Last units of Bio 204
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
species are more likely to be invasive if
-they have a high fecundity
-selfing
-there is a lack of natural predators
What species are unlikely to be able to shift geographical
acclimate
behavior flexibility as a mechanism for cooing with climate change
how do humans affect the biogeographic filter
because humans move species around they get rid of the biogeographic filter
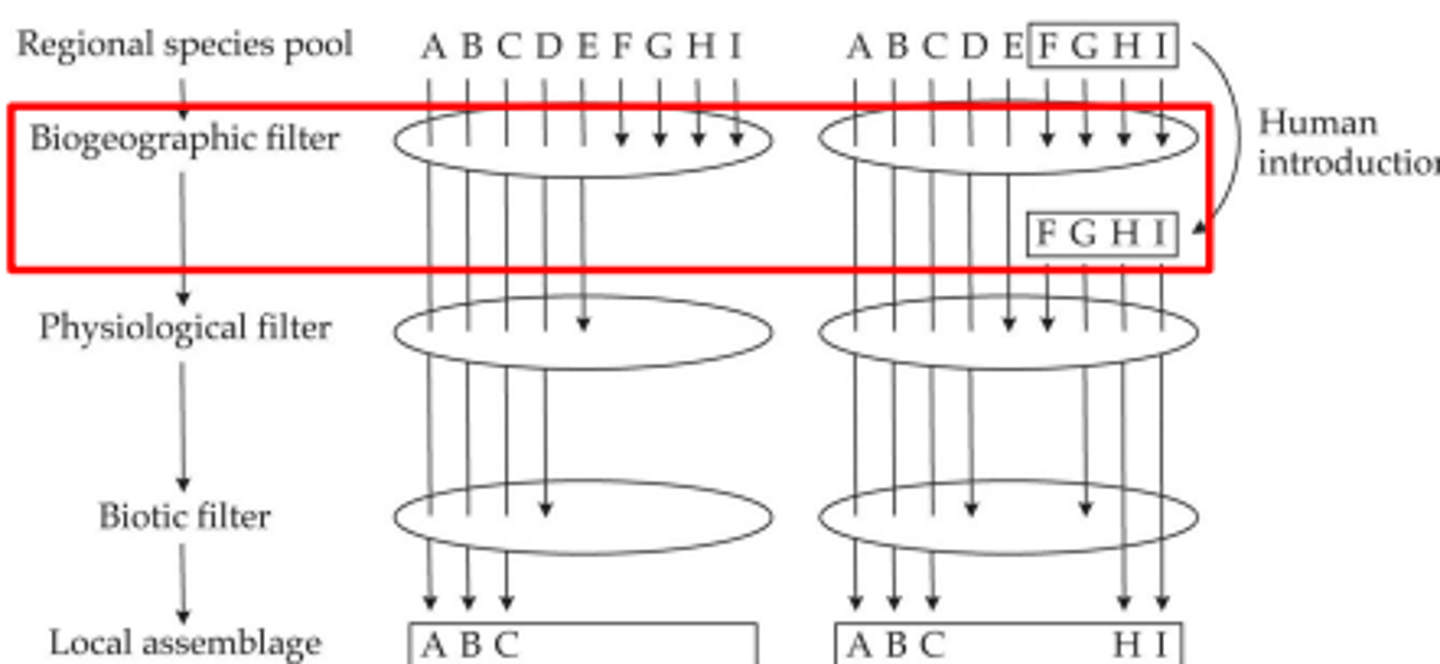
physiological filter
can a species survive in that area
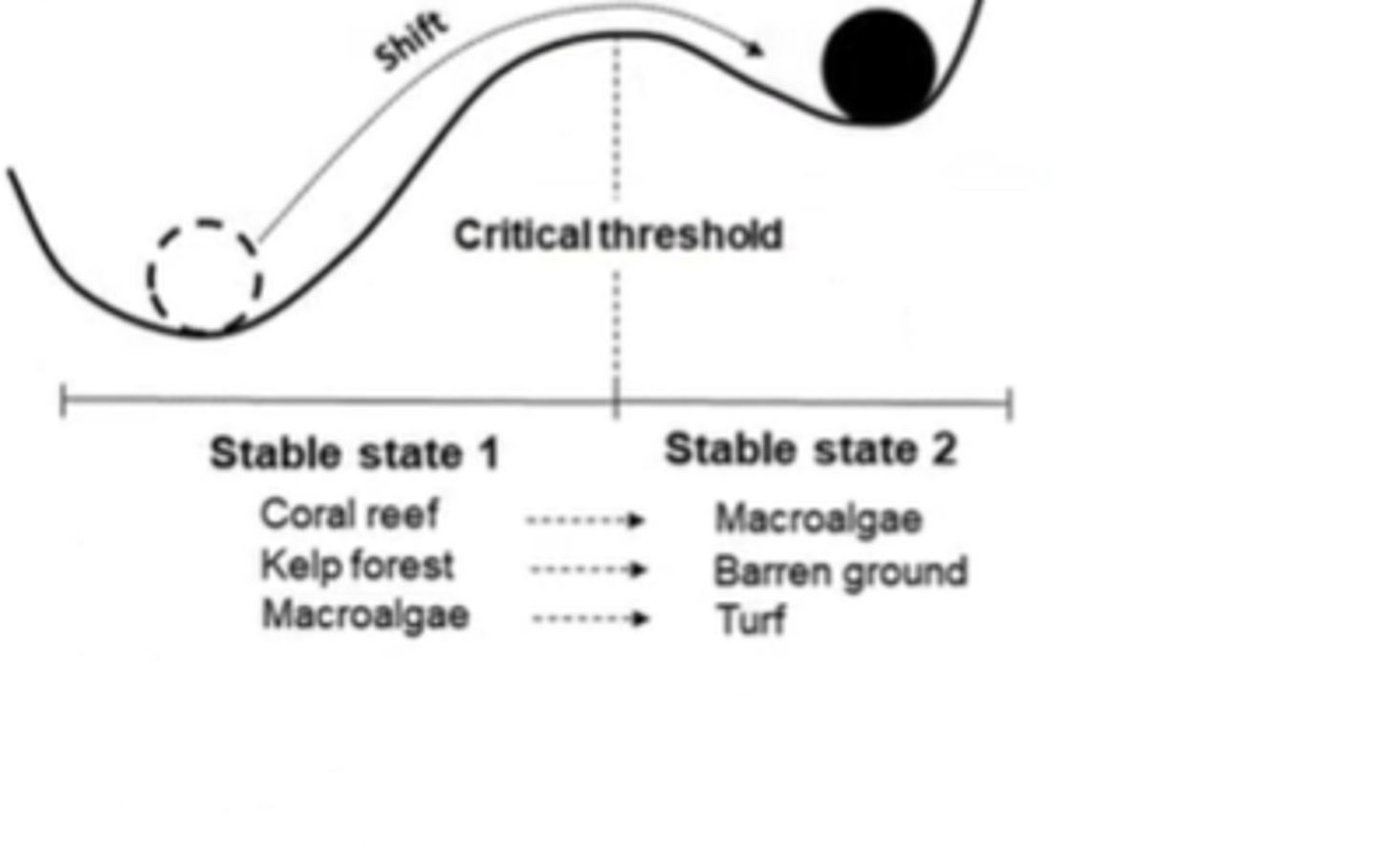
explain this graph : graph with black and white ball
left is a native community the right is dominated by either native species or a combination of both native and invasive species. Restoration can be represented by an arrow going back to the left.
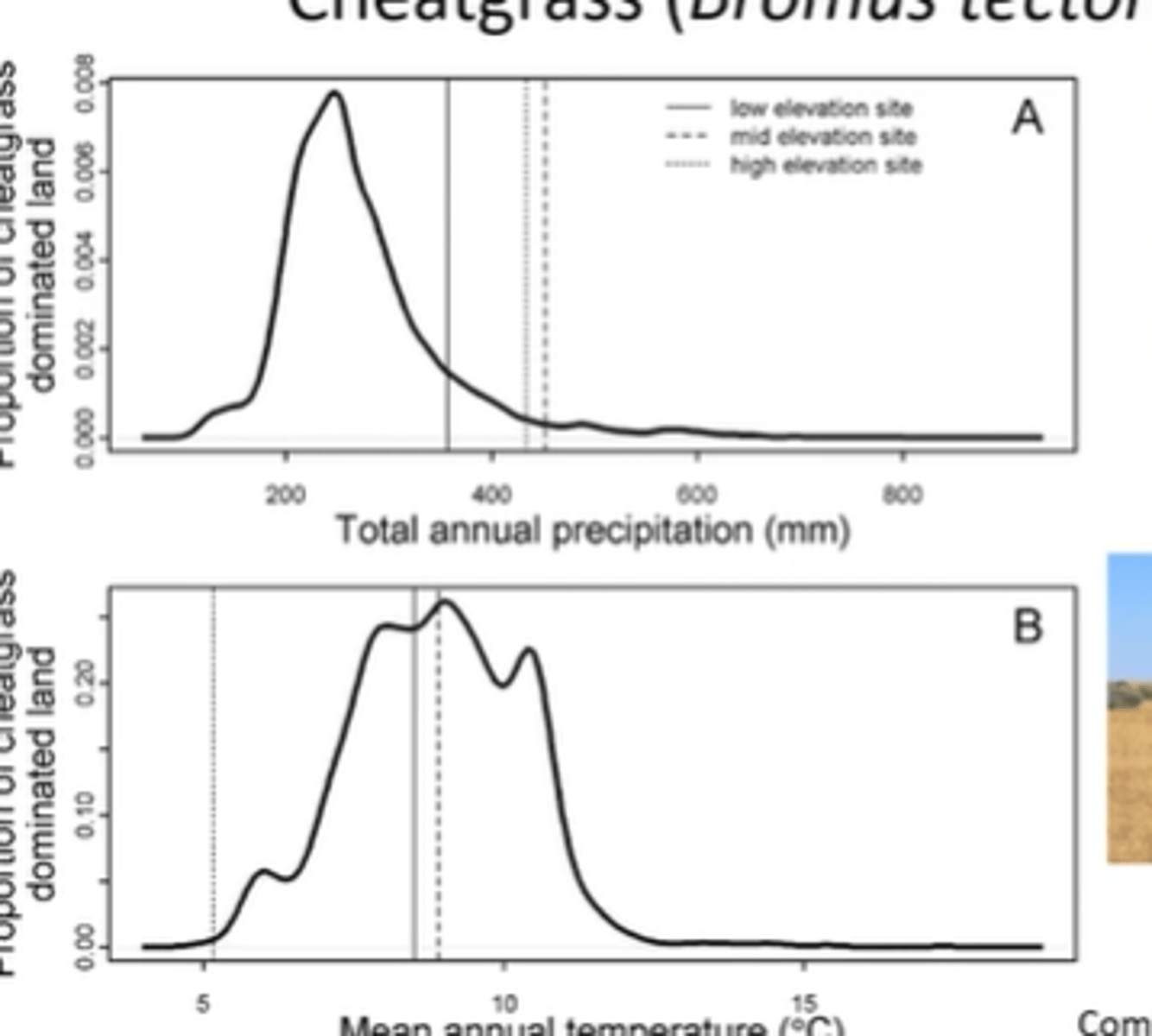
explain physiological graph
this is to determine the region where a species can grow. For this species, it can grow in an environment with little rain and lower elevations
r vs K species
r species produce many babies with very little parental care a K species will have very few offspring with a lot of care. r species can invade easier
Local assemblage
this is also called a top down affect where a species becomes a new predator and can cause detrimental affects to local species.
-competition is another factor in this
phenotypic plasticity
when an individual is able to adjust to new conditions either through behavior or physically
what are some of the effects of agriculture on the environment
-drug resistance
-hormone disruption
-decline of bee populations (specifically from fungicides)
urban homogenization
human influenced invasions and common urban challenges cause biodiversity of cities to become increasingly more alike
evolutionary responses to climate change
phenotypic changes- such as ladybugs getting darker
what is a protist
-Usually unicellula r
-Often aquatic• Membrane‐bound nucleus, -linear DNA, internal membranes • Motile via cilia, flagella, or amoeboid motion
- Sexual and asexual
What makes a protist stand out from everything else?
nothing, a protist is the oldest eukaryote that is anything that isnt a plant animal or fungi
5 major eukaryotic groups
1.Archaeplastida
2.SAR supergroup
3.Excavata
4.Amoebozoa
5.Opisthokona
what is malaria
a protist
how do biologists believe a nuclear envelope developed
the nuclear envelope is what divides other eukaryotes and protists
this could've been through a nuclear plasma membrane infolding on itself
this created endoplasmic reticulum
bees are postivily effected as opposed to butterflies because by urban structures because
people keep bees, there are less fungicides in the urban areas,
how did plants come to be?
vascular tissue.
cuticle and stomata
seeds
have an embryo
goes dormant until conditions are favorable
different ways plants reproduce
-moss way, requires water for reproduction
-angiosperms- double fertilization allows for pollen dispersal and does not require water
why did angiosperms radiate so quickly
unoccupied niches
what process best describes a eukaryotic cell engulfing another eukaryote
secondary endosymbiosis
Fungi and animal commonalities
chitin,flagella,glycogen
What event caused the rapid development of animals
cambrian explosion
key characteristics of animals
-no cell walls
Protosome vs Deuterosome development
protosome- mouth parts develop first
deuterosome- butt develops first
how do animals intake nutrients
they are ingestive heterotrophs
diploblast vs triploblast
tripoblast has three layers-mesoderm,endoderm and ectoderm
diploblast- two layers and no mesoderm
three types of coelum presentation
coelomates- lined with mesoderm and have a closed coelum
-aceolomates-have no coelum
-pseudocoelomates only lined with mesoderm
what are the advantages of a coelom
it allows an animal to move,it can protect an animal from shock
types of symmatry
radial-can be split into 4ths
bilateral-can be split in half
Benefits of radial symmetry
-easier movement
-easier to find prey
-seek shelter
Hox genes
series of genes that controls the differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo
Oviparous
egg laying
viviparous
live birth
differences between viruses and living organisms
they can have double or single stranded dna
-they do not have a plasma membrane
-they have no metabolic capabilities
-they can not carry out translation independently
how biologists study viruses
Culture or Infectivity Assays Genome Sequencing Nucleic Acid Detection Assays Serology (Antibody) Assays Microscopy Assays
most viruses are present in
the sediments