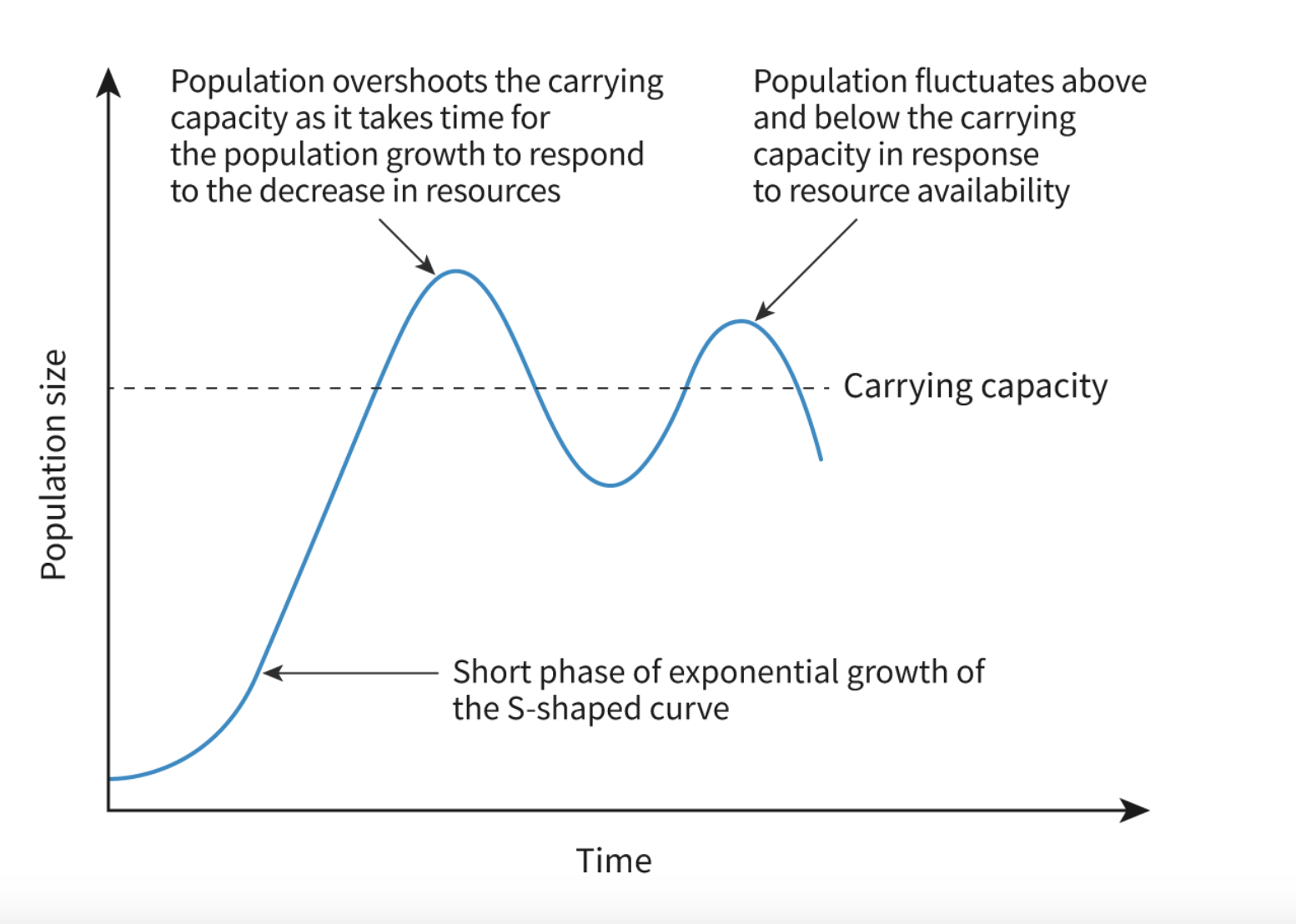
Human population
limiting factors have been eliminated
Eliminate limiting factors
Reduce natural predation, tech advancement, medical care, agriculture
Consequences for ecosystems
resource depletion, pollution, and habitat destruction
Human Carrying Capacity cannot be easily estimated due to
Broad/changing niches, tech advancements, mobility of resources, change in consumption patterns
Population abundance can be measured by
estimating, using random sampling, systematic sampling, or transect (stratified) sampling
Random sampling
each member of population has equal chance
Systematic sampling
study area includes an environmental gradient, transects used to systematically sample
Stratified sampling
proportionate number of observations taken from each part of population, divided into zones, samples from each zone
Random quadrant sampling for non motile organisms
population abundance, population density, percentage cover, and percentage frequency
For motile populations
capture-mark-release-recapture can be used
Capture-mark-release-recapture
capture organisms, mark, release back, recapture, and determine ratio of marked vs unmarked
Lincoln Index
(M x N) /R, m = number of individuals captured and marked, n = total number of individuals recaptured, r = marked indivdiuals recaptured