3E- Ensure Modifications are Made to the RC Plan
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TMC: 18 questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
A patient receiving oxygen at 10 L/min via nonrebreathing mask has a PaO2 of 600 mm Hg. You should recommend which of the following?
change to a partial rebreathing mask
change to a simple mask at 8 L/min
discontinue oxygen therapy
remove the valve at the reservoir bag
discontinue oxygen therapy
A patient with history of CHF is admitted in the ICU. On physical assessment you note bilateral wheezing, severe pedal edema, hepatomegaly and jugular venous distension. The ICU resident wants your opinion on the management of his condition. Which of the following would you recommend?
giving a bronchodilator treatment
obtaining an arterial blood gas
pushing an IV fluid bolus
administering an inotropic agent
administering an inotropic agent
In patients with CHF, signs of fluid retention (wheezing, pedal edema, hepatomegaly and jugular venous distension) are common. The use of inotropic medications to increase heart contractility and diuretics to decrease the fluid overload are very important in the management of CHF, as is careful I&O monitoring. Because wheezing in CHF is usually due to peribronchial edema, bronchodilator therapy generally is not warranted. Rapid fluid administration would be contraindicated in this scenario and obtaining a blood gas does nothing to help manage the immediate problem at hand.
A 150 lb female patient is receiving volume controlled SIMV with a volume of 600 mL, a mandatory rate of 12/min with 5 cm H2O pressure support. You note that her total rate of breathing is 45/min, and that she is using her scalene muscles during most spontaneous breaths. Which of the following is the most appropriate action at this time?
increase the set tidal volume
increase the inspiratory flow
increase the pressure support level
decrease the mandatory breath rate
increase the pressure support level
The tachypnea (spontaneous rate = 33/min) and active accessory muscle use indicate increased work of breathing. To decrease the patient's spontaneous work of breathing, you should increase the pressure support level. This normally boosts the spontaneous tidal volume, decreases the respiratory rate and lessens the work of breathing.
The respiratory therapist notes in the medical record of a 65-year-old male that the patient is ordered to receive bronchodilator therapy with Albuterol. The therapist also notes the patient is receiving beta-blocker medication. The therapist should recommend
Administer Dexamethasone (Decadron) in place of Albuterol
Switch from Albuterol to ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
Add Xopenex to the bronchodilator regimen
Replace Albuterol with Beclomethasone (Beclovent)
Switch from Albuterol to ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
Because albuterol is a beta-agonist medication, patients who are taking beta-blockers should utilize other bronchodilation medication.
A 54- year-old patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of cardiogenic pulmonary edema. His pulse is 130 and pounding, his respiratory rate is 35, with labored with shallow breaths. The PaO2 on a simple mask at 10 L/min is 48 torr and the PaCO2 is 30 torr. What change in therapy would you recommend for this patient?
switch the patient to a nonrebreathing mask @ 12 L/min
initiate mask CPAP, initially with 100% oxygen
provide an IPPB treatment with ethyl alcohol
intubate and provide full ventilatory support
initiate mask CPAP, initially with 100% oxygen
Mask CPAP can be an effective treatment for patients with cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Initially, the FIO2 should be set to 100% to assure adequate oxygenation. Intubation should be avoided if possible.
A respiratory therapist is working with a 55-year-old patient who had open heart surgery yesterday. He is awake, has stable vital signs, and has acceptable weaning parameters. After breathing 40% oxygen on a T-piece adapter for 40 minutes, he starts to bleed heavily through his mediastinal chest tube. The respiratory therapist should recommend:
Let him continue breathing on the T-piece.
Draw an ABG sample.
Suction out his endotracheal tube.
Place him back on the ventilator.
Place him back on the ventilator.
This patient is unstable and should be put back on the ventilator. It would be helpful to have blood gas data, but the patient's safety must be the first priority.
A 48-year-old patient is receiving VC, A/C ventilation with a rate of 12/min and a VT of 7.4 mL/kg IBW. Serial observations of a pressure-volume loop over the last 3 days shows a steady movement of the loop toward the X axis (the loop is "lying down" and is nearly parallel to the horizontal axis). Plateau pressure is 38 cm H2O and peak pressure is 54 cm H2O. Which of the following would be most helpful at preventing lung injury?
sedation and controlled ventilation
inverse I:E ratio ventilation
reduction in tidal volume
reduction in minute ventilation
reduction in tidal volume
Which of the following strategies would you recommend for a cooperative patient with an intact upper airway who requires home ventilatory support?
invasive positive pressure ventilation
noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
abdominal displacement ventilation
negative pressure ventilation
noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
A patient receiving volume-controlled ventilation in the assist/control mode has a peak inspiratory pressure of 55 cm H2O. Both dynamic and static compliance have decreased over the last few days. The patient will benefit most from which of the following?
pressure-cycled ventilation
Bi-level therapy
pressure control ventilation (PCV)
pressure support
pressure control ventilation (PCV)
A peak pressure over 50 cmH2O is an indication for pressure control ventilation. This is true only if the cause of the peak pressures are not a result of temporary conditions such as secretions in the airway or a kinked ET tube. The problem states that the patient's dynamic and static compliance has been decreasing over the last few days, indicating pulmonary changes. This data suggests that the source of the high airway pressure is not caused by a temporary condition.
A pressure-volume graphic observed on a volume-controlled ventilator has a pronounced "beak". What strategy can be used to manage this issue?
increase I:E ratio
decrease VT
increase flow
decrease PEEP
decrease VT
A pronounced "beak" on a pressure-volume loop graphic is an indication of over-distension. This can best be addressed by decreasing the tidal volume.
A patient with congestive heart failure, who is demonstrating moist crepitant rales upon auscultation, would benefit most from
Lasix
administration of aminoglycoside medication
postural drainage and percussion
PEP therapy
Lasix
A patient with congestive heart failure who is demonstrating moist crepitant rales is most likely in a state of fluid overload. The administration of Lasix is most appropriate in order to diurese the patient.
A patient with a chronic neuromuscular disorder requires nocturnal positive pressure ventilation over the long-term. Which of the following airways would you recommend for this patient?
oral endotracheal tube
fenestrated tracheostomy tube
laryngeal mask airway
standard tracheostomy tube
fenestrated tracheostomy tube
A fenestrated tracheostomy tube is the best choice to support patients needing intermittent (e.g., nocturnal) ventilatory support. For positive pressure ventilation, the inner cannula is inserted to close the fenestration and the cuff inflated to provide a seal. When not on the ventilator, the inner cannula is removed (to open the fenestration), the cuff is deflated, and the tube is plugged. This allows normal use of the upper airway.
Under which of the following circumstances should a respiratory therapist consider stopping a PEP therapy treatment of a child?
Middle ear infection
Bronchitis
Cold
Lingular lobe pneumonia
Middle ear infection
PEP therapy is contraindicated by sinusitis, epistaxis, and a middle ear infection.
A patient with asthma who is receiving an albuterol (Proventil) treatment via small volume nebulizer every six hours complains of wheezing before the next treatment. You should recommend which of the following?
increasing the frequency of administration
adding cromolyn sodium (Intal) to the treatment
adding oral steroids to the treatment regimen
changing to a metered dose inhaler (MDI)
increasing the frequency of administration
If a patient’s symptoms return before the next scheduled drug treatment, the likely reason is that the medication effect has worn off (duration of action exceeded). Because albuterol’s duration of action can be as short as 3 hours, this is the likely problem. The best solution would thus be to increasing frequency of treatment (e.g., to every 4 hours) and re-assess the patient’s response.
A 14-year-old, 66-kg (145-lb) female patient with a history of asthma is in the emergency room (ER) in response to an exacerbation of asthmatic symptoms over the last 2 hours. While en route the patient received 2 small volume nebulizer treatments with 0.5 mL albuterol. Paramedics report no appreciable responses to the bronchodilator. The respiratory therapist should recommend
heliox therapy with 80%/20% gas mixture.
heliox therapy with 60%/40% gas mixture.
starting continuous albuterol therapy at 10 mg/hr.
administering a single dose of aerosolized ipratropium bromide (Atrovent).
starting continuous albuterol therapy at 10 mg/hr.
The next logical step in this case is to provide continuous bronchodilator therapy. While Atrovent may provide some minor assistance to the patient, the action is not aggressive enough. The use of helium-oxygen gas therapy is premature and is usually used when most other approaches have been ineffective.
Which of the following agents would be most beneficial for a patient with asthma experiencing an acute exacerbation of symptoms?
terbutaline (Bricanyl)
montelukast (Singulair)
acetylcysteine (Mucomyst)
cromolyn sodium (Intal)
terbutaline (Bricanyl)
Patient with asthma experiencing an acute exacerbation of symptoms should receive O2 to relieve hypoxemia, a short acting beta agonist (‘reliever’) like terbutaline (Bricanyl) to relieve airflow obstruction, and (if symptoms are severe) inhaled ipratropium bromide. Patients who fail to respond promptly and completely to beta agonist therapy should also receive systemic corticosteroids. Cromolyn and montelukast are indicated for control of mild persistent asthma and acetylcysteine can worsen bronchospasm.
A 17-year-old patient has been admitted through the emergency room to ICU. He is in a coma after taking an overdose of sedatives. His chest X-ray film indicates bilateral atelectasis. To help correct this problem, you should recommend:
applying PEEP
lowering the tidal volume
increasing the inspiratory flow
using a low machine rate
applying PEEP
Applying PEEP, airway pressure release ventilation (APRV), and application of recruitment maneuvers are all ways to increase the transpulmonary pressure gradient and help open up collapsed alveoli (atelectasis). Low rates or high inspiratory flows lengthen the expiratory time, which is used to avert air-trapping, not treat atelectasis.
A known COPD patient is receiving oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula. An ABG on that setting reveals a PaO2 of 59. A new medical resident orders the patient's oxygen low be increased to 6 L/min. What is the best course of action for you to take?
check the patient's chart
tell the nurse
call the physician
make the change
call the physician
Which of the following medications should be started FIRST for a patient in the emergency room with a pulmonary infection experiencing status asthmaticus?
inhaled bronchodilators
antibiotics
IV steroids
MDI corticosteroids
inhaled bronchodilators
A 45-year-old patient with asthma is prescribed 0.3 mL of albuterol (Proventil) in 3 mL normal saline via small volume nebulizer. Before initiating therapy, you note from chart review that the patient is severely hypertensive and has been experiencing episodes of superventricular tachycardia. You should do which of the following?
dilute the albuterol with extra normal saline
administer the treatment as ordered
postpone the treatment and consult the physician
decrease the amount of albuterol administered
postpone the treatment and consult the physician
Albuterol is a beta-adrenergic drug that can increase heart rate and blood pressure. For this reason, hypertension and tachycardia are contraindications to its administration. Whenever a contraindication exists to drug administration, you normally should postpone the treatment and consult with the ordering physician.
A patient in the emergency room (ER) is showing inverted T waves on the 12-lead ECG tracing. The physician is interested in decreasing the work of the heart. The respiratory therapist should suggest
adminsitration of Nitroclycerin (Isordil)
administration of Crytodigin (digitalis)
oxygen by nasal cannula at 5 L/min
oxygen by nasal cannula at 2 L/min
oxygen by nasal cannula at 5 L/min
Inverted T waves indicate cardiac ischemia, or the absence of oxygen reaching the heart. When this is observed, supplemental oxygen is indicated. The amount of oxygen indicated is the adult therapeutic range, which is 40 to 55%. Of the options offered, this percentage can best be achieved by nasal cannula at 5 L/min. 2 L/min by nasal cannula may be tempting because many emergency room protocols indicate this amount of oxygen delivery for the presence of chest pain. However, this patient is demonstrating inverted T waves, which is a more significant indicator of cardiac ischemia.
A premature 1850 g newborn infant is receiving 40% oxygen in an oxyhood. A chest X-ray shows a ground-glass appearance bilaterally, with air bronchograms. An arterial blood gas reveals the following:
pH 7.36
PaCO2 44 torr
PaO2 45 torr
HCO3 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
What would you recommend at this time?
intubate and initiate 10 cm H2O CPAP
place the neonate in an Isolette with an FIO2 of 0.60
administer 5 cm H2O nasal CPAP with an FIO2 of 0.50
intubate and initiate mechanical ventilation
administer 5 cm H2O nasal CPAP with an FIO2 of 0.50
As suggested by the X-ray and blood gas, the likely problem is Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Since the blood gas indicates adequate ventilation but poor oxygenation (P/F ratio of about 100), a trial of noninvasive CPAP is the place to begin. 5 cm H2O is a reasonable starting point, with the FIO2 slightly elevated (0.50) to ensure adequate oxygenation. Intubation is not yet indicated, and raising the FIO2 alone will not help overcome the shunting that occurs in IRDS.
While administering postural drainage and percussion with the head of bed down 30 degrees, the therapist begins to note signs of distress including shortness of breath and PVCs. The therapist should immediately
sedate the patient, continue therapy
raise the head of bed up by 15 degrees, continue therapy
stop therapy, report findings to the physician
perform postural drainage with the patient in prone position
stop therapy, report findings to the physician
A patient who has mild stridor following endotracheal extubation would benefit most from which of the following?
racemic epinephrine
reintubation
tracheostomy
heated aerosol
racemic epinephrine
Which of the following diuretics would you recommend for a patient in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
furosemide (Lasix)
spironolactone (Aldactone)
chlorothiazide (Diuril)
acetazolamide (Diamox)
furosemide (Lasix)
For rapid diuresis, a loop diuretic like furosemide (Lasix) is indicated. Thiazide diuretics like chlorothiazide and potassium-sparing agents like spironolactone simply cannot produce as much urine as fast as can the loop diuretics. Acetazolamide has weak diuretic properties but is seldom used exclusively for this purpose.
In preparation for a patient who will be receiving oxygen by nasal cannula at 2 L/min at home, the respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following devices for primary oxygen delivery?
bulk liquid oxygen conversion system
bank and manifold of H tanks
3-5 E cylinders
molecular sieve device
molecular sieve device
Patients who are in need of low-flow oxygen at home (between 1-6 L/min) are best served by using an oxygen concentrator. This is also called a molecular seive device.
Immediately after endotracheal tube extubation, an adult patient exhibit a high-pitched inspiratory noise, heard without a stethoscope. Which of the following actions would you recommend?
careful observation of the patient for 6 hours
a STAT heated aerosol treatment with saline
immediate reintubation via the nasal route
a STAT racemic epinephrine aerosol treatment
a STAT racemic epinephrine aerosol treatment
Stridor is a high pitched noise heard during inspiration. In adults, stridor indicates that the airway is reduced to 5 mm or less in diameter. Stridor is more serious than hoarseness, indicating increased airway resistance and work of breathing. Stridor is often treated with racemic epinephrine (2.25% Vaponephrine) via aerosol. This reduces glottic edema by mucosal vasoconstriction. Steroids may also be added to the aerosol to further reduce the inflammation.
A patient is receiving 100% oxygen via a large volume nebulizer set at 15 L/min and an aerosol mask. The respiratory therapist notices the aerosol disappears completely with each inhalation. The therapist should do which of the following?
increase oxygen flow rate to 20 L/min
switch to a non-compensated flow meter
add a second (tandem) nebulizer
set the air-entrainment device to FIO2 0.6
add a second (tandem) nebulizer
The disappearance of the aerosol emitting from the aerosol mask during each inspiration is an indication that the inspiratory flow rate is insufficient for the patient. Since the patient is on 100% by large-volume nebulizer, the maximum achievable flow from the oxygen flow meter is about 15 L per minute. This is due to back pressure that limits the total flow of oxygen through the flow meter. This means that the system is already operating in at a max and will not be able to achieve a higher flow rate. The solution is to provide a second, or "tandem" device to allow the doubling of the total flow of gas to the patient and meet thier inspiratory demand. A "tandem" device is when two large-volume nebulizers are used and the output is T'd into a single corrugated tubing that goes to the patient.
An 16-hour-old, 28-week gestational age neonate is being maintained in an O2 hood with an FIO2 of 0.5. The neonatologist believes that the patient has infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS). The following blood gas results are from an umbilical artery sample:
pH = 7.35
PaCO2 = 37 mm Hg
HCO3 = 24 mEq/L
BE = 0 mEq/L
PaO2 = 47 mm Hg
Based on this information, what should you recommend?
start nasal CPAP at 5-8 cm H2O
intubate and begin mechanical ventilation with PEEP
get a chest X-ray to look for a pneumothorax
increase the O2 hood concentration to 100%
start nasal CPAP at 5-8 cm H2O
The acid-base balance for this infant is within normal range; however, the patient has severe hypoxemia (P/F ratio ~ 100), probably due to shunting caused by the IRDS. In most centers, an initial trial of nasal CPAP would precede any attempt to intubate and provide mechanical ventilation.
A patient in the emergency room is receiving oxygen by nasal cannula at 3 L/min. Blood gases reveal the following:
pH 7.53
PaCO2 30 mmHg
PaO2 51 torr
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
The respiratory therapist should immediately
increase flow to 5 L/min
place the patient on a Venturi mask at 40%
place the patient on a non-rebreathing mask
decrease flow to 1 L/min
place the patient on a non-rebreathing mask
Which of the following pulmonary vasodilators can be administered via the inhalation route?
iloprost (Ventavis)
sildenafil (Viagra)
bosentan (Tracleer)
tadalafil (Adcirca)
iloprost (Ventavis)
Pulmonary vasodilators administered via the inhalation route currently include three prostacyclins: epoprostenol (Flolan), treprostinil (Tyvaso) and iloprost (Ventavis). Only treprostinil (Tyvaso) and iloprost (Ventavis) are approved for administration via the inhalation route, typically for use by outpatients. Both require use of breath-actuated handheld portable nebulizers, with iloprost requiring a vibrating mesh system (I-neb AAD System). Bosentan (Tracleer) is an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) and sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Adcirca) are phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors. All three of these agents are also pulmonary vasodilators but are administered orally.
A 32-year old patient is receiving an initial small-volume nebulizer treatment with Albuterol. Prior to administration, the patient's pulse was 74/min. During the treatment the pulse rises to 88/min and remains steady. The respiratory therapist should
Discontinue the treatment, assess the patient in 15 minutes
Contact the physician to obtain direction
Decrease future doses to half strength
Complete the treatment, continue to monitor pulse rate
Complete the treatment, continue to monitor pulse rate
When administering a breathing treatment, monitoring the patient for adverse reactions is important. A negative cardiac response is present when the heart rate rises more than 20 beats above baseline. In this case, the heart rate has risen only 14 beats above baseline and therefore is not considered an adverse reaction. The treatment should be continued, but the patient's heart rate should be continually monitored.
A patient presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath and severe nasal/sinus congestion. SPO2 on air is 86%. She is placed on a nasal cannula at 4 L/min but complains that she cannot breathe through her nose. The therapist should
change to a 35% air-entrainment mask
change to 100% cool aerosol mask
increase to 6 L/min nasal cannula
change to a 40% venture mask
change to a 35% air-entrainment mask
When a patient's nose is occluded with secretions or for any other reason a nasal cannula may not be appropriate. Switching to a mask will allow gases to be delivered by mouth. The FIO2 coming from a nasal cannula is approximately 3 to 4% per liter. Thus, a 35% Venturi mask most closely approximates the FIO2 of a nasal cannula running at 4 L/min.
A homecare patient complains that her oxygen concentrator is not working correctly because she does not feel like she is getting enough oxygen. The therapist will immediately instruct the patient to
change the filter
switch to an E cylinder oxygen tank
check the circuit breaker
push the reset button on the machine
switch to an E cylinder oxygen tank
When a patient complains they are not receiving enough oxygen, the first step is to ensure oxygen delivery by changing to a different modality. Then, the therapist can troubleshoot the problem and resolve it. In this case changing to an E cylinder is most appropriate.
A 150 lb female patient is receiving volume controlled SIMV with a volume of 600 mL, a mandatory rate of 12/min with 5 cm H2O pressure support. You note that her total rate of breathing is 45/min, and that she is using her scalene muscles during most spontaneous breaths. Which of the following is the most appropriate action at this time?
increase the set tidal volume
increase the inspiratory flow
increase the pressure support level
decrease the mandatory breath rate
increase the pressure support level
The tachypnea (spontaneous rate = 33/min) and active accessory muscle use indicate increased work of breathing. To decrease the patient's spontaneous work of breathing, you should increase the pressure support level. This normally boosts the spontaneous tidal volume, decreases the respiratory rate and lessens the work of breathing.
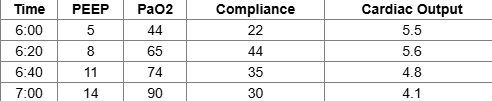
The following results of a PEEP study are obtained. Which of the following PEEP levels is indicated?
14 cm H2O
5 cm H2O
11 cm H2O
8 cm H2O
8 cm H2O
One approach to selecting PEEP levels is to choose the pressure that yields the highest compliance with an acceptable PaO2 and cardiac output. According to these criteria in this case, the optimal PEEP level is 8 cm H2O.
A patient with thick secretions who is receiving an aerosol therapy with 10% acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) reports shortness of breath after her treatments. Which of the following would you recommend for this patient?
dilute the acetylcysteine to 5% mixture
add albuterol (Proventil) to the aerosol mixture
discontinue the acetylcysteine treatments
add cromolyn sodium (Intal) to the aerosol mixture
add albuterol (Proventil) to the aerosol mixture
Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) can be very irritating to the airways and can cause bronchospasm. For this reason, it normally is given with or after a bronchodilator.
What is the best treatment for a patient who has a 45% pneumothorax?
Insert a pleural chest tube
Have the patient begin flutter valve therapy.
Insert a mediastinal chest tube.
Increase the patient's inspired O2 percentage.
Insert a pleural chest tube
A pneumothorax is air in the pleural space. A pleural chest tube is needed to remove it. A mediastinal chest tube is used to removal air or blood from around the heart. The heart or related structures could be damaged by the insertion of a mediastinal chest tube. No blood gas values are available for interpretation. Supplemental O2 will not correct the patient's underlying life-threatening problem. When the pneumothorax has been corrected and the patient's lung reexpands, oxygenation will improve.
Following administration of a bland aerosol treatment, coarse rhonchi are detected upon auscultation. You should
encourage the patient to cough
recommend administration of a bronchodilator
recommend discontinuation of therapy
discontinue the treatment and administer oxygen
encourage the patient to cough
A patient with COPD is receiving volume-controlled ventilation with an I:E ratio of 1:2. A chest radiograph shows increased air-trapping. Which of the following will decrease air-trapping?
decrease expiratory time
decrease inspiratory flow
increase minute ventilation
decrease rate
decrease rate
While working with a mechanically ventilated patient, the respiratory therapist notices that the peak pressure has increased by 10 cm H2O over the past hour. The plateau pressure has not changed. The patient has significant wheezing in both lungs that was not present earlier. The respiratory therapist should recommend
Nebulizing a corticosteroid.
Increasing the VT by 100 mL
Nebulizing a beta-agonist bronchodilator.
Suctioning the patient
Nebulizing a beta-agonist bronchodilator.
A 87-year-old nursing home patient is admitted with pneumonia. On assessment the patient presents with a 103.2 °F temperature, dry mucous membranes, urine output of 10 mL/hr for the past two hours, mild hypotension, and increased hematocrit on his CBC. Which of the following should you recommend to the ER physician?
beginning diuretic therapy
initiating IV fluids immediately
maximizing insensible water loss
clinical nutrition consultation
initiating IV fluids immediately
Dehydration is very common in the elderly due to improper fluid intake and altered fluid metabolism. Common signs of dehydration are: dry mucous membranes, hypotension, diminished urine output, decreased skin turgor, increased hematocrit, thick and tenacious secretions, decreased central venous pressure (CVP), and decreased pulmonary artery (capillary) wedge pressure (PAWP/PCWP). In this instance, IV fluids should be recommended.
Your patient had her spleen removed 2 days ago and is still reluctant to take a deep breath. The doctor asks for your recommendation to prevent the development of atelectasis. Which of the following would you suggest?
bronchodilator therapy
incentive spirometry
IPPB
bedside spirometry
incentive spirometry
Incentive spirometry (IS) is a good way to encourage deep breathing and prevent pulmonary complications in postoperative patients. IPPB is an alternative lung expansion therapy, but should only be considered if simpler, less costly approaches such as IS do not work.
A respiratory therapist desires to modify the therapy of a patient who is receiving 2.5 mg of Albuterol via mouthpiece every 2 hours via small volume nebulizer because the patient has experienced cardiac palpitations and a headache. What is the appropriate modification in this scenario?
Change to 1.25 mg Proventil.
Reduce the frequency.
Discontinue therapy.
Reduce the dosage.
Discontinue therapy.
Because the patient has not tolerated the therapy, the respiratory therapist should discontinue it and notify the ordering physician. A note about the patient's tolerance should also be made in the medical record.
A 23 year old patient is admitted to the Emergency Department with dyspnea and right-sided pleuritic chest pain. A chest X-ray indicated a 10% right sided pneumothorax. What treatment would you recommend for this patient?
chemical pleurodesis
O2 via nonrebreathing mask
needle decompression
insertion of a chest tube
O2 via nonrebreathing mask
Small spontaneous pneumothoraces (< 10-15%) often resolve themselves without treatment. Reabsorption of pleural air in a small pneumothorax can be hastened with the administration of high O2 concentrations. In general larger pneumothoraces that significantly compromise gas exchange are best resolved by tube thoracostomy and pleural drainage (insertion of a chest tube).
An adult patient with asthma is receiving Albuterol by small volume nebulizer Q.I.D. at a dosage of 0.5 mL. The patient complains of dizziness, tingling in his fingers, and anxiety with each treatment. The therapist should
switch to Mucomyst 20%
decrease dosage to 0.15 mL
increase dosage to 1.0 mL
switch to Xopenex 0.63 mg
switch to Xopenex 0.63 mg
When a patient experiences an adverse reaction, the first step is to stop the therapy and then modify the therapy to accomplish the same objective. In this case, decreasing the dose of Xopenex is suitable because 0.63 mg is still in the adult therapeutic range.
A patient shows signs of hypoxemia while on a heated aerosol set at 40% with the flow rate set to 8 L/min. The patient's minute ventilation is 38.0 L. Which of the following changes should be made?
decrease FIO2 to 28%, maintain flow rate
increase to FIO2 to 1.0 with a flow rate to 15 L/min
increase flow rate to 10 L/min
increase FIO2 to 0.5, maintain flow rate
increase flow rate to 10 L/min
This question requires one to recognize that the flow rate is not meeting the patient's ventilatory demand. It requires a little math to determine how much total flow the patient is receiving. In this case the ratio for 40% is 3:1. If you add 3+1, you get 4. Then, if you multiply 4 times 8 L/min. you get a total flow of 32 L per minute. The patient's reported minute ventilation is 38 L per minute. This would cause the patient to entrain extra air and would ultimately lower FIO2, resulting in an increase in hypoxemia.
A patient with a history of dyspnea, fatigue and chest pain when engaging in minimal activity has a mean pulmonary artery pressure of 33 mm Hg and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure of 8 mm Hg. The patient would most benefit from receiving a drug from which of the following category?
a pulmonary vasodilator
an angiotensin receptor blocker
an ACE inhibitor
an antiarrhythmic agent
a pulmonary vasodilator
According to the clinical information, the patient has advanced (Class III) pulmonary hypertension not associated with heart failure (normal PCWP). For these patients a pulmonary vasodilator is indicated. Common drug agents include IV or inhaled prostacyclins, oral PDE inhibitors or a guanylate cyclase stimulators.
A 63-year-old female patient is admitted to the emergency department with shortness of breath, chest pain and diaphoresis. The ER Nurse Practitioner is busy with another patient and asks for your recommendation. You should now recommend:
maximum inspiratory pressure
sputum culture & sensitivity
O2 mask at 10 L/min
end-tidal CO2 analysis
O2 mask at 10 L/min
Based on the data available, the patient may have experienced a myocardial infarction. Oxygen should be administered and gas exchange monitored (via pulse oximetry and ABG). Obtaining a maximum inspiratory pressure measurement, a sputum C&S or end-tidal CO2 is not indicated when treating a suspected MI and would only waste valuable time.
Which of the following medication you would recommend to help quiet an ICU patient who is breathing asynchronously on a ventilator?
dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine)
cisatracurium (Nimbex)
fluoxetine (Prozac)
midazolam (Versed)
midazolam (Versed)
Common medications used to sedate mechanically ventilated patients include benzodiazepines like midazolam (Versed); hypnotics like propofol (Diprivan); and alpha-2 agonists like dexmetatomidine (Precedex) or clonidine (Catapres). Opioid analgesics like fentanyl (Sublimaze) or remifentanil (Ultiva) also can be used as sedating agents. Cisatracurium (Nimbex) is a neuromuscular blocking agent (not a sedative!), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine) is a stimulant, and fluoxetine (Prozac) an antidepressant.
A patient recovering from myasthenia gravis has been receiving volume control ventilation (assist/control) for 8 weeks, and is now exhibiting signs of respiratory muscle atrophy. Which of the following approaches would you recommend to help "recondition" her muscles?
implement PEEP
switch to the SIMV mode
decrease the sensitivity
changeover to CPAP
switch to the SIMV mode
A pressure-volume graphic observed on a volume-controlled ventilator has a pronounced "beak". What strategy can be used to manage this issue?
decrease PEEP
decrease VT
increase flow
increase I:E ratio
decrease VT
Beaking = overdistention
Clinical signs and a chest X-ray confirm that a patient receiving volume control SIMV has suffered a tension pneumothorax. Which of the following actions would you recommend to treat this problem?
performing a tube thoracostomy
lowering the peak inspiratory pressure
obtaining a stat arterial blood gas
switching to pressure control SIMV
performing a tube thoracostomy
A tension pneumothorax is a medical emergency. Treatment always involves decompression of the pleural space by either needle or tube thoracostomy chest tube insertion. Lowering the peak pressure will help prevent worsening of the problem, but does nothing to treat it. Likewise obtaining an ABG it is not a priority and will not help resolve the pneumothorax.
A COPD patient receiving volume control SIMV with a VT = 500 mL, rate = 8/min, pressure support = 10 cm H2O and PEEP = 5 cm H2O undergoes a spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) via T-tube. After 5 minutes the patient has to be placed back on the ventilator due to severe tachypnea. What approach would you recommend for the next SBT?
extubate the patient then provide nasal BiPAP
provide sedation prior to ventilator withdrawal
provide pressure support only via ET tube
provide pressure support + CPAP via ET tube
provide pressure support + CPAP via ET tube
A 38-week gestational age infant delivered 4 hours prior shows signs of hypoxemia. In preparation for oxygen administration at 30% by oxygen hood, the therapist should utilize which of the following devices?
high-flow hydrator
bubble humidifier
blender
heat-moisture exchanger
blender
When using an oxygen hood, it is appropriate to premix gases by use of an oxygen-air blender. Use of a large-volume nebulizer at low FIO2 could cause excessive noise transmitted to an oxygen hood which could promote hearing damage and restlessness of the infant. For this reason use of blender is more appropriate.
An appropriate way to respond to an asthmatic patient who experiences nausea and tingling in her digits with albuterol therapy is to
explain in simple words that these are normal, harmless side effects.
reduce the dosage of the medication within limits.
reduce the flowrate to the nebulizer during therapy.
tell the patient not to breathe so deeply during the treatment.
reduce the dosage of the medication within limits.
A 17-year-old patient has been admitted through the emergency room to ICU. He is in a coma after taking an overdose of sedatives. His chest X-ray film indicates bilateral atelectasis. To help correct this problem, you should recommend:
using a low machine rate
lowering the tidal volume
increasing the inspiratory flow
applying PEEP
applying PEEP
Applying PEEP, airway pressure release ventilation (APRV), and application of recruitment maneuvers are all ways to increase the transpulmonary pressure gradient and help open up collapsed alveoli (atelectasis). Low rates or high inspiratory flows lengthen the expiratory time, which is used to avert air-trapping, not treat atelectasis.
Soon after endotracheal tube extubation, an adult patient exhibit a high-pitched inspiratory noise, heard without a stethoscope. Which of the following actions would you recommend?
a STAT heated aerosol treatment with saline
careful observation of the patient for 6 hours
immediate reintubation via the nasal route
a STAT racemic epinephrine aerosol treatment
a STAT racemic epinephrine aerosol treatment
Following extubation, a nurse places a patient on a heated nebulizer with an FIO2 of 35%. Soon thereafter, the patient begins to exhibit mild stridor. Which of the following specific changes would you recommend?
switch to cool mist therapy via jet nebulizer
increase the heat setting on the nebulizer
switch to O2 therapy via nasal cannula @ 3 L/mn
provide O2 therapy via a 35% venti-mask
switch to cool mist therapy via jet nebulizer
A COPD patient is in the emergency room. A quick assessment reveals a respiratory rate of 28, spontaneous tidal volume of 200 mL, use of accessory muscles, and venous distension. The patient is receiving oxygen by nasal cannula at 2 L/min and oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry is 88%. Which of the following would provide most help to the patient at this time?
non-rebreathing mask
flutter valve therapy
NIPPV
adult mechanical ventilation
NIPPV
A patient shows signs of hypoxemia while on a heated aerosol set at 40% with the flow rate set to 8 L/min. The patient's minute ventilation is 38.0 L. Which of the following changes should be made?
decrease FIO2 to 28%, maintain flow rate
increase flow rate to 10 L/min
increase FIO2 to 0.5, maintain flow rate
increase to FIO2 to 1.0 with a flow rate to 15 L/min
increase flow rate to 10 L/min
This question requires one to recognize that the flow rate is not meeting the patient's ventilatory demand. It requires a little math to determine how much total flow the patient is receiving. In this case the ratio for 40% is 3:1. If you add 3+1, you get 4. Then, if you multiply 4 times 8 L/min. you get a total flow of 32 L per minute. The patient's reported minute ventilation is 38 L per minute. This would cause the patient to entrain extra air and would ultimately lower FIO2, resulting in an increase in hypoxemia.
A patient with emphysema receiving volume control A/C ventilation develops signs of air trapping (auto-PEEP). The doctor does not want to switch to SIMV. Which of the following actions would help resolve this problem?
increase the length of time available for exhalation
increase the preset frequency of breathing by 30%
decrease the length of time available for exhalation
increase the inspiratory time by decreasing the flow
increase the length of time available for exhalation
A patient receiving pressure controlled SIMV develops progressive atelectasis in the lower lobes and now requires 70% O2 to keep his SaO2 above 80-85%. Comparison chest X-rays indicate a generalized decreas in lung volume. What would you recommend to help correct the problem?
add CPAP/PEEP to the circuit
increase the FIO2 to 80%
suction the patient more frequently
switch to volume controlled A/C
add CPAP/PEEP to the circuit
The atelectasis/reduced lung volume is causing a refractory hypoxemia. In patients refractory hypoxemia, PEEP is indicated. PEEP increases the FRC by recruiting collapsed alveoli, which improves oxygenation by decreasing shunting.
A patient receiving mechanical ventilation with active heated humidification has very tenacious secretions. Which of the following actions would you recommend in order to facilitate suctioning of these secretions?
instill 5 mL normal saline into the ET tube before suctioning
increase the proximal airway temperature setting to 45 °C
suction the patient for 20 to 30 seconds on each attempt
assure that the patient has adequate systemic hydration
assure that the patient has adequate systemic hydration
A patient with asthma shows a small improvement in peak expiratory flow rates from 45% to 49% of predicted after 1 hour of continuous bronchodilator therapy with 10 mg/hr albuterol. Which of the following should the therapist consider NEXT?
hyperbaric therapy
ECMO
1.25 mg Xopenex q 20 min X 3 doses
heliox therapy
heliox therapy
A patient is receiving a treatment with 2.5 mg of albuterol (Proventil) and 2.5 mL of normal saline in the emergency department. The heart rate prior to therapy is 80/min, and at the end of therapy is 138/min. You should:
add acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) to the treatment
recommend decreasing the dosage of albuterol
increase the amount of saline per treatment to 3 mL
recommend changing to ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
recommend decreasing the dosage of albuterol
An ECG is performed on a patient in the emergency room (ER) who is complaining of chest pain. The respiratory therapist notices flipped T waves on the ECG tracing. Which of the following best remedies this finding?
oxygen therapy
Coumadin
changing ECG electrodes
aspirin therapy
oxygen therapy
Which of the following would be a sufficient reason to discontinue a spontaneous breathing trials
blood pressure increases from 110/80 to 118/88 mmHg
development of confusion or disorientation
respiratory rate increases from 18 to 26
heart rate increases from 78 to 92 bpm
development of confusion or disorientation
A patient with a fenestrated tracheostomy tube in the speaking configuration has experienced a complete cardiopulmonary collapse. In preparation for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the respiratory therapist should FIRST do which of the following?
insert the inner cannula
cap the tracheostomy tube
deflate the cuff
remove the tracheostomy tube
insert the inner cannula
A respiratory therapist enters the patient's room to do a routine breathing treatment and finds the patient has no obvious chest movement. After calling for help, the first action of the therapist should be to
Begin mask-valve ventilation
Place the patient on a 100% nonrebreathing mask
Perform chest compressions
Check for a pulse
Begin mask-valve ventilation
A physician has ordered an aerosol treatment with 4 mL acetylcysteine (Mucomyst), 20% concentration. The patient develops end-expiratory wheezes. You should:
change to 2.5 mg albuterol (Proventil)
discontinue therapy and notify the physician
administer 10 mg beclomethasone (Vanceril)
administer the treatment as ordered
discontinue therapy and notify the physician
Mucomyst is very irritating to the airways and can cause bronchospasm. It should always be given with a bronchodilator. In this case, you should stop the therapy and notify the physician - making the recommendation of adding a bronchodilator if the Mucomyst is still indicated.
A mother with a history of preeclampsia delivers a 1200-gram infant who is 32 week of gestation after spontaneous onset of premature labor. The mother has a history of narcotic use but denies use for the past 5 months. Which of the following would most likely help the ventilation status of the infant?
Infasurf (califactant)
Narcan (naloxone)
Romazicon (flumazenil)
Lasix (furosemide)
Infasurf (califactant)
If a patient's pulse rate increases by 40 per minute during a respiratory therapy treatment, you should:
terminate the treatment and notify the physician
stop the treatment and report the reaction to the next shift
continue the treatment and monitor the patient's pulse
shorten the duration of the treatment
terminate the treatment and notify the physician