1.2 carbohydrates
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is the monomer from which larger carbohydrates are made and what are three examples?
A monosaccharide: glucose, galactose and fructose
what forms when there is a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides?
A glycosidic bond
how are disaccharides formed
Through a condensation reaction between 2 monosaccharides, with one molecule of water being removed
monomers of maltose
alpha glucose + alpha glucose
monomers of sucrose
glucose and fructose
monomers of lactose
glucose and galactose
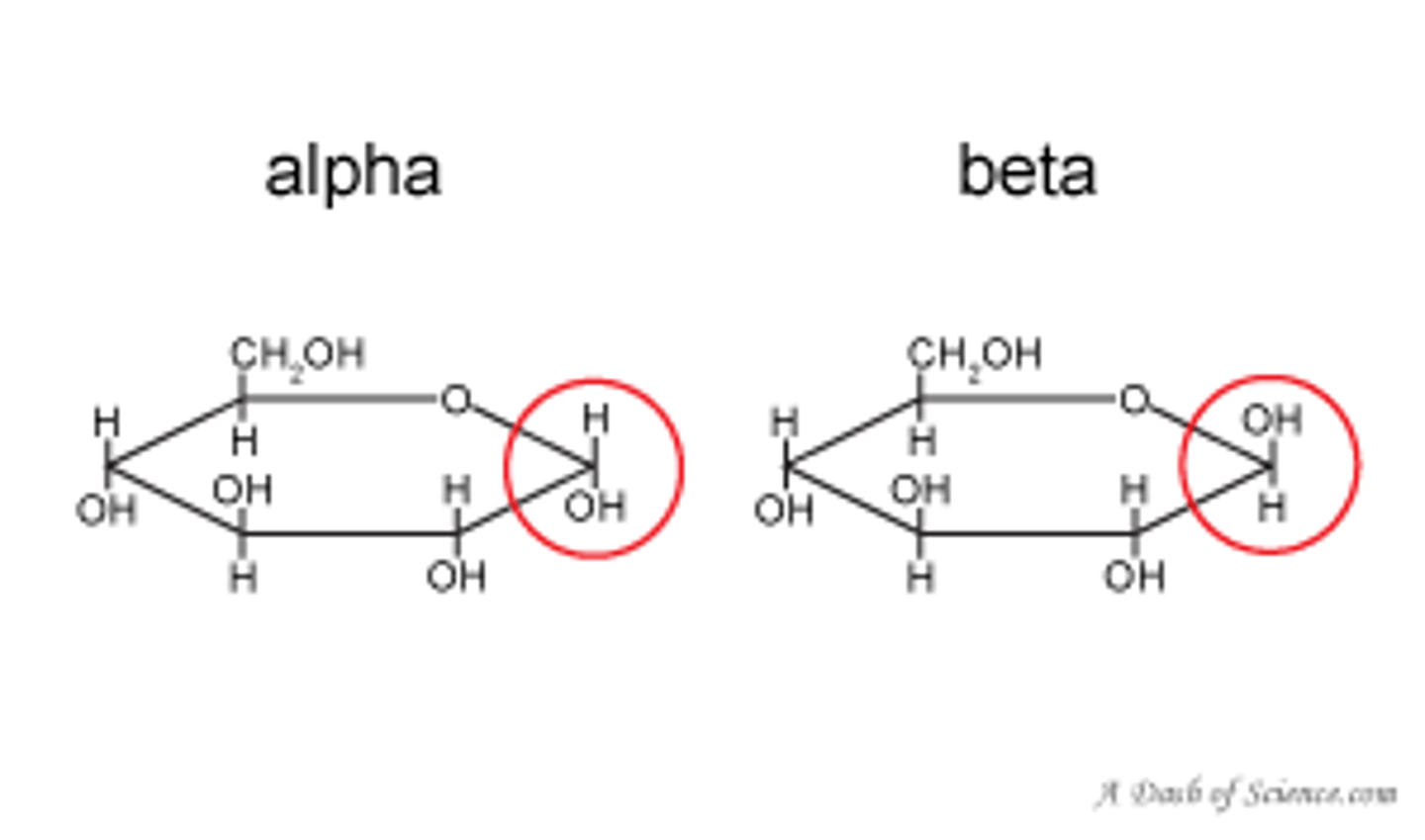
two isomers of glucose and what differentiates them
alpha glucose and beta glucose - alpha glucose has a hydroxyl above the ring where as beta glucose has the hydroxyl group below the ring
how are polysaccharides formed
Through the condensation of many monosaccharides
what is formed by the condensation of alpha glucose
glycogen or starch
what is formed when beta glucose condenses
Cellulose
structure and function of starch
Structure:
- insoluble: therefore doesn't affect the cells water potential
- Large (and insoluble): doesn't diffuse out of cells
- Coiled: compact/ a lot can be stored in a small space
- Hydrolysed to form alpha glucose which can be easily transported and readily used in respiration
- Branched (sometimes) which has many ends which can be hydrolysed simultaneously
Function:
- Energy storage molecule in plants
structure and function of glycogen
Structure:
- insoluble (doesn't affect water potential or diffuse out)
-coiled: compact / easily stored in a small place
- highly branched: rapidly broken down into glucose monomers
Function:
- a storage of energy for animals and bacteria (more metabolically active then plants)
structure and function of cellulose
structure:
- made from monomers of b-glucose linked via condensation reactions forming 1,4 glycosidic bonds
- straight unbranched chains which run parallel to one another using hydrogen bonds to form cross linkages
- cellulose molecules are grouped together to form microfibrils which are arranged in parallel groups called fibres
Function:
- provides rigidity to cell walls of plants
- prevents cell from bursting as water enters by osmosis
test for reducing sugars, process and results
- add 2cm^3 of the sample and an equal volume of benedict's reagent to a test tube
- Heat the mixture in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minutes
Positive test = brick red
low concentrations = green to orange
negative test = blue
Test for non-reducing sugars
heat with benedict's solution and if no result:
- Heat with dilute HCl to break down into monosaccharides
- add sodium hydrogen carbonate to neutralise the solution
- add benedicts solution
test for starch
add aqueous iodine solution to a sample (orange) if starch is present, the solution will go blue / black
How to quantitively measure the data from qualitative tests
Use a colorimeter: the more concentrated a solution, the less light will be able to travel through.
you can make a calibration curve with five solutions of known concentration to compare the results with