Unit C - heat transfer
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
How is heat transferred ?
Higher temperature to lower temperature
Name the three methods by which heat is transferred ?
1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Radiation
Heat transfer in conduction , give example
Occurs in a solid body and still fluids
Heat a metal rode with gas , heat felt at end of rod
Heat transfer in convection, give example
Occurs through moving fluids
boiling
Heat transfer in radiation , example
Occurs between surfaces , ie between gases
sun rays penetrating earth
Describe what occurs in conduction
1. Temperature increase and molecules gain more energy and collide with slower moving neighbors
2. Energy of thermal motion passed from one molecule to next
Why are metals good conductors of heat ?
Free electrons so when molecules vibrate free electrons can detach and can share energy from one molecules to the next
Steady-state in relation to heat transfer
Temperature remains constant with time
- heat transfer always from high temp to low temp
Equation for Heat conduction through walls in a state state
Q = k x A( T1 - T2 ) / L
k = coefficient of thermal energy
A = area
T1-T2 = temp difference
L = wall thickness
Equation for heat transfer in a non-steady conditions
Fourier's equation
Q = -k x A dT/dx
k = coefficient of thermal energy
X/k = thermal resistance
A = area
dT/dx = temp gradient
If we increase thermal resistance , what will happen ?
Heat loss will be reduced
Why is stainless steel a good conductor of heat ?
Free electrons so when molecules vibrate free electrons can detach and can share energy from one molecules to the next
Little thermal resistance
Idea for use of lagging jack to retain heat ?
- jacket had a fibre air mixture which prevented heat loss to external enviornment -
increases thermal resistance which decreases heat flow and increases heat retention
Why is cork a poor conductor of heat ?
It is a porous material and has a high thermal resistance , decrease heat flow and increases heat retention
What is natural or free convection ?
Heated materials flow due to difference in density
buoyancy forces induced by this
Describe the process of natural convections
Example with kettle for making tea
1. Surface below the kettle is heated
2. Heat conducted from surface to first layer of water causing it to decrease in density and expand
3. First layer rises upwards
4. New fresh water comes in contact same occurs
- continuous process
5. First layer becomes cooler and then reaches heated surface and rises agin
In natural convection what drives flow ?
Temperature differences
What is forced convection ?
Heated fluid is forced to move by an external force blower , stirrer oven
What factors affect the equation for heat transfer in convection
1. Flat or curved surface
2. Horizontal or vertical surface
3. Is fluid a gas or liquid
4. Density,viscosity,heat and thermal conductivity of the fluid
5. Is there laminar or turbulent flow
6. Evaporation or condensation
Equation for convection
Q/t = h A (T - Ts)
H = convection coefficient
A = area of surface
T = temperature of many body of fluid
Ts = temp of surface
When is conduction seen in heat transfer in fluids ?
- natural free convection : heat the surface and transfer to water in kettle
Explain the heat exchange between fluids across a solid boundary
Pool boiling
Boiling caused by a heater in contact with pool of water
Forced circulation boiling
Movement of boiling water helped by external agitator which forces liquid over heating surface
What is a pan evaporator ?
- made of stainless steel and heat is supplied by a jacket
- allows for pool boiling and vapour removed by pipe
Draw a diagram of heat transfer in boiling
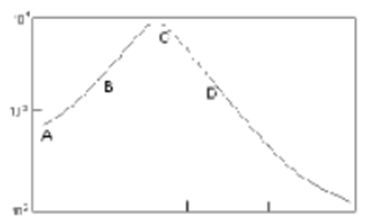
[boiling heat transfer curve] Explain what occurs at A-> B
- First sign of boiling : bubbles
- Bubbles move to surface by natural convection so little surface disturbances
- low heat flux
Explain what occurs at B-C
Nucleate boiling : higher temperature causes bubbles to form more rapidly
Explain what occurs at C
Peak flux - mass heat transfer
What occurs beyond C
Vapour film forms at surface and at bottom with poor conductivity
What occurs if you continue boiling after D ?
Films boiling but this can cause damage to evaporator
· In pool boiling, what is the critical temperature drop and why is it important to know what it is?
From the boiling heat transfer graph in the slides:
As the temperature difference (ΔT) increases, heat flux rises through natural convection and nucleate boiling.
It reaches a peak heat flux at point C, where “ΔT = critical temperature drop”.
Beyond this point, a vapour film forms, which has poor conductivity, causing heat flux to decrease sharply (film boiling).
Knowing the critical temperature drop is essential because exceeding it causes the formation of a vapour film that drastically reduces heat transfer efficiency, which can lead to overheating of heating surfaces.
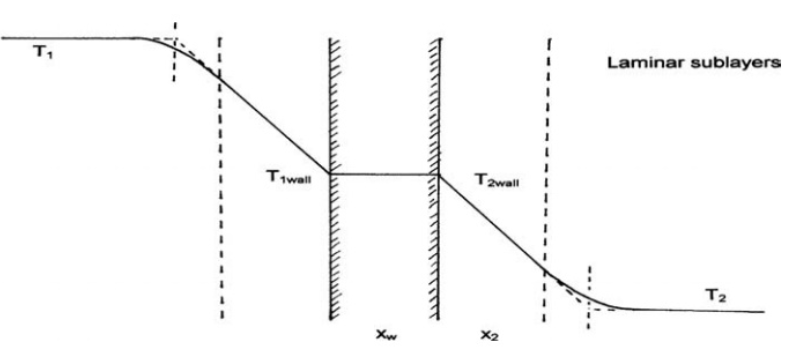
· Explain the process of heat transfer between fluids across a solid boundary. Where might you see this approach used in pharmaceutical processing?
When fluids are separated by a solid wall heat transfer occurs in 3 steps
1. Convection from the hot fluid to the surface of the solid wall
2. Conduction through the solid wall
3. Convection from the other side of the wall into the cooler fluid
We can see this approach in pharmaceutical processing in jacketed vessels, tubes and processes such as evaportation, distillation and crystallisation
· Is conduction involved in heat transfer in fluids? If so, explain where and how.
Yes. Conduction occurs in fluids at the fluid–solid boundary, where a thin laminar layer of almost-still fluid transfers heat only by conduction. Because fluids have low thermal conductivity, this layer has a high temperature gradient. Even during convection, the initial heat transfer from the hot surface to the first layer of fluid happens by conduction before the fluid begins to move