Dosage Forms and Compounding Lecture 8: Powder and Granules Dosage Forms and Plant Derived Supplement Dosage Forms
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Describe a powder as a dosage form
A dosage form composed of a solid or mixture of solids reduced to a finely divided state and intended for internal or external use
A powder is a formulation in which a drug powder has normally been mixed with other _______________________ to produce the final product
powdered excipients
T/F: Powders represent one of the oldest dosage forms. They have been replaced largely by capsules and tablets
TRUE
- still represent a portion, although small, of the solid dosage forms currently being employed
Application of medicated powders can be...
internally and externally
What are the different routes of administration of powders?
- oral/pulmonary
- topical
- IV
Medicated powders for oral use may be intended for...****
A. Local effects only
B. Systemic effects only
C. Both local and systemic effects
D. None of the above
C. Both local and systemic effects
The different dosage forms of powders and granules (7)
1. Bulk powders [and granules]
2. Divided powders [and granules]
3. Effervescent granulated salts
4. Dusting powders
5. Powders [and granules] for oral solution or suspension
6. Powders for injection
7. Powder for inhalation
Bulk powders and granules
Mixed ingredients are packed into a suitable bulk container (ex: wide-mouthed jar)

Bulk powders are frequently administered using a....
device suitable for measuring the dose
Are bulk powders or granules suitable for the administration of potent drugs?
A. Yes
B. It depends on the drug
C. No
C. No
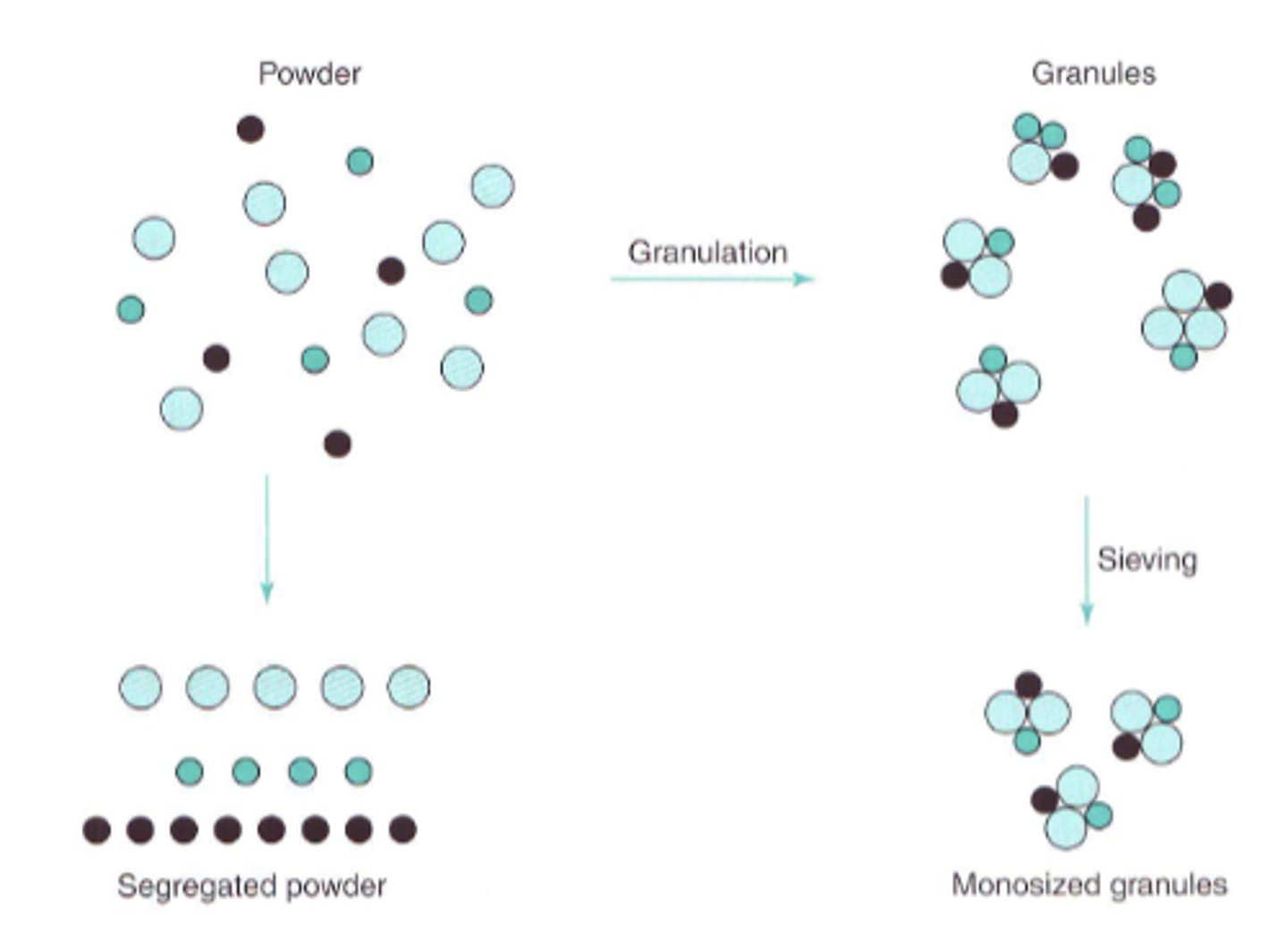
Reasons for granulation:
1. To prevent ________________ of the constituents of the powder mix by making it ___________________
2. To improve the __________________ of the mix
3. To improve the ________________________ characteristics of the mix
4. To improve the ___________________ of a powder by increasing its ________________________
5. To reduce _________________ associated with the generation of ___________________ during handling
1. prevent segregation of the constituents of the powder mix by making it less cohesive
2. to improve the flow properties of the mix
3. to improve the compaction (density) characteristics
4. to improve the solubility of a powder by increasing its surface area
5. To reduce hazards associated with the generation of toxic dust during handling
Divided powders
single-dose preparations for internal use
- traditionally were wrapped in paper
- packet (commercial)
- is used for administration to both adults and pediatric patients

What kind of drugs are divided powders used for?
for drugs that should be administered in accurate dosing
- patient/caregiver does not measure dose

T/F: Divided powders formulation is similar to bulk powders
TRUE
What is contained in effervescent granulated salts: formulation?
- drug
- sodium bicarbonate
-citric acid and tartaric acid (1:2)
- tartaric acid alone- granules readily lose their firmness and crumble
- citric acid alone- a sticky mixture difficult to granulate

Effervescent granulated salts are....
A. Granules only
B. Coarse to very coarse powders only
C. Granules or coarse to very coarse powders
C. Granules or coarse to very coarse powders
Dusting powders
Medicated powders for external use are dusted on the affected area from a 'Sifter-type container'
- powder must flow well from such a container

Dusting powders should be dispensed...
A. In a very fine state of subdivision
B. Coarse
C. Neither. For dusting powders there is no rule of thumb regarding fineness/coarseness of powder
A. In a very fine state of subdivision
T/F: All the needed excipients are included in powders and granules for oral solution or suspension
TRUE
Advantages of powders and granules as dosage forms (6)
• Some drugs are too bulky to be formed into tablets or capsules
• Faster dissolution rate than tablets/capsules (ex: Tums powder)
• Easy swallowing
• Stability [shelf life]
• More stable than liquid
• Convenient for large dose drugs vs tablets
Disadvantages of powders and granules as dosage forms (8)
• Inconvenient for transport versus tabs/caps (Portability)
• Difficult to mask unpleasant drug taste/texture
• Challenging to achieve precise and uniform dosing
• Not effective for administration of low-dose (potent) drugs because it is hard to measure powders
• Not suitable for drugs that are inactivated in the stomach
• Increase risk of inhalation during administration, especially for infants and those with respiratory issues.
• Increase cost when in more convenient packaging
• Preparation is time consuming
Dietary supplements
term used by FDA for natural products
Natural product is an umbrella term and includes: (3)
- herbals (plant products)
- vitamins
- substance that exist in nature, but are not plant-derived (glucosamine from shellfish)
Plant-based supplements are derived from ____________________ as opposed to _________________
- natural sources
- chemical sources
Natural sources for plant-based supplements include....
herbs, flowers, leaves, and stems, bark, seeds, nuts, spices, vegetables, fruits, and other naturally- occurring botanical ingredients
Ingredients for plant-derived dietary supplements are very...
very variable and difficult to characterize
Plant-derived dietary supplement ingredients: there is no guarantee of their.... (4)
- identity
- purity
- strength
- bioavailability
What are two major concerns regarding the manufacturing of dietary supplements?
- may not follow "good manufacturing practices" (GMP), resulting in poor-quality products
- the manufacturer does not have to PROVE product SAFETY and EFFECTIVENESS before it is marketed
T/F: A single product may contain a number of active ingredients
TRUE
In plant-derived dietary supplements the active ingredients are...
A. Always known
B. Frequently unknown
B. Frequently unknown
Obtaining a high-quality product
• Manufacturing procedures used in processing
• The quality of the raw material is crucial in efficacy of the dosage form
Once the plant has been dried it is.....
ground into particles using either a blender or a mill
Effective extraction of plant depends on the....
size of plant particles
Which particles will lead to more efficient extraction?
A. Small
B. Large
A. Small
Extraction***
the act of drawing one part out of a compound
Extract
a preparation of a substance obtained from plants, animals, or bacteria and used as a drug or in drugs
Extract is produced from a dried plant by a technique involving the use of __________________ or by ____________
- use of selective solvents
- by physical means
A concentrated preparation of..
- Liquid
- Semisolid
- Solid
Liquid: tincture, infusion, decoction
Semisolid: paste, cream, gel
Solid: dry or powdered extract
Extraction of plant materials method
Different methods of extraction (2)
- Conventional extraction
- Advanced/Modern extraction
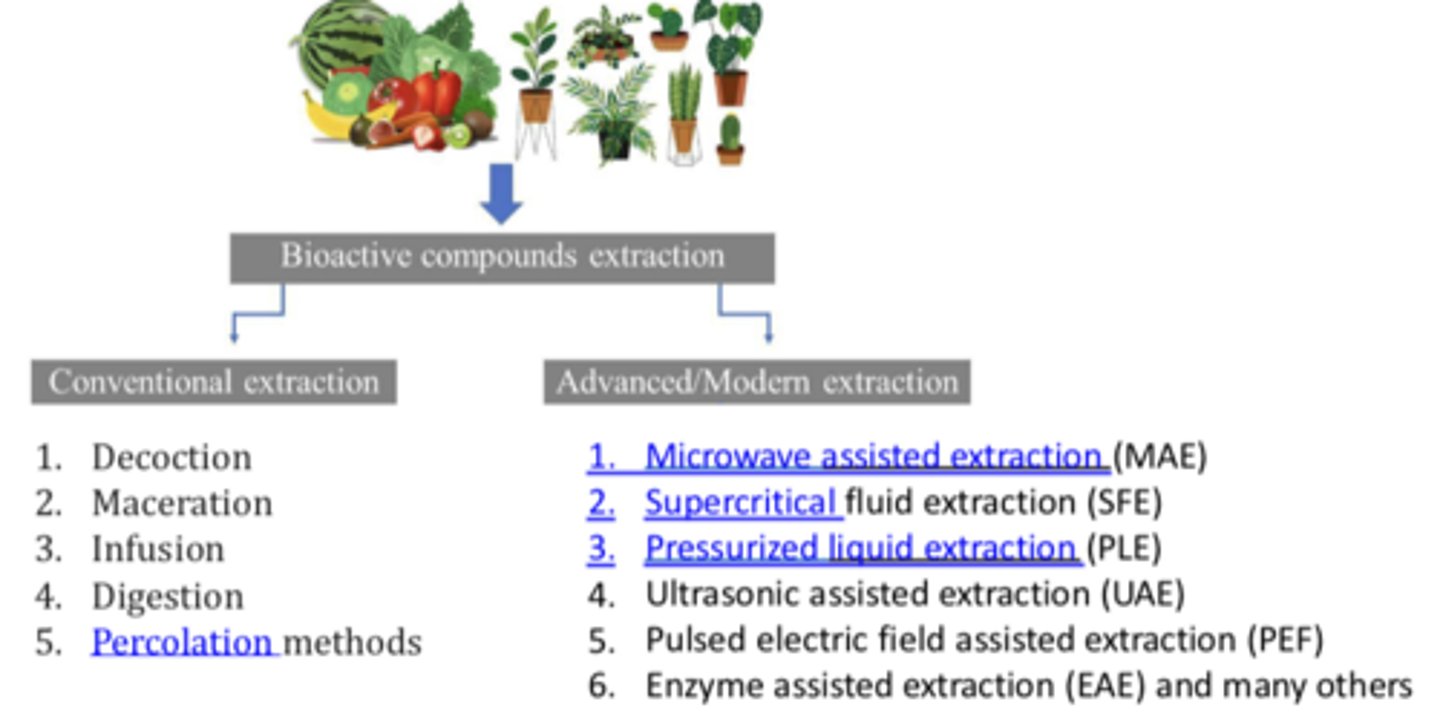
Conventional extraction methods*** (5)
1. Decoction
2. Maceration
3. Infusion
4. Digestion
5. Percolation methods

Advanced/Modern extraction methods:*** (6)
1. Microwave assisted extraction (MAE)
2. Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE)
3. Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE)
4. Ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE)
5. Pulsed electric field assisted extraction (PEF)
6. Enzyme assisted extraction (EAE) and many others

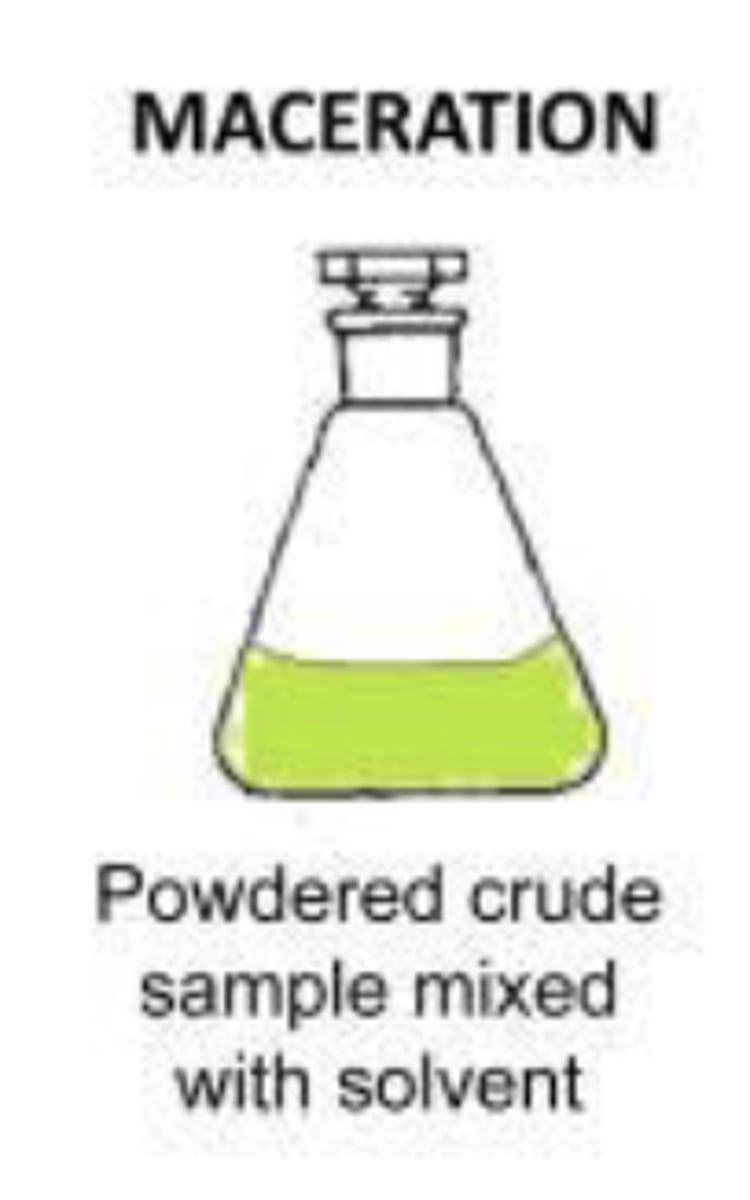
Conventional methods of extraction: Maceration
powdered crude sample mixed with solvent
- maintaining contact between the plant and a liquid for a period at room temp. at least 3 days in a warm place with frequent agitation, until soluble matter is dissolved
Conventional methods of extraction: Infusion
powdered crude sample mixed with cold or boiling water
- process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water or alcohol by allowing the material to remain suspending in the solvent over a period of tike (known as steeping or soaking). for readily soluble constituents of crude drugs
Conventional methods of extraction: Digestion
powdered crude sample mixed with solvent and macerated with gentle heat
Conventional methods of extraction: Decoction
powdered crude sample mixed with water and boiled
- method of extracting actives by boiling plant material in a solvent. may result in more oil-soluble chemicals in decoctions because of temperature
Conventional methods of extraction: Percolation
powdered crude sample mixed with solvent and is extracted in a percolator
- the continuous extraction method that involves the slow descent of a solvent through a powdered substance until it absorbs certain constituents and drips out through the filtered bottom of the container. Performed by passing a solvent that can dissolve the active material
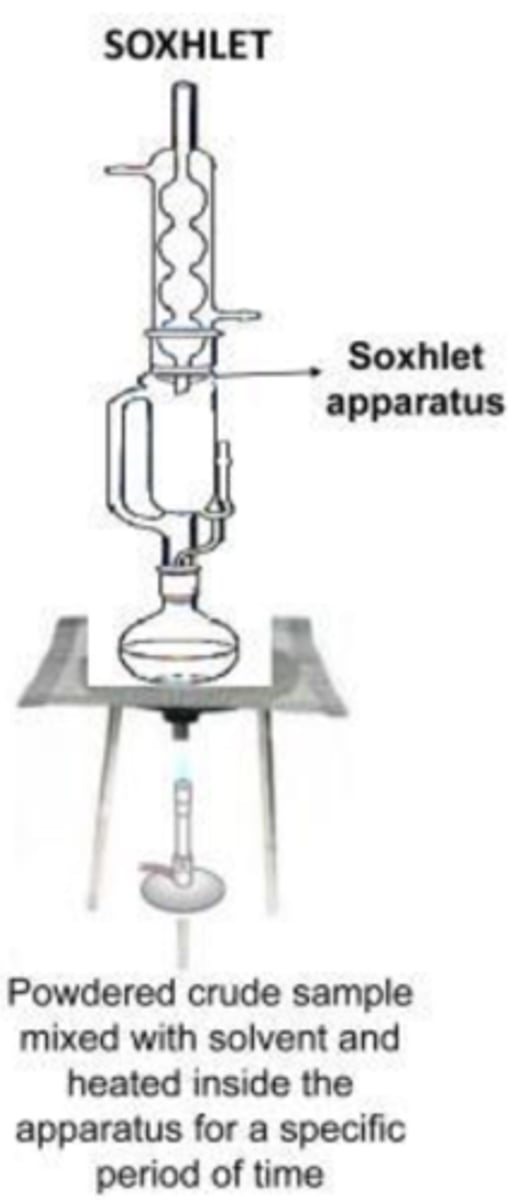
Conventional methods of extraction: Using Soxhlet
powdered crude sample mixed with solvent and heated inside the apparatus for a specific period of time
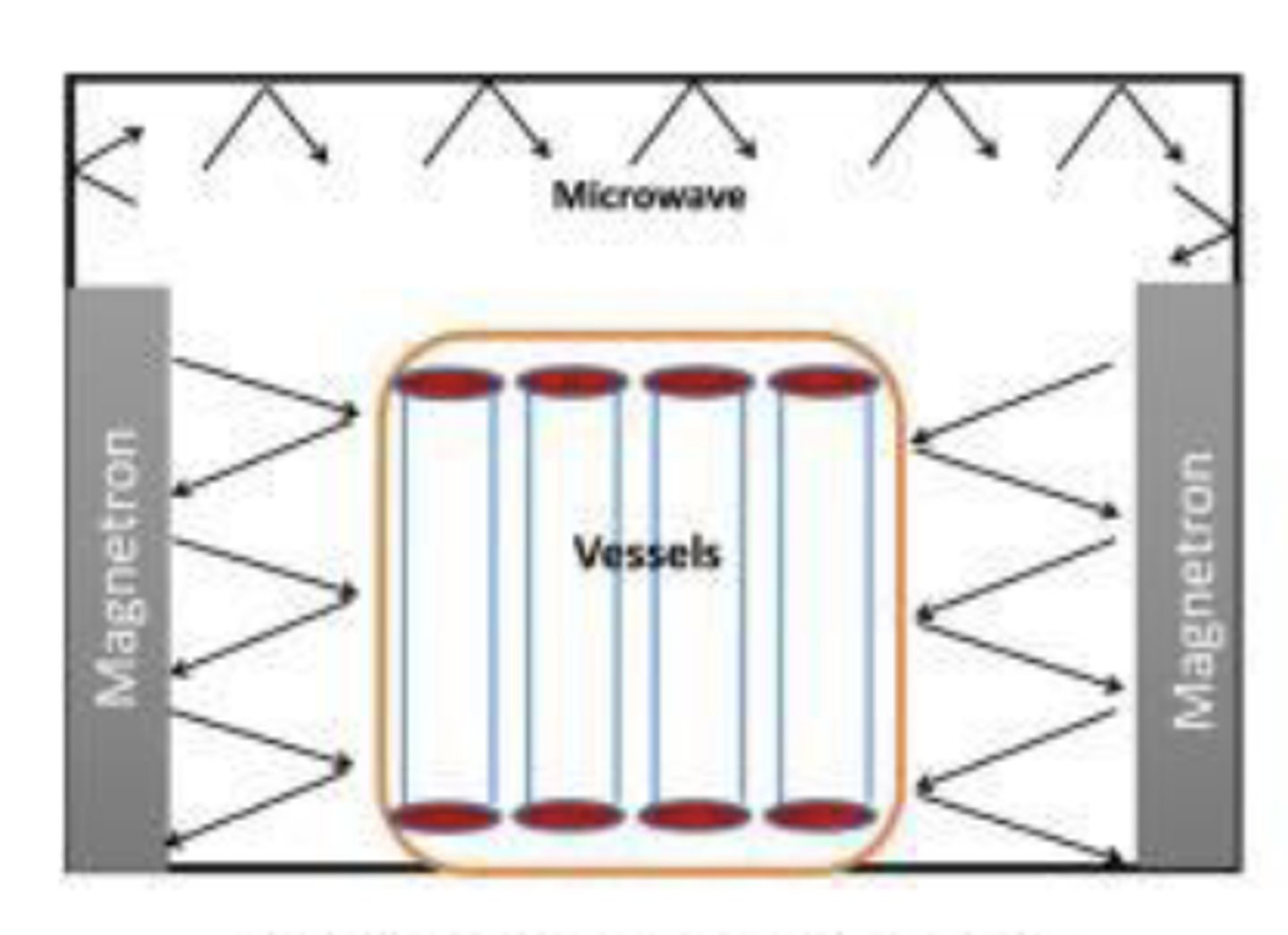
Advanced Extraction Methods: Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE)
sample mixed with organic solvent and heated by microwaves through ionic conductance and dipole rotation
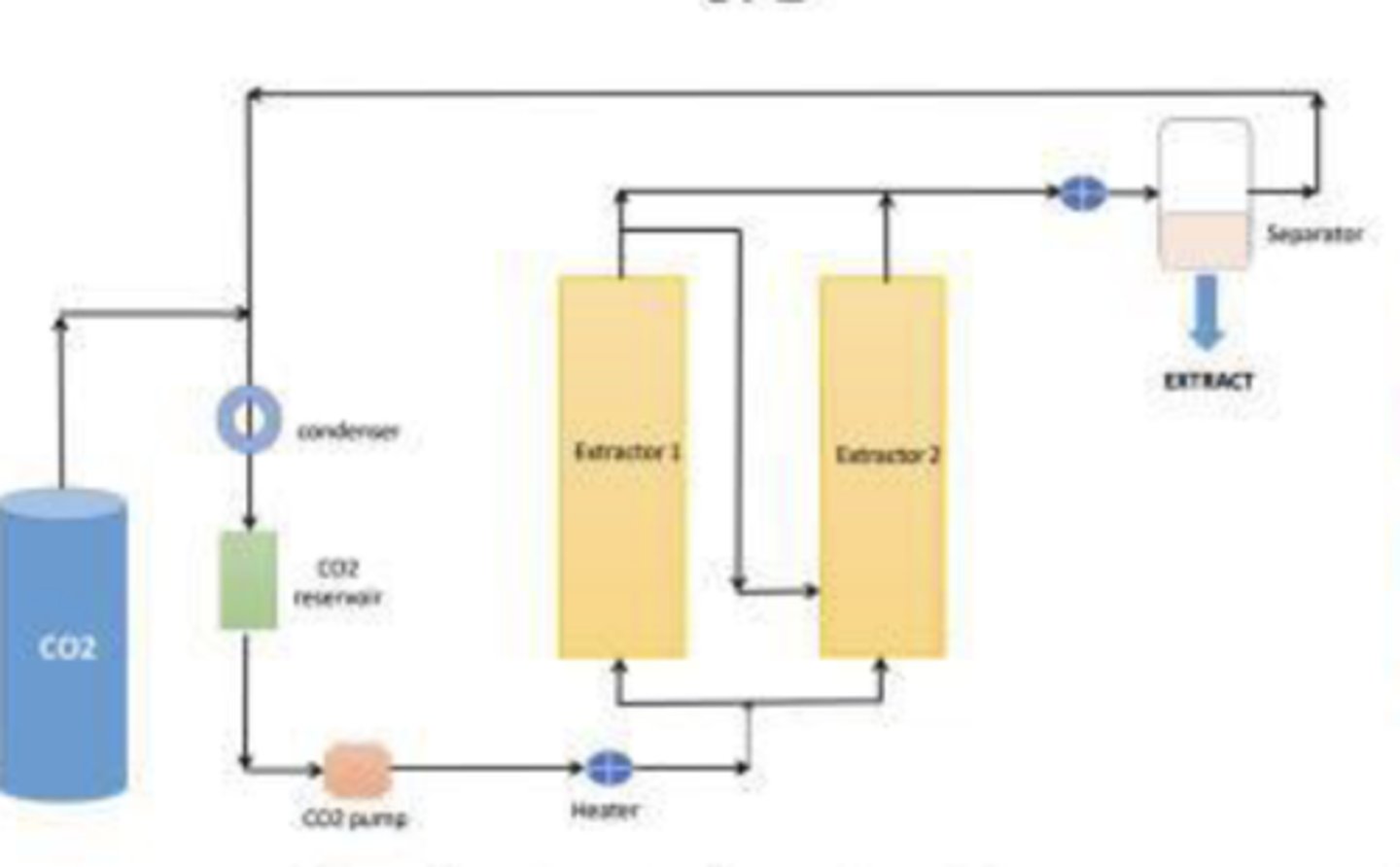
Advanced Extraction Methods: Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE)
sample extracted by using CO2 as a solvent which depend on the critical point
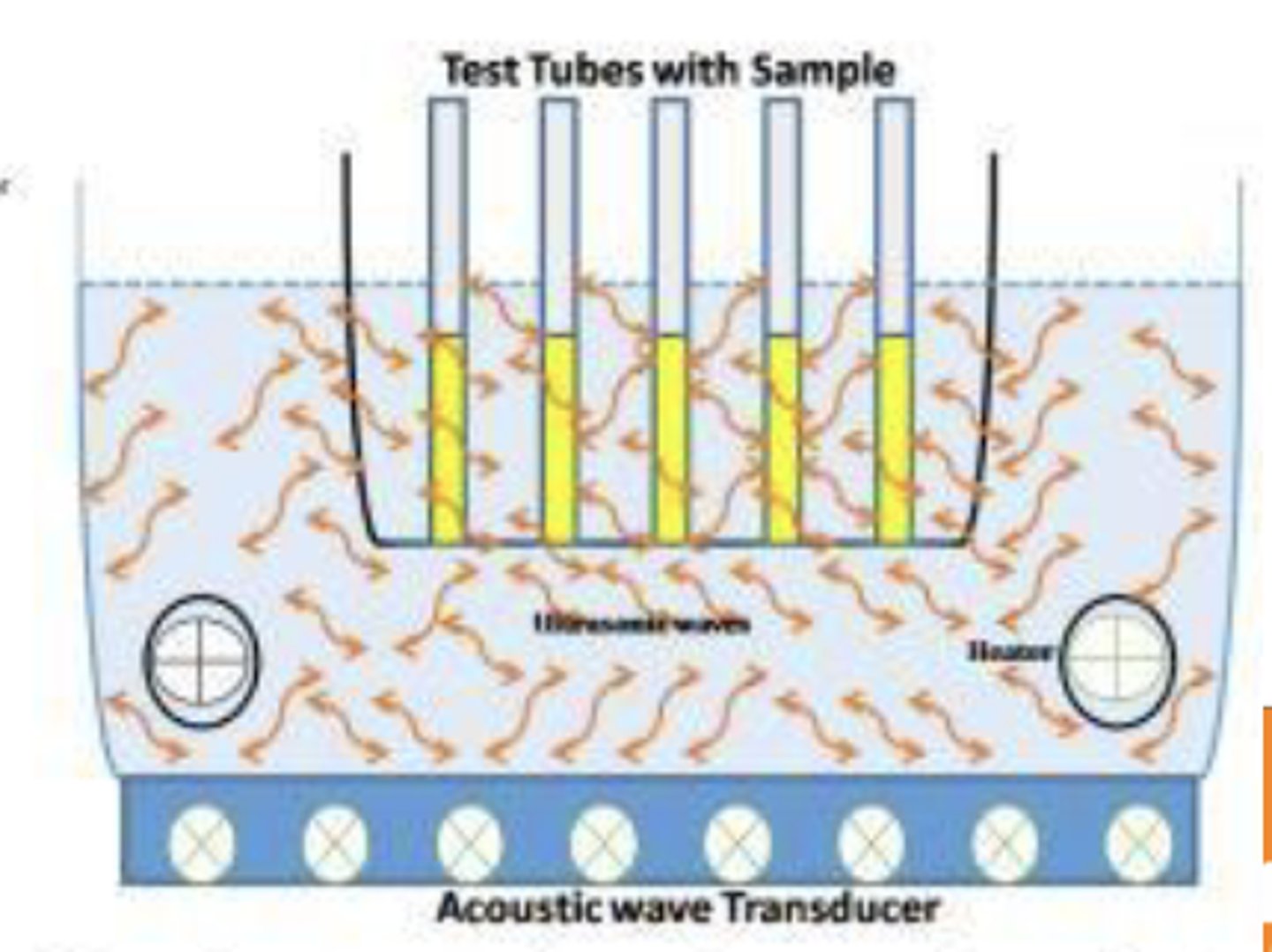
Advanced Extraction Methods: Ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE)
sample extracted by using organic solvent which under ultrasonic wave form cavitation bubbles
The major stages in the conversion of plant material into a concentrated extract
Harvesting:
Drying:
Size reduction (comminution):
Extraction of active constituents:
Extract concentration:
Harvesting: stop metabolism at optimum time. Constraint: weather
Drying: inactivate enzymes, inhibit microbial infestation. Constraint: plant part & temp. determine speed. essential in tropical conditions
Size reduction (comminution): increase surface area for effective solvent extraction. Constraint: Solvent flow impeded if particles too small, possible release of excessive mucilage which hinders later filtration
Extraction of active constituents: production of most active base for formulation. Constraint: financial constraints to complete (100%) extraction
Extract concentration: minimize volume/weight of extract, for ease of transport, storage, and ease of distribution in the final formulation. Constraint: as above, but extra investment

Active ingredients in extracts or dried plants may vary for a variety of reasons including: (6)
• Soil
• Sunlight
• Temperature
• Rainfall
• Part of the plant that is used
• Methods of drying, storage, and processing
Verification for dietary supplements
- USP offers verification services for dietary supplement and ingredients used to make them
- when they meet all requirements, including a GMP audit, product and ingredient testing, and manufacturing documentation review- are awarded use of the distinctive USP Verified Marks

Dosage forms of plant derived supplement (3)
1. Hydroalcoholic extracts
2. Solid extracts
3. Aqueous extracts
Hydroalcoholic extracts
- tinctures
- fluid extracts (concentrated)
Solid extracts
- ex: tablets, capsules
- are based on solid extracts
Aqueous extracts
- infusions
- decoctions
Tinctures (3)
- hydroalcoholic extracts
- alcohol proportion is 15% to 80%
- 10 mL usually represents 1-2 g of plant (ex: 1 g of plant is soaked in 5 mL of liquid)
When are tinctures used?
when the active ingredients are water-insoluble
Which statement is true?
A. All tinctures are based on vegetable materials
B. Some tinctures are not based on vegetable materials
B. Some tinctures are not based on vegetable materials
After extraction of the plant, the resulting solutions can be concentrated into...
fluid extracts or solid extracts
Fluid extracts are...
concentrated liquid preparations of a plant or substance, usually obtained through a process of percolation or maceration
solid extracts are...
concentrated forms of a substance that are usually in a solid or semi-solid state, such as powders, crystals, or thick pastes
Fluid extracts
- are liquid preparations of....
- _______ represents 1 g of plant
- _____________ concentrated than tinctures
- vegetable materials
- 1 ml represents 1 g of plant
- more concetrated than tinctures
Preparation of fluid extracts
1. Extraction
2. Distillation of some of the solvent- usually without heat
Solid extracts
- the most _____________ form of a plant
- prepared by ______________________________ used to remove the active ingredients from the plant
- _______ g solid extract usually represents _____g of plant
- Usually _________________ for ease of administration
- the most concentrated form of a plant
- prepared by evaporating all of the solvent used to remove the active ingredients from the plant
- 1 g solid extract usually represents 2-8 g of plant
- usually encapsulated for ease of administration
Solid (powdered) extracts can be incorporated into....
tablets or capsules
Excipients for solid dosage forms are frequently similar to those used in....
dosage forms of drugs
infusion = dilute solution of the _____________ constituents of plant material
dilute solution of the readily soluble constituents of plant material

How are infusions prepared?
by pouring boiling water over the plant material and letting it soak
T/F: In infusions, the plant material and water are boiled together
FALSE
are not boiled together
Are infusions infusions relatively weak/strong in action compared to:
- Tinctures
- Fluid extracts
- Solid extracts
Tinctures: alcohol-based extracts that pull out both water and alcohol-soluble constituents, making them stronger and more concentrated than infusions
Fluid extracts: even more concentrated than tinctures, provide a potent dose.
Solid extract: most concentrated form, significantly stronger than infusions
- infusions are the weakest compared to tinctures, fluid extracts, solid extracts
Factors that effect the infusion (3)
• Extent of comminution of the plant
• Amounts of plant and liquid
• Method of extraction
- Temperature
- Length of time
Preparation of decoctions
• Plant material is placed in cold water
• Heating to boiling
- Boiling for ~8-15 minutes
• Straining to remove the plant material
• Appropriate for water soluble components that are heat stable
Infusions Vs. Decoctions
Infusions
• Lighter, leafier, or flowery plant parts
-Active ingredients are easily rendered from this gentle process
Decoctions
• Tougher, woodier, or rooty plant parts
-Plant materials need softening before the active constituents can be released
-Use of heat
-May contain oily ingredients
Gelatin capsules
- made from gelatin, protein derived from animal collagen, sourced from bovine or porcine sources
- 2 main types: hard gelatin capsules and soft gelatin capsules
- HGC usually used for dry, powdered ingredients, but also contain granules or mini-tablets
- softgel capsules are often used for delivering oil-based ingredients
Vegetable capsules
- made from plant-derived materials such as cellulose, starch, or other plant-based polymers
- alternative to traditional gelatin capsules, suitable for vegetarian/vegan ppl
- low moisture content and wide temperature range stability
- no risk of BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy)
- slower dissolution and costly
Which is correct?
A. SGCs are ideal for liquid or semi-solid formulations, including oils, suspensions, and pastes.
B. HGCs are commonly used for dry powder formulations, such as powdered drugs, vitamins, and minerals
.C. Gelatin is a natural protein found in the skin, bones, and connective tissues of animals.
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
Soft vegetable capsules are...
A. Used in dietary supplements only
B. Used in drugs only
C. Used in dietary supplements and drugs
D. Are not used regularly
C. Used in dietary supplements and drugs
Plants should be grown without exposure to: (3)
- heavy metals
- pesticides
- other contaminants and adulteration
T/F: Adverse effects seem more common with plants outside Europe and North America
TRUE
T/F: Small quantities of trace elements are invariably present in plant materials
TRUE
Under certain circumstances, levels of some metals can increase to unacceptable concentrations (4)
- lead
- cadmium
- copper
- mercury
The flowers and leaves of St. John's wort contain active ingredients such as ____________. St. John's wort is available as a supplement _____, ____________, __________ and _____________
- hyperforin
- teas, tablets, liquids, and topical preparations

Roots of St. John's Wort may incorporate....
heavy metals from the soil
- lead, copper, manganese, and mercury
What are major concerns with St. John's Wort? (5)
• Drug interactions (induces CYP 3A4 >> 2C9 > 1A2)
• Photosensitivity
• Allergic reactions
• GI upset, dizziness, or fatigue
• Anxiety and mental health concern
T/F: Legislation about pesticides is not lacking in any country
FALSE
legislation in many developing countries/practice is large ignored
- might contain DDT
FDA seized imported ginseng products contaminated with unacceptable levels of......
quintozene and procymidone
Intentional adulteration
the herbal plant is substituted partially or fully with other inferior products (ex: using other parts of the same plant with no active ingredients)
Why would traders of plants be involved in intentional adulteration?
to manage dosage/effectiveness of plant product
Examples of plant-derived dietary supplements adulterated with unlabeled drugs
- "sleeping buddha" contained estazolam
- fenfluramine, warfarin, glyburide, caffeine, acetaminophen, corticosteroids
Unintentional adulteration
deterioration may contribute to unintentional adulteration, especially during storage
- loss of the active ingredients
- production of inactive metabolites
- production of toxic metabolites-rare
T/F: total bacteria counts does not vary from plant to plant
FALSE
they vary enormously
What are higher bacterial counts associated with.....
- slower drying process
- plants that are richer in nutrients