Carbohydrate Metabolism and Glucose Structure in Clinical Chemistry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the three main elements that compose carbohydrates?
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O).
What are the four general properties used to classify carbohydrates?
Size of the base carbon chain, location of the carboxyl functional group, number of sugar units, and stereochemistry.
How are carbohydrates classified based on the size of the carbon chain?
They can be classified as Trioses, Tetroses, Hexoses, etc.
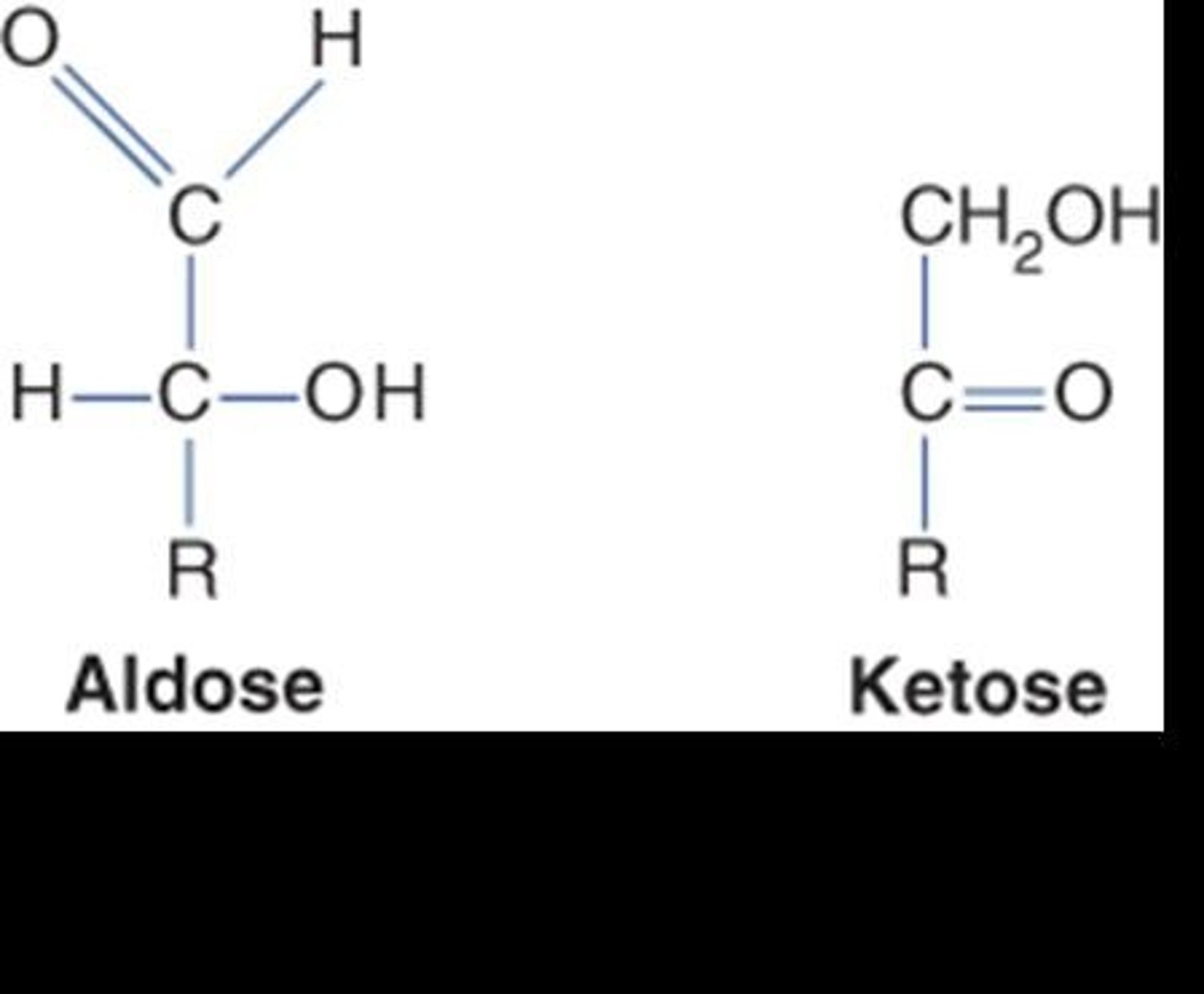
What distinguishes aldoses from ketoses?
Aldoses have a terminal carbonyl group (aldehyde), while ketoses have a carbonyl group in the middle of the molecule.
What are the classifications of carbohydrates based on the number of sugar units?
Monosaccharides (one), Disaccharides (two), Oligosaccharides (three to ten), and Polysaccharides (ten or more).
What is the glycosidic bond?
The bond that links monosaccharides together in carbohydrates.
What are stereoisomers in carbohydrates?
Compounds with the same types and order of bonds but different spatial arrangements.
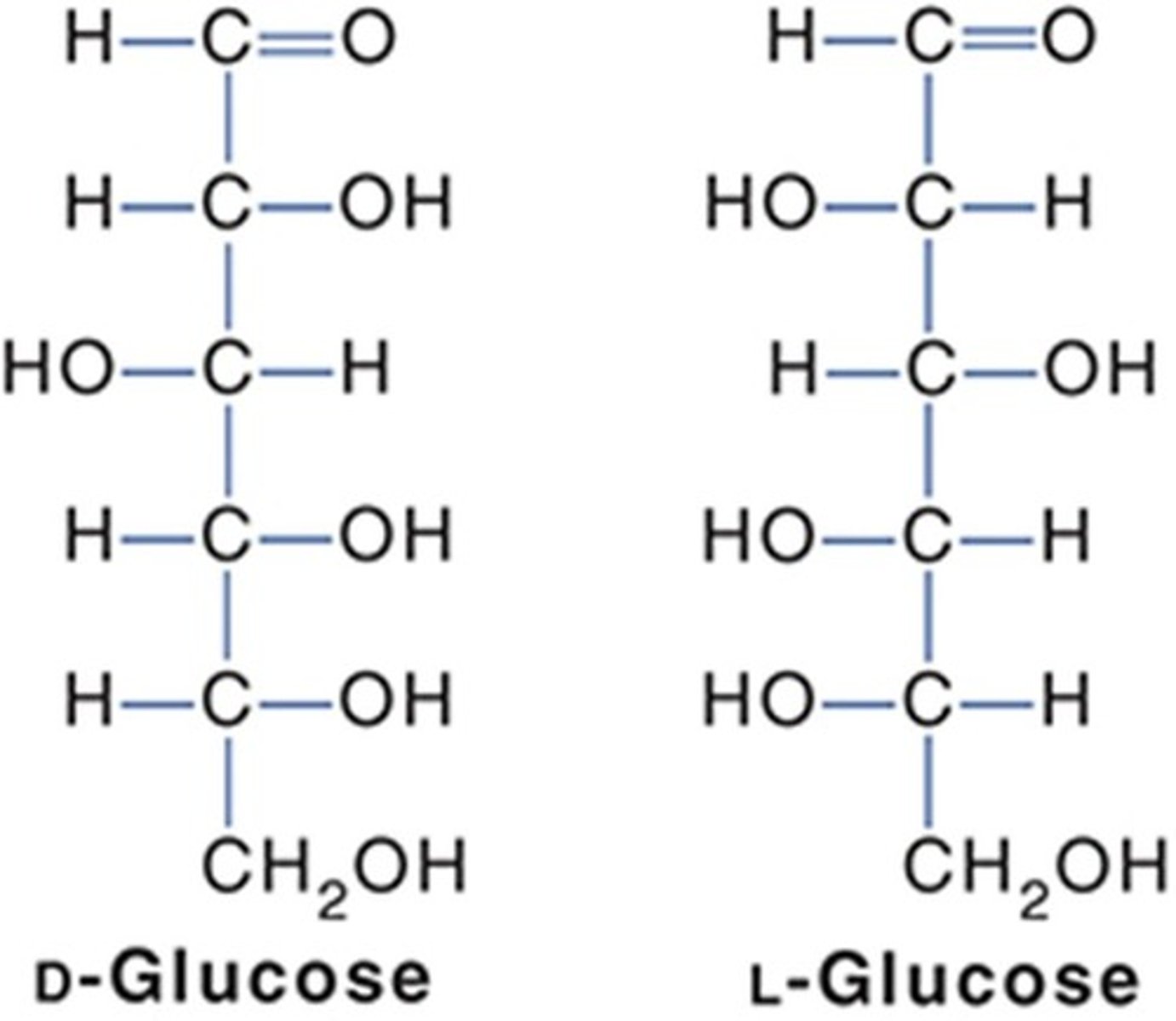
What are the two forms of glucose based on stereochemistry?
D-Glucose (right) and L-Glucose (left).
What is the fate of glucose after ingestion?
It is primarily ingested as starch and glycogen, then digested into monosaccharides for absorption.
Which enzymes are responsible for digesting carbohydrates into monosaccharides?
Salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase, maltase, sucrase, and lactase.
What is the only carbohydrate that can be used directly as an energy source?
Glucose.
What are the three metabolic pathways glucose can enter upon entering a cell?
Glycolysis, glycogenesis, and the pentose phosphate pathway.
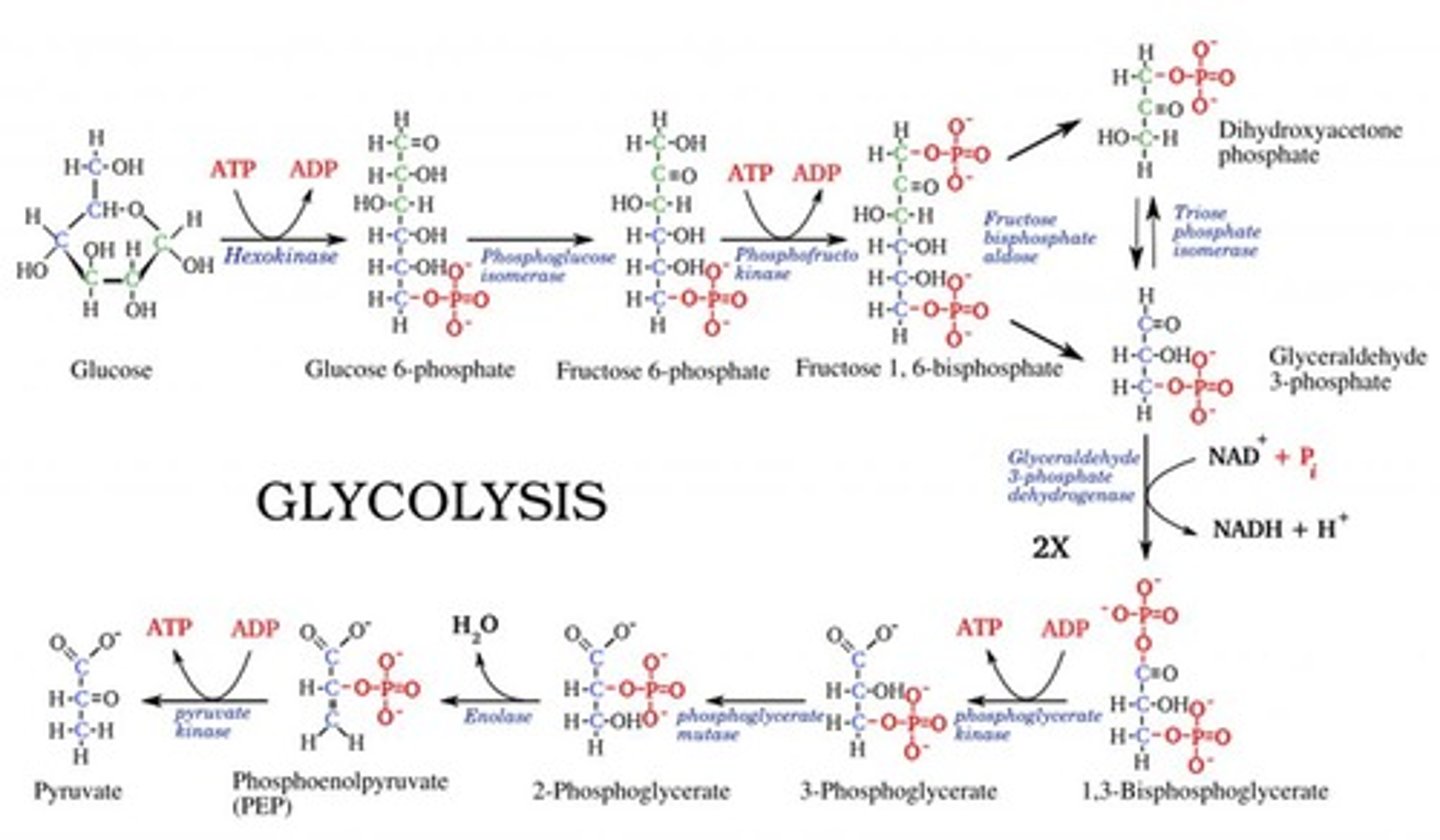
What is the first step in glucose metabolism?
Phosphorylation of glucose to form glucose-6-phosphate by Hexokinase or Glucokinase.
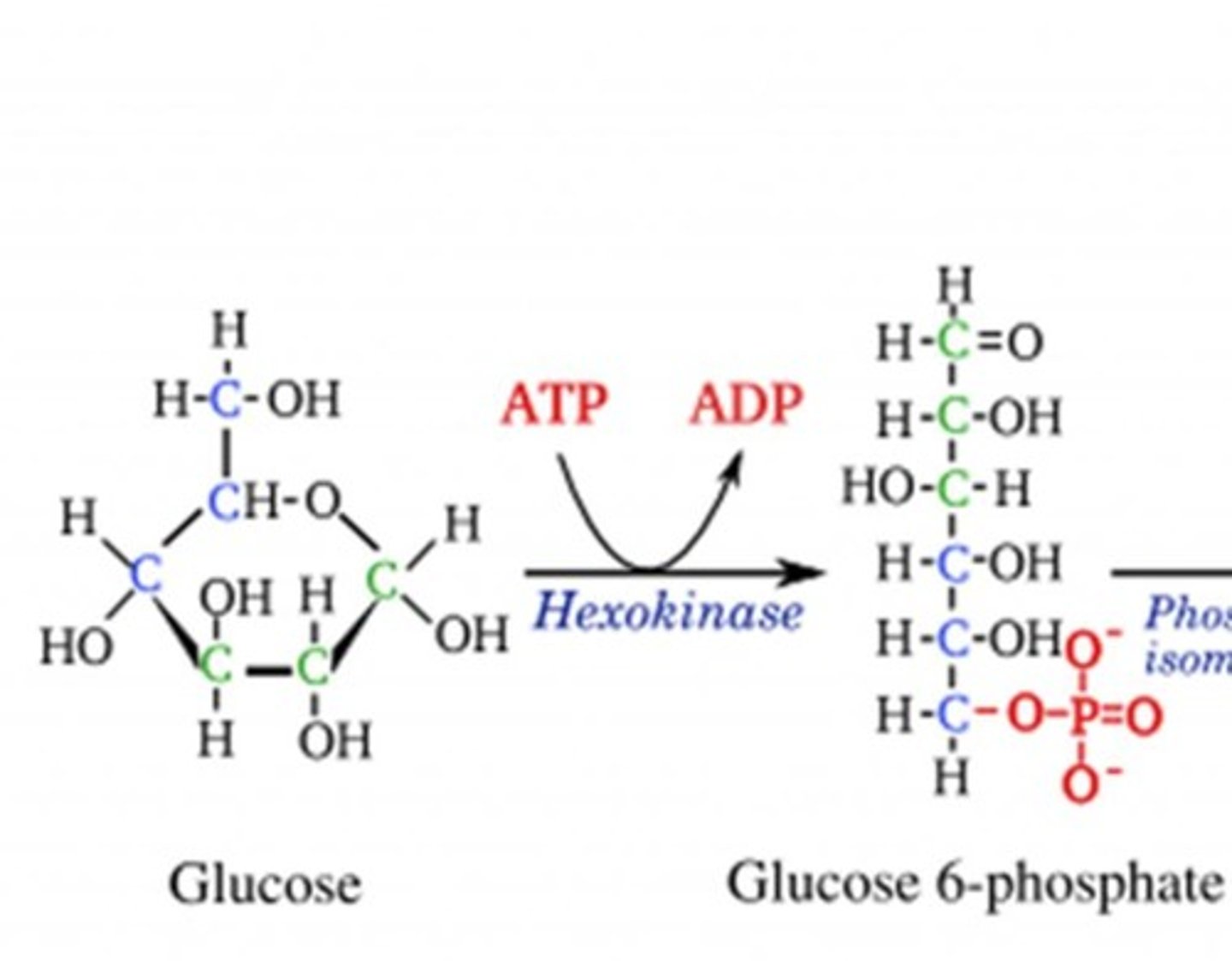
What is the role of Hexokinase in glucose metabolism?
Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose in all cells except the liver and pancreas.
What is the role of Glucokinase in glucose metabolism?
Glucokinase phosphorylates glucose specifically in the liver and pancreas.
What happens in the second step of glucose metabolism?
Isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucose isomerase.
What occurs during the third step of glucose metabolism?
Phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase-1.
What is the significance of the cleavage in step four of glucose metabolism?
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G-3-P).
What is the outcome of step six in glucose metabolism?
Oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, generating NADH.
What is formed in step ten of glucose metabolism?
Pyruvate is formed from phosphoenolpyruvate by pyruvate kinase.