Week 11: Attitudes and Attitude Changes
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
There have been many definitions of attitude, what are the 3 central ones?
fit and ready for action (Vaughan & Hogg, 2014)
Attitudes are evaluations of people, objects, or ideas (Banaji & Heiphetz, 2010)
"..a psychological tendency that is expressed by evaluating a particular entity with some degree of favour or disfavour" (Eagly & Chaiken, 1993)—relatively stable disposition
Explain how attitudes are formed?
through experiences, communication, and personal evaluations, resulting in significant variation from person to person
backgrounds and experiences shape individual perspectives, often leading to diverse attitudes even within the same social group
Can attitudes change? Explain your answer?
Attitudes tend are stable over time but can be influenced by significant life events, societal changes, or new experiences, making them resistant to change
What happens when you hold a negative attitude?
Results in undesirable outcomes—ignoring the good in people and situations
What happens when you hold a positive attitude?
Results in positive outcomes—paying attention to the good in people and situations
What are the 3 components to an attitude?
behavioural intentions
belief
affect
Regarding the components to an attitude: what is it meant by beliefs?
Cognitive component based on properties of an attitude object
Regarding the components to an attitude: what is it meant by affect?
Feelings stemming from moral and religious beliefs
How can affect be influenced in terms of attitude?
Classical Conditioning: Learning through association
Operant Conditioning: Reinforced through rewards
Regarding the components to an attitude: what is it meant by behavioural?
based on observation of own behaviour
Before the conclusion of three main components to an attitude, what were proposed and who by?
thurstone—proposed a one-component model only including affect
allport—proposed a two-component model; affect and mental readiness
What do we mean by mental readiness?
It is a defining factor of an attitude—as it an element of reaction towards a particular stimuli
Explain how classical conditioning can impact attitude/s?
Classical conditioning bases itself on association—when we create attitudes, certain events or situations can bring up those attitudes or encourage it
having a positive attitude towards chocolate:
stimuli 1 + stimuli 2 = curated attitude
caramels + grandma’s house = happy affect = positive attitude
Explain how operant conditioning can impact attitude/s?
Operant conditioning is based on behaviour being fuelled through reward or punishment—this in turn would mean feeling and thoughts lead to attitudes as a result of being rewarded or punished
behaviour towards a thing/person + positive reinforcement = positive attitude
Explain how observational learning can impact attitude/s?
Forming attitudes by observing others, especially figures of authority or caregivers. This form of social learning emphasizes the impact of role models on personal attitude development
What are implicit attitudes?
involuntary and automatic evaluations; could be favourable or unfavourable, covert
How are implicit attitudes measured?
physiological indicators
non-verbal behaviour
Implicit Association Test (IAT)—existing measure (not valid)
What are explicit attitudes?
deliberate and controlled evaluations, overt
How are explicit attitudes measured?
self report inventories
questionnaires
The existence of attitudes are attributed to 4 functions: what are they?
adaptive (instrumental)
knowledge
value expressive/ego-expressive
ego defence
Explain the adaptive function of why attitudes exist?
Help people to attain desired goals and rewards, avoid undesirable circumstances and punishment
Explain the knowledge function of why attitudes exist?
Makes the world more understandable, predictable, and knowable—simplifies the understanding of complex realities, leading to comfort in predictable environments
Explain the value expressive function of why attitudes exist?
Helps express personal values and integrates those values into one’s self-concept and identity—enables us to express ourselves
Explain the ego defensive function of why attitudes exist?
Protects a person from damaging information; but may involve some bias
Can attitudes predict behaviour?
Yes
In 1930 La Pierre conducted an experiment as he travelled America with a Chinese couple—what were the findings?
during a period of heavy racism towards Chinese people: it was found that the experience of the Chinese couple was relatively positive—with many accepting their presence
after his travels he contacted the establishments—where he found that most, if not all, wouldn’t accept Chinese customers
La Pierre’s findings provided major implications on the relationship between attitudes and behaviours—what was it?
Attitudes and overt behaviour are not related in a one-to-one fashion
In what way can attitudes be predicted by behaviour?
behavior under specific conditions—spontaneous behaviors often reveal true attitudes because they occur without the influence of social pressures (attitudes must be accessible)
Deliberation is often a factor that affects the statement of “attitudes can predict behaviour”—what does that mean?
Self-predicted behaviour—by having an explicit thought process on how you react attitudes became misaligned, due to:
societal norms and expectations = causing discrepancies between one's beliefs and actions = leading to perceived hypocrisy
What is the Theory of Planned Behaviour (Fishbein & Ajzen, 2010)?
Follows the premise where it links beliefs to intentions, which then shape behavior
The Theory of Planned Behaviour has three distinct categories: what are they and what do they mean?
(specific) attitudes—personal behavioural beliefs and attitudes that are attributed to knowledge and experiences: weighted by outcome evaluations
subjective norm—our subjective perception/normative beliefs and how we view the ideas of other people: weighted by motivation to comply
perceived behavioural control—the control belief of the extent to which we believe we can control our behavior: weighted by influence by control of beliefs
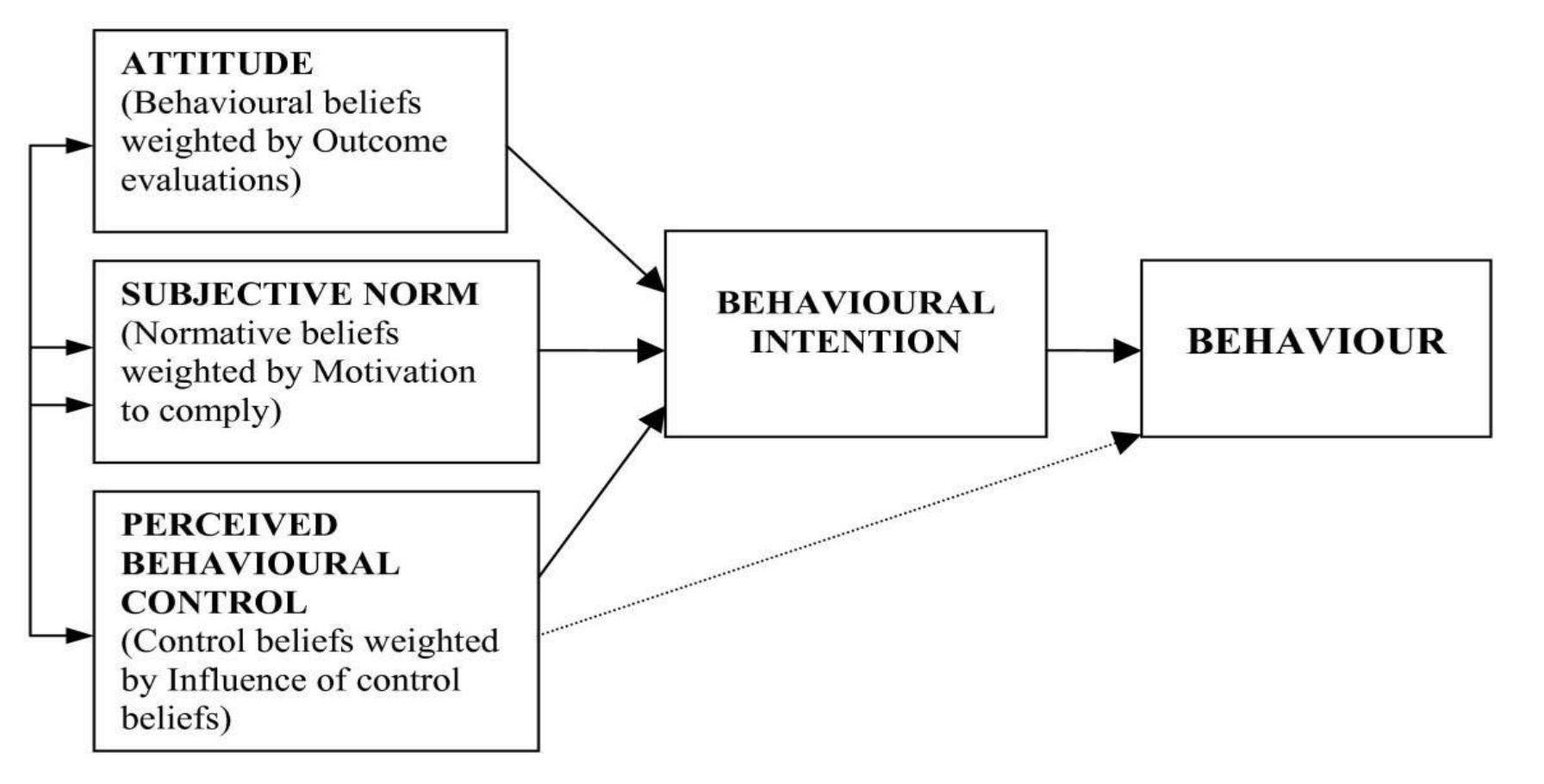
Explain the function of this model via the diagram
Quintessentially, this model provide the best predictors to a behaviour:
Best predictors of planned behaviour are intentions
Best predictors of intentions are attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioural control
More specific attitudes = better prediction of behaviour
Subjective norms = how others they care about will view behaviour in question
Behavioural Control = ease with which behaviour can be performed
Present the if’s of this statement: attitudes will predict behaviour
IF “other influences” are minimized
IF the attitude corresponds very closely to the predicted behaviour (as in voting studies)
IF the attitude is potent (because something reminds us of it, or because we acquired it by direct experience)
How can attitude changes occur?
The answer to this is presented through the Cognitive Dissonance Theory?
What is the Cognitive Dissonance Theory?
Refers to the psychological discomfort in the reconstruction of one’s beliefs and attitudes due to inconsistencies and conflict that occur—positioning the individual to rationalise/re-interpret their belief to fit the current situation
Define persuasion
It is a core factor in the process of changing attitudes by way of effective communication
What is the Yale Attitude Change Approach?
a model that describes the process and conditions under which people tend to change their attitudes
What are the 3 components to the Yale Attitude Change Approach?
communicator
message
audience
Regarding the Yale Attitude Change Approach: what is the communicator component? what does it mean?
[WHO BY] Quintessentially the source of which the message is originating from—experts, popular and attractive people; further shaped by credibility, expertise, and trustworthiness—presentation of an individual will either be recieved or rejected
The role of the communicator has 3 characteristics: what are they?
Empathy: Ability to understand and connect with the audience's feelings.
Conviction: The degree to which the communicator believes in the message.
Expertise or popularity: These factors can enhance credibility, making the audience more likely to accept the message.
How is the role of the communicator relevant to the ABC model in persuasion?
Affect: Emotional resonance with the audience.
Behavior: Promoting actionable outcomes.
Cognition: Engaging the audience's thought process.
Regarding the Yale Attitude Change Approach: what is the message component? what does it mean?
[WHAT] Refers to the content and structure of the message itself—clarity, emotional appeal, factual backing, and the sequencing of arguments (primary vs. recency); appeal of the message impacts the effectivity of its influence
Can you explain what it means by primary vs recency effect in the message component of the Yale Attitude Change Approach?
The order of information presented can affect memory and influence immediate responses, with the last item often being more memorable;
primary effect—People are more likely to remember items at the beginning of a list; first items have less competition for limited memory capacity
recency effect—People are more likely to remember items at the end of a list; items may still be available in short-term memory
Can you explain what it means by sleeper effect in the message component of the Yale Attitude Change Approach?
Some messages might take time to resonate; initial resistance may fade with repetition, leading to eventual acceptance
Can you explain what it means by discounting cue in the message component of the Yale Attitude Change Approach?
Any disclaimer or reason leading you to doubt the credibility of the message's source
Explain the connection between discounting cue and sleeper effect, with a provided example.
it is the way a message, when paired with some sort of discounting cue, has a delayed impact on the recipient—in other words, the sleeper effect shows that discounting cues will be gradually forgotten over time
Regarding the Yale Attitude Change Approach: what is the audience component? what does it mean?
[WHO FOR] Features of the audience that affect persuasion are attention—background, predispositions, intelligence, self-esteem, age, gender, individual experiences; these aspects impact the way the message is received
Why would age matter in presenting a message?
Younger individuals often show a greater susceptibility to persuasive messages due to their developing critical thinking skills—this can also be true to those of the older generation; appealment of the message and consideration of following can be impacted by the target age
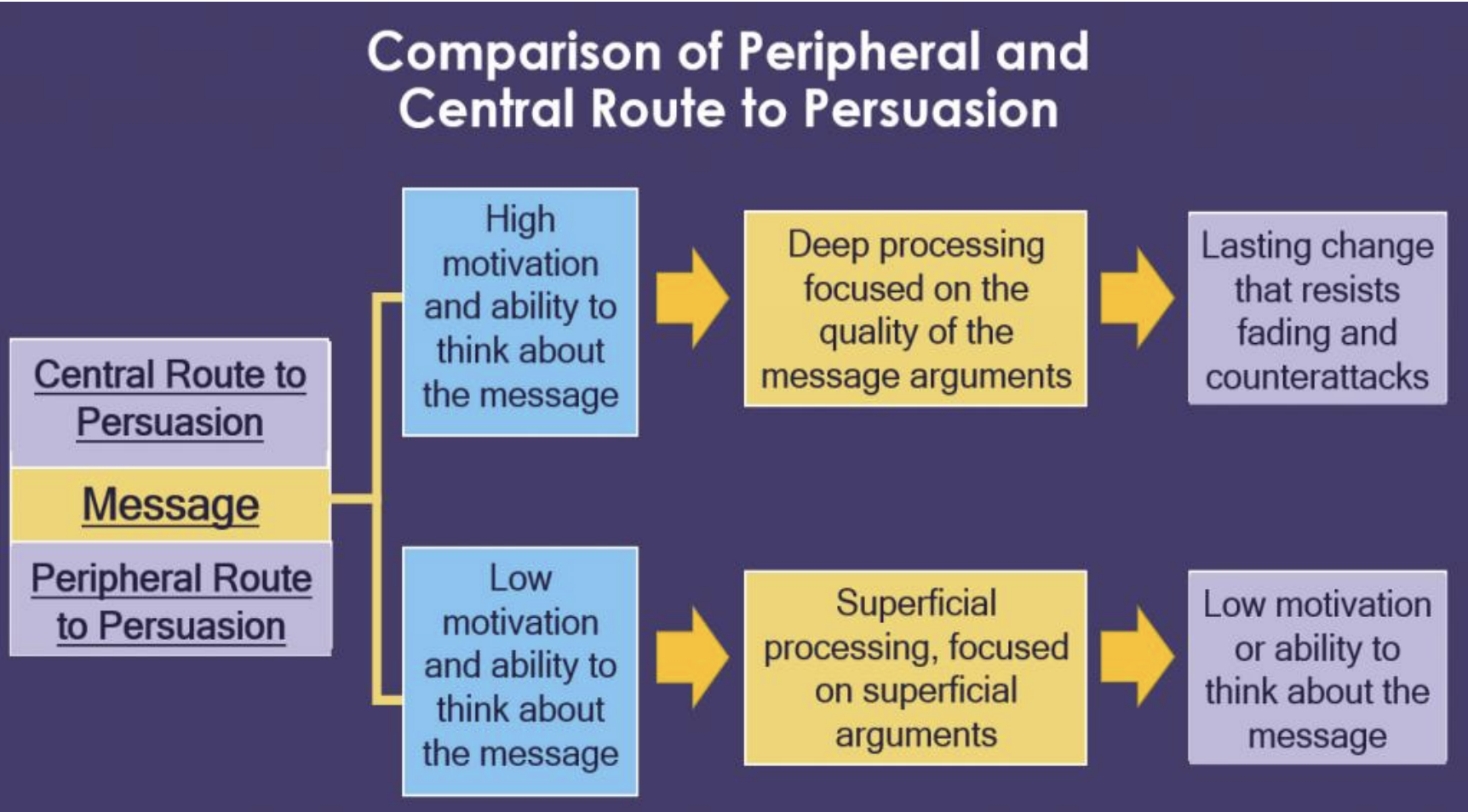
What is the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion?
Otherwise known as the Elaboration-Likelihood Model—it seeks to explore how humans process stimuli differently and how the outcomes of these processes result in changing attitudes and, consequently, behavior
How does the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion function?
The model explores the thought processes of the individual through 2 routes; peripheral and central
Regarding the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion; what is the peripheral route?
Involves superficial processing, low-level arguments, where individuals are influenced by extraneous cues—attractiveness of the communicator
Changes from this route may be short-lived and easily reversed
Regarding the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion; what is the central route?
Involves deep processing of the message, engaging critically with strong arguments—typically results in more enduring attitude changes as it demands cognitive engagement
According to the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion, which type of attitude change is more stable over time?
Change produced through the central route
What factor is most likely to lead someone to process a persuasive message through the peripheral route rather than the central route?
Low motivation or low ability to think about the message
Compare the 2 routes of the Dual-Process Model of Persuasion
What are some effective advertising techniques?
Anything that essentially targets the emotional and rational aspects of consumer decision-making; engaging visuals, relatable narratives, and emotional storytelling
What is Split Cable Market Tests?
Process of understanding consumers buying attitude regardings advertisements
How does the Split Cable Market Tests functions?
This is done through a split of ads between different regions—by the distribution of those ads, companies can figure out if consumers buy their products (through tracking the special ID card) after the ad distribution
How are public health campaigns effective pieces of persuasion?
Product placement, behaviour of admired figures—invoke different emotional reactions and responses, from embarrassment, shame, fear, and guilt, to inspiration, empowerment, and pride
What are the factors that result in the resistance to change attitudes?
Attitude Inoculation—a psychological technique used to strengthen an individual's beliefs and attitudes, making them more resistant to persuasion or counter-arguments; cultural truism
Resisting peer pressure—linked to people’s values and emotions; most vulnerable to adolescents
Being alert to product placement—inserting brands or products in media; can influence our implicit attitudes
Explain the process of attitude inoculation?
Weak Exposure: The individual is exposed to a small, easily refuted argument that opposes their current belief or attitude. This "mild" argument challenges their stance just enough to engage them without overwhelming them
Counter-Argument Building: When faced with the mild challenge, the person is encouraged to think of counter-arguments to defend their beliefs. This process helps them solidify their original attitude by actively engaging in defense
Strengthened Attitude: After successfully countering the weak argument, the individual becomes more confident in their stance. They build "resistance" to future persuasive messages that might be stronger or more persuasive
What is Reactance Theory?
Reverse psychology—the idea that people will try to regain and reassert their lost freedom when their freedom is either threatened or eliminated
What is the boomerang effect in Reactance Theory?
Attempts to control others’ behavior may induce them to engage further in the prohibited actions, counteracting the intended outcome
Why would attitude changes be inherently positive?
Change your attitude if you can’t change the situation
Reduce prejudice and discrimination
Positive behaviour change
Helps coping with daily hassles