Histology Quiz 5
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
1
New cards
walls of heart
where in the body is cardiac muscle found?
2
New cards
intercalated discs
specialized features of cardiac muscle cells that promote coordinated, synchronized contraction and connect cells
3
New cards
skeletal
what type of muscle?

4
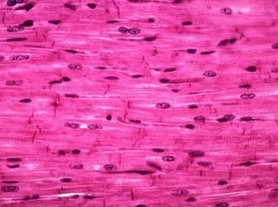
New cards
cardiac
what type of muscle?
5
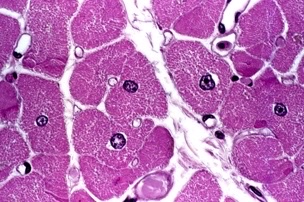
New cards
cardiac
What muscle type?
6
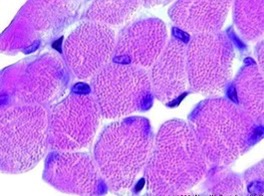
New cards
skeletal
what muscle type?
7
New cards
involuntary contractions in digestive and urogenital systems and blood vessels
function of smooth muscle
8
New cards
less powerrful
how does the power of smooth muscle contractile machinery compare to other muscle types
9
New cards
layers
how is smooth muscle typically arranged
10
New cards
long, tapering
smooth muscle cells are _____,__ with ________ ends to allow them to pack tidily into a layer
11
New cards
less
smooth muscle is ______ acidophilic than cardiac and skeletal
12
New cards
no
does smooth muscle include myofibrils or sarcomeres?
13
New cards
dense bodies
Specialized junctions in smooth muscle which connect both \n intermediate filament and actin cytoskeletons of adjacent cells
14
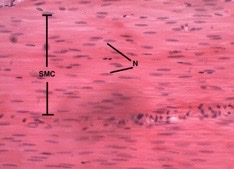
New cards
smooth
what type of muscle?
15
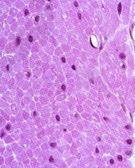
New cards
smooth
what type of muscle?
16
New cards
circulate blood carrying nutrients, oxygen ect through body
function of the circulatory system
17
New cards
heart
propels blood through body
18
New cards
blood vessels
carries blood through body
19
New cards
blood
contains materials that need to circulate through body
20
New cards
endocardium
inner layer of heart walls made of epithelium and connective tissue
21
New cards
myocardium
middle, thickest layer of the heart made of cardiac muscle (cardiomyocytes) cells that is highly vascularized
22
New cards
epicardium
outer layer of the heart wall, contains embedded blood vessels and nerves often with extensive white adipose tissue
23
New cards
left ventricle
where is myocardium typically thickest
24
New cards
atria
blood enters which heart chambers from veins?
25
New cards
endothelium
simple squamous epithelium layer of the endocardium
26
New cards
no
does the myocardium contain a lot of connective tissue?
27
New cards
mesothelium
simple squamous epithelium layer lining epicardium
28
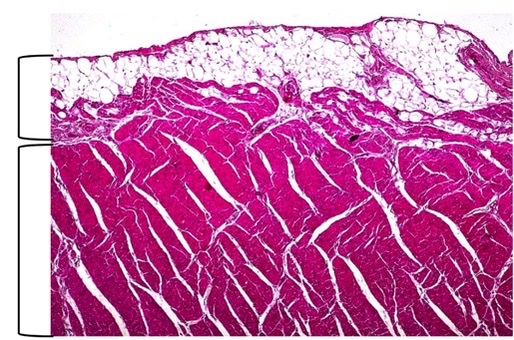
New cards
epicardium, myocardium
which heart layers?
29
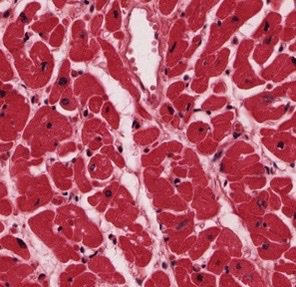
New cards
myocardium
which heart layer?
30
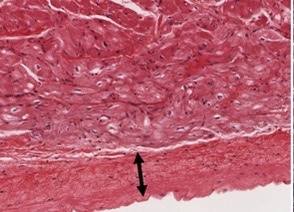
New cards
endocardium
which heart layer?
31
New cards
ventricles
contract simultaneously to force blood into arteries
32
New cards
atria
contract simultaneously to force blood into relaxed ventricles
33
New cards
delay
what occurs between atrial and ventricular contractions
34
New cards
sinoatrial node
generates initial impulse to begin contraction
35
New cards
AV node
impulse signal delayed briefly here before traveling down into ventricles, thus introducing delay between atrial and ventricular contractions
36
New cards
purkinje fibers
specialized cardiomyocytes that conduct contractile impulse rapidly through ventricles to induce ventricular contractions
37
New cards
ventricles, they are larger
in which chambers can you find purkinje fibers? why?
38
New cards
paler cytoplasm w/o striations and only found in endocardium
how do purkinje fibers differ from typical cardiomyocytes?
39
New cards
intercaulated discs
what contractile structure of the heart?
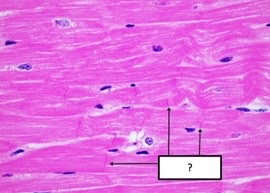
40
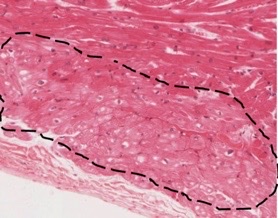
New cards
purkinje fibers
what contractile structure of the heart?
41
New cards
CT lined w/ epithelia
what are heart valves made of?
42
New cards
hypertrophy
individual heart cells and nuclei enlarge in response to stress
43
New cards
not accompanied by increased vascularization
problem with hypertrophy
44
New cards
Myocardial infarction
Occur when a region of the heart is deprived of its blood supply, often due to a severe arterial blockage. Tissue is invaded by immune cells and replaced w/ fibrous tisssue
45
New cards
arteries
carry (typically oxygenated) blood away from heart
46
New cards
veins
carry (usually deoxygenated) blood back to heart
47
New cards
capillaries
site of gas exchange within tissues
48
New cards
arteries, veins
blood at high pressure in _____ and low pressure in ______
49
New cards
tunics
what are layers of blood vessels called
50
New cards
Tunica Intima
Innermost layer of blood vessel lining lumen. Present in all blood vessels bc it contains endothelium
51
New cards
tunica medica
middle smooth muscle layer of blood vessel
52
New cards
tunica adventitia
outer CT layer of blood vessel not always present in smaller vessels
53
New cards
inner elastic lamina
underlying layer of elastic fibers in the tunica intima of some larger vessels
54
New cards
prevent clotting, regulate blood flow, mediate material exchange
functions of blood vessel endothelium
55
New cards
muscle contraction to control vessel diameter/ bp
tunica media function
56
New cards
arteries, veins
_____ have more elastic fibers and a thicker tunica media because they play a more important role in regulating blood \n pressure while ________ often have a thicker, better developed adventitia to provide additional structural support
57
New cards
valves, veins
___ are found in _______ to prevent backflow of blood due to low pressure?
58
New cards
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica adventitia
what blood vessel layers?
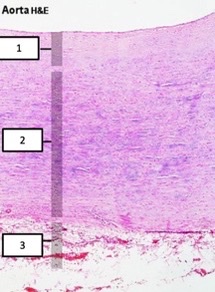
59
New cards
tunica intima
what blood vessel layers?
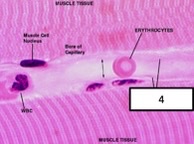
60
New cards
elastic arteries
\-largest arteries closest to heart
\-Aorta, pulmonary arteries, and their largest branches \n -Greatest need for smooth muscle (to regulate blood \n pressure) and flexibility (to accommodate changes in \n blood pressure and volume)
\-Aorta, pulmonary arteries, and their largest branches \n -Greatest need for smooth muscle (to regulate blood \n pressure) and flexibility (to accommodate changes in \n blood pressure and volume)
61
New cards
muscular arteries
large vessels branching off of elastic arteries to distribute blood to organs
62
New cards
arterioles
distribute blood throughout organs and tissues
63
New cards
tunica media
what layer is very thick in elastic arteries?
64
New cards
lamellae
alternating layers of smooth muscle and elastic fibers in the tunica media
65
New cards
muscular
in what type of artery would you find the inner elastic lamina?
66
New cards
vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta
order of blood flow through heart