Bio 160 Fall 2023: Exam 1
1/175
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
5 Characteristics of Life
Consists of 1 or more cells
Processes Information
Capable of replication/reproduction
Processes Energy
Is a Product of Evolution
Cell Theory
All organisms are made of cells and all cells come from pre-existing cells
5 Core Concepts of Biology
Evolution
Structure and Function
Information Flow, Exchange, and Storage
Pathways & Transformation of Energy & Matter
Systems
Valence Electrons
number of electrons in an atom’s outer shell
Ionic Bond
a metal and non-metal lose and gain electrons respectively to become more stable, which creates electrically attracted ions
Covalent Bond
2 non-metals share electrons to achieve stability
Polar Covalent Bonds
2 non-metals with unequal electronegativities
Non-polar Covalent Bonds
2 non-metals with equal electronegativities
Hydrogen Bonding
specific kind of intermolecular force where Hydrogen bonds to Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Fluorine
Solvent
liquid that other substances are dissolved in (Ex: Water in a glass of salt water)
Hydrophilic
Water loving, will dissolve and interact with water
Hydrophobic
Water fearing, will not dissolve or interact with water
Cohesion
Molecules stick to one another
Adhesion
molecules stick to polar or charged surfaces
What allows water to resist changes in temperature?
Polarity and Hydrogen Bonding
In a glass of pure water, list 2 different kinds of bonds occurring and indicate strongest & weakest.
Polar Covalent (Strongest) and Hydrogen Bonds (Weakest)
Why does ice float?
Liquid water is denser than solid water (ice) due to hydrogen bonding
What makes something an Organic Molecule?
Contains at least 1 C-H Bond
What does pH stand for?
Potential Hydrogen
Acids are found ______________ on the pH scale because they have a ___________ concentration of Hydrogen (H+) ions
from 1-6.999, higher
Bases are found ______________ on the pH scale because they have a ___________ concentration of Hydrogen (H+) ions
from 7.001-14, lower
What substance has a pH of 7?
Pure Water
How many bonds can carbon form?
4
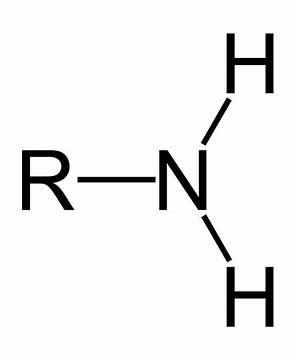
What Functional Group is this?
Amino Group
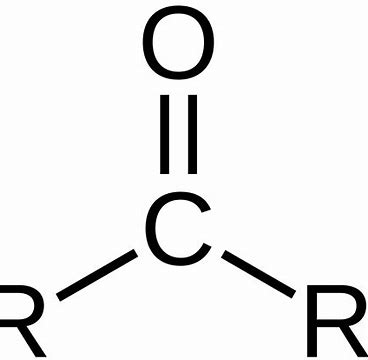
What Functional Group is this?
Carbonyl Group
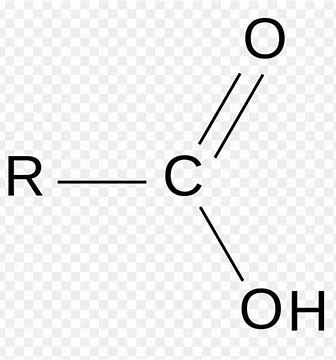
What Functional Group is this?
Carboxyl Group
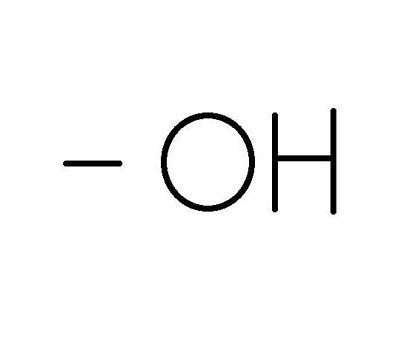
What Functional Group is this?
Hydroxyl Group
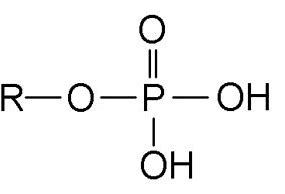
What Functional Group is this?
Phosphate Group
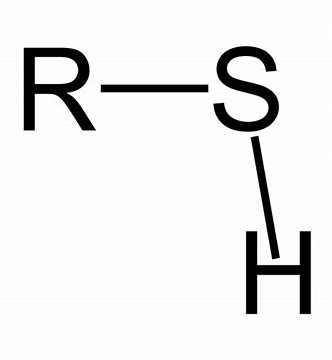
What Functional Group is this?
Sulfhydryl Group
Condensation Reactions ___________ a bond and ___________ a molecule of water
form, release
Hydrolysis Reactions ___________ a bond and ___________ a molecule of water
break, use/require
Which functional groups act as acids?
Carboxyl, Hydroxyl
Which functional group acts as a base?
Amino
Sulfhydryl Functionals groups can link together via _____________ bonds
Disulfide bonds
Name some of the functions of Proteins
structure, energy storage, movement, transport, catalysis, defense, and signaling
What kind of protien catalyzes reactions?
Enzymes (they usually end in “-ase”
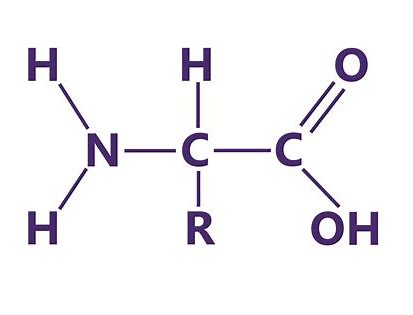
Define Amino Acid.
monomer of proteins
What part of the Amino Acid determines identity?
The side-chain
If the R group has a negative charge, it’s __________
acidic
If the r group has a positive charge, it’s ____________
basic
If the r group contains Oxygen it’s _________
polar
If the r group isn’t charged and doesn’t contain Oxygen, it’s probably
Non-polar
What kind of bond links Amino Acids
Peptide Bond
Is a peptide bond a hydrolysis or condensation reaction?
Condensation
Protein’s Primary Structure
Peptide Chain
Protein’s Secondary Structure
α-helix or β-pleated sheets
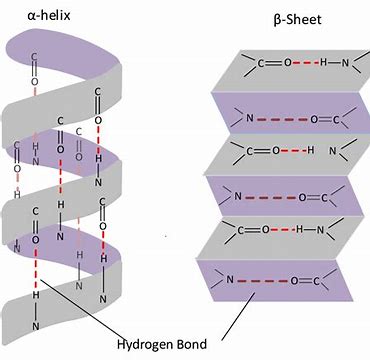
Protein’s Tertiary Structure occurs when the α-helix or β-pleated sheets begin to fold in on themselves. What causes this?
Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, Van Der Waals forces, and disulfide bonds
What is protein’s quaternary structure?
Multiple proteins linked together and functioning as a unit
Proteins must be ____________ correctly or they cannot function
folded
What do Prions do?
cause protiens to misfold in brain cells, leading to death
What is a nucleotide?
monomer of nucleic acids
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
Which part of a nucleotide determines identity?
Nitrogenous base
How do we number the carbons on our 5-carbon sugar?
starting with the carbon linked to the nitrogenous base and moving clockwise
List the 5 Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cuytosine, and Uracil
Which nitrogenous base is ONLY found in RNA?
Uracil
Which nitrogenous base is ONLY found in DNA?
Thymine
Adenine pairs with_____ and ________
thymine and uracil
Guanine Pairs with
Cytosine
Purines (double ring)
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines (single ring)
Thymine, Uracil, and Cytosine
What is the bond that links 2 nucleotides?
Phosphodiester Linkage
How does a Phosphodiester Linkage form?
The 3’ carbon on the 5-carbon sugar links to the phosphate group of the nucleotide being added.
The 5’ end always has an exposed ______________ group
Phosphate
The 5’ end always has an exposed ______________
3’ carbon
New nucleotides are always added to the 3’ end of the strand
Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids
Polynucleotide
2 DNA strands together form a ______________, the secondary structure of nucleic acids
Double Helix
Complementary DNA strands run __________
Anti-parallel
In RNA, a single strand doubles back on itself to form a ___________
hairpin
What bond forms between 2 nitrogenous bases?
hydrogen bonds
Is a phosphodiester linkage a condensation or hydrolysis reaction?
Condensation
Polar molecules are hydro_________
philic
Non-polar molecules are hydro_________
phobic
Carbohydrates contain what elements?
C, O, and H
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
Monosachharides
Most Carbohydrates end in ________
-ose
How many carbons do typical carbohydrates have?
Minimum 3, Rarely more than 6
Carbohydrates can be _________ or _____________
linear, ring structure
If a carbonyl group is in the middle of the carbon chain, then it’s an _______
aldose
If a carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon chain, then it’s a _______
ketose
How are monosaccharides bonded together?
Glycosidic Linkages
If the 2 carbons involved in bonding have the same stereochemistry, it’s an __________
α-1,4 Glycosidic Linkage
If the 2 carbons involved in bonding have different stereochemistry, it’s a ____________________
β-1,4 Glycosidic Linkage
Glycosidic linkages always occur between which carbons?
1 and 4
What other macromolecule contains a monosaccharide?
Nucleotide
Which polysaccharides store chemical energy?
Starch and Glycogen
Which polysaccharides are present in cell walls?
Cellulose, Chitin, and Peptidoglycan
Starch’s monosaccharide is __ glucose
α
Glycogen’s monosaccharide is __ glucose
α
Cellulose’s monomer is ___________
β-glucose
Chitin’s monomer is _______
NAG
Peptidoglycan’s monomers are _______ & __________
NAG and NAM
Does Glycogen form arrays or helices
Helices
Does Starch form arrays or helices
Helices
Does Celluose form arrays or helices
arrays
Does Chitin form arrays or helices
arrays
Does Peptidoglycan form arrays or helices
arrays
Parallel strands in Cellulose are joined by______________
hydrogen bonds
Parallel strands in Chitin are joined by______________
Hyrdogen bonds