Exam 2 Patho Cardiac portion
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
What are pulmonary and systemic circulations?
- Pulmonary: Blood going to the lungs
- Systemic: Body wide
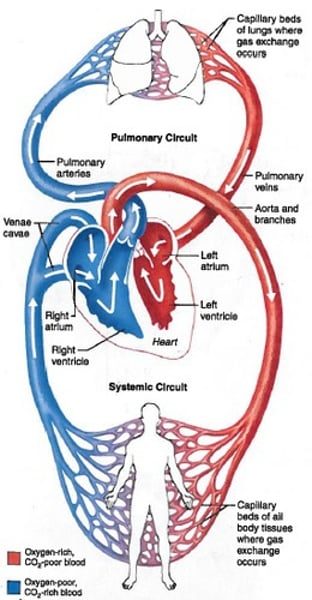
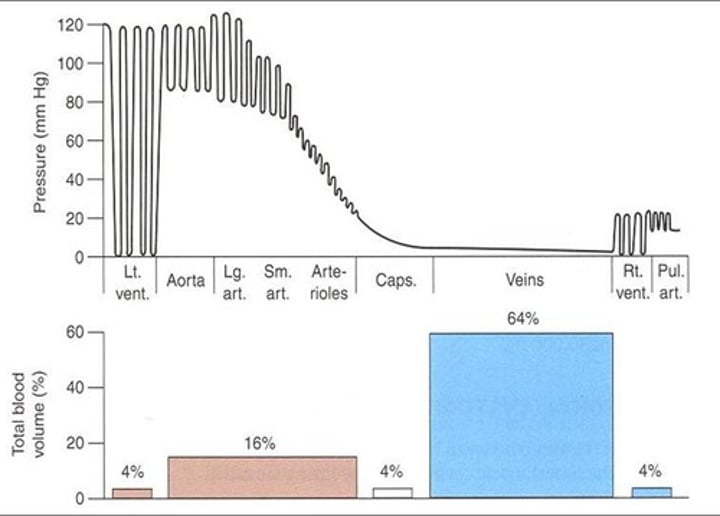
What is pressure and volume distribution of the heart?
4% of blood in L heart
16% of blood in arteries and arterioles
4% of blood in capillaries
64% in venules and veins
4% in right heart
Reference picture for pressure
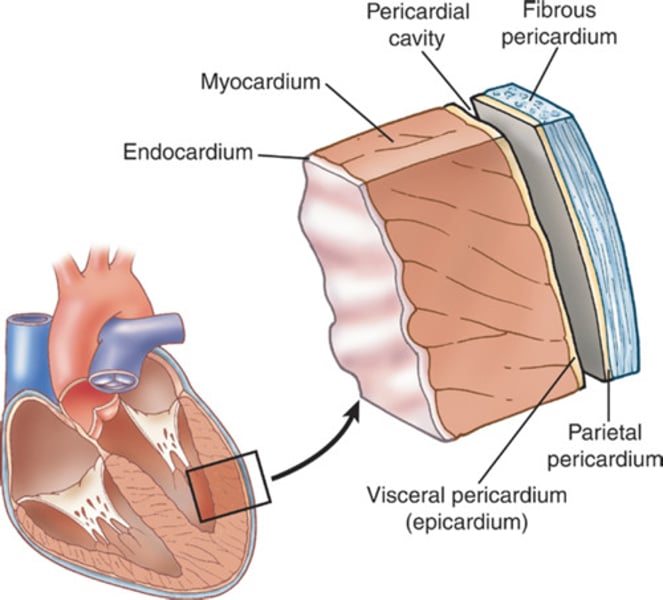
What are the layers of the heart?
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium (visceral pericardium), pericardial cavity, parietal pericardium, fibrous pericardium
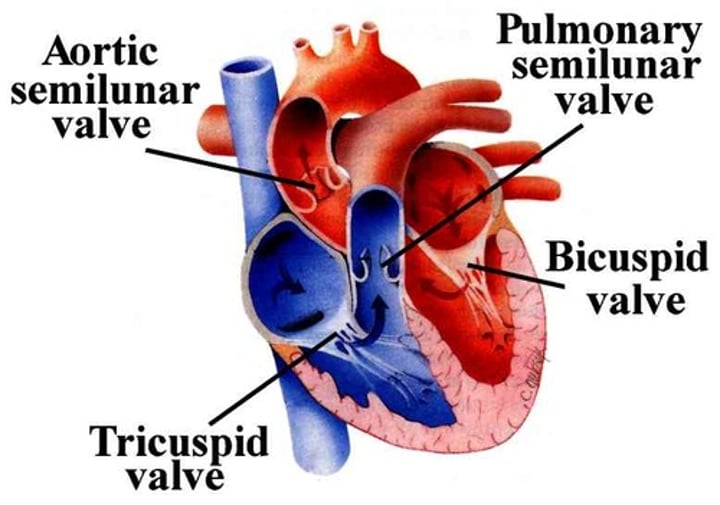
What is the flow through the heart?
-venous blood comes from the superior/inferior vena cava
-filters into the right atrium
-passes the tricuspid valve
-filters into right ventricle
-passes the pulmonary valve
-goes to the pulmonary trunk and then the right and left pulmonary arteries
-Right and Left lungs give O2
-blood rushes back into the left atrium
-passes the mitral valve (bicuspid valve)
-filters into the left ventricle
-passes the aortic valve
- goes to the aorta and rest of the body
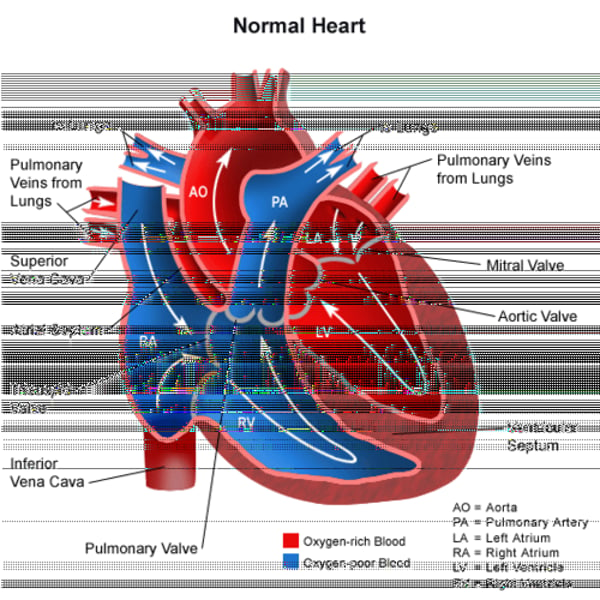
What are the valves of the heart?
Right and left atrioventricular (AV); aortic and pulmonic valves (semilunar valves)
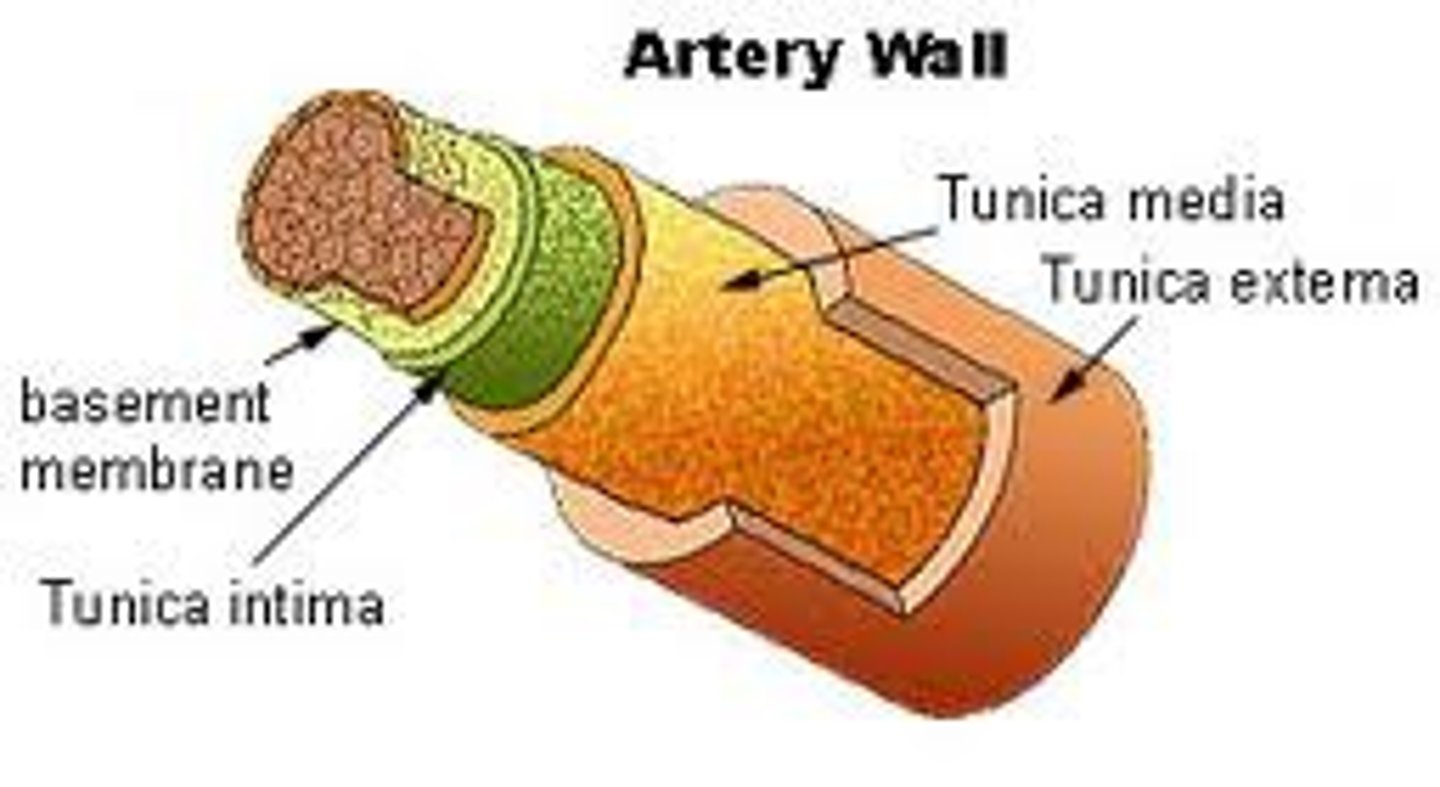
What are the artery layers?
tunica externa, tunica media, tunica intima
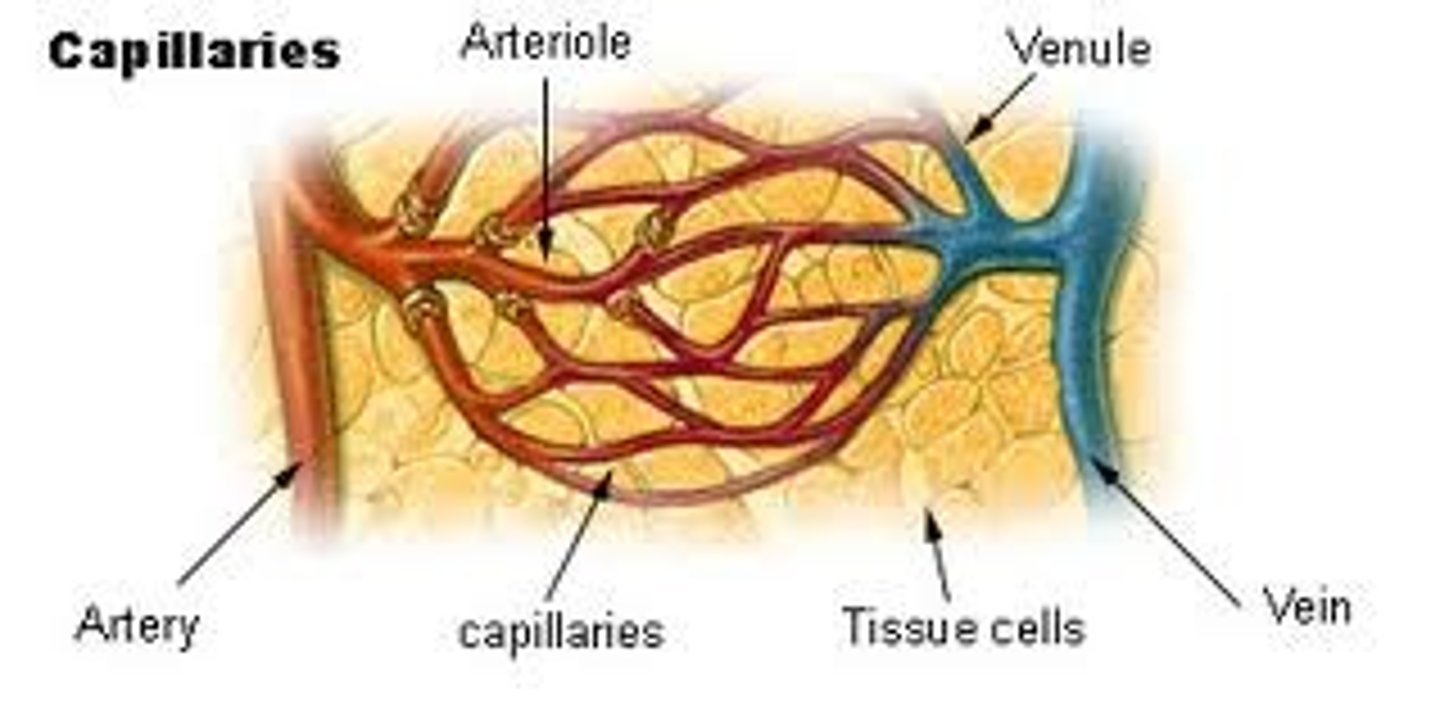
What are the differences between artery, vein, and capillary?
Artery: round with thick boarder; largest, increased pressure, hollow, away from heart (usually oxygenated)
Vein: bendable, thin and squishy, goes toward heart
Capillary: smallest, "purple," connecting point between artery and vein
What is coronary artery disease?
atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries
What is coronary heart disease?
the same as coronary artery disease
What is the issue with coronary artery disease?
deprives heart of oxygen
What is the leading cause of heart attack or stroke?
atherosclerosis
What is an atheroma?
cholesterol rich plaque
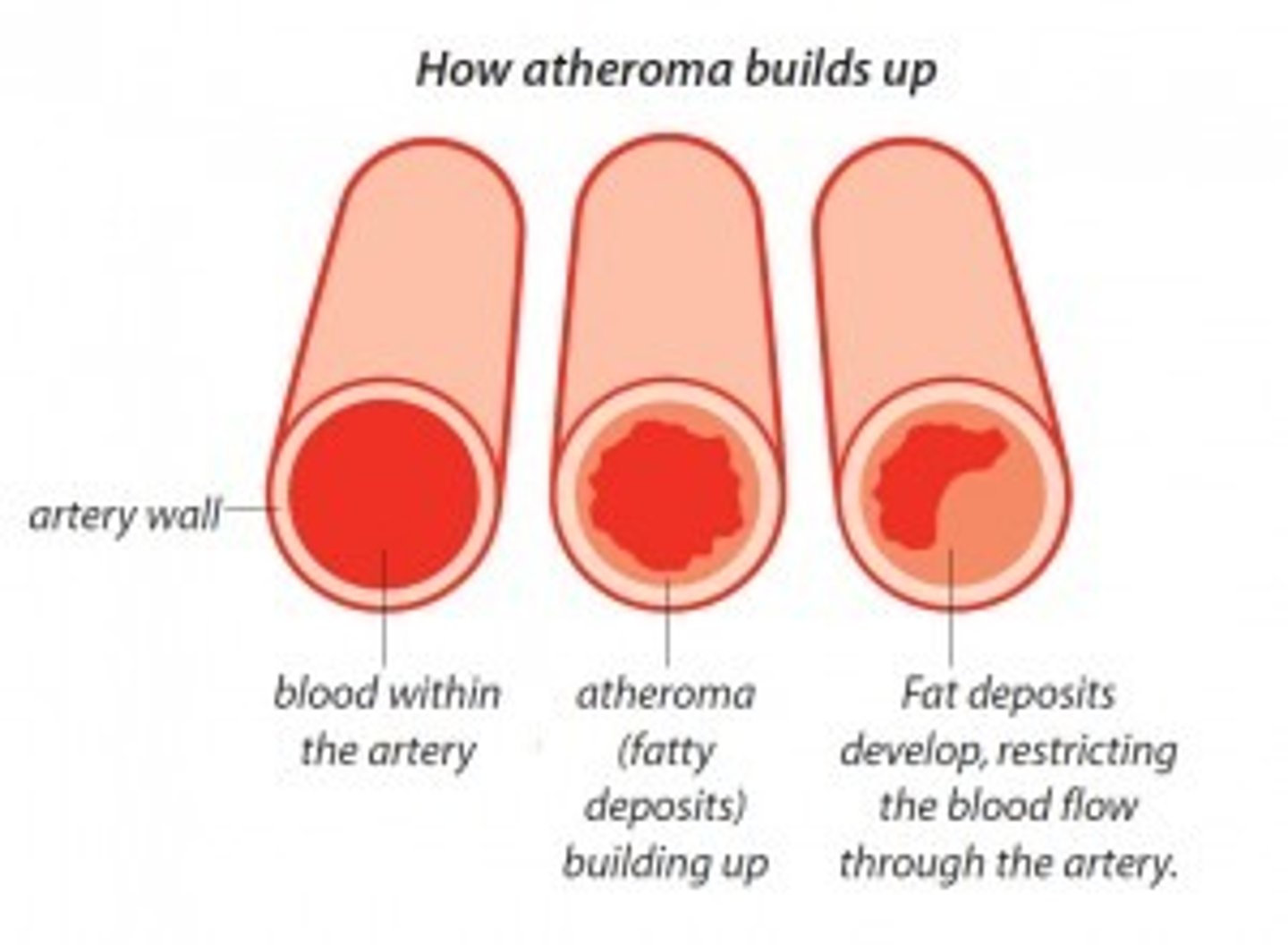
What is the issue with an atheroma?
allows less blood flow, causing less oxygen delivery
Coronary artery disease can be _____.
systemic
What is arteriosclerosis?
hardening of the arteries, part of the normal aging process
What is the issue with arteriosclerosis?
Become less compliant in the hardening process, is not as elastic so causes higher BP
What is the stroke volume?
the amount of blood ejected by the heart in any one contraction; 70 mL
What is something important to take away from atherosclerosis?
it is not a single disease
What are the 5 arteries that are more likely to be clogged?
1) abdominal aorta, 2) coronary arteries, 3) femoral/popliteal arteries, 4) internal carotid arteries, 5) vertebral, cerebral, basilar
- In order of frequency to be clogged
Information about the abdominal aorta?
- size of a quarter, can get more clogged since so big
- most common for cholesterol build up
- ilia region
Information about the coronary arteries?
- size of coffee straw, so small can tell effects easier
- heart
Information about the femoral/popliteal arteries?
- build up here causes cut off blood to legs, peripheral
- leg and back of knee
Information about the internal carotid arteries?
- increases risk stroke
- neck going up
Information about the vertebral/cerebral/basilar arteries?
- increases risk of stroke
- clavicle region and L region
What are some nonmodifiable risk factors of atherosclerosis?
1. age: as get older arteries harden and cholesterol builds up
2. biological sex
3. genetic predisposition: familial hypocholesterolemia
Why does biological sex affect risk of getting atherosclerosis?
- females are less likely to get than age matched males before menopause
- after menopause they are the same (estrogen drops)
What is a modifiable risk factor for atherosclerosis?
- hypercholesterolemia
- hypertension
- hyperhomocysteinemia
- inadequate diabetes mellitus care
- tobacco use
What are some primary causes of hypercholesterolemia?
- defective synthesis of apoproteins (transport lipids)
- means that the body physically cannot make the transport lipids
- lack of receptors for the lipids to bind to
What are some secondary causes of hypercholesterolemia?
obesity, diabetes mellitus, increased cholesterol intake from diet
Why are lipids insoluble in plasma?
they are primarily water
How are lipids transported?
lipoproteins
What are the protein component in lipoproteins?
apoproteins
What are some examples of apoproteins?
A,B,C, and E
What are the things transported in lipoproteins?
triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol
Where are triglycerides found?
in American diets
What are the exogenous and endogenous pathways for triglyceride and cholesterol transport?
map out the picture shown
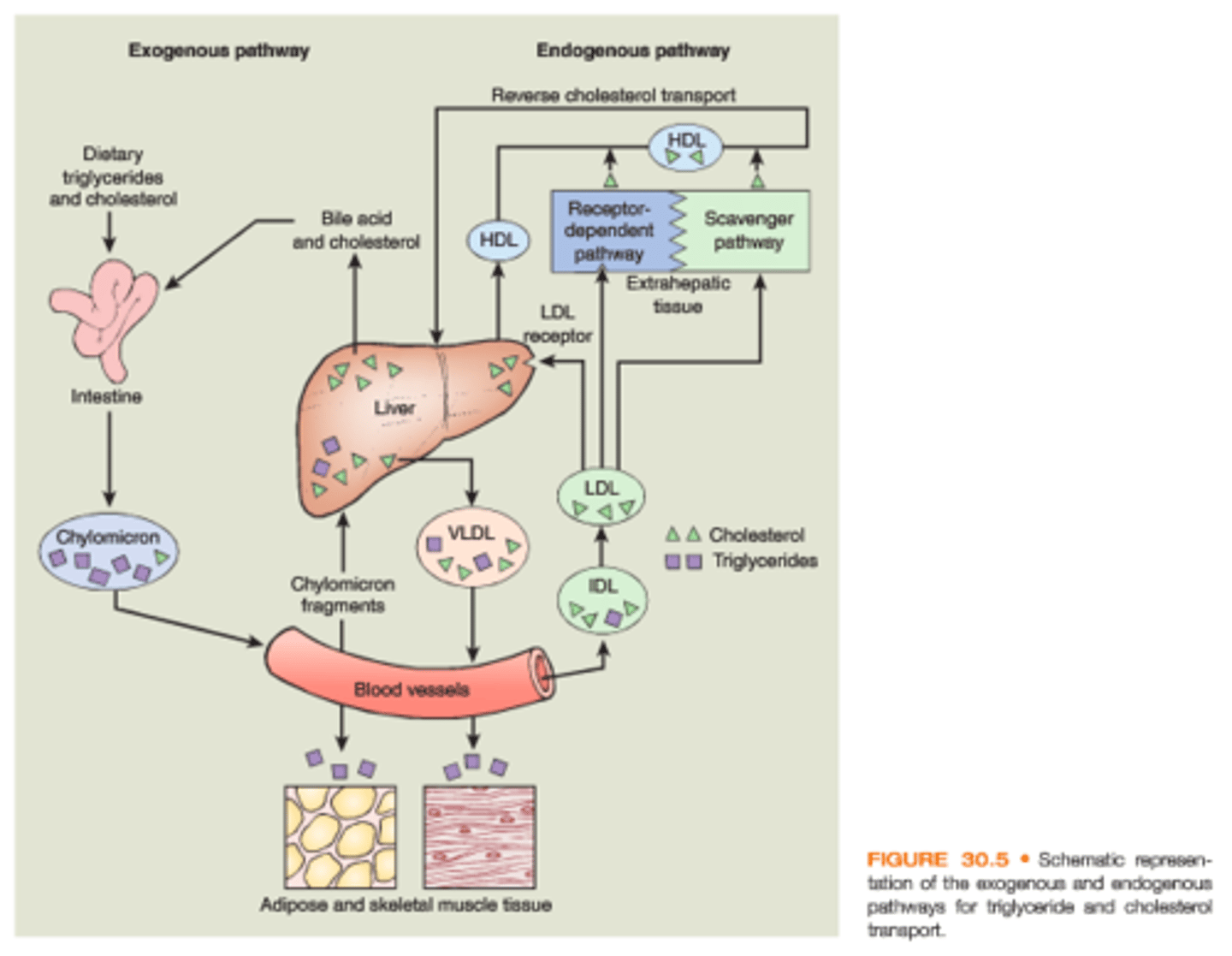
What and where does chylomicron drop off?
triglycerides; adipose and skeletal muscle tissue
What and where does LDLs drop off?
cholesterol; LDL receptor on the liver
If cholesterol enters the blood stream, who would pick it up to take it to the liver?
HDLs
How are lipoproteins classified?
by density
more protein = higher density
HDLs are?
high density lipoproteins; lots of this is healthy
LDLs are?
low density lipoproteins; lots of this lethal
Why is cholesterol important?
- part of plasma membrane
- helps with production of estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, vitamin D, adrenal gland cortisol, aldosterone
What does cortisol stress do?
- reduces B cell, T cell, Cytoxic cell productions
- lack vitamin D
What are low density?
chylomicrons and LDLs
What are high density?
HDLs
What is the percentage of carrying for chylomicrons?
80-90% of triglycerides, 2% proteins
What is the percentage of carrying for LDLs?
10% triglycerides, 50% cholesterol, 25% protein
What is the percentage of carrying for HDLs?
5% triglycerides, 20% cholesterol, 50% protein
Chylomicrons are in where?
small intestine
LDLs are made by what?
hepatocytes
When LDLs drop of cholesterol what is it used to make?
estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
Where does the rest of the cholesterol go?
On LDL receptor to the small intestine to be excreted
If there is an excessive amount of cholesterol, it will attract what?
macrophages
What is hypertension?
high blood pressure
Hypertension does what in regards to anthromas?
increases risk of anthroma
What is normal BP?
120/80 mmHg
What does mmHg mean?
millimeters of mercury
Why is it mmHg?
how far the BP can push a column of mercury
What does the 120 stand for?
Refers to the systolic pressure (Ventricular Contraction)
What does the 80 stand for?
Refers to the diastolic pressure (Ventricular Relaxation)
What is stroke volume?
the amount of blood ejected by the heart in any one contraction (ventricle per minute)
What is ejection force?
how forceful the blood is
What influences ejection force?
blood calcium levels
How does blood calcium levels influence ejection force?
more calcium = more contraction = more force
What is artery compliance?
elasticity of artery
How does atherosclerosis relate to artery compliance?
no give to arteries (increases BP)
What are the 3 things that influence systolic pressure?
stroke volume, ejection force, artery compliance
What influences diastolic pressure?
peripheral resistance
What is peripheral resistance?
resistance of the arteries to blood flow moving forward
What influences peripheral resistance?
- a lot of capillaries (very big to small)
- think of a highway to an ally
If you weigh more, you will have more what?
capillaries
What does the RAAS system stand for?
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
where does RAAS take place?
kidneys, lungs, liver,
What does the RAAS do?
responsible for regulation of body's blood pressure by Juxtaglomerular (JG) cell
Some examples of what makes low BP?
dehydration and body positions
What is the flow of RAAS?
draw out and reference photo here and in book
pg 718
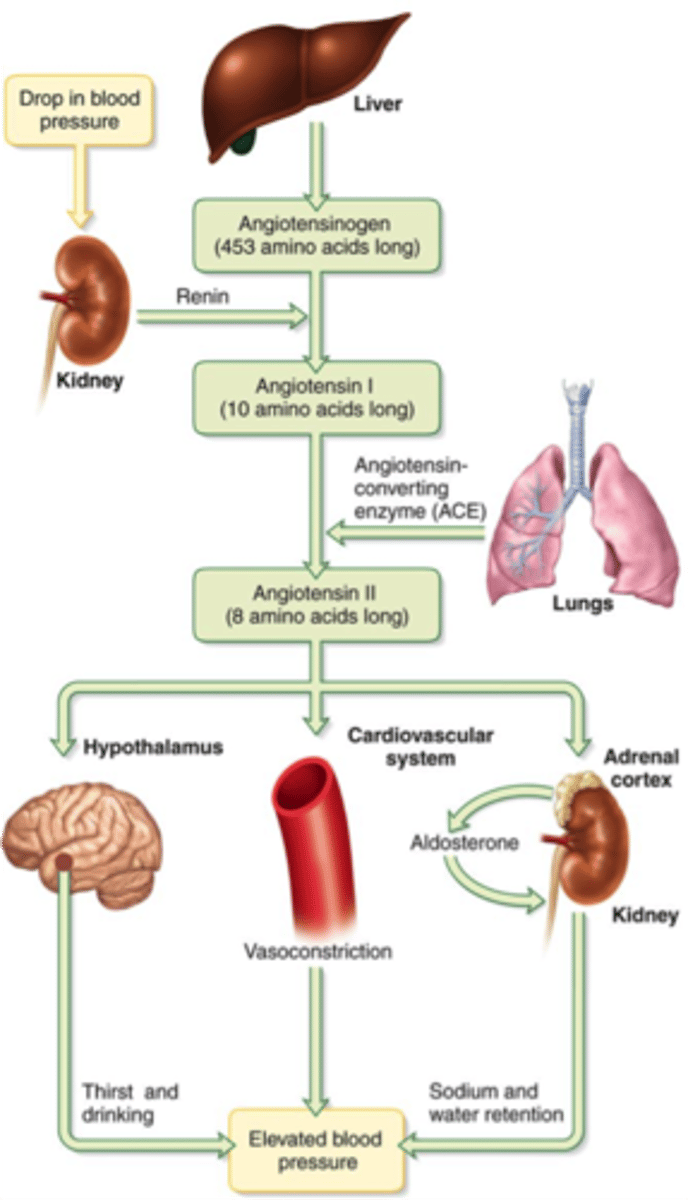
People with high BP will take what?
ACE inhibitor supplements
What will ACE inhibitors do?
it will inhibit production of ACE production from Angiotensin I (this causes vasoconstriction), which allows for vasodilation
What is essential (primary) hypertension?
- increases with age
- more common in men than women (equal after menopause)
- more common in Black people
What produces renin in the kidneys?
JG cells
What organ produces ACE?
lungs
What organ produces angiotensinogen?
liver
What is the other way that the body raises BP?
neurohypophysis
What is neurohypophysis?
posterior lobe of the pituitary gland
- produces antidiuretic hormone to conserve water to higher blood volume to higher BP
What happens with chronic untreated hypertension?
- left ventricular hypertrophy
- retinopathy
- kidney disease
What is the issue with left ventricular hypertrophy?
has to work harder to open aoritc valve (smaller lumen and more o2 and muscle too thick to contact symmetrically)
- think open a door with lots of people outside
What is the issue with retinopathy?
causes blindness (due to pressure)
- damages blood vessels
What is the issue with kidney diseases?
higher BP causes kidney cell damage
- consequences: no regulate BP, accumulate metabolic waste
What is hyperhonocysteinemia?
- too much homocystein (inhibits anticoagulation cascade)
- clot would persist longer
- heavy coffee drinking is associated with high levels
how to lower homocysteine levels
- take folate to lover levels
- vegetables/multivitamins
What is diabetes mellitus?
An error in glucose metabolism
- primarily causes high glucose levels, increases free radicals
What are long term effects of diabetes mellitus?
- reduces nitric oxide: creates higher BP
- abnormal metabolites: increases thrombus, formation, promotion of inflammation
What does nitric oxide do?
vasodilation
What is the issue with tobacco use?
- smoking a pack a day increases likelihood of coronary thrombosis and heart attack
- when acute myocardial infarction does occur it is more fatal in smokers
Why is smoking very dangerous/causes high BP?
- damages vascular endothelium
- enhances platelet aggregation
- lowers HDL levels
- nicotine stimulates release of epinephrin and norepinephrine (vasoconstriction)
What are the functions of endothelium tissue?
- regulates platelet adhesion
- regulates immune/inflammatory reactions
- regulars smooth muscle cell growth
What are the 5 portions of development of atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta?
- damage to endothelial cells (the ones that make up the tunica intimia)
- blood platelets and lipoprotein deposits
- platelets release growth factors that penetrate into vessel wall
- monocytes adhere to the injured endothelium
- proliferating smooth muscle and fibroblast surround fatty streak
What can damage the endothelial cells?
- increased cholesterol = macrophages swarm area = inflammation
- smoking
- higher BP
What happen with the blood platelets and lipoprotein deposits?
- high LDLs will deposit these on the inside lining and aggrogate