Anatomy and Positioning: Chapter 2 and Chapter 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
What is contained in the thoracic cavity?
Pleural membranes, lungs, heart, pericardium, esophagus, trachea
2
New cards
What is contained in the abdominal cavity?
Peritoneum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach, intestines, kidneys, uterus
3
New cards
How many regions are there in the abdominal cavity?
9
4
New cards
What is located in the superior region of the abdominal cavity?
Right hypochondrium, epigastrium, left hypochondrium
5
New cards
What is located in the middle region of the abdominal cavity?
Right lateral, umbilical, left lateral
6
New cards
What is located in the inferior region of the abdominal cavity?
Right inguinal, hypogastrium, left inguinal
7
New cards
What areas are affected by body habitus?
Heart, lungs, colon, diaphragm, stomach, gallbladder
8
New cards
What are the 4 areas and their percentages of body habitus?
Sthenic (50%)
Hyposthenic (35%)
Asthenic (10%)
Hypersthenic (5%)
Hyposthenic (35%)
Asthenic (10%)
Hypersthenic (5%)
9
New cards
What is osteology?
Study of bones
10
New cards
How many bones are there in your body?
206 bones
11
New cards
What are the 2 main groups of bones?
Axial (80 bones)
Appendicular (126 bones)
Appendicular (126 bones)
12
New cards
What does the axial bones support?
Head and trunk. Middle part of the body
13
New cards
What does the appendicular bones support?
Upper and lower extremities. Allows for movement.
14
New cards
What are 2 features that comprise a bone?
Compact and spongy bone
15
New cards
What is the compact bone?
Dense outer layer of bone
16
New cards
What is the spongy bone?
Inner, less dense layer. Contains speculated network of trabeculae.
17
New cards
What is trabeculae?
Filled with yellow and red marrow. Kind of looks like a spider web
18
New cards
What is the medullary cavity?
Central cavity for long bones, contains trabecular filled with yellow marrow, red marrow found in ends of long bone.
19
New cards
What is the endosteum?
The lining of the medullary cavity
20
New cards
What is the periosteum?
A tough fibrous connective tissue. Covers all bony surface except the articular surfaces (ends)
21
New cards
What is the articular cartilage?
Located at the end of the bones, connects the joints together.
22
New cards
What is ossification?
Process of bone formation (forming, developing)
23
New cards
When does ossification begin?
Second month of embryonic life
24
New cards
What are the 2 processes of bone development?
Intermembranous and endochondrial
25
New cards
Which process of bone development is before birth and why?
Intermembranous so that the child's head is not squashed during childbirth
26
New cards
What bone is formed from intermembranous ossification?
Flat bones
27
New cards
What bones are formed by endochondrial ossification?
Short, irregular, long bones
28
New cards
What are the 2 centers of development from endochondrial ossification?
Primary and secondary ossification
29
New cards
What is primary ossification?
Begins before birth and forms long central shaft in long bones
30
New cards
What is secondary ossification?
After birth when bones begin to separate and develop at both ends of long bones.
31
New cards
What are the ends of bones called
Epiphyses
32
New cards
Where are common sites of fractures in children?
At the epiphyses of the bone, because it is not fused together with the diaphysis.
33
New cards
What are some examples of a long bone?
Humerus and femur
34
New cards
What are some examples of flat bones?
Sternum and cranium
35
New cards
What are some examples of irregular bones?
Vertebrae and facial bones
36
New cards
What are some examples of a sesamoid bone?
Patella or big toe
37
New cards
What is arthrology?
Study of joints or articulations between bones
38
New cards
What are the 2 ways arthrology can be classified as?
Functional and structural
39
New cards
What are the 3 types of connective tissue from structural classification?
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
40
New cards
What are the 3 types of joints in the fibrous joints category?
Syndesmosis, suture, and gomphosis
41
New cards
Is a syndesmosis moveable?
only very slightly moveable, or immoveable
42
New cards
Suture and gomphosis are both \________&\__________ joints.
Immoveable & fibrous
43
New cards
What are the 2 types of cartilaginous joints?
Symphysis and synchodrosis
44
New cards
What are the 6 types of synovial joints? (Free range of motion; moveable)
Gliding, hinge, pivot, ellipsoid, saddle, and ball and socket
45
New cards
Where can gliding joints be found in the body?
Intercarpal and intertarsal joints (hand and feet)
46
New cards
Where can a hinge joint be found in the body? (hinge of a door)
Elbow and knee
47
New cards
Where can the pivot joint be found in the body? (rotation)
atlantoaxial joint (C1-C2). rotates head back and forth
48
New cards
Where can the ellipsoid joint be found in the body? (circular,adduction,abduction,flexion,extension)
Radiocarpal joint (wrist)
49
New cards
Where can the saddle joint be found in the body?
Carpometacarpal joint between trapezium and first metacarpal. Base of the thumb
50
New cards
Where can the ball and socket joint be found in the body?
Hip and shoulder
51
New cards
What are the 4 different types of fractures?
Closed, open, nondisplaced, displaced
52
New cards
What is a closed fracture?
When a break in the bone does not break through the skin
53
New cards
What is an open fracture?
When a break in the bone breaks through the skin.
54
New cards
What is a nondisplaced fracture?
When the bone still remains it its normal position
55
New cards
What is a displaced fracture?
When the bone is out of normal alignment
56
New cards
What are the 8 common classifications of fractures?
compression, compound (open), simple (closed), greenstick, transverse, spiral/oblique, comminuted, and impacted
57
New cards
Radiographs are usually viewed in \___________________ position
anatomical (palms up)
58
New cards
What position are you located in when you are lying face down:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Prone
59
New cards
What position are you located in when you are lying supine with the head higher than the feet:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Fowler
60
New cards
What position are you located in when you are lying on your back:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Supine
61
New cards
What position are you located in when you are lying supine with your head lower than your feet:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Trendelenburg
62
New cards
What position are you located in when you are lying down in any position:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Recumbent
63
New cards
What position are you located in when you are erect or marked by a vertical position:
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
trendelenburg, fowler, recumbent, prone, supine, upright
Upright
64
New cards
On which hand surface should the hand be rested when performing the lateral projection image of the fourth or fifth hand: lateral(radial), posterior(dorsal), medial(ulnar), anterior(palmar)
Medial (ulnar)
65
New cards
For the lateral projection of the wrist, how should the elbow be positioned?
fully extended, flexed 45 degrees, flexed 90 degrees
fully extended, flexed 45 degrees, flexed 90 degrees
Flexed 90 degrees
66
New cards
How much should the wrist be rotated for the PA oblique projection?
35 degrees, 45 degrees, 25 degrees
35 degrees, 45 degrees, 25 degrees
45 degrees
67
New cards
How many interphalangeal joints are found in one upper extremity?
9,14,8,10
9,14,8,10
9
68
New cards
Which bones comprises the palm of the hand?
carpals, phalanges, metacarpals, metatarsals
carpals, phalanges, metacarpals, metatarsals
Metacarpals
69
New cards
What bones are classified as short bones?
Carpals
70
New cards
A cephalad angle means that the xray tube is angled toward the head.
True or false
True or false
True
71
New cards
A horizontal xray beam denotes (indicates) a decubitus position.
True or false
True or false
True
72
New cards
The cranium is considered a flat bone.
True or false
True or false
True, the cranium and sternum are considered flat bones
73
New cards
What is it called when the movement of the foot is turned outward at the ankle joint.
Eversion
74
New cards
What is it called when the turn of the forearm so that the palm of the hand faces forward (think anatomical position)
Supinate (holding soup)
75
New cards
What is it called when the movement of the foot is turned inward at the ankle joint
Inversion
76
New cards
What is it called when the movement of a part toward the central axis of a body or body part
Adduction
77
New cards
What is it called when you a turning away from the regular standard or course
Deviation
78
New cards
Forced or excessive flexion of a body part
Hyperflexion
79
New cards
What is it called when turning the forearm so that the palm of the hand faces backward (think anatomical position)
Pronate
80
New cards
What is it called when the movement of a part is that the sagittal plane is angled so that it is not parallel with the long axis of the body
Tilt
81
New cards
What is it called when there is forced or excessive straightening of a joint.
Hyperextension
82
New cards
What is it called when there is a circular movement of a limb
Circumduction
83
New cards
What is it called when you are turning an axis
Rotate
84
New cards
What is it called when there is bending movement of a joint whereby the angle between the contiguous bones are diminished
Flexion
85
New cards
What is it called when you are straightening a join
Extension
86
New cards
What is it called when the flexion of the foot is toward the leg
Dorsiflexion
87
New cards
What is the sagittal plane?
divides the body into left and right
88
New cards
what is the coronal plane?
divides the body into front and back
89
New cards
what is the horizontal plane?
divides the body into a top and bottom
90
New cards
what is the oblique plane?
any angle
91
New cards
anterior
towards the front of the body
92
New cards
posterior
towards the back of the body
93
New cards
caudad
parts away from the head
94
New cards
superior
towards the head
95
New cards
inferior
towards the feet
96
New cards
distal
farthest from the point of attachment
97
New cards
proximal
closes to the point of attachment
98
New cards
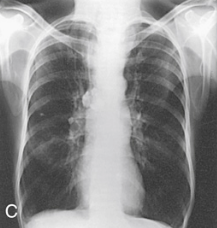
Which of the following is the X-ray showing and why?
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
\
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
\
Asthenic: Long lungs, elongated heart
99
New cards
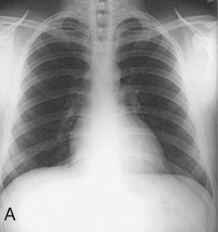
Which of the following is the X-ray showing and why?
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
Sthenic: normal, clear
100
New cards
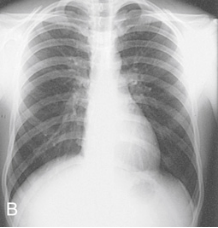
Which of the following is the X-ray showing and why?
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
Sthenic
Hyposthenic
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
Hyposthenic: Between Sthenic and asthenic (not as narrow as sthenic), normal-ish but less clear