Reproduction #12 (pt 1: Asexual Reproduction)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture #12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Reproduction
definition: the biological process of producing new individuals
two types:
asexual
sexual
asexual and sexual reproduction
what are the two forms of reproduction?
asexual reproduction
definition: the production of offspring that does not involve fertilization
offspring are genetically identical (clones) of their mother
Pros: faster, safer, and energetically “cheaper”
Cons: lower genetic diversity
the only true means of reproduction among prokaryotes (occasionally found in eukaryotes)
the production of offspring that does not involve fertilization
what is the definition of asexual reproduction?
female
definition: the sex that creates eggs
Genetic diversity
definition: the variation within the genome of a species
number of different alleles for every gene in the populations collective DNA
it enables evolution
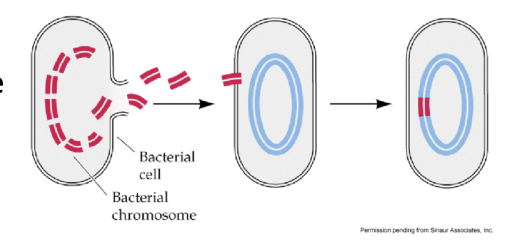
Binary Fission
the type of asexual reproduction that prokaryotes do to reproduce
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Definition: the movement of genetic material between genetically unrelated individuals
adding genes to the individual libraries of prokaryotes
prokaryotes employ this to counteract the lack of genetic diversity that comes with Binary Fission
3 types of this:
transformation
conjunction
transduction
very different inheritance patterns than species practicing sexual reproduction
individual bacterial within the same species are highly variable
ex) two cells of E. coli can differ by as much as 30% of their genome (more than all the genetic diversity across all vertebrates)
transformation, conjunction, transduction
what are the 3 types of horizontal gene transfer?
Horizontal Gene Transfer - Transformation
Definition: Taking stray DNA from the environment and incorporating it into your genome
possible bc when a unicellular organism dies:
its membranes collapse and its DNA is released into the environment
Loose DNA is absorbed by other cells
this DNA does not have to come from the same species
Tardigrades (water bears)
eukaryotes that perform horizontal gene transfer - transformation
animals, distantly related to arthropods
as much as 17.5% of its DNA are from completely unrelated organisms (plants, fungi, bacteria etc.)
outside versions of genes completely replace the tardigrade version
How?: they can desiccate and enter a type of resting stage
Genome with partially break apart during this phase
Incorporate environmental DNA when they rehydrate and reconnect their genome
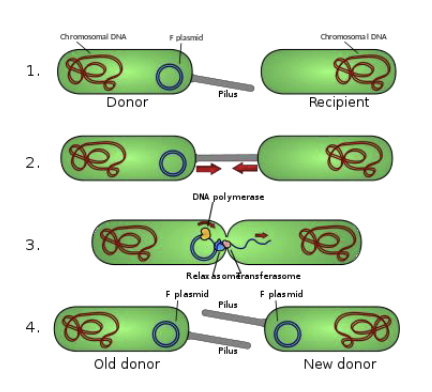
Horizontal Gene Transfer - Conjugation
Definition: two living cells intentionally share plasmid DNA through a connective structure known as a pilus
as close as prokaryotes get to sexual reproduction (still not quite the same thing)
Horizontal Gene Transfer - Transduction
Definition: DNA transfer mediated by viral infection
steps:
1) a virus infects a prokaryotic cell
2) during infection, the cell is killed and some of the viral particles incorporate the DNA of their host into their own
3) Virus with host DNA infect new cell, but does not kill it
passing on DNA of old host to the new cell
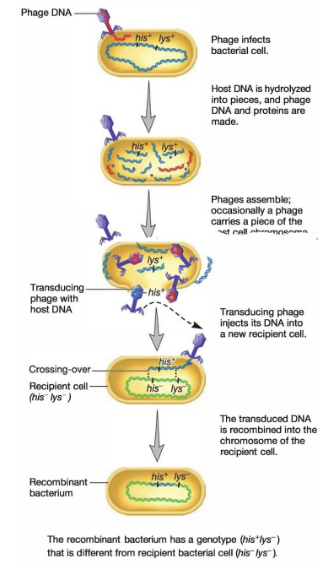
1) a virus infects a prokaryotic cell, 2) during infection, the cell is killed and some of the viral particles incorporate the DNA of their host into their own, 3) Virus with host DNA infect new cell, but does not kill it
what are the steps to Horizontal Gene Transfer - Transduction?
For gene therapy, stem cells can be altered or corrected in a lab to become cells to fight disease
Why is Horizontal Gene Transfer - Transduction a tool for medicine?