Volatile Oils
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are volatile oils?
AKA essential oils
Volatile when heated
At room temp they give off a pungent odour, characteristic to each oil
How are volatile oils used pharmaceutically?
Flavouring
Aroma agents
Therapeutically:
Anti-bacterial agents and bronchodilators in cold cure preparations
Counter-irritants for the skin in ointments
Analgesics, anaesthetic and anti-inflammatories particularly for toothache
Treatment of GI problems in indigestion preparations
What is the largest use of volatile oils
Cosmetic industry
Used in the formulation of perfumes and deodorants
How are volatile oils obtained?
From a variety of plant sources using steam distillation
What are volatile oils a mixture of?
Low molecular weight terpenes and phenylpropenes
What is eugenol?
A phenylpropene component of clove oil
Similar structure to aspirin
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent which inhibits the COX enzyme
Aim of experiment
Isolate and characterise eugenol from clove oil via infrared spectroscopy
After the addition of ferric chloride to ethanol, what colour was the resulting solution?
Yellow
Following the change in colour after the eugenol is added, what has happened to the ferric ion?
It has been reduced
The colour change occurs because Fe³⁺ forms a complex with the phenoxide ion, involving electron donation from the phenol
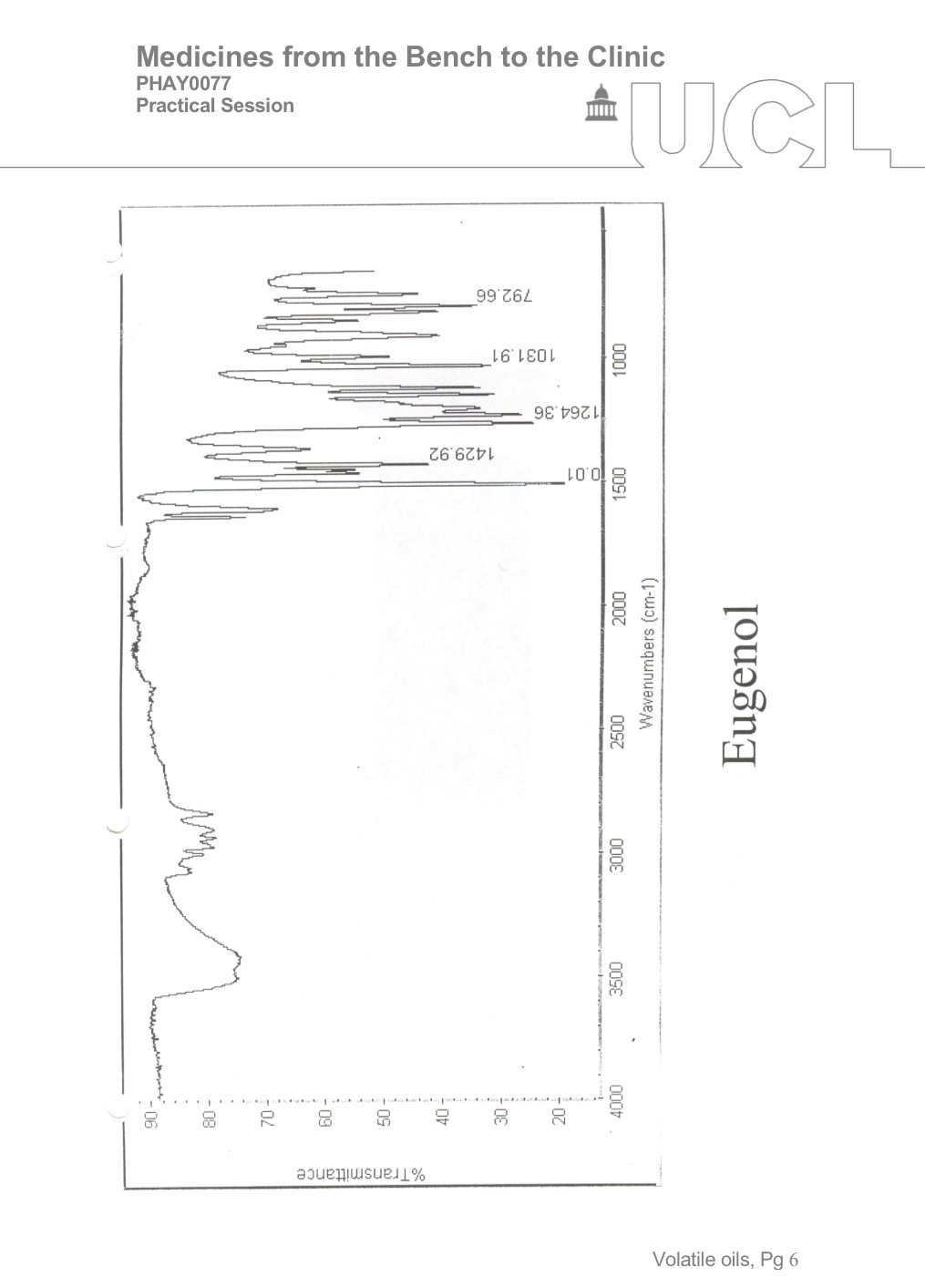
Looking at your IR spectrum, which of the following statements is true?
A. My sample is pure
B. My sample is contaminated
C. It is not possible to say if my sample is pure
D. My sample has traces of sodium sulphate in it
E. My sample has other compounds present
A. My sample is pure
Looking at your IR spectrum of eugenol, what functional groups occur at approximately 3000 cm-1
A. C-H
B. C-O
C. O-H
D. C-Cl
E. C-Br
A. C-H
To which class of natural product does eugenol belong
A. Phenylpropene
B. Phenylethene
C. Phenylethylamine
D. Phenothiazine
E. Phencyclidine
A. Phenylpropene
Which is the best technique to separate volatile oils
A. NMR spectroscopy
B. UV spectroscopy
C. HPLC
D. TLC
E. Gas chromatography
E. Gas chromatography
Volatile oils are best separated by GC due to their volatility and thermal stability
Why is a base used in this extraction?
Used to extract acidic molecules e.g. eugenol