Multiple Choice 7
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Choose an example in which the momentum of a system is not constant
A freely falling metal ball, with the ball as the system
Two identical balls with equal speed hit a wall. Ball 1 hits the wall and stops. Ball 2 bounces off with half of its initial speed, moving in the opposite direction. Which of the following is true?
The change in momentum of Ball 1 is less than the change in momentum of Ball 2
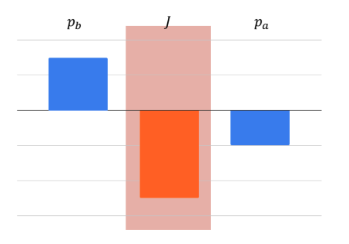
Which of the following scenarios could be described by the momentum bar chart below?
A tennis ball moving in the air is hit by a tennis racket and rebounds. The system is the tennis ball
A basketball bounces off the gym floor. The system is the basketball
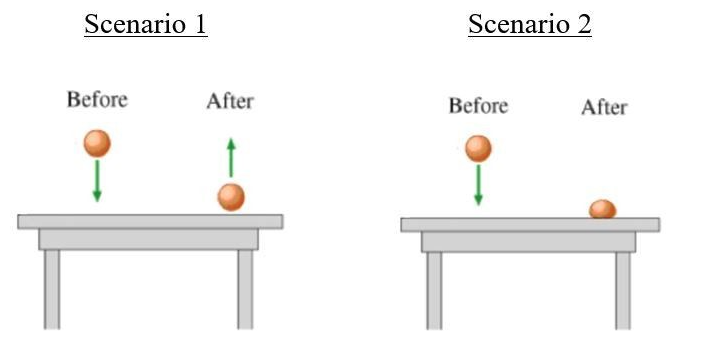
Moving vertically, two objects of the same mass strike a flat tabletop at the same speed, as shown above. However, in Scenario 2 the object stops when it hits the table, and in scenario 1, the object bounces off the table with an equal speed in the opposite direction. Which of the following statements is true about the change in momentum of the two objects?
The object’s change in momentum is larger in Scenario 1
A toy car with very low friction wheels and axles rests on a level track. In which situation will its speed increase more
It is hit by a rubber ball with the same mass and velocity of the clay that rebounds in the opposite direction after hitting the car
In which situation does the momentum of a tennis ball change more?
It hits the racket and flies off in the opposite direction
Two separate boxes, of masses m and 2m, are initially at rest on a frictionless sheet of ice. A constant force is exerted horizontally on the smaller box, for a horizontal distance d. After this, the smaller box has a final momentum p. Now the application of force is repeated for the larger box, until it has traveled the sfame horizontal distance d. What will be true about the larger box’s final momentum?
The larger box will have a final momentum that is greater than p
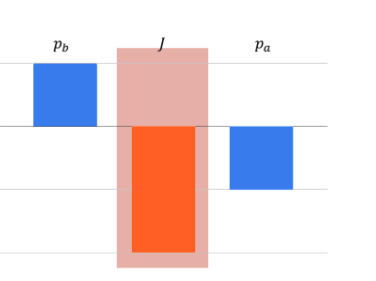
Which scenario could be represented with the momentum bar chart shown below?
A tennis ball traveling to the right with a speed of 10 m/s hits a tennis racket and travels to the left with a speed of 10 m/s
The same sum of forces is exerted for the same time interval on an object with mass “m” and an object with mass “2m.” The magnitude of the change in momentum of the object with mass “2m” mass is
equal to the magnitude of the change in momentum of the less-massive object
The gravitational force that Earth exerts on an object causes an impulse of +10 N s in one experiment and +1 N s on the same object in another experiment. How can this be?
The time intervals during which the force was exerted are different
When can you apply the idea that momentum is constant to solve a problem?
When the system is isolated
Which is a safer car bumper in a collision, one that is flexible and retracts or one that is rigid? Why?
The retractable bumper, because it extends the time interval of the collision, thus reducing the force exerted on the car
A bullet fired at a door makes a hole in the door but does not open it. Your finger does not make a hole in the door but does open it. Why?
A finger exerts a smaller force but the time interval is much longer