Biology First Semester Exam Review
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
261 Terms
The 2 domains of bacteria
Archaea and Eubacteria
Archaea Characteristics
No peptidoglycan, live in extreme environments, distinct ribosomal RNA
Eubacteria Characteristics
Have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, found in a variety of environments, and are true bacteria.
Groups in Archaea
Methanogens, halophiles, thermophiles
Methanogens
microorganisms that produce methane as a byproduct of metabolic processes, typically found in anaerobic environments.
Halophiles
organisms that thrive in high-salt environments, such as salt lakes and salt mines.
Thermophiles
organisms that thrive in extremely hot environments, often above 45°C, such as hot springs and hydrothermal vents.
Groups in Eubacteria
Cyanobacteria, Chemoautotrophic, and Heterotrophic
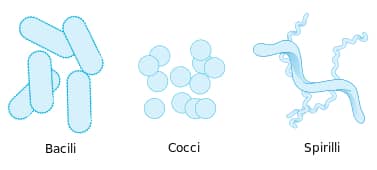
Cocci
spherical-shaped bacteria that can exist individually or in clusters.
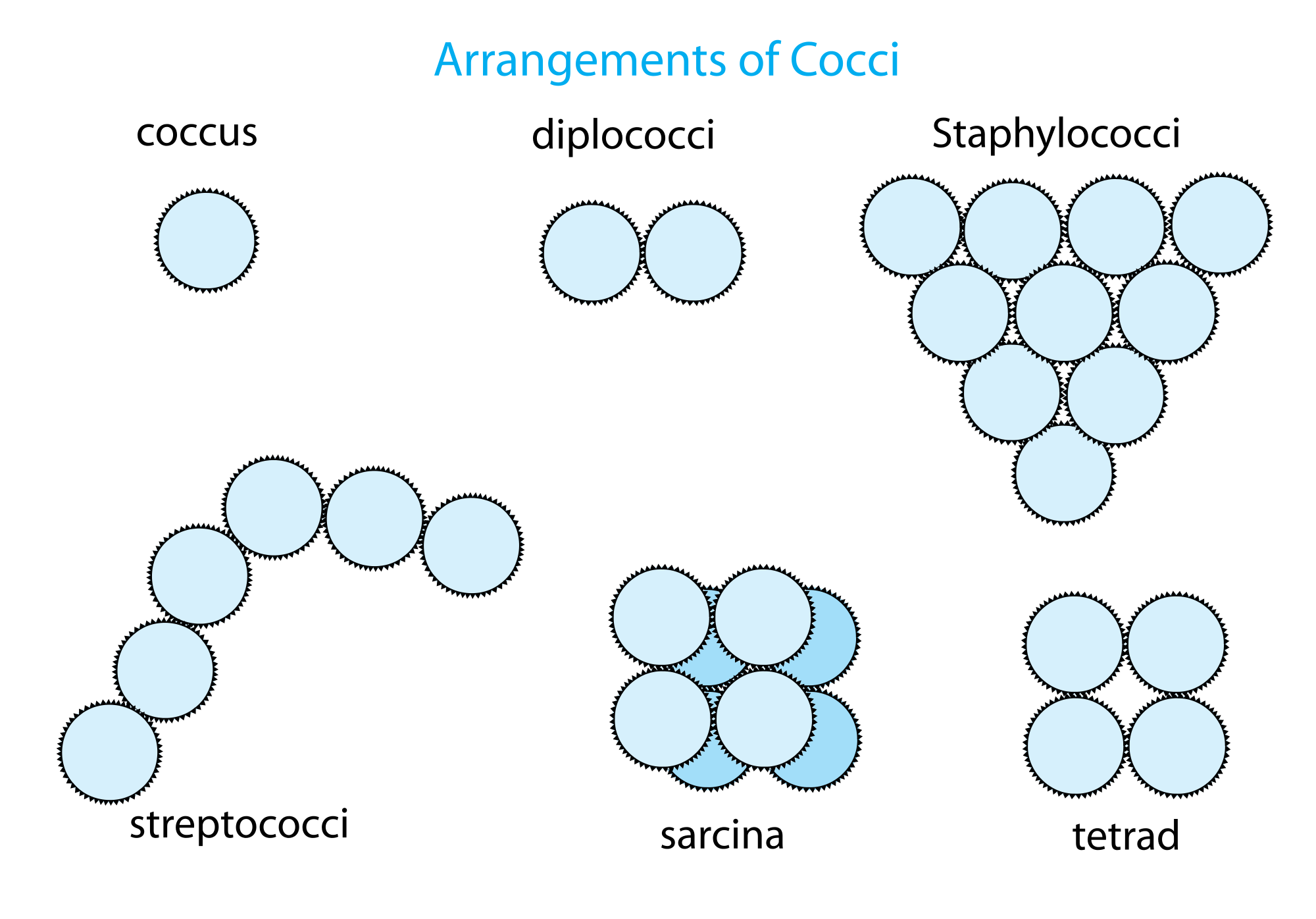
diplococcus
a type of cocci that occurs in pairs
streptococcus
a type of cocci that forms in chains
staphylococcus
a type of cocci that forms in cluster
bacilli
rod-shaped bacteria
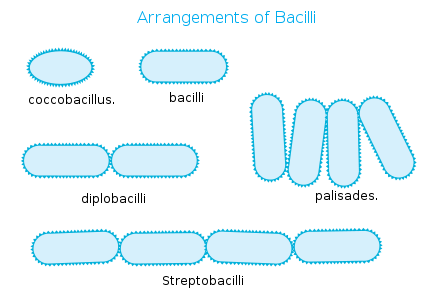
diplobacillus
a pair of rod-shaped bacteria that usually occur in pairs.
streptobacillus
a chain of rod-shaped bacteria that occur in a linear arrangement.
sprilla
spiral-shaped bacteria that can be found singly, NO chains or clusters
Why is heat fixing important?
Heat fixing is important because it kills bacteria and makes it stick to the slide.
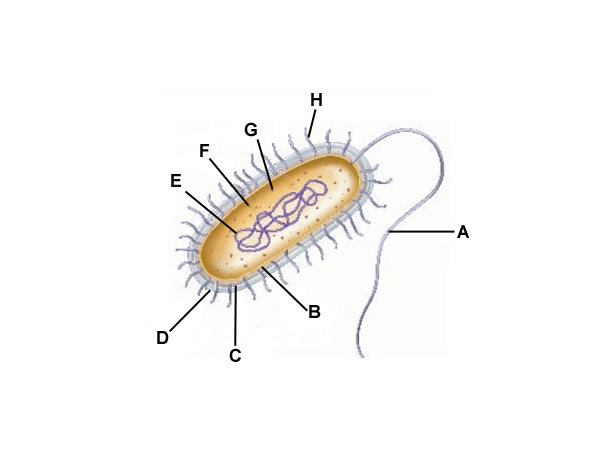
A
Flagella
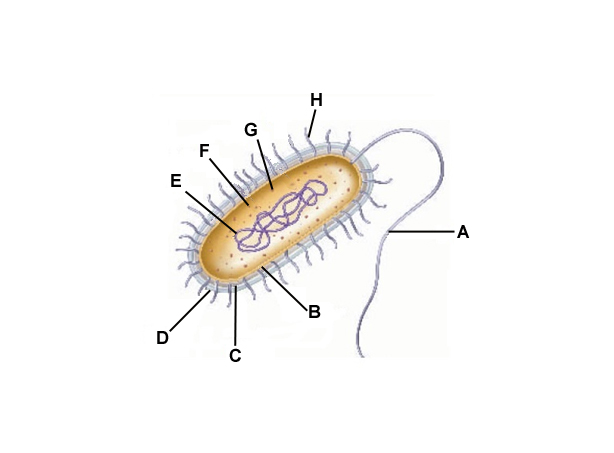
B
Cell membrane
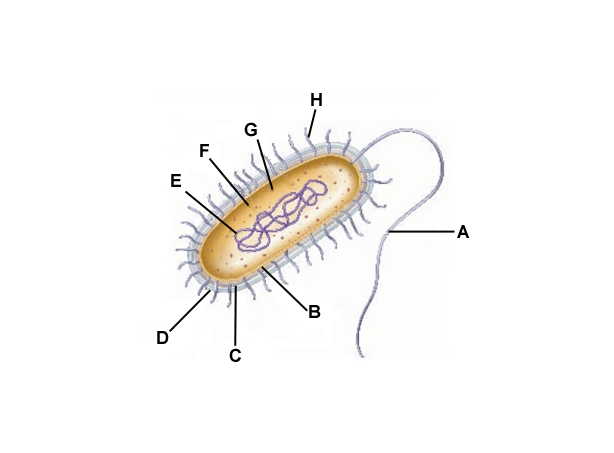
C
Cell wall
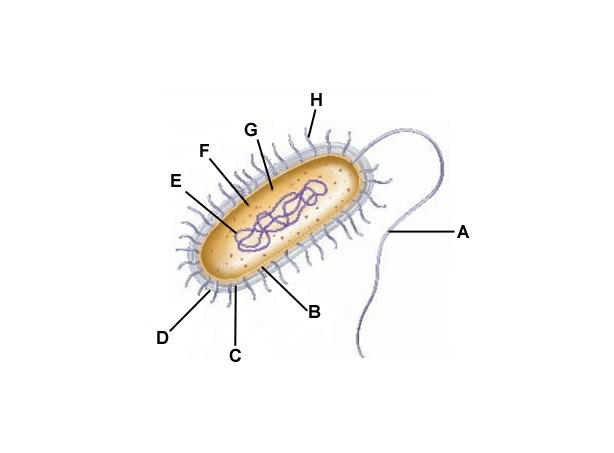
D
Capsule
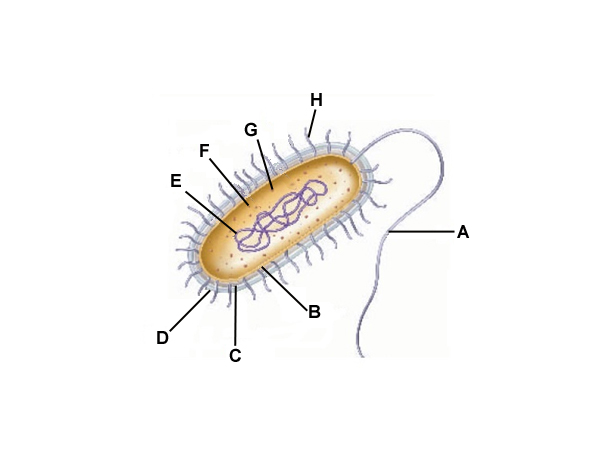
E
DNA
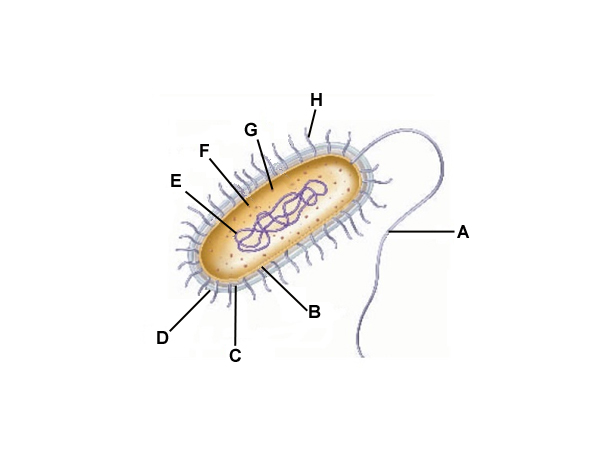
F
Cytoplasm
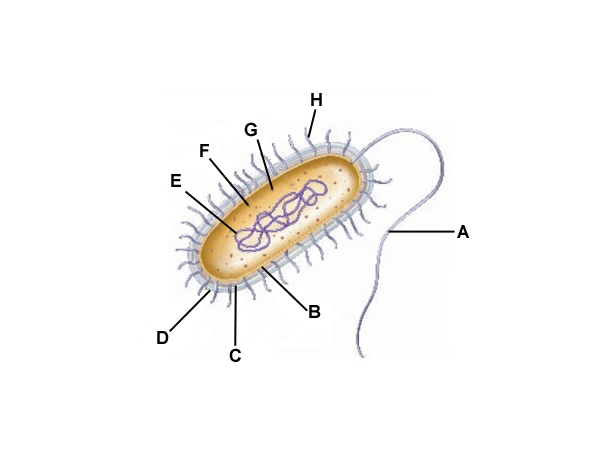
G
Ribosomes
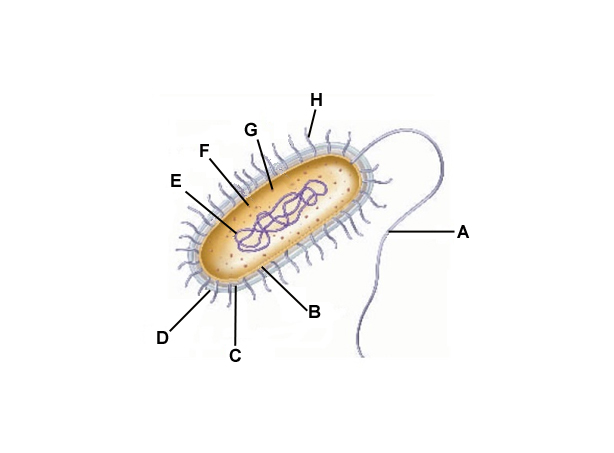
H
Pilli
How would you treat a bacterial infection?
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial infections by targeting and killing the bacteria or inhibiting their growth.
4 ways bacteria is good for you and the environment
Nitrogen Fixation, Decomposers, Normal Flora, and Production of Foods
Nitrogen fixation
the process of converting nitrogen gas from the air to a form plants can use
Decomposers
break down dead material and return nutrients to the soil
Normal Flora
bacteria needed by the body. It digests your foods in the intestines, they compete with harmful bacteria and prevent them from taking over.
Production of foods
Bacteria is used in cheese, pickles yogurt, and some medicines
How does Phylum Ciliophora move?
By using Cilia, an example is paramecium
How do bacteria obtain nutrients?
Photosunthesis, heterotrophs, and chemoautotrophs are the main methods.
Photosynthesis
convert light energy into chemical energy, using carbon dioxide and water
Chemoautrophic
get energy from gases
Heterotrophic bacteria
obtain nutrients by consuming organic compounds produced by other organisms, most are aerobic
Charecteristics of Protozoans
eukaryotic, unicellular organisms, live in the water, heterotrophic, move using cilia
Charecteristics of Algae protists
eukaryotic, autotrophic, mostly unicellular or multicellular, live in aquatic environments, most use flagella
Charecteristics of Fungus-like protists
eukaryotic, decomposers, feed on dead and decaying matter
Anaerobic
organisms that do not require oxygen for growth.
Aerobic
organisms that require oxygen for growth.
Diseases caused by protists
Malaria and African Sleeping Sickness
Viruses
NOT living, they require a host to replicate and are made up of genetic material.
How do you observe viruses?
using a electron microscope, and they are measured in nanometers
Capsin
A type of protein that forms the outer shell of a virus, encapsulating its genetic material.
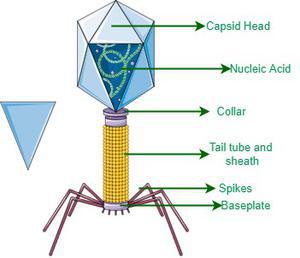
DNA
genetic material in the capsin in the bacteriophage.
Sheath
The elongated structure of a bacteriophage that attaches to the host cell and helps inject viral genetic material.
Base Plate
The structure at the base of a bacteriophage that anchors it to the host cell and plays a role in the infection process.
Tall Fiber
A long, hair-like projection on a bacteriophage that assists in attaching the virus to the host cell and initiating infection.
2 ways bacteria reproduces
Binary Fission and Conjugation
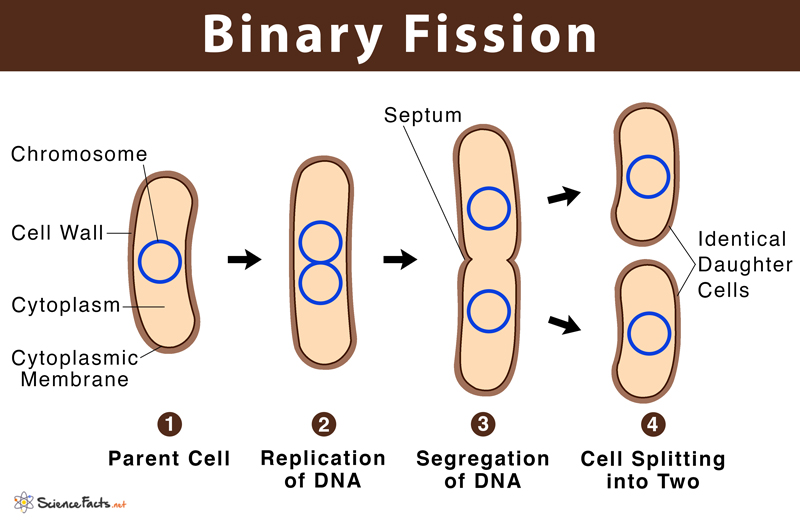
Binary Fission
A method of asexual reproduction in bacteria where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same genetic material.
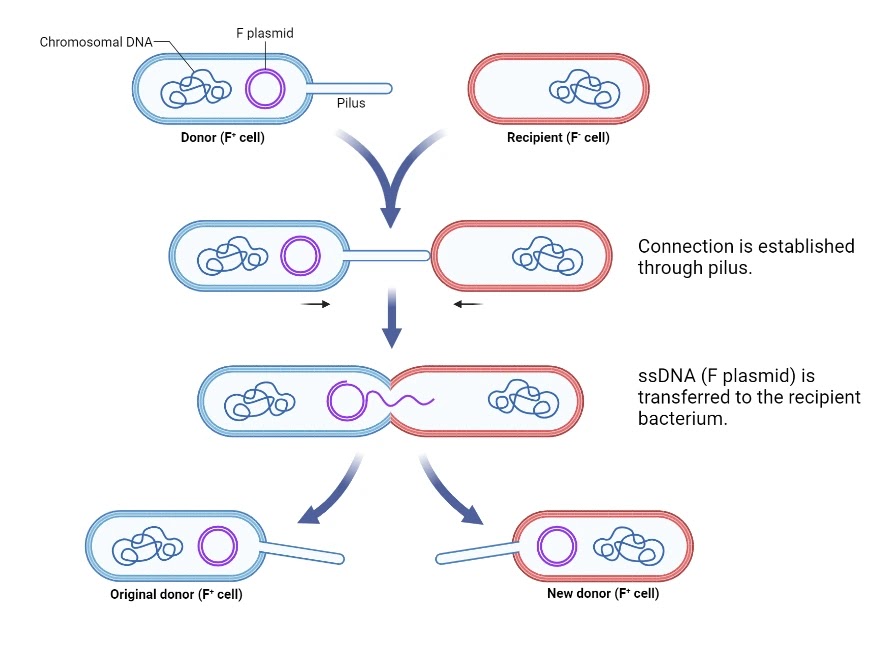
Conjugation
A process by which two bacterial cells transfer genetic material to each other through direct contact, often leading to genetic diversity.
How do viruses reproduce?
Viruses reproduce by attaching to a host cell, injecting their genetic material, and hijacking the host's cellular machinery to produce new virus particles, which are then released to infect additional cells.
Attachment
the virus attaches to the surface of the host cell; specific to surface proteins.
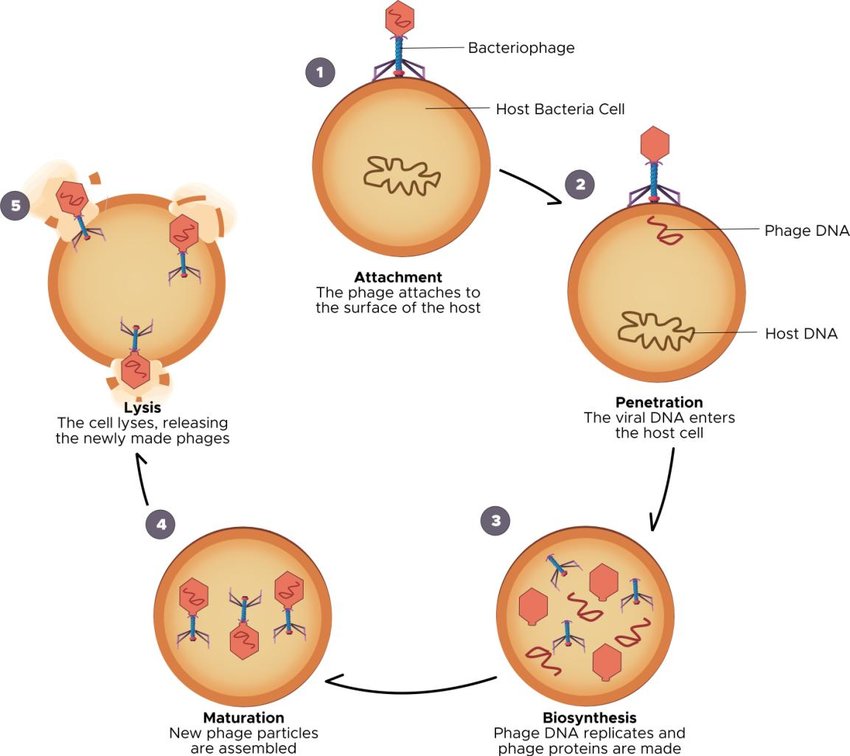
Injection
the viral DNA or RNA enters the host and becomes part of the host cell’s DNA
Replication
Viral DNA takes over the host cell and produces viral proteins and nucleic acid
lysis and release
the cell membrane breaks destroying the host cell and releases teh new virus particles.
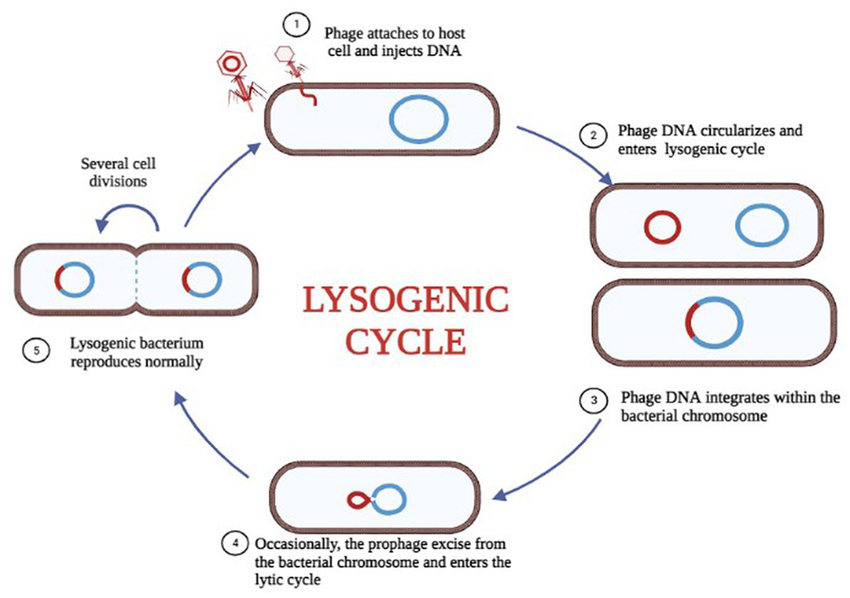
Lysogenic Cycle
viral DNA enters into the chromosome of the host cell, viral DNA instructs the host cell to make viral DNA, infected cell will have viral genes forever genes may lie dormant, once activated cell goes into the lytic cycle
What are the phylum’s we studied?
Ciliophora, Euglenaphyta, Chlorophyta
Prokaryotes
no nucleaus, unicellular, simplest living organisms
What are viruses made of?
made of protein and nucleic acid
Virus core
made up of nucleic acid either DNA or RNA
Bacteriophage
Virus that attacks bacteria
What are Prokaryotes?
Cells that do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, are smaller and simpler than eukaryotes, and contain genetic material.
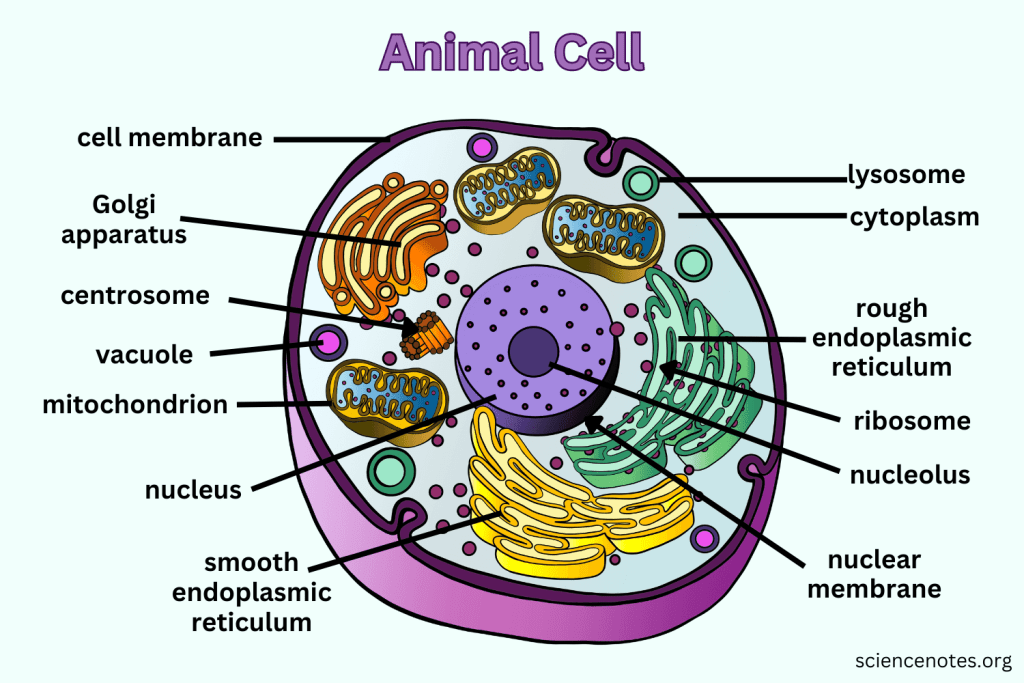
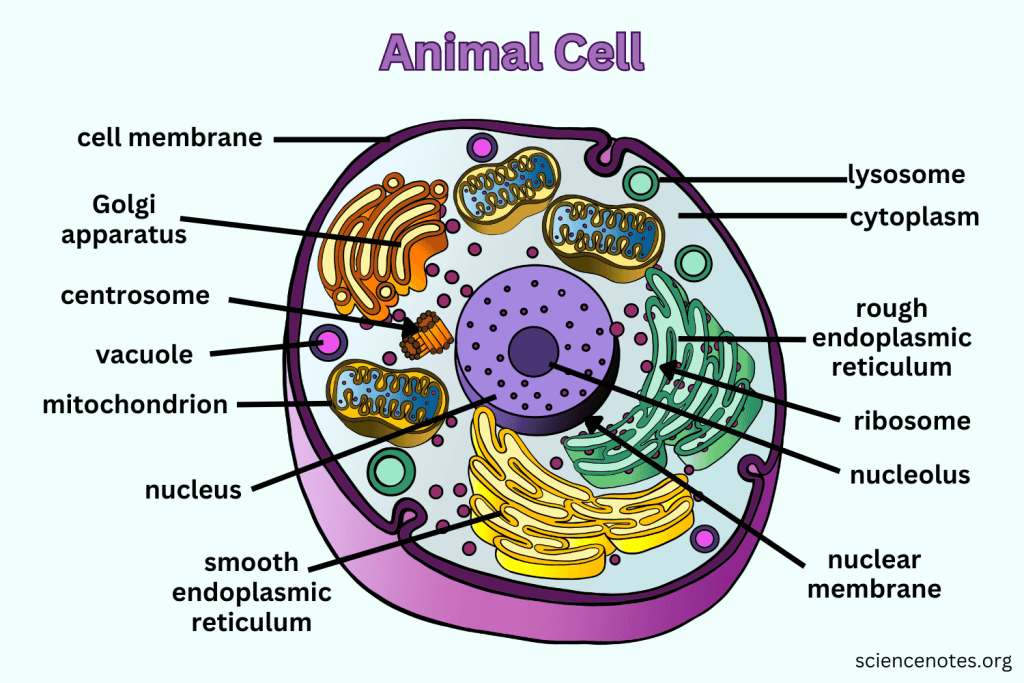
What distinguishes Eukaryotic cells from Prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, are larger and more complex, and display great variety.
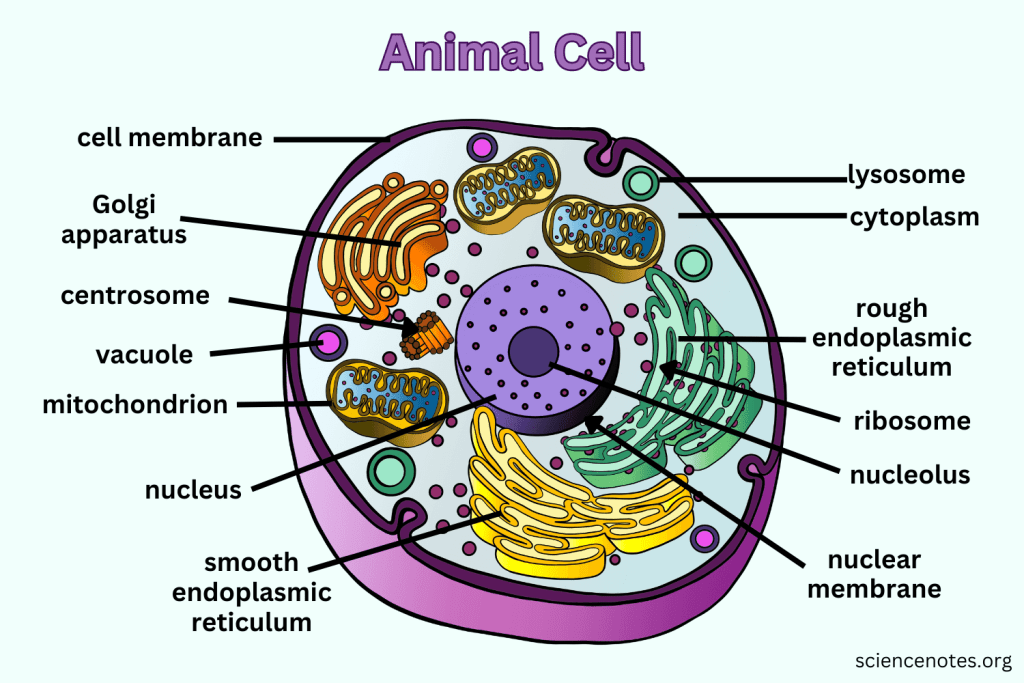
What is the function of the Nucleus?
Contains nearly all the cell's DNA, coding instructions for building proteins, and is surrounded by a nuclear envelope with nuclear pores.
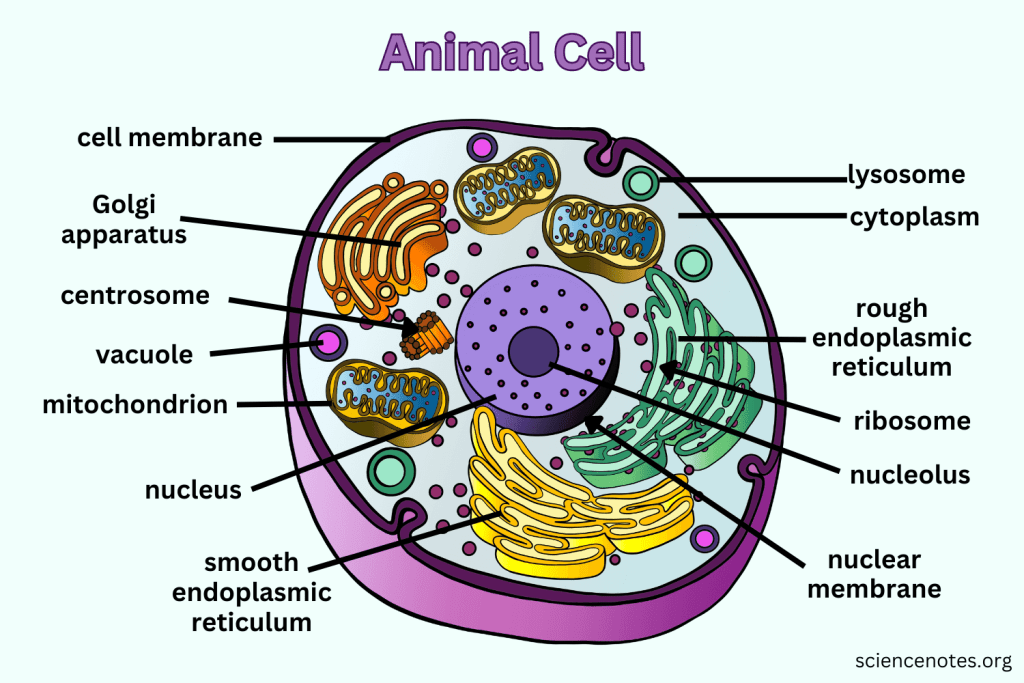
What are Ribosomes responsible for?
They are the site of protein synthesis, receiving coded instructions from the nucleus.
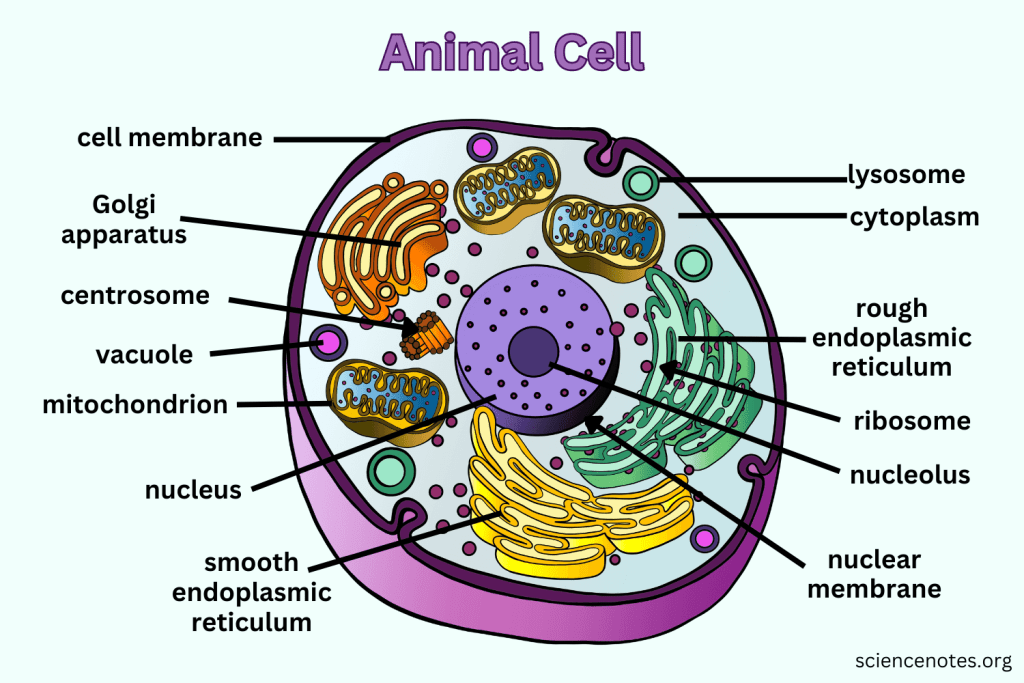
What does the Endoplasmic Reticulum do?
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is an organelle involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins and lipids. It also plays a key role in transporting materials within the cell.
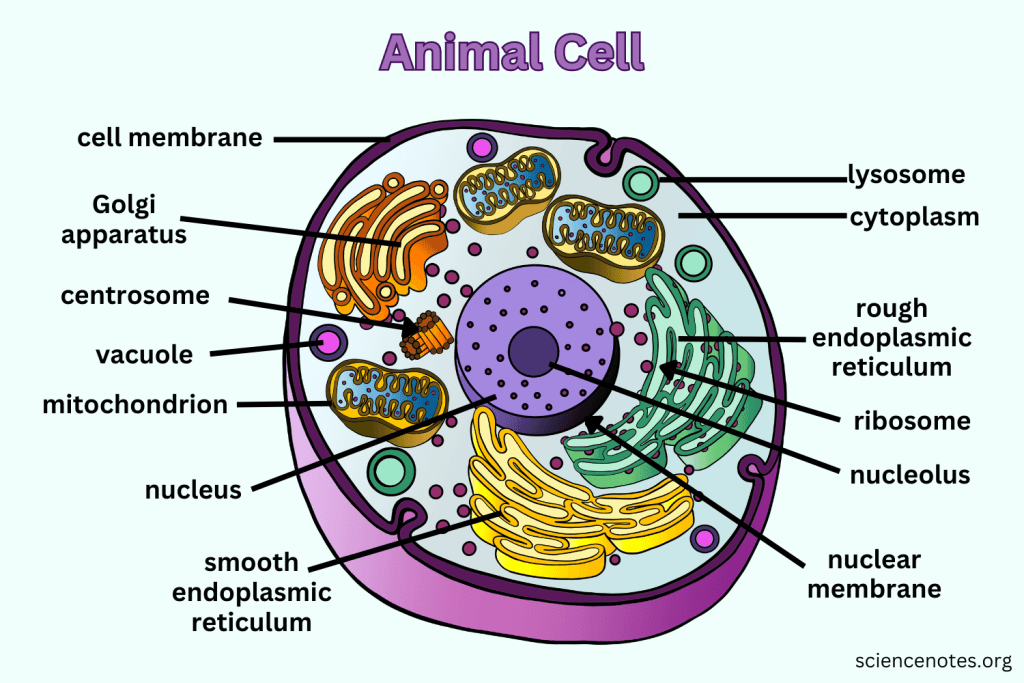
What is the difference between Smooth ER and Rough ER?
Rough ER is studded with ribosomes and processes proteins; Smooth ER does not have ribosomes and processes lipids and carbohydrates.
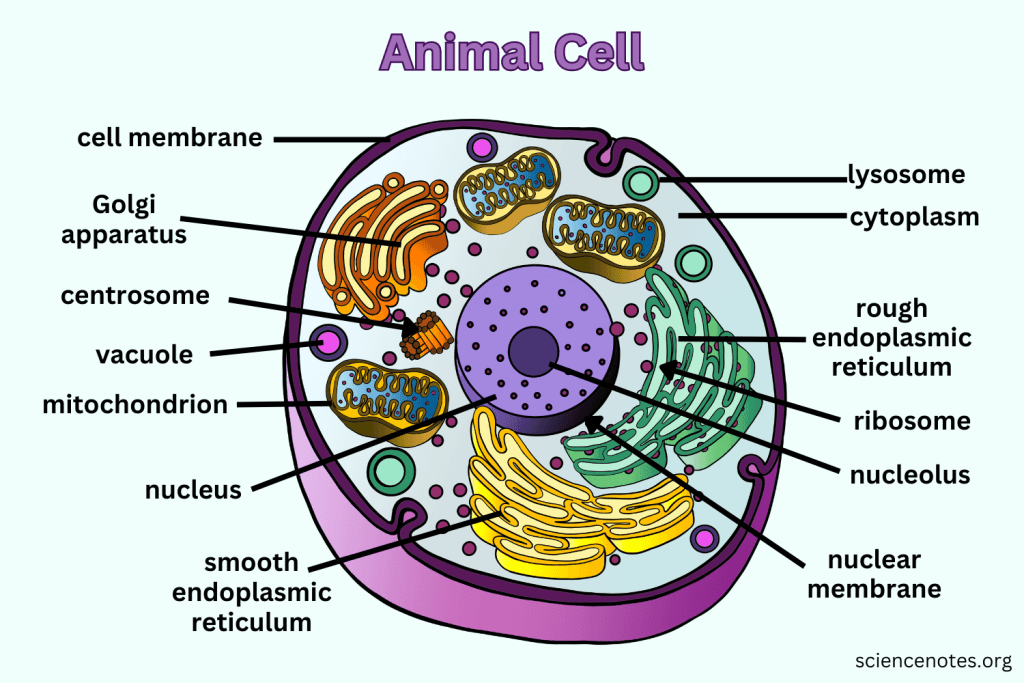
What is the main function of the Golgi apparatus?
To modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from the ER for storage or export.
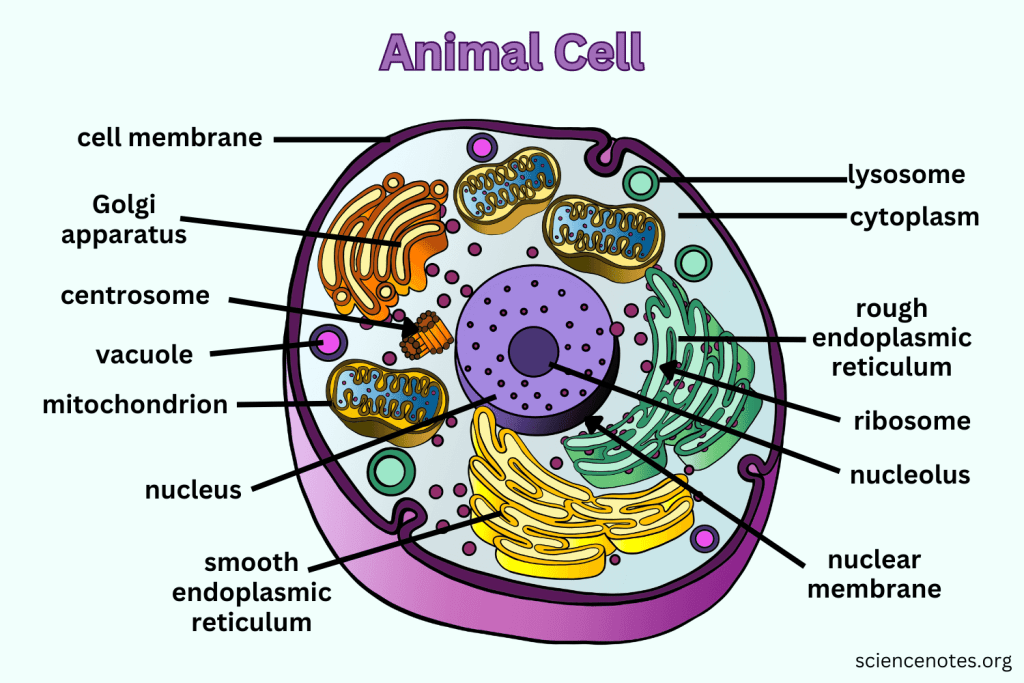
What do Lysosomes do?
They are small organelles filled with enzymes used to digest and break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Mostly in animals cells.
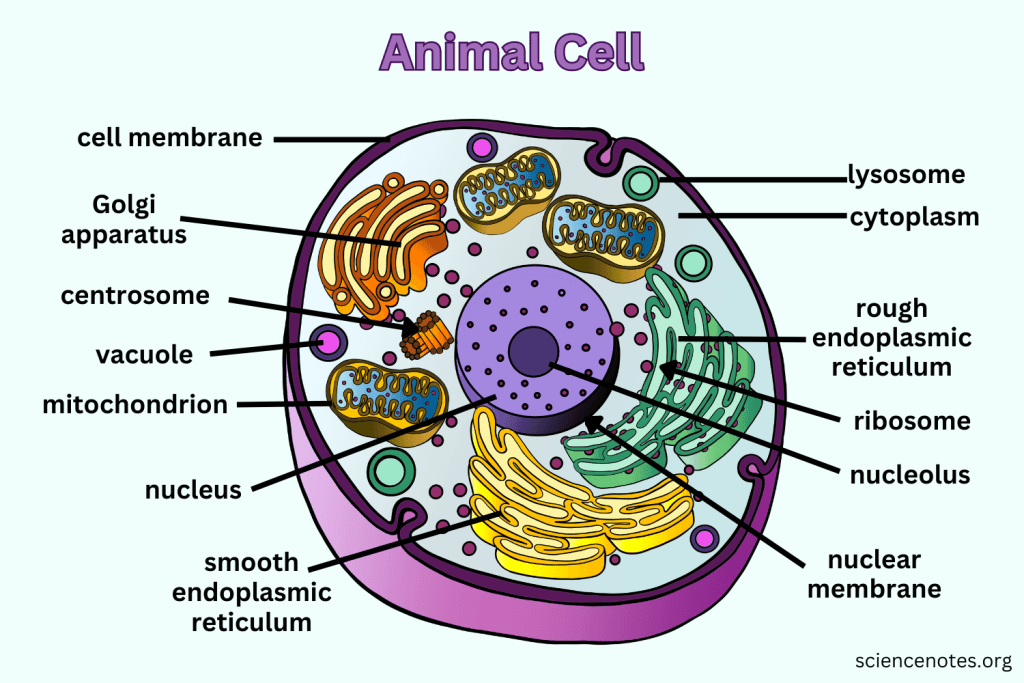
What is the function of Mitochondria?
They are the 'Powerhouse' of the cell, converting chemical energy in food into usable compounds.
What is the purpose of the Cytoskeleton?
Maintains the 3-D shape of the cell, helps with cell movement, and is made up of long strands of protein.
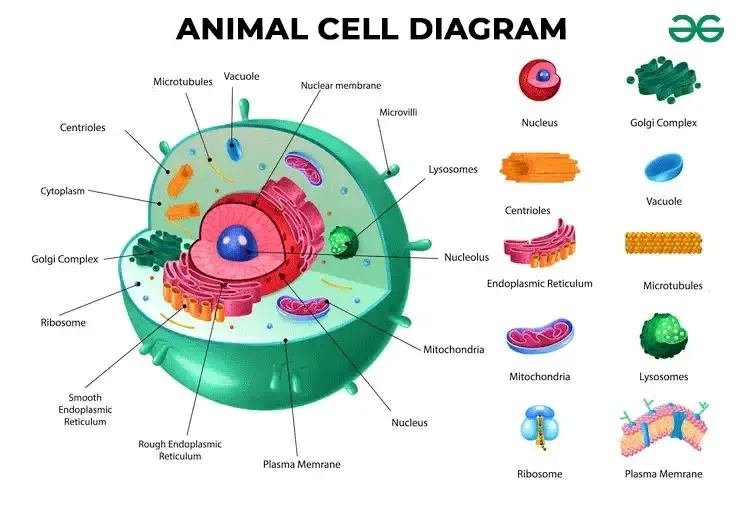
What are Centrioles and their function?
Paired bundles of microtubules located near the nucleus, helping organize cell division. Only in animal cells.
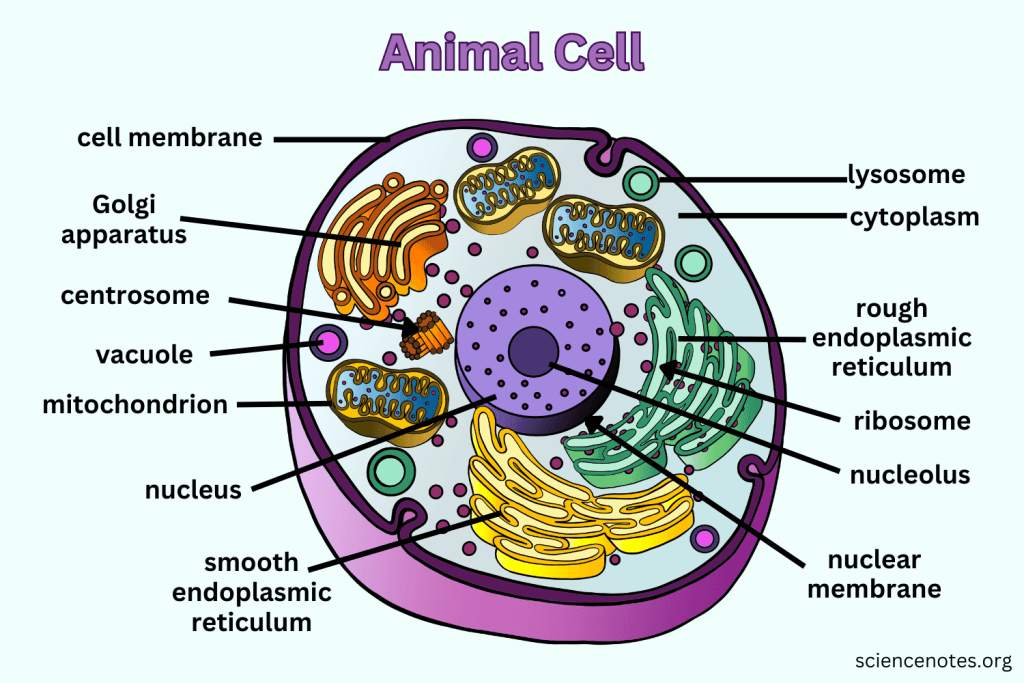
What is the function of the Cell Membrane?
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell while providing protection and support.
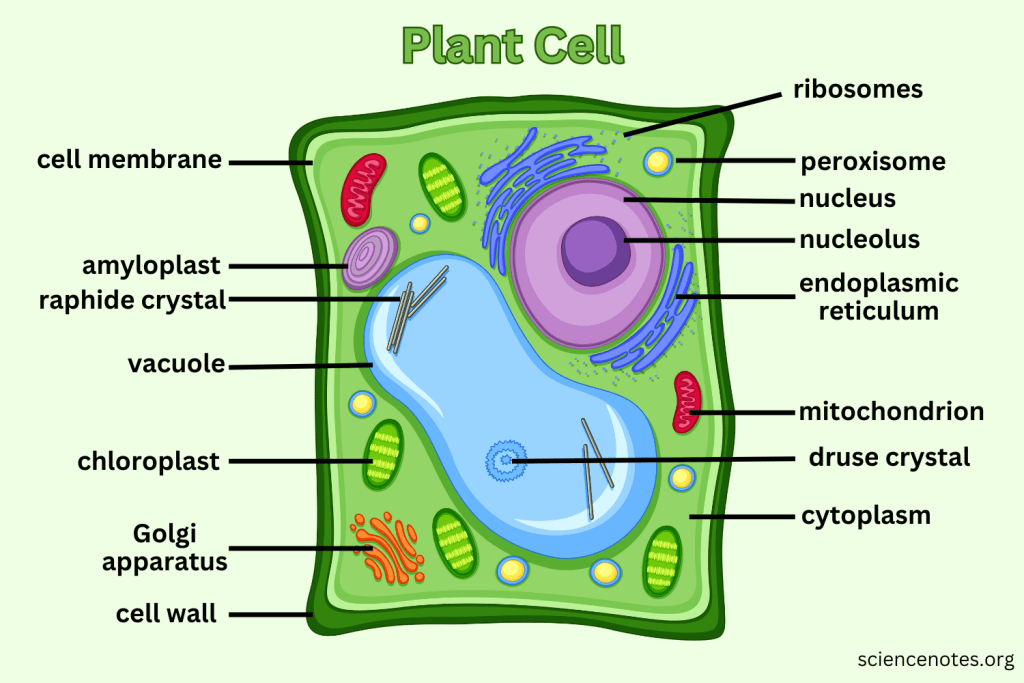
What extra structures do Plant Cells have that Animal Cells do not?
Cell Wall, Central Vacuole, and Chloroplasts.
What is the function of the Cell Wall?
Provides support and protection for plant cells without replacing the cell membrane.
What do Vacuoles do in plant cells?
Can take up to 90% of the plant cell and help support structure by creating pressure; also serve as storage.
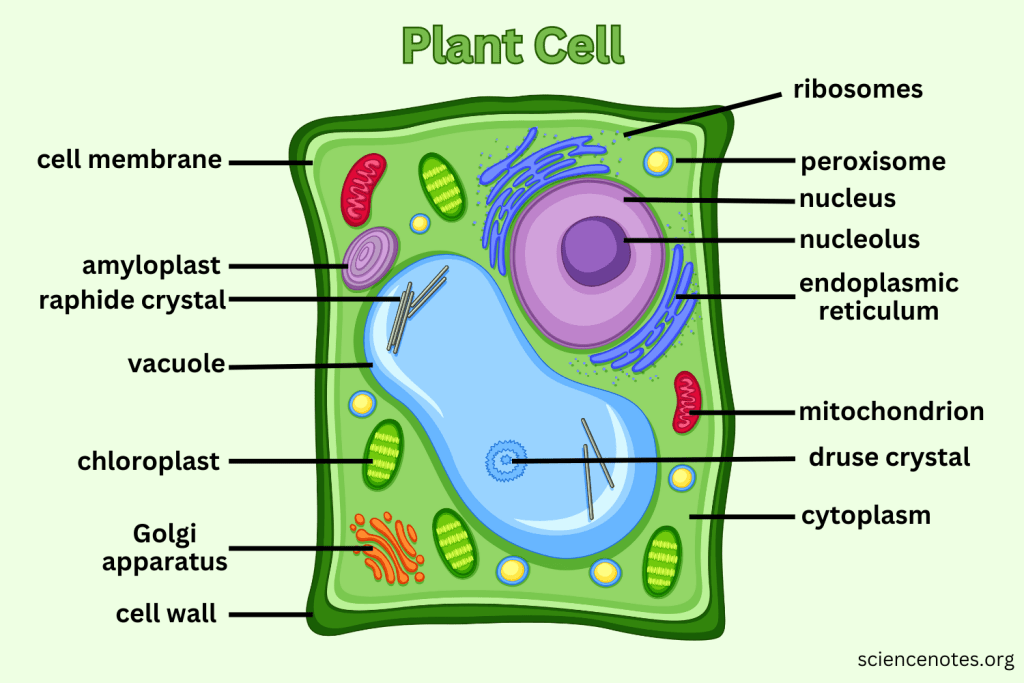
What is the function of Chloroplasts?
Capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
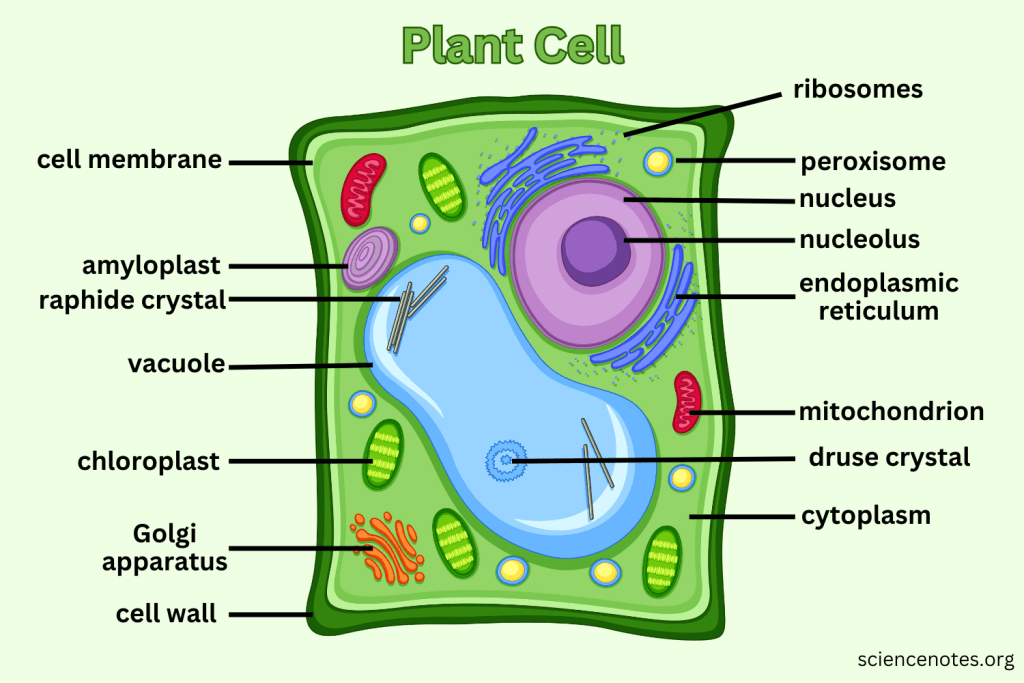
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells?
Chloroplast.
What does Cytoplasm do?
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance within the cell membrane that contains organelles and supports the cell's internal structure, allowing for the movement of materials.
What does the Nucleolus do?
The nucleolus is a structure within the nucleus of a cell that is primarily responsible for producing and assembling ribosome components, essential for protein synthesis.
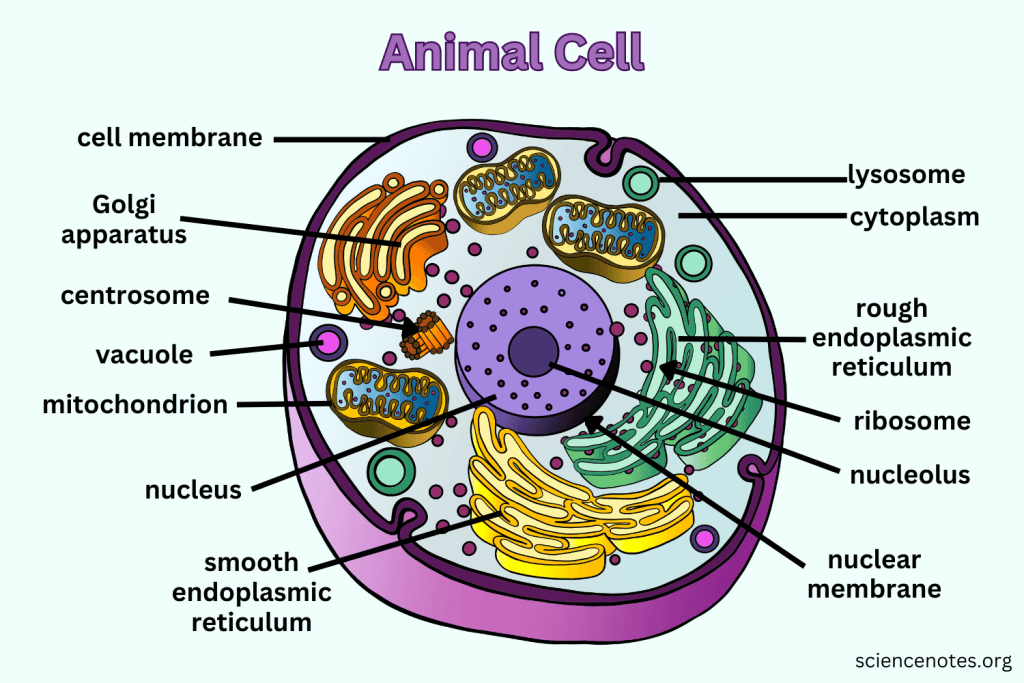
What does the Nuclear Membrane do?
The nuclear membrane, also known as the nuclear envelope, surrounds the nucleus and controls the flow of substances in and out of the nucleus, protecting the genetic material within.
What do Nuclear Spores?
Nuclear spores are openings in the nuclear membrane that allow for the transport of molecules such as RNA and proteins between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
What does the Mitochondria create?
Mitochondria create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy carrier in cells, through the process of cellular respiration.
Eukaryotic examples
include animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Prokaryotic examples
include bacteria and archaea.
Cilia
are hair-like structures on the surface of some eukaryotic cells that help with the movement of a cell
Flagella
are long, tail-like structures that aid in the movement of some cells
Cellular Transport
process by which materials enter and leave he cell
Selectively Permeable
some substances can pass across them and others cannot
Passive Transport
is the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy, typically following a concentration gradient, from high to low
Diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, due to random movement of molecules, passive transport
Concentration
the number of molecules in a solution
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, moving from an area of high solute concentration to low solute concentration, passive transport
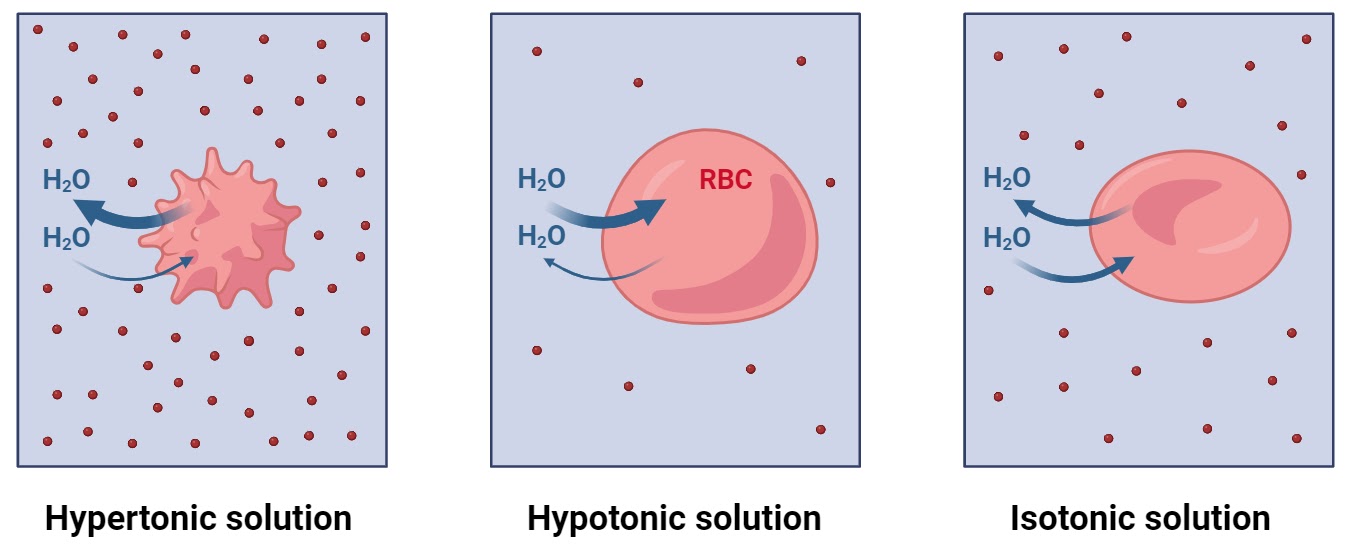
Hypertonic Solution
a high solute concentration outside of the cell causes water to diffuse out of the cell making the cell shrink
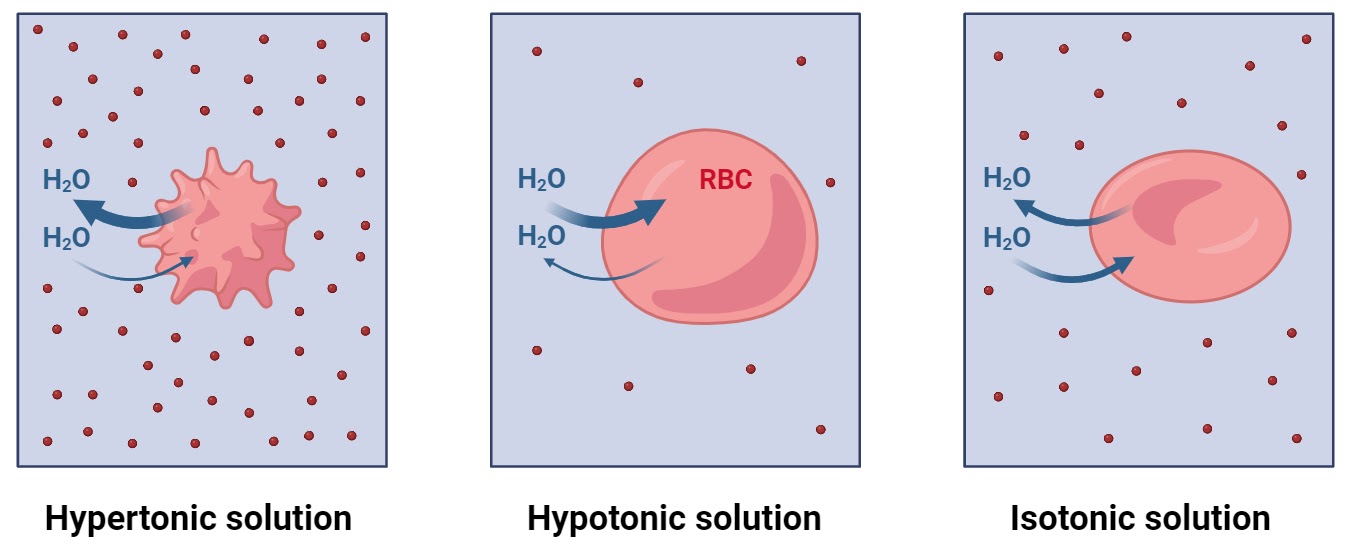
Hypotonic Solution
a high solute concentration inside the cell causes water to diffuse into the cell causing the cell to swell and expand.
Isotonic Solution
the concentration of solute is the same on both sides of the membrane, the water goes in and out of the cell, the cell will stay the same
Facilitated Diffusion
uses carrier protein to move materials across the cell membrane, no energy is needed, passive transport