5- Cornea 1
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Katherine H.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What portion of the eye does the cornea make up?
Anterior 1/6th of the eye
What is the area of the cornea?
1.3 cm^2
What is the horizontal measurement of the cornea in the anterior view?
11.7-12.6 mm
What is the vertical measurement of the cornea in the anterior view?
10.6-11.7 mm
What is the horizontal measurement of the cornea in the posterior view?
11.7 mm
What is the vertical measurement of the cornea in the posterior view?
11.7 mm
External Scleral Sulcus
The merger of the Cornea and Sclera
What is the radius of curvature of the posterior cornea?
6.5 mm
What is the radius of curvature of the anterior cornea?
7.8 mm
What is the average radius of curvature of the cornea?
7.6 to 7.7 mm
What is the index of refraction of the cornea?
1.376
What is the overall dioptric power of the cornea?
+43.1 D to +48.8 D
-anterior surface = +49.00 D
-posterior surface = -6.00 D
-total dioptric power = +43.00 D
Topographic map or curvatures across normal cornea
-flatter in men
-Aspheric = Flattens towards periphery and Steep centrally
-most refractive error is axial
Contact lens curvature
Asphericity of the cornea is the reason why contact lenses have a central radius of curvature on their inside curve (i.e. Base curve) and at least one flatter curvature in the periphery
Astigmatism
Unequal curvature or the cornea or crystalline lens
-Prevents light from being focused to a single point on the retina
Regular astigmatism
flat and steep meridians are 90 degrees apart
-difference = the amount of astigmatism
With-the-rule astigmatism
steeper in vertical meridian (most corneas)
Against-the-rule asigmatism
steeper curvature in the horizontal meridian
Oblique Astigmatism
steeper curvature in oblique axis
Irregular asitgmatism
steepest and flattest meridians are not 90 degrees apart
Lenticular astigmatism
unequal curvature of the lens
Average central corneal thickness
520-550 um
Average peripheral corneal thickness
670 um
Thicker corneas
high IOP measurement (flattens less readily with applanation tonometer)
Thinner corneas
lower IOP measurement (flattens more readily with applanation tonometer)
-Thinner corneal thickness is a risk factor for Glaucoma
-African-Americans generally have thinner corneas
Pachymeter
measures central corneal thickness using ultrasound
Gives result in microns 0.52mm = 520 microns
Bulbar limbus
Fascia Bulbi (Tenon's capsule) strongly adheres to episclera and conjunctiva
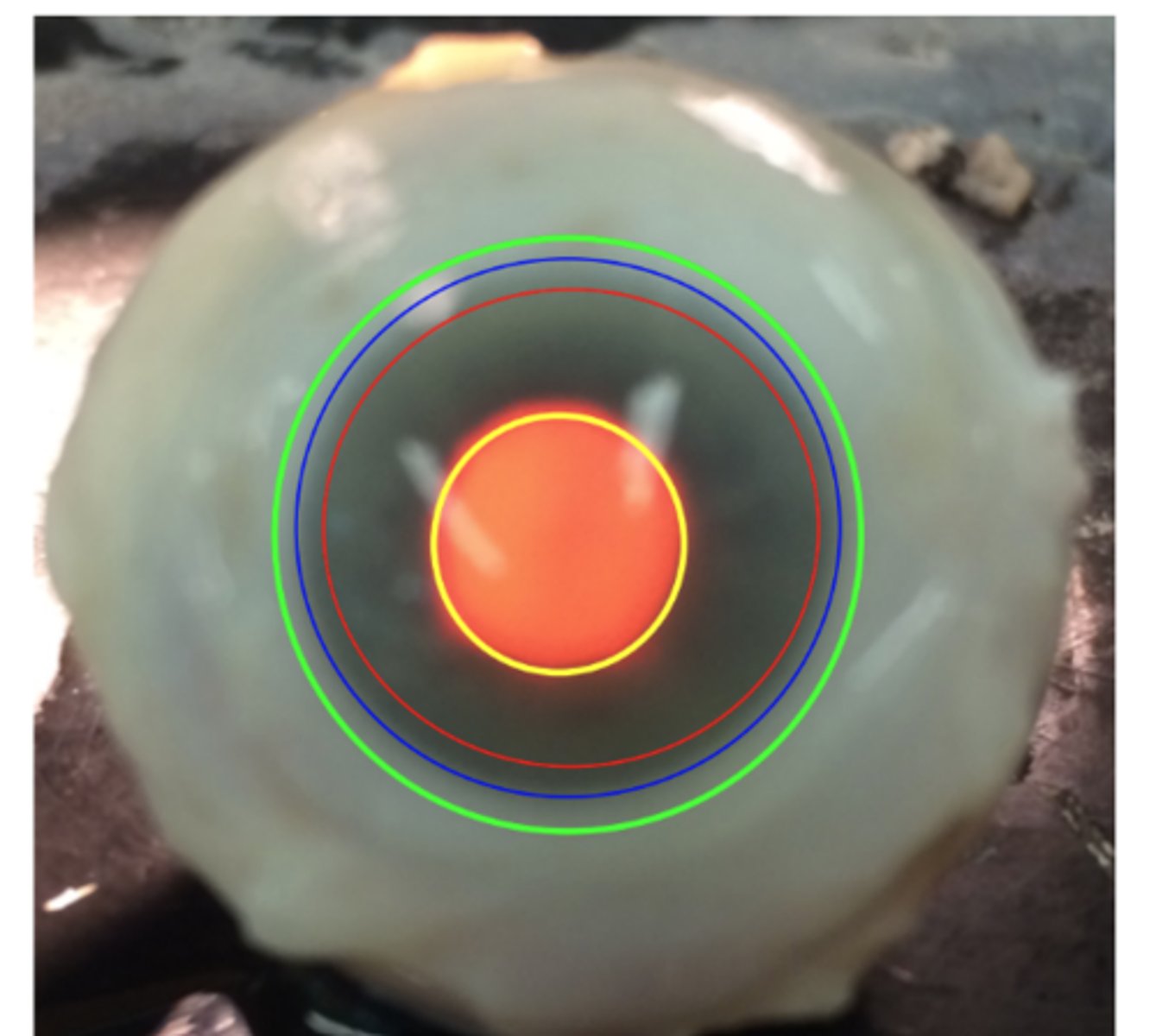

Corneoscleral limbus
Juncture of cornea and sclera, 1-2 mm wide
Conjunctival Limbus
conjunctiva extends 1 mm beyond corneoscleral limbus
Optical zone
central 4 mm of cornea
What is the thickness of the corneal tear film?
3 microns thick
What is the volume of the corneal tear film?
6.2 ± 2 microliters
What is the rate of production of the corneal tear film?
1.2 microliters/minute
What components are found in the corneal tear film?
Electrolytes, metabolites, proteins, enzymes, and lipids
How many layers does the corneal tear film have?
3 layers
What is the lipid layer of the corneal tear film secreted by?
Meibomian glands in the palpebrae and caruncle
What is the aqueous layer of the corneal tear film secreted by?
Lacrimal gland & accessory lacrimal glands
What is the mucous layer of the corneal tear film secreted by?
Goblet cells in the conjunctiva
What is the function of the oily layer in the corneal tear film?
Helps prevent the aqueous layer from evaporating
What does the mucous layer of the corneal tear film do?
Decreases surface tension and provides a smooth, wettable surface for the aqueous layer
Are the tear film layers discrete?
No, they are not discrete
What forms the colloidal matrix of the corneal tear film?
The interaction of the tear film layers
What is the lipid phase of the corneal tear film composed of?
Aggregates of lipid held together by hydrophobic forces
What is found beneath the surface of the aqueous mucinous phase?
Aqueous components, both soluble and gel-forming mucins
What do the aqueous components interact with in the corneal tear film?
A base layer of epithelial membrane-bound mucins
What is the glycocalyx in the corneal tear film?
Secreted by epithelial cells and includes several transmembranous mucins
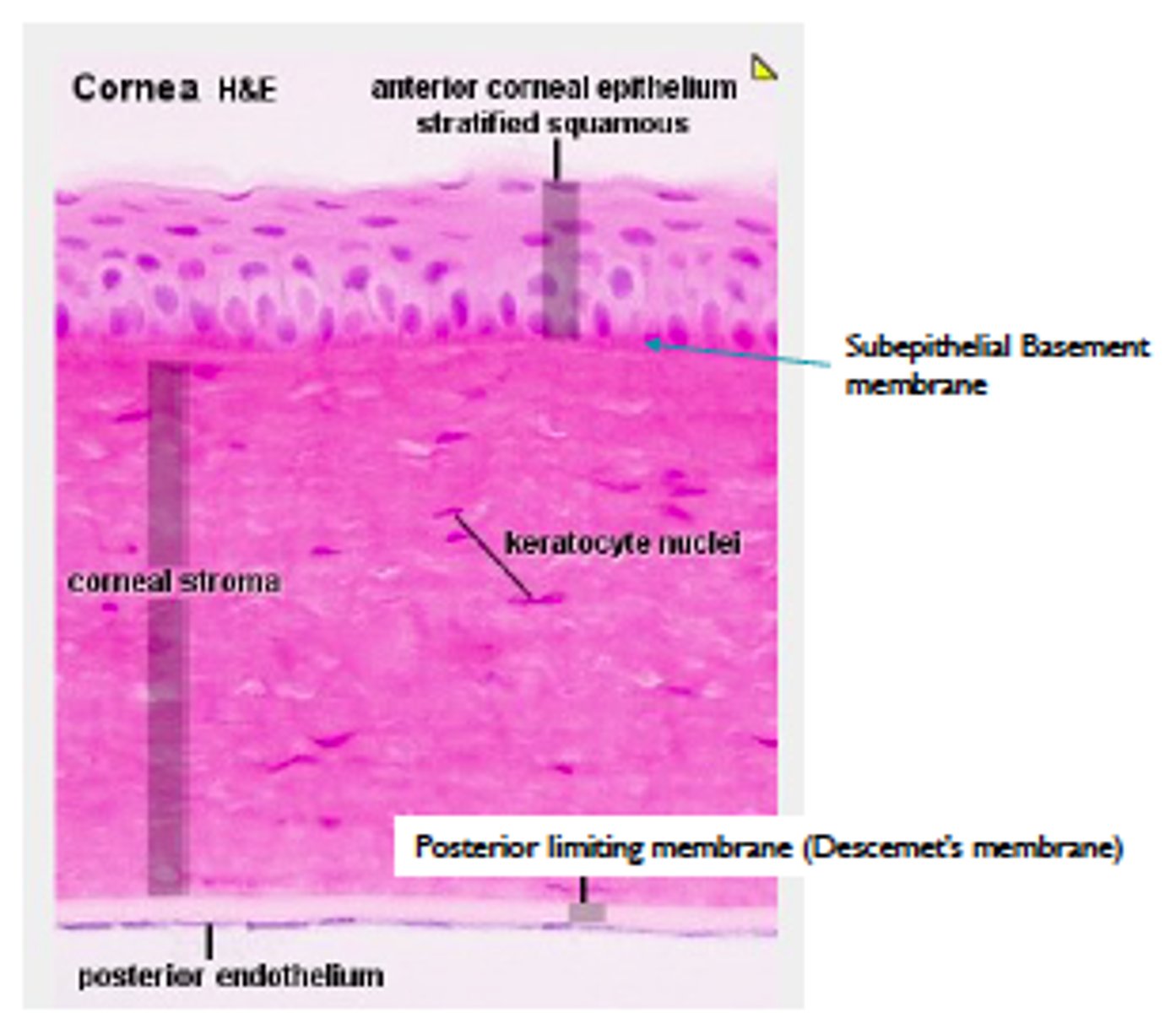
Corneal Histology
-Predominantly extracellular material
-Covered on each surface by sheet of cells
-Anterior Epithelium has 5-7 layers
-Endothelium is monolayer
-Attach via basement membranes
-Stroma is bulk of cornea - ordered layers of collagen
Five layers of the cornea
-Epithelium
-Bowman's Layer
-Stroma
-Descemet's Membrane
-Endothelium
What type of epithelium is the corneal epithelium?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What is the thickness of the corneal epithelium?
50-60 um
With which structure is the corneal epithelium continuous?
Bulbar conjunctival epithelium
What types of cells are present in the peripheral cornea?
Melanocytes and Langerhans cells
What anchors the corneal epithelium to the underlying tissue?
A basement membrane
How does the thickness of the corneal epithelium change with age?
Central thickness remains constant, while paracentral and peripheral epithelium thins
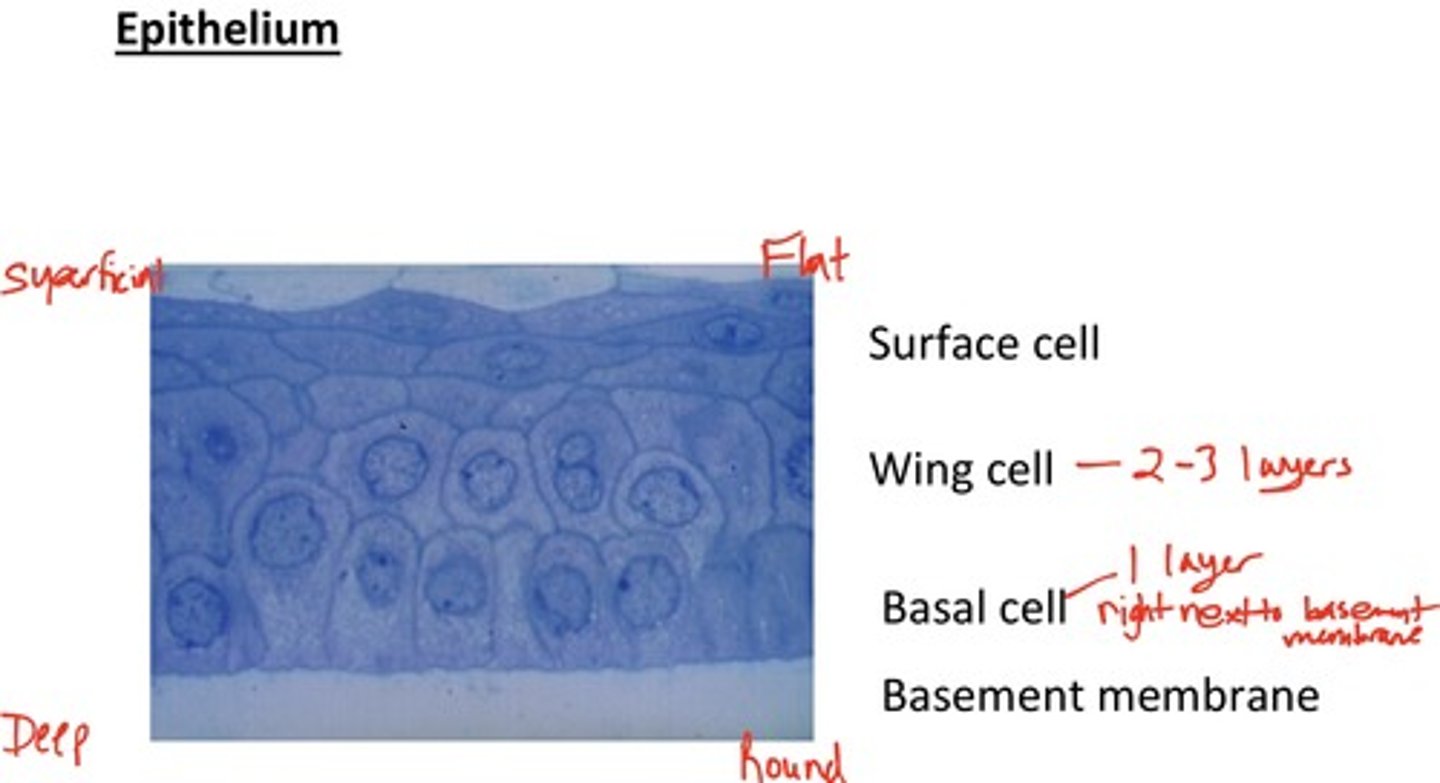
How many cell layers compose the corneal epithelium?
5-7 cell layers
What is the structure of the apical layer of the corneal epithelium?
1-2 layers of flattened, squamous cells
What type of cells are found in the wing cell layer of the corneal epithelium?
2-3 layers of wing cells
What type of junctions attach wing cells to each other?
Desmosomes and gap junctions
What type of cells are in the basal layer of the corneal epithelium?
Columnar basal cells
Which cells in the corneal epithelium undergo mitotic division?
Basal layer cells
What holds the basal layer cells to Bowman's layer?
Hemi-desmosomes
How do stem cells from the limbus migrate in the basal cell layer?
In a vorticeal pattern
What do microplicae on the surface of the corneal epithelium do?
Pick up O2 from the air dissolved in tears
What can cause loss of surface microplicae?
Regular use of contact lenses
What do tight junctions between apical cells represent?
The intercellular permeability barrier of the corneal epithelium
How long does it take for Zonula Occludens to reform?
1 hour
What happens to tight junctions in the presence of preservatives in certain eye drops?
They are temporarily compromised in order to increase permeability to allow the medication to have better penetration.
-Underlying cells secrete a layer of mucin to prepare for tear exposure.
-Preservatives in contact lens solutions can be toxic to the cornea too.
Wing Cells
2-3 layers of wing cells centrally, 4-5 layers peripherally
-Posterior surface is concave and anterior surface is convex
-Attached to adjacent wing cells via desmosomes and also have gap junctions
-Become progressively flatter moving anteriorly towards the surface
What is the shape of the apical head of a basal cell?
Rounded to accommodate the wing cells located above.
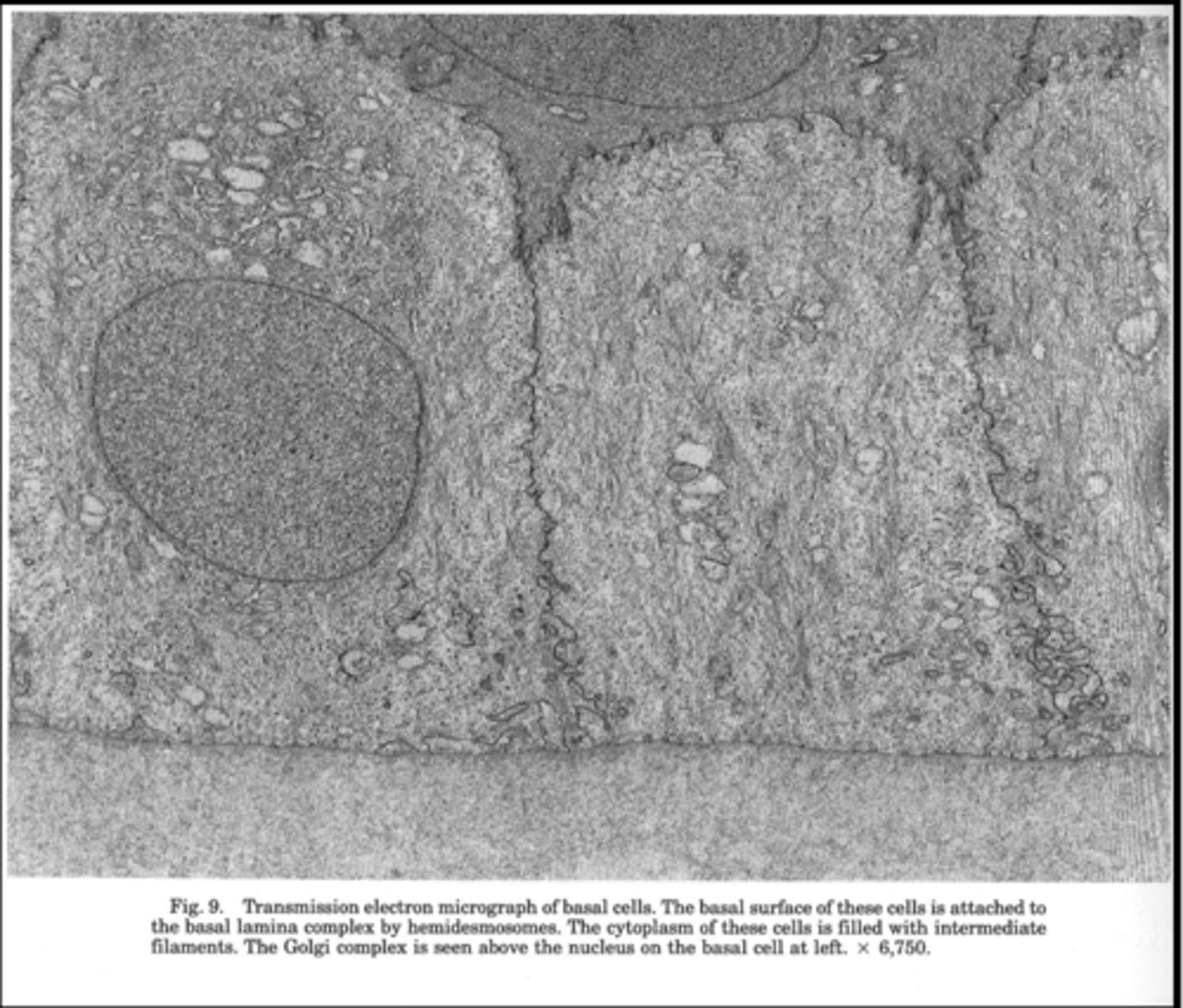
How do basal cells attach to wing cells?
Via desmosomes
How do adjacent basal cells communicate?
Via gap junctions
What type of junctions do adjacent basal cells use to attach to each other?
Desmosomes
What process do basal cells undergo?
Mitotic division
What happens to hemidesmosomes during basal cell division?
They break
What remains for new basal cell attachment after division?
Anchoring fibrils
What is the thickness of the basement membrane?
75-100 nm thick
-2x thickness by 60 years of age
How long does it take for damage to the basement membrane to repair?
It can take months to repair.
What is the lamina lucida?
A translucent layer that underlies the cell membrane, containing fibronectin and laminin 5.
What attaches the lamina lucida to the lamina densa?
Hemidesmosomes
What is the lamina densa composed of?
It is composed of collagen type VII.
What layer underlies the lamina lucida?
The lamina densa.
What are the components of the adhesion complex?
Hemidesmosomes and Actin-Based Focal Adhesions
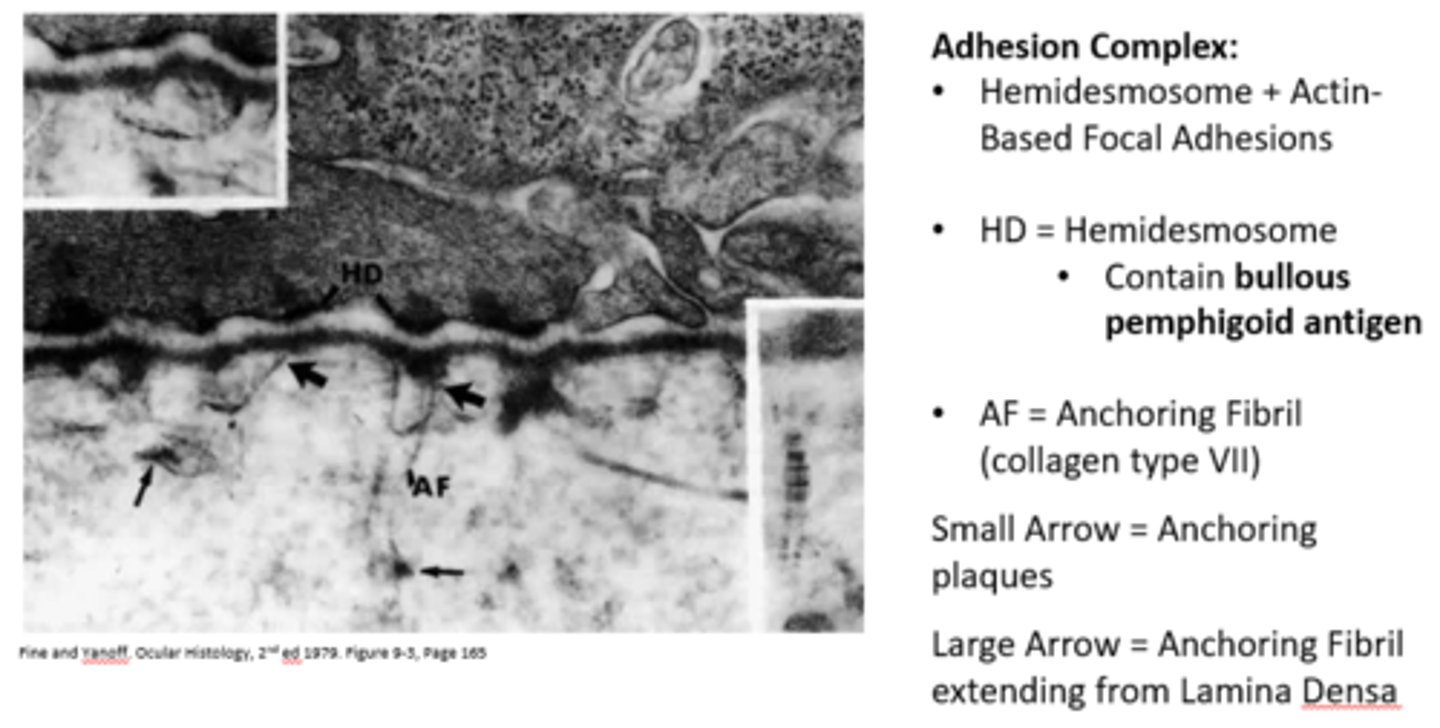
What antigen is contained in hemidesmosomes?
Bullous pemphigoid antigen
What is the function of the adhesion complex?
It is responsible for the firm attachment of the epithelium to the underlying stroma.
Where is integrin found?
Intercellularly or at the cell-matrix junction
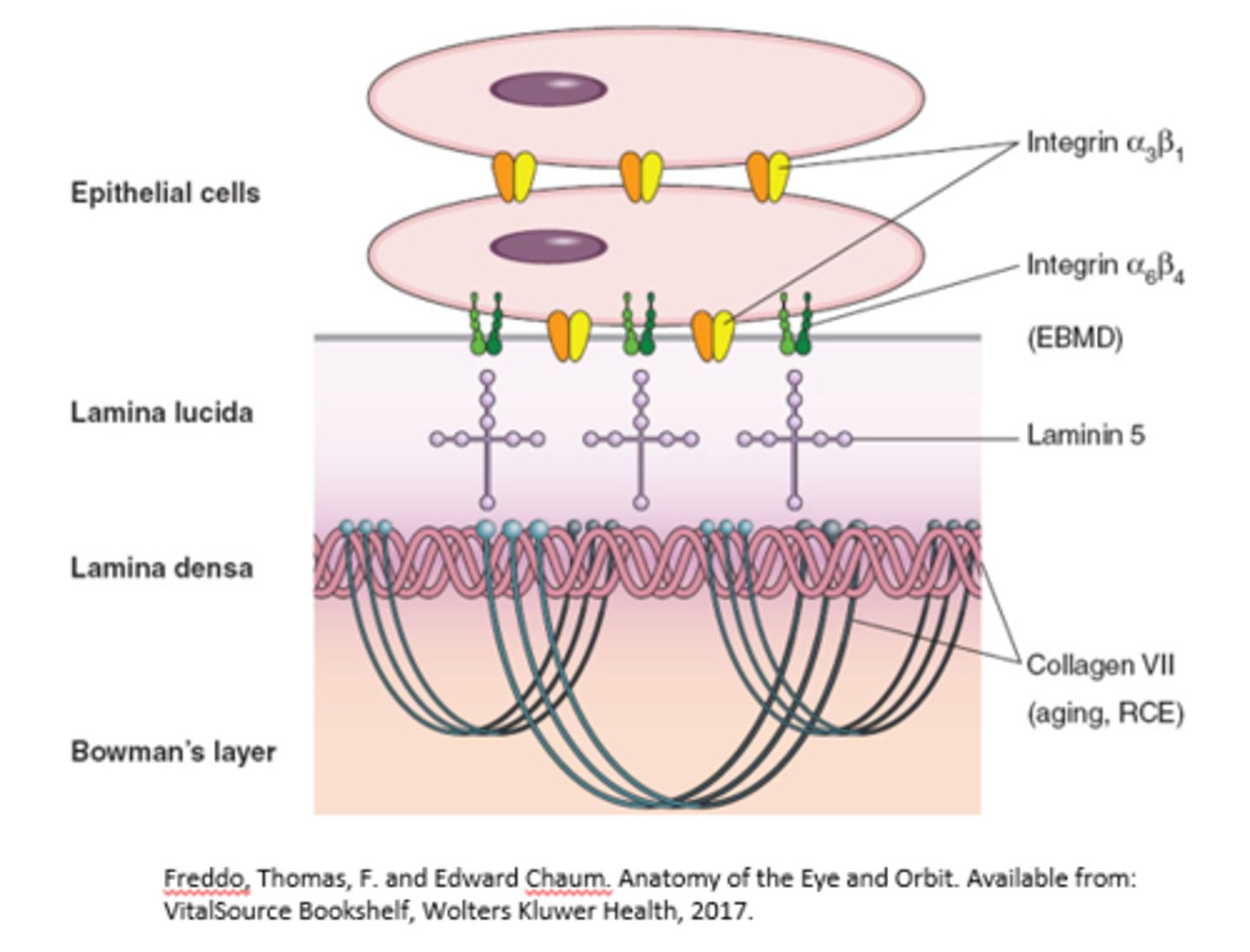
What is a characteristic of epithelial basement membrane dystrophies (EBMD)?
They have abnormal integrin.
What is abnormal in recurrent corneal erosion (RCE)?
Abnormal collagen type VII.
Langerhan's Cells
-Present in the peripheral cornea
-Less than 10% Langerhan's cell density compared to conjunctiva
-Antigen recognition and processing
-Non in central cornea to minimize immune response that could cause scarring worse than the initial traumatic insult (can migrate to central cornea in HSK and EW contact lens users - increase risk of scarring)
Melanocytes
small population present in peripheral cornea
Palisades of Vogt
radial projections of limbal epithelium & stroma that extend into cornea in spike-like fashion
-the alternating pattern of epithelial thickening and thinning that outline fibrovascular connective tissue channels containing arterial, venous, and lymphatic vessels
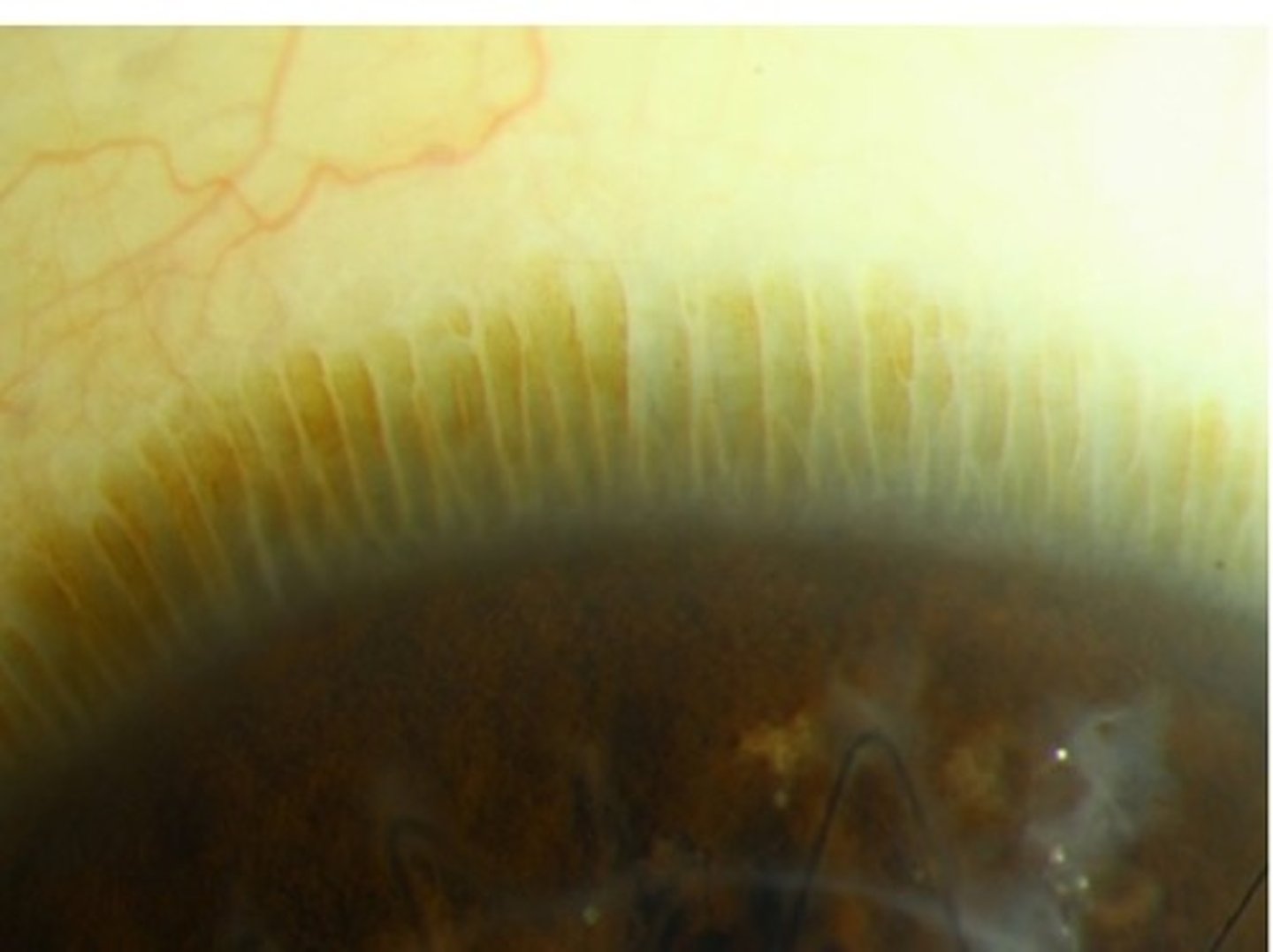
Corneal abrasion
a scratch on the cornea, usually painful but not severe
Symptoms: Pain, feeling that something is in eye, tearing, and discomfort when blinking
What to do: rinse with clean water or saline, do not rub
Treatment: See eye care professional. Aggressive lubrication. Antibiotic ointment or drops.
Fluorescein dye used to assess size and depth of the corneal abrasion.
Corneal Epithelial Dystrophies
-Meesman's Dystrophy
-Subepithelial Mucinous Dystrophy
-Gelatinous Drop-like Dystrophy
What is the function of Bowman's Layer?
Believed to provide structural support
What type of collagen fibers are found in Bowman's Layer?
Randomly oriented collagen fibers
Does Bowman's Layer contain keratocytes?
No, it is acellular
What is the thickness of Bowman's Layer?
8 to 12 um thick
What does Bowman's Layer contain for nerve fibers?
Channels (pores) for passage of corneal nerve fibers
Can Bowman's Layer be stripped away from the stroma as a continuous sheet?
No, it cannot be stripped away
Does Bowman's Layer regenerate if damaged?
No, it does not regenerate
When is Bowman's Layer formed?
Formed prenatally