Nuclear Chemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
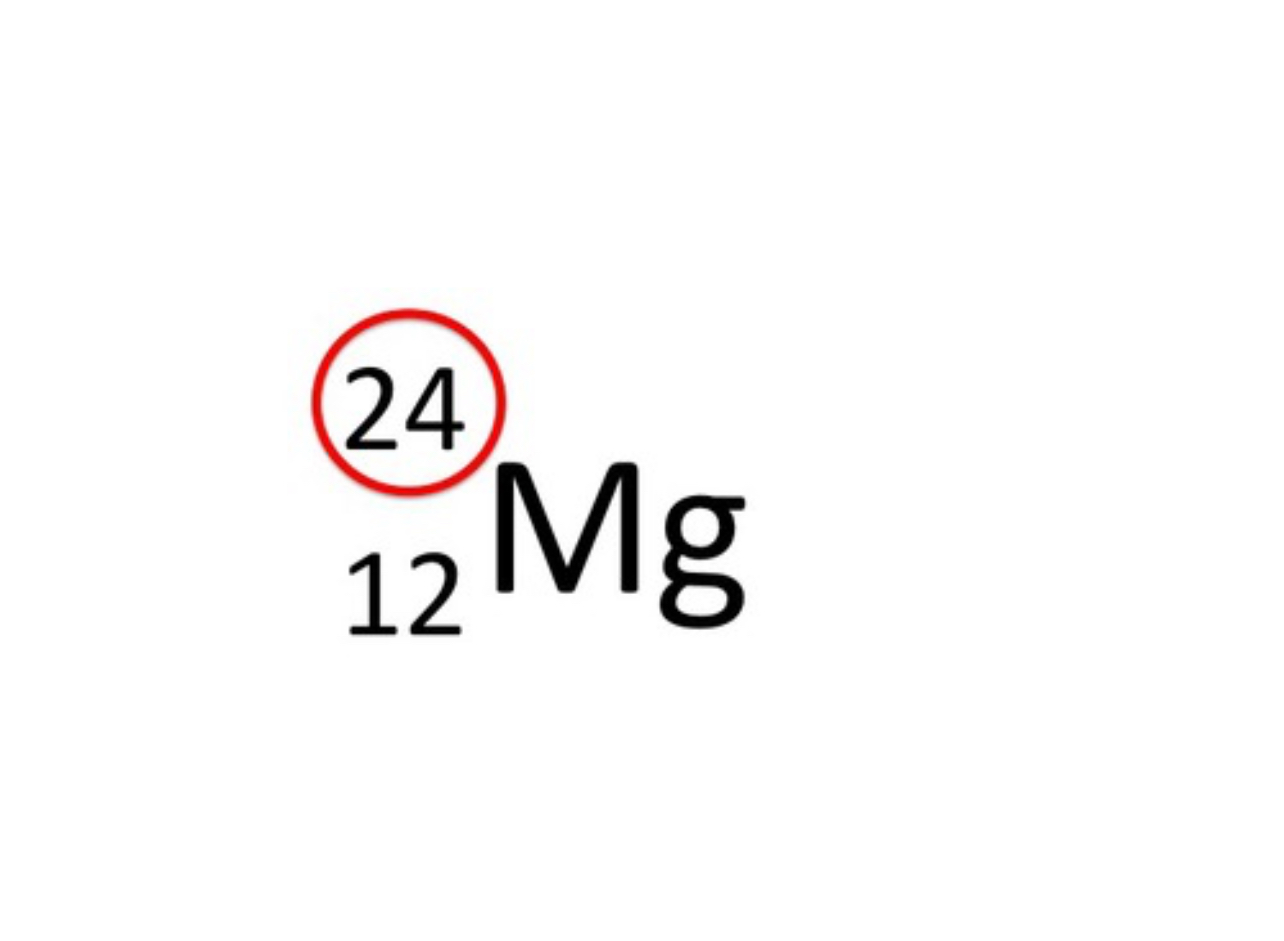
What does the mass number represent, and is it the top or bottom number in isotope notation?
it represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom and is indicated by the top number in isotope notation
What does the atomic number represent, and is it the top or bottom number in isotope notation?
It represents the number of protons in an atom and is indicated by the bottom number in isotope notation
What defines an element?
The number of protons - as soon as you change the number of protons, the element becomes a different one!
What particles are in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and neutrons
What is a nucleon?
A nucleon is either a proton or a neutron; the total number of nucleons in an isotope is given by the mass number.
What is the symbol for a proton?
L
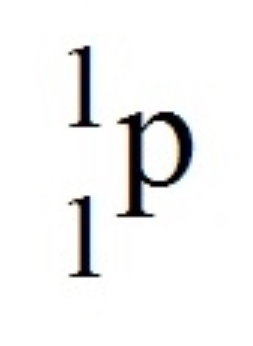
What is the symbol for a neutron?
L
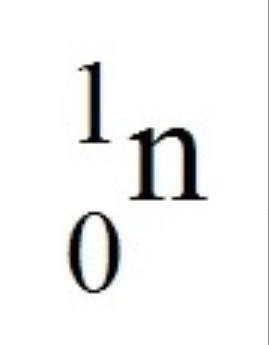
What is the symbol for a beta particle?
The same as an electron but with much more kinetic energy.
What is the symbol for an alpha particle?
Later
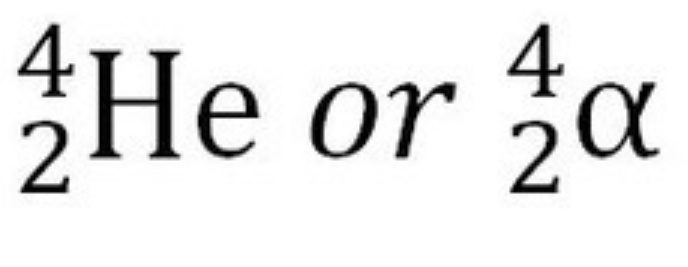
What is the symbol for a gamma ray?
L
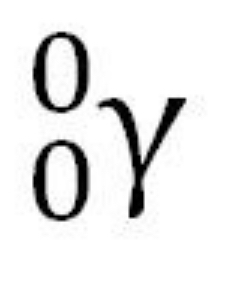
What is the symbol for a positron?
L
In radioactive decay, the light particle will be located on the (reactants/products) side.
Products
In particle capture, the particle will be located on the (reactants/products) side.
Reactants
What kind of atoms undergo alpha decay?
Those with more than 83 protons (an atomic number > 83)
If an isotope has a mass number greater than the atomic mass on the periodic table, the isotope has (too few/too many) neutrons. It will need to convert a (neutron/proton) to a (neutron/proton) via (beta decay/positron emission/electron capture).
Too many neutrons; convert a neutron to a proton via beta decay
If an isotope has a mass number less than the atomic mass on the periodic table, the isotope has (too few/too many) neutrons. It will need to convert a (neutron/proton) to a (neutron/proton) via (beta decay/positron emission/electron capture).
Too many protons; convert a proton to a neutron via positron emission/electron capture
In rate = kN, what does k represent?
Rate constant
In rate = kN, what does N represent?
Number of radioactive atoms (a big number)
What is the definition of 1 Becquerel?
1 disintegration/second
What is the definition of binding energy?
The amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus into its component nucleons
Binding energy should always be (negative/positive).
Positive
How do you calculate the mass defect if given the mass of the atom's nucleus?
Δm = [total mass of protons + total mass of neutrons] - [mass of the atom's nucleus]
How do you calculate mass defect if given the mass of the whole atom?
Δm = [total mass of protons + total mass of neutrons + total mass of electrons] - [mass of the whole atom]
What unit must the mass defect be in in order to plug it into BE =Δmc²?
kg
What is nuclear fission?
Larger atom splits into smaller atoms and releases a large amount of energy
What is nuclear fusion?
Combination of 2 light nuclei to form a heavier one
(Fission/fusion) results in a chain reaction.
Fission (because fission produces neutrons that can bump into the nucleus of another atom and cause even more fission, etc.)