Protozoans
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Protozoa
Free living single eukaryotic cells
Injest food through a cytosome
reproduce asexually or sexually.
When exposed to new temps of environmental changes, they secrete a protective coat to create a cyst
This is the form that is infective when injested
once injested, converts back into the motile trophozoite form
Cyst
A dormant, protective form of protozoa that can survive harsh environmental conditions and is infective when ingested.
Trophozoite
The active, motile feeding stage of protozoa that reproduces and carries out metabolic processes.
2 stages of plasmodium life cycle
sexual repoductive stage in mosquito hosts
asexual reproductive stage in human hosts with 2 cycles:
one in RBCs (erythrocytic cycle)
one in Liver (exo-erythrocytic cycle)
Primaquine
Drug that is active against the quiescent hypozonites of P. vivax and P. ovale
eg, can kill the hyphozoites hiding in the liver
This drug MUST be added to malaria regimens for P vivax and P ovale
Plasmodium Species
Transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito generally in resource-limited settings
Africa accounts for 94% of cases globally
4% for the rest of the Americas
U.S.: Travelers with 2000/cases a year
• 85% from Africa with the majority from West Africa
Plasmodium species incubation periods
Bitten by mosquito: 2 hours later migrate to liver and stay there
Asymptomatic for 12-35 days after infection
Symptoms begin b/c parasite enters erythrocytic stage → red blood cells to rupture and release merozoites, which cause fever and other symptoms
What is unique about P vivax and P ovales incubation periods?
They can remain dormant in the liver as hypnozoites, leading to relapses after initial infection. Relapses may occur within 2-3 years
P Falciparium and P Malariae
DO NOT RELAPSE
Clinical Presentation of uncomplicated plasmodium
Fever at intervals
Anemia
Palpable spleen
mild jaundice
Dx: blood smears and rapid tests
Fever interval for P vivax and P ovale
Every other day
Fever interval for P malariae
Every third day
P Falciparium differentiating characteritstics
Banana shaped gametocyte
more than one organism in a RBC
more than one organism seen in a blood smear
Has HIGH infectivity and a HIGH parasite load
Duffy blood group factor
Required by P vivax to invade RBCs
Sickle Cells
Protects you from getting P falciparium
Partial immunity
displayed by those living in endemic areas of malaria; however, if they move away and return years later, they will get malaria again
P Falciparium is commonly resistant to
chloroquine
Nephrotic syndrome
Can be caused by P malarie due to a mixed immunoglobin IgM and IgG basement membrane immune complex neuropathy
G6PD patients
Primaquine CANNOT be used in these individuals (causes hemolysis)
Main causes of malaria in the US
Not taking prophalylaxis
Stopping prophalylaxis too soon
Babesia Microti
Nantucket island, Massachusetts, Northeast, Uppermidwest
Tick bite
coinfection with lyme
Asymptomatic infection is common
May see haptosplenomagaly
Sever disease seen in immunocomp or older:
splenic infarcts and rupture
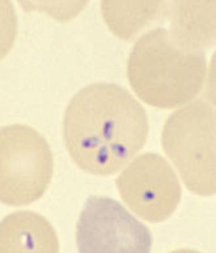
Maltese cross
Babesia Microti
Toxoplasma gondii
Cats are the only animal where they can complete their reproductive cycle
Humans inject oocytes, organisms invade to intestinal epithelium and disseminate throughout the body
can encyst in ANY nucleated cell and lie dormant in host
Increased risk of injesting oocytes: owning 3 or more kittens!
Vertical transmission from mother to baby: TORCH
Pregnant woman CANNOT clean out litter boxes
Toxoplasma Gondii clinic presentations
Most asymptomatic
If ill, bilateral, symmetrical, nontender cervical adenopathy
Dx: ELISA, PCR, serology
Tx: symptomatic
Toxoplasma Gondii TORCH
Transplacental transmission is HIGHEST in 3rd trimester
HOWEVER! The earlier the infection the more likely severe issues will occur
Severe manifestations at birth: Microcephaly, cerebral calcifications, seizures, psychomotor retardation
Others appear normal but develop symptoms months or years later
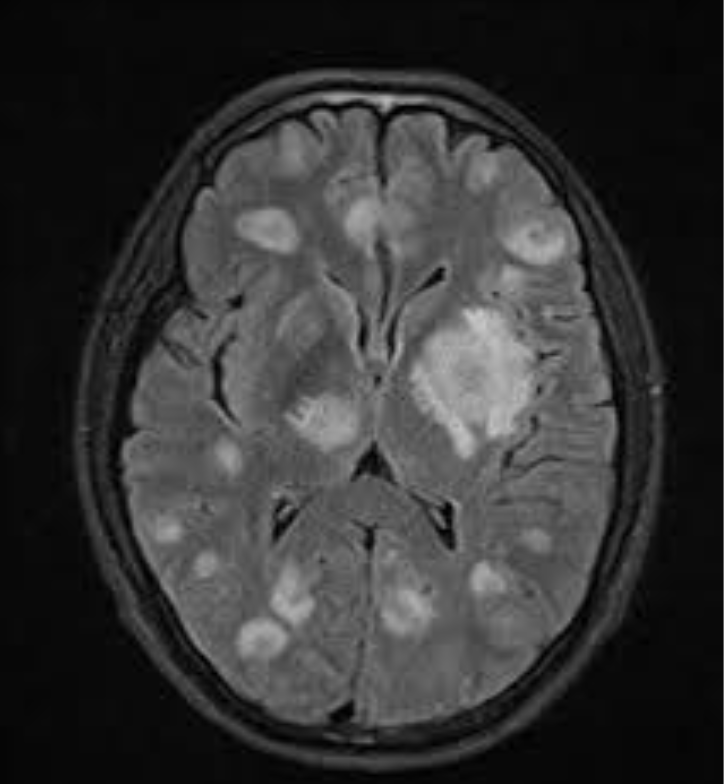
Chorioretinitis
Chorioretinitis
due to Toxoplasma Gondii ToRCH infection
Presents during teens or 20s. (Thought to be reactivation latent tissue cysts)
Accounts for 25% of all granulomatous uveitis in the U.S
Cryptosporidium
Life cycle can be completed in humans!
Injest oocytes → excystation in small intestine → release of sporozoites that infect intestinal epithelial cells.
3 main scenario we see this organism
Sporadic, water-related outbreaks of self-limited diarrhea in
immunocompetent hostsChronic, life-threatening illness in immunocompromised (HIV)
Diarrhea and malnutrition in young children in resource poor countries
Source of infection: contaminated water
SWIMMING POOL OUTBREAKS! PONDS/LAKES. “Occasionally in tap water!”
Clinical Manifestations of Cryptosporidium
Secretory diarrhea and can be very minimal or up to 25L/day of watery stool
Resolves without therapy in usually 10-14 days in immunocompetent
AIDS: longer course and extraintestinal disease
Biliary involement in 10-30%
Dx: PCR
oocytes in stool are acid-fast positive
Tx: immunocomp need Nitazoxanide or Paromomycin
Cyclospora
Initial U.S outbreak (TEXAS) were raspberries from Guatemala
Lettuce, basil, snap peas, cilantro and prepackaged salads from
Guatemala and Mexico
Usually asymptomatic, but if symptoms watery diarrhea and low grade fever
Dx: Acid-fast stain of stool! 8-10 microns (Cryptosporidium is smaller)
TX: Trimethoprim/sulfamethazine (important to distinguish from Cryptosporidium because of this!)
Cystoisopora belli (formerly isopora belli)
In contrast to all the other protozoan diarrheal illnesses
(Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora) this organism causes EOSINOPHILIA
Balamuthia
A free-living amoeba that causes weeks to months of chronic neurologic disease with skin lesions
Naegleria Fowleri
Thermophilic ameboflagellate protozoan parasite in water and soil
Risks:
Swimming in a Texas Cow pond
TAP WATER
NETI POTS Be sure to use DISTILLED WATER!!!
Primary amebic meningoencephalitis
Dx: Motile trophozoites on exam of centrifuged CSF wet mount
Primary amebic meningoencephalitis
Caused by Naegleria Fowleri
99% mortality rate
Mean incubation period is 5 days
High fever, H/A, photophobia
Rapid deterioration with severe cranial hypertension leading to herniation and death in a few days
Acanthamoeba
Most common ameba found in nature
Found humidifiers and contact lens!!
Transmission has been by inhalation of cysts carried by wind through respiratory tract or direct skin contact with subsequent hematogenous spread
Can occur simultaneously with Legionella, Listeria, and Mycobacterium
Causes opportunistic infection in immunocompromised hosts (except for eye disease in immunocompetent contact lens wearers)
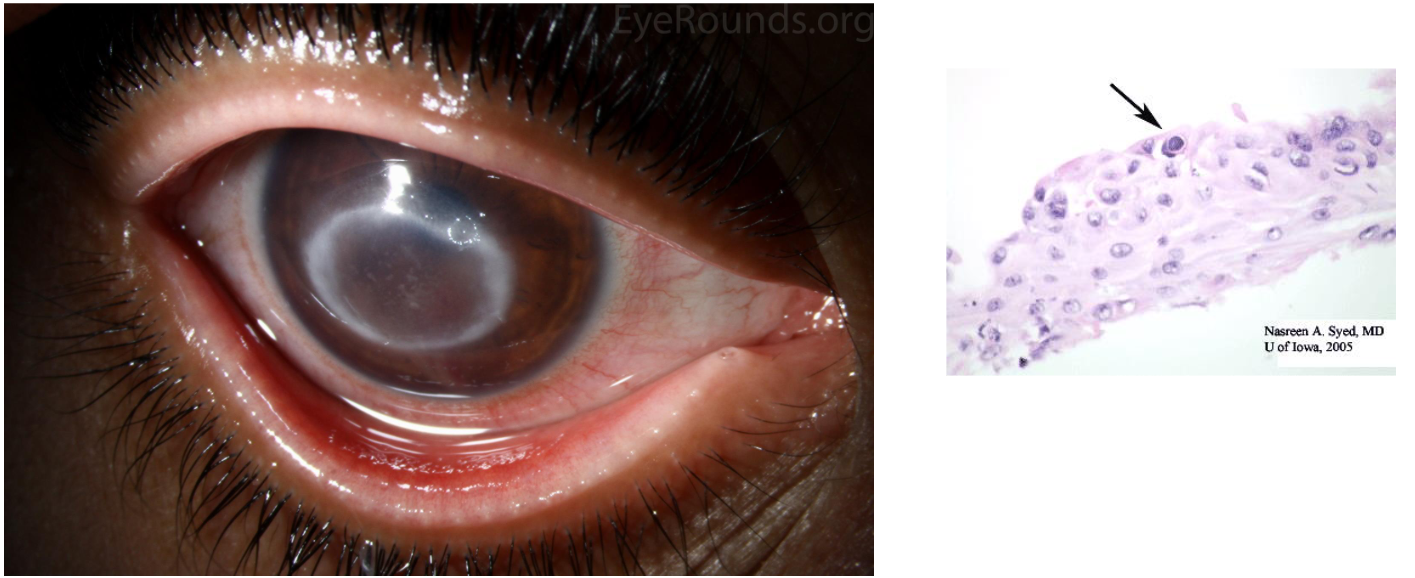
Keratitis
Caused by Acanthamoeba
Contact lens wearers
• Using non-sterile tap water to put contact lens in the eye
• COMMERCIAL contact lens solutions (SCARY!!)
• Showering while wearing contact lens!
• Symptoms: Conjunctival hyperemia, tearing, pain, photophobiaDx: See organisms via staining corneal scrapings with florescent dye calcofluor
Entamoeba hisolytica
Can cause intestinal AND extraintestinal disease
Worldwide (seen in US immigrants)
2 forms
cyst stage (infective)
trophozoite stage (causes invasive disease)
Infection from ingesting cysts from contaminated food or water or sexual contact through fecal-oral contact
1 single cyst can cause disease
Entamoeba histolytica disease process
Ingest a cyst, the cyst passes into the small intestine and it excysts to form a trophozoite
Trophozoite penetrates the colon → tissue destruction and increased intestinal secretions resulting in bloody diarrhea
The trophozoite can kill epithelial cells AND inflammatory cells!
It secretes proteinases
Kills human cells by apoptosis
Forms amebapores
Changes intestinal permeability via disruption of tight-junction proteins
Clinical Presentations of Entamoeba histolytica
Asymptomatic 90%
Clinical acute
Mild diarrhea to severe dysentery
Extraintestinal disease
Amebic liver abscess
4th leading cause of death by parasite worldwide
Dx: Stool antigen or PCR
Tx: EVERYONE is treated
asym: paromycin to prevent future issue
sym: Metronidazole (systemic therapy) followed by paromomycin (to complete intraluminal killing)
Amebic Liver Abscess
Caused by Entamoeba histolytica infection
4th leading cause of death by parasite worldwide
Reach the liver by ascending the portal venous system
7-10x more likely in adult men between 30-50 years of age
Clinical Manifestations
Median 12 weeks (8-20 weeks) presentation with 1-2 weeks of Right upper
quadrant (RUQ) pain and fever. Pain can be referred to right shoulder.
• Diarrhea is NOT present
• PE: Hepatomegaly and point tenderness over the liver
Rupture of the liver abscess can occur and can go into the chest (most likely)! Or peritoneal cavity
Dx: Stool is NOT helpful here!!! KNOW THIS! (unless has diarrhea [rare])
BLOOD serologic test and radiologic imaging of the liver
U/S, CT or MRI
“Anchovy paste liver”
Tx for extraintestinal Entamoeba histolytica
Systemic agent: Metronidazole or tinidazole
Luminal agent: Paromomycin
Other extraintestinal sites of Entamoeba histolytica ASIDE from liver abscess
Pleuropulmonary (occurs in 20-35% of those with liver abscess
Risk factor: Chronic alcoholism, Atrial septal defect (ASD) with a left-to-right shunt
Pain, cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea
Cough can be nonproductive or “LARGE AMOUNTS OF AMEBIC PUS”
Dx: BLOOD serology
Tx: Aspirate pleural effusions if present and same antibiotics
Can affect the heart, brain, and skin more rarely
Flagellates general characteritics
widespread in nature
binary fission
Originates from an intracellular focus known as a kinetosome (basal body)
Kinetosome
It extends to the cell wall as a filamentous axoneme composed of microtubules arranged in the typical 9 pairs and 2 central microtubular pattern and continues extracellularly as a free flagellum
A pair of dynein arms extends from each outer microtubule of a pair to an adjacent
microtubular pair and is responsible for flagellar beating through ATP hydrolysis.The whole flagellar unit and its associated organelles are called a mastigont system
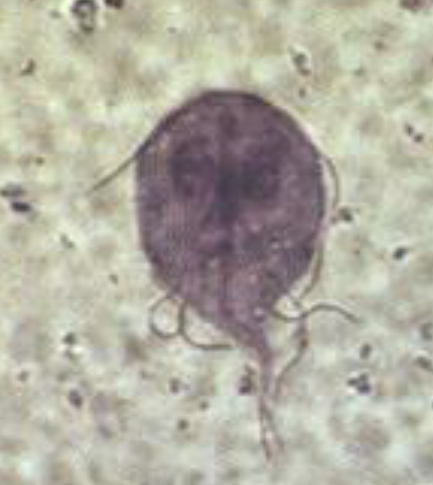
Trichomonas vaginalis
most common nonviral STI
infects squamous epithelium
It is pear- or round-shaped with 4 anterior flagella and an undulating membrane that causes characteristic motility seen on wet-mount slide of vaginal sections
Trichomonas vaginalis clinical presentation
Purulent, malodorous, thin vaginal discharge with burning, itching, dysuria, frequency, lower abdominal pain and/or dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
Exam: Erythema of the vulva and vaginal mucosa
Dx: PCR or microscopy
We do test of cure in women (only); return in 3 weeks to
3 months and get retested to make sure it’s cured.
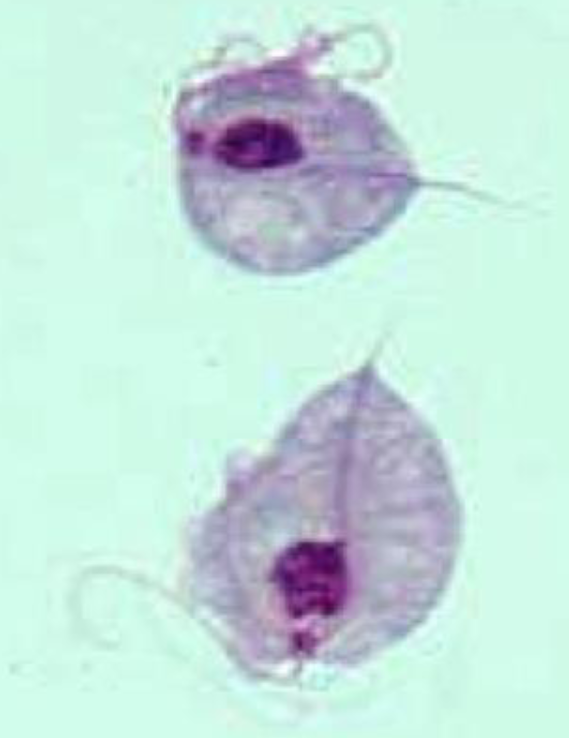
Giardia duodenalis
Sting-ray shaped flagellate with 2 life forms
Cysts
infectious form
excreted in stool
following infection, excytation in the duodenum and jejunum
Trophozoites
live in duodenum and jejunum
Does NOT invade mucosal epithelium
Secretory immunoglobulin A antibodies appear to be important for humoral immunity
Giardia Duodenalis risk factors
international travel
Drinking water from a river, lake, stream, etc
“Phenotypic Patient We see in Colorado”
• Caused by Coors Beer, but not due to consumption!Contact with children in diapers (daycare!)
Giardia Duodenalis clinical manifestations
Acute Infection
• Incubation period of 7-14 days (less than this is likely NOT giardia)
• Diarrhea, malaise, “stinkiest stools you will ever smell,” flatulence,abdominal cramps and bloating
• “Sulfuric belching”Chronic Infection
• 50% of acute if not treated will go on to develop chronic infection
• Loose stools but not diarrhea, profound weight loss (10-20% body weight!), malabsorption, depression, abdominal cramping
• Borborygmi• Deficiencies of Vitamin A, B12, and folate
• 40% will get acquired lactose intolerance!
Dx: PCR
Leishmaniasis
Blood and Tissue Flagellates
complex of vector-borne diseases caused by the genus
Species determines the diease process
cutaneousm→ may or may not heal
visceral → highly lethal
Transmitted by sandflies
complement mediates macrophage attachment
BUT sandfly salivary peptides inhibit macrophage killing
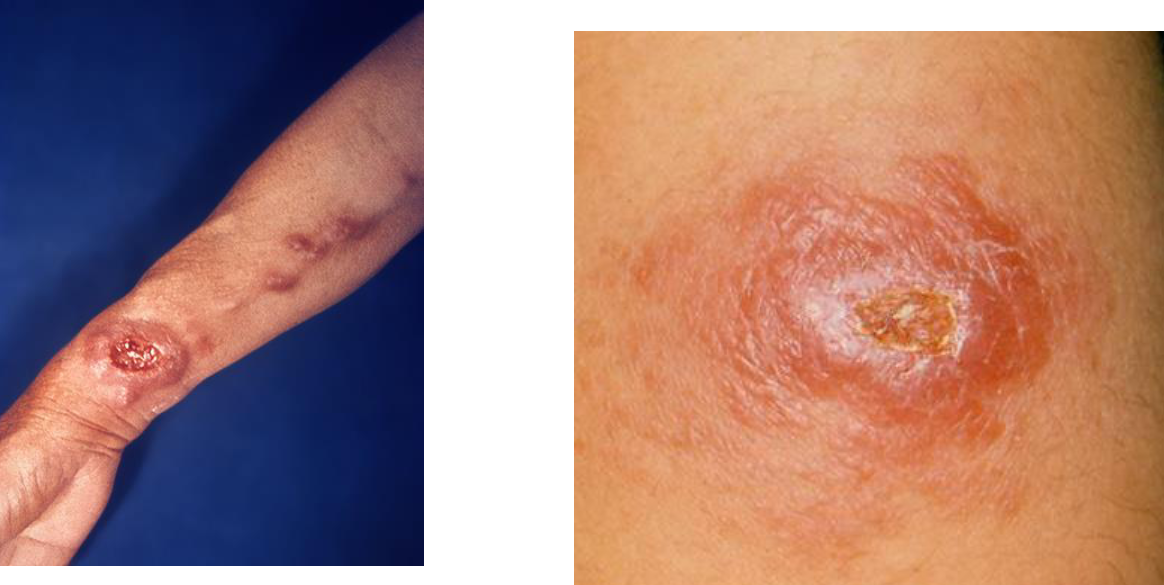
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Incubation period of weeks to months and even years (asymptomatic infection in about 10%)
Wide spectrum of disease
Localized Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Lesions on exposed skin bc sand fly mouthparts cannot
penetrate through clothingStarts as painless pink papule → a large nodule → painless ulceration with an indurated border
Gradual healing over months/years
Reactivation can develop during the subsequent year or later for mucosal leishmania (which is very destructive of nasal and other cartilage!)
Dx: Skin histology, culture or PCR (usually all 3)
Tx: Azoles, pentavalent antimony, etc
Visceral Leishmaniasis
Known as Kala-azar (black fever)
invade and replicate within host macrophages
Infection persists after clinical cure of primary infection
Many keep the infection “in check” and are asymptomatic and have the infection for life without any symptoms
2-6 month incubation (range weeks to years)
Insidious or subacute onset with slow progression of fever, weight loss and splenomegaly over weeks to months
May complain of abdominal discomfort and fullness of LUQ
Dx: smears showing Leishman-Donovan
bodies (amastigotes seen in mononuclear phagocytes on blood smear)
Human African Trypanosoma
Sleeping sickness
Transmitted by tsetse flies
Acute form: East and Southern Africa
rhodesiense HAT
FAST
incubation is less than 3 weeks
rapidly progressive
Chronic form: West and Central Africa
gambiense HAT
SLOW
incubation is months
slowly progressive
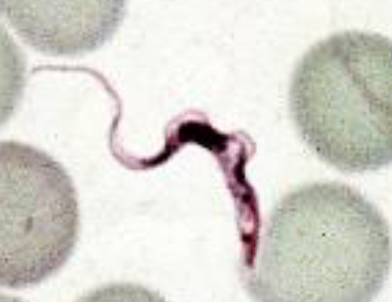
Stages of Trypanosomiasis
First stage
penetration of skin
chancre at site ot tsetse bite
Rhodesiense: Lymphadenopathy less commonly and submandibular, axillary, inguinal regions
Gambiense: Posterior cervical node lymphadenopathy
Second stage
Profound fatigue, changes in behavior, Sleep cycle reversed—awake night/sleep day, anxiety, delirum
CNS involvement
Dx: lymph node aspirate
American Trypanosoma (T. Cruzi)
Chagas Disease
Leading cause of chronic heart disease and accounts for 25% of all deaths in 25-44 year olds
3 cm large insect hides and comes out at night to feed on its sleeping hosts (reduviid, “Kissing bug”)
~300,000 in the U.S. who immigrated here are infected and do not know it
How is American trypanosomi different from African trypanosomi?
The bloodstream trypomastigotes do not replicate. Replication resumes only when the parasites enter another cell or are
ingested by another vector
Clinical Presentation of Chagas disease
The patients has 8-12 weeks of circulating trypomastigotes that only cause mild symptoms (fever, malaise) or are asymptomatic
Rarely at the site of inoculation inflammation/swelling occur called a chagoma
Usually on the face or extremities
If on the conjunctiva (OUCH!), it leads to a painless swelling of upper and lower eyelid known
as Romaña's sign.
< 1% will have severe acute disease with acute myocarditis, meningoencephalitis
Dx: Microscopy of fresh blood or “buffy coat”= you spin down a vial of blood and between the red blood cells and the plasma is a thin layer of just white blood cells, AKA the buffy coat
Tx: Benznidazole and nifurtimox
Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy
• Asymptomatic or have dyspnea on exertion, palpitations
Present with ventricular arrhythmias, abnormalities of the
conduction systemCardiac exam findings:
• Mitral and or tricuspid regurgitation murmurs
• Wide splitting of the 2nd heart sound due to right bundle branch blockCXR will show cardiomegaly
Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy 4 major types of disorders
Heart failure
Arrythmias
Thromboembolism
Chest pain syndrome
Chronic Chagas Gastrointestinal Disease
Occurs between ages 20-40 years
Can be any part of GI tract
A big dilated poorly functioning esophagus develops with difficulty and pain
with swallowing.Regurgitation of food is likely
A dilated colon (Megacolon) result in constipation and abdominal pain
Weeks may occur before they have a bowel movement