NURS320 MIDTERM
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Pre-19th Century
19th Century -
20th Century
Pre-19th Century
Religious orientation; no set guidelines, education, training
19th Century -
Florence Nightingale
Modernized nursing
Recognized nursing as separate from medicine
Set standards
Developed training and educational preparation
Conducted nursing research
20th century
Hospital nursing program emerged
1950's-present: Nursing broadened in all areas
Practice -
Specific body of knowledge -
Nursing research -
Role of nursing defined -
Nursing knowledge -
Definition of Nursing
ICN definition-
ANA definition-
ICN definition- Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups, and communities, sick or well and in all settings.
ANA definition- "the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations"
aims in nursing
1. Promote health
2. Prevent illness
3. Restore health
4. Facilitate coping with disability or death
5. Knowledge, Skills, Attitudes --> (Knowledge = all cognitive information; Skills = hands-on skills; Attitude = caring communication)
6. Critical Thinking (Observation, analysis, inference, communication, problem solving)
Four Blended Competencies
Cognitive
Technical
Interpersonal
Ethical/Legal
QSEN Competencies
Patient-centered care
Teamwork and collaboration
Quality improvement
Safety
Evidence-based practice
Informatics
Healthy People 2030 Health Promotion Guidelines
Objectives:
Health conditions
Health behaviors
Populations
Settings & systems
Social Determinates of Health
education, health care, neighborhood, social and community context, economic stability
preventing illness, detection, restoring health, facilitating coping with disability and death
Preventing illness = Primary level of protection
What measures can nurses take?
Seat belts, helmets, vaccines
Detection = Secondary level of protection
Examples = Colonoscopy, mammograms
Restoring health = Tertiary level of protection (when someone is already sick)
Facilitating coping with disability and death
Palliative - comfort care → for people with or without a terminal illness
I.e chronic condition from a vehicle accident and is now paralyzed; end of life care/hospice (For people within about 6 months of their end of life)
Which phrase best describes the science of nursing?
The skilled application of knowledge
The knowledge base for care
Hands-on care
Respect for each individual person
The knowledge base for care
What is the purpose of the ANA’s scope and standards of practice?
To describe the ethical responsibilities of nurses
To define the activities that are special and unique to nursing
To establish nursing as an independent and free standing profession
To regulate the practice of nursing (this answer would be if we were talking about the state)
To define the activities that are special and unique to nursing
Nursing as a Professional Discipline
Well-defined body of specific and unique knowledge
Strong service orientation
Recognized authority by a professional group
Code of Ethics
Professional organization that sets standards
Ongoing research
Autonomy and self-regulation
nursing practice acts
Defines legal scope of nursing practice
Defines legal requirements
Establishes criteria for the education and licensure of nurses
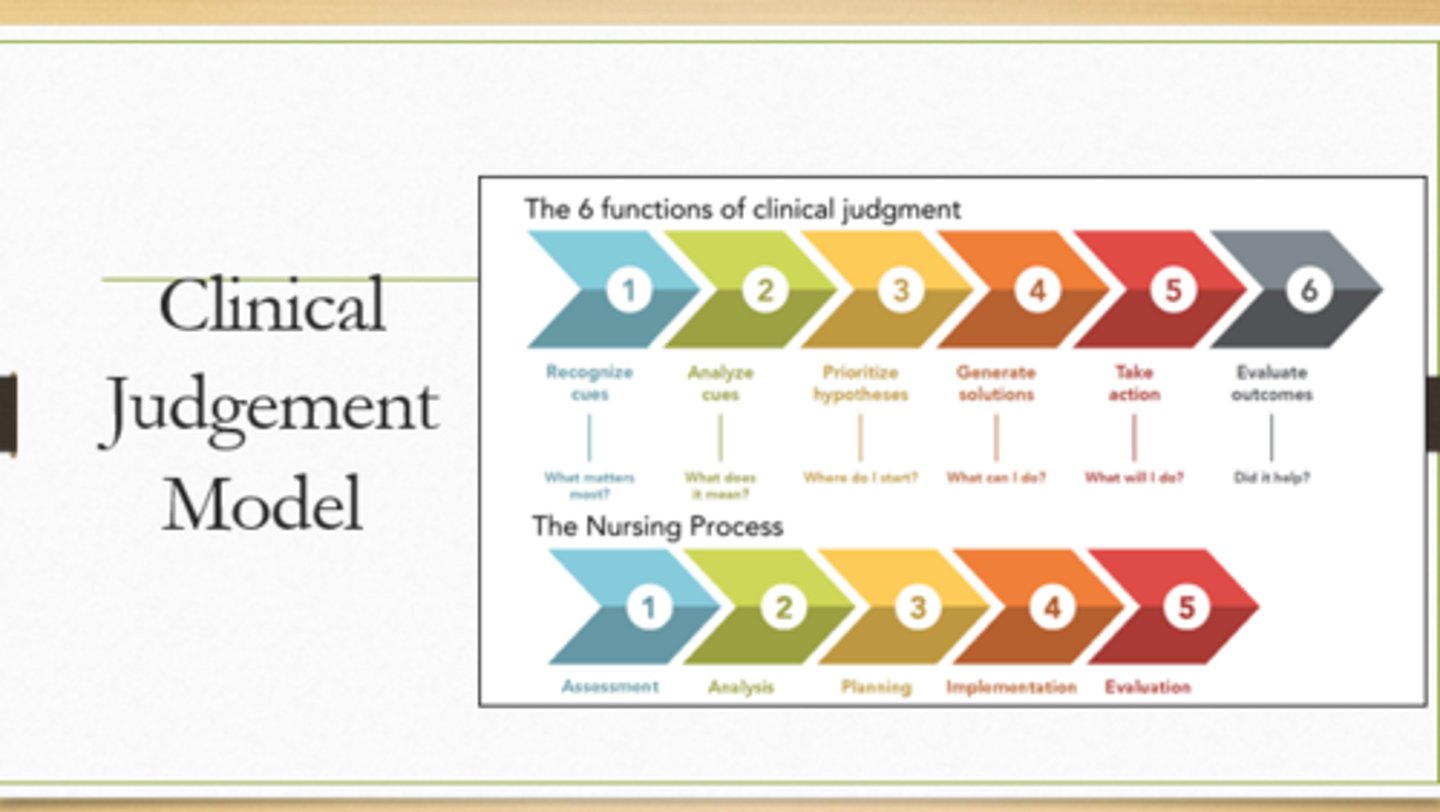
nursing process
assessment --> analysis --> planning --> implementation --> evaluation
clinical judgment model: 6 functions of clinical judgment
recognize cues --> analyze cues --> prioritize hypothesis --> generate solutions --> take actions --> evaluate outcomes
profession =
Body of knowledge
Scope of practice
Agreed upon values, ethics
Oath or code
Accountability
how is professionalism judged
Against a set of expectations or standards
From our own personal values set and understanding of what "professionalism" means
May be situational in nature
Strongly influenced by culture
how is professionalism determined
Our image
Our communication
Our competence
Our Demeanor
professional organization
ANA =
NCSBN =
NLN =
Sigma Theta Tau International-
AACN =
ANA (American Nursing Association
NCSBN (National Council of State Boards of Nursing)
NLN (National League of Nurses)
Sigma Theta Tau International-
AACN (American Association of Critical-care nurses)
ANA scope of practice
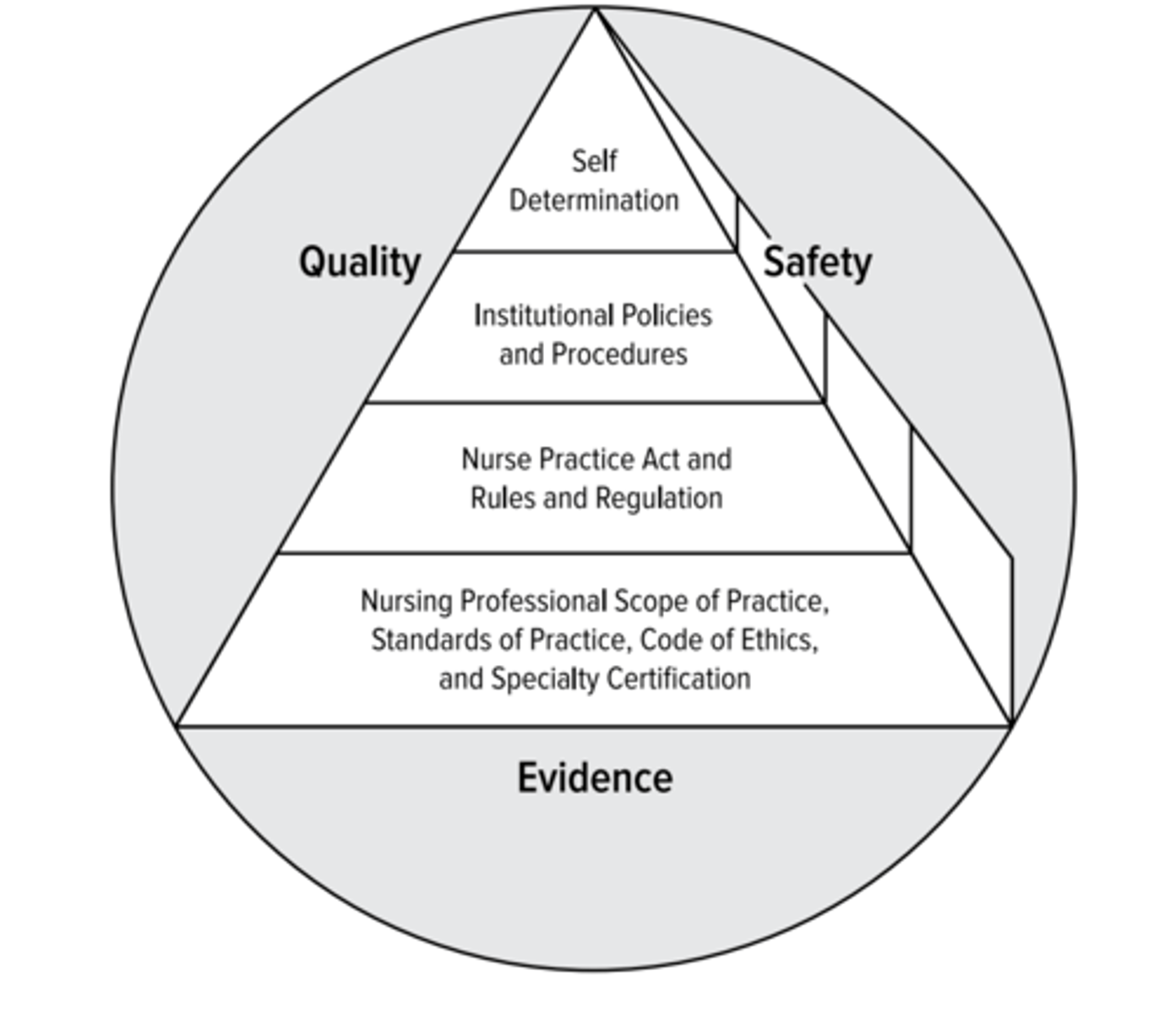
standards of practice: (6)
Standard 1: Evidence-Based Assessment
Standard 2: Diagnosis identy actual/potential practice gaps l/t pt compliance issues
Standard 3: Outcomes identification - develop measurable outcomes
Standard 4: Planning w/DEI, interprofessionalism
Standard 5: Implementation 5-A: coordination w/stakeholders, teams, transitions 5-B: health teaching, health promotion
Standard 6: Evaluation achievement of progress towards desired outcomes
SMART goals
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Realistic
Timely
Example:
standards of professional performance (7-18)
Standard 7: Ethics code of ethics
Standard 8: Advocacy supporting a cause/course of action
Standard 9: Cultural Humility social equity for marginalized people
Standard 10: Communication EB tools, non-judgmental/specific feedback
Standard 11: Collaboration
Standard 12: Leadership formal/informal, emotional intelligence, shared-decision making, just culture
Standard 13: Education ongoing learning
Standard 14: Scholarly Inquiry research
Standard 15: Quality of Practice QI
Standard 16: Professional Practice Evaluations reflection, self-eval, evaluating others
Standard 17: Resource Stewardship safe, efficient, financially responsible, judicious
Standard 18: Environmental Health SDOH, address incivility, emotional intelligence
code of ethics slideshow in week 1
sources of knowledge
Traditional-
Authoritative-
Scientific-
Traditional-
Authoritative-
Scientific-
types of nursing knowledge:
Science-
Philosophy-
Process-
Science-
Philosophy-
Process-
influences on nursing knowledge
Historical influences -
Societal influences-
framework of nursing theory: concepts vs theory
Concepts- abstract impressions organized into symbols of reality
Theory- group of concepts that describe a pattern of reality
deductive vs inductive reasoning
Deductive = general to specific
Dolphins are mammals
Mammals have kidneys
Dolphins have kidneys
Inductive = reasoning that takes specific information and makes a broader generalization
interdisciplinary base for nursing theory:
General system theory-
Adaptation theory-
Development theory-
General system theory- theory for universal application; break whole things into parts to see how they work together in systems
Adaptation theory- adjustment of living matter to other living things and environment
Development theory- orderly and predictable growth and development from conception to death
benefits of nurisng theory
Directs nurses toward common goal
Leads to improved patient care
Provides rational and knowledgeable reasons for nursing actions
Gives nurses knowledge base necessary for appropriate actions
Helps resolve current nursing issues
Prepares nurses to question assumptions and values
Serves research, education, and practice
goals of theoretical frameworks
Holistic patient care
Individualized care to meet needs of patients
Promotion of health
Prevention or treatment of illness
4 concepts r/t nursing theory
Person/Patient-
Health-
Environment-
Nursing -
Person/Patient-
Health-
Environment-
Nursing -
FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE'S ENVIRONMENTAL THEORY
Defined nursing as "the act of utilizing the environment of the patient to assist him in his recovery."
5 factors for a healthy envi according to Nightingale
Pure or fresh air
Pure water
Efficient drainage
Cleanliness
Light, especially direct sunlight
nightingale's general concepts of envi santitation
Proper ventilation
Adequate lighting
Cleanliness
Adequate warmth
Quiet
Diet
goals of research: general vs goals of nursing research
nursing research goals according to national institute of nursing:
Build the scientific foundation of clinical practice
Prevent disease and disability
Manage and eliminate symptoms caused by illness
Enhance end-of-life and palliative care
methods of nursing research: quant vs qual
Quantitative
Involves concepts of basic and applied research
Qualitative
Conducted to gain insight by discovering meanings
Belief that perceptions differ for each person and change over time
terms of quantitative research:
Variable
Dependent variable
Independent variable
Hypothesis
Data
Instruments
Descriptive
Correlational
Quasi-experimental
Experimental
Variable =
Dependent variable =
Independent variable =
Hypothesis =
Data =
Instruments =
Descriptive =
Correlational =
Quasi-experimental =
Experimental =
steps of quant research
State the research problem
Define purpose of the study
Review related literature
Formulate hypotheses and variables
Select population and sample
Collect data
Analyze data
Communicate findings and conclusions
qualitative research methods
Phenomenology
Grounded theory
Ethnography
Historical
Phenomenology =
Grounded theory =
Ethnography =
Historical =
evaluating the ethics of clinical research studies
Value
Scientific validity
Fair subject selection
Favorable risk-benefit ratio
Independent review
Informed consent
Respect for enrolled subjects
evidence based practice =
steps in implementing EBP
Cultivate a spirit of inquiry
Ask the burning clinical question in PICOT format
Search/collect most relevant best practice
Critically appraise the evidence
Integrate
Evaluate
Disseminate
PICOT =
impediments to nursing research
Limited time to participate in research
Restricted access to resources
Lack of educational preparation
Communication slides!!
IOM Recommendations: Communication
Improve communication verbally and in writing between professionals
key points =
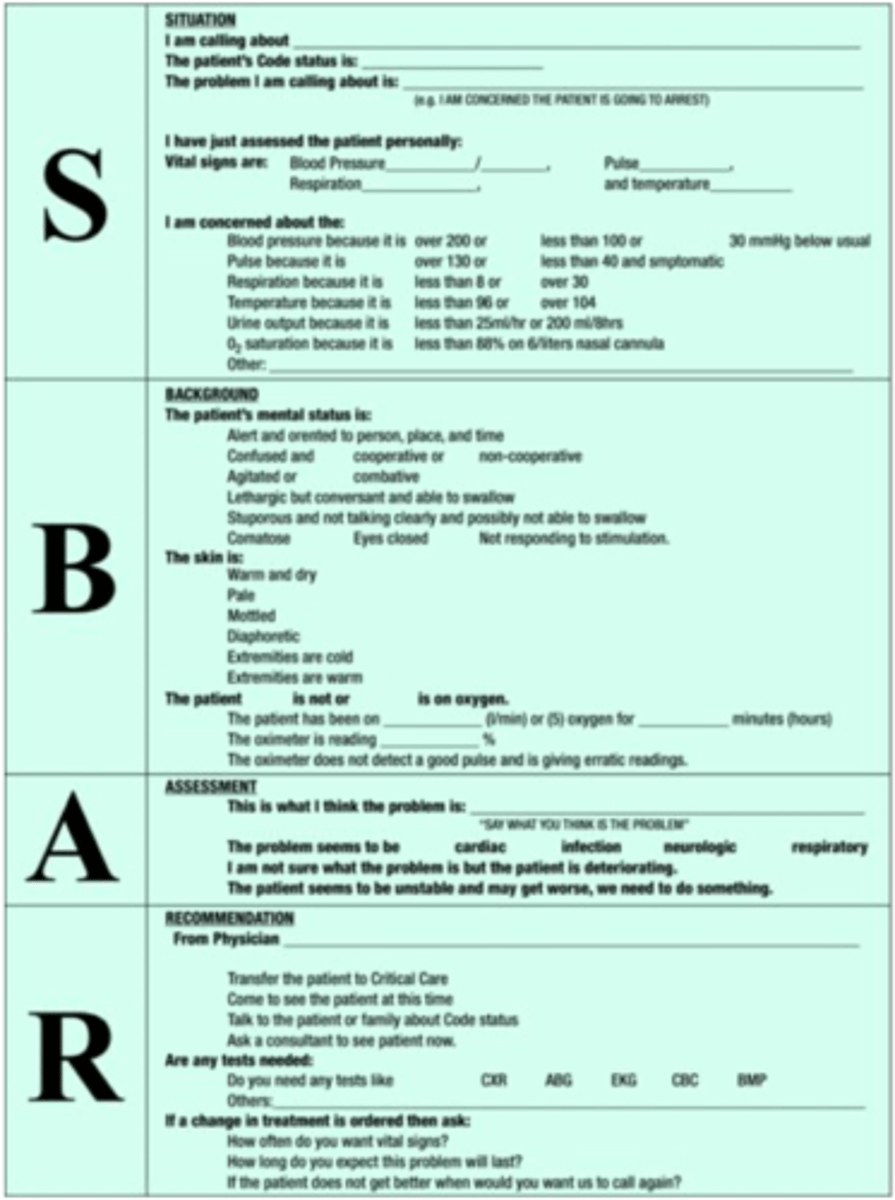
using hand off communication: SBAR technique
bidirectional conflict possibilities
patient--> nurse --> other healthcare workers and vice versa
conflict resolution
Recognize it
Find the right time
Discuss both sides
Document the issue with the relevant topics
Mediation
Negotiation/compromise
Agree to disagree
teamwork for conflict resolution and prevention
Communication
Coaching
Patient satisfaction
Servant Leadership (greenleaf, 1973):
important factors with inter-professional communication
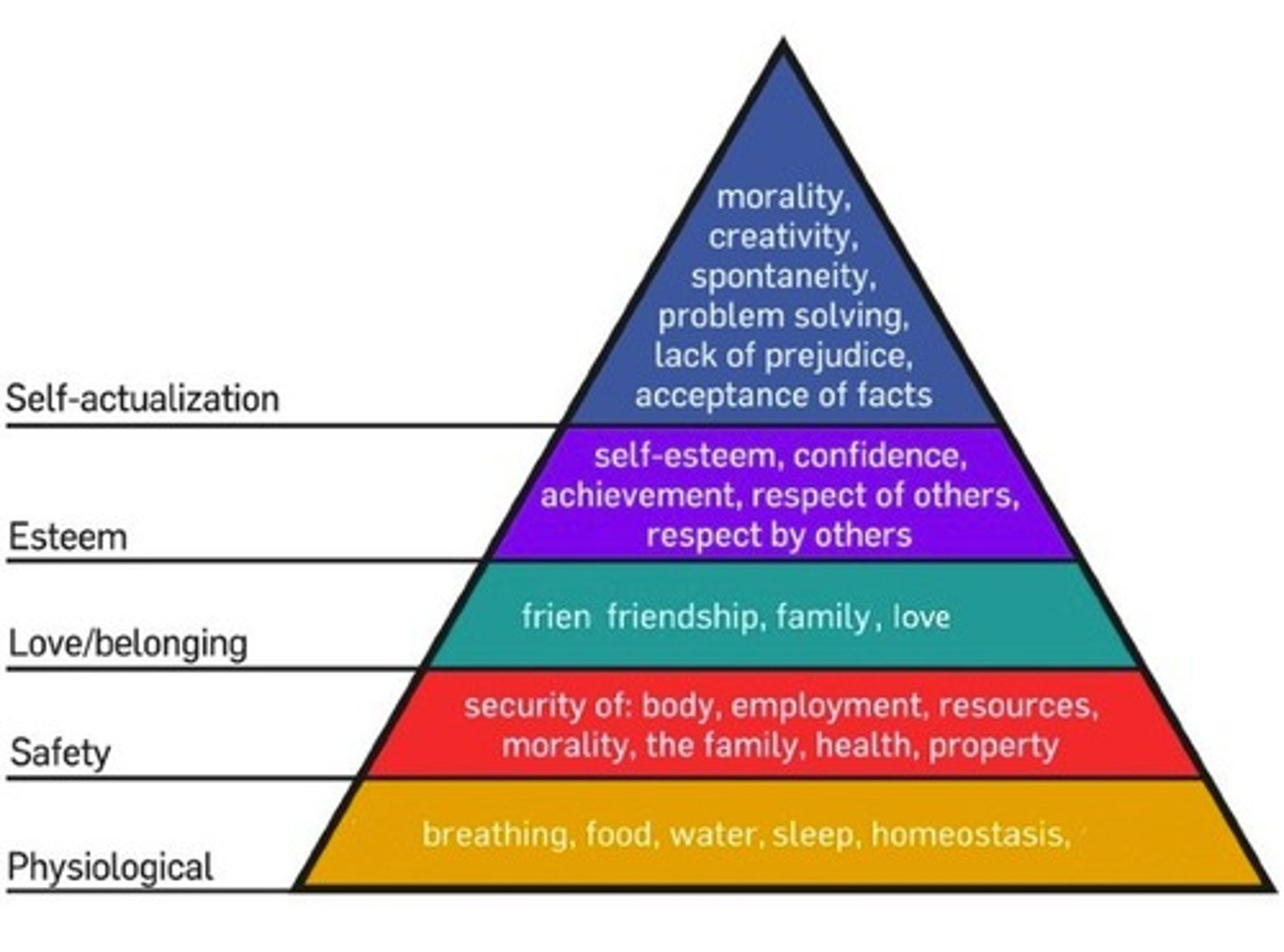
maslow's hierarchy of human needs
family structures:
Family:
Nuclear family:
Extended family:
Blended family:
Single-parent family:
Family: any group of people who live together and depends on one another for physical, emotional, and financial support
Nuclear family: traditional family; two parents and their children
Extended family: includes aunts, uncles, and grandparents
Blended family: two parents and their unrelated children from previous relationships
Single-parent family: may be separated, divorced, widowed, or never married
family functions
Physical
Economic
Reproductive
Affective and coping
Socialization
risk factors for aaltered family health
Lifestyle risk factors
Psychosocial risk factors
Environmental risk factors
Developmental risk factors
Biologic risks
community factors affecting health
Social support systems
Community health care structure
Economic resources
Environmental factors
nursing informatics =
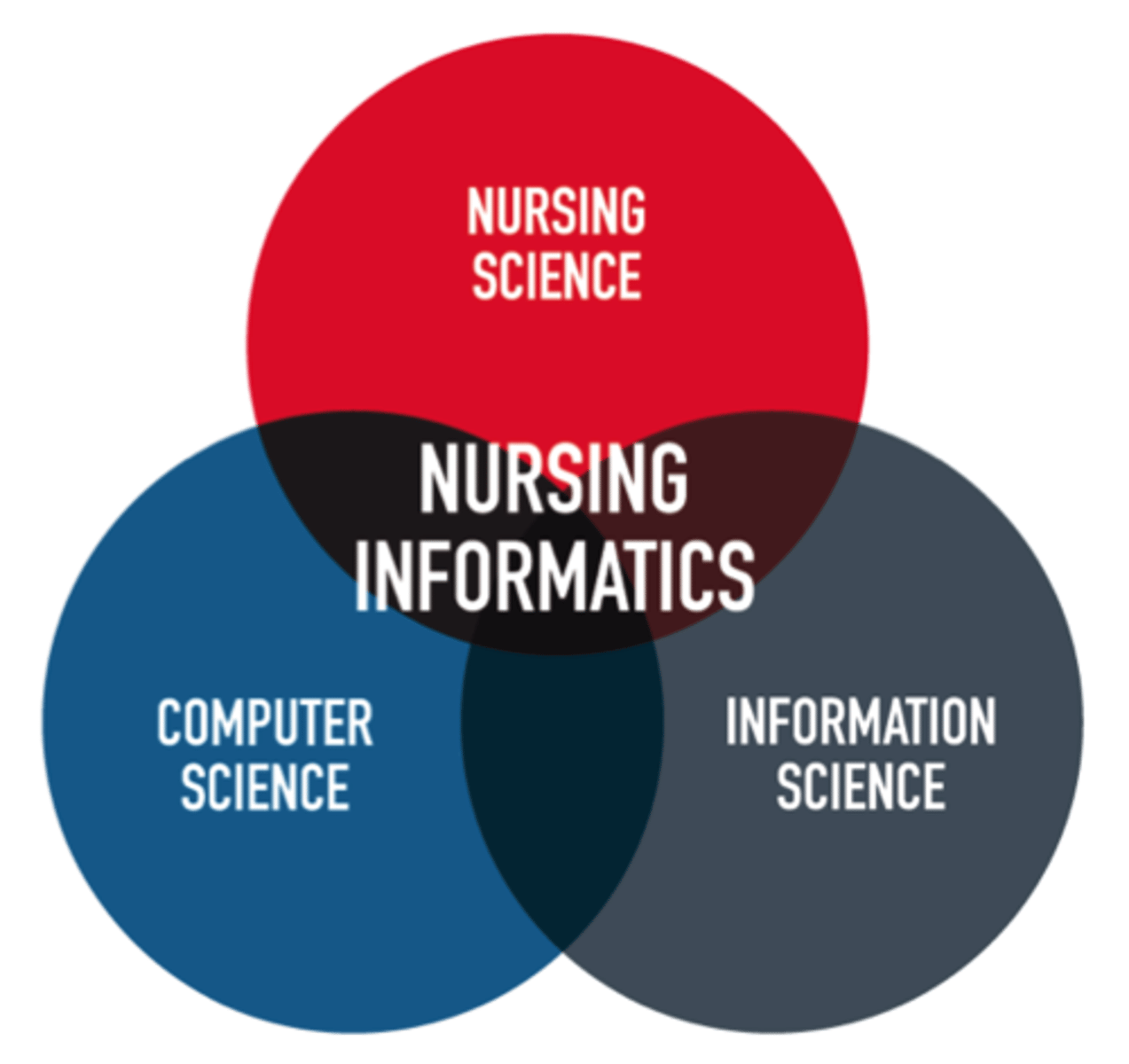
examples of informatics used in today's nursing profession
EHR
Telehealth
Mobile devices
Patient portals
Data analytics
Technologies for educating nurses in academic settings
Technologies for conducting research
meaningful use of electronic health records
Improve quality, safety, efficiency
Reduce health disparities -
Engage patients and family
Improve care coordination - how broadly?
Public health reporting
Maintain privacy and security of patient health information - how so?
results of meaningful use compliance (EHR)
Better clinical outcomes
Improved population health outcomes
Increased transparency and efficiency
Empowered individuals
More robust research data on health systems
ANA definition of nursing informatics
The specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information management and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice"
nursing informatics specialist
pic on slides
daily tasks of informatics nurse
Use technology to sustain nursing work processes
Redesign clinical workflow
Help patients manage their own health through information systems
Analyze clinical and financial data
Perform research based on clinical data and trials
Develop storage and analytic technology to help optimize data for research
Keep technology up to date and accessible to medical personnel
Deliver nursing content to standardized languages
Assist with change management
Encourage provision of high-quality, evidence-based care
types of nursing informaticists
1. The informatics nurses
2. A registered nurse with an interest or experience in an informatics field
- Super-user
- The informatics nursing specialist
3. A registered nurse with formal graduate-level education in the field of informatics
- Often responsible for strategy development, implementation, and maintenance and evaluation of clinical systems requiring collaboration with multiple disciplines
system development life cycle (SDLC
analysis --> design --> development --> testing --> implementation --> maintenance --> planning
important informatics concepts
System usability
System optimization
Standard terminologies
Interoperability
Security and privacy
uses of patient portals
1. Access medical history and other health information
2. Complete various forms and questionnaires online
3. Communicates securely and conveniently with providers
4. Request prescription refills
5. Pay bills
6. Review lab results
7. Schedule appointments
8. Receive reminder for appropriate screenings
9. Enter clinical data, such as blood pressure, glucose levels, weight, Fitbit data, and other activity tracking data
10. Review progress notes
11. Access educational material based on diagnosis or procedure
benefits and downsides of patient portals
predictive analytics
data --> reporting/analysis (what and why happened) --> monitoring (what is hap now) --> predictive analysis (what is going to happen in the future)
bigdata
1. volume
2. velocity
3. variety
4. veracity
5. value
6. validity
7. variability
8. venue
9. vocaab
10. vagueness
telehealth and mobile tech:
Telehealth:
Telemedicine:
Telecare:
Telehealth: the use of electronic information and telecommunications technologies to support and promote long-distance clinical health care, patient administration
Telemedicine: the use of telecommunications technologies to support the delivery of all types of medical, diagnostic, and treatment-related services, usually by physicians and nurse practitioners
Telecare: technology that allows consumer to stay safe and independent in their own homes
telenursing =
The use of information and communication technology to transmit data relevant to any aspect of nursing activity, encompassing many activities:
Triage
Teleconsultations
Home care
Education
Research