week 8 - uncertainty, value, time
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Fiorillo et al. (2003) - discrete coding of reward prob and uncertainity by dope neurons
pavlovian task experimental design
pavlovian conditioning > 5 stimuli predict rewards with diff probability but magnitude of reward holds constant.
Fiorillo et al. (2003) - discrete coding of reward prob and uncertainity by dope neurons
behavior response
as reward probability increased, licking went on for longer
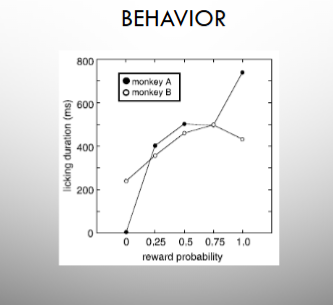
Fiorillo et al. (2003) - discrete coding of reward prob and uncertainity by dope neurons
reward response
with low probabilty of the reward, dope neurons respond to the reward itself, as probability increases dope neurons respond to the cue that predicts the reward with high probability.
as reward probability increased > median response decreases (its expected, not a PDE)
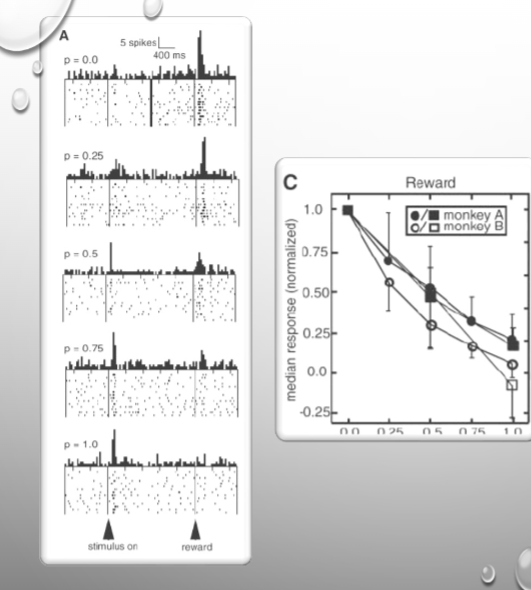
Fiorillo et al. (2003)
what was response of dope neurons when reward not delivered?
what was response to the cue as probability increased?
more supression in response when probability of the reward increases and reward is not delivered
response to cue increases as probability of the reward increase
Fiorillo et al. (2003)
novel ramping activity?
subset of neurons with a differential response during the time between the cue and reward with the response betwen maximal at 50% probability.
these neurons encodes probability of reward outcome
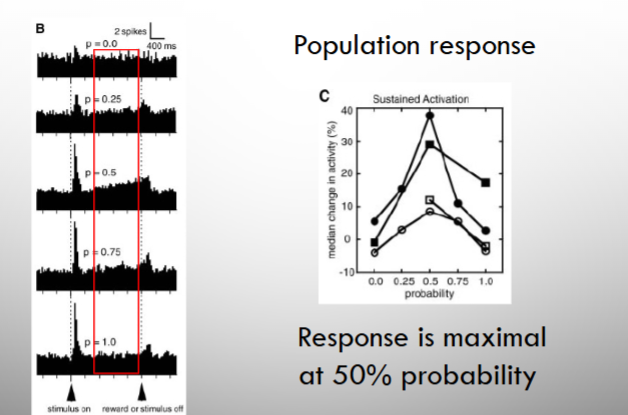
model of uncertainty encoding
uncertainty = standard distribution of lottery
Max uncertainty = .5
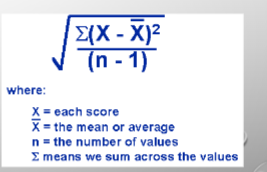
the neurons that respond during the time between the cue and reward and maximal at 50% probability are encoding standard deviation!
the response at the time of cue that increases as probability gets larger encodes expected value!!
true! one respone encodes EV (response to cue), the other encodes uncertainty (response between cue and reward), and we are most uncertain at 50/50
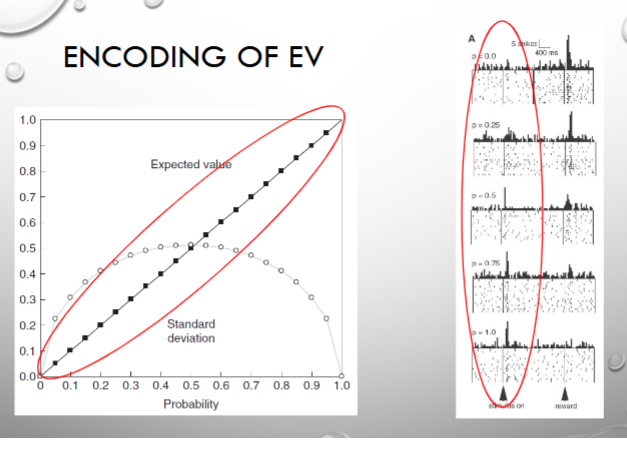
Fiorillo et al. (2003)
conclusion
uncertainty is related to probability of outcome
accuracy of prediction depends on being able to measure uncertainity in estime
increase in activity after cue and before outcomes encodes uncertainty
Common Currency
what is common currency?
transformation of information into a common representational space > once all information is transformed in this sapce, comparisons can be made
Schioppa et Assad (2006) - neurons in OFC encode economic val.
experimental design
1) monkeys fixate on screen
2) offer is made (1 yellow block vs 3 blue blocks)
3) reaction time look to preferred option (saccade)
4) decision time
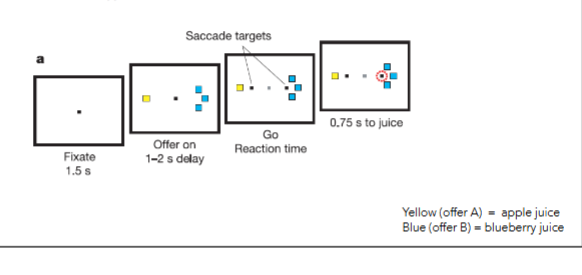
Schioppa et Assad (2006) - neurons in OFC encode economic val.
choice preference results
the chance of picking B is less when the ratio of B is less in comparison to A
example
Strongly prefers 10 drops of blueberry to 1 drop of apple juice
Strongly prefers 1 drop of apple juice vs. 0 drops of blueberries
point of subjective equivalence = 4:1
monkey preference is represented on continum
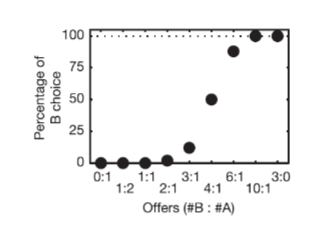
Schioppa et Assad (2006)
how is value of blueberry vs apple assigned for sommone currency scale?
common currency is like..
4 blueberry drops = 1 apple drop
value(1A) = value(4B)
4 drops blue = 4
1 drop apple = 4
just multiply the number of apples by 4 to convert into common currency
1A = 4.1B. when option is 0:1, monkey always select 1 apple which is value of 4.1 in framework.
common currency is like utility, everything must get converted into utility then compare
c
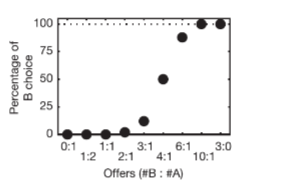
Schioppa et Assad (2006)
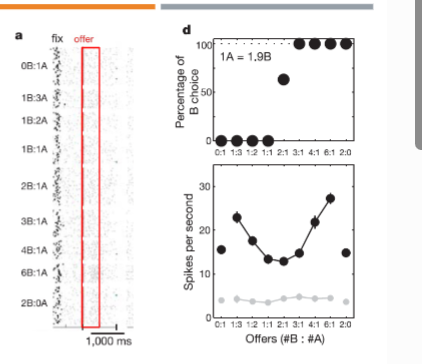
choice results
1 drop A = 1.9 drop B > map data and find indifference point
B chosen for 3,4,6:1
A chosen for 1:3, 1:2, 1:1
activity observed just follow juice deliery is top graph, gray daata is from period before choice options visible
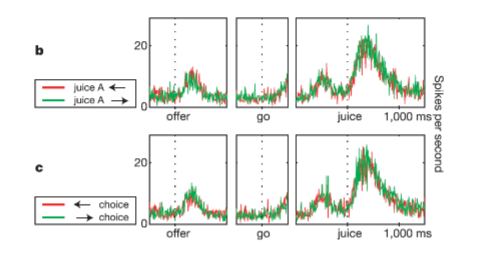
in a pure reward signal, representatiosn should be independeent of what?
is the OFC response to juice a pure reward signal?
in a pure reward signal, representatiosn should be independeent of behavior and stimulus features
——
yes, no spatial or motor info contained in signal > no info about amount of taste encode in chosen value signal
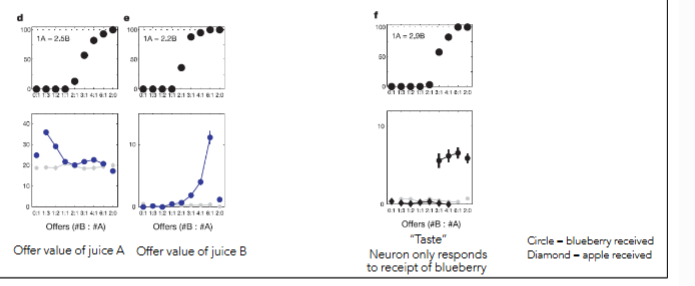
offer value vs taste encoding
what is the order in which neurons encode info from choice task?
offer value: some neurons encode value info related to specific offer
taste: some neurons respond at the same level regardless of amount for a particular juice
1) offer value (value of each individual optoin)
2) chosen value repreentation (value of juice option that will be selected by monkey)
3) taste (before or after juice delivery)
Schioppa et Assad (2006)
conclusions
OFC neurons signals important for decisions-making
OFC encoode chosen value > related for behaivor
OFC has pure value signal > not related to stimlus propertie
signal underlying choice
neural representation of subjective value
what did economist Jevons 1871 say?
to secure max benefit in life, all future events, pleasures, and plans should act upon us with the same force as if they were present
time plays an influence on our decision-making process > all things we know we need to concern about in the future, should evoke same concern as if it was present and in the moment but most people shrug off future things and push it off.
examples: retirement, health care, disease, adddiction, diet
modeling temporal discounting
over time, relative value decreases and the rate of decrease defines the concept of impulsivity vs self-control
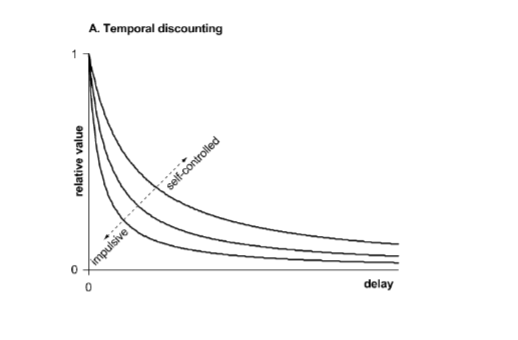
exponential discount function
Vreward= value / (1+r)^t
r = discount rate (baseline impulsivity)
t = time
small R = less discounting & more self control
big R = more discounting & more impulsive
used if only magnitude of outcome, not time considered
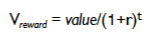
hyperbolic discount function
Vreward = magnitude / (1 +(k * delay))
k = steepness
small k = less discounting more self control
big k = more discounting more impulsive

proximal vs distant
proximal = value small immediate
distant = value big delayed
difference between hyperbolic and expontential
hyperbolic predicts reversal of preference, exponential does not
time considered in hyperbolic, time not considered in exponential; ideal for a utilty maximizer
McClure et al (2004)
experimental design
choice taks betweeen small early and large but delayed
$5 now and $10 in two weeks
$5 tomorrow and $40 in a month
McClure et al (2004)
brain regions of interest and results
PCC
MPFC
VS
MOFC
these clusters were activated for immediate rewards comapred to delayed. these brain regions recieve dopamine signals