L4: Regulation of Digestion
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Functions gastrointestinal tract
Digestion
Absorption
Secretion
Motility
Digestion
Breakdown of large macro-nutrients
Absorption
Absorption digested nutrients in blood
Secretion
Endocrine and exocrine secretion
Motility
Movement of food through gastrointestinal tract
General anatomy gastrointesinal wall
Mucosa - surround intestinal lumen
Submucosa - connective tissue
Muscularis externa - smooth muscle
Serosa - connective tissue
Enteric nervous system
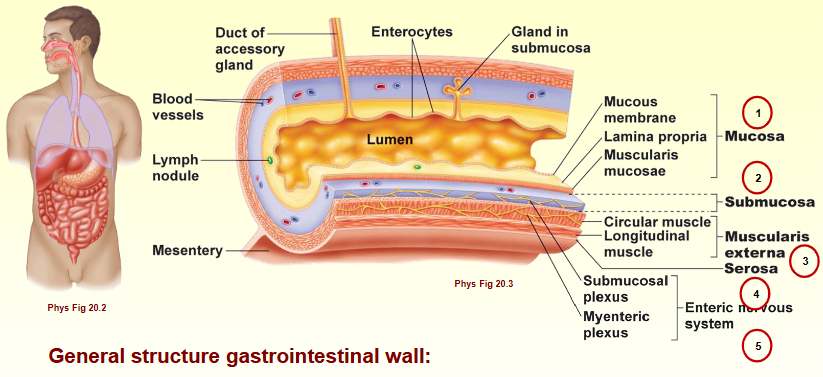
Mucosa consists of
Mucous membrane
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosae
Muscularis externa consists of
Circular muscle
Longitudinal muscle
Enteric nervous system consists of
Submucosal plexus
Myentreic plexus
Anatomy gastro tract
Fundus
ody
Antrum
Fundus: thin flexible (stretch) wall (secretion)
Body: rugged wall (secretion)
Antrum: muscular wall (knead, propel)
Fundus+ body: gastric pits (secretion)
Exocrine
Chief cells, pepsinogen
Parietal cells, HCl
Endocrine
Gastric cells, gastrin
Secretion gastric juice
2-4L/day, pH2
anti-bacterial
protein denaturation
activation pepsinogen
pH-optimum pepsin
what casues the low pH in gastric juice
Parietal cells
H+ and HCO3- production (carbon anhydrase, CA)
Net result: H+ and Cl- in lumen, HCO3- in interstitial tissue
Anatomy intestinal tract
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Colon
Intestianl tract - function
Absorption nutrients and water
Intestinal tract - increase surface area
Vili in mucusa
Microvilli, brush border (enzymes), (blood and lymph vessels in vili)
Accessory glands
Salivary glands
Liver
pancreas
Salivary glands - function
HCO3-
Mucus (lubricates food)
Amylase (digestion starch)
Lysozyme (killing bacteria)
Pancreas
Can be either endocrine or exocrineP
Pancreas - endocrine
Islet cells
secretion hormones
Insulin
Glucagon
Exocrine pancreas
Pancreatic juice secretion
Acini: H20, electrolytes, enzymes (primary secretion)
Ducts (converging): increase volume, bicarbonate (secondary secretion)
Pancreas exocrine (acini)c
Secretion bicarbonate and digestion enzymes:
amylase (starch)
lipase (fat)
proteases (protein)
nucleases (nucleic acids)
Liver function production and secretion bile
contains (a.o. salt, bicarbonate)
continuous production in liver, periodic secretion in duodenum
storage in gallbladder
(regulation via sphincter of oddi)
function liver
metabolic conversion nutrients
absorptive phase
Glucose | → | Glycogen |
Amino acid | → | Fatty acids |
Triglyceride, cholesterol | → | Lipoproteins |
postabsorptive phase
Glycogen | → | Glucose |
Fatty acids | → | Ketone bodies |
Gluconeogenesis |
Digestion macronutrients
Function
To go from poly to monomersD
Digestion macronutrients
Digestion enzymes
Mostly hydrolases
Amylase - carbohydrate
Peptidase - protein
Lipase -fat
Digestion macronutrients - regulation enzymes
pH-optimum
T-optimum
Carbohydrates; digestion
Carbohydrates (sugars, saccharides)
Polymers
polysaccharide
starch (plant)
glycogen (animal)
disaccharides
maltose
sucrose
lactose
only monomers are absorbed
Carbohydrates - what is the route of digestion
Luminal (mouth, intestine)
Amylase: polymers → oligo, dimers
Cell-surface (brush-border intestine)
Oligo, dimers → monomers
maltase
sucrase
lactase
Carbohydrates - absorption
to portal blood (liver)
monomers via carriers (secondary active transport, facilitated diffusion)
Proteins: digestion
Proteins
Polymers
di, tri, oligo, polypeptides
Monomers
amino acid
monomers and oligomers are absorbed
Proteins - digestion - enzymes
Peptidase, protease
endo-peptidase
exo-peptidase
zymogen, activation needed (HCl, enterokinase)
Proteins: what is the route of digestion
luminal (stomach, intestine)
polymers → oligo, tri, di, monomers
cell-sruface (brush border intestine)
oligo, tri, dimers → tri, di, monomers
intracellular (intestine)
tri, dimers → monomers
Fat digestion
fats and oils (lipids)
triglycerides
cholesterol, fatty acids
digestion
fat - hydrophobic, lipase - hydrophilic
bile acid: emulsification → increase surface availability for lipase
fat digestion enzymes
lipase (saliva, stomach, pancreas)
fat - absorption
diffusion in the enterocytes (lipophilic)
repackaging in triglycerides
packed in chylomicrons (lipoproteins)
exocytosis to interstitial fluid
uptake in lymphatic system (lacteals)
regualtion gastrointestinal function
maximizing digestion and absorption (function of gastrointestinal tract)
neuronal and hormonal)
Neuronal regulation gastrointestinal tract
plexus of meissner or submucosal plexus
plexus of auerbach or meyenteric plexus
neuronal regulation - nerves
input
receptors gastrointestinal tract (mechano, osmo, chemoreceptors)
autonomic nervous system
output
plexus of Meissner; exocrine and endocrine glands, blood flow
plexus of Auerbach; smooth muscle → motility
plexus of meissner - function
exocrine and endorcine glands, blood flowp
plexus of auerbach function
smooth muscle → motility
neuronal regulation function
regulates motility, secretion
externally independent (some autonomic regulation)
regulation gastrointestinal tract: reflexes
phases
cephalic
gastric
intetsinal
cephalic phase
stimuli arising from the head
gastric phase
stimuli arising form stomach (CNS, ENS or endocrine)
intestinal phase
stimuli arising from intestine (CNS, ENS, or endocrine)
Regulating secretion saliva
taste and texture food → mechano and taste receptors in mouth → salviary centre in brain stem → activating autonomic nerve system: cortex
cephalic regulation
parasympatic, increase watery saliva
sympaticL increase viscous, portein rich saliva
Regulating secretion gastric juice
HCl and pepsinogen secretion
parasympathetic and gastrin (G-cells)
cephalic and gastric stimuli: increase
intestinal stimuli decrease
regulation of secretion pancreatic juice primarily by
intestinal stimuli
regulating secretion pancreatic juice
acid, protein, fat (chemo), chyme (mechano)
CCK: stimulation acini cells (primary secretion: enzymes etc)
Secretin: stimulation duct cells (secondary secretion: bicarbonate etc)