U of U PA School Stroke and TIAs
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a stroke?
Neurologic deficiency attributed to an acute focal injury of the CNS by a vascular cause
Includes
-Cerebral infarct
-Intracranial hemorrhage
-Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Where do strokes occur?
Any portion of the brain
Retina
Spinal cord
What are the cortical signs of a stroke? (5)
Localize to specific lobe of the brain
-Speech/language
-Cognitive function
-Spatial orientation
-Vision
-Eye gaze deviation
What are the non cortical signs of a stroke? (4)
Weakness
CN deficits
Ataxia
Sensory loss
What things mimic a stroke? (5)
Conversion disorder
Hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypoglycemia
Complicated migraine
Seizures
What is a TIA?
Transient episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord, or retinal ischemia without acute infarction
How do TIAs and migraines differ?
TIAs
-Sudden, maximal onset
-Last 10-60 minutes
-Usually have vascular risk factors
Migraine
-Marching progression
-Usually numbness/dizziness
-Aura, nausea, mental dulling
What are the ABCDD features predictive of 7 day risk of stroke in patients with TIA?
Age
->59 years old = 1 point
BP
-Systolic >140 and/or diastolic >89 = 1 point
Clinical features
-Unilateral weakness = 2 points
-Speech disturbance without weakness = 1 point
-Other symptoms = 0 points
Duration (in minutes)
->59 minutes = 2 points
-10-59 minutes = 1 point
-<10 minutes = 0 points
Diabetes = 1 point
How does the scoring of ABCDD predict stroke risk after a TIA?
<5 = <1% risk
5 = 12% risk
>6 = 31% risk
What are the types of strokes?
Ischemic
-Thrombotic
-Embolic
Hemorrhagic
-Intracerebral
-Subarachnoid
How does the flow for stroke work up look?
Is it potentially a stroke?
If yes - CT head
-Hemorrhagic or non hemorrhagic?
If non hemorrhagic appearance - presumed ischemic stroke
What is the ischemic penumbra?
Perimeter around the core ischemic area
Area can progress to infarction
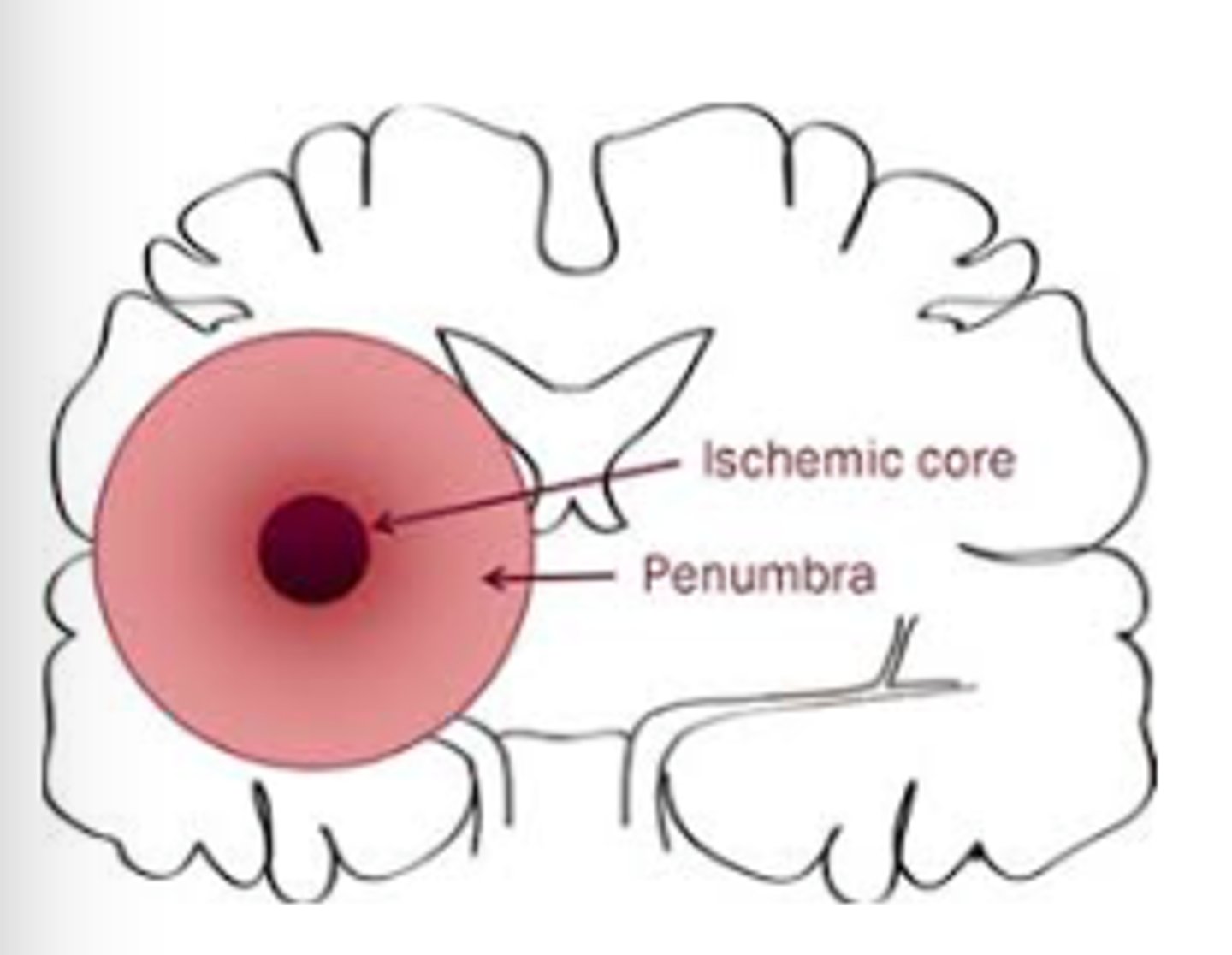
What does stroke treatment aim to recover?
Area of ischemic penumbra
What is used for acute treatment of a stroke?
IV thrombolytics
-tPA (alteplase)
-TNK-tPA/TNK (tenecteplase)
Mechanical thrombectomy
What are the inclusion criteria for IV thrombolytics? (5)
Clinical diagnosis of ischemic stroke causing measurable deficit
Symptom onset <4.5 hours
BP <185/110
>18 years old
Informed consent
-If no proxy or unable, implied consent
What is the goal time for administration of IV thrombolytics?
Administer within 60 minutes of ED admission
What are the absolute exclusion criteria for IV thrombolytics? (7)
Outside administration window
CT evidence of blood
BP >185/110 refractory to treatment
Concern for subarachnoid hemorrhage even with negative imaging
Platelets <100,000
LMWH treatment dose in last 24 hours
Anticoagulants - factor Xa, GbIIb/IIIa inhibitors
What should be done for a patient still symptomatic after IV thombolytics?
CT angiography or MR angiography (MRA) of brain to find clot
What is a mechanical thrombectomy? What timeframe can it be done?
Extraction of clot from large vessels
Can be done up to 24 hours after start of symptoms at a specialty center with advanced imaging
What are the types of ischemic strokes?
Lacunar
Hemispheric
Large artery stroke
How are ischemic strokes classified?
Lacunar
-Smaller vessel stroke
Hemispheric
-Involves whole hemisphere
Large artery stroke
-Anterior/middle/posterior cerebral arteries - MCA most common
-Vertebrobasilar artery
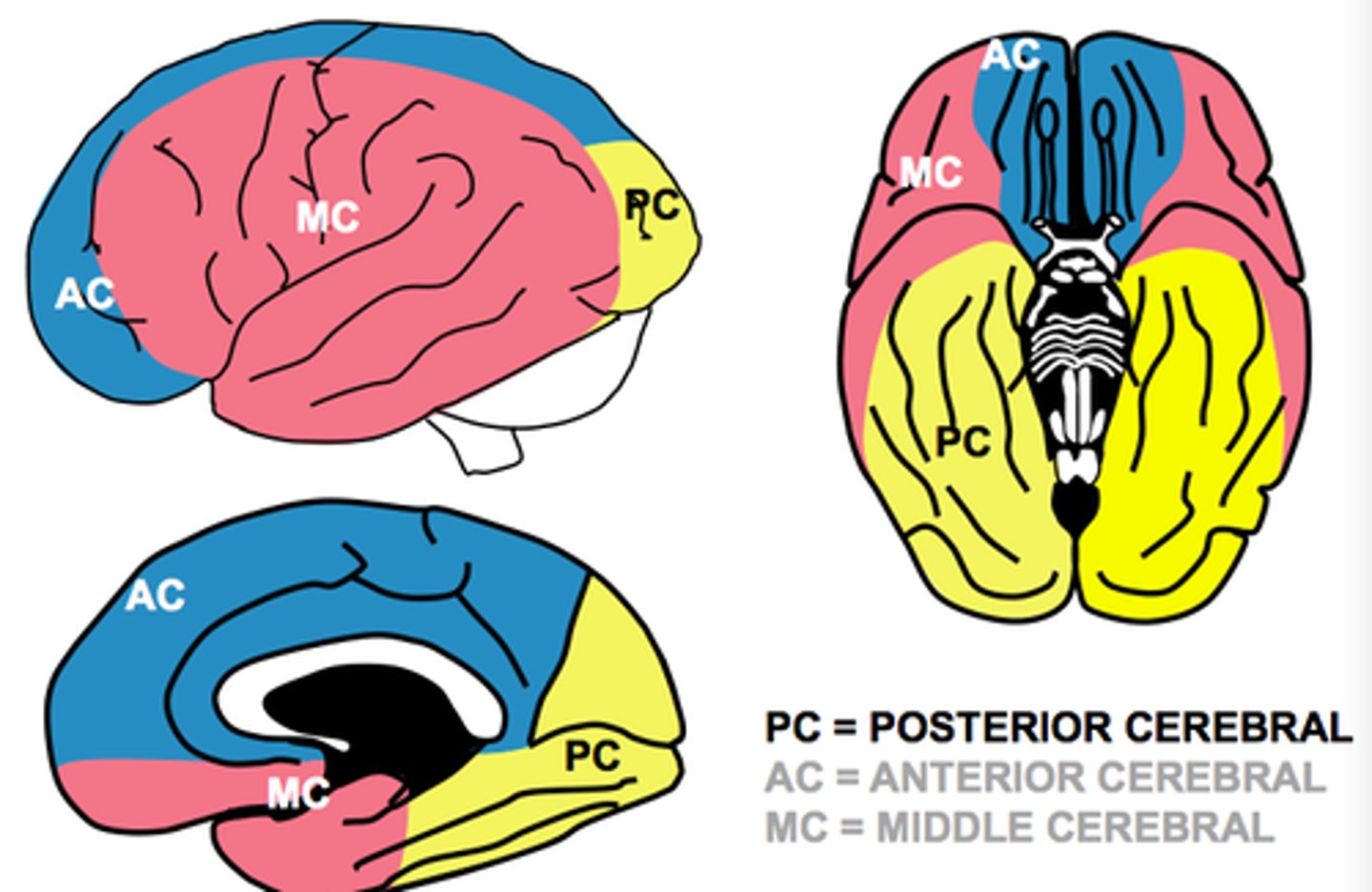
What areas and functions are supplied by the MCA?
MCA
-Temporal - receptive speech
-Portion of frontal - motor+sensory of face, arm, and expressive speech
-Parietal - neglect
What areas and functions are supplied by the ACA?
ACA
-Portion of frontal - motor+ sensory of legs
What areas and functions are supplied by the PCA?
PCA
-Occipital cortex
-Parietal - sensory
What area is supplied by the vertebrobasilar artery? What does a blockage of this artery cause?
Brainstem
- hemiparesis, bilateral weakness, hemisensory loss, bilateral sensory, CN deficits
How do plaque and embolism differ in clot formation?
Plaque - clot forms at site of blockage
Embolism - clot travels to site of blockage
What is the pathophysiology mechanism of large artery stroke?
Thrombotic
-Blood clot forms in blood vessel in brain
Embolic
-Blood clots forms in heart or major blood vessels dislodges and lodge in blood vessels of brain
Cryptogenic
-Mechanism for the stroke is unknown
What is the pathophysiology mechanism of cardioembolism ischemic stroke?
Embolic
-Blood clots forms in heart or major blood vessels dislodges and lodge in blood vessels of brain
What is the pathophysiology mechanism of lacunar stroke? How does it present?
Very small blood vessel of the brain progressively narrows until completely occluded
Pure motor deficit or ataxia hemiparesis
What is done for secondary ischemic stroke prevention? (4)
Control modifiable risks
Blood vessel imging
Antiplatelets of anykind
CHASVASC2 score for anticoagulants
What are the modifiable risks of a stroke? (10)
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Smoking
Sleep apnea
Coronary artery disease
History of TIA
A fib
Carotid stenosis
Obesity
How is hypertension managed with a stroke?
Initially after a stroke hypertension is permissible for 24-48 hours unless
->220/120
-End organ failure
-Active ischemic coronary disease
-Aortic dissection
-Preeclampsia
After 48 hours - oral antihypertensives
What is blood vessel imaging looking for? (4)
Intracranial atherosclerosis
Carotid atherosclerosis
Dissection
TTE if suspected cardioemboic source
What is done for subacute/chronic management post stroke?
Management of risk factors
Rehab with speech, PT, OT, and rehab physician
How does a hemorrhagic stroke present?
Same as ischemic stroke - based on location
Symptoms can rapidly change
What is the most common cause of a hemorrhagic stroke?
Hypertension
What additional things can cause a hemorrhagic stroke? (4)
Transition of ischemic to hemorrhagic stroke
Aneurysm rupture
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Subarachnoid hemorrhage - berry aneurysm rupture
What is the treatment for hemorrhagic stroke?
Acute
-Reverse INR
-Clotting factor replacement
how should hemorrhagic strokes be evaulated?
Is it in the brain (intraparenchymal) or around the brain subarachnoid)
Was it secondary hemorrhage to ischemic stroke, hypertension, or vascular malformation
What imagining is used for acute diagnostic evaluation of a stroke? What are the advantages/disadvantages of each
Noncontrast head CT
-Quick
-May miss acute ischemia
-Better for blood/mass effect
Rapid MRI
Better for
-Localization
-Size
-Etiology
-Both ischemia and hemorrhage