Skin and Body Membranes : Chapter 4 (Marieb, Elaine. Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Body membranes
Cover surfaces,
line body cavity,
form protective (and often lubricating) sheets.
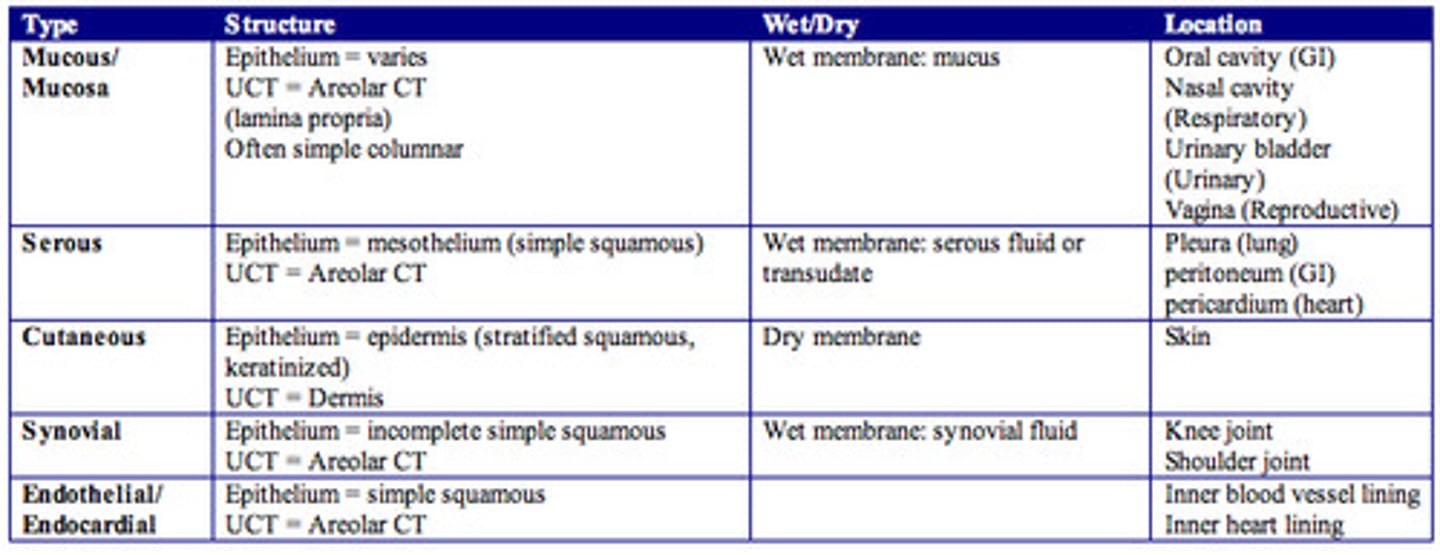
Two major groups of body membranes
1. Epithelial Membranes
2. Connective Tissue Membranes
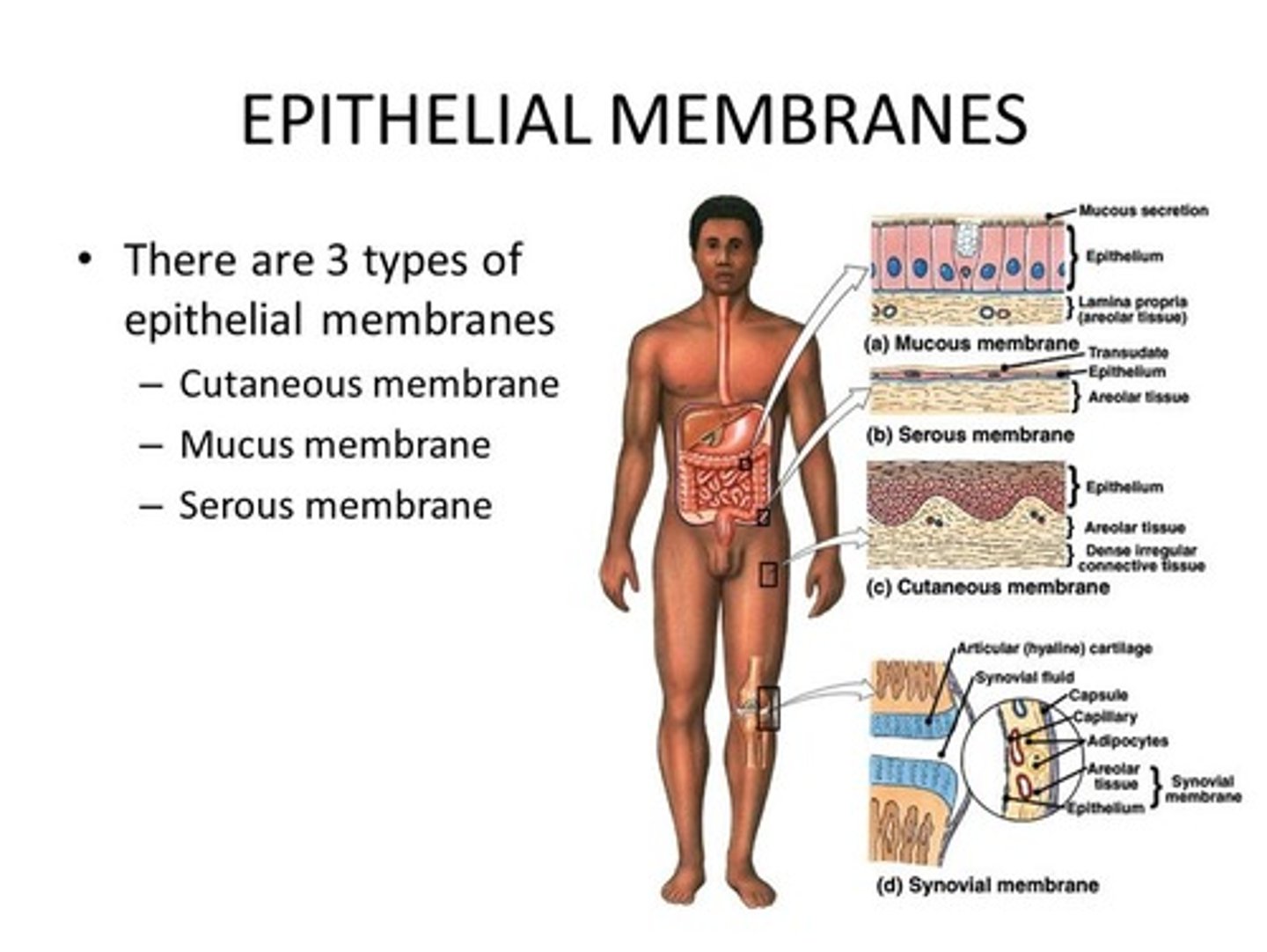
Epithelial Membranes
covering and lining membranes:
1.cutaneous membrane (skin)
2.mucous membranes
3.serous membranes
Connective Tissue Membranes
synovial membranes (in joint capsules)
Cutaneous Membrane
= skin = the integument;
composed of a keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium.
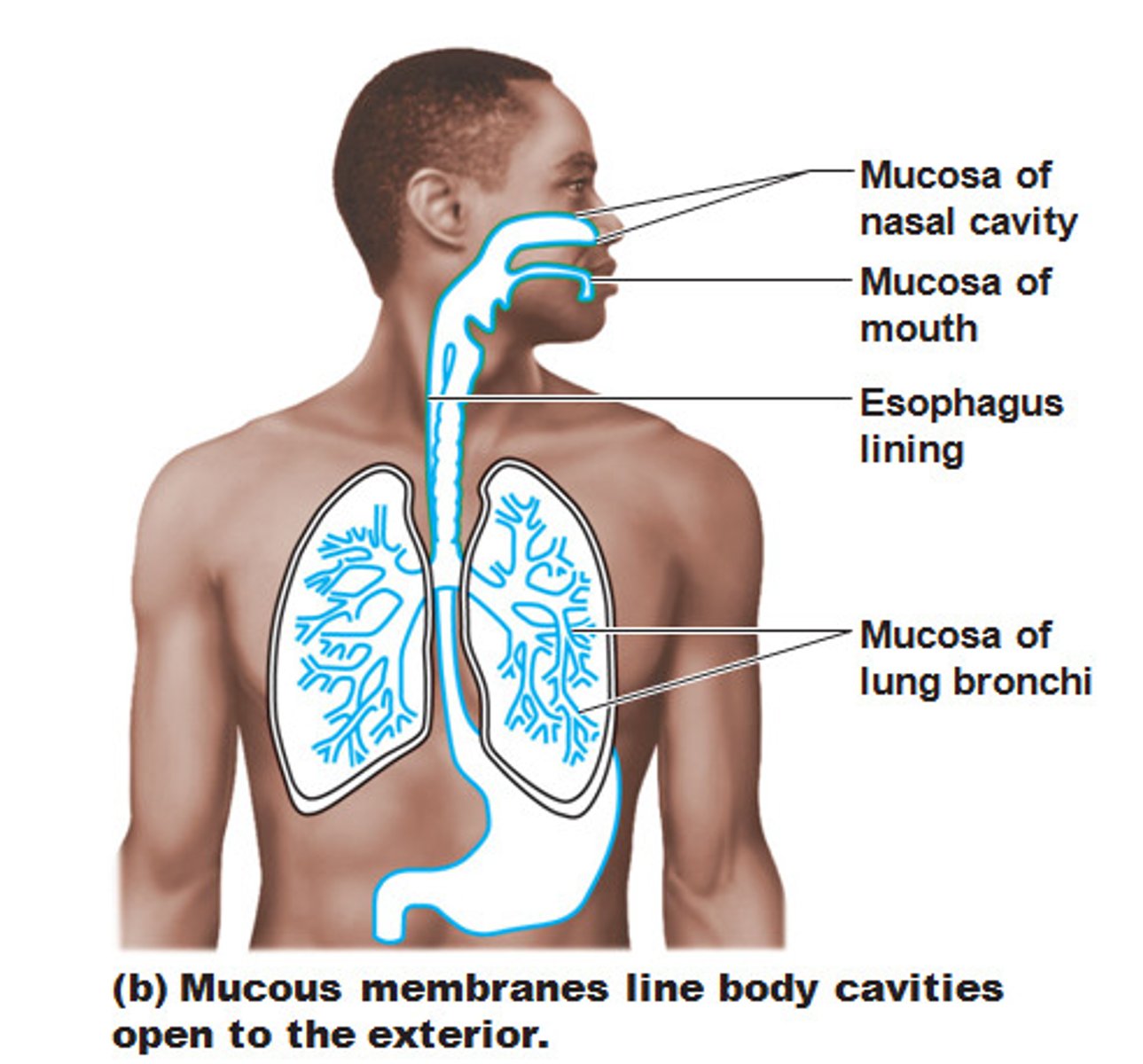
Mucous Membrane (mucosa)
lines all body cavities that open to the exterior;
(hollow organs in the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts);
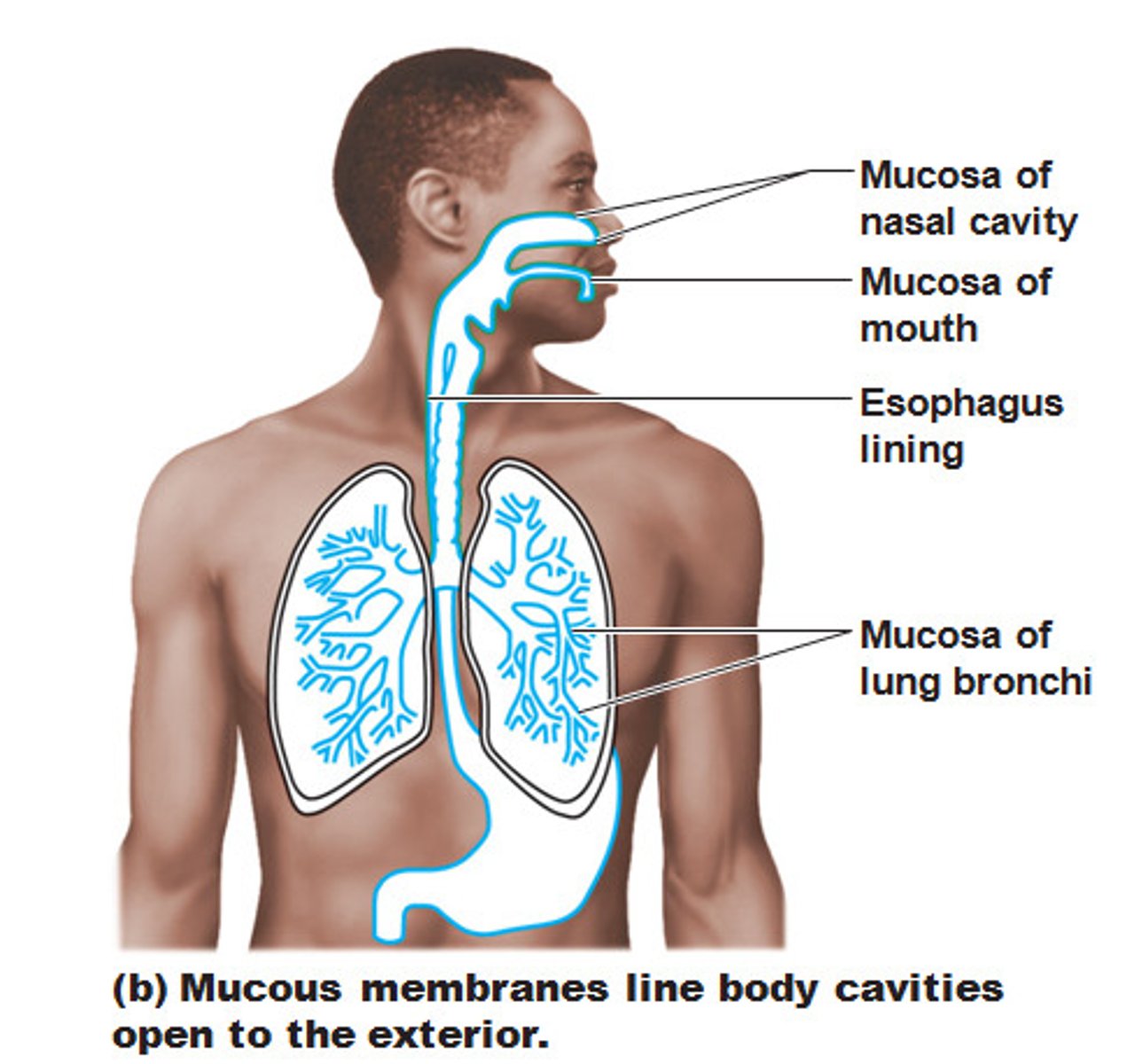
mucous
lubricating fluid in mucous membranes;
reduces friction
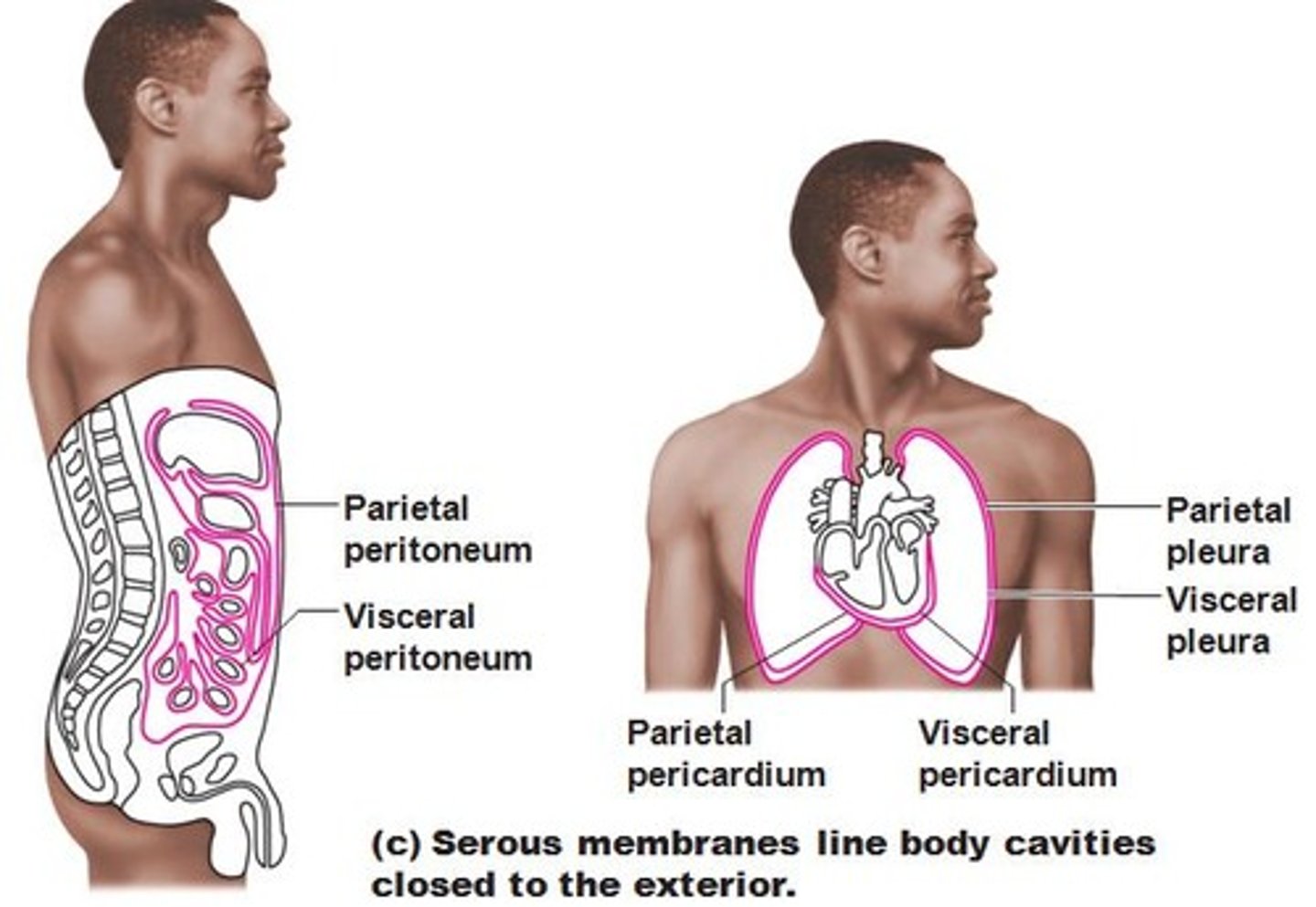
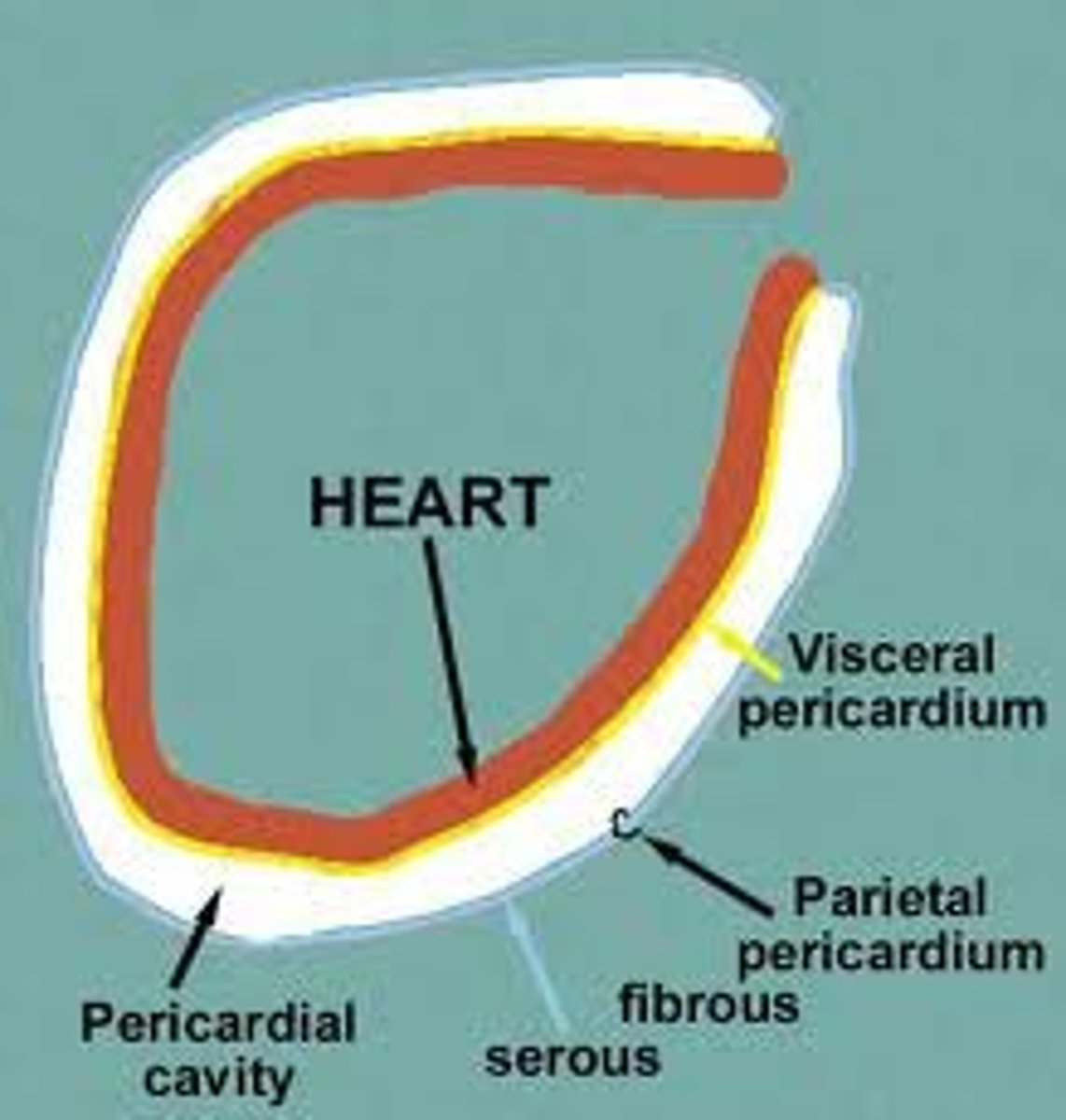
Serous Membranes (serosa)
lines body cavities that are closed to the exterior cavity;
(heart, lungs, digestive organs)
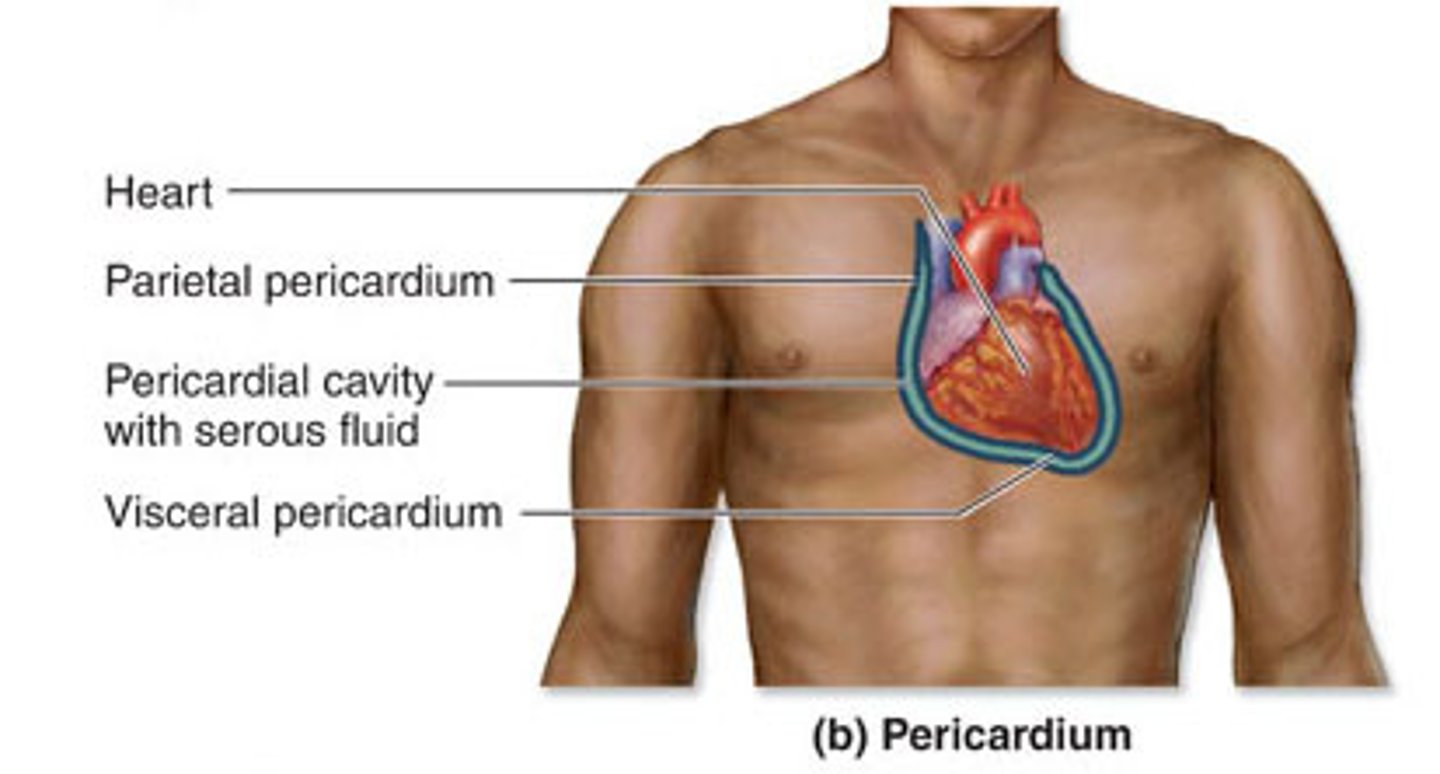
serous fluid
lubricating fluid of serous membranes;
reduces friction;
between the outer parietal serous membrane and the inner visceral membrane
parietal layer and visceral layer
Serous membranes occur in pairs. (2 layers)
parietal--on cavity;
visceral--on organ
parietal layer
Lines a specific portion of the wall of the ventral body cavity.
visceral layer
Layer which covers the outside of the organs in that cavity.
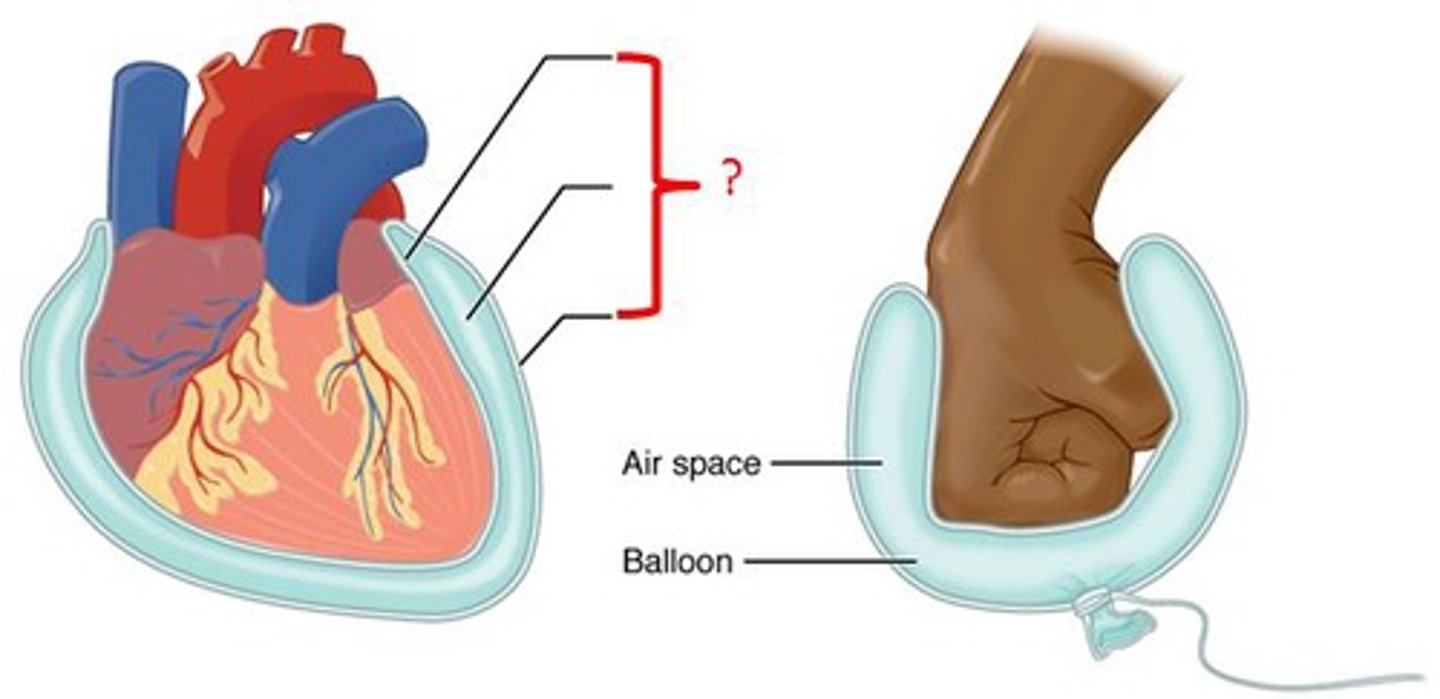
parietal pericardium
lines the pericardial cavity = mediastinum
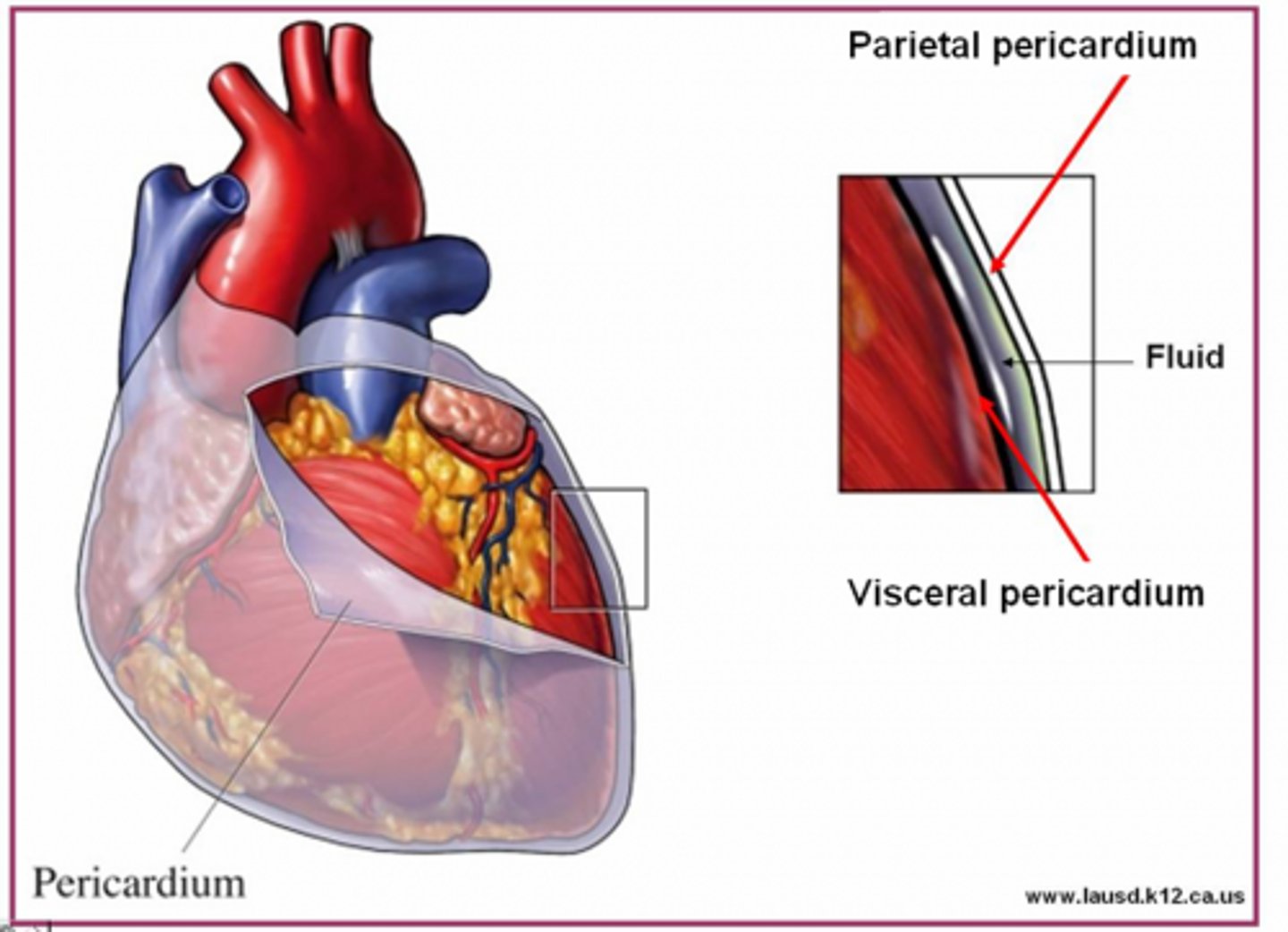
visceral pericardium (epicardium)
covers the heart's outer surface (ON the surface)
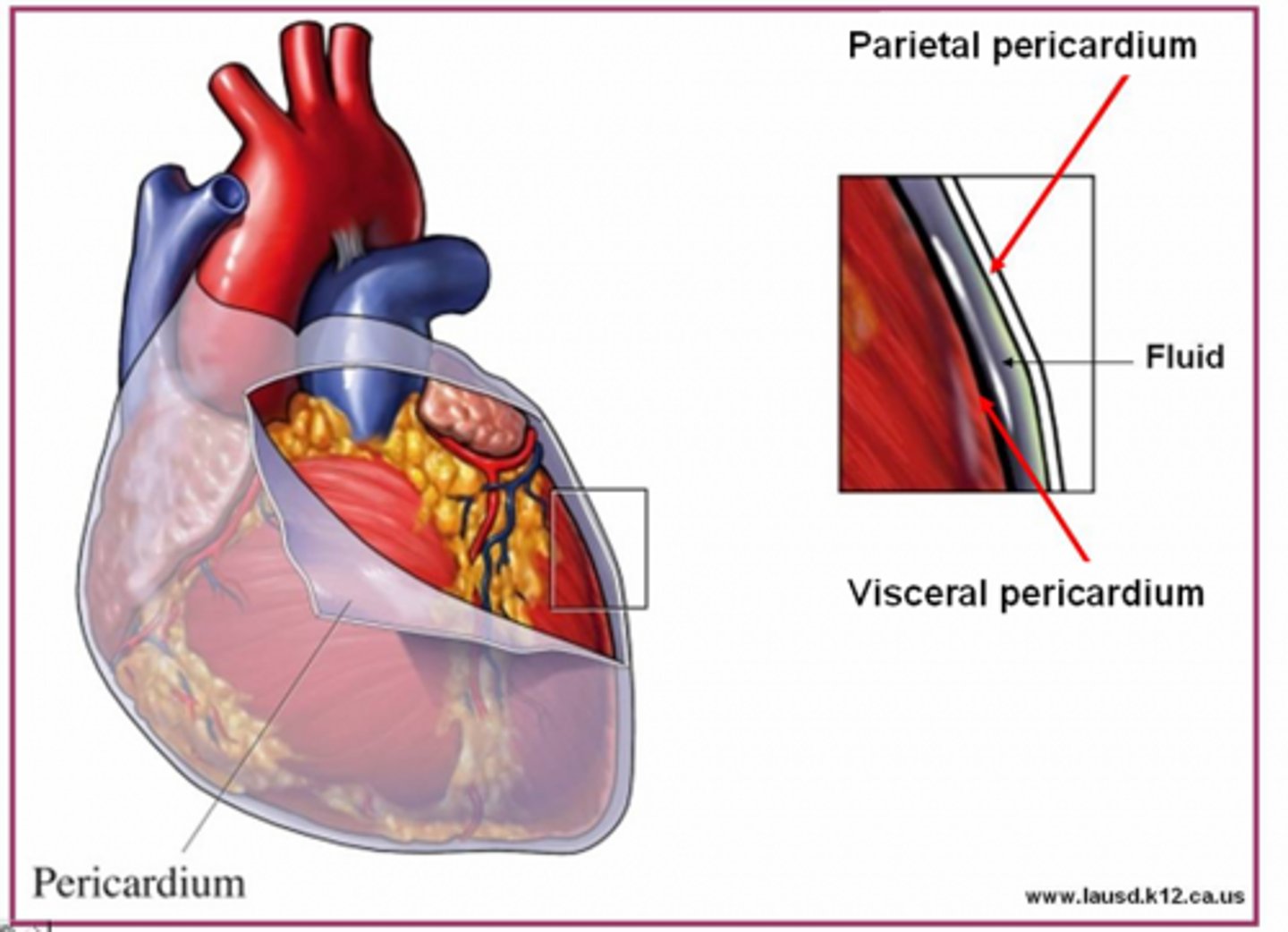
mediastinum
medial cavity that "houses" the heart and everything in the mid-thoracic cavity (NOT the lungs)
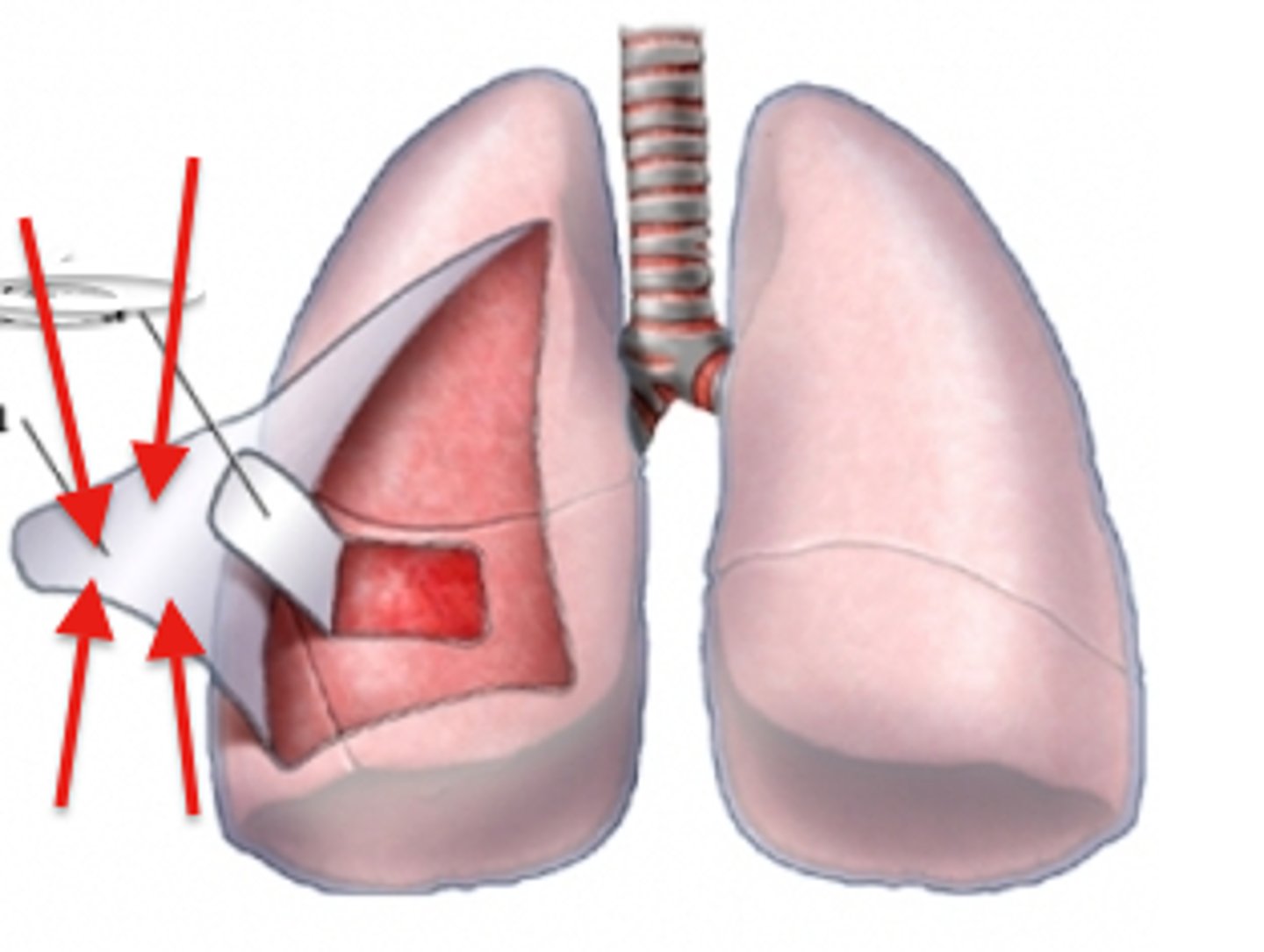
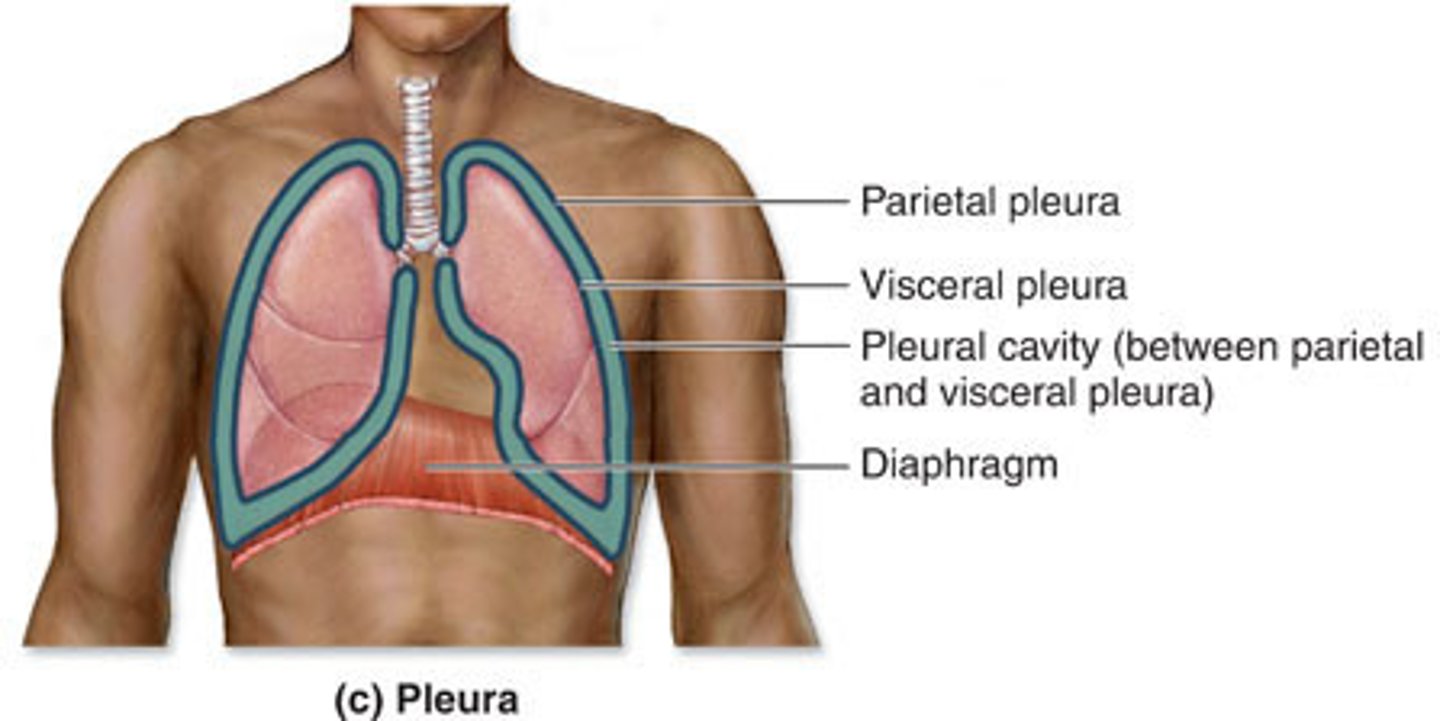
parietal pleura
lines the walls of the thoracic cavity where the lungs are "housed"
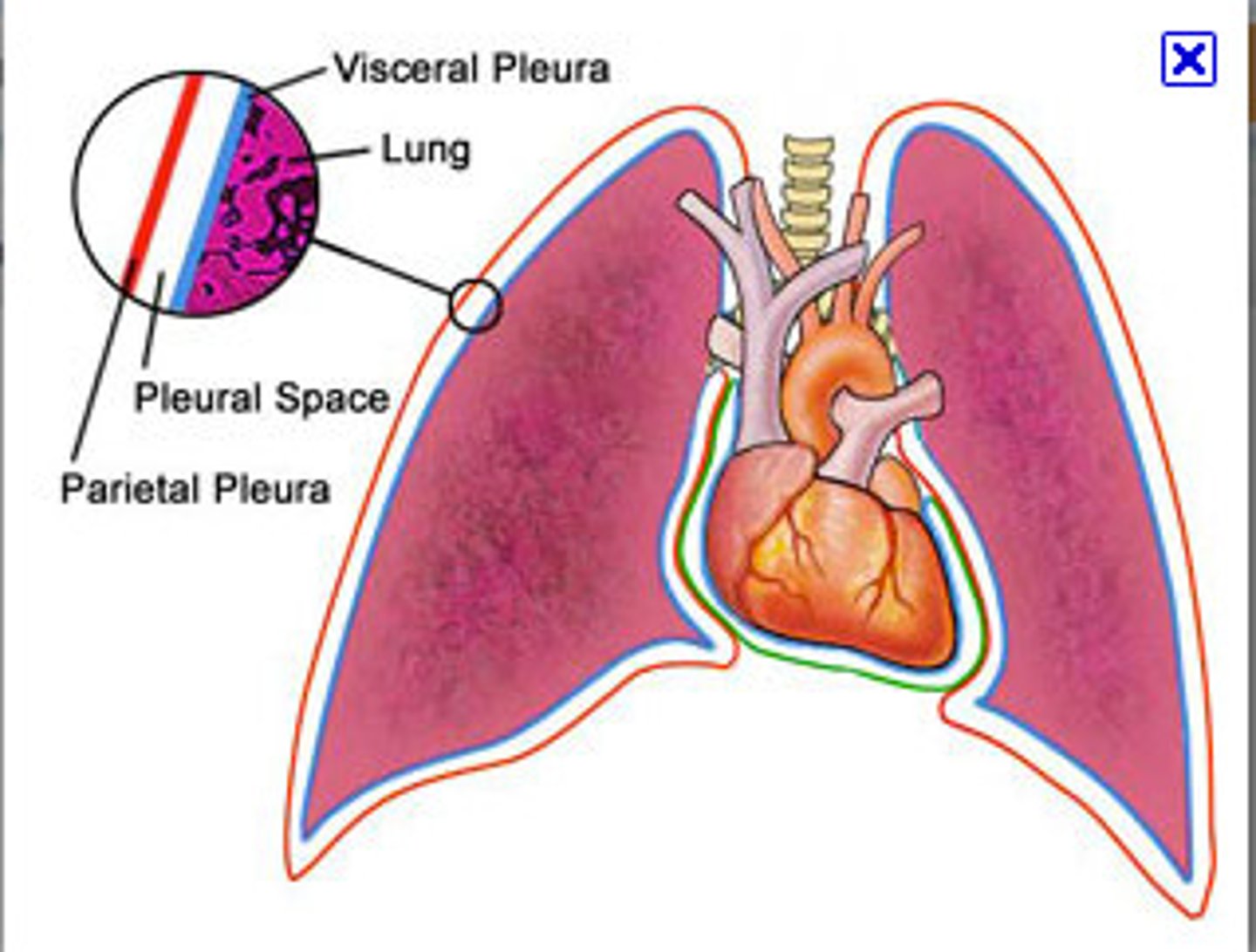
visceral pleura
covers the lungs (ON the lungs)
parietal peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity
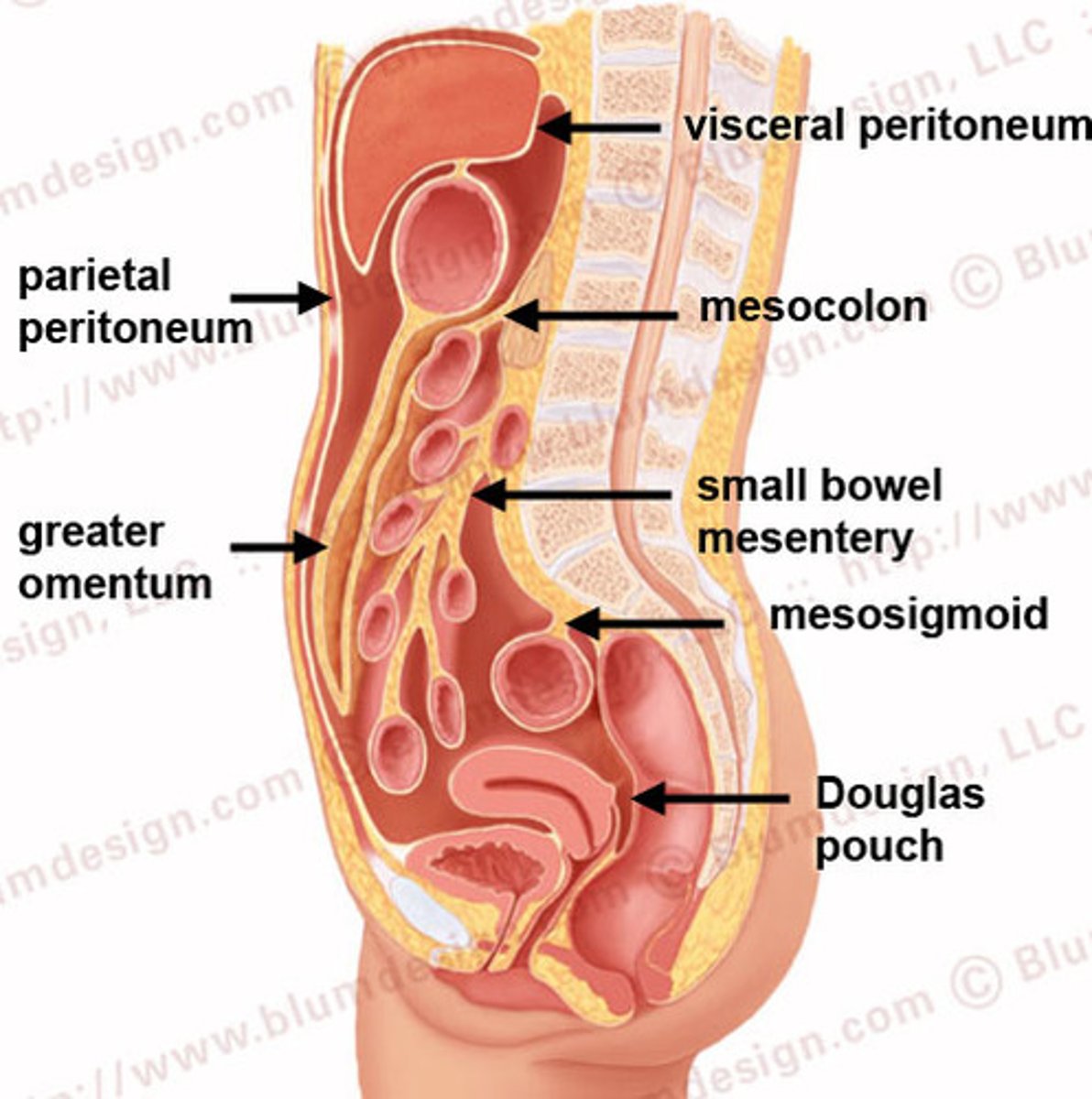
visceral peritoneum
covers abdominal organs (ON the organs)
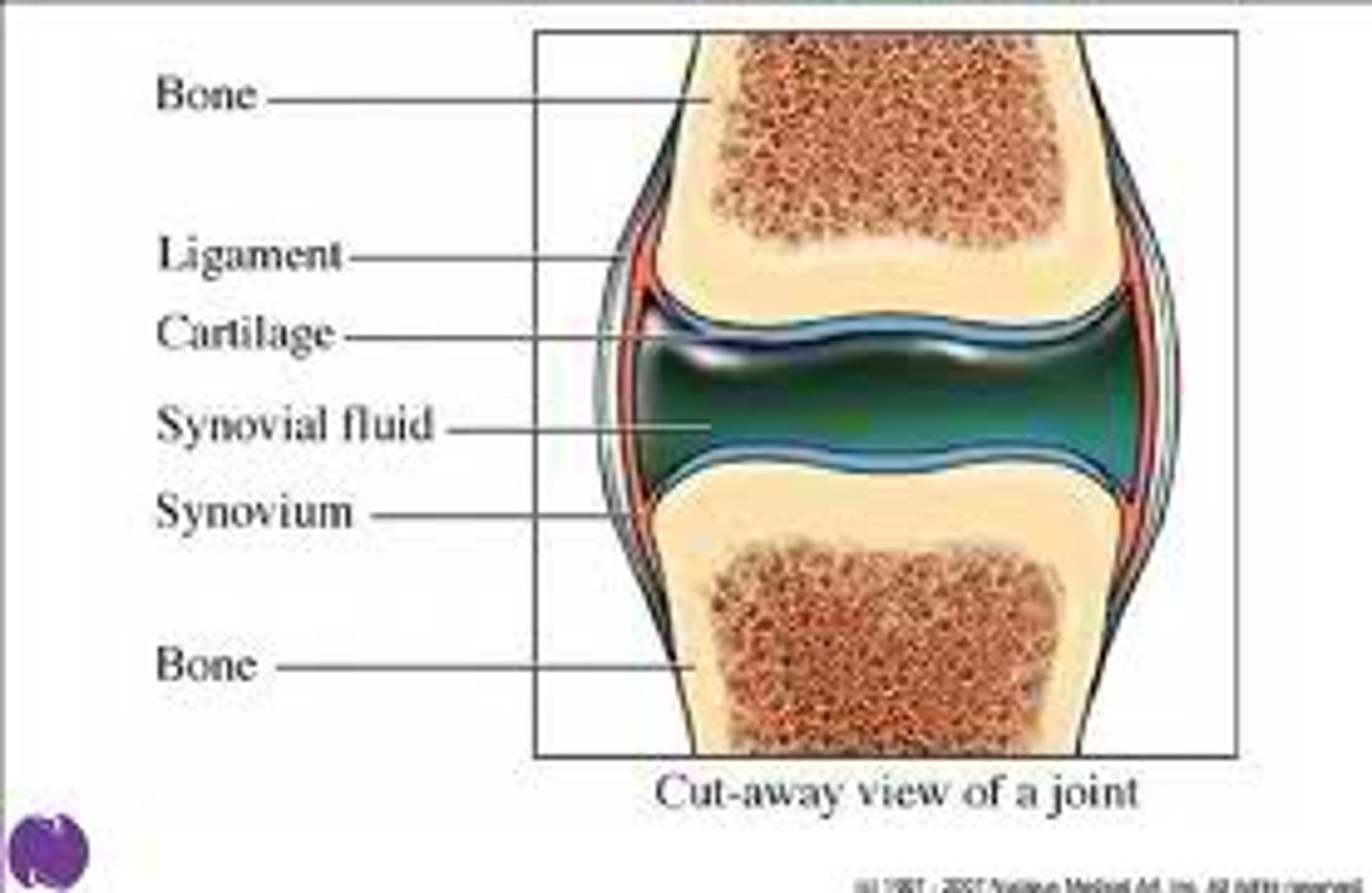
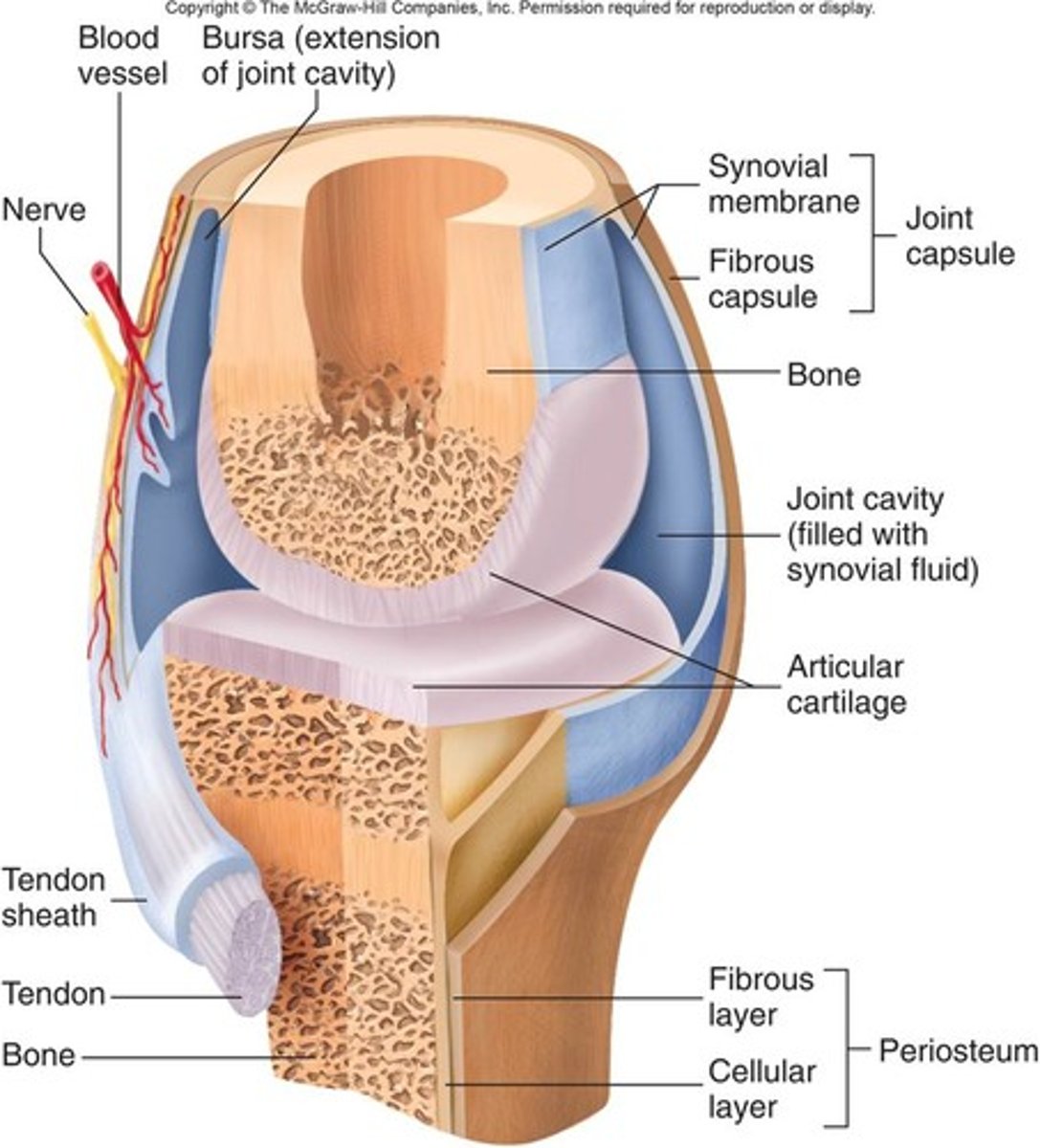
synovial membranes
composed of soft areolar connective tissue;
NO epithelial tissue;
Lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints;
provides lubricating fluid = synovial fluid
Functions of Integumentary System
1. Protection (mechanical (bumps/cuts), chemical (acids/bases), bacterial, UV radiation, thermal (hot/cold), desiccation (drying out);
2. Body Temperature Regulation;
3. Cutaneous Sensation (touch, pressure, pain, temp );
4. Metabolic Functions (Synthesizes (makes) Vitamin D);
5. Blood Reservoir (dermis layer);
6. Excretion (perspiration)
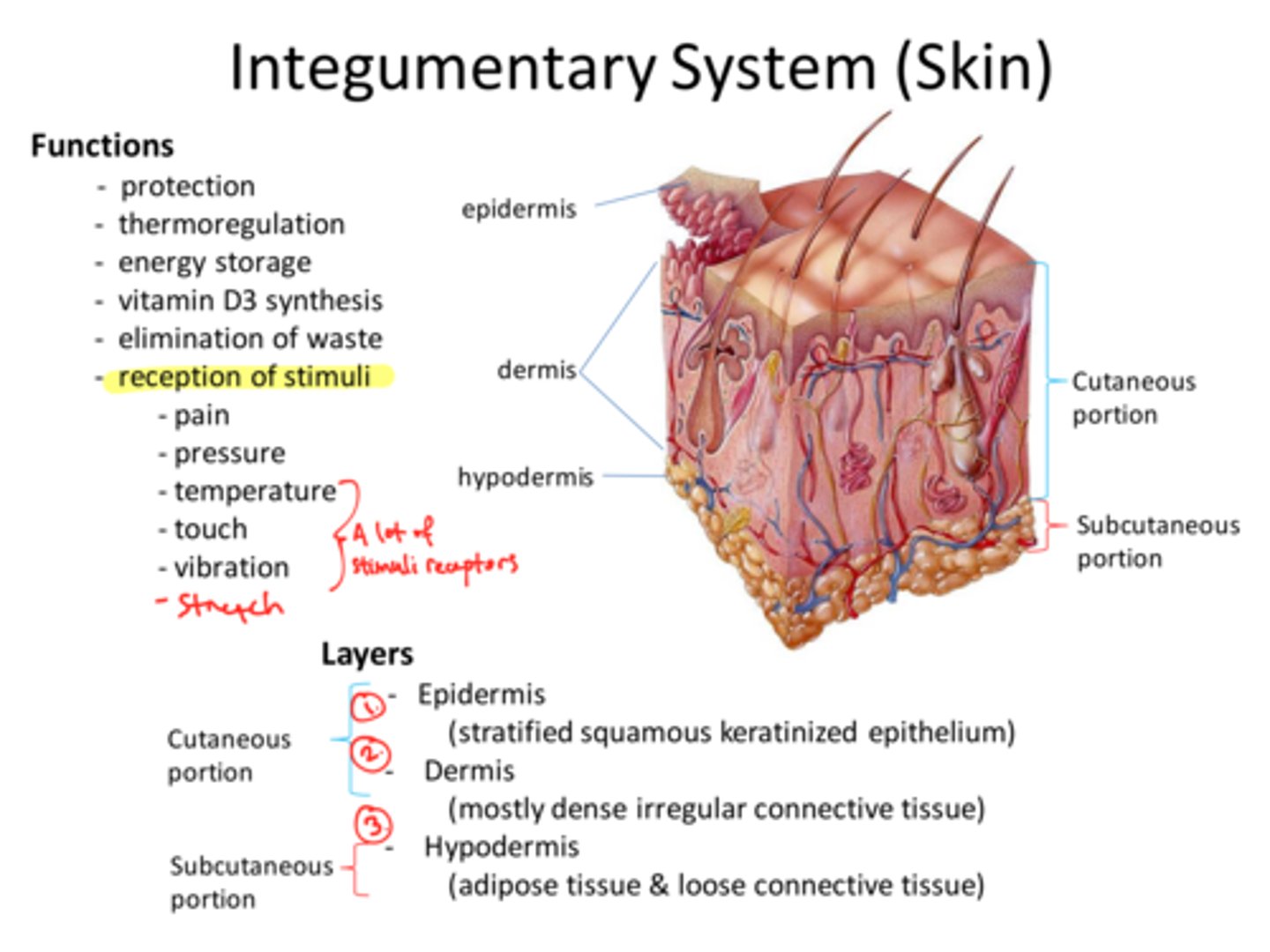
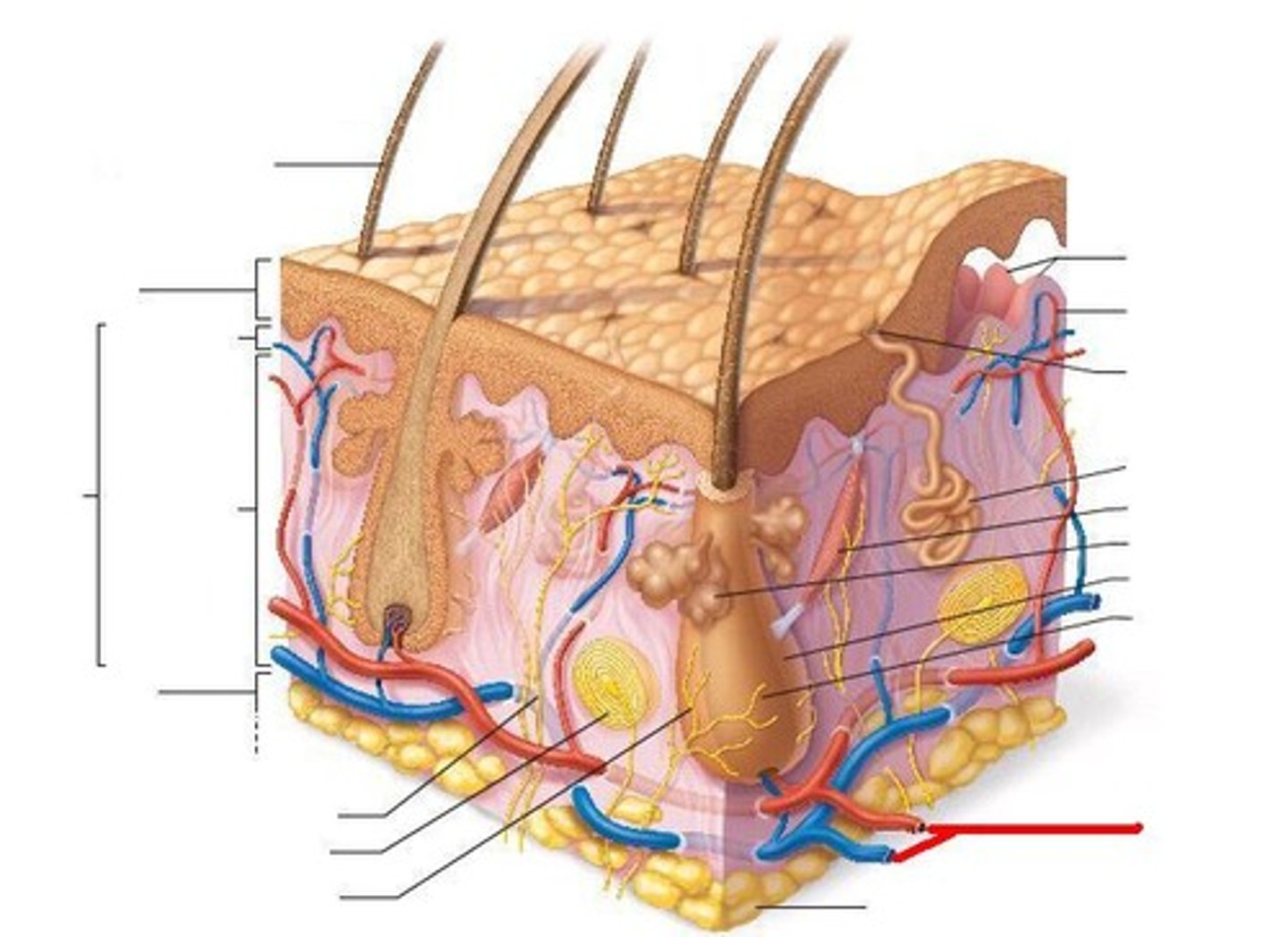
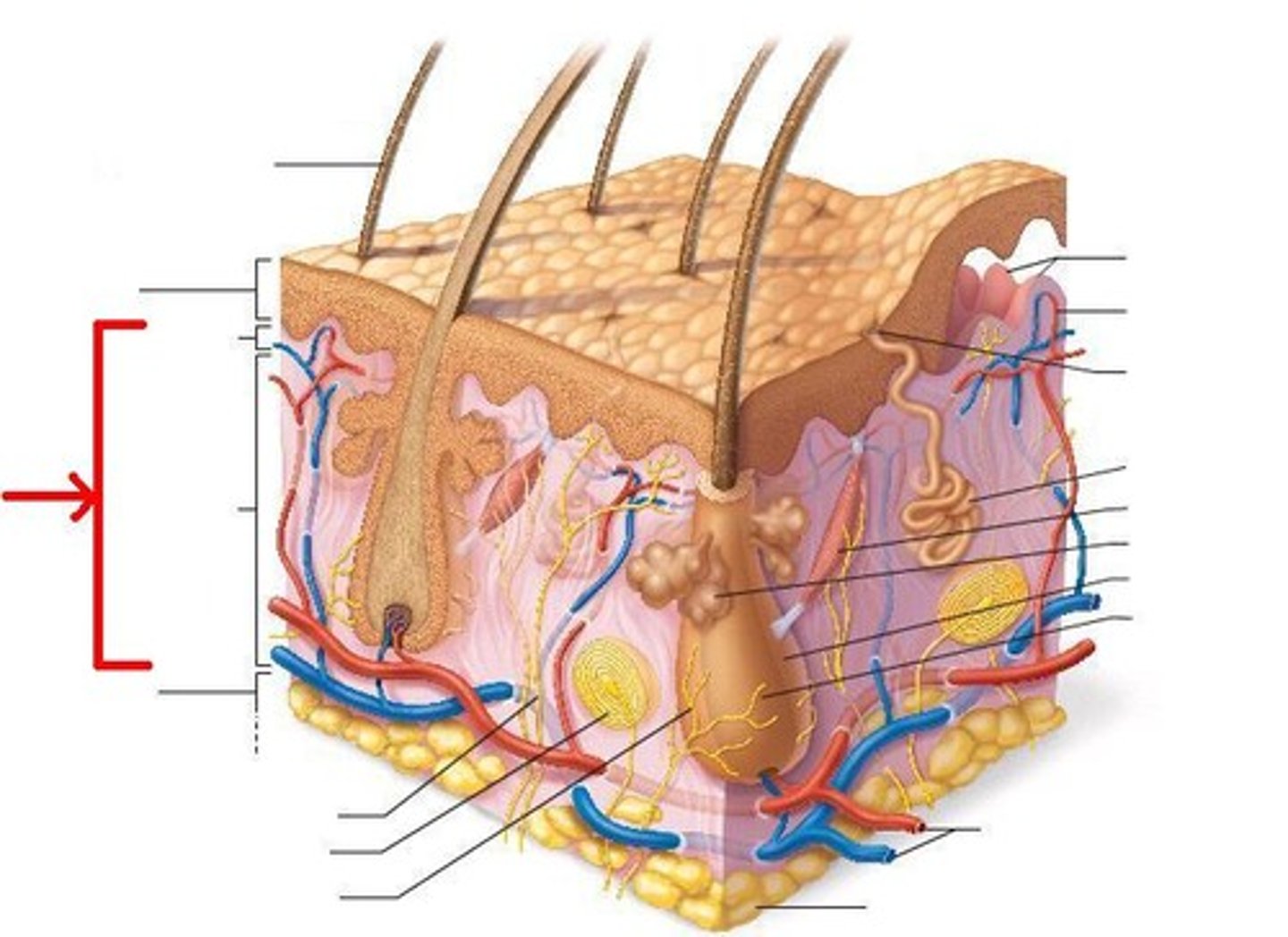
The skin is composed of two layers of tissue:
Epidermis = superficial layer;
Dermis = deep layer
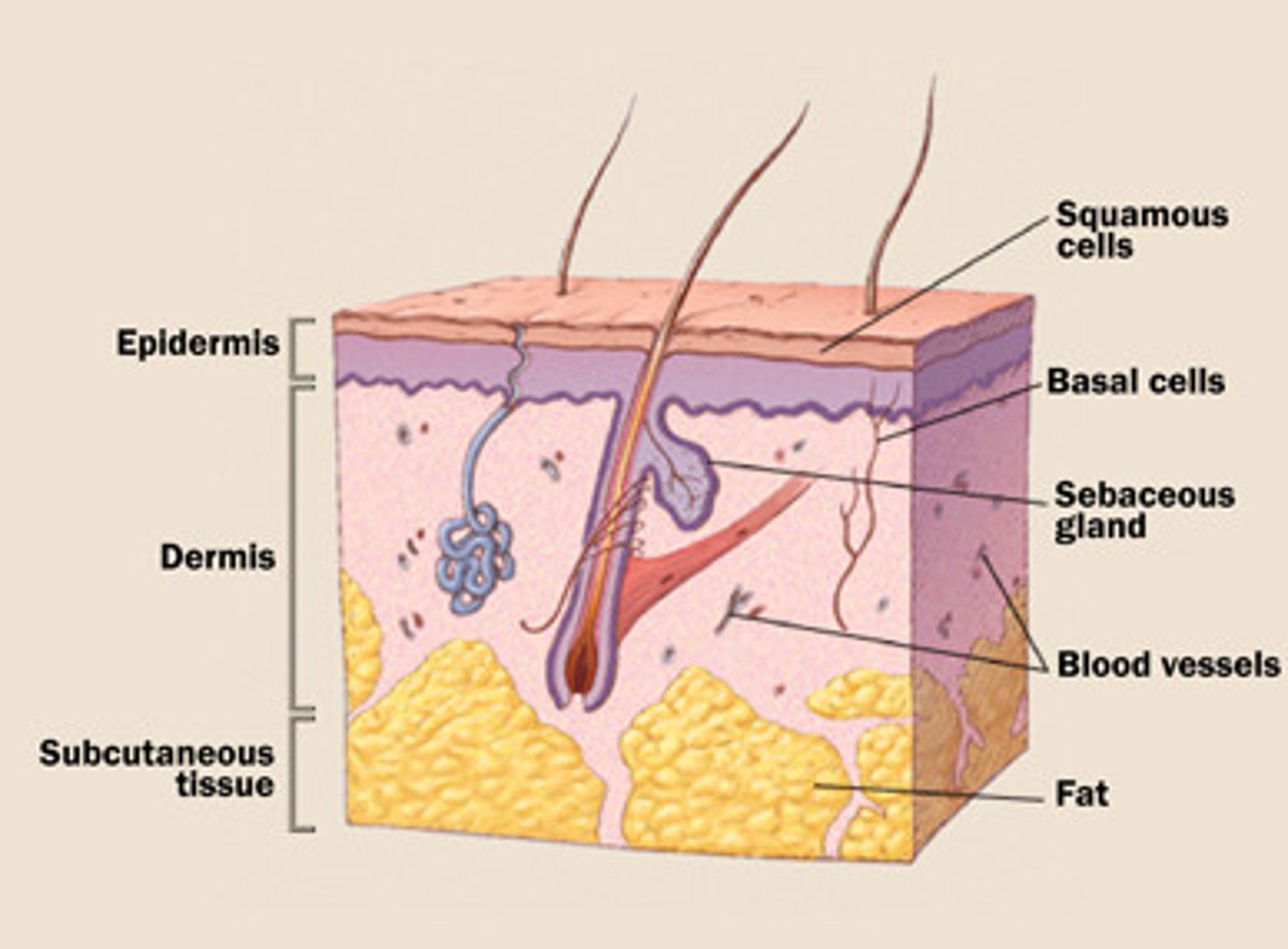
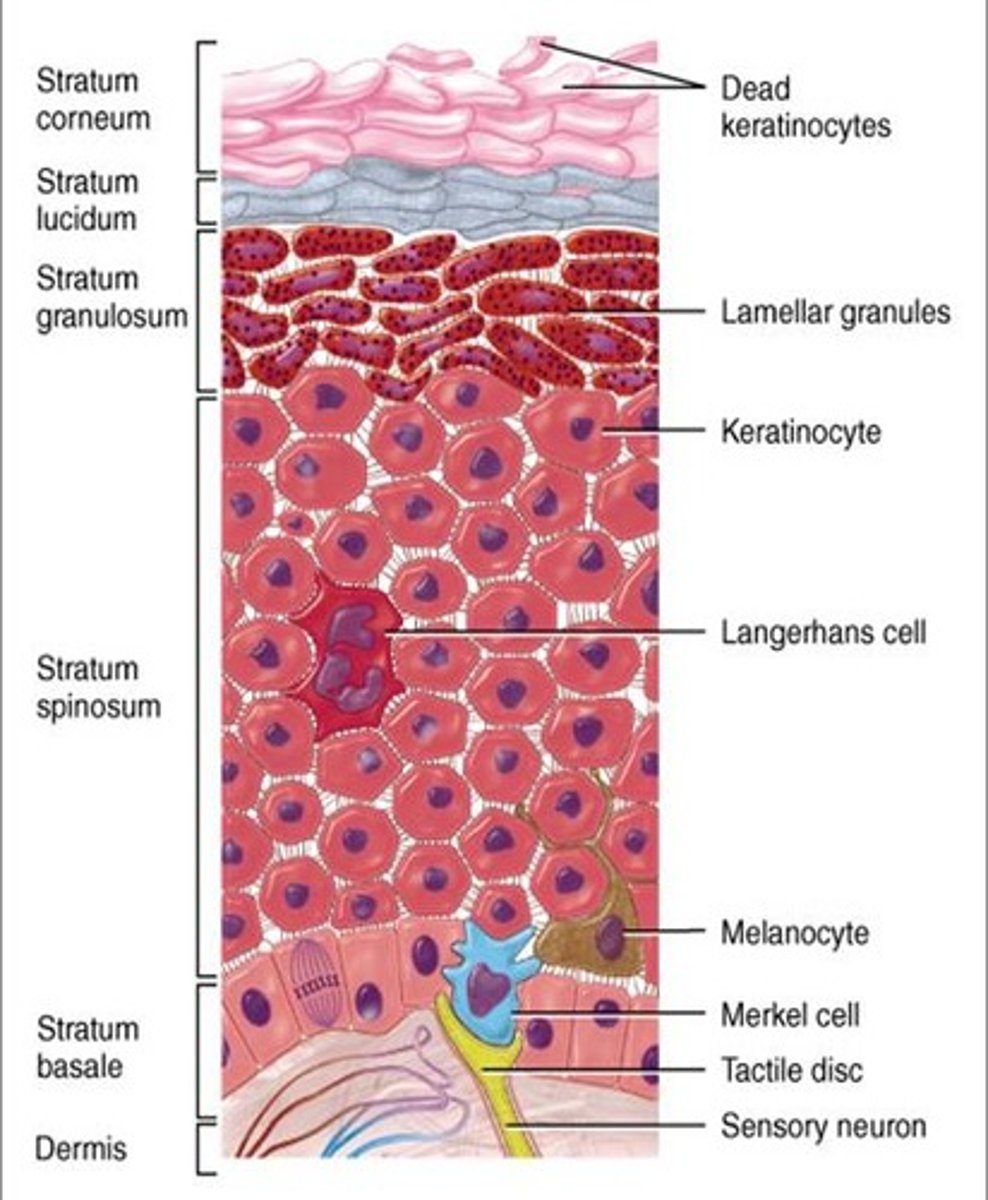
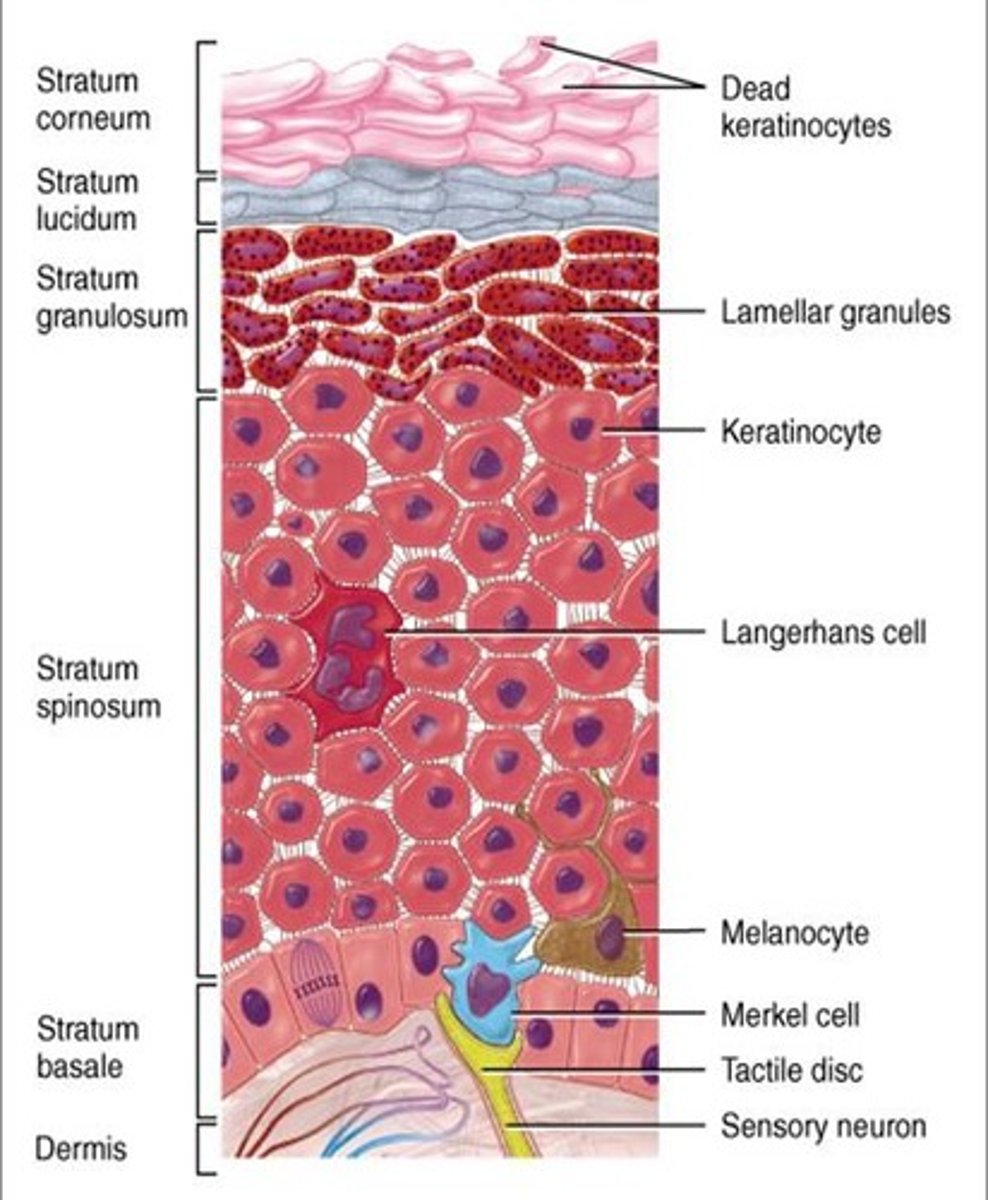
Epidermis
The outer layer;
made up of stratified squamous epithelium;
5 layers in "thick" skin;
4 layers in "thin" skin
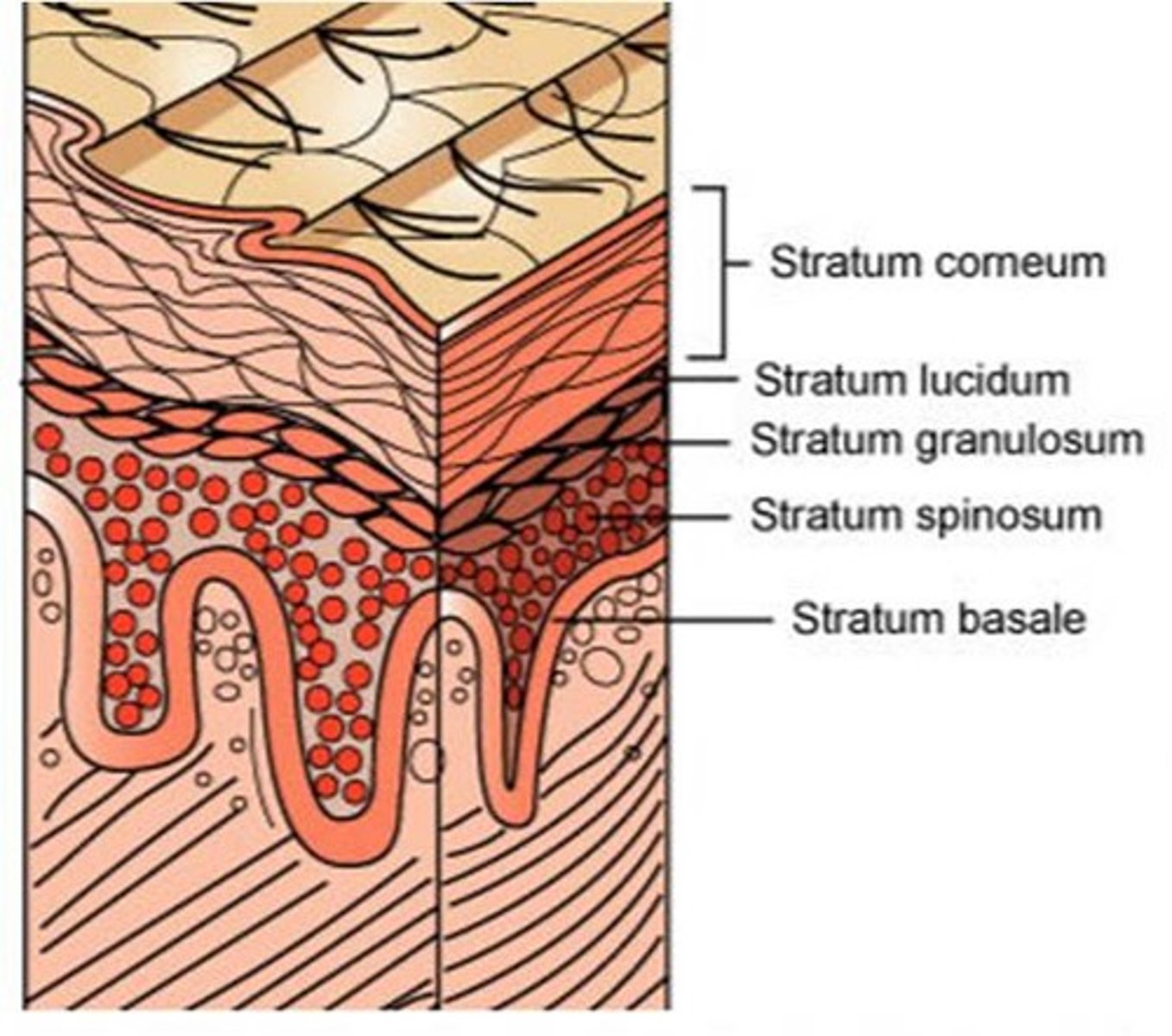
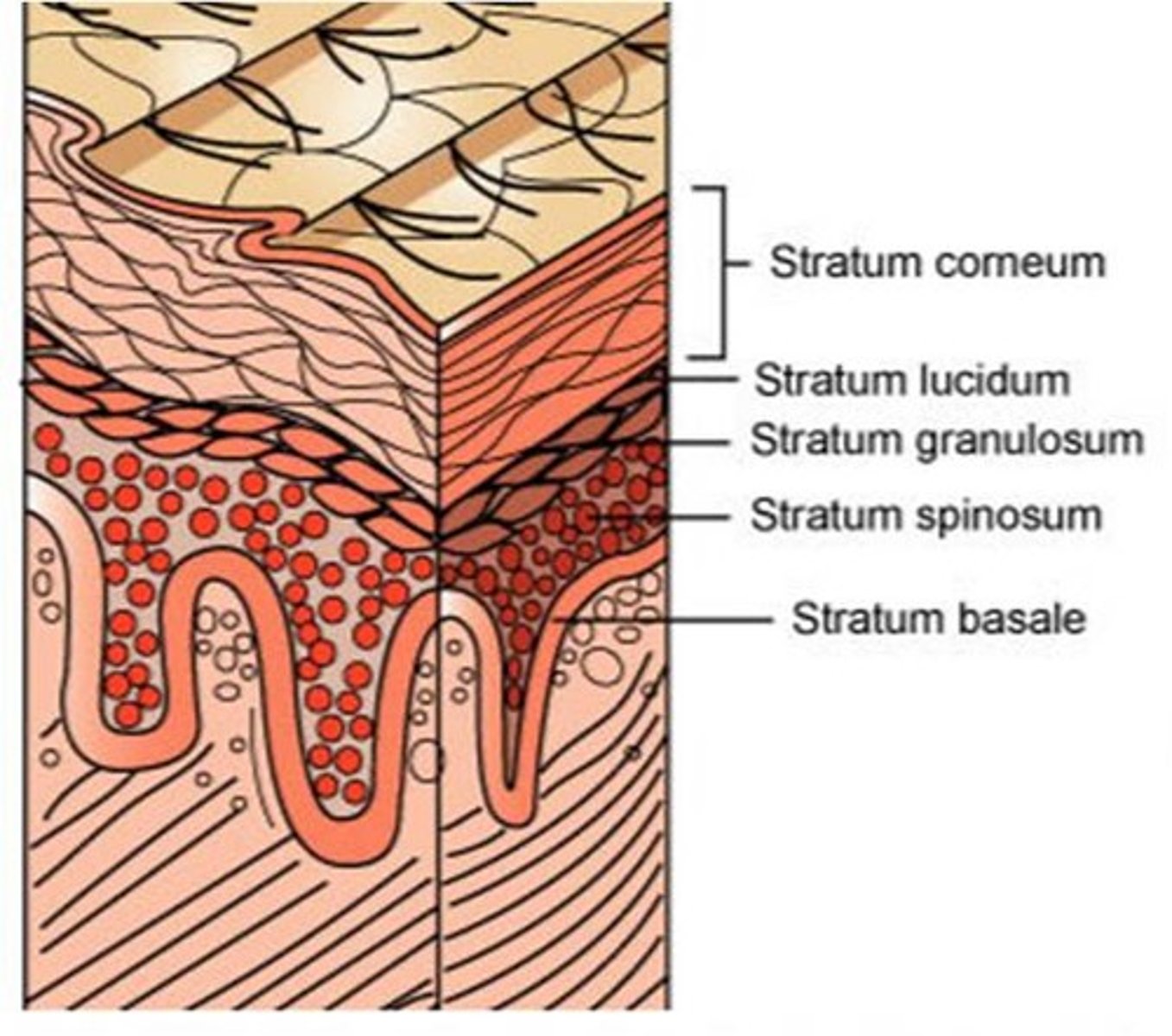
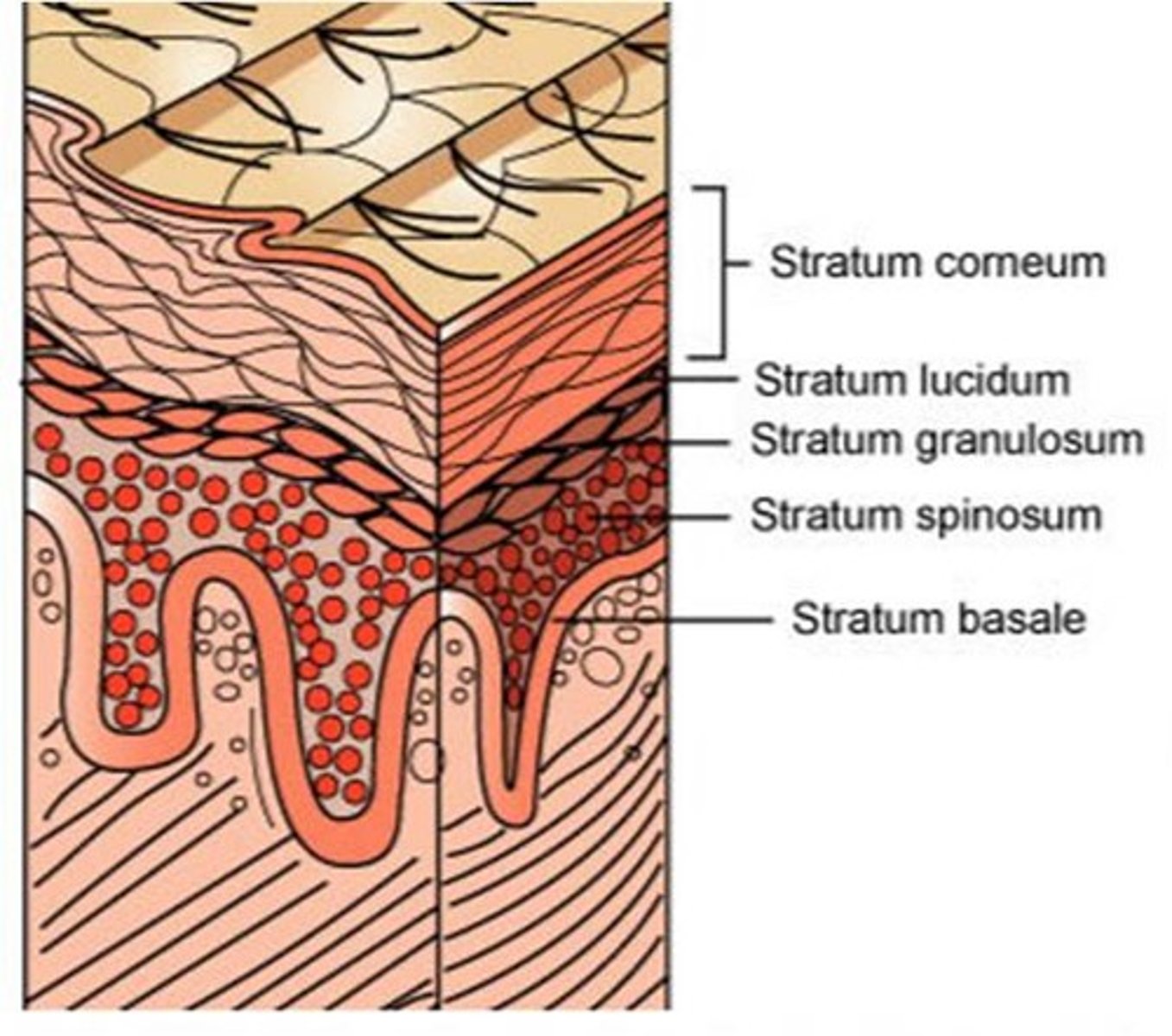
Layers of Epidermis in "thick" skin
From superficial to deep: (palms of hands/soles of feet)
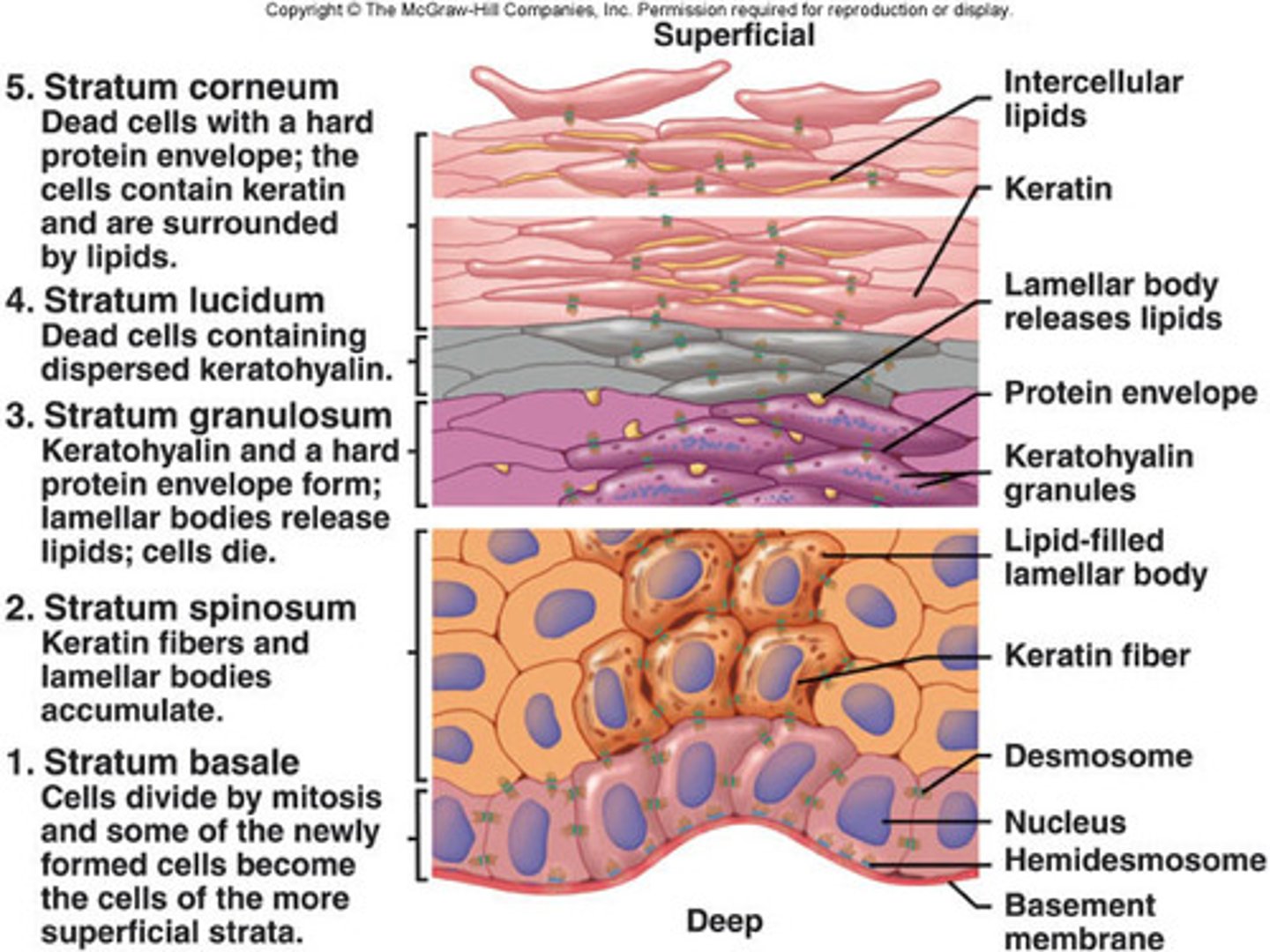
1. stratum corneum,
2. stratum lucidum,
3. stratum granulosum,
4. stratum spinosum,
5. stratum basale (germinativum)
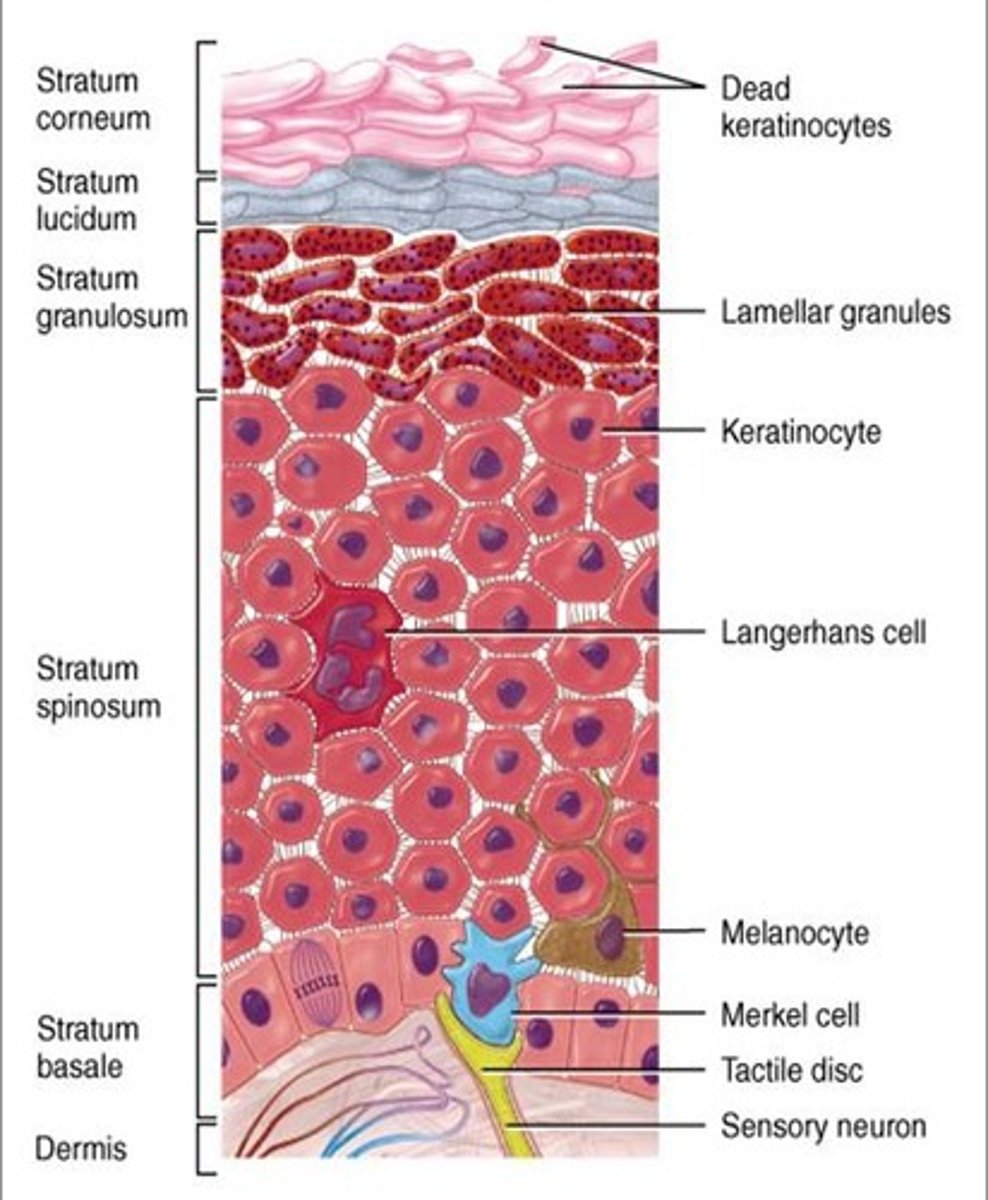
stratum lucidum (clear layer) of the epidermis
found in "thick" skin or hairless skin;
made of dead epithelial cells filled with keratin
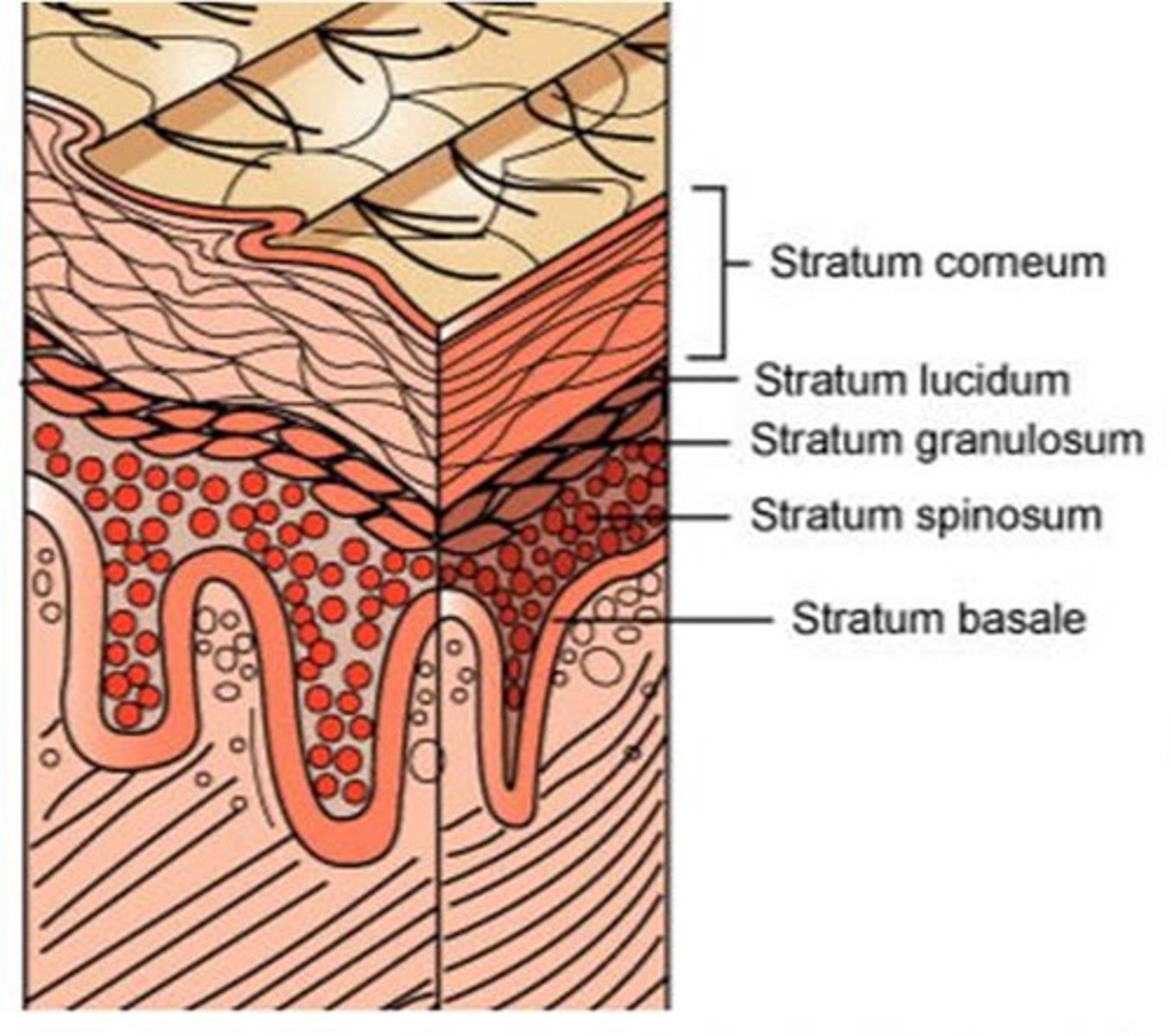
Layers of Epidermis in "thin" skin
From superficial to deep: (does NOT include palms of hands/soles of feet)
1. stratum corneum,
2. stratum granulosum,
3. stratum spinosum,
4. stratum basale (germinativum)
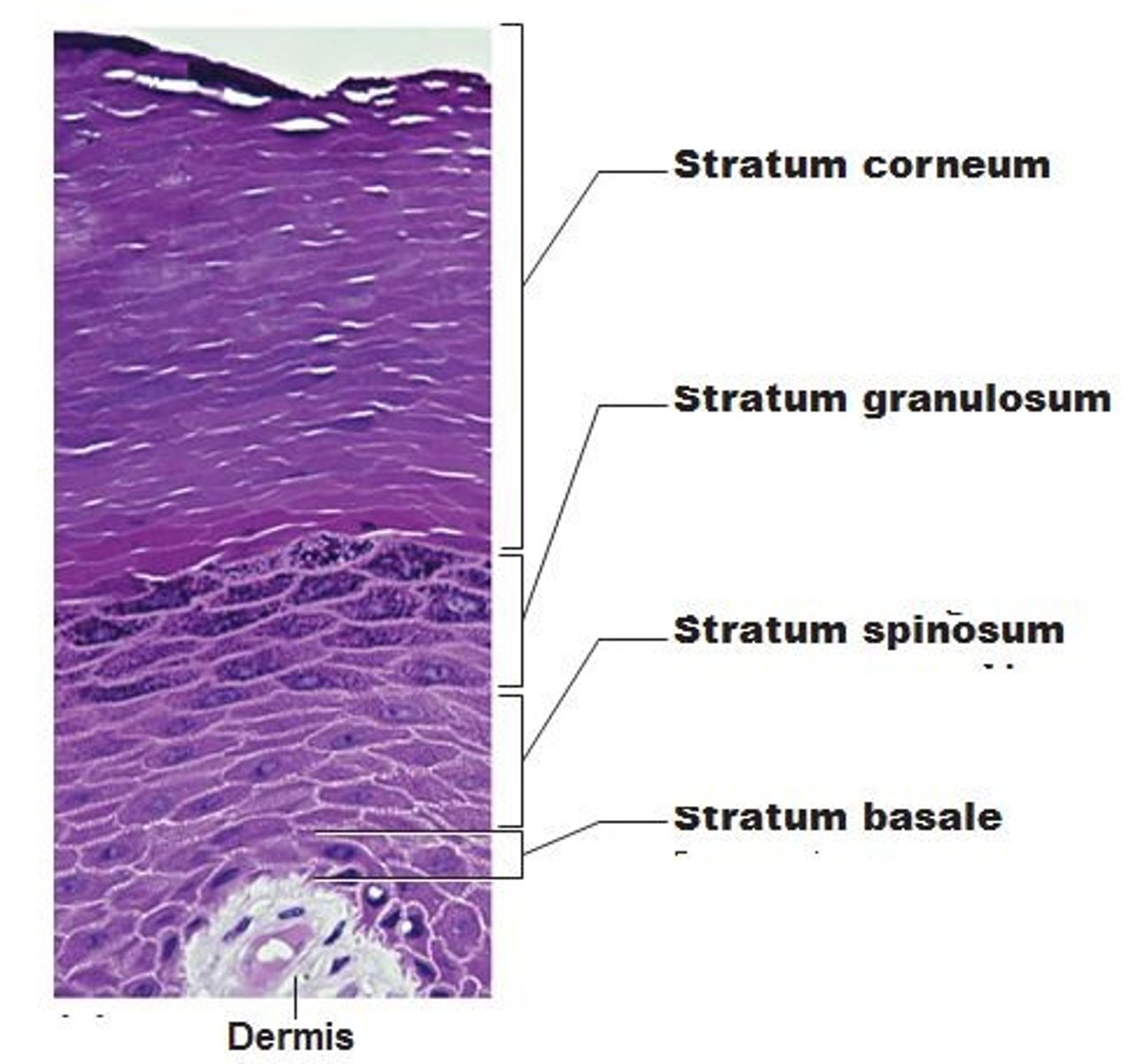
stratum granulosum of the epidermis
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata (layer) and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
stratum spinosum of the epidermis
The spiny layer just above the stratum basale (germinativum) layer.
stratum basale (stratum germinativum) of the epidermis
- deepest layer of epidermis
- lies next to dermis
- cells undergoing mitosis
- daughter cells are pushed upward to become the more superficial layers
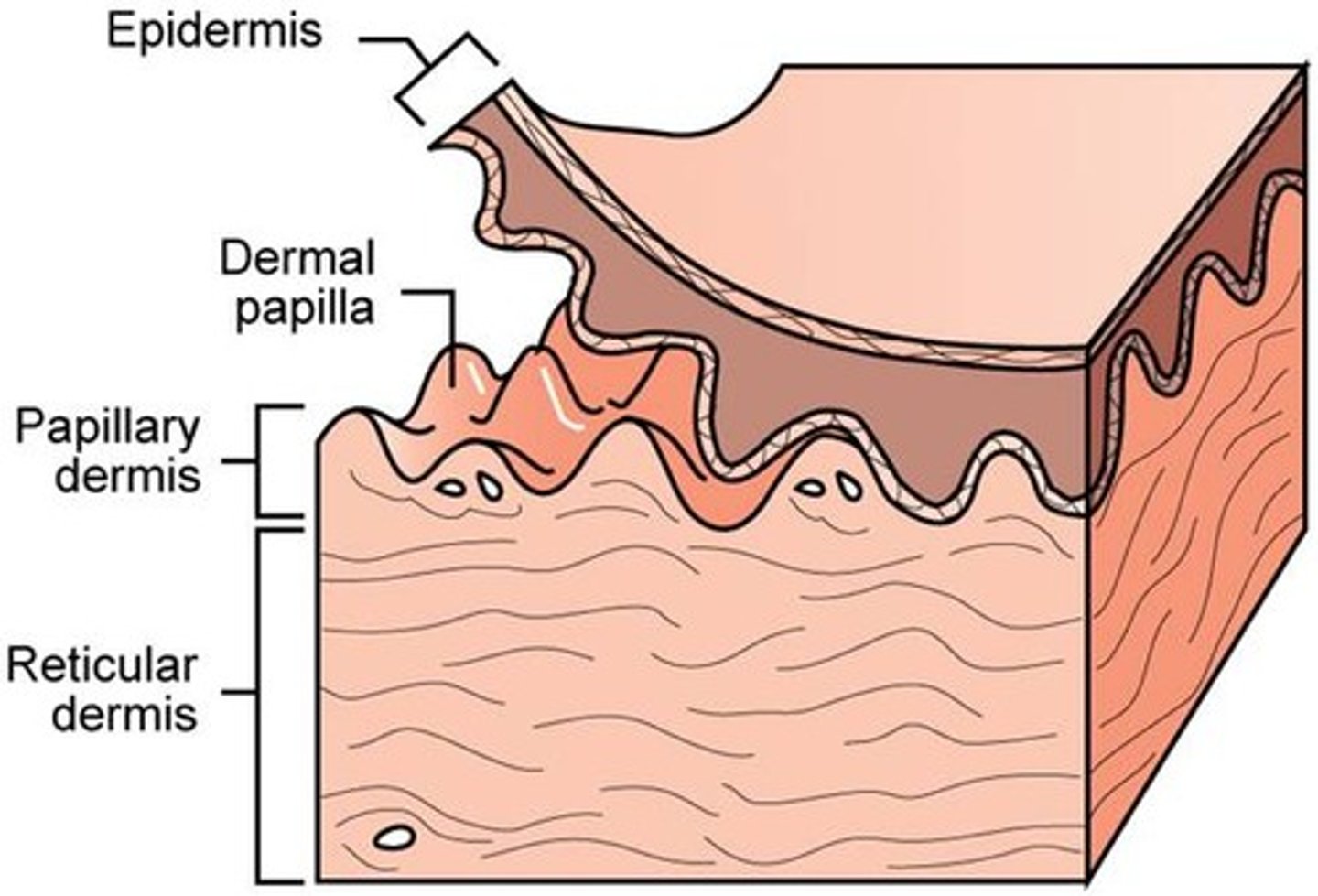
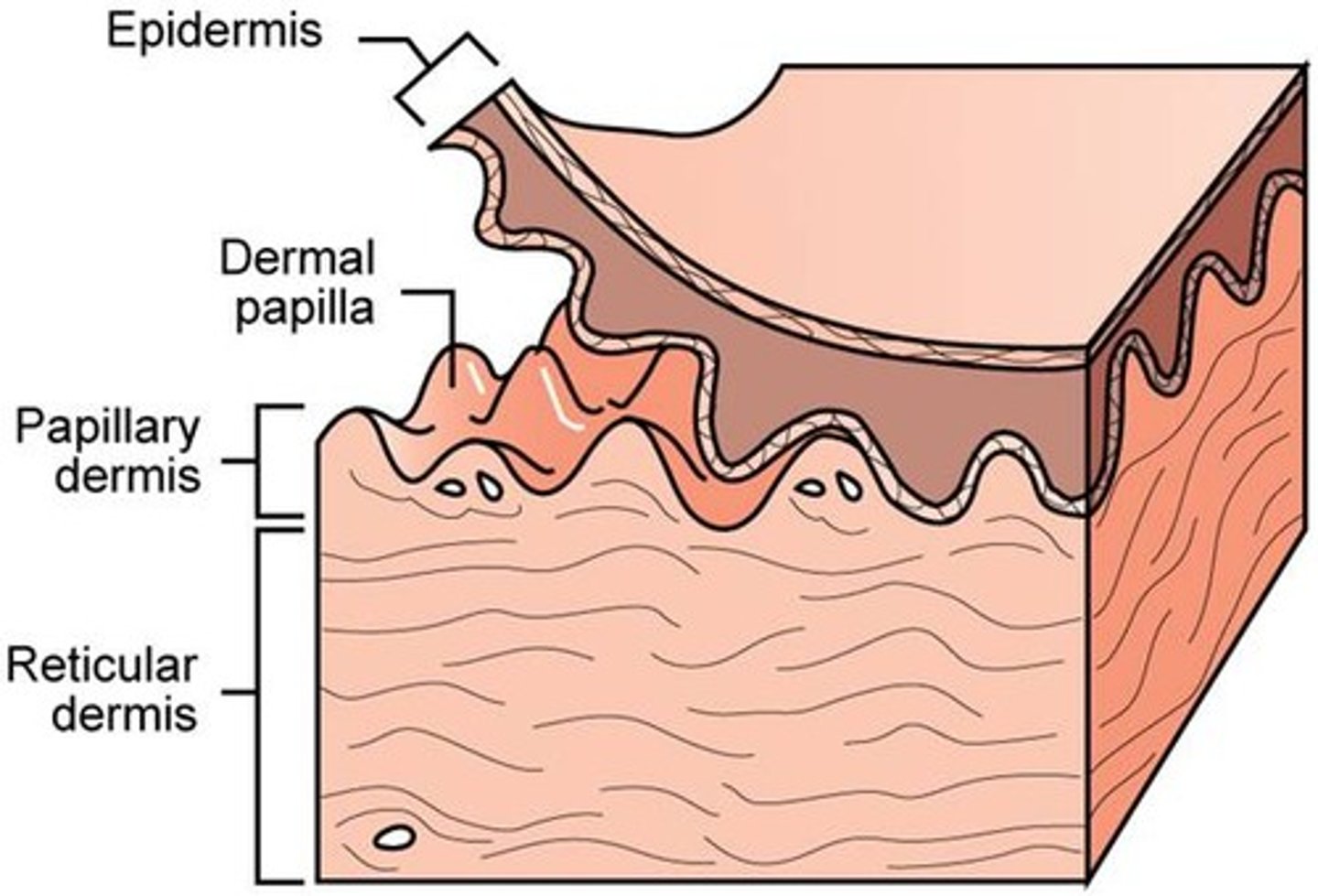
Dermis
Made of 2 layers:
1. papillary layer--upper dermal region
2. reticular layer--lower dermal region
Contains the appendages of the skin and blood vessels
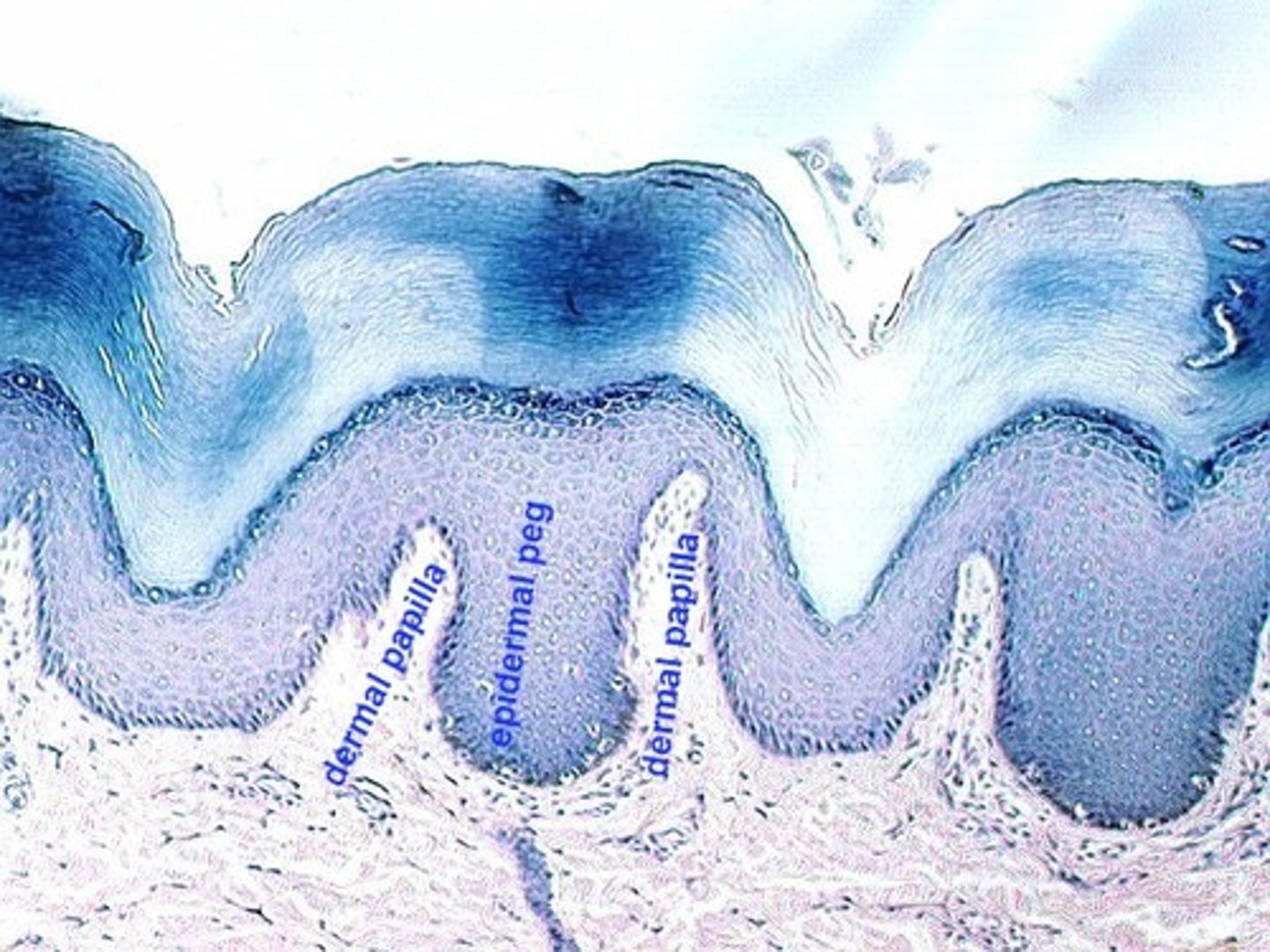
papillary layer of the dermis
upper layer of the dermis;
forms dermal papillae (fingerprints)
dermal papillae
Found in the upper layer of the dermis (papillary layer), they create your fingerprint pattern
reticular layer of the dermis
lower dermal region;
contains blood vessels, sweat and oil glands, and deep pressure receptors
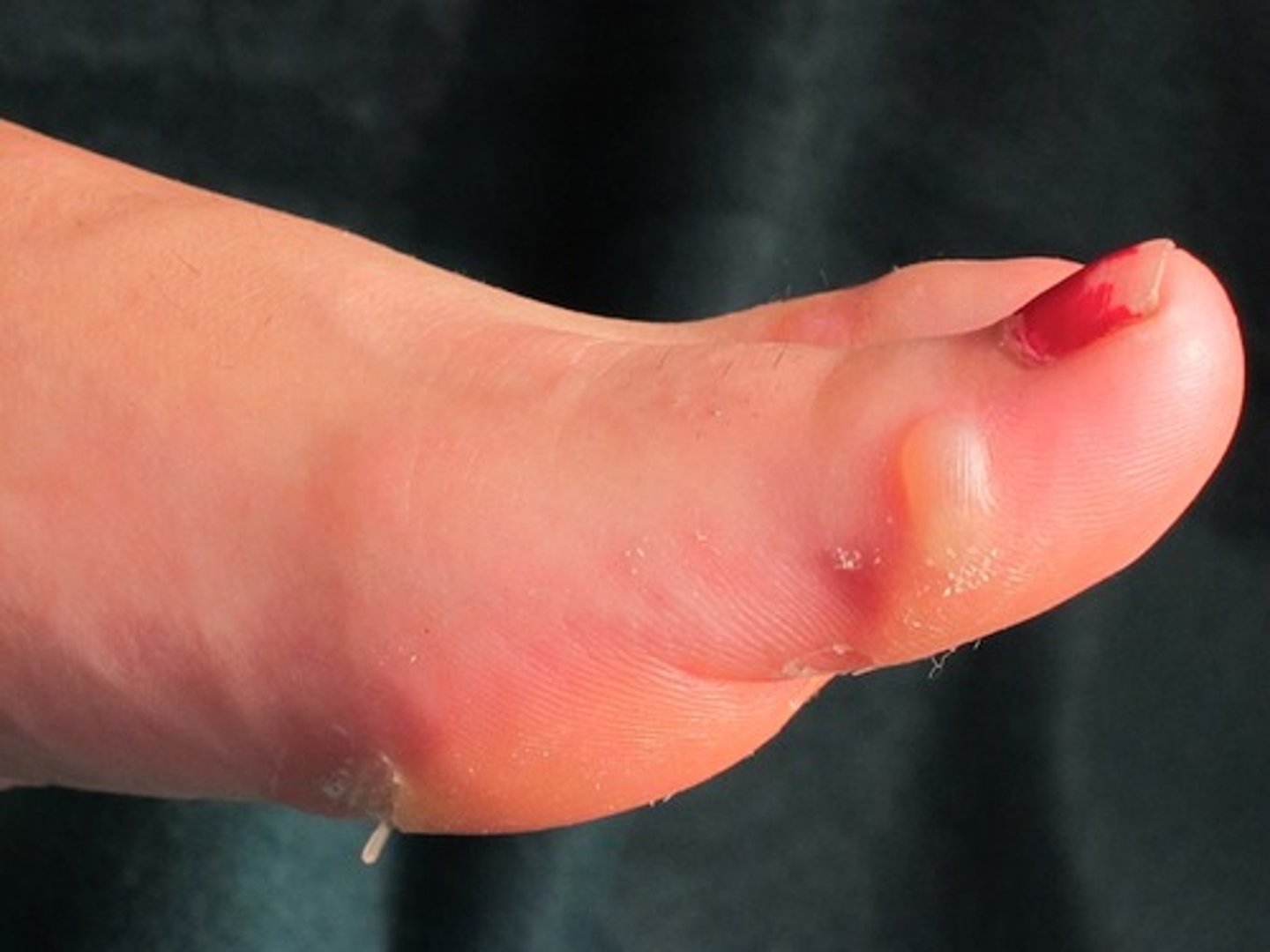
blister
A burn or friction (such as rubbing of a poorly fitting shoe) may cause the epithelial layers to separate or the epidermis and dermis to separate; fluid accumulates between the layers
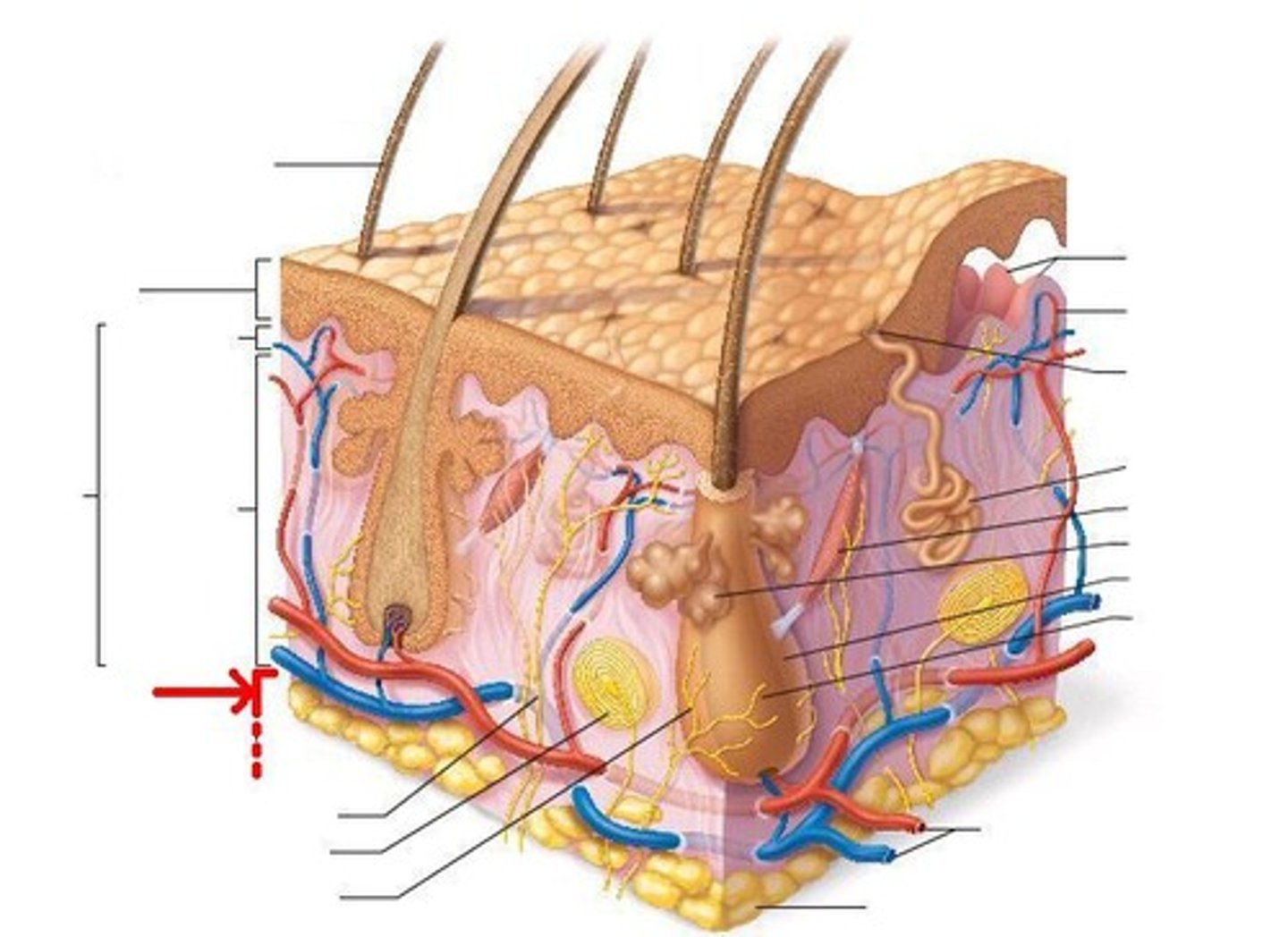
Subcutaneous Membrane or Hypodermis
Deep to the dermis;
mostly adipose tissue (fat storage--lipids);
anchors to underlying organs (such as muscles)
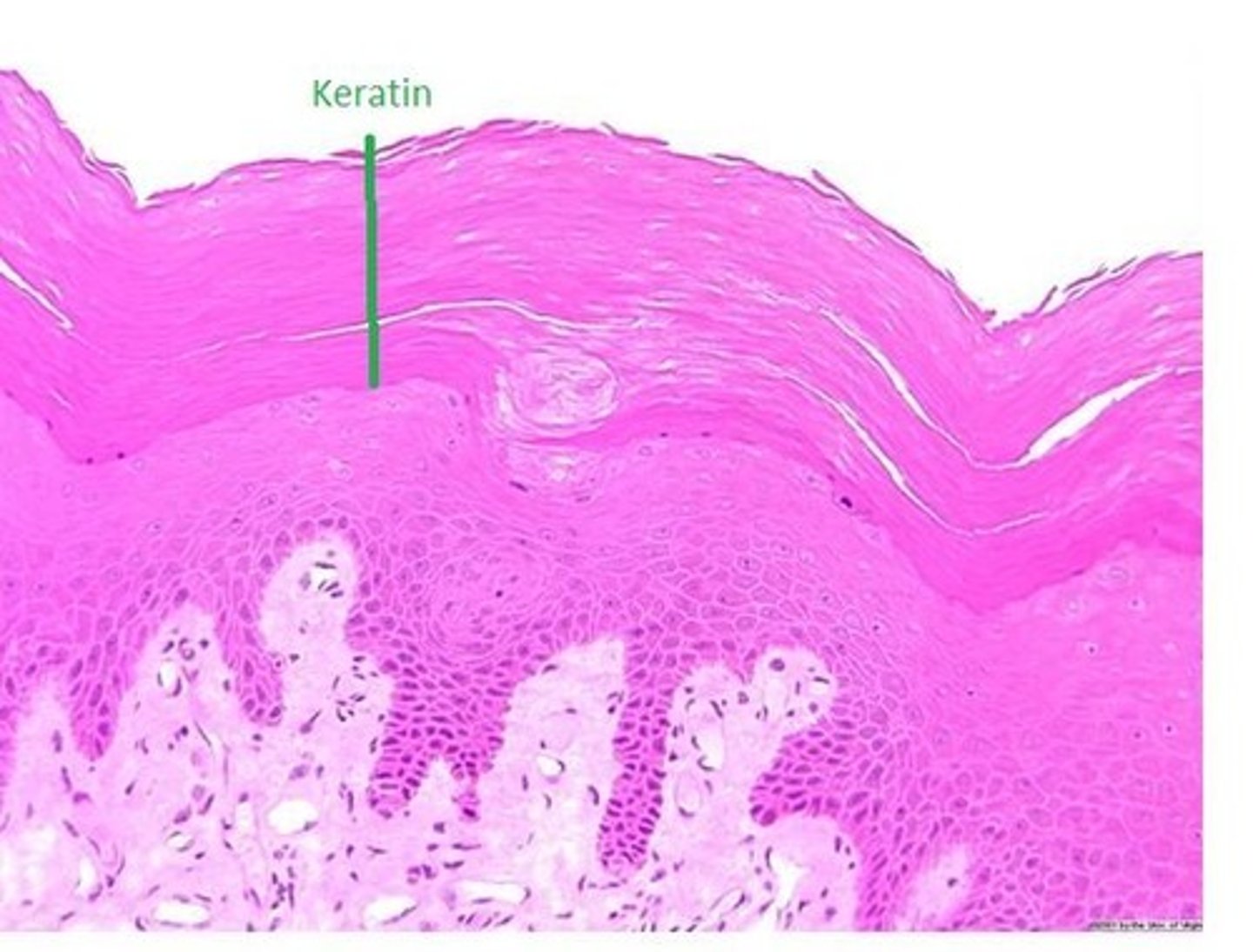
stratum corneum (horny layer of epidermis)
superficial layer of epidermis;
20 to 40 cell layers of dead, flat keratinized cells, accounts for up to 3/4s of epidermal thickness.
Functions: Protects from abrasion and penetration, Waterproofs, Barrier against biological, chemical, and physical assaults
Fibers found throughout the Dermis
collagen fibers--toughness of dermis; attract water molecules to keep skin hydrated;
elastic fibers--gives skin elasticity (while young)
Avascular
has NO BLOOD supply; EX. Epidermis
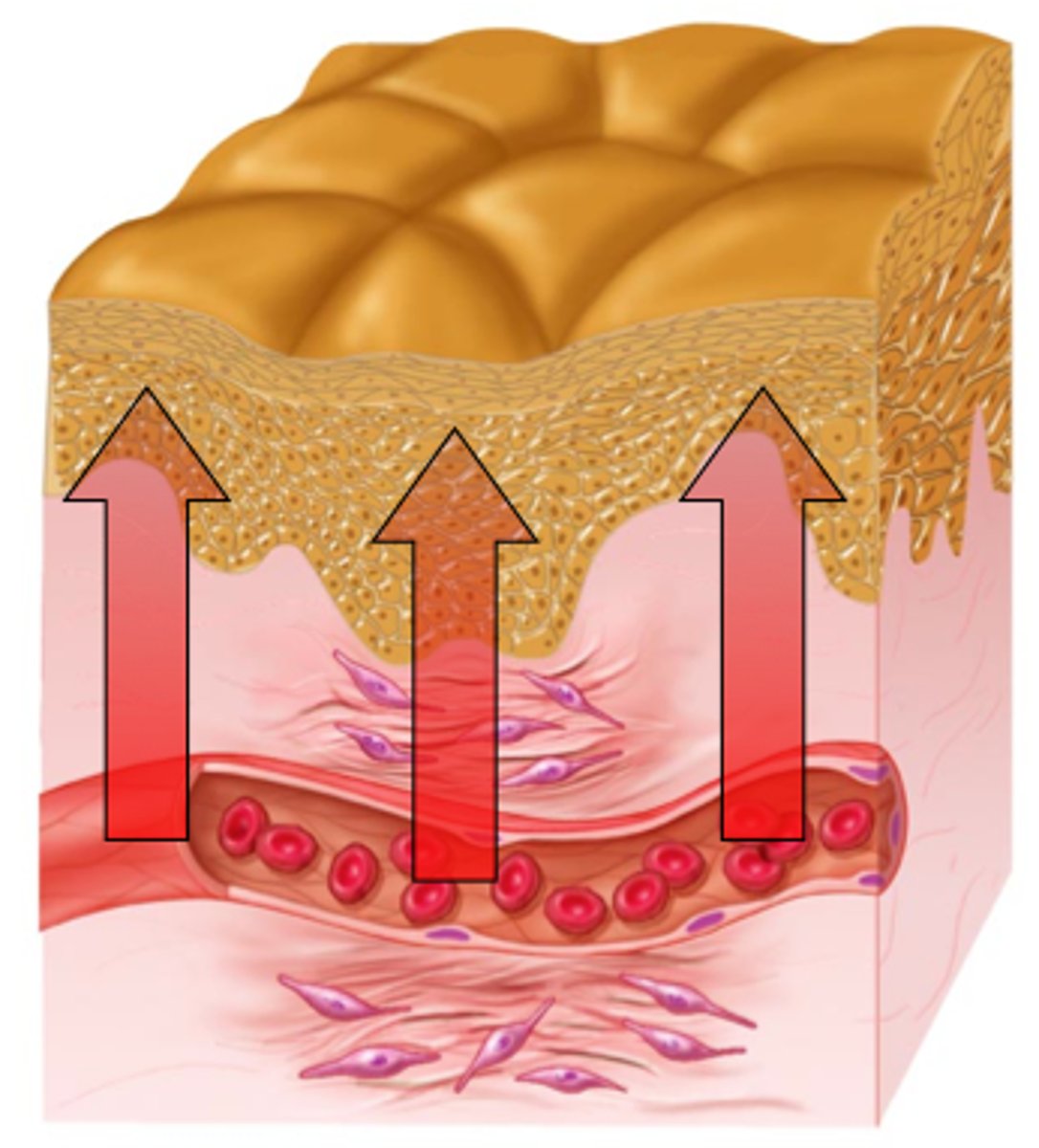
vascular
has a blood supply; EX. Dermis
Keratinocytes
Most of the cells of the epidermis are composed of ____.
Keratin
fibrous protein that makes the epidermis a tough protective layer
Melanin, melanocytes
______ is a pigment that ranges in color from yellow to brown to black.
Produced by a spider-shaped cells called ______ found chiefly in stratum basale (germinativum).
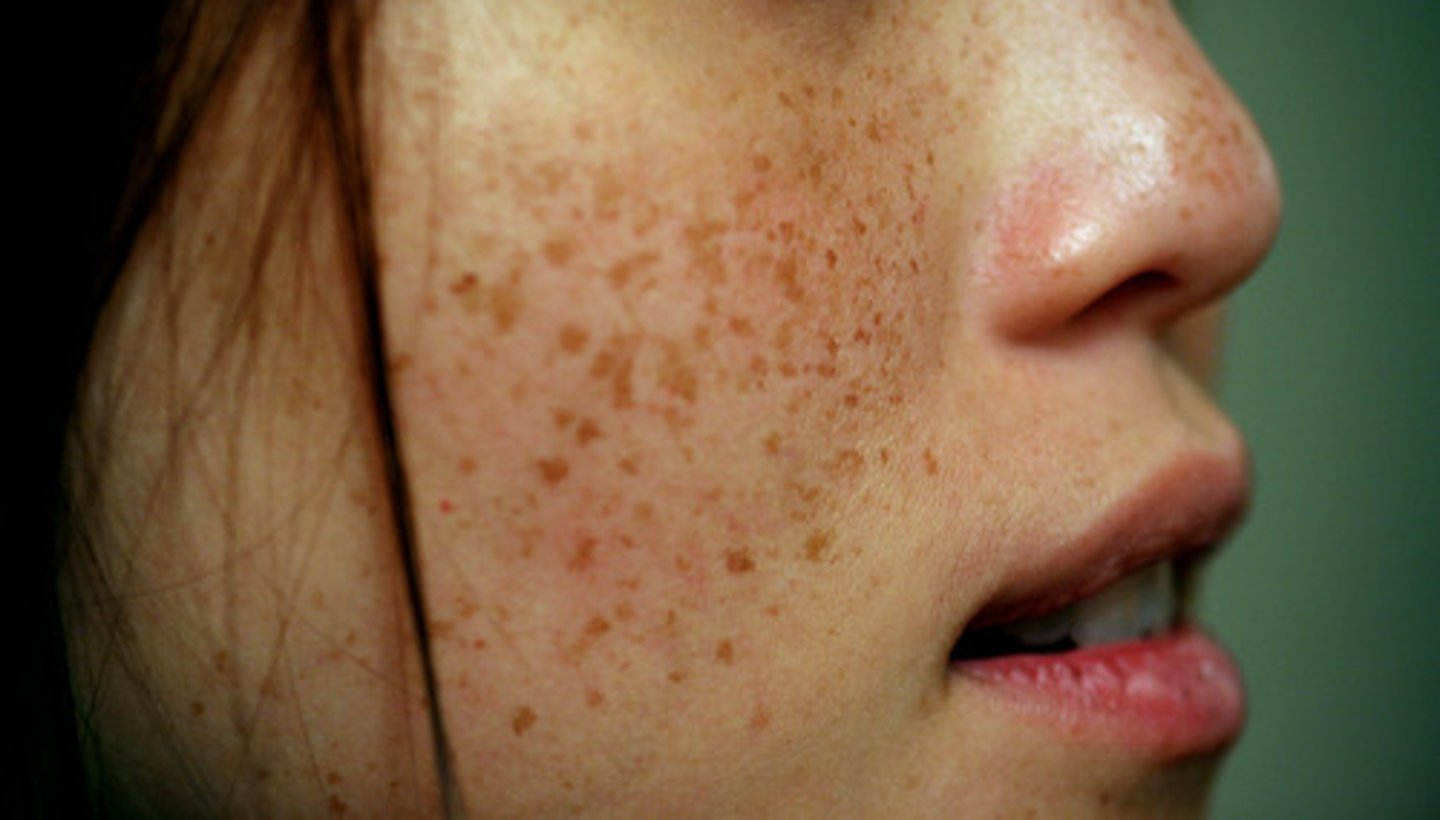
Freckles or moles
Are seen where melanin is concentrated in one spot.
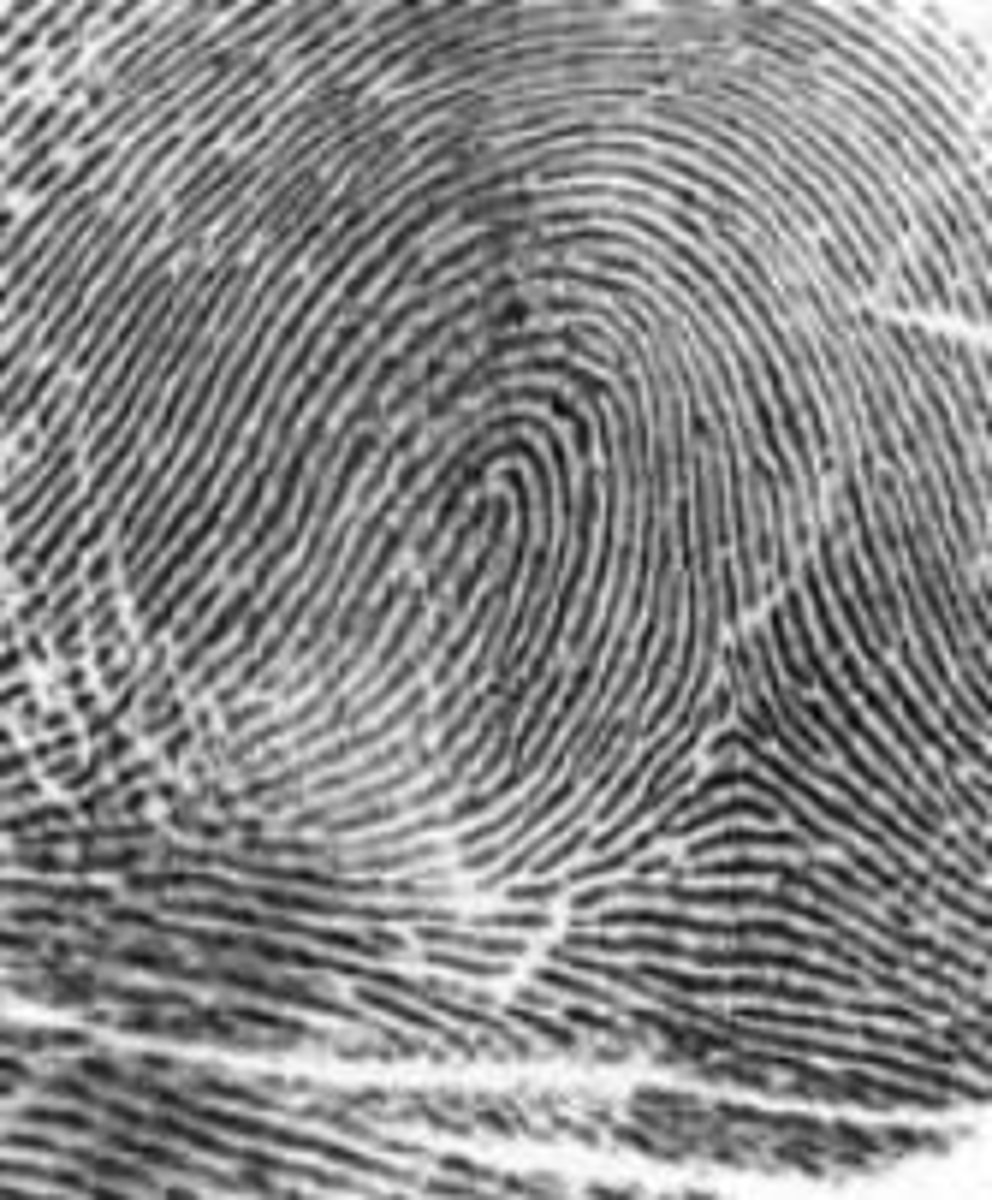
Fingerprints
The friction ridges of the fingertips w/ well provided sweat pores that leaves a unique identifying films of sweat.

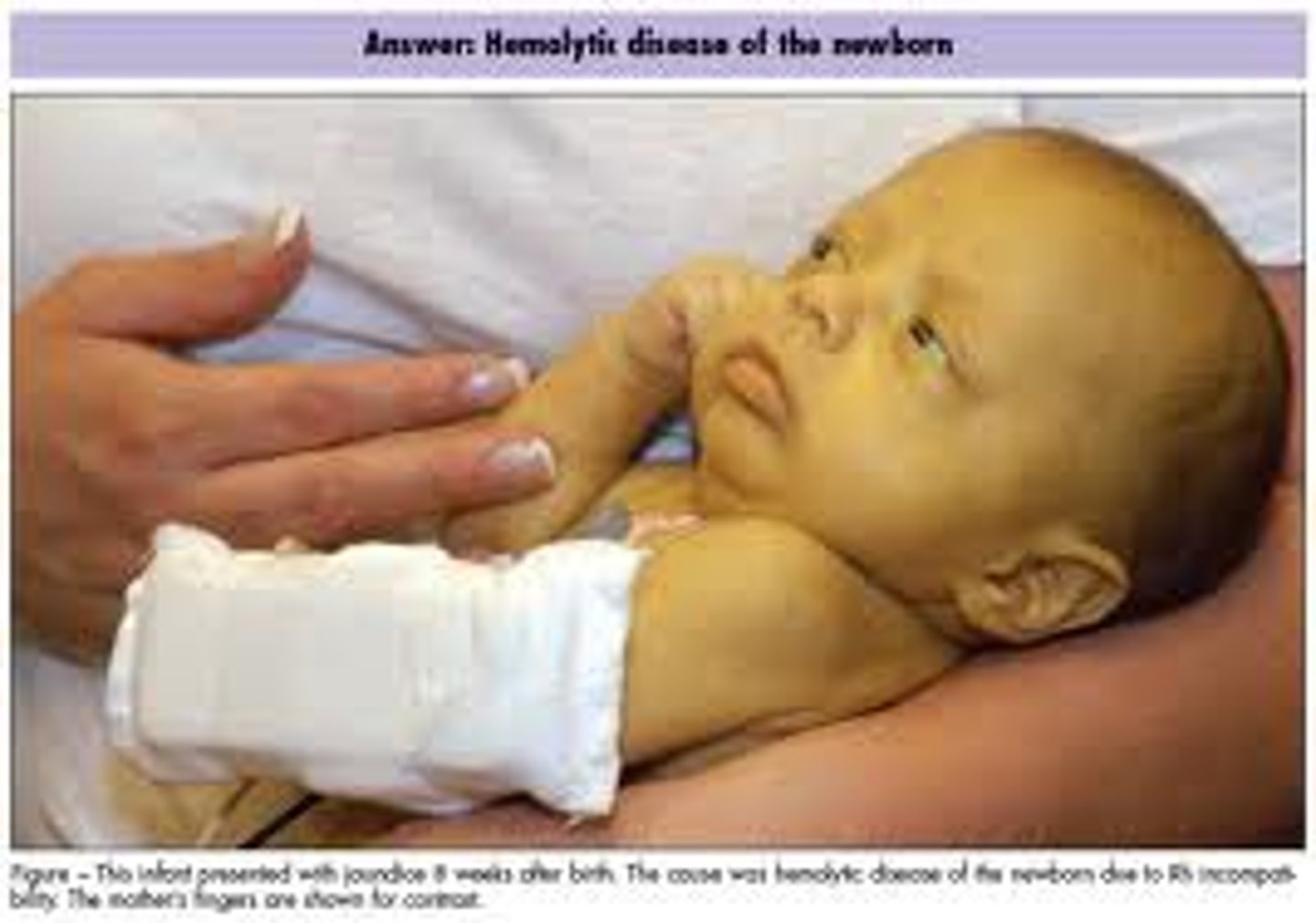
Jaundice
Or a yellow cast. An abnormal yellow skin tone usually signifies a LIVER DISORDER in w/c excess bile pigments are absorbed into the blood, circulated throughout the body, and deposited in body tissues.
Skin appendages (derivatives)
Include:
cutaneous glands,
hair,
hair follicles,
nails
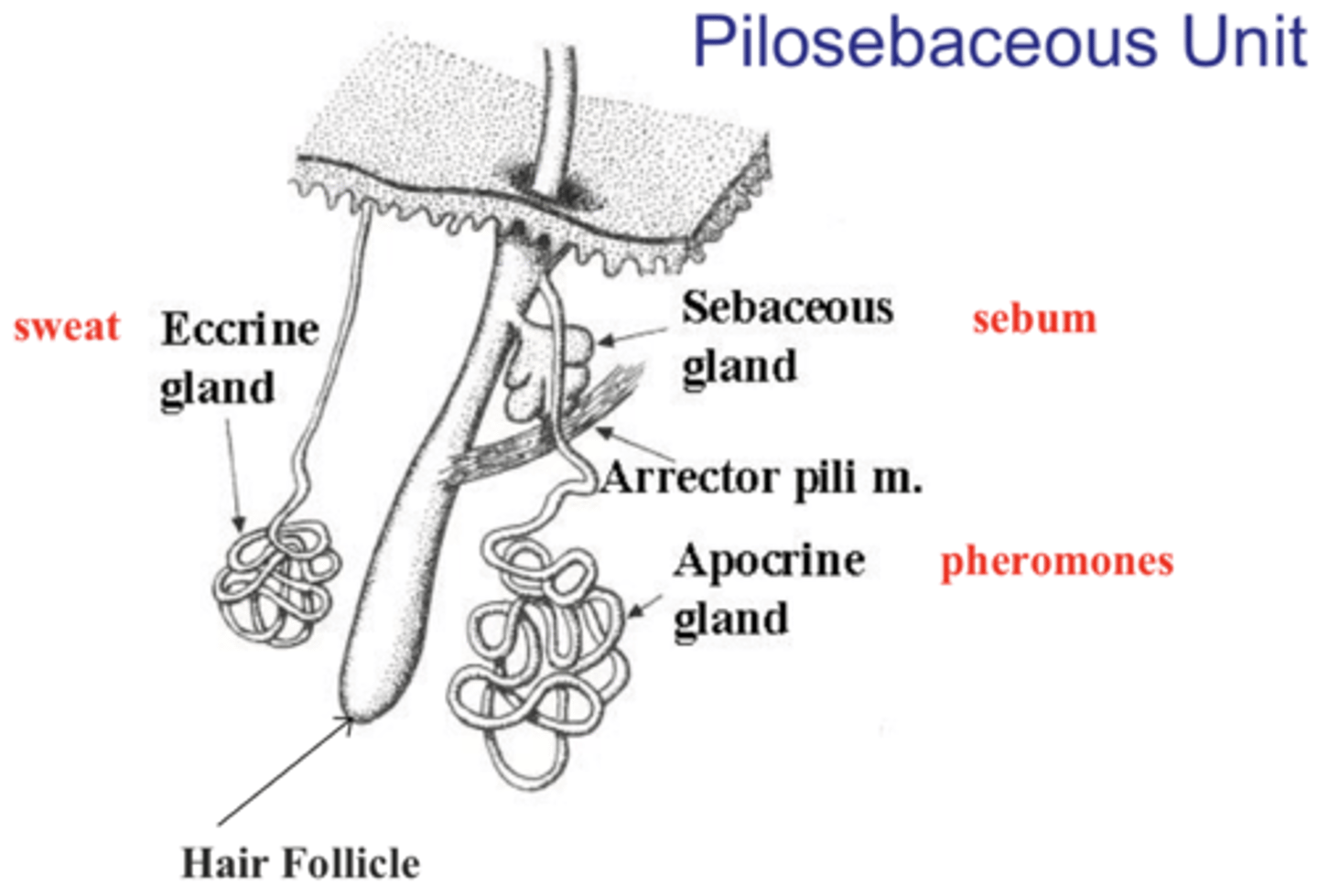
Cutaneous Glands
ALL exocrine glands--release secretions to the skin surface via ducts:
sebaceous glands and sweat glands (sudoriferous)
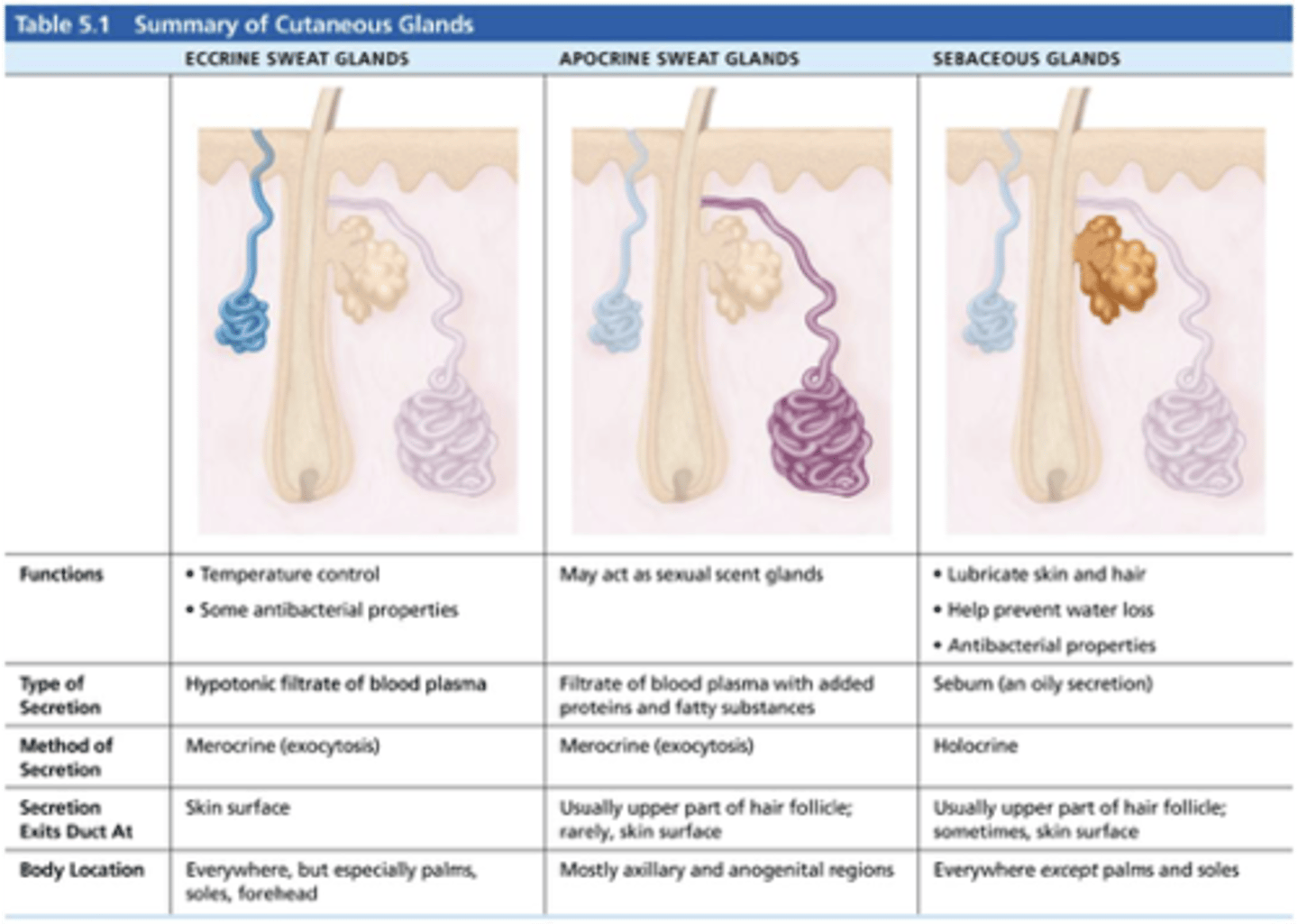
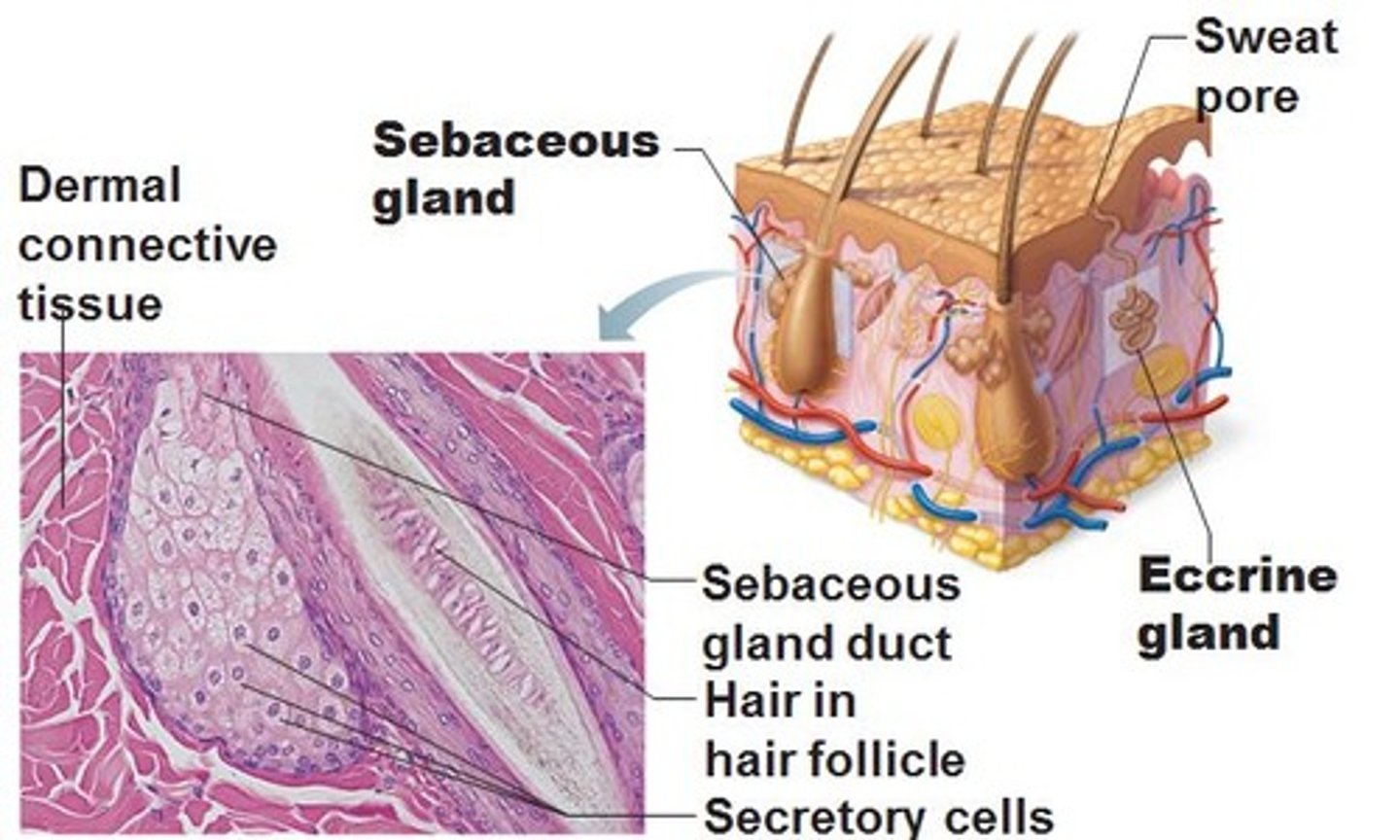
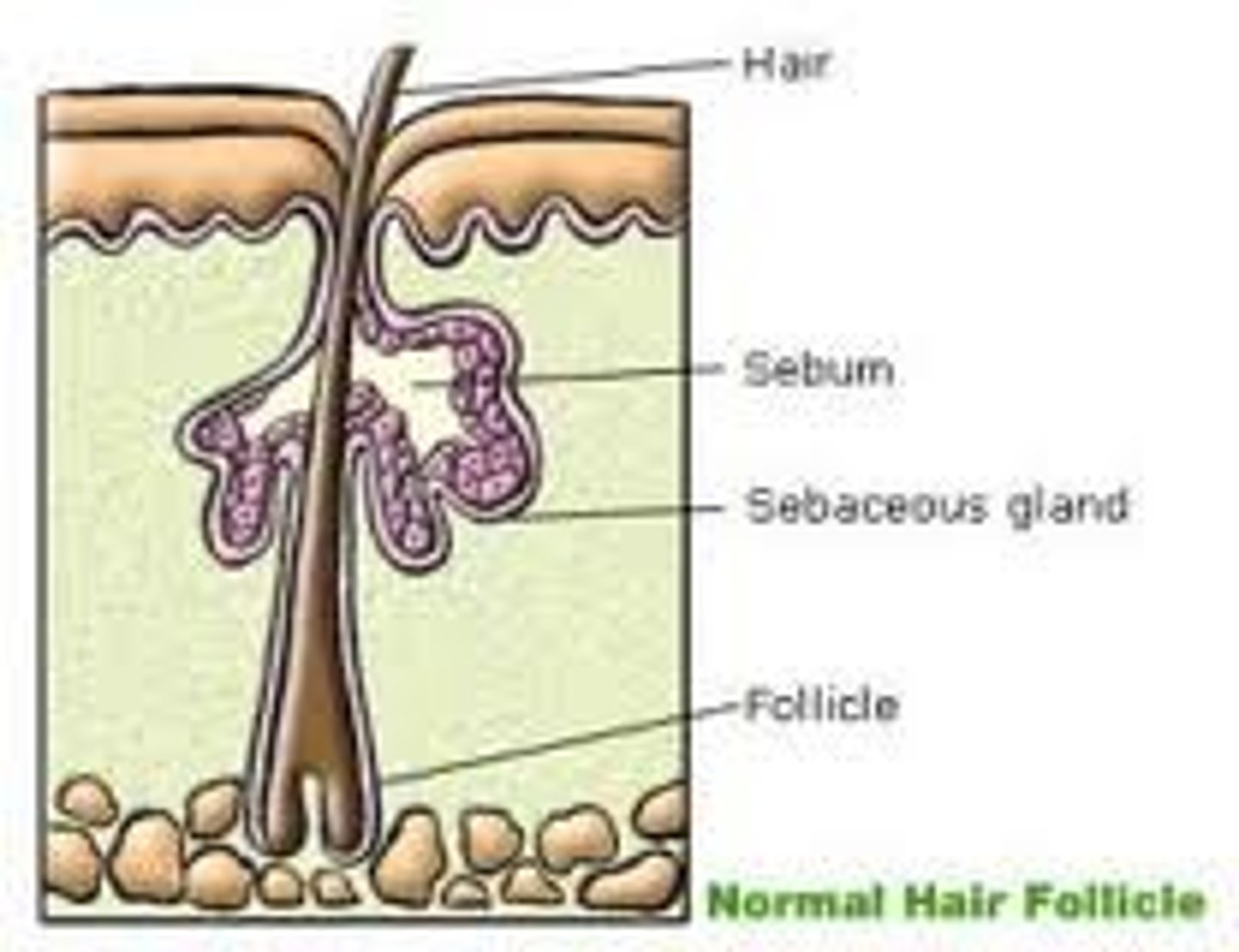
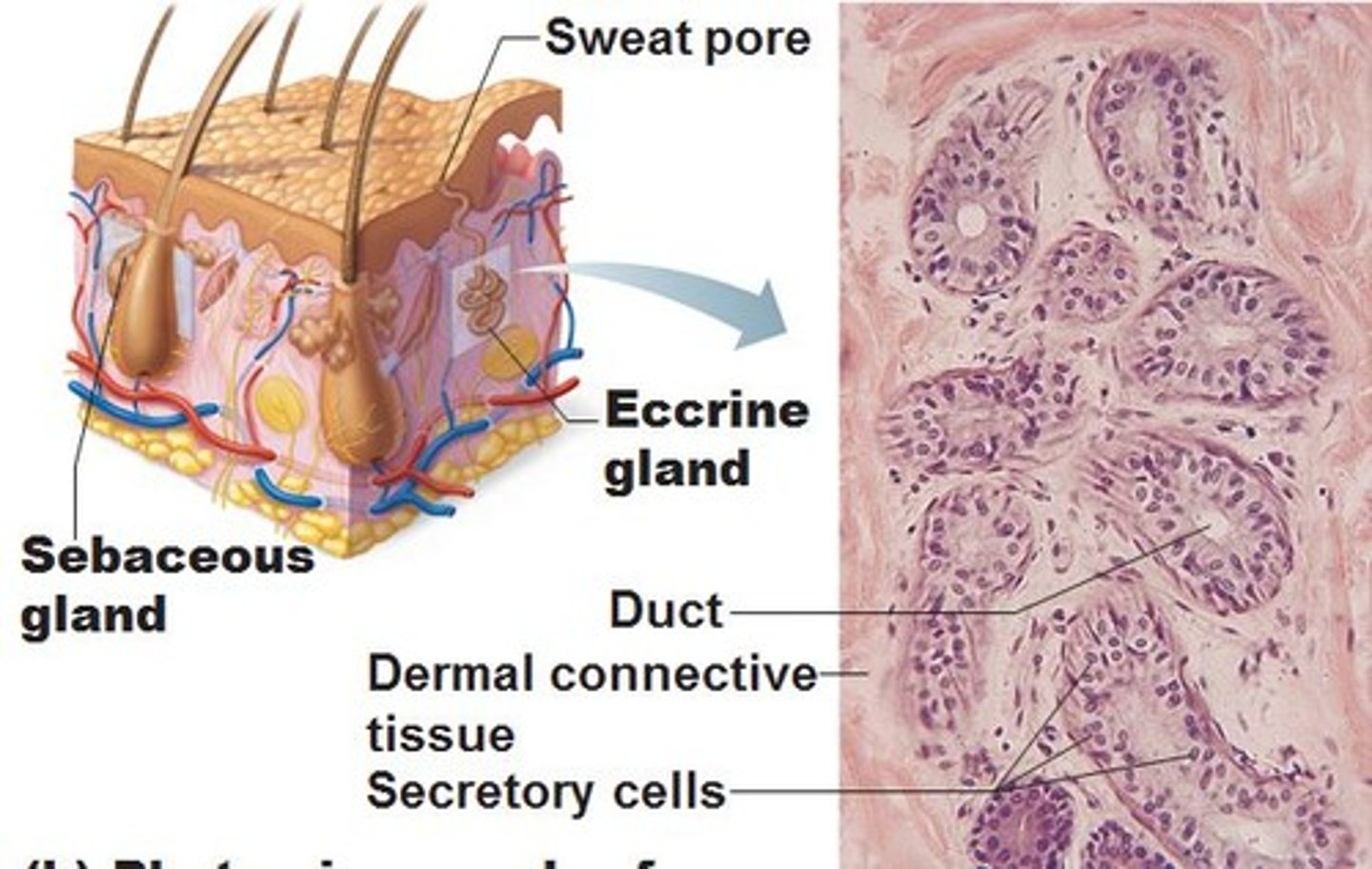
Sebaceous glands
oil glands;
found all over the skin except on the palms of the hands and in the soles of the feet;
their ducts USUALLY empty into a hair follicle.
Sebum
The oily product of sebaceous glands
Sweat glands
sudoriferous glands;
widely distributed in the skin;
2 types:
1. eccrine glands
2. apocrine glands
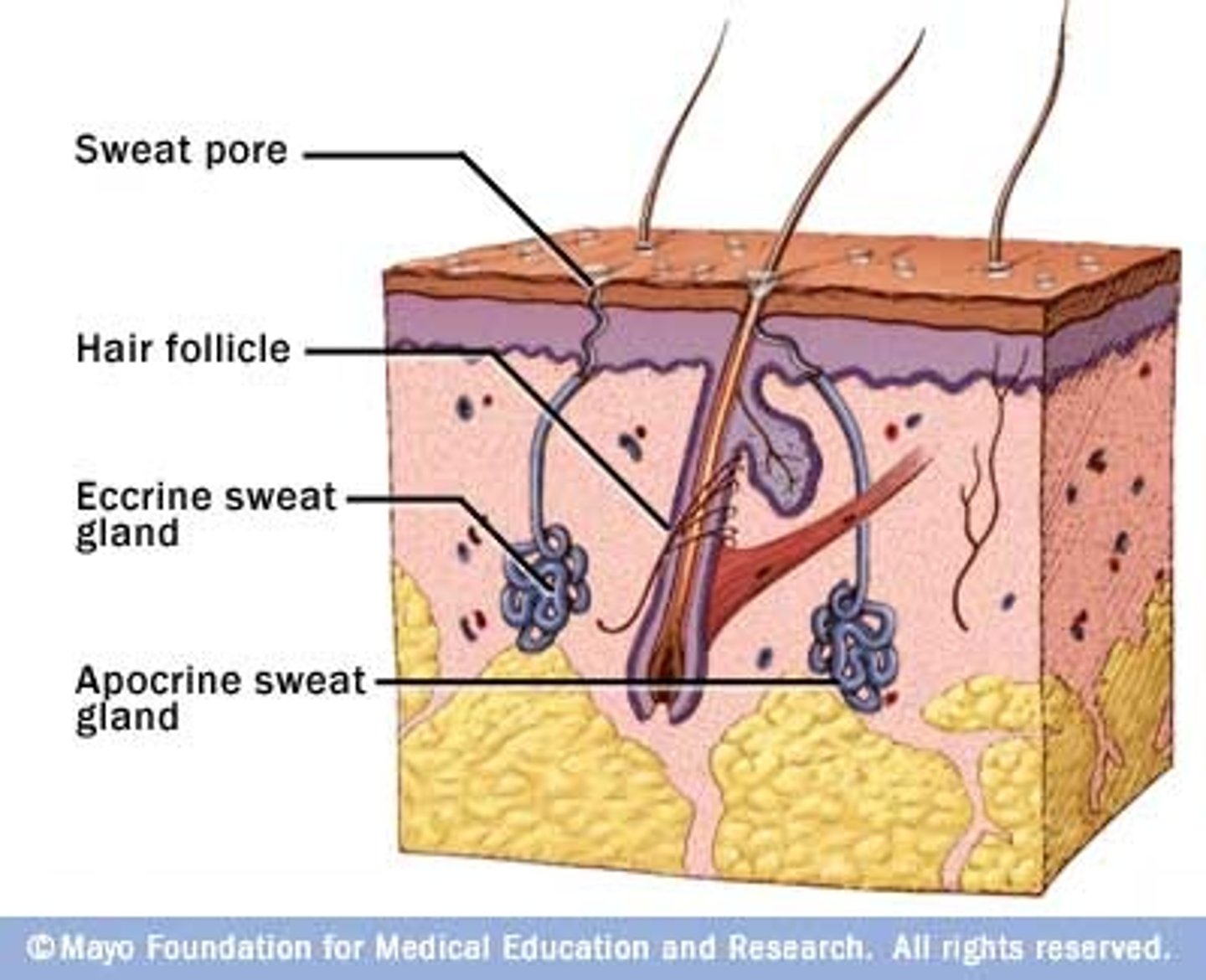
Eccrine glands
Primarily distributed all throughout the body;
Secretes sweat.
Apocrine glands
Mainly found in the axillary (armpit) and genital ("private")areas.
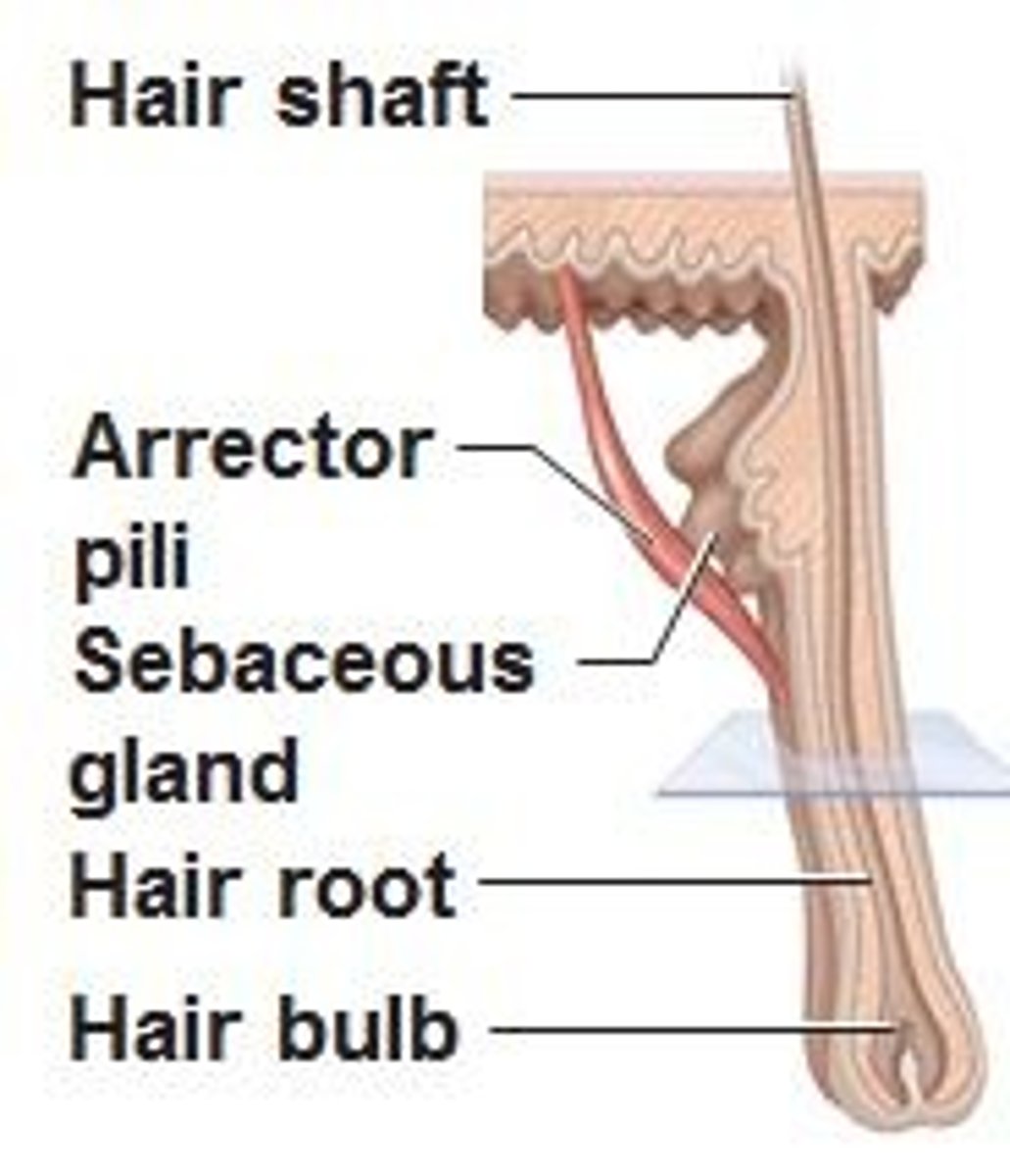
Hairs
produced by a hair follicle;
mostly nonliving material
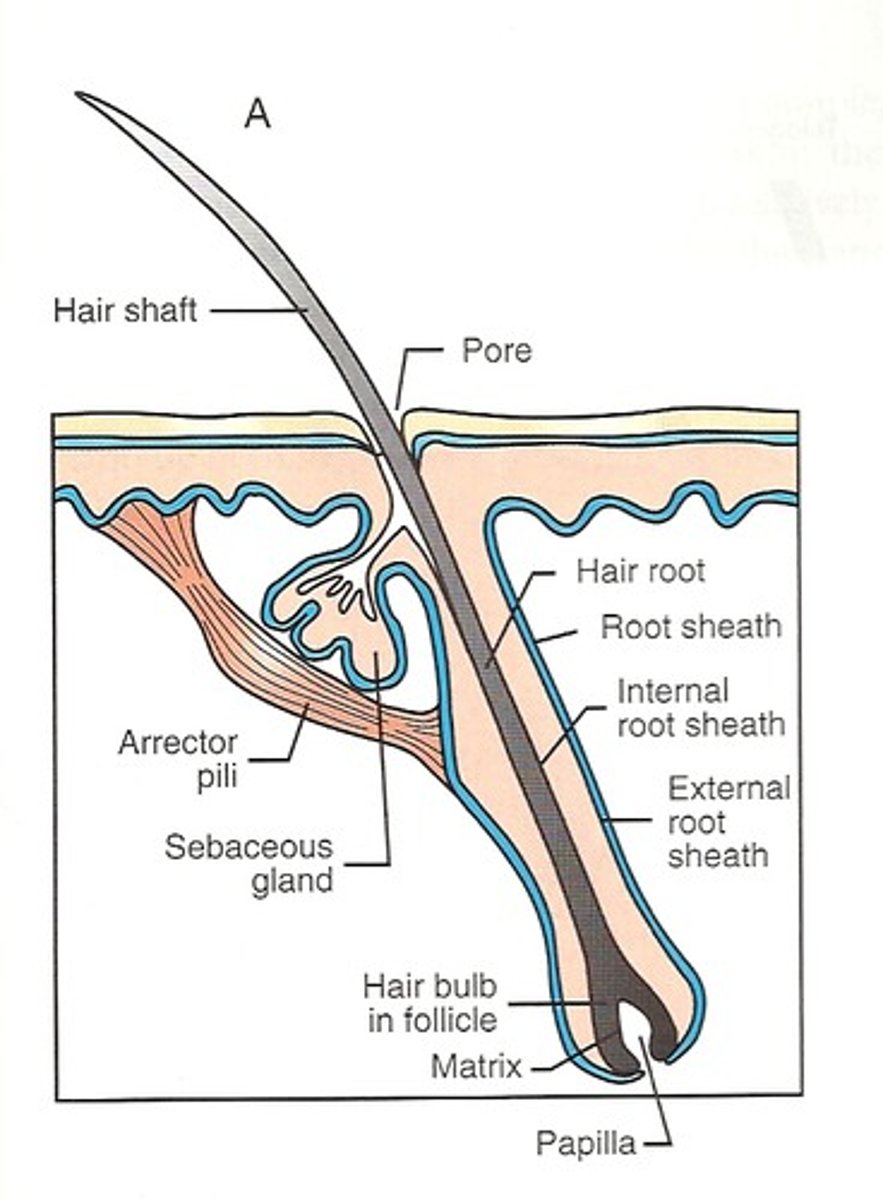
Hair papilla
Provides blood supply to the matrix in the hair bulb.
Arrector pili
"Raiser of the hair"
Nail
A scalelike modification of the epidermis that corresponds to the hoof or claw of other animals;
mostly nonliving material
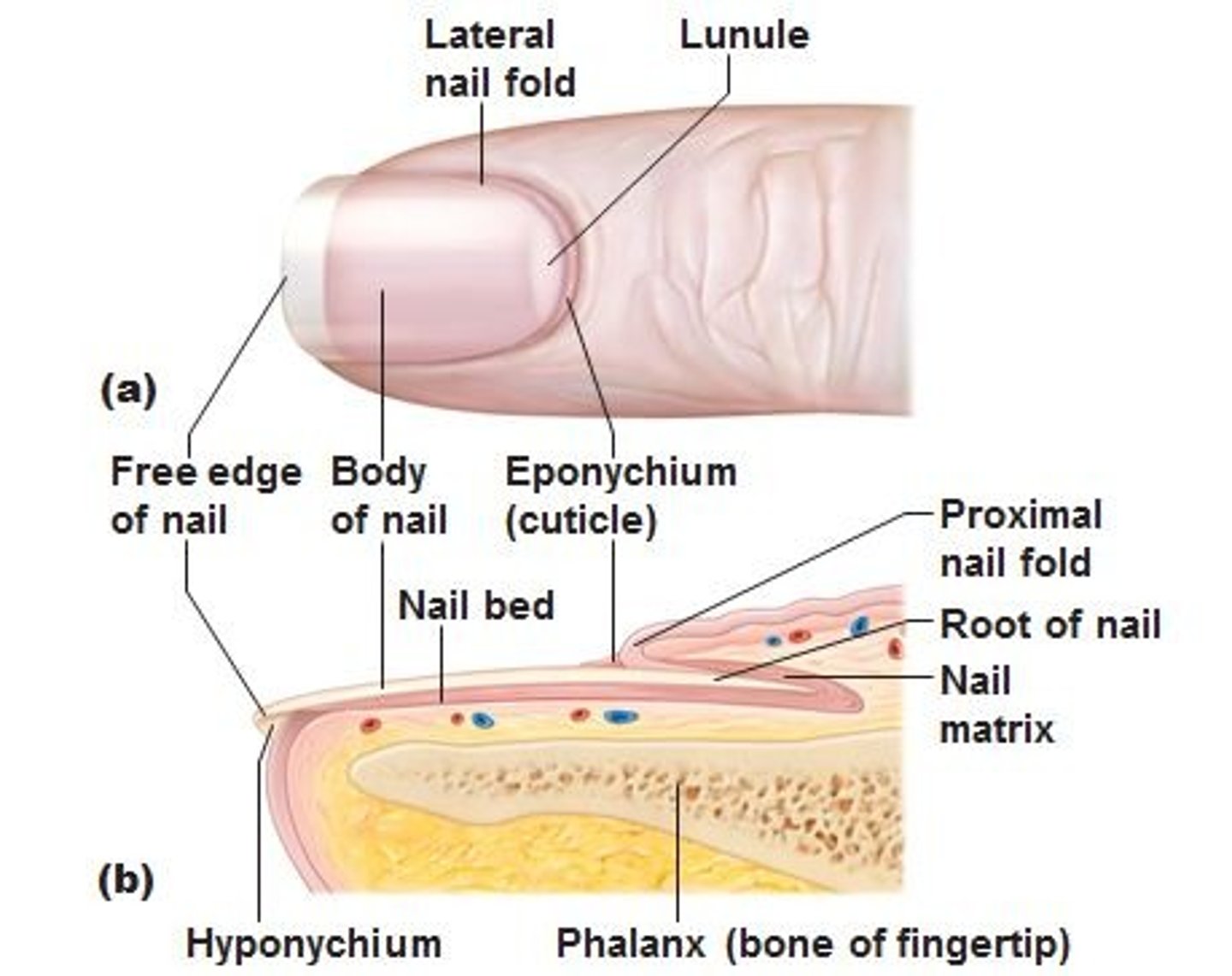
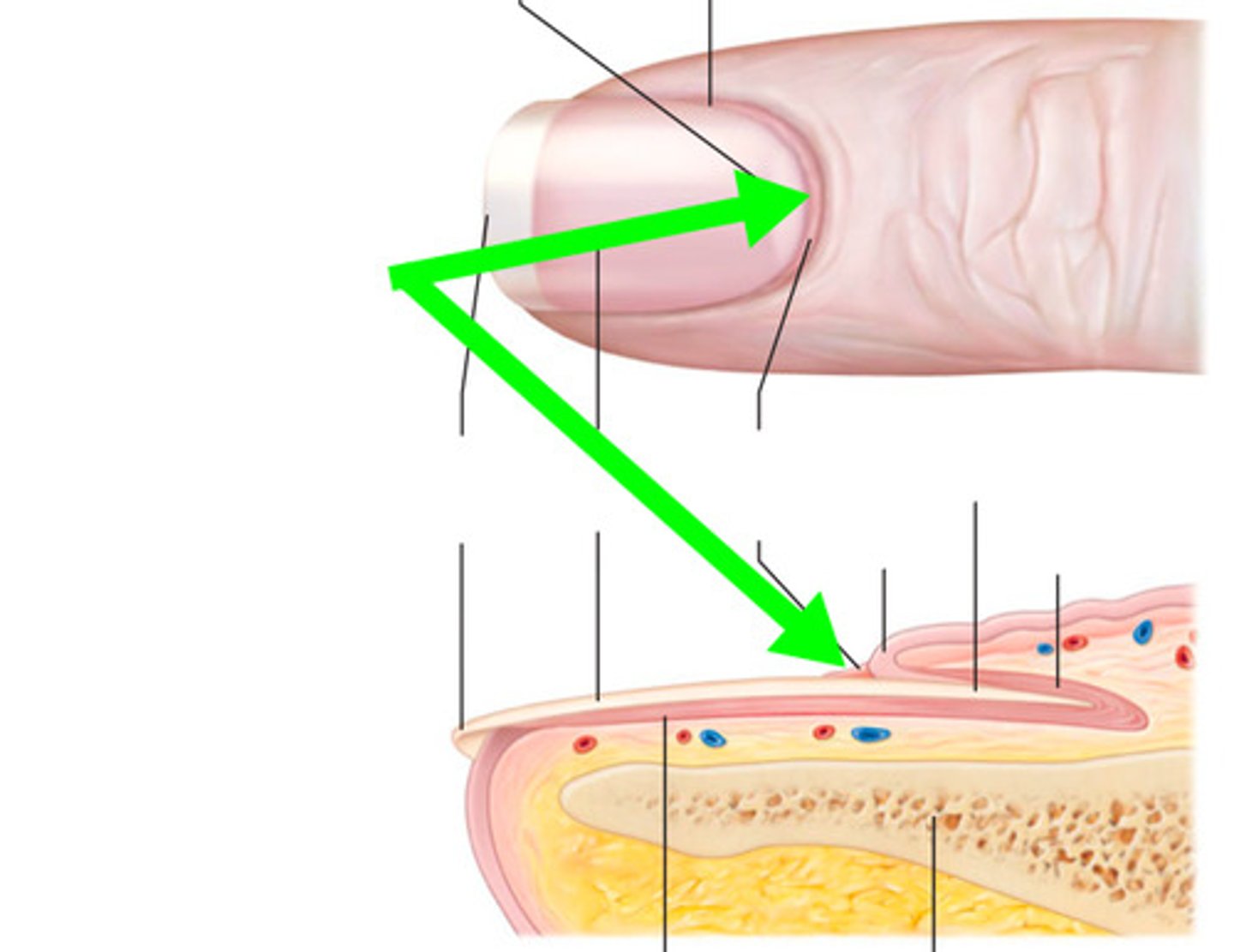
Cuticle
The edge of the thick proximal nail fold is commonly called the _____.
Nail bed
Stratum basale (germinativum) that extends beneath the nail.
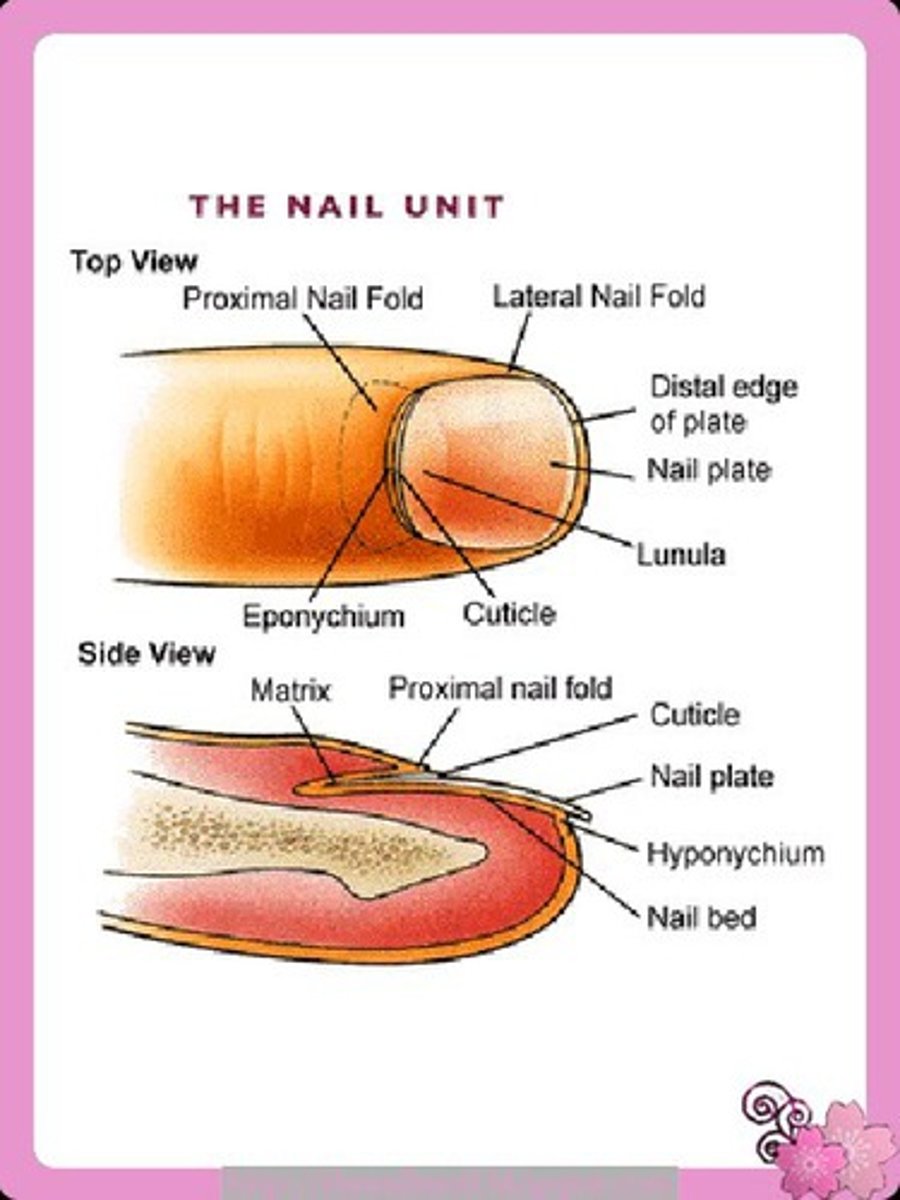
nail matrix
the part of the nail beneath the body and root from which the nail is produced
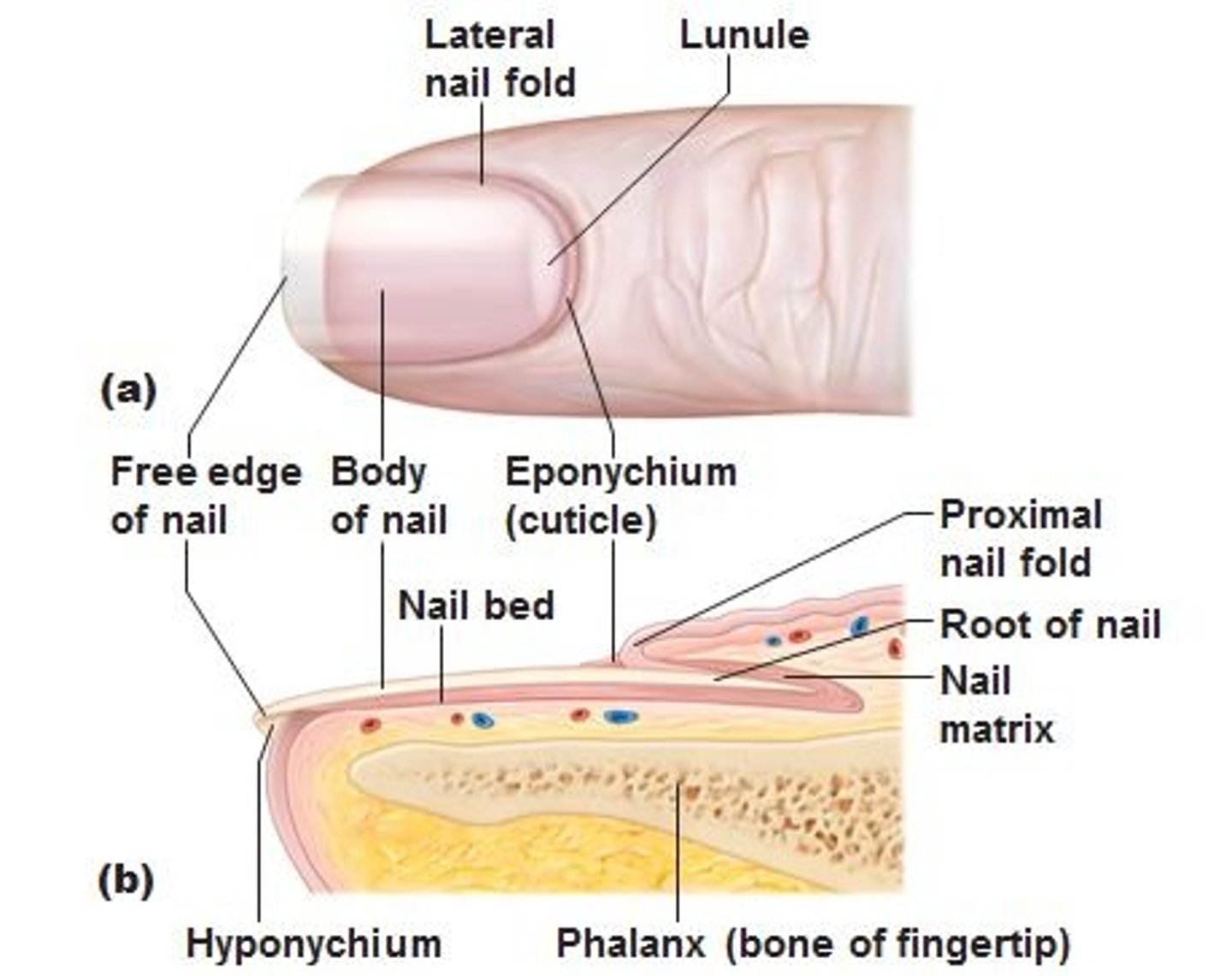
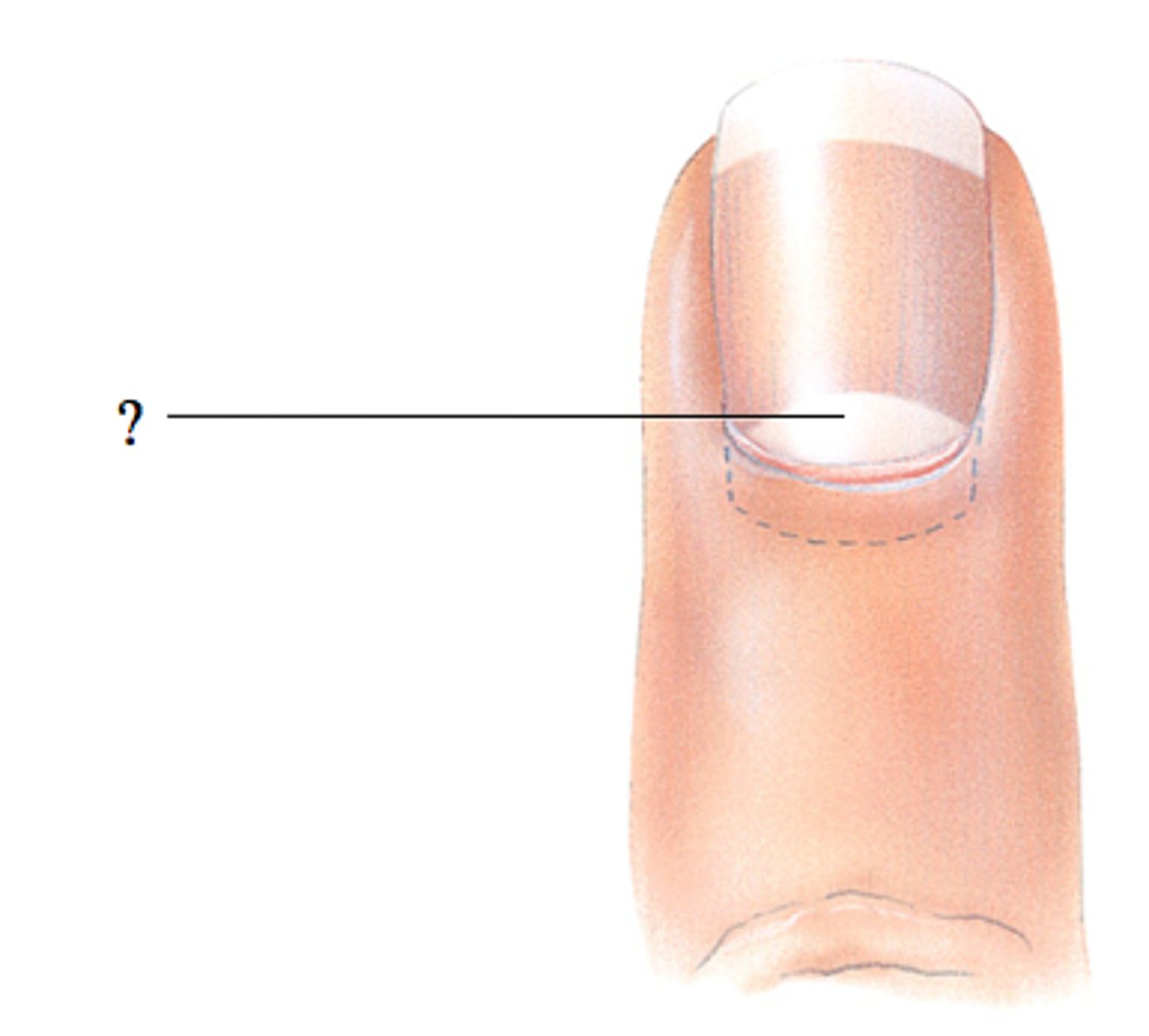
lunula of nail
The white crescent of the nail;
if damaged, the nail will be permanently deformed
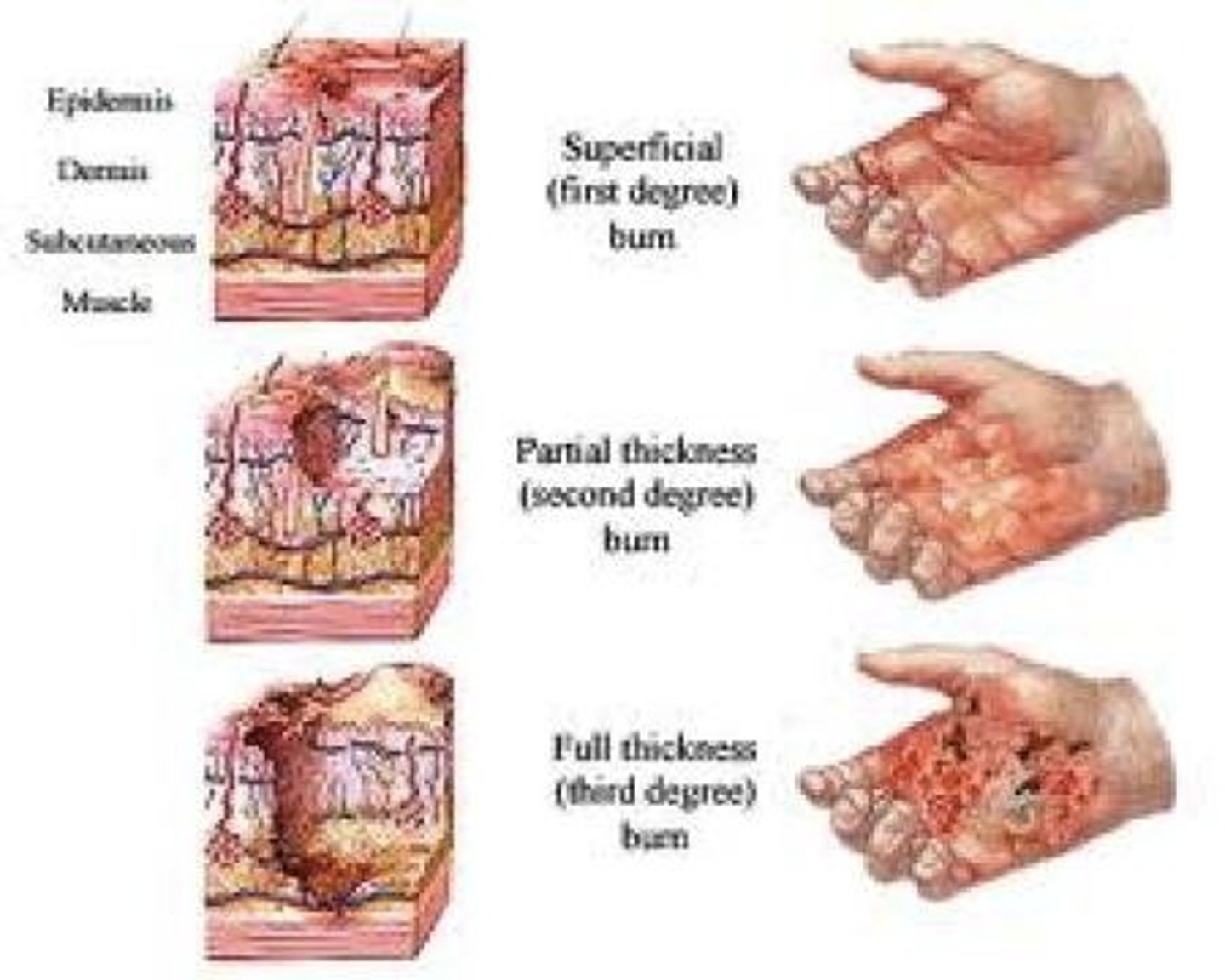
Burns
Is tissue damage and cell death caused by intense heat, electricity, utlraviolet radiation, or certain chemicals.
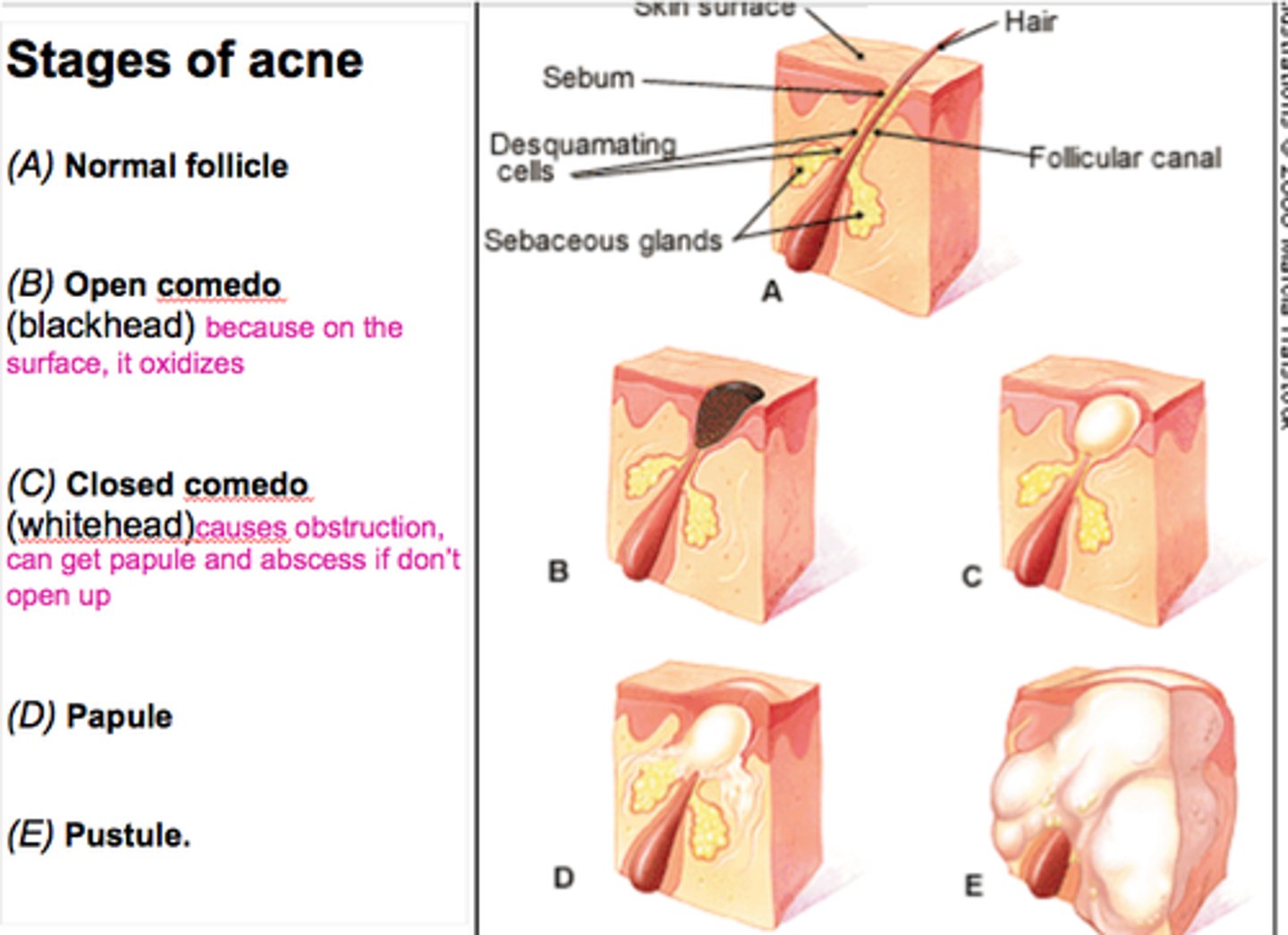
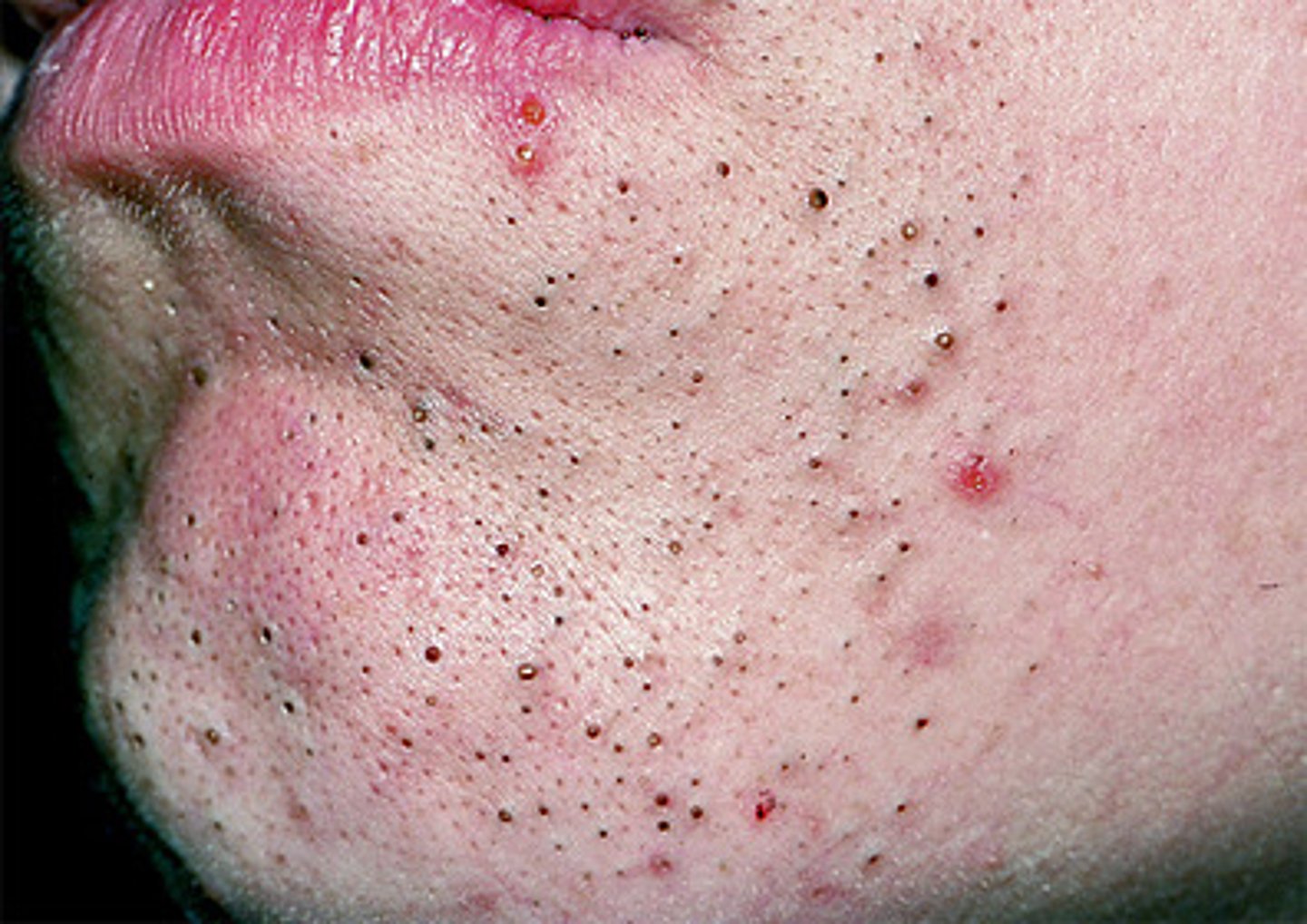
Blackhead
If the accumulated whitehead material oxidizes and dries, it darkens, forming a _____.
Whitehead
If a sebaceous gland's duct is blocked by sebum, a ______ appears.
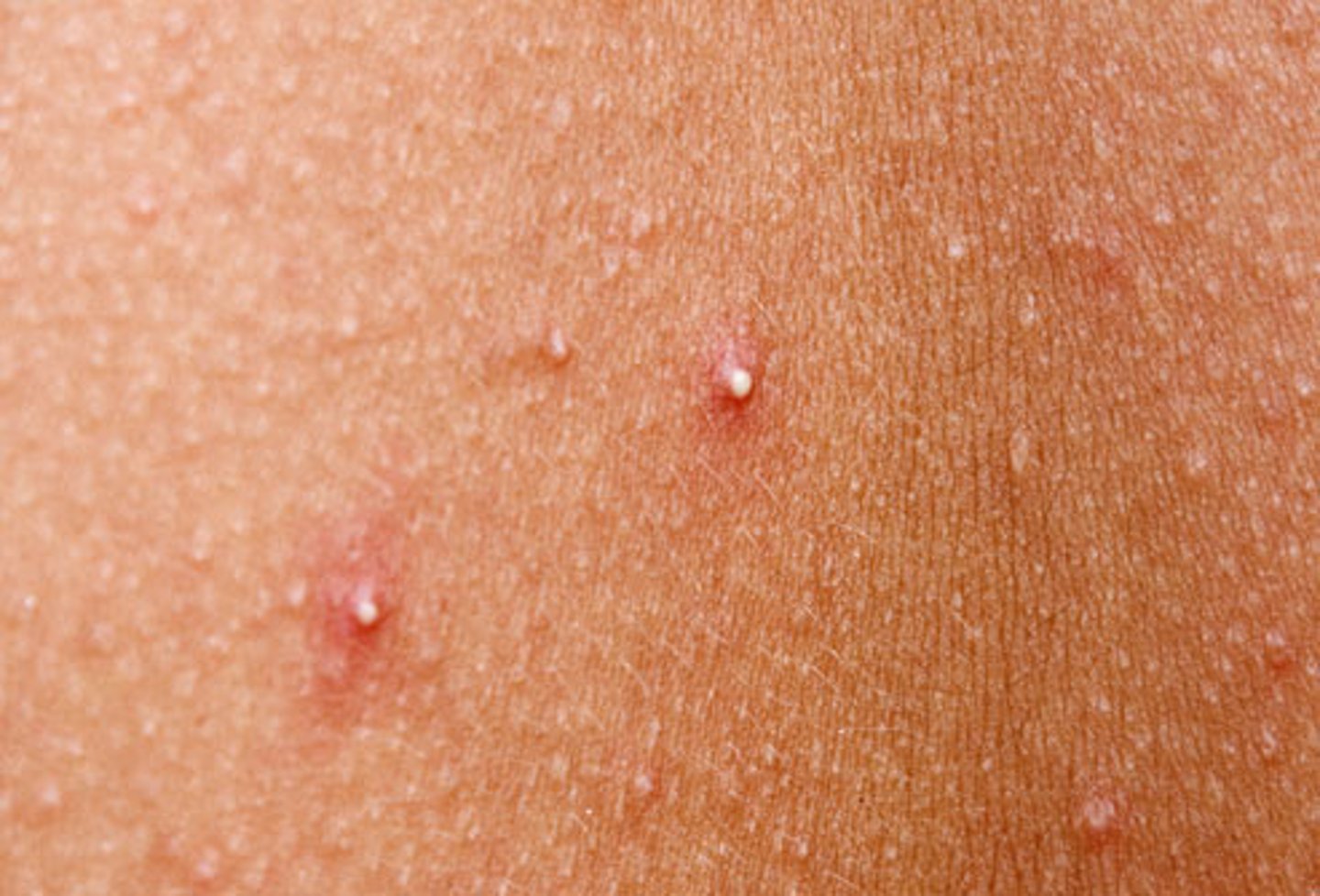
Stages of Acne
Is an active infection of the sebaceous glands accompanied by pimples on the skin. It can be mild or extremely severe, leading to permanent scarring.