Arteries and veins
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:00 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
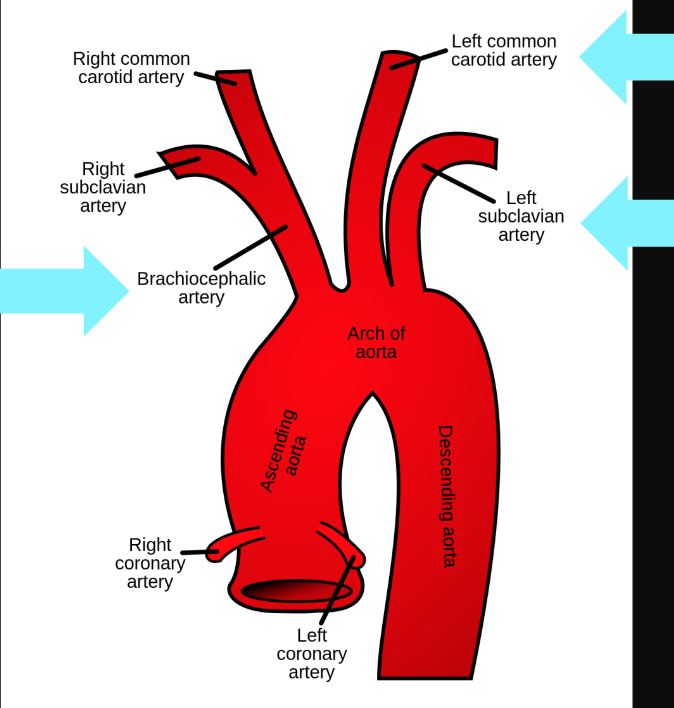
What are the branches of the aorta?
brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid, left subclavian
2
New cards
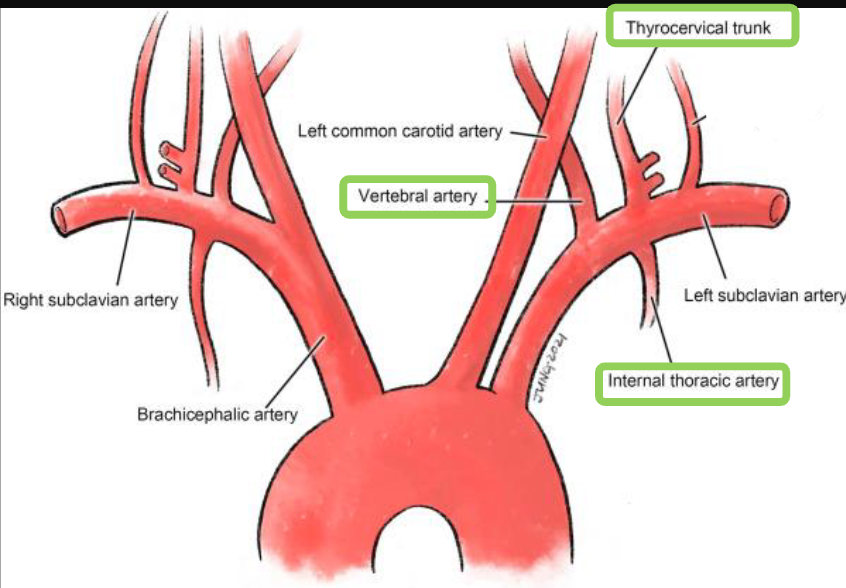
branches oof the subclavian artery
vertebral artery, internal thoracic artery, thyrocervical trunk
3
New cards
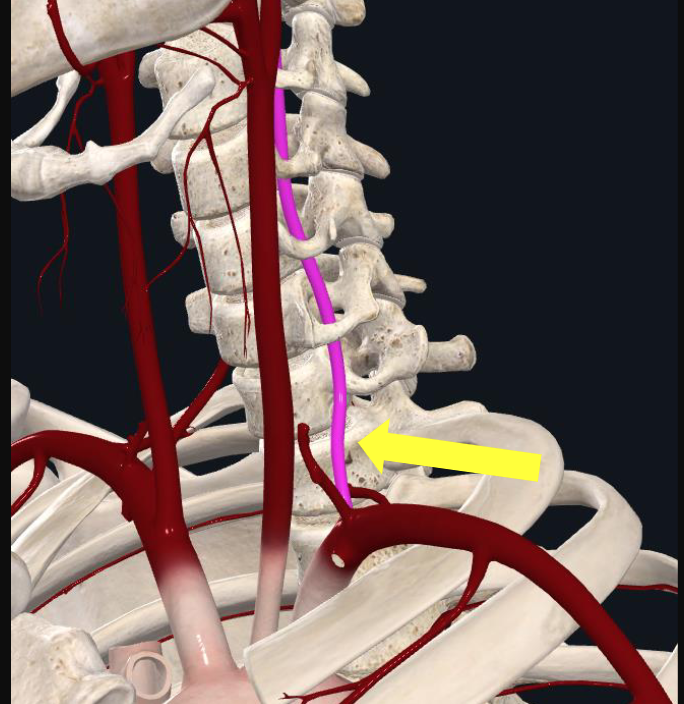
what foramen does the vertebral artery travel through?
transverse foramen
4
New cards
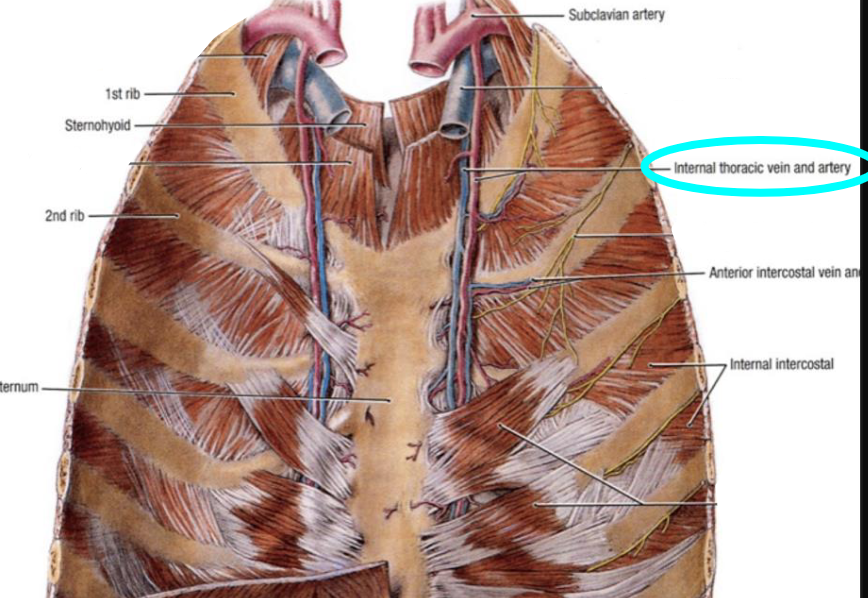
what structures does the internal thoracic artery supply?
the anterior chest wall and breasts
\-GOLD standard for use in CABG surgery
\-GOLD standard for use in CABG surgery
5
New cards
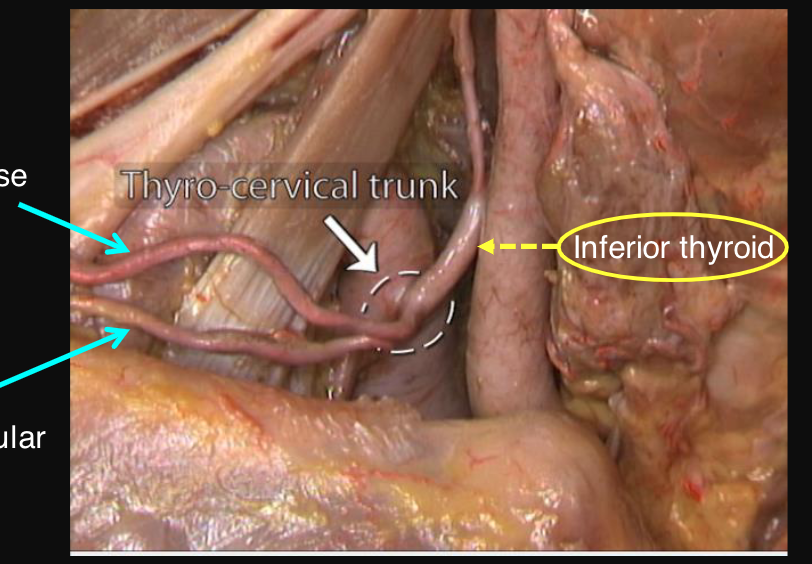
what is the most important branch of the thyrocervical trunk?
inferior thyroid artery which supplies the thyroid gland and larynx
6
New cards
branches of the common carotid artery
internal and external carotid arteries
7
New cards
what branches does the internal carotid artery give off?
gives off NO branches in the neck; it ascends and enters the skull through the carotid canal
8
New cards
what structures does the external carotid artery supply?
neck, face, thyroid, pharynx, and side of the head
9
New cards
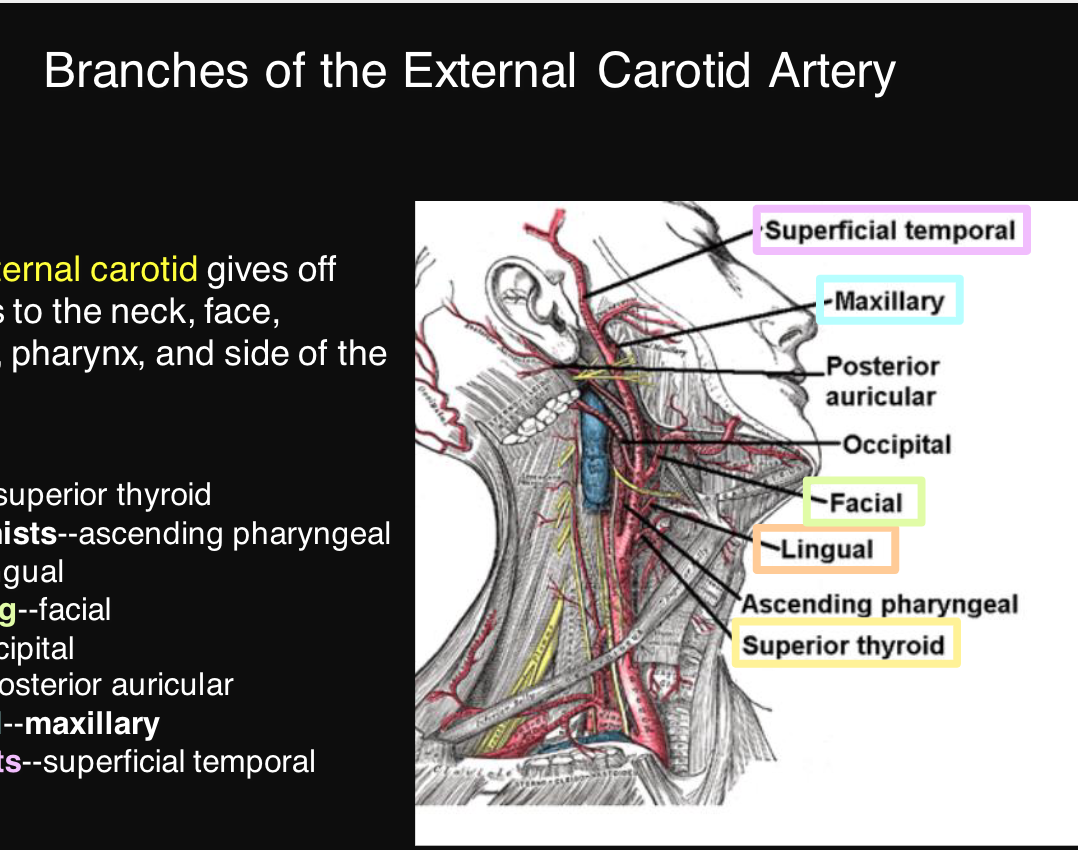
name the branches of the external carotid artery
superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal
\
some anatomists like freaking out poor medical students
\
some anatomists like freaking out poor medical students
10
New cards
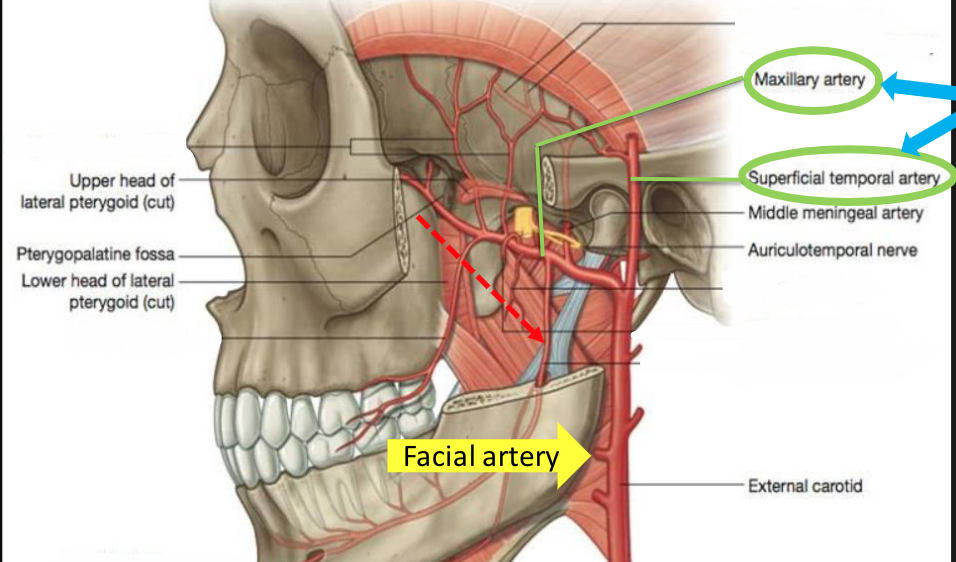
facial artery
\-branch of external carotid
\-supplies the superficial structures of the face
\-supplies the superficial structures of the face
11
New cards
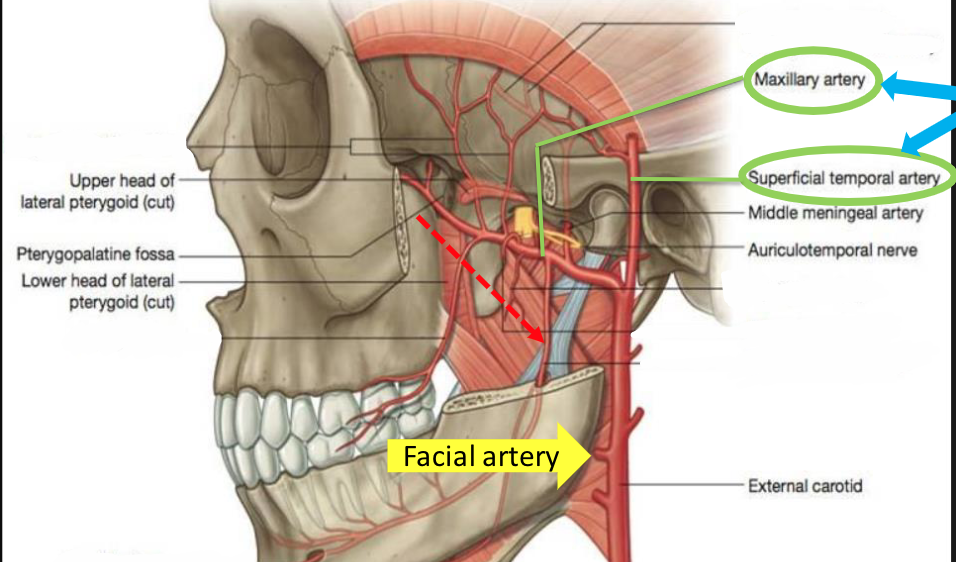
maxillary artery
supplies many of the internal structures of the face
\-branch of external carotid
\-branch of external carotid
12
New cards
what is the course of the maxillary artery
\-starts in the infra temporal fossa and then travels medially to go to the pterygopalatine fossa and into the nasal cavity
13
New cards
what are the three important branches off of the maxillary artery
middle meningeal, sphenopalatine, inferior alveolar
\
McDonald’s Sprite is Interesting to the max!
\
McDonald’s Sprite is Interesting to the max!
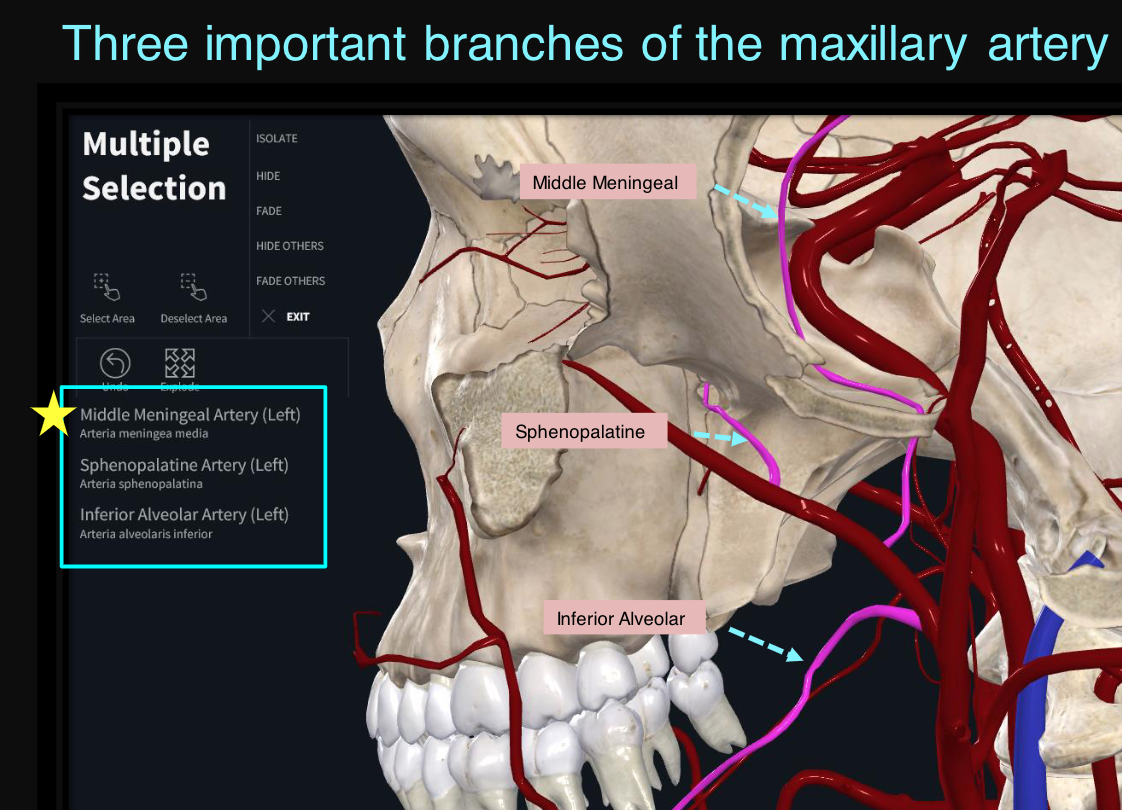
14
New cards
course of the middle meningeal artery
branch of maxillary artery; can be found in the infratemporal fossa between two roots of the auriculotemporal nerve
15
New cards
supply by the middle meningeal artery
supplies most of the dura and calvaria
16
New cards
what artery is involved with epidermal hematoma
\-middle meningeal artery
\-emergency treatment usually involves decompression of the hematoma
\-emergency treatment usually involves decompression of the hematoma
17
New cards
list the veins of the thorax
azygos vein, accessory hemiazygos vein, hemiiazygos vein (superior -→inferior)
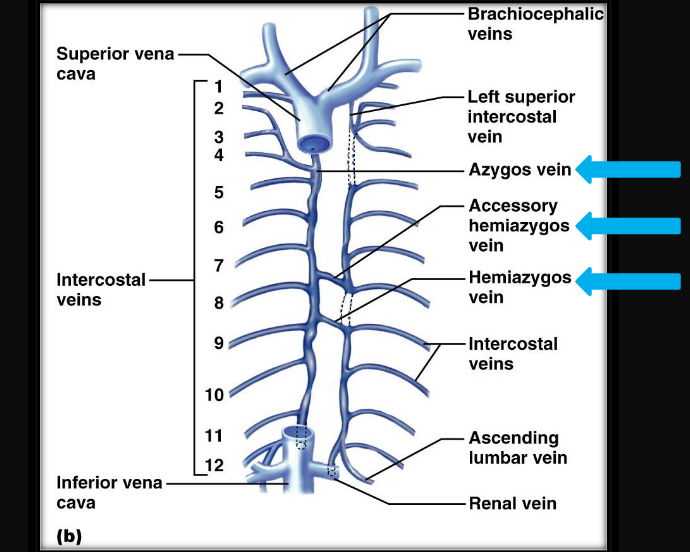
18
New cards
what are the boundaries of the axillary artery?
lateral border of the first rib to the inferior border of the trees major
19
New cards
describe the first part of the axillary artery
\-proximal to the pec minor
\-has 1 branch
\-has 1 branch
20
New cards
describe the 2nd part of the axillary artery
\-posterior to the pec minor
\-2 branches
\-2 branches
21
New cards
3rd part of the axillary artery
distal to pec minor
\-3 branches
\-3 branches
22
New cards
what nerve runs with the lateral thoracic artery?
long thoracic nerve
23
New cards
what is the continuation of the subscapular artery?
thoroacodorsal artery
\-supplies the latissimus doors
\-supplies the latissimus doors
24
New cards
list the branches of the axillary artery
supreme thoracic, thoracoacromial, lateral thoracic, anterior humeraal circumflex posterior humeral circumflex, sub scapular
\
save the lions and protect the species
\
save the lions and protect the species
25
New cards
what are the branches of the thoracoacromial?
clavicular, acromial, deltoid, and pectoral
\
cadavers are dead people
\
\
cadavers are dead people
\
26
New cards
whaat is the importance of the quadrangular space?
The quadrangular space is an anatomical region located in the posterior aspect of the shoulder. It serves as a passageway for the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery, which are important structures that innervate and vascularize the shoulder joint and surrounding muscles. Damage to these structures due to trauma or compression within the quadrangular space can result in shoulder weakness, numbness, and pain.
27
New cards
what artery runs with the axillary nerve
the posterior humeral circumflex artery in the quadrangular space
28
New cards
where does the axillary artery become the brachial artery?
past the teres major
29
New cards
deep brachial artery
branch of the brachial artery in the shoulder area that a pieces the triceps and travels with the radial nerve
30
New cards
what are the two major branches of the brachial artery in the forearm?
radial and ulnar arteries
31
New cards
what is anastomosis
A surgical connection between two structures, such as blood vessels, intestines, or nerves, to allow the flow of fluids or information.
32
New cards
physiologic examples of anastomosis
superficial palmar arch and deep palmar arch, circle of willis, anterior and posterior inter ventricular artery
33
New cards
pathologic examples of anastomosis
fistulas, intestines
34
New cards
possible types of anastomosis
arterioarterial, venovenouos, arteriovenous
35
New cards
formation of the superior palmar arch in the hand
\-ulnar artery
\-completed laterally by superficial branches of the radial artery
\-completed laterally by superficial branches of the radial artery
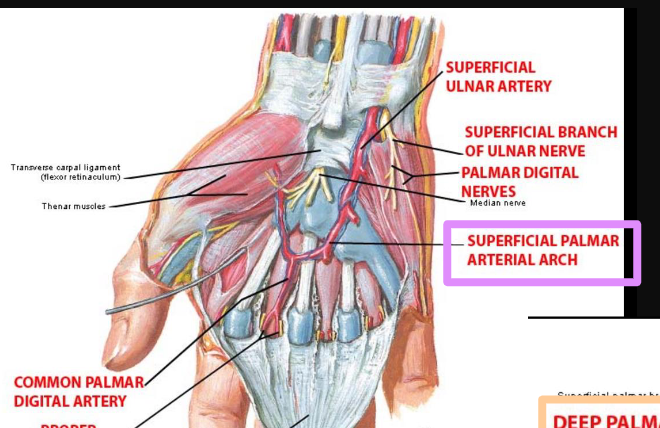
36
New cards
what forms the deep palmar arch in the hand?
radial artery
37
New cards
list the superficial veins of the arm and forearm
basilic, cephalic, antecubital
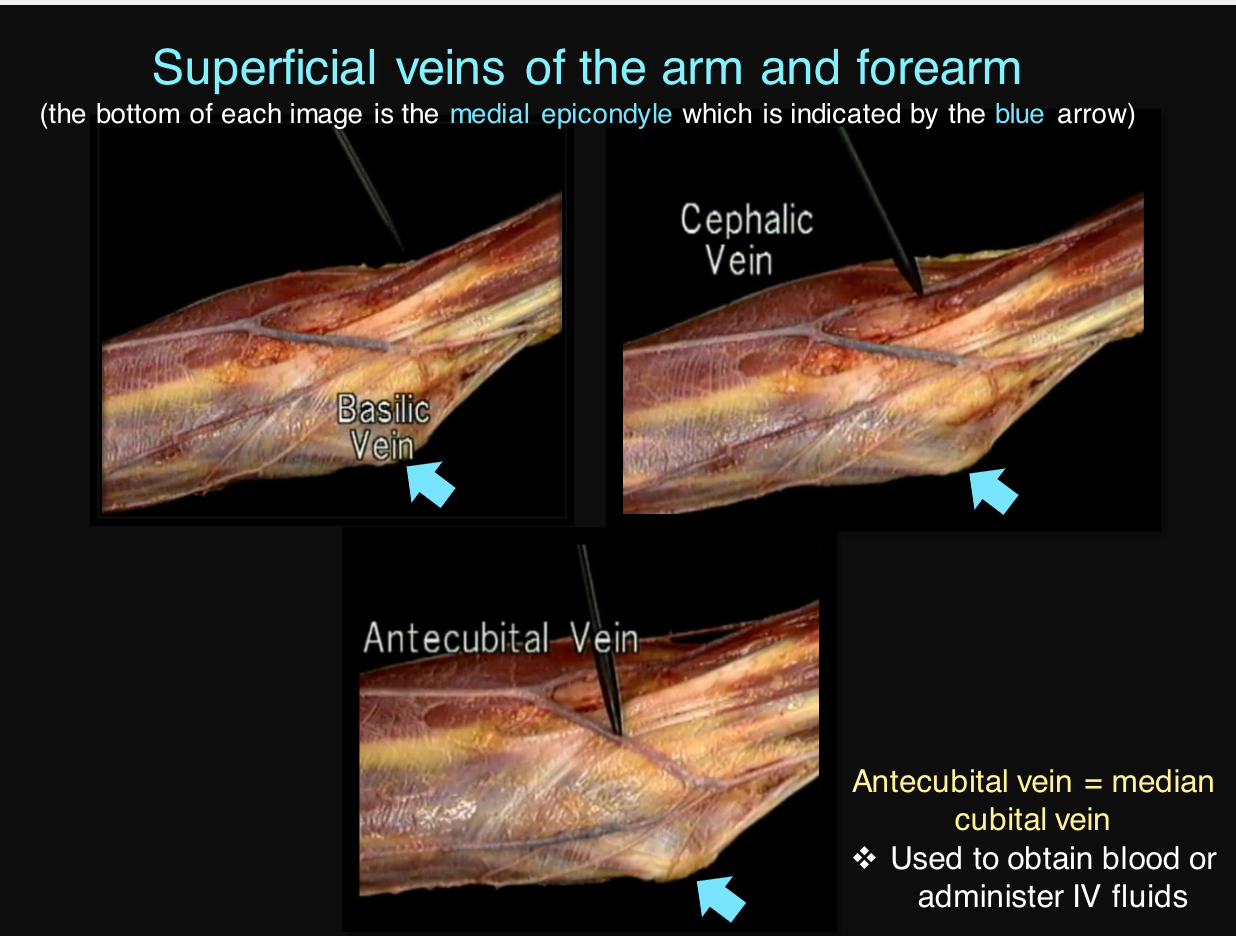
38
New cards
antecubital vein
median cubital vein
\-used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids
\-used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids
39
New cards
important branches of the descending aorta
\-bronchial arteries
\-phrenic arteries
\-phrenic arteries
40
New cards
what are the paired branches off of the abdominal aorta
gonadal and renal
41
New cards
order of the femorals
femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein
42
New cards
what is the main branch of the femoral artery?
deep femoral artery
43
New cards
what rarer the branches of the deep femoral artery?
medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries
44
New cards
course of the branches of the deep femoral artery
\-medial passes posteriorly to the femur
\-lateral pasases anterioly
\-lateral pasases anterioly
45
New cards
supply by the medial circumflex artery
the main artery that supplies the head and neck of the femur
46
New cards
clinical significance of medial circumflex femoral artery
damage to this artery following a femoral neck fracture can result in avascular necrosis of the femoral head
47
New cards
when does the femoral artery become the popliteal artery?
past the adductor hiatus
48
New cards
location of the popliteal artery
runs between the two heads of the gastrocnemius and gives rise to the tibia arteries
49
New cards
name the branches of the popliteal artery
anterior tibial, posterior tibial, a bunch of genicular arteries
50
New cards
what artery gives rise to the dorsals pedis artery?
anterior tibial (branch of popliteal)
51
New cards
what artery gives rise to the fibular artery?
posterior tibial (branch oof popliteal)
52
New cards
clinical significance of dorsals pedis artery
\-on the anterior side of the ankle
\-major source of blood supply to the foot and its pulse can be palpated
\-major source of blood supply to the foot and its pulse can be palpated
53
New cards
what arteries give rise to the arterial circle (circle of willis) in the brain?
internal carotid and vertebral
54
New cards
what are the arteries that make up the circle of willis?
anterior cerebral, anterior communicating, posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotids
NO middle cerebral arteries
NO middle cerebral arteries
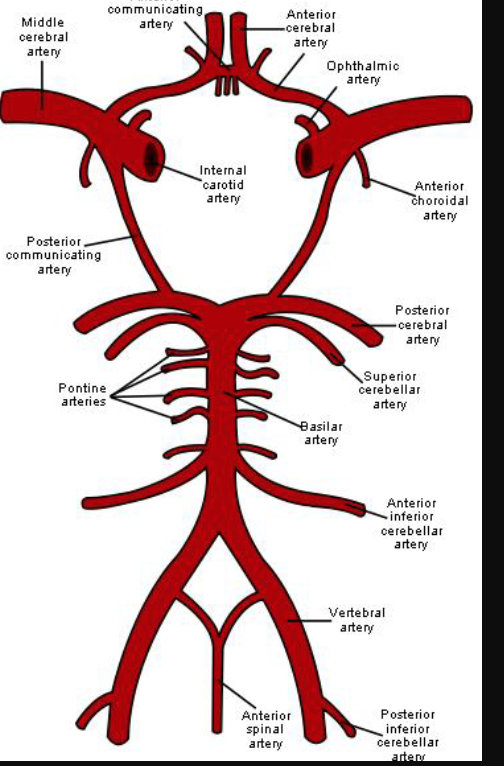
55
New cards
define sinuses
veins that drain the brain
56
New cards
where do dural sinuses eventually drain?
the internal jugular vein
57
New cards
location of cavernous sinus
runs with internal carotid artery
58
New cards
which cranial nerves can go through the cavernous sinus?
III, IV, V1, V2, and VI
59
New cards
clinical manifestation of tumors in cavernous sinus
can adversely effect the cranial nerves that travel through this sinus
60
New cards
name the superficial veins
great saphenous vein and small saphenous vein
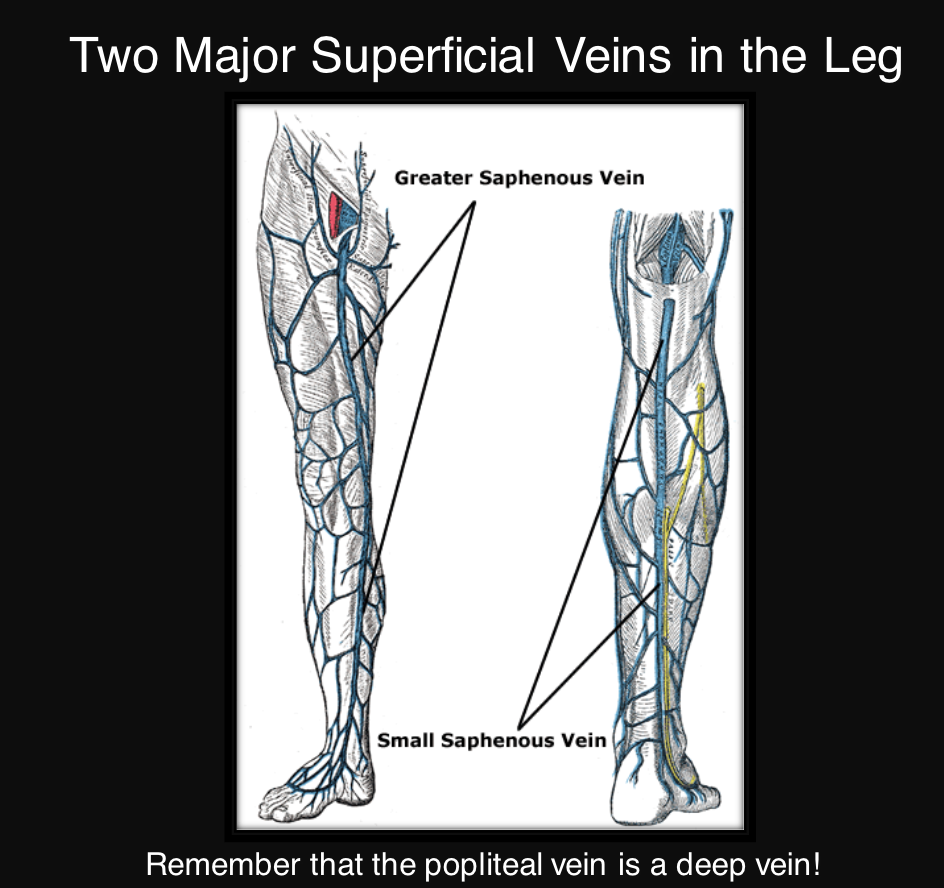
61
New cards
great saphenous vein empties what?
femoral vein
62
New cards
small saphenous vein empties into what?
popliteal vein
63
New cards
examples of deep veins in the upper limb
brachial, axillary, subclavian
64
New cards
examples of deep veins in the lower limb
femoral vein, deep femoral vein, popliteal vein, anterior and posterior tibial vein
65
New cards
deep vein thrombosis
\-a blood clot in a deep vein
\-symptoms: pain, swelling, nonspecific
\-symptoms: pain, swelling, nonspecific
66
New cards
what is the most serious complication of a DVT?
aa blood clot can break off and travels through the blood stream to the lungs causing a pulmonary discipline
67
New cards
name the warning signs of pulmonary embolism
shortness of breath, chest discomfort, general sense of anxiety
68
New cards
what is the role of the lymphatic system?
\-ducts collect toxins, dead cells, extra fluid, and fat
\-content is returned to the venous system via two asymmetrical lymph vessels
\-content is returned to the venous system via two asymmetrical lymph vessels
69
New cards
what are the main two lymphatic vessels
thoracic duct, right lymphatic duct
70
New cards
where does the right lymphatic duct drain?
into the right subclavian
71
New cards
where does the thoracic duct drain?
drains into the junction of left subclavian and left internal jugular vein
\-drains a much larger portion of the body
\-drains a much larger portion of the body
72
New cards
cisterna chyli
drains the lymph from the lower limbs and the intestines (right and left lumbar trunks and the instestinal trunk)
73
New cards
what are the tributaries to the superior vena cava?
\-right brachiocephalic vein
\-left brachiocephalic vein
\-azygoous vein
\-left brachiocephalic vein
\-azygoous vein
74
New cards
what does the azygous vein drain?
RIGHT posterior thorax and posoterior intercostal veins
\-tributary of svc
\-tributary of svc
75
New cards
what arteries are direct branches from the aorta
brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid, left subclavian, left coronary artery, right coronary artery
76
New cards
what nerve travels alongside middle meningeal artery?
auriculotemporal nerve in the infratemporal fossa
\-CN IX
\-CN IX
77
New cards
what is the superficial palmar arch formed from?
ulnar artery
78
New cards
what are the branches of the popliteal artery?
anterior tibial artery, posterior tibial, vehicular arteries
79
New cards
label the circle of willis
A circulatory system structure found at the base of the brain, consisting of arteries that supply blood to the brain and surrounding structures. It includes the anterior cerebral arteries, posterior cerebral arteries, and the internal carotid arteries.
80
New cards
For example, when the
_____ __has an obstructed blood__ \n __flow, the__ _____ __can supply blood flow to the anterior__ \n __compartment of the brain through__ ____.
_____ __has an obstructed blood__ \n __flow, the__ _____ __can supply blood flow to the anterior__ \n __compartment of the brain through__ ____.
internal carotid
vertebral artery
basilar artery
vertebral artery
basilar artery
81
New cards
which dural sinuses drain into the confluence of sinuses?
superior and inferior sagittal sinus
82
New cards
what does the accessor hemiazygos and hemiazygos veins drain?
left posterior thorax and posterior intercostal
83
New cards
CT manifestation of PE
the diameter of the RV is enlarged and bigger than the LV
84
New cards
what vessel is the gold standard for use in CABG surgery?
internal thoracic artery, branch of subclavian
85
New cards
branches of external carotid
some anatomists like freaking out poor medical students
superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal
superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal
86
New cards
what is the course of the maxillary artery?
begins in the infrartemporal fossa; travels medially to goo to the pterygopalatine fossa and into the nasal cavity
87
New cards
what are the branches of the maxillary artery?
middle meningeal, sphenopalatine, inferior alveolar
88
New cards
what artery supplies most of the dura and calvaria?
middle meningeal artery; rupture causes epidural hematoma
89
New cards
what are the veins of the thorax
azygos vein, hemiazygos, accessory hemiazygos
90
New cards
first part of axillary artery
\-proximal to pec minor
branch: superior thoracic artery
branch: superior thoracic artery
91
New cards
second part of axillary artery
posterior to pec minor
branches: thoraco-acromial artery, lateral thoracic artery
branches: thoraco-acromial artery, lateral thoracic artery
92
New cards
third part of axillary artery
distal to pec minor
branches: anterior circumflex artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery, sub scapular artery
branches: anterior circumflex artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery, sub scapular artery
93
New cards
list the branches of the axillary artery
Save the Lions and Protect the Species
supreme thoracic, thoracoacromial, latereal thoracic, anterior humeral circumflex, posterior humeral circumflex, sub scapular
supreme thoracic, thoracoacromial, latereal thoracic, anterior humeral circumflex, posterior humeral circumflex, sub scapular
94
New cards
list the branches of thoracoacromial
second part of axillary
cadavers are dead people
clavicular, acromial, deltoid,a nd pectoral
cadavers are dead people
clavicular, acromial, deltoid,a nd pectoral
95
New cards
what is the importance of the quadrangular space?
This space is crucial for the passage of vital structures such as the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. It also serves as a landmark for identifying the teres minor and major muscles in the shoulder region.
96
New cards
what arteries wrap around the surgical neck of the humerus?
anterior and posterior humeral circumflex arteries
97
New cards
what artery forms the superficial palmar arch in the hand?
ulnar artery
98
New cards
what artery forms the deep palmar arch?
radial artery
99
New cards
what are the branches of deep femoral artery
medial and lateral circumflex femoral arterriese
medial passes psosterriorly
medial passes psosterriorly
100
New cards
what is the main artery supplying the head and neck of the femur?
medial circumflex femoral artery
\-damage to this artery following a femoral neck fracture can result in avascular necrosis of femoral head
\-damage to this artery following a femoral neck fracture can result in avascular necrosis of femoral head