Disease Detectives 2025 Surveillance flashcards
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Clinical Approach
Primary role is diagnosis and treatment of illness in individuals, with preventive medicine addressed recently.
Public Health Approach
Primary role is in control and prevention of disease in populations or groups of individuals.
Primary Focus of Public Health
Populations.
Primary Focus of Clinical Medicine
Individuals.
Emphasis in Public Health
Prevention.
Emphasis in Clinical Medicine
Diagnosis.
Health Promotion in Public Health
Treatment.
Whole Community
Focus of Public Health.
Whole Patient
Focus of Clinical Medicine.
Paradigm of Public Health
Interventions aimed at Environment, Human Behavior and Lifestyle, and Medical Care.
Paradigm of Clinical Medicine
Analytical (Epidemiology), Organ (Cardiology), Patient Group (Pediatrics), Setting and Population (Occupational Health), Substantive Health Problem (Nutrition), Etiology, Pathophysiology (Oncology, Infectious Disease), Technical Skill (Radiology).
Skills in Public Health
Skills in Assessment, Policy Development, and Assurance.
Hippocrates
Attempted to explain disease occurrence from a rational viewpoint around 400 B.C.
John Graunt
Published a landmark analysis of mortality data in 1662.
James Lind
Designed the first experiment using a concurrently treated control group while studying scurvy in the 1740s.
Edward Jenner
Developed the smallpox vaccine using clinical trials with cowpox in the 1790s.
William Farr
Built upon Graunt's work by systematically collecting and analyzing Britain's mortality statistics in 1800.
Father of modern vital statistics
William Farr.
******
British sailors known for preventing scurvy with limes.
Epidemiology
The study of how diseases affect the health and illness of populations.

Vital Statistics
Data related to births, deaths, marriages, and health of populations.
Surveillance in Public Health
The systematic collection and analysis of health data.
Clinical Trials
Research studies performed on people that follow a pre-defined protocol.
John Snow
The father of field epidemiology who formed and tested hypotheses on the origin of cholera as waterborne transmission in London.
Louis Pasteur
Recognized the bacterial cause of diseases and developed a vaccine for anthrax in the 1880s.
Robert Koch
Formalized standards (postulates) to identify organisms with infectious diseases from 1843 to 1910.
Flu pandemic
A significant outbreak of influenza that occurred in the 1910s.
Joseph Goldberger
Published a descriptive field study in 1920 showing the dietary origin of pellagra.
Fluoride supplements
Added to public water supplies in randomized community trials during the 1940s.
Framingham study
Initiated in 1949 to study risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Cigarette smoking and lung cancer
Epidemiological studies in 1950 linked smoking to lung cancer, demonstrating the power of case-control study design.
Salk polio vaccine
The field trial conducted in 1954 was the largest formal human experiment.
Mantel and Haenszel
Developed a statistical procedure for stratified analysis of case-control studies in 1959.
MacMahon
Published the first epidemiologic text with a systematic focus on study design in 1960.
US Surgeon General's Report on Smoking and Health
Established criteria for evaluation of causality in 1964.
North Karelia and Stanford Three Communities
Large community-based trials implemented in the 1970s.
Chronic disease and injury epidemiology
Focused on chronic diseases, injuries, and occupational epidemiology during the 1980s.
Edward Sydenstricker
Pioneer public health statistician in the early 1900s.
Behavioral risk factor epidemiology
Prevention of adverse health outcomes through policies and regulations in the 1990s.
Genetic and molecular epidemiology
Emerging focus in the 2000s addressing health disparities and racialism.
9/11
A significant event in 2001 impacting public health and safety.
Bioterrorism
Concerns regarding anthrax and smallpox threats and vaccinations in 2002.
SARS
Outbreak in 2003 leading to quarantines and public health law considerations.
2009 H1N1 pandemic
A global influenza pandemic that occurred in 2009.
Public health problems
Diverse issues including infectious diseases, chronic diseases, emergencies, injuries, and environmental health problems.
Surveillance
The process of determining if there is a public health problem.
Risk Factor Identification
The process of determining the cause of a public health problem.
Intervention Evaluation
The assessment of what works in addressing public health problems.
Implementation
The method of executing public health interventions.
Clinical care
Prevention, treatment, and management of illness through medical and allied health services.
Determinant
A factor that contributes to the generation of a trait.
Epidemic or outbreak
Occurrence of cases of an illness in excess of normal expectancy in a community.
Health outcome
Result of a medical condition that directly affects the length or quality of a person's life.
Health Determinants
Factors influencing health including genes, health behaviors, social characteristics, and access to health services.
Total environment or ecology
The remaining 75% of what determines our health as a population, including the social environment, health behaviors, genes, and biology.
Determinants of health
Factors that influence individual choices and overall health, including nutrition, physical activity, social and cultural norms, environmental characteristics, and sector influences.
Health Impact Pyramid
A framework that categorizes public health issues based on their impact on population health.
Public health problems in the US
The 10 most important public health problems listed by the CDC include alcohol-related harms, food safety, healthcare-associated infections, heart disease and stroke, HIV, motor vehicle injury, nutrition, physical activity and obesity, prescription drug overdose, teen pregnancy, and tobacco use.
Epidemiology
The study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations, and the application of this study to the control of health problems.
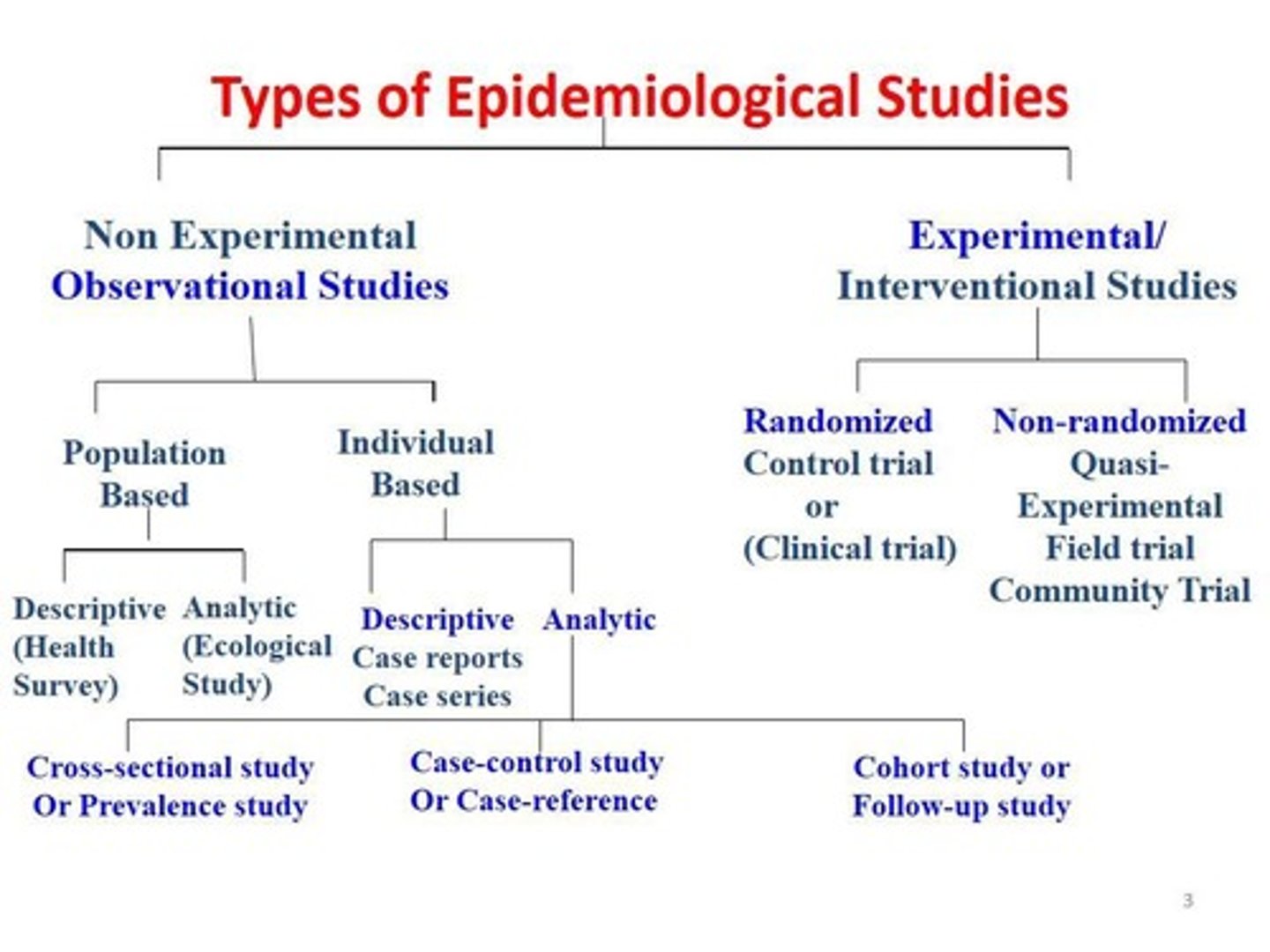
Purposes of Epidemiology
To determine the agent, host, and environmental factors affecting health, assess the relative importance of causes of illness, identify high-risk population segments, and evaluate health program effectiveness.
Types of disease agents
Biologic, physical, and chemical agents that can affect health.
Steps in Solving Health Problems
1. Collect Data - Surveillance, determine Time/Place/Person triad; 2. Assessment - Inference; 3. Hypothesis testing - Determine how and why; 4. Action - Intervention.
Descriptive Epidemiology
Involves identifying the time, place, and person involved in the onset of health-related events.
Analytical Epidemiology
Concerned with finding the causes of health-related events and identifying interventions for health problems.
Hypothesis in Epidemiology
Descriptive epidemiology generates hypotheses, while analytic epidemiology tests these hypotheses.
Interventions in Epidemiology
Intervention studies are not performed in descriptive epidemiology, but are analyzed in analytic epidemiology.
Experimental Study
A study where investigators control certain factors from the beginning, such as a vaccine efficacy trial.
Observational Study
A study where the epidemiologist does not control the circumstances, which can be further subdivided into descriptive and analytic.
Nutrition and physical activity
Essential elements in producing optimal health influenced by environmental factors.
Social and cultural norms
Influences on food choices and physical activity.
Environmental characteristics
Factors such as availability of healthy food, open space for exercise, or safety in urban neighborhoods.
Sector influences
Factors such as the marketing of processed food that affect health choices.
Health behaviors
Actions taken by individuals that affect their health, influenced by various determinants.
Population health
The overall health outcomes of a group of individuals.
Public Health Practice
The application of epidemiological findings to improve population health.
Surveillance in Epidemiology
The ongoing systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health data.
Time/Place/Person triad
A framework used in epidemiology to collect data about health-related events.
Vaccine efficacy trial
An experimental study to determine the effectiveness of a vaccine.
Descriptive Study
In a Descriptive Study, the epidemiologist collects information that characterizes and summarizes the health event or problem.
Analytic Study
In the Analytic Study, the epidemiologist relies on comparisons between different groups to determine the role of different causative conditions or risk factors.
Endemic
Disease or condition present among a population at all times.
Outbreak
(localized epidemic) - more cases of a particular disease than expected in a given area or among a specialized group of people over a particular period of time.
Epidemic
Large numbers of people over a wide geographic area affected.
Pandemic
An epidemic occurring over a very wide area (several countries or continents) and usually affecting a large proportion of the population.
Cluster
An aggregation of cases over a particular period esp. cancer & birth defects closely grouped in time and space regardless of whether the number is more than the expected number.
Sporadic
A disease that occurs infrequently and irregularly.
Risk
The probability that an individual will be affected by, or die from, an illness or injury within a stated time or age span.
Rate
Number of cases occurring during a specific period; always dependent on the size of the population during that period.
Ratio
Value obtained by dividing one quantity by another - a ratio often compares two rates.
Proportion
The comparison of a part to the whole as the number of cases divided by the total population - does not have a time dimension.
Normal flora
Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms.
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit.
Commensalism
One organism benefits and the other is not harmed or helped.
Parasitism
The condition when one organism is helped and the other is harmed, which takes place when humans are invaded by infectious microbes.
Natural history of disease
Refers to the progression of a disease process in an individual over time, in the absence of treatment.
Incubation period
The stage of subclinical disease, extending from the time of exposure to onset of disease symptoms, usually for infectious diseases.
Latency period
The stage of subclinical disease for chronic diseases, extending from the time of exposure to the onset of disease symptoms.
Asymptomatic
A period during which the disease is said to be without symptoms.
Typical incubation period for hepatitis A
As long as 7 weeks.
Latency period for leukemia
Ranged from 2 to 12 years, peaking at 6-7 years.