EXSC 2510 Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/169
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
1
New cards
Endocrine system
composed of endocrine organs and structures that produce and secrete hormones. It regulates and controls bodily functions
2
New cards
endocrine glands
glands that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream
3
New cards
exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances outward through a duct and outside the body
4
New cards
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves
5
New cards
target cells
cells that have receptors for a particular hormone
6
New cards
target organs
organs that respond to a particular hormone
7
New cards
Feedback in the endocrine system
how hormone secretion is regulated
8
New cards
negative feedback
the affected hormone or product causes the process to slow down
9
New cards
positive feedback
the affected hormone or product causes the process to speed up
10
New cards
infundibulum
connects pituitary gland to hypothalamus
11
New cards
Hypothamalus
Regulates basic biological needs (ex. hunger, thirst, temperature control)
12
New cards
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
13
New cards
regulatory hormones
Control release of hormones from anterior pituitary
14
New cards
anterior pituitary hormones
Growth hormone (GH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
15
New cards
releasing hormones
chemical that stimulates other glands to release their hormones
16
New cards
inhibiting hormones
prevent synthesis and secretion of hormones from the anterior lobe
17
New cards
posterior pituitary gland
Does not produce its own hormones but it stores 2 hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic.
18
New cards
Antidiruetic hormone (ADH)
helps control the balance of water in the body
19
New cards
Oxytocin (OT)
Stimulates contraction of the uterus and release of milk from breast.
20
New cards
adrenal medulla
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
21
New cards
anterior lobe of pituitary gland
*
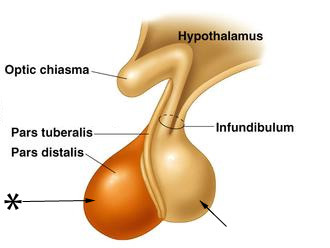
22
New cards
posterior lobe of pituitary gland
*
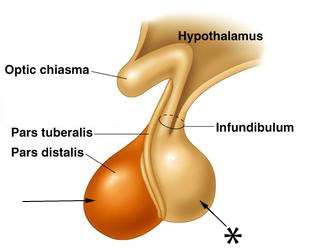
23
New cards
pars distalis
the largest and most anterior portion of the pituitary gland
24
New cards
pars intermedia
scant region between the pars distalis and the posterior pituitary
25
New cards
pars tuberalis
wraps around infundibulum
26
New cards
hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
portal veins that shunt blood carrying regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary
27
New cards
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
stimulates thyroid gland
28
New cards
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
secreted by the pituitary gland to stimulate maturation of the egg cell (ovum)
29
New cards
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
secreted by the pituitary gland to promote ovulation
30
New cards
Adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
Released by pituitary in response to CRH by hypothalamus
31
New cards
tropic hormones
hormones that stimulate other glands to release their hormones
32
New cards
Thyrotropic cells
secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
33
New cards
gonadotropic cells
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
34
New cards
corticotropic cells
secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
35
New cards
somatotropic cells
secrete growth hormone, stimulates cell growth, and affects most body cells
36
New cards
Growth Hormone (GH)
regulates the growth of the body
37
New cards
nontropic hormones
directly stimulate cellular metabolism and other activities
38
New cards
Mammotropic cells
secrete prolactin (PRL)
39
New cards
Prolactin (PRL)
stimulates milk production
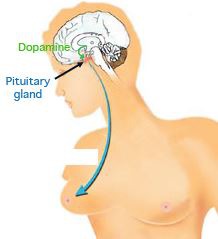
40
New cards
pars nervosa
posterior pituitary
41
New cards
infundibular stalk
connects hypothalamus to pituitary
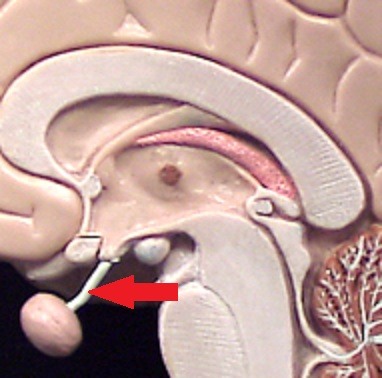
42
New cards
supraoptic nucleus
part of the hypothalamus that controls the release rate of vasopressin
43
New cards
paraventricular nucleus
produces oxytocin
44
New cards
neurosecretory cells
Neurons that secrete neurohormone rather than neurotransmitter.
45
New cards
parafollicular cells
produce calcitonin
46
New cards
Calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium levels
47
New cards
chief cells
secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH)
48
New cards
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism
49
New cards
zona glomerulosa
aldosterone
50
New cards
mineralocorticoids
Promote reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of K+ in kidneys
51
New cards
zona fasciculata
glucocorticoids (cortisol)
52
New cards
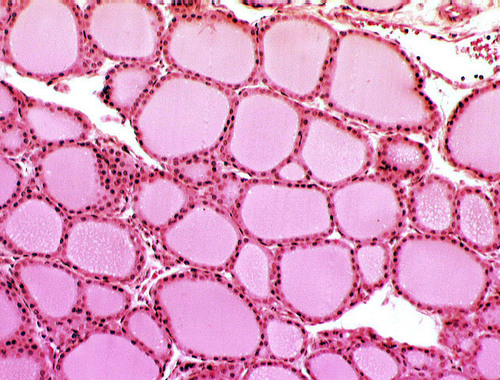
thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
53
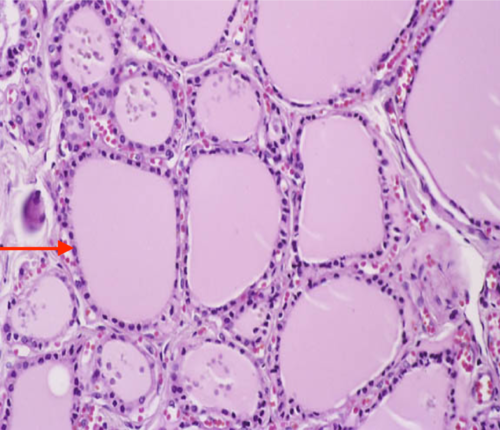
New cards
follicular cell
54
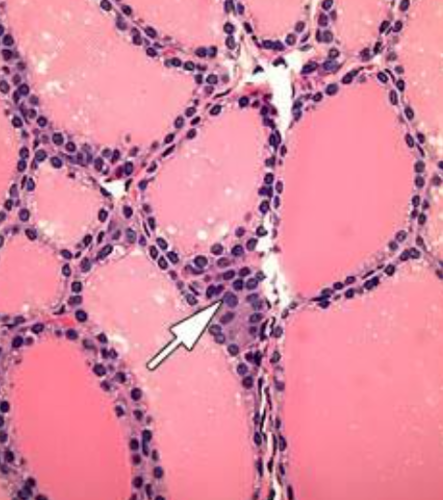
New cards
parafollicular cell
55
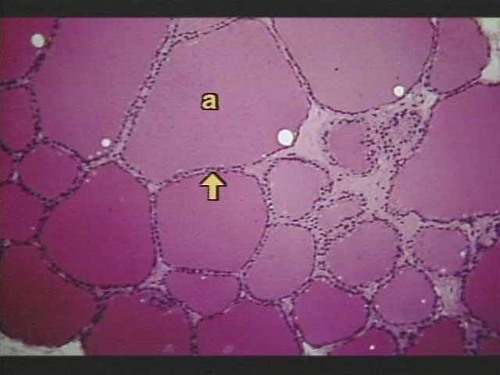
New cards
follicle cell
56
New cards
Thyroglobulin
secreted by follicle cells; binds with iodine to produce T4 and T3
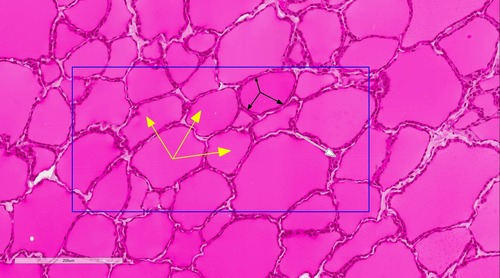
57
New cards
thyroid hormone
modulates activity of growth hormone, ensuring proper proportions
58
New cards
thyroid hormone precursor
Iodine
59
New cards
parathyroid hormone
reacts to low blood calcium levels and increases them
60
New cards
parathyroid gland
posterior surface of the thyroid gland
61
New cards
calcitriol
active form of vitamin D
62
New cards
adrenal gland
secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress (adrenaline)
63
New cards
capsule of adrenal gland
#1
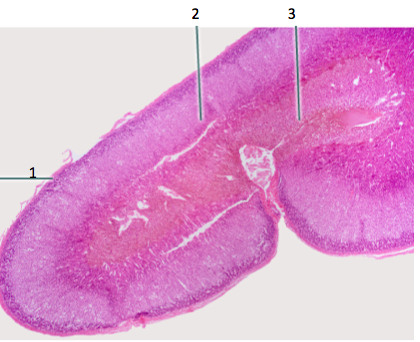
64
New cards
adrenal cortex
2
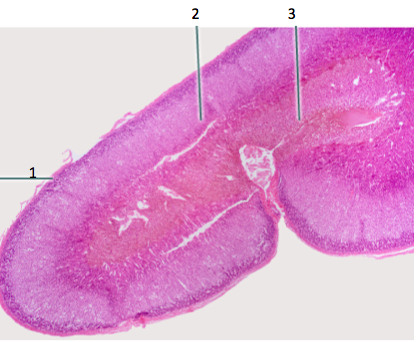
65
New cards
Corticosteroids
A group of hormones, including cortisol, released by the adrenal glands at times of stress
66
New cards
zona reticularis
produces gonadocorticoids
67
New cards
hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
68
New cards
chromaffin cells
the cells in the adrenal medulla that secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
69
New cards
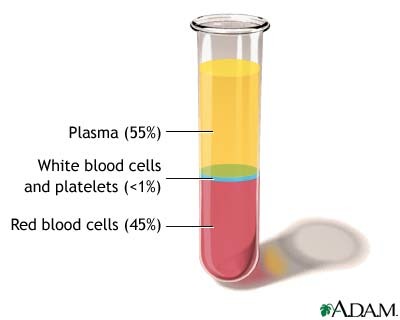
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that transport oxygen
70
New cards
buffy coat
white blood cells and platelets
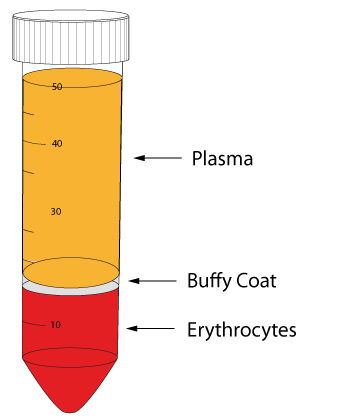
71
New cards
Plasma
Liquid part of blood
72
New cards
interstitial fluid
fluid between cells
73
New cards
Leukocytes
white blood cells
74
New cards
Platelets
help with blood clotting
75
New cards
blood smear
evaluation of the appearance and number of blood cells and the different types of white blood cells
76
New cards
hematocrit
percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells
77
New cards
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in red blood cells
78
New cards
globin chains
joined to heme to form a hemoglobin unit
79
New cards
Erythrocyte life span
120 days
80
New cards
antigen
A protein that, when introduced in the blood, triggers the production of an antibody
81
New cards
antibody
a substance produced by the body that destroys or inactivates an antigen that has entered the body
82
New cards
surface antigens
cell surface proteins that identify cells to immune system
83
New cards
ABO blood groups
based on having an A, B, both or no antigens on red blood cells
84
New cards
ABO blood type
2 surface antigens
85
New cards
Type A blood
A antigens and B antibodies
86
New cards
Type B blood
B antigens and A antibodies
87
New cards
Type O blood
no antigens, A and B antibodies
88
New cards
Type AB blood
A and B antigens, no antibodies
89
New cards
A can receive
A or O
90
New cards
B can receive
B and O
91
New cards
O can receive
O
92
New cards
AB can receive
A, AB, B, O
93
New cards
Rh factor
antigen on red blood cells of Rh-positive individuals
94
New cards
Rh blood
Can receive only Rh- blood
95
New cards
Rh positive
presence of antigens
96
New cards
Rh negative
absence of antigens
97
New cards
Diapedis
WBCs are able to move into and out of blood vessels
98
New cards
chemotaxis
Cell movement that occurs in response to chemical stimulus
99
New cards
granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
100
New cards
Agranulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes