Unit 3: Diffusion, Osmosis, Sodium Potassium Action Potential
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Diffusion:
movement of ions or molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Osmosis
movement of water across a cell membrane, from an area of higher concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of lower concentration (higher solute concentration)
Entropy
the tendency of systems to reach a state of higher disorder or randomness
Concentration Gradient
a difference in a substance's concentration in space—usually across a cell membrane
Potential Energy
energy of position or stored energy
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion of substances across cell membranes through integral membrane proteins
Passive Transport
Movement of ions or molecules that does not require an input of energy. Passive transport occurs down a gradient and is spontaneous because it increases entropy.
What is active transport?
Movement of ions or molecules that requires an input of energy.
Does active transport occur with or against a gradient?
Against a gradient.
Is active transport spontaneous or nonspontaneous?
Nonspontaneous.
How does active transport affect entropy?
It decreases entropy.
What is an example of active transport's effect on a single-celled organism?
It makes the inside of a single-celled organism more organized than the non-life outside.
Channel
An integral membrane protein that offers a "conduit" (or tunnel or pore) for a specific ion to cross the lipid bilayer passively, via diffusion.
Carrier
An integral membrane protein that transports a specific molecule across the lipid bilayer passively, usually via diffusion, by changing shape once the molecule binds to it.
Pump
An integral membrane protein that transports specific ions or molecules across the lipid bilayer actively, often using energy carried by ATP, against their gradients.
Voltage-gated channel:
An ion channel that opens and closes based on the potential of the membrane it's embedded in.
Myelin sheath
A structure made up of Schwann cells that insulates axons and functions in faster action potential propagation.
Schwann cell
A type of glia that wraps its membrane around the axons of many types of neurons and speeds signal propagation.
Synapse
The junction where two neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell communicate across a space called the synaptic cleft.
Presynaptic neuron
A neuron whose axon terminus communicates with a postsynaptic neuron via neurotransmitters.
Postsynaptic neuron
A neuron that receives signals from a presynaptic neuron via neurotransmitters.
Synaptic vesicles
Small membrane-bound spheres that hold neurotransmitters and deliver them to the synaptic cleft.
What are neurotransmitters?
Signaling molecules that are released from a pre-synaptic neuron
What do neurotransmitters do after being released?
They diffuse across the synaptic cleft
What do neurotransmitters bind to in the post-synaptic neuron?
Ligand-gated channels
Ligand-gated channels
Ion channels that open in response to binding a neurotransmitter or other ligand.
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
A depolarization in a postsynaptic cell, making it more likely to fire an action potential.
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
A hyperpolarization in a postsynaptic cell, making it less likely to fire an action potential.
At a chemical synapse, what triggers the opening of ligand-gated ion channels on the postsynaptic membrane?
Binding of neurotransmitters released from presynaptic neuron
Which of the following correctly contrasts voltage-gated and ligand-gated ion channels in neural signaling?
Voltage gated channels propagate action potentials along the axon, ligand gated channels initiate post-synaptic responses at synapse
Hormone
A molecule that acts as a long-distance signal between cells in the same multicellular individual.
What is a ligand?
Any molecule that binds to a receptor and triggers a response.
What types of signals can ligands include?
Both long-distance and short-distance cell-to-cell signals as well as intracellular signals.
What is signal transduction?
A change in the form of a signal within a cell.
What is an example of a signal in signal transduction?
A hormone that binds to a receptor on the surface of a cell.
What can occur inside the cell during signal transduction?
A second messenger or phosphorylation cascade.
Kinase
An enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group from ATP to a recipient molecule.
What is a phosphorylation cascade?
A chain reaction that amplifies the signal from a chemical messenger.
What role do kinases play in a phosphorylation cascade?
Each kinase phosphorylates multiple target proteins.
What happens after a kinase phosphorylates a target protein in a phosphorylation cascade?
The target protein goes on to phosphorylate multiple other target proteins.
What is a second messenger?
An ion or small molecule that is released in response to a chemical messenger binding to a cell-surface receptor.
What role does a second messenger play in a cell?
It acts as an intracellular signal.
Homeostasis
Self-regulating biological processes that maintain stable conditions in the body in the face of changing external conditions.
positive feedback
response that increases the amount that a regulated condition differs from the normal level. It is the self-limiting step.
Negative feedback
A response that returns a regulated condition back to the normal and preferred level. It is a corrective, self-limiting step.
Stimulus
A change in an organism's surroundings that causes the organism to react
Organizational effects
effects of hormones that can impact long term permamently
Activational Effects
the effect of a hormone that occurs in the fully developed organism; are temporary & reversible
SRY Gene
Gonadal sex determining region of the Y chromosome.
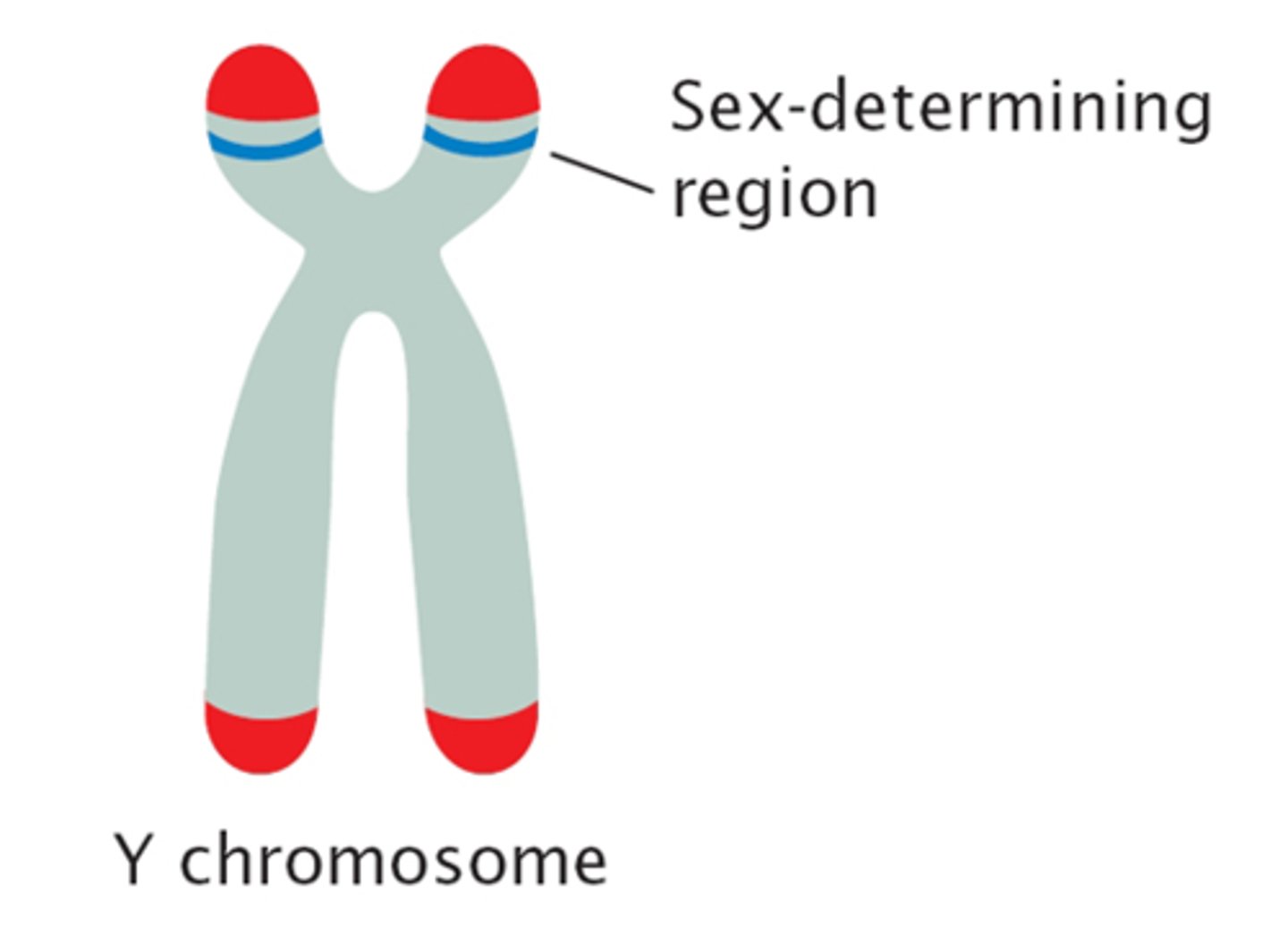
The initial cellular construction and formation of the ovaries during prenatal development is determined by
No factor
What makes the post synaptic potential excitatory or inhibitory?
The neuron will produce a IPSC/ EPSP based on the neurotransmitter released into the synapse. If the NT is excitatory, Na+ will enter to depolarize the cell, if the NT is inhibitory, Cl- ions will enter and hyperpolarize the cell. This is outside of resting membrane potential.
Action potentials require the action of voltage-gated sodium and voltage-gated potassium channels. Why?
Voltage-gated sodium channels open much more quickly in response to membrane depolarization than voltage-gated potassium channels do. &
The electrochemical gradient for sodium is directed into the cell, while the electrochemical gradient for potassium is directed out of the cell.
cortisol
steroid, stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex receptor glutocorticoid
Epinephrine
amine hormone, activates receptors in the body)
HPA Axis
the hypothalamus release to, pituitary gland release to, adrenal gland releasing cortisol
Effects of Cortisol & Epinephrine
Heightened alertness & sensory perception
Eustress
optimal stress for enhanced performance
What is the role of voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels in propagating an action potential?
They open quickly after the membrane starts to depolarize, causing the membrane voltage to swing to a positive value.