Respiratory volumes, capacities, and pressures
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
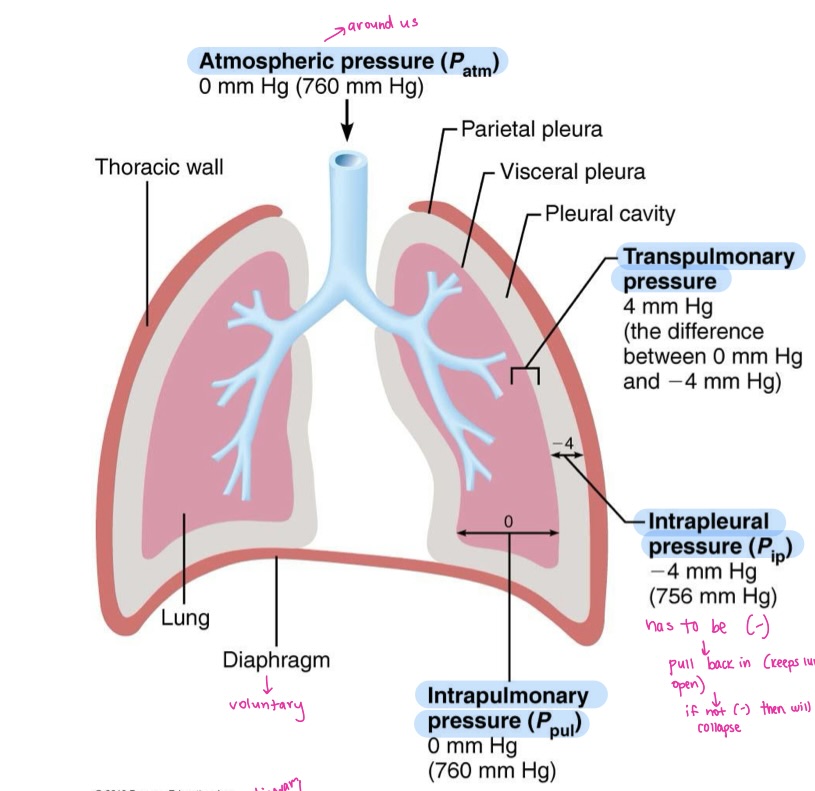
Intrapulmonary pressure
pressure in the alveoli
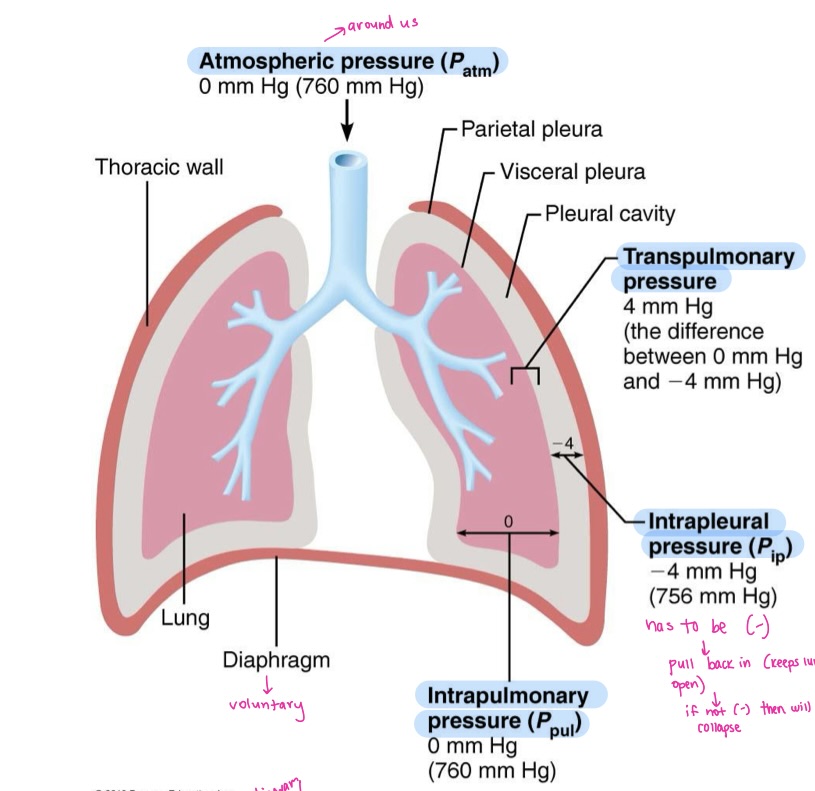
Intrapleural pressure
pressure in the pleural cavity
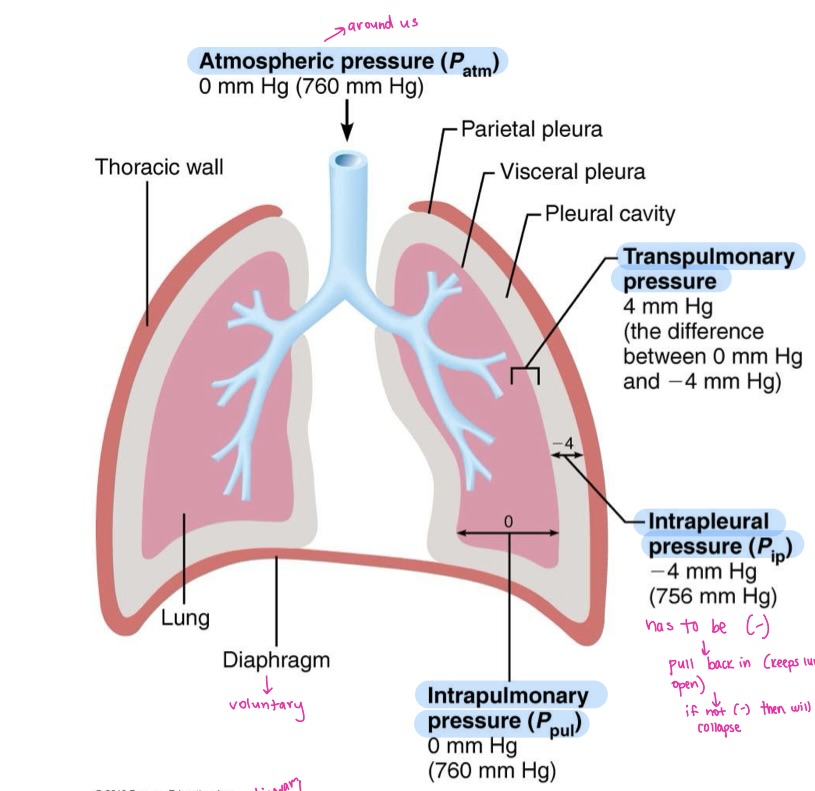
Transpulmonary pressure
difference between intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressure
Tidal volume (TV)
amount of air inhaled / exhaled throughout rest
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
amount of air forcefully inhaled after normal inspiration
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
amount of air forefully exhaled after normal exhalation
Residual volume (RV)
amount of air remaining in lungs after forced expiration
Total lung capacity (TLC)
maximum amount of air in lungs after maximum inspiration
TLC = TV + IRV + ERV + RV
Vital capacity (VC)
maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation
VC = TV + IRV + ERV
Inspiratory capacity (IC)
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after normal expiration
IC = TV + IRV
Funcitonal residual capacity (FRC)
volume of air remaining in the lunfs after a normal expiration
FRC = ERV + RV
External respiration
O2 diffuses from lungs to blood; CO2 diffuses from blood to lungs
Internal respiration
O2 diffuses from blood to tissues; CO2 diffuses from tissues to the blood
Type 1 alveolar cells
squamous epithelium; form alveolar walls
Type 2 alveolar cells
cuboidal epithelium (secrete); secrete surfactant (prevents alveolous from collapsing); secrete antimicrobial proteins