APBIO Unit 6
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
single strand binding proteins (SSB)
bind to the unpaired DNA strands, keeping them from re-pairing
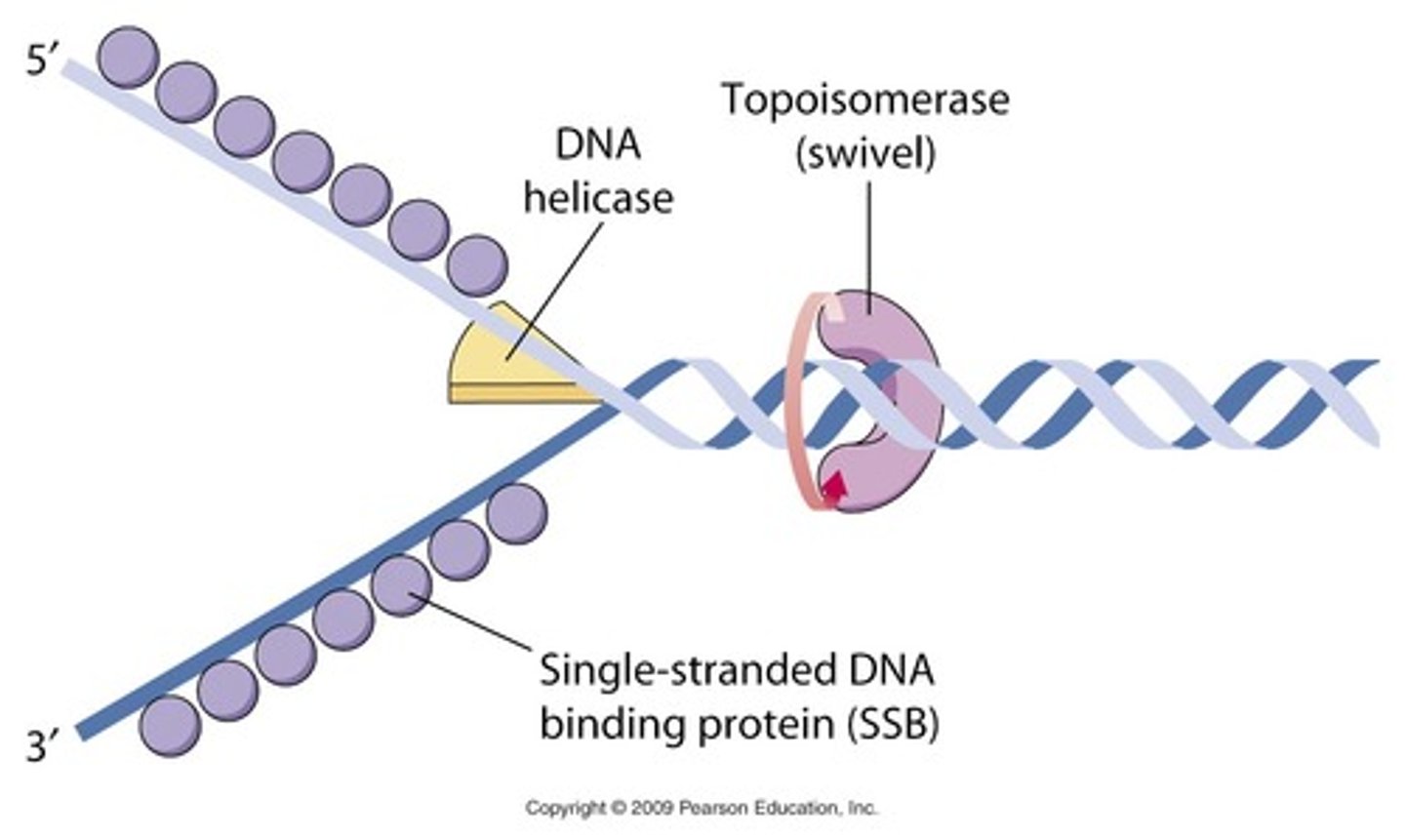
Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
Helicase
Unwinds DNA, breaks the hydrogen bonds
semiconservative
the new DNA strand contain one strand that is old and one that is new
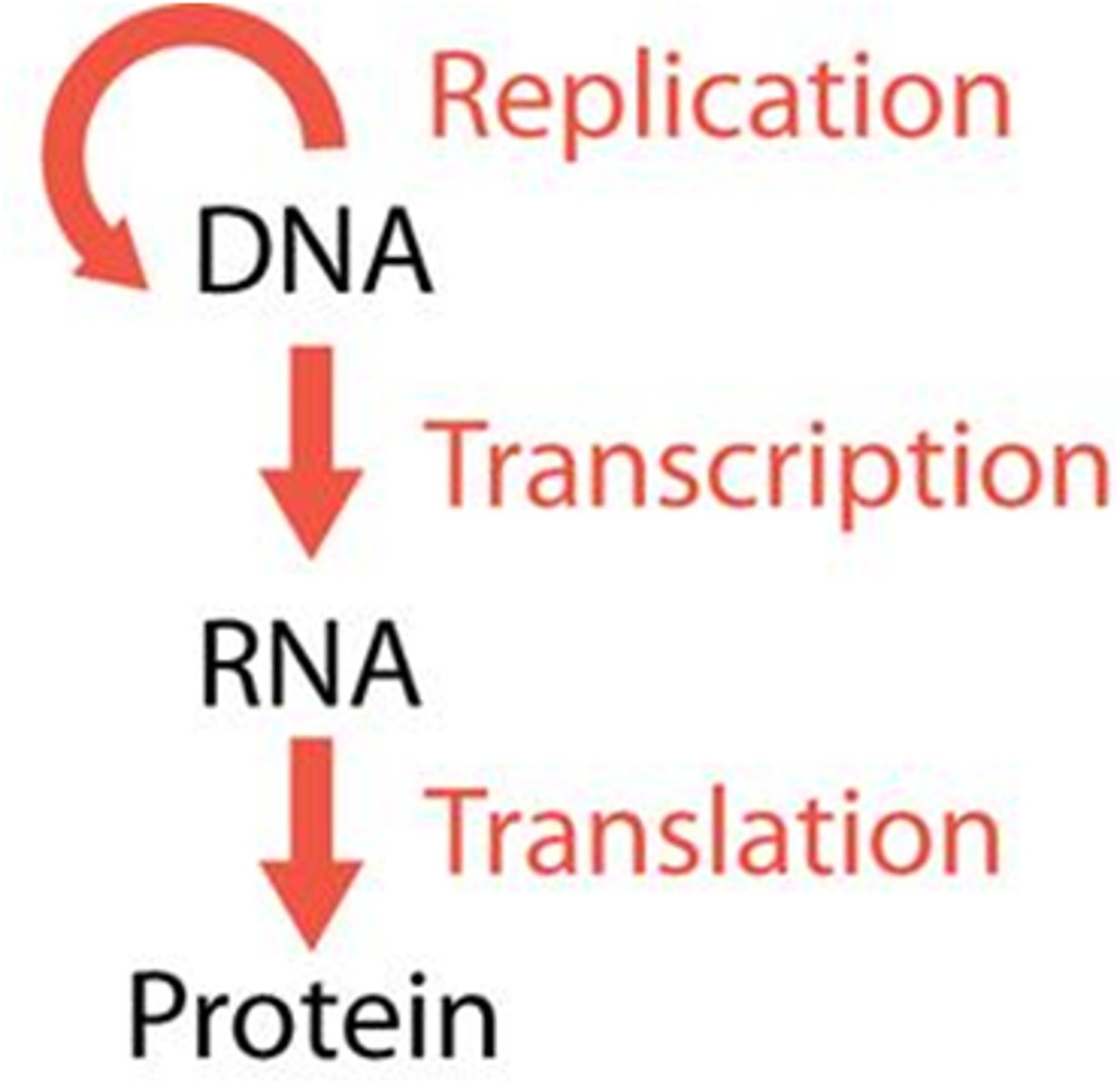
Central dogma
DNA to mRNA to Protein
poly-A tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides.
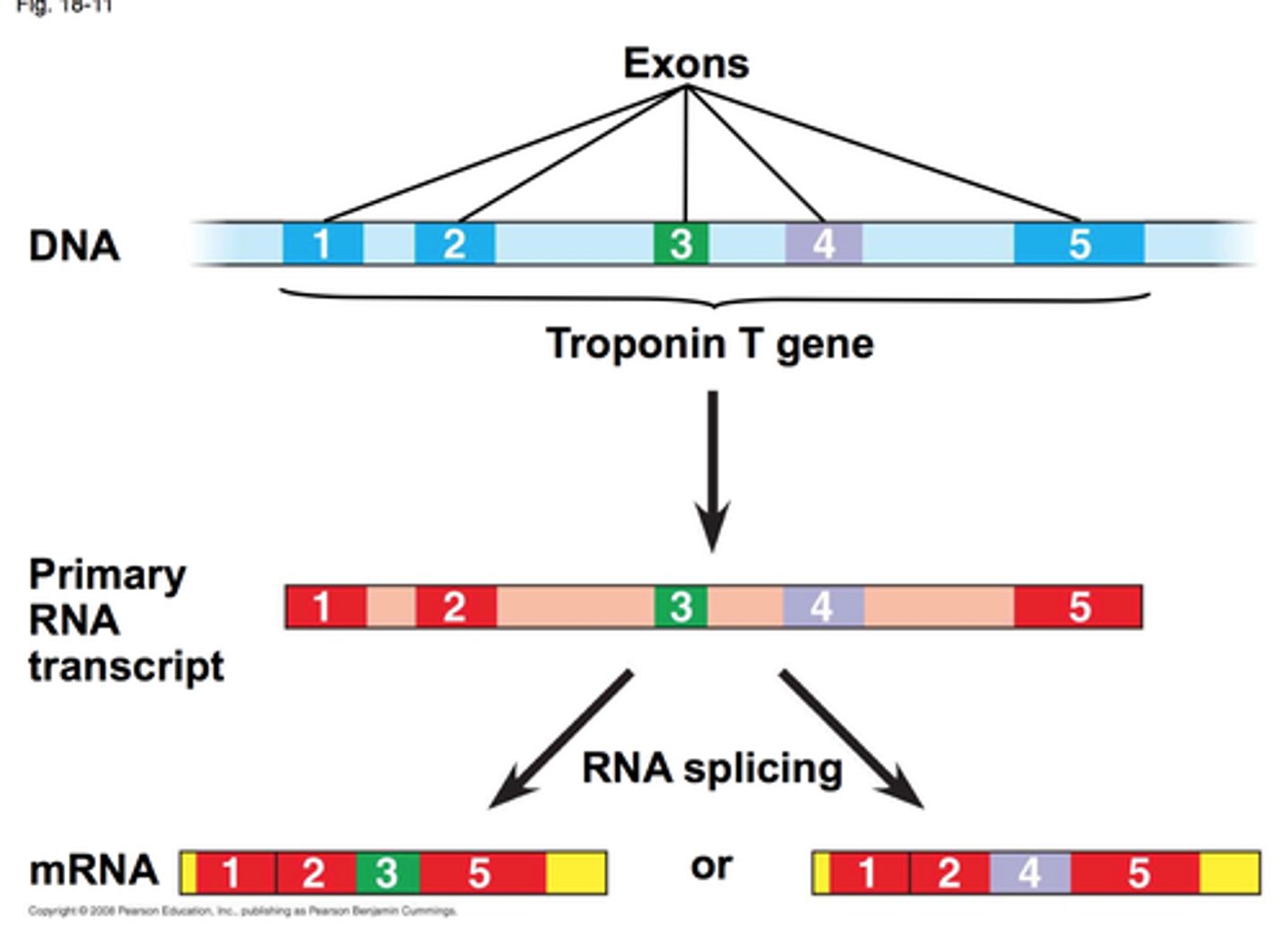
Alternative RNA splicing
Different RNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and introns. Supports why there are many proteins in our bodies.
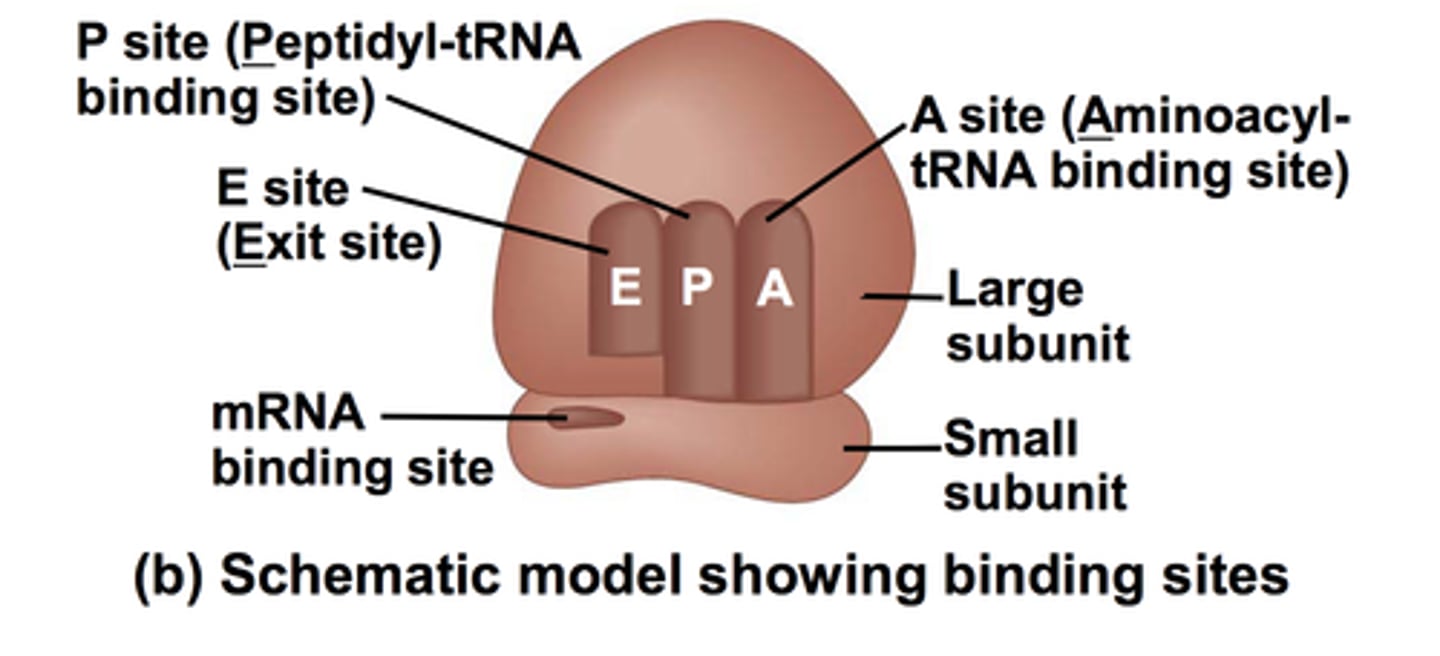
What are the three sites on a ribosome?
A site (tRNA initially binds, bringing an amino acid for the chain), P site (growing polypeptide/amino acid chain), E site (tRNA leaves)
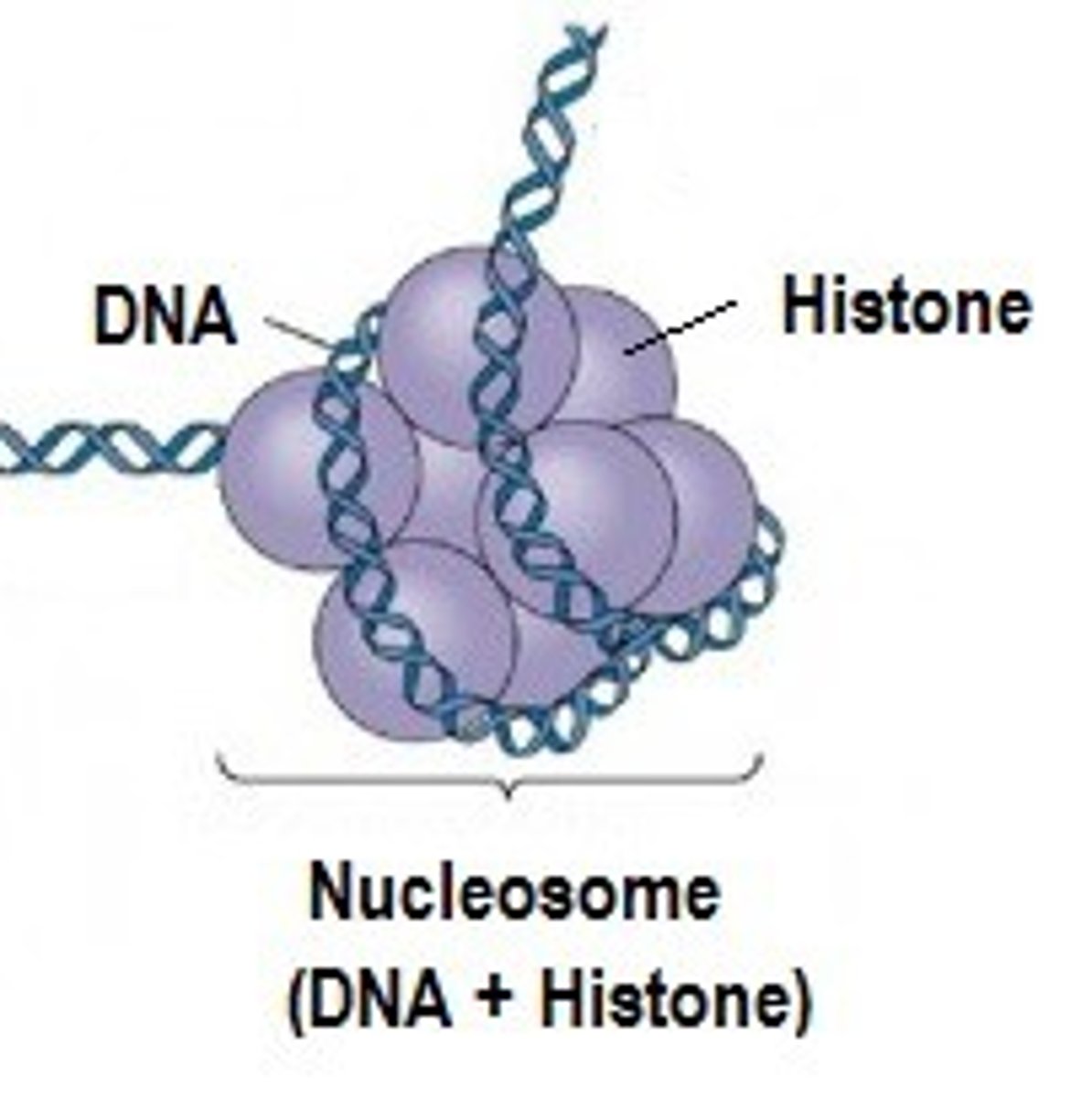
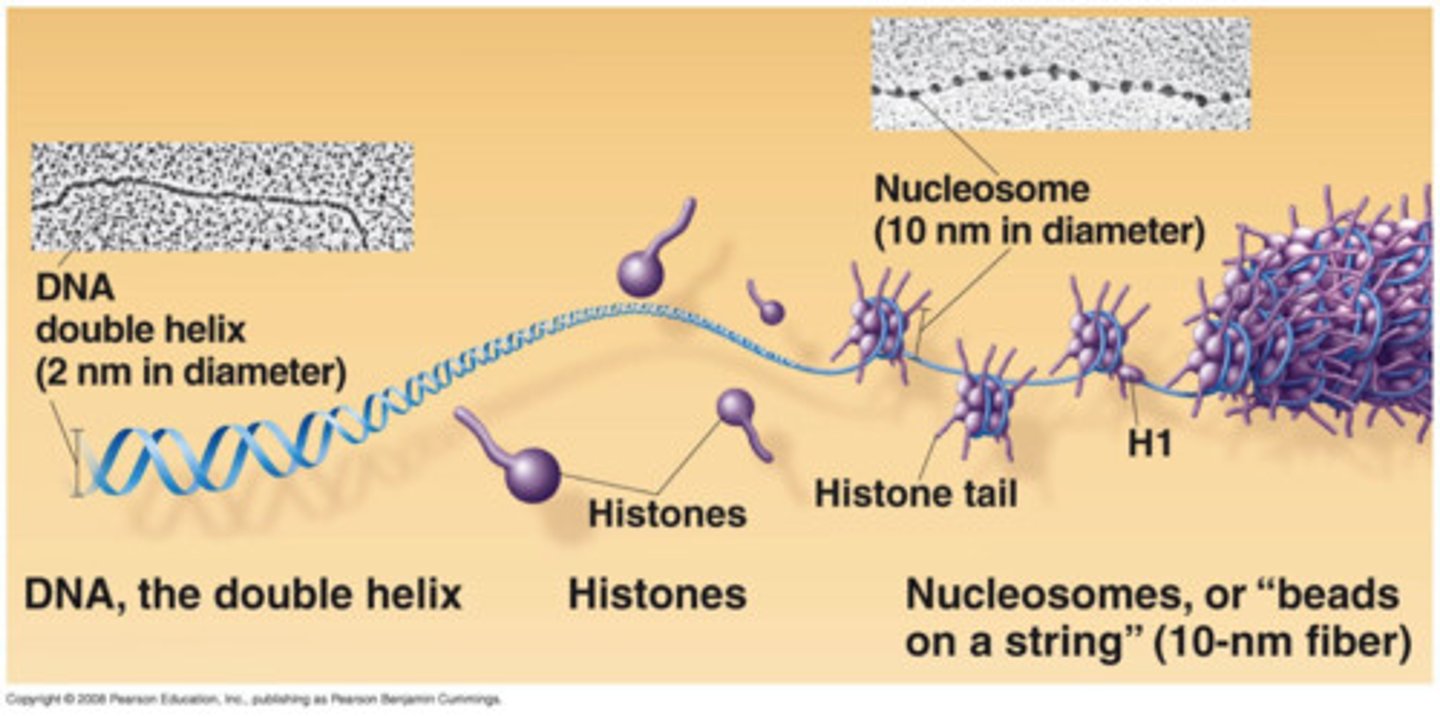
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin. Tightly coiled = harder to express genes.
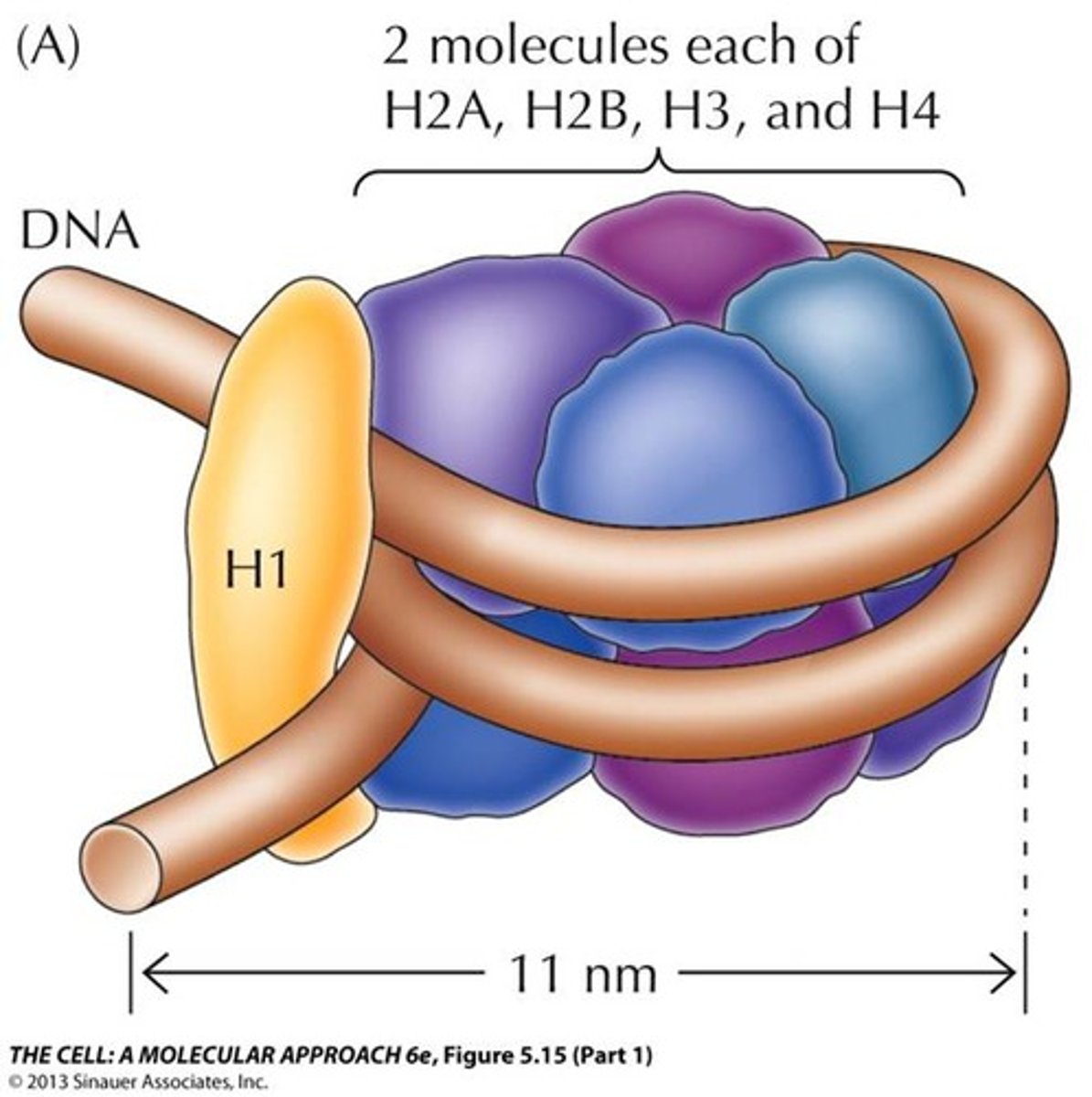
Nucleosomes
Bead-like structures formed by histones and DNA
How to deactivate a gene?
Methylation = deactivation. Makes DNA more coiled, making transcription harder.
How to activate a gene?
Acetylation = activation. Makes it less coiled, easier to transcribe gene.
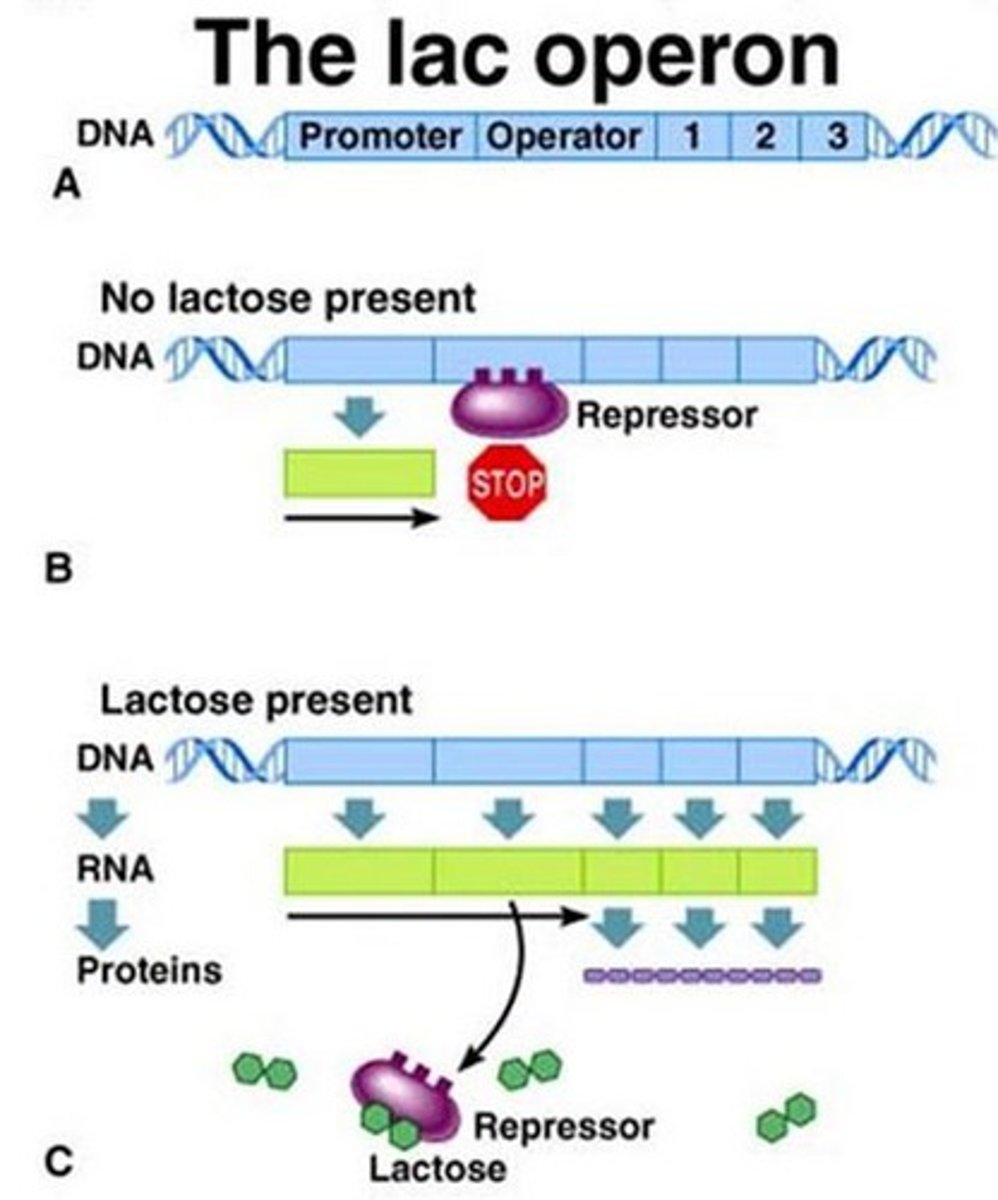
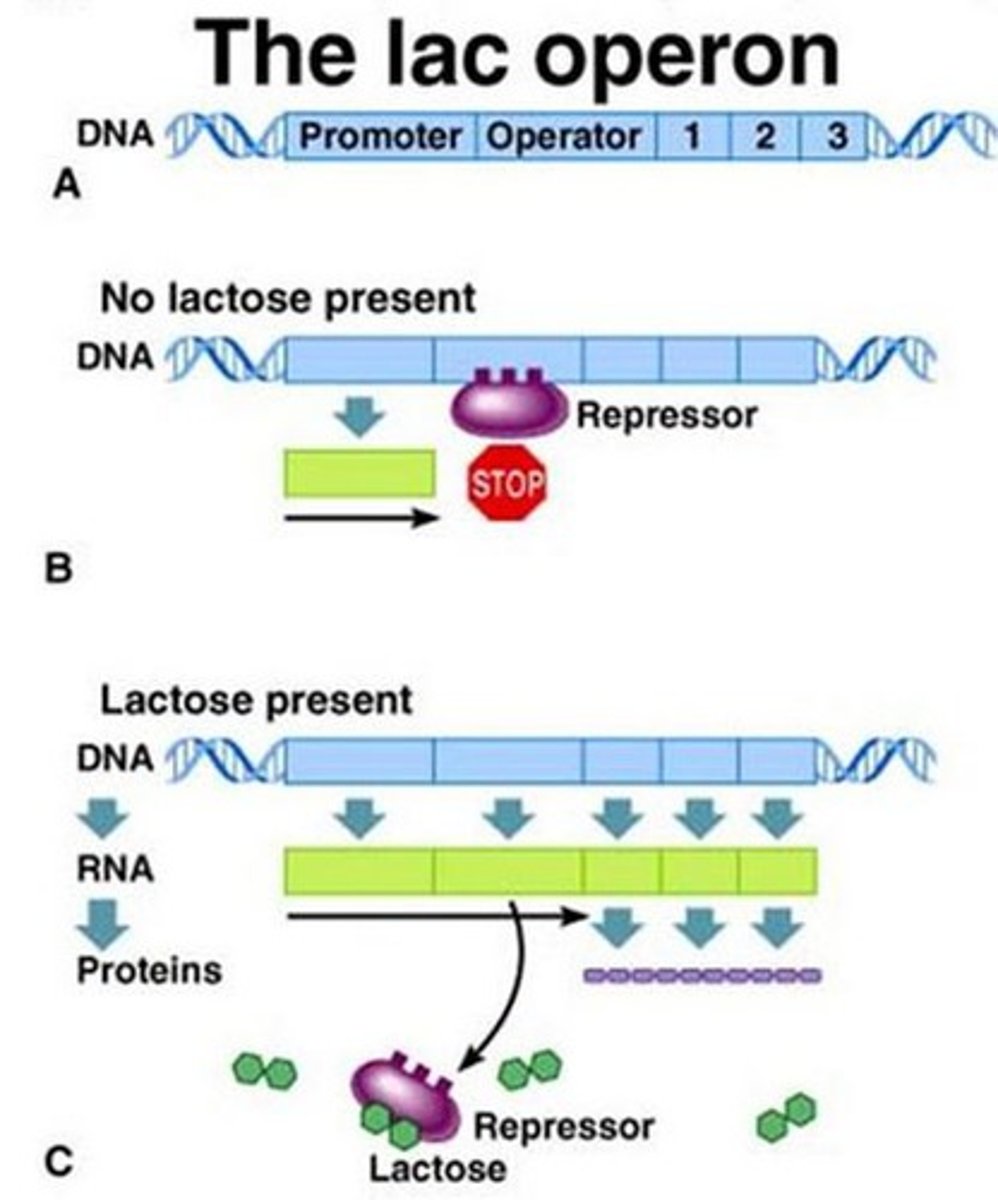
What are the parts of the operon?
Promoter, operator, genes.
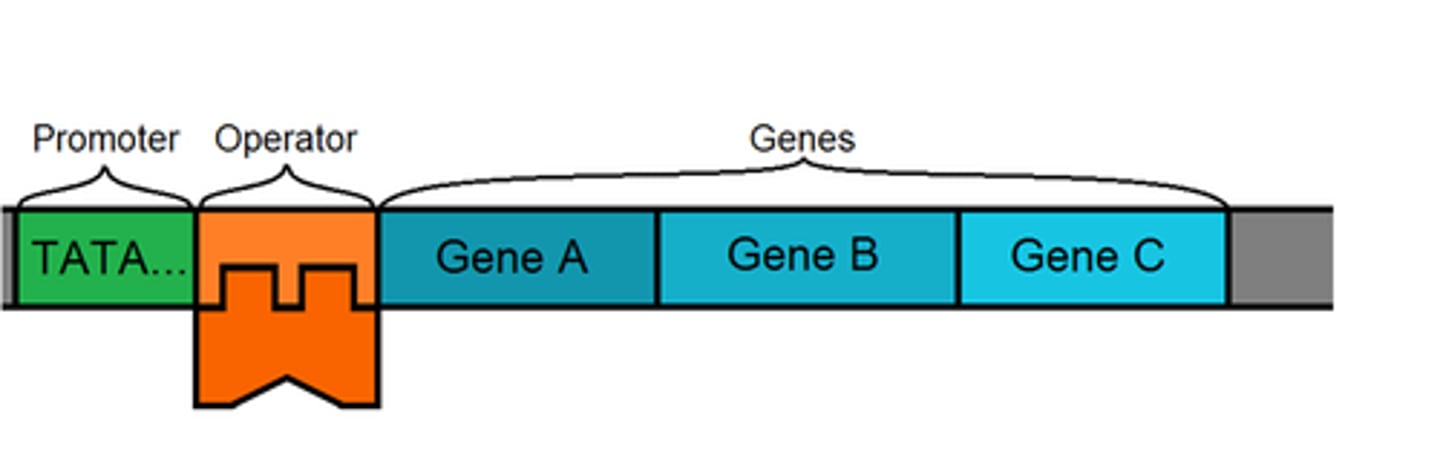
Purpose of enhancers
Transcription factors can bind there and regulate how much the genes are being expressed.
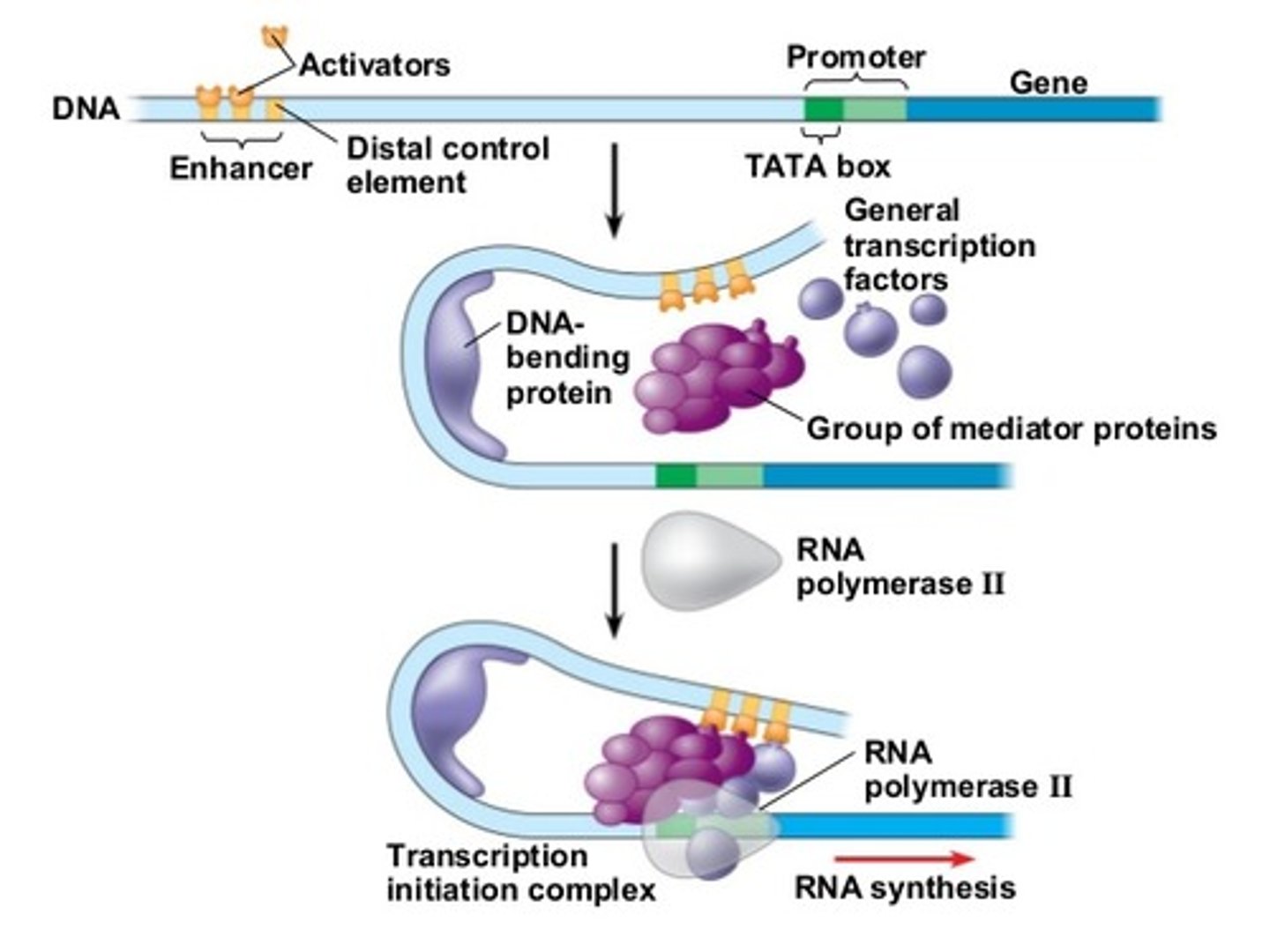
Transcription factors
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes.
Inducible operon
usually off, but can be stimulated (induced) when a specific small molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (example lac operon). Breaks down the molecule.
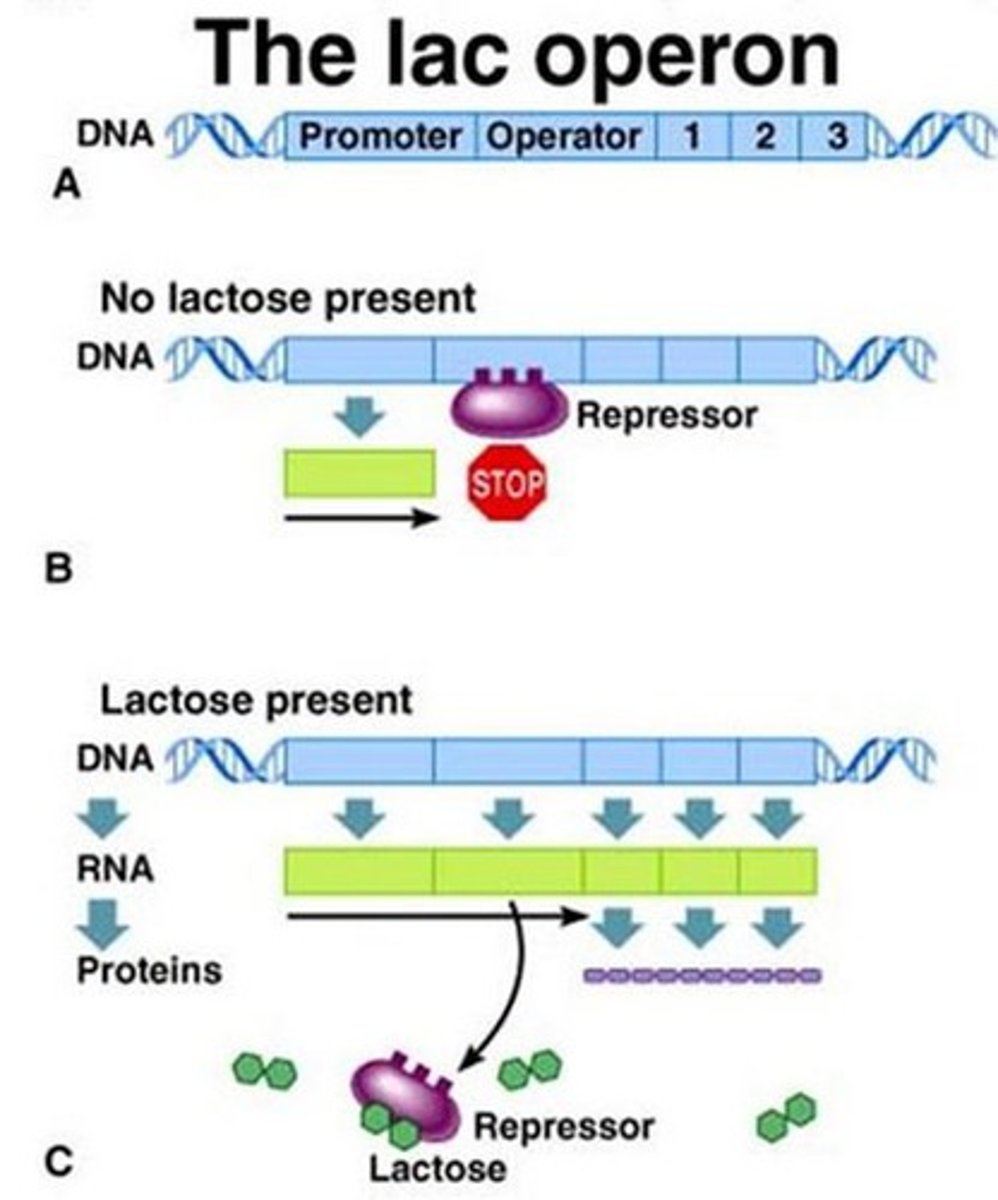
Repressible operon
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a specific small molecule binds allosterically to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan). Creates molecules.
Inducer
A specific small molecule that binds to the repressor, making it unable to bind to the operator.
Repressor
protein that binds to the operator in an operon to switch off transcription
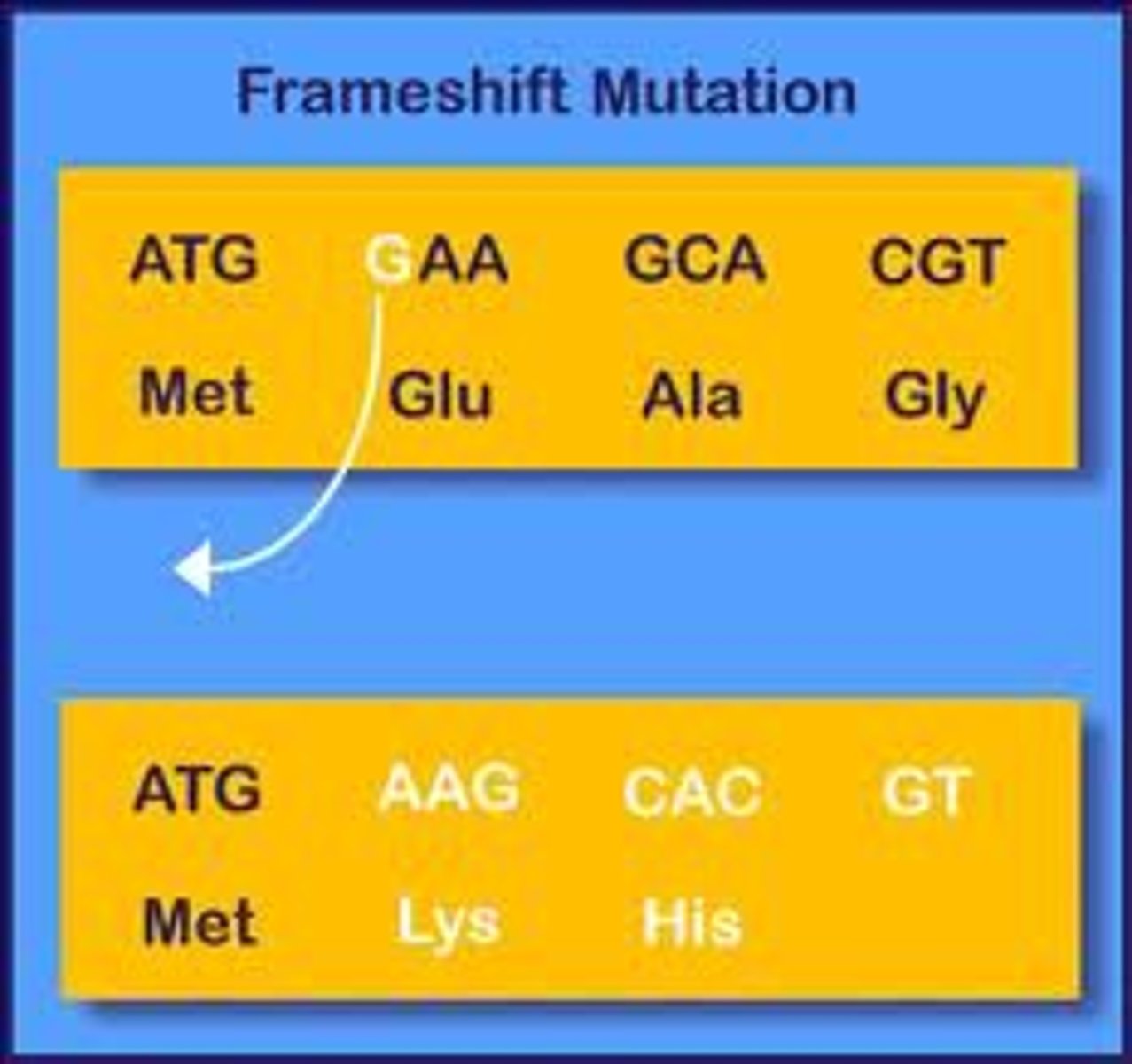
Frameshift mutation
mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence. changes reading frame.
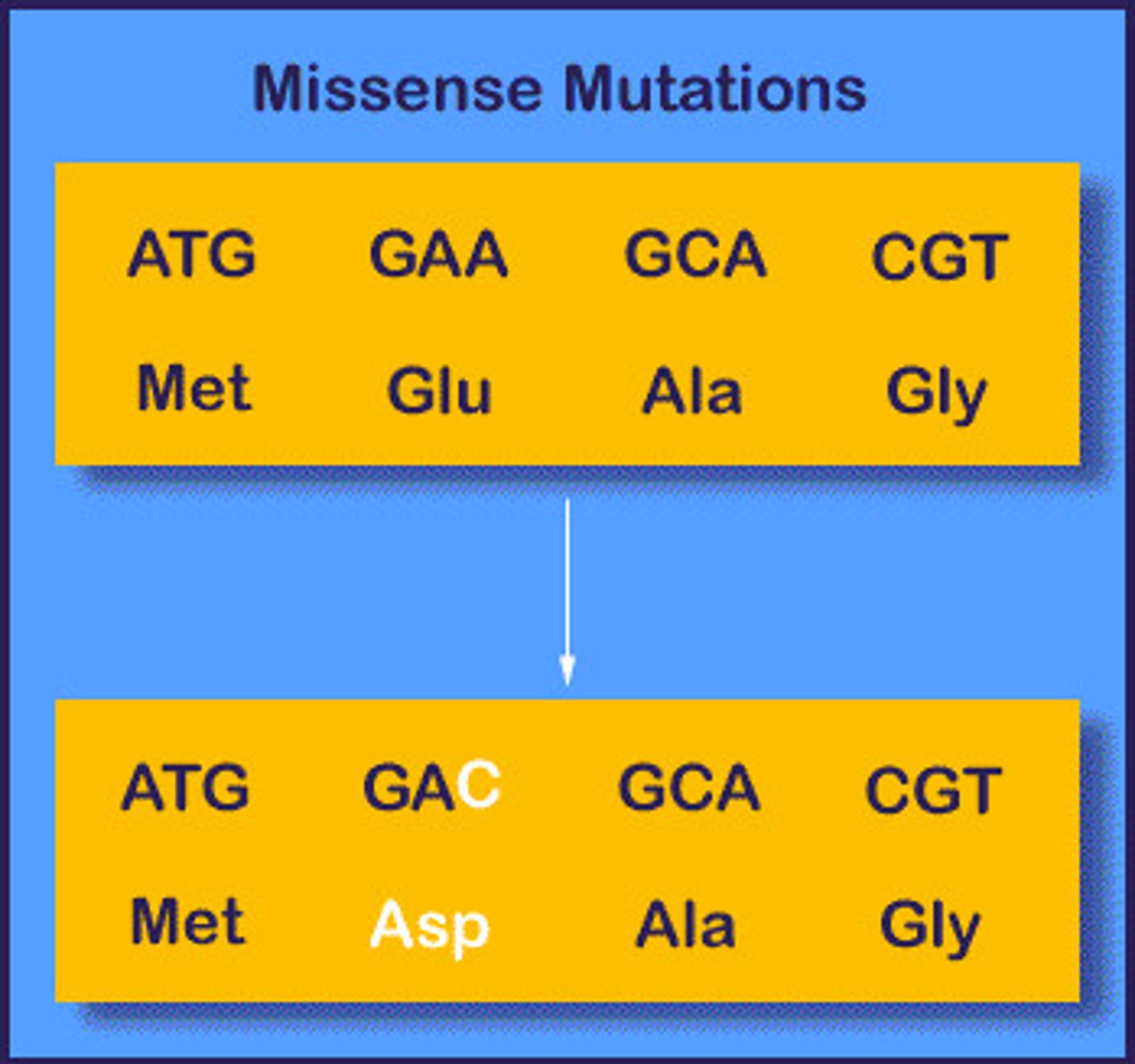
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
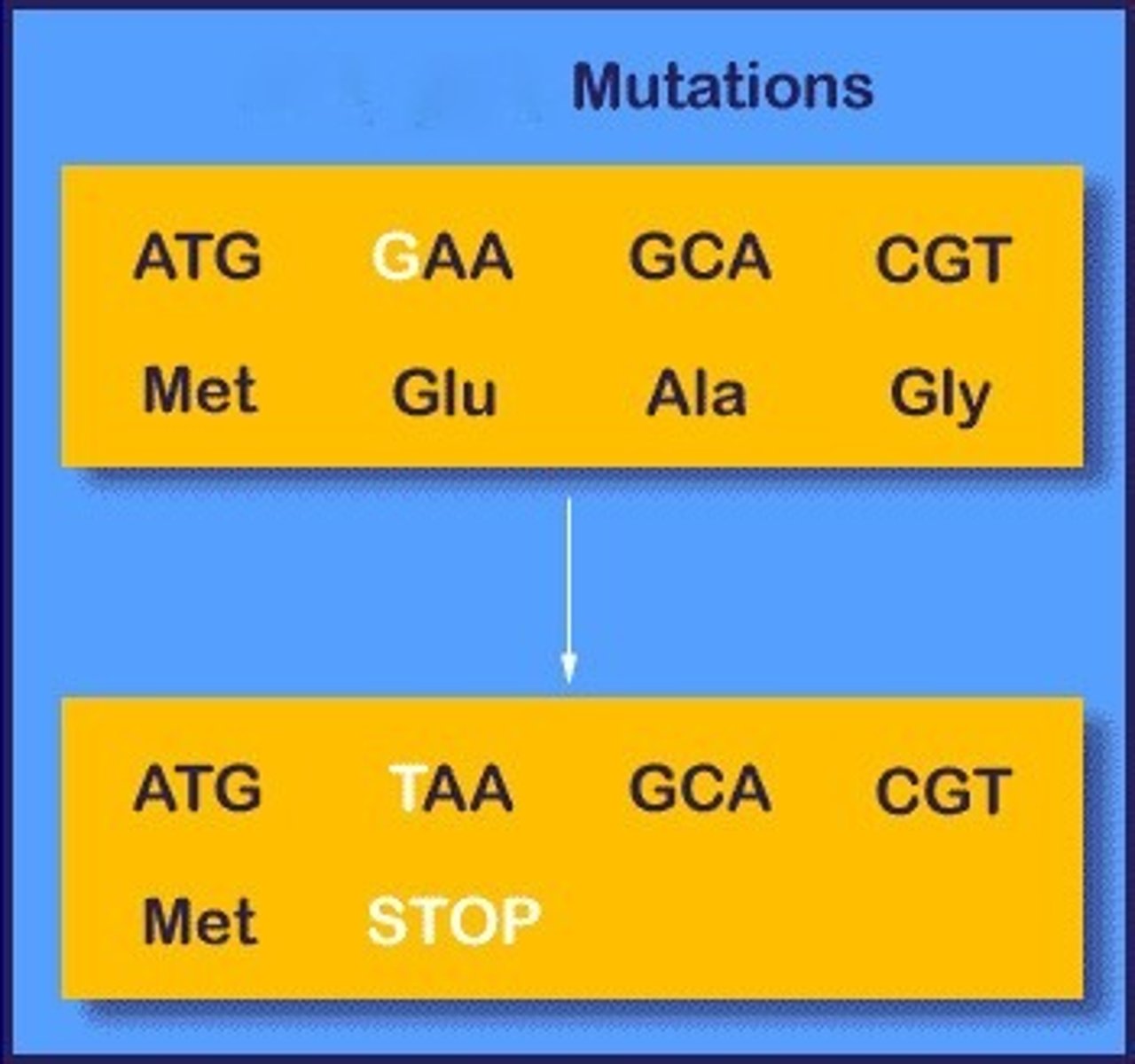
nonsense mutation
changes a normal codon into a stop codon
Mutations and genetic diversity
Organisms with a trait that makes them survive allows for them to reproduce and pass this trait to the next generation
What are the three processes that allow genetic diversity in bacteria?
Transduction, transformation and conjugation
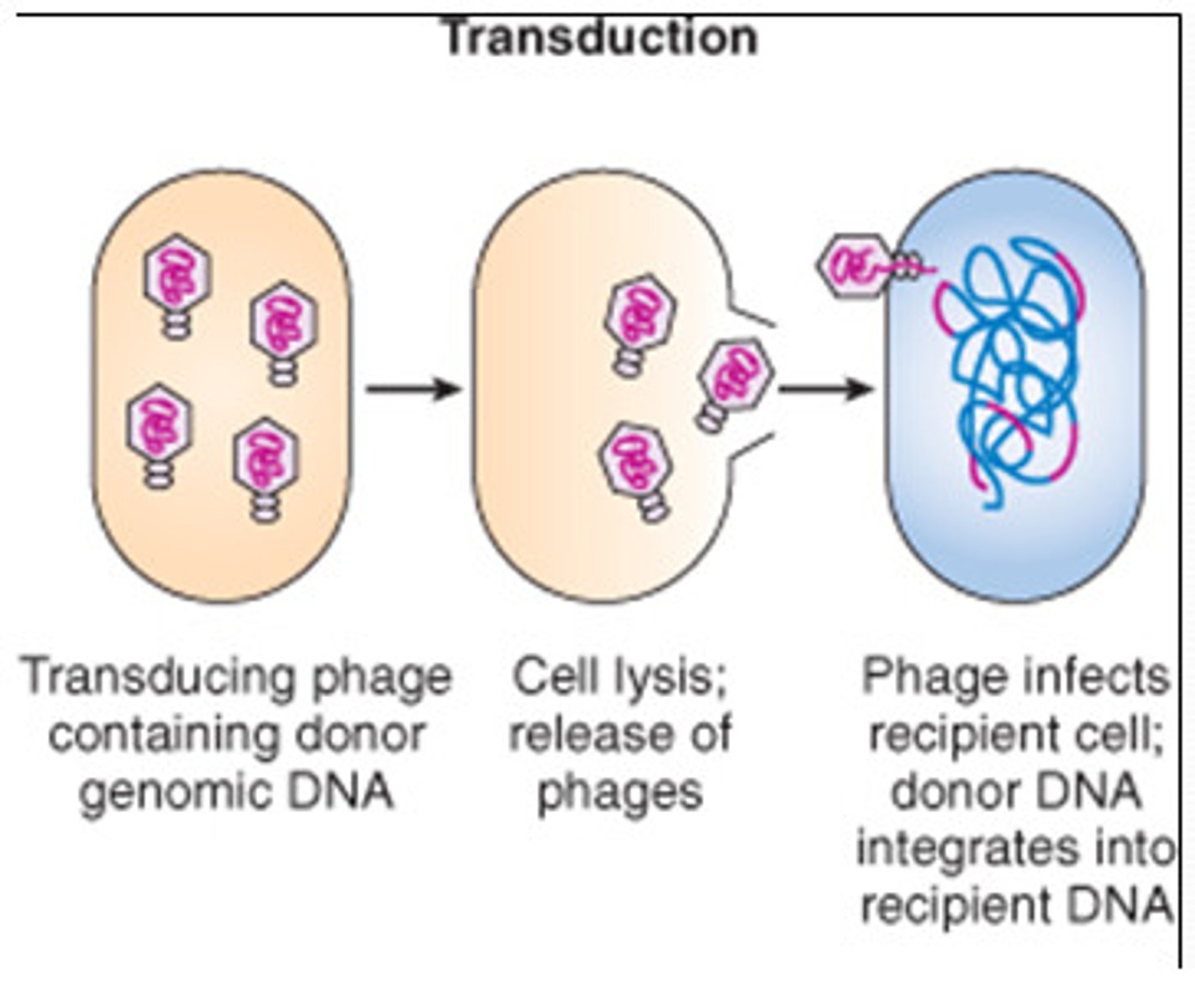
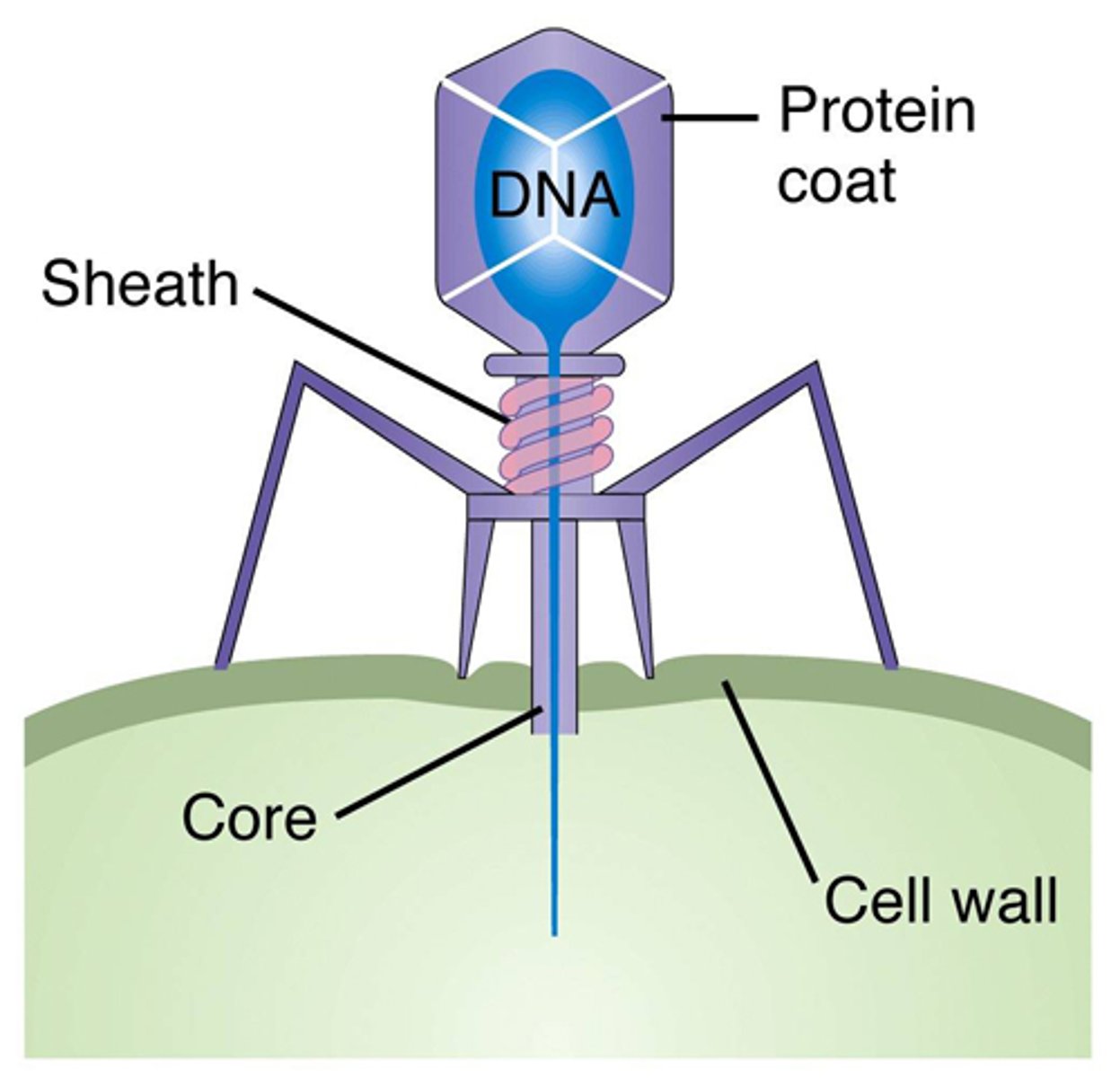
Transduction in bacteria
DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient via a bacteriophage
Transformation in bacteria
bacteria takes in genes from their environment
Conjugation in bacteria
Bacterial cells can join together and pass plasmid DNA from one bacterial cell to another.
Name some uses of biotechnology
Gene cloning, PCR, gel electrophoresis, DNA sequencing

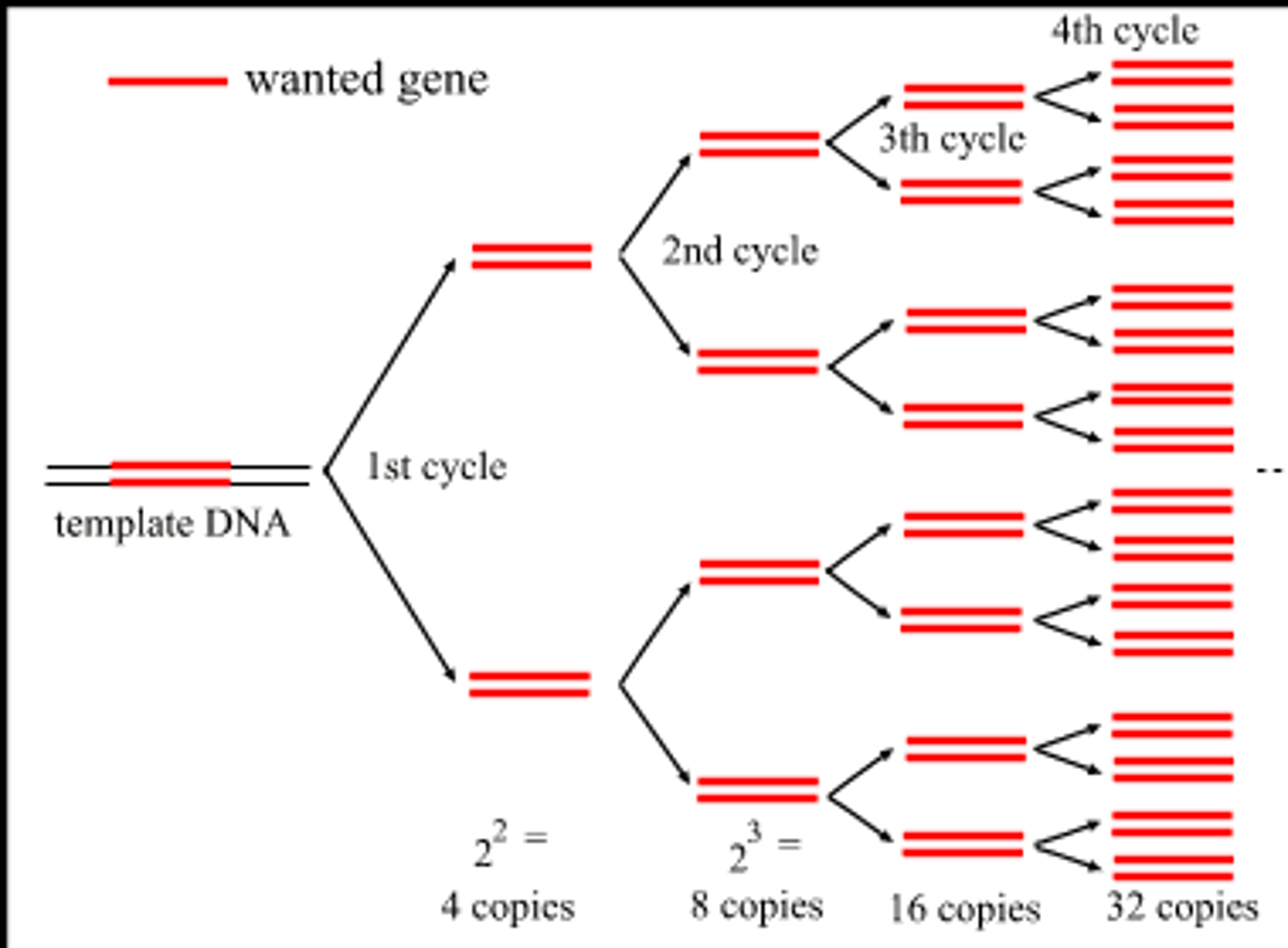
PCR
a method used to rapidly make multiple copies of a specific segment of DNA; can be used to make millions of copies of DNA from a very small amount of DNA. AMPLIFY!!!!!
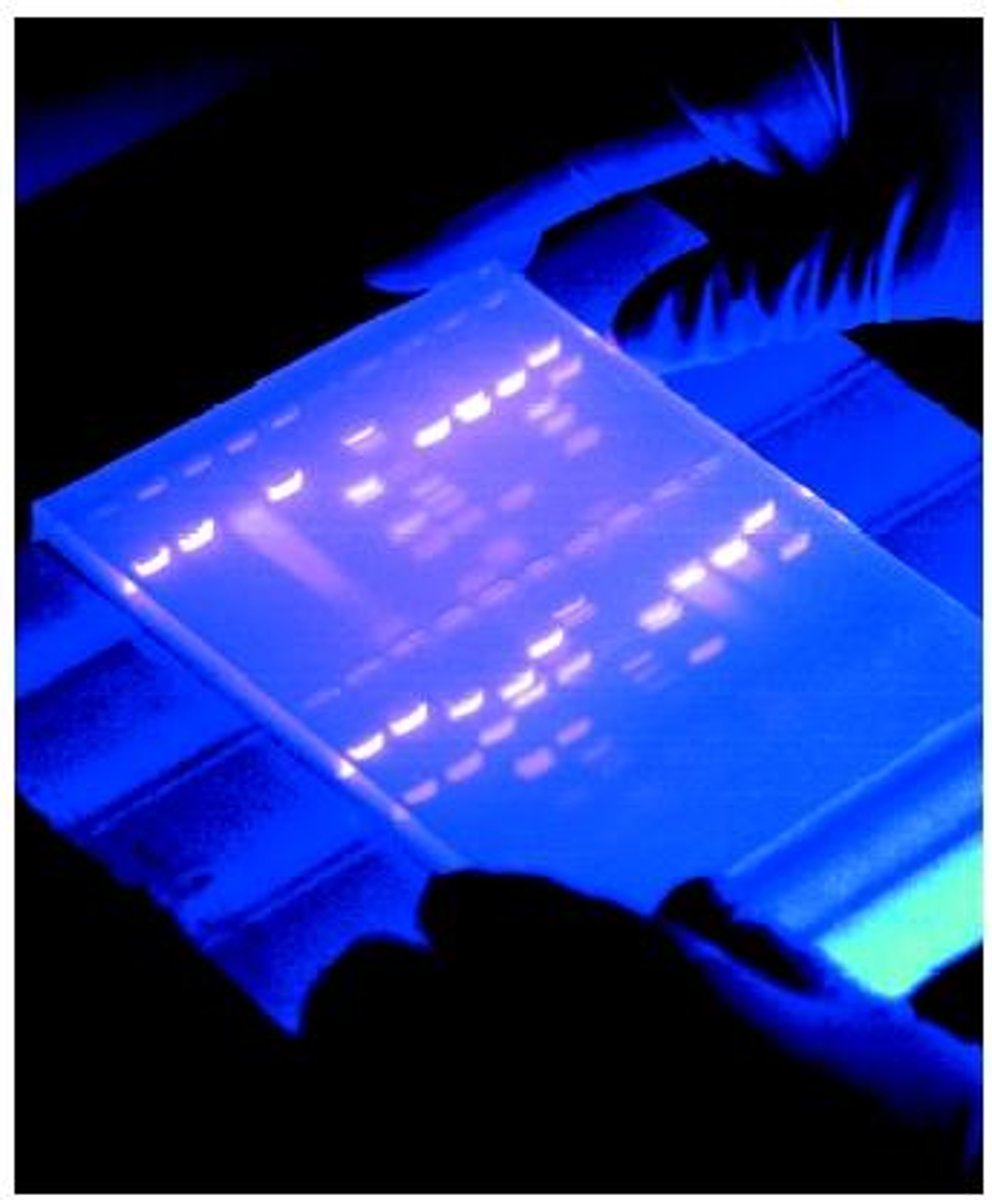
gel electrophoresis
separates DNA molecules according to size and charge.
DNA sequencing
Determining the exact order of the base pairs in a segment of DNA.
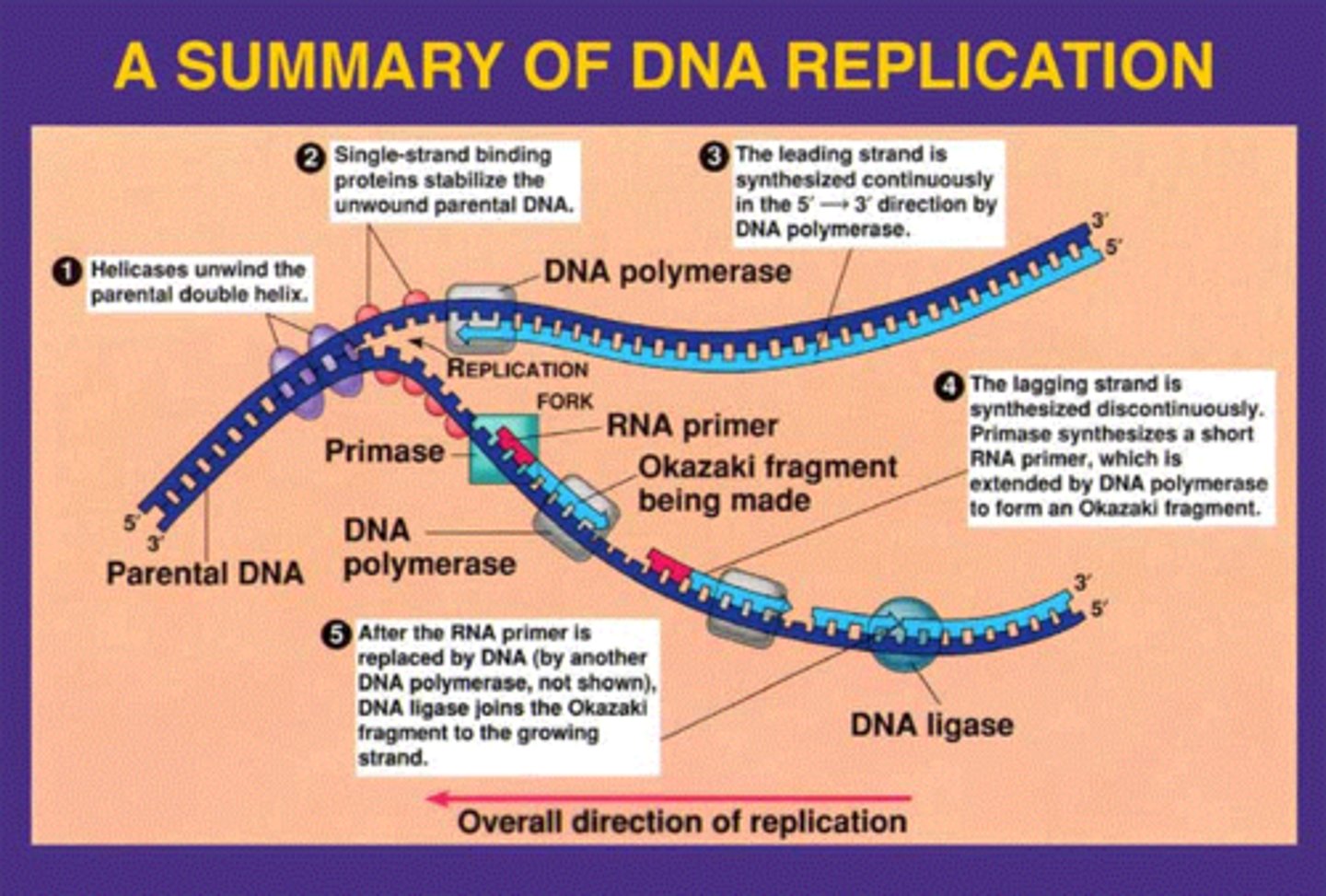
Summarize DNA replication
- Helicase opens up the DNA at the replication fork.
- Single-strand binding proteins coat the DNA around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of the DNA.
- Topoisomerase works at the region ahead of the replication fork to prevent supercoiling.
- Primase synthesizes RNA primers complementary to the DNA strand.
- DNA polymerase III extends the primers, adding on to the 3' end, to make the bulk of the new DNA.
- RNA primers are removed and replaced with DNA by DNA polymerase I.
- The gaps between DNA Okazaki fragments are sealed by DNA ligase.
What direction is the leading strand formed?
Toward the replication fork in an unbroken, linear fashion
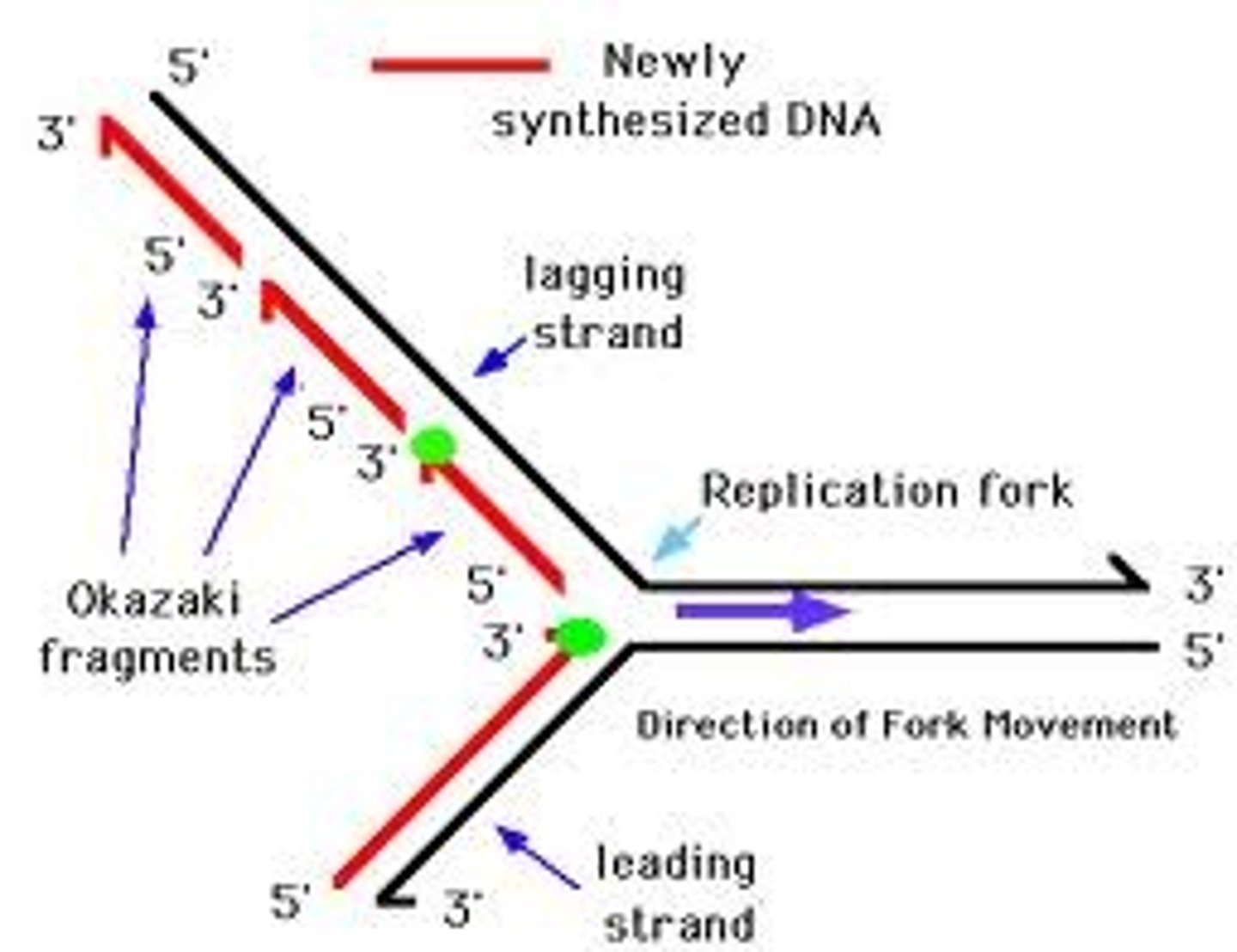
What direction is the lagging strand formed?
Away from the replication fork in a series of fragments called Okazaki fragments
RNA primer
pre-existing chain made of RNA to which DNA nucleotides are added
Origin of replication
Site where the replication of a DNA molecule begins.
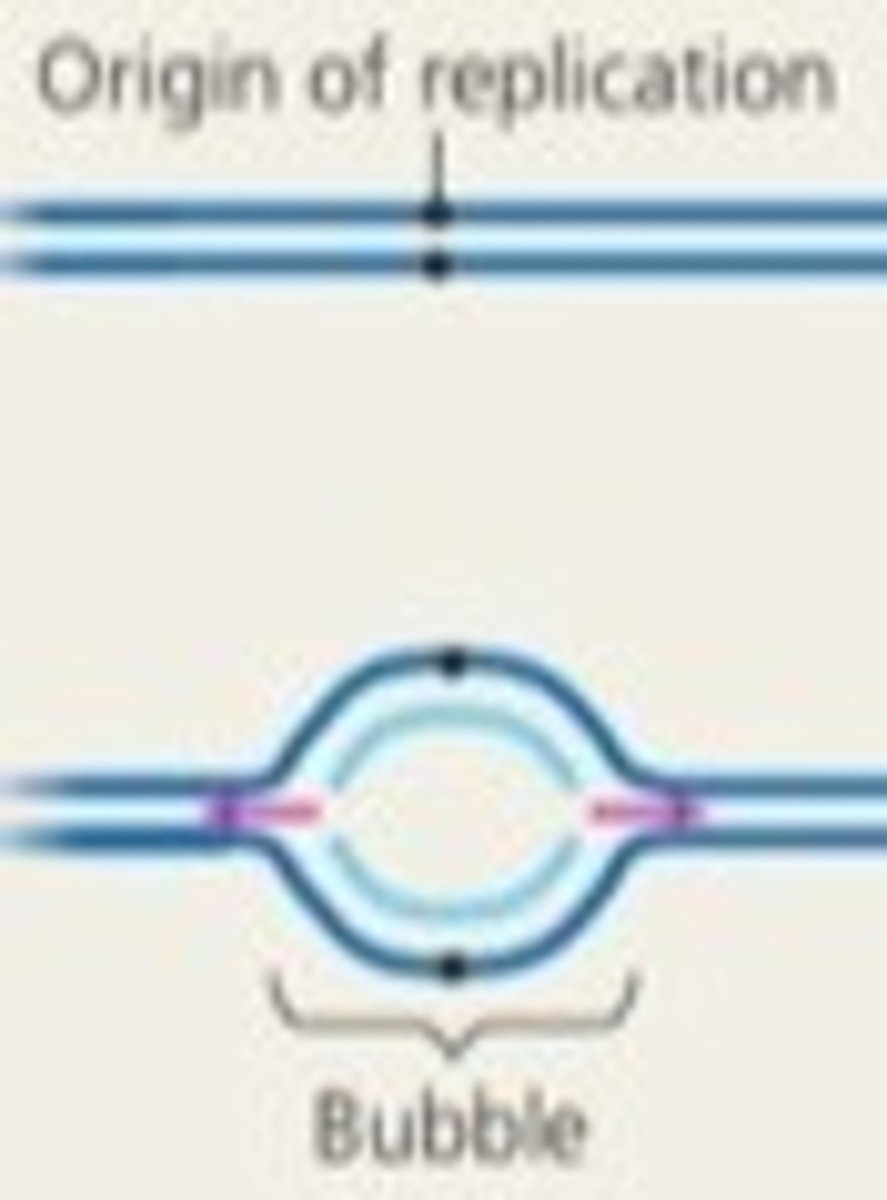
Replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing. Located at the end of each replication bubble.
Function of DNA polymerase
- attach free floating nucleotides to the 3' of a preexisting chain
- carry out mismatch repair; proofreading that corrects errors. damaged regions are cut out by DNA nuclease.
What does DNA nuclease do?
Cut out damaged regions of DNA
Summarize transcription
Initiation: After RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, the DNA strands unwind and the polymerase initiates RNA synthesis at the start point on the template strand
Elongation: The polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript 5'-3'. Because of transcription, the DNA strands re-form a double helix
Termination: Eventually, the RNA transcript is released and the polymerase detaches from the DNA
Roles of the Three Types of RNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
- Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) transfer amino acids to protein chain
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) protein production
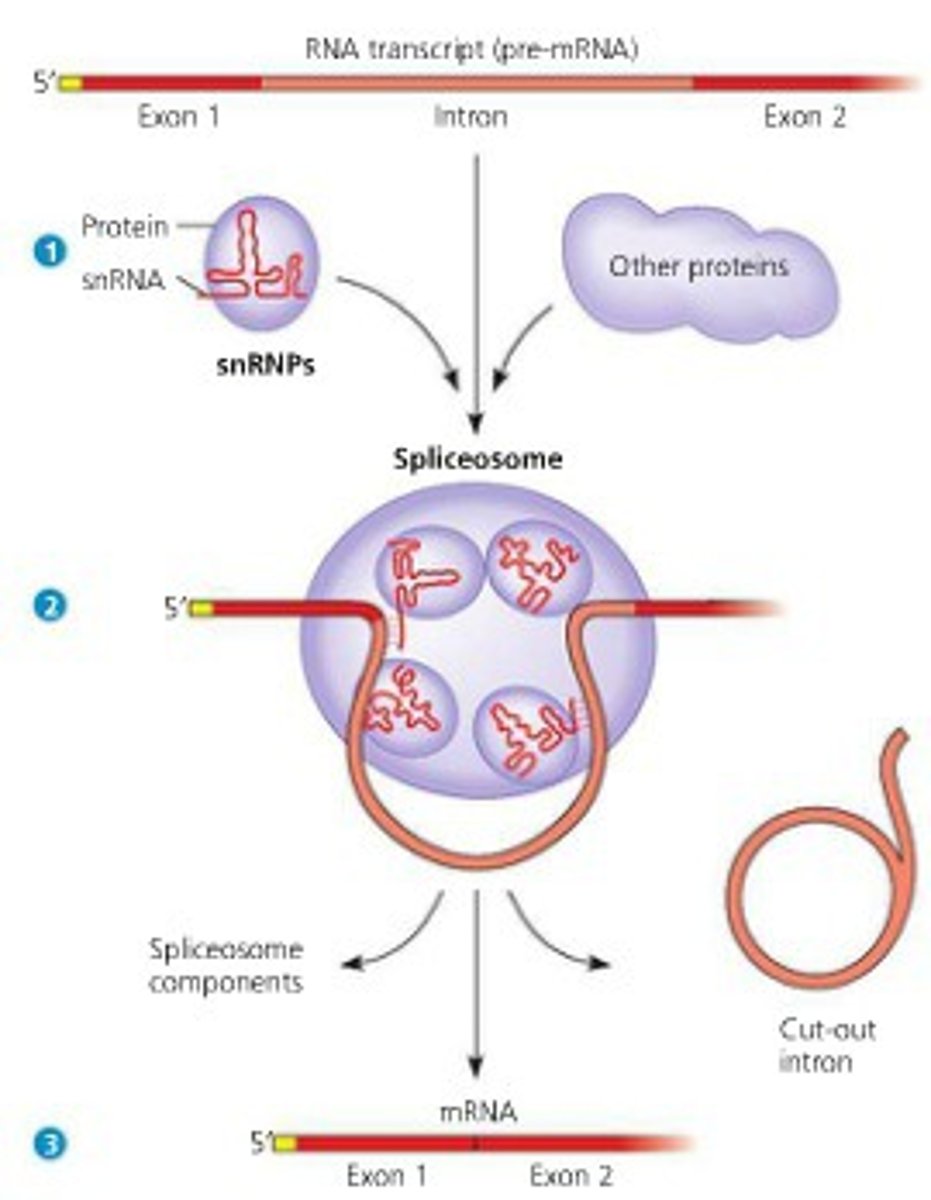
What is RNA splicing?
removal of introns and joining of exons
Summarize translation
- Small subunit attaches to mRNA, then the large.
- tRNA with correct anticodon arrives at the A site, peptide bond will be formed in a growing chain of amino acids.
-Ribosomes move using ATP, tRNA translocates to next site, exits from E site.
- When stop codon is reached, a release factor causes the peptide to be released and the ribosome to fall apart.
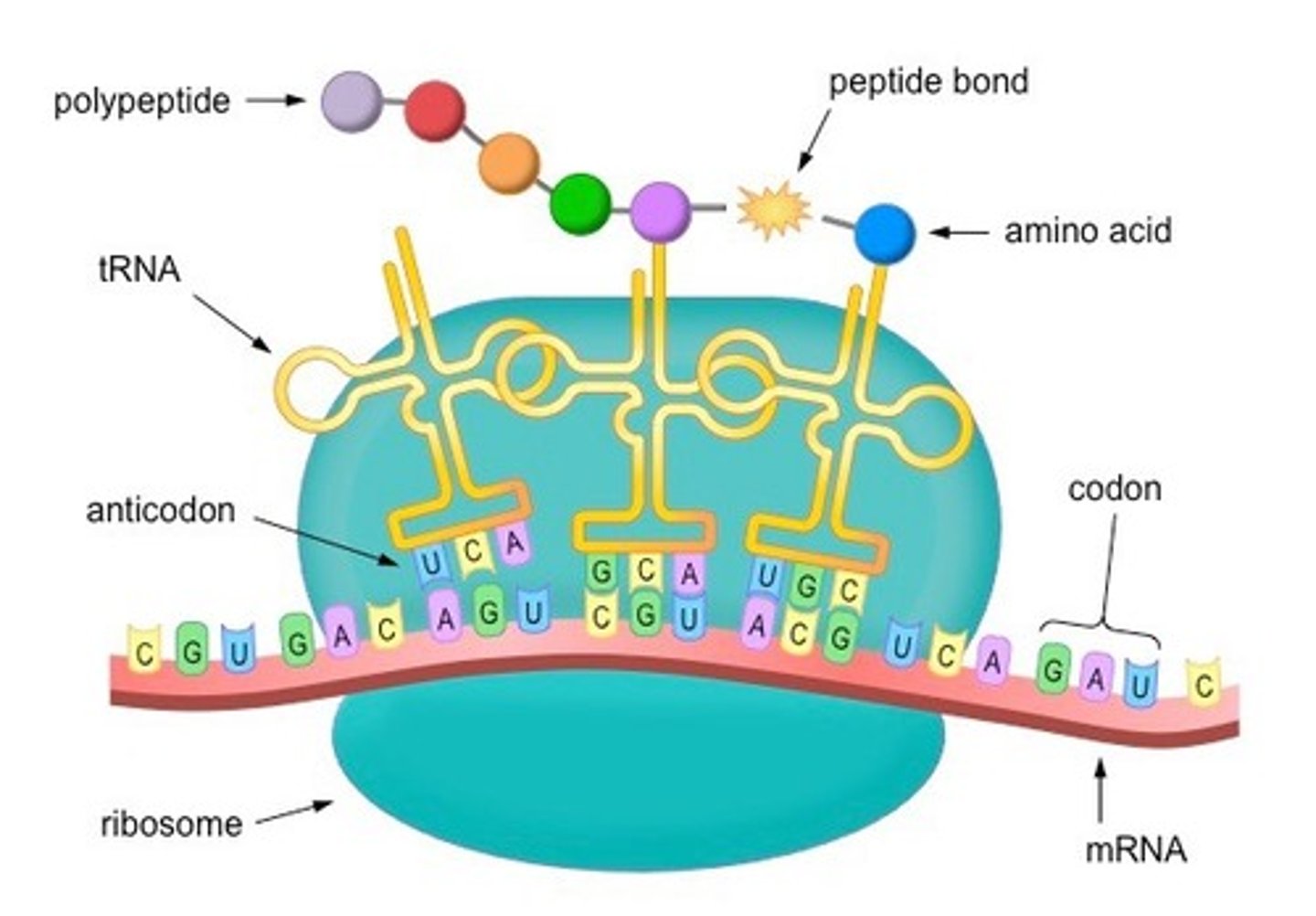
What do release factors do?
Cause the ribosome and new protein to break off of the mRNA strand
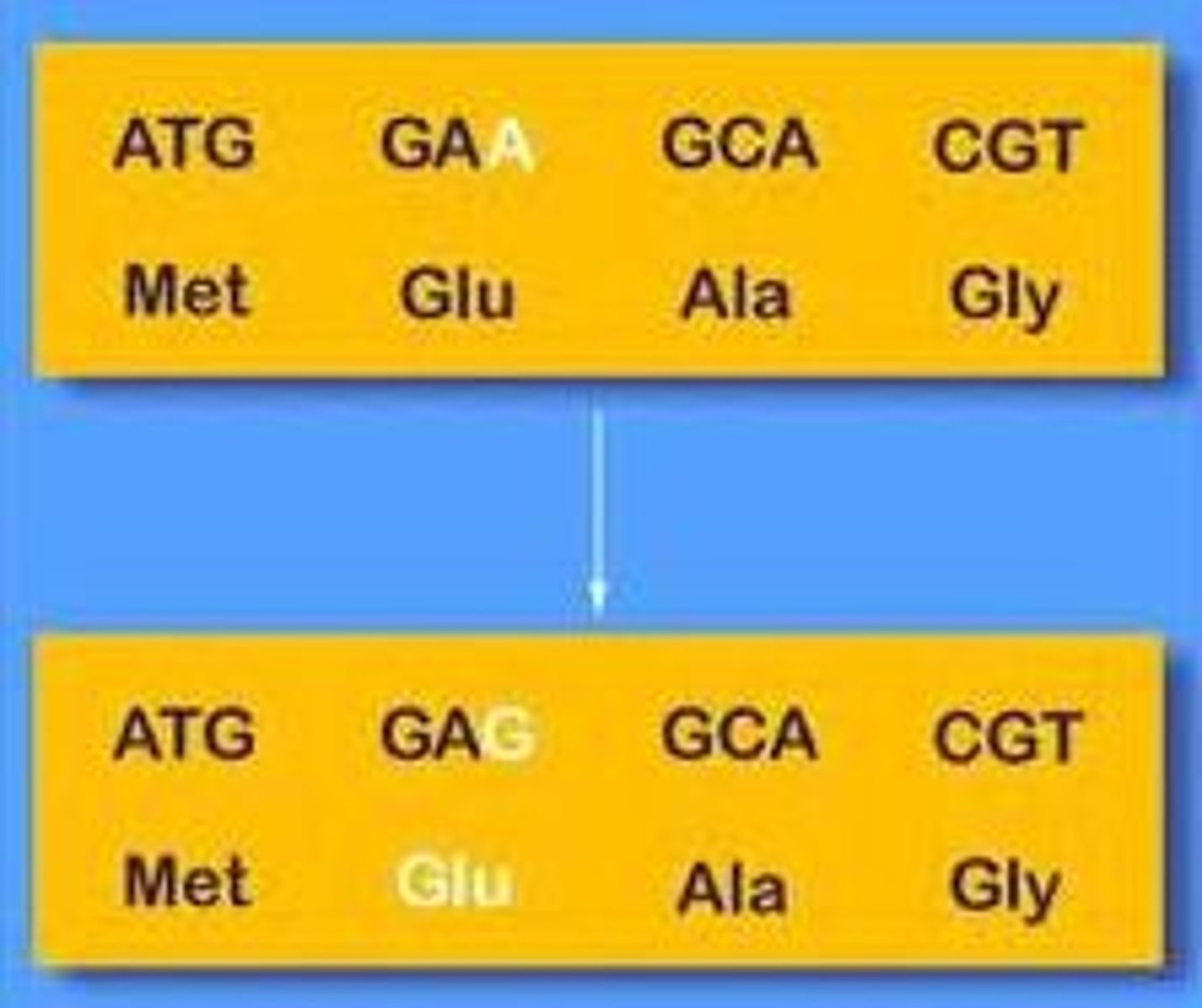
Silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
bacteriophages (phages)
viruses that infect bacteria
DNA Primase
synthesis of RNA primer. Once there is a primer, DNA polymerase starts adding nucleotides.
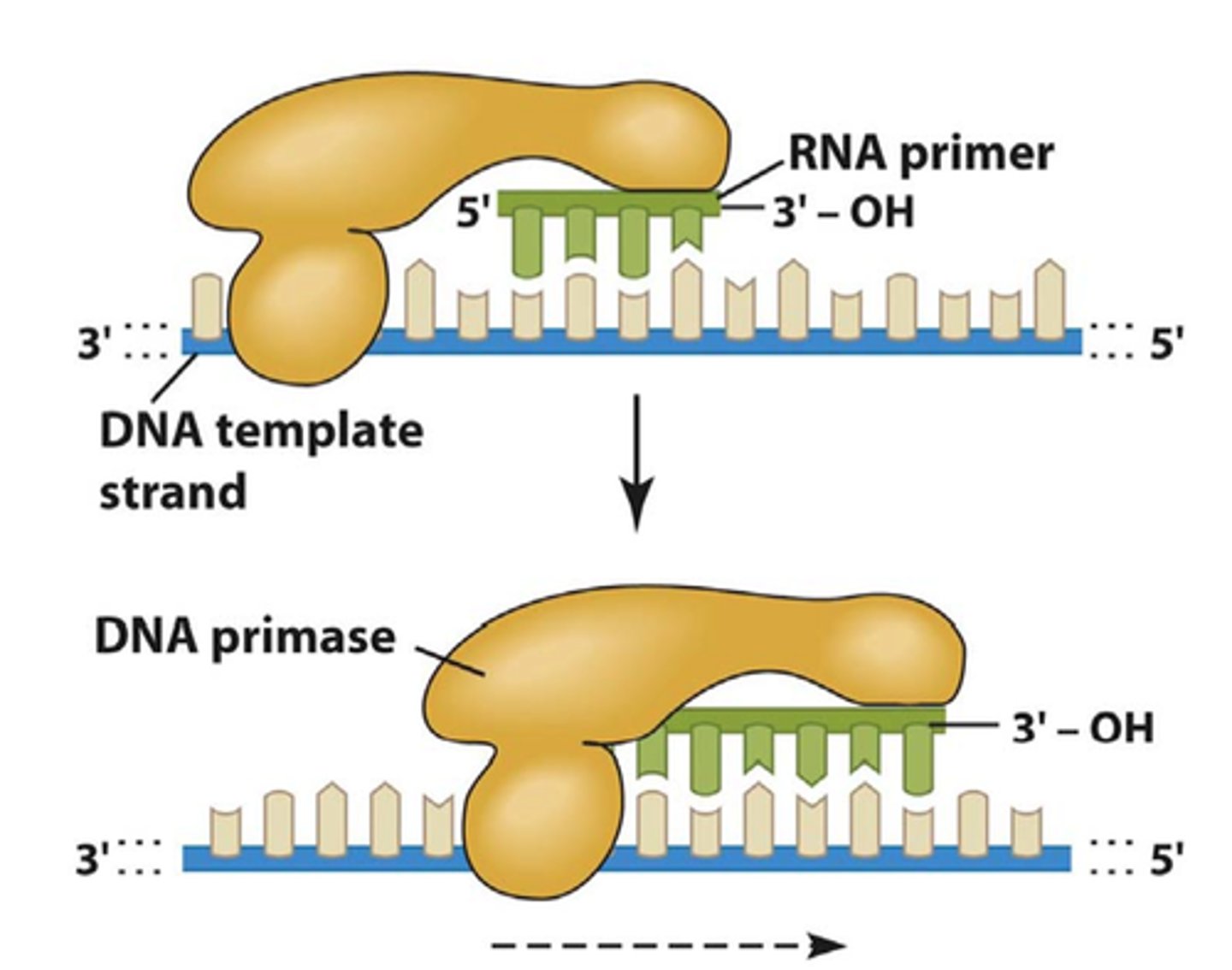
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. (follows the unzipped DNA molecule basically).
coding strand vs RNA vs template strand
Template strand: Original strand that is essentially converted
Coding strand: Uses template strand to convert to its complimentary strand with thymine
mRNA: Uses template strand to convert to its complimentary strand with uracil
When does mature mRNA form?
When the introns are spliced out of the pre-mRNA, it becomes mature mRNA with the exons joined together.
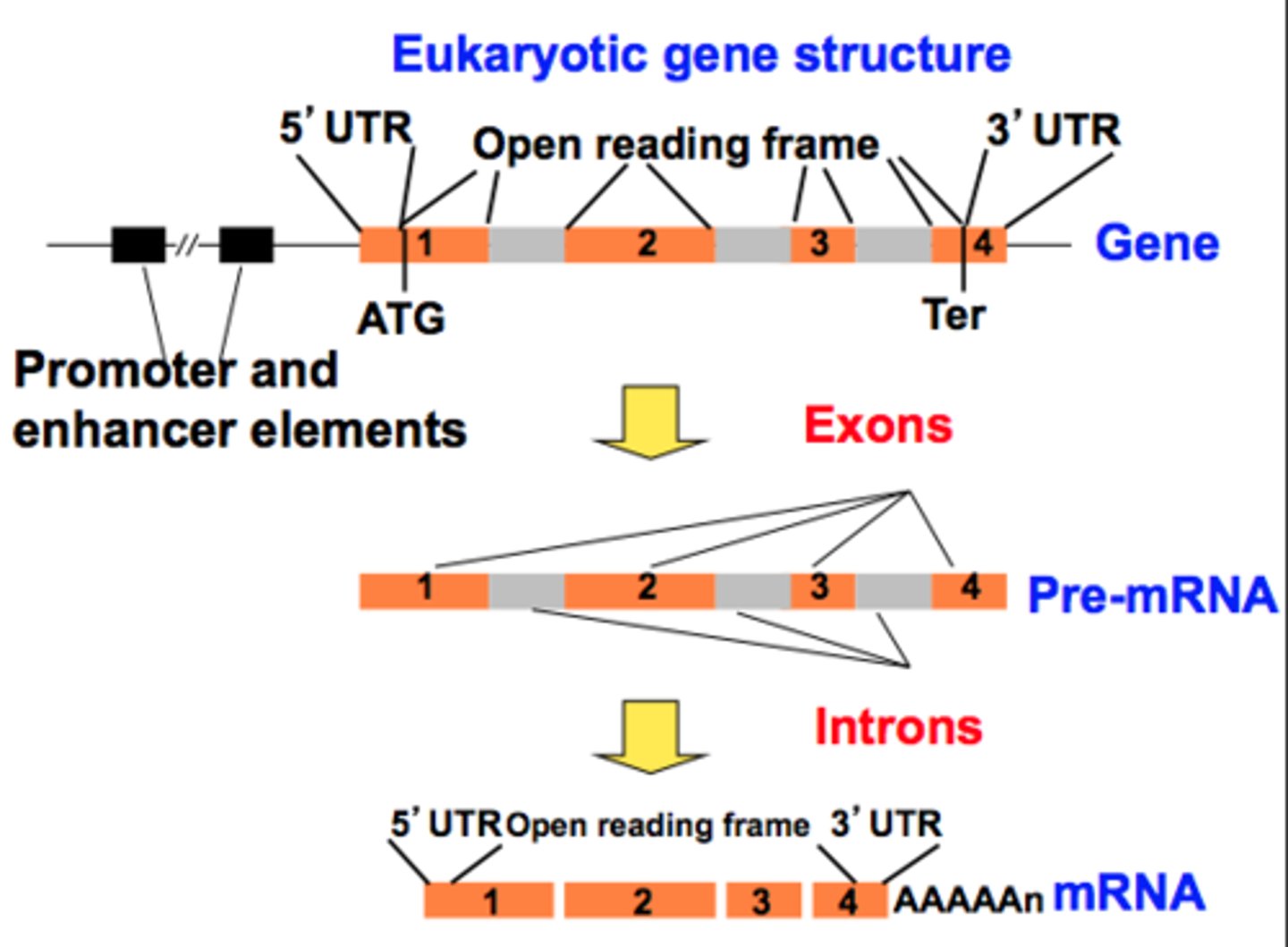
purpose of 5' cap and poly-A tail
1) facilitate export from the nucleus
2) protect against degradation from exonucleases
3) promotes ribosomal binding
(essentially stabilizes the mRNA for translation)
What direction does RNA polymerase synthesize mRNA?
5' to 3'
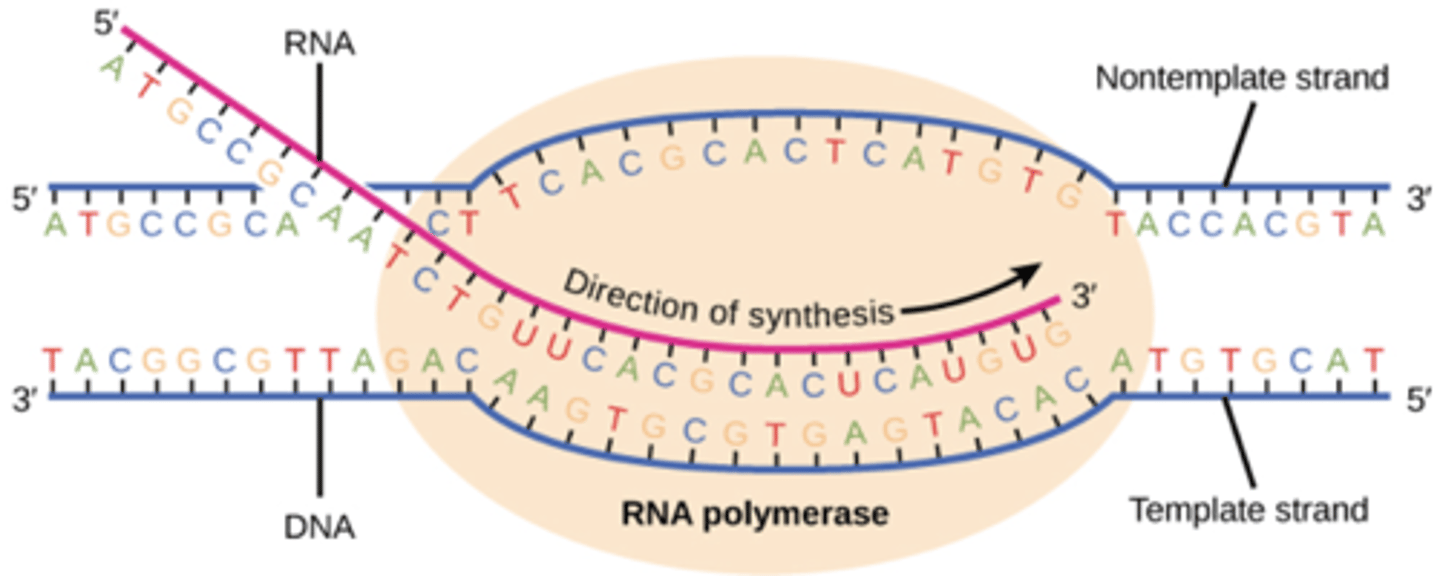
What is the template strand also called?
non-coding strand, antisense strand or minus strand
Translation and transcription in prokaryotes
Happens simultaneously. Translation of mRNA occurs while it is being transcribed
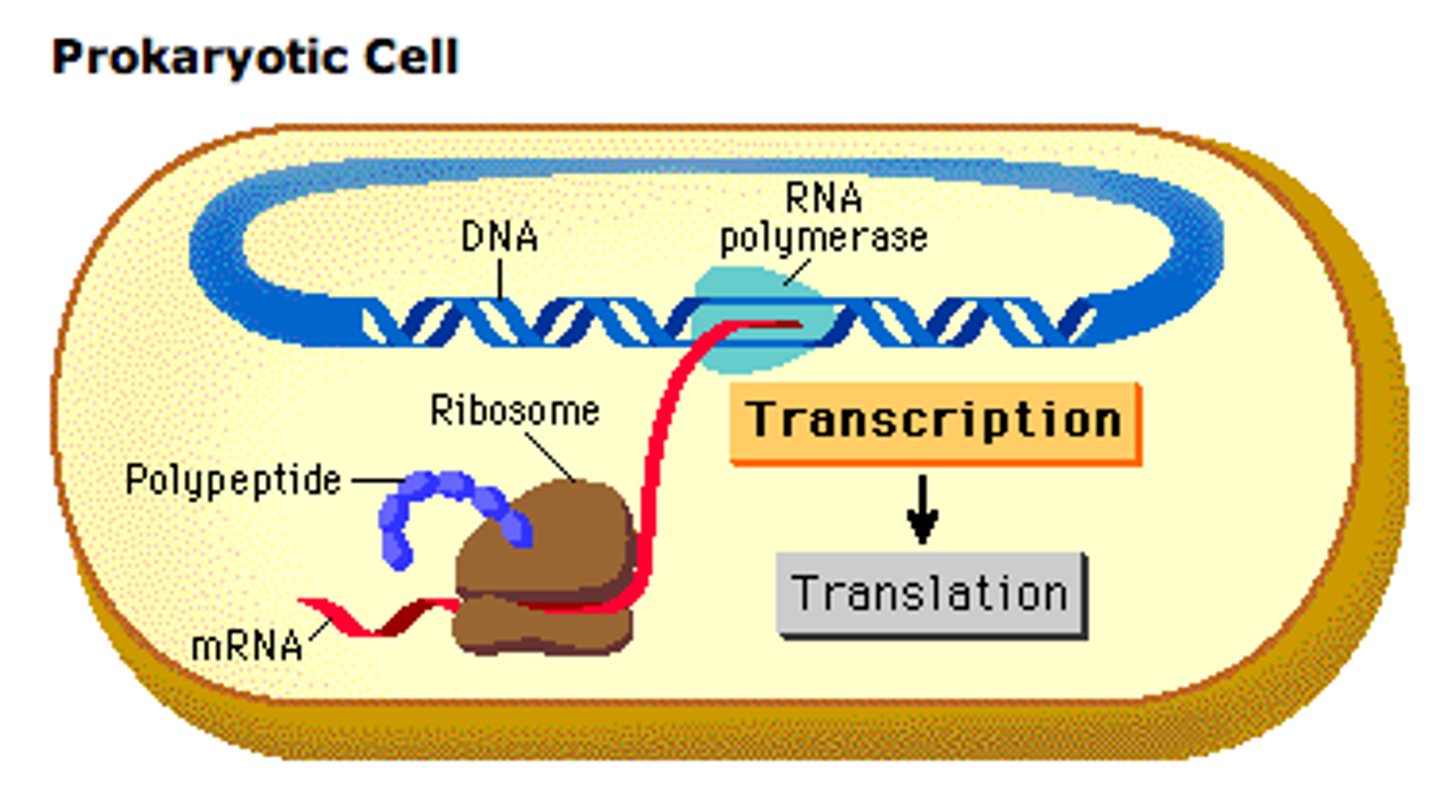
Genetic code
the nucleotide triplets of DNA and RNA molecules that carry genetic information in living cells. All organisms share the same genetic code.
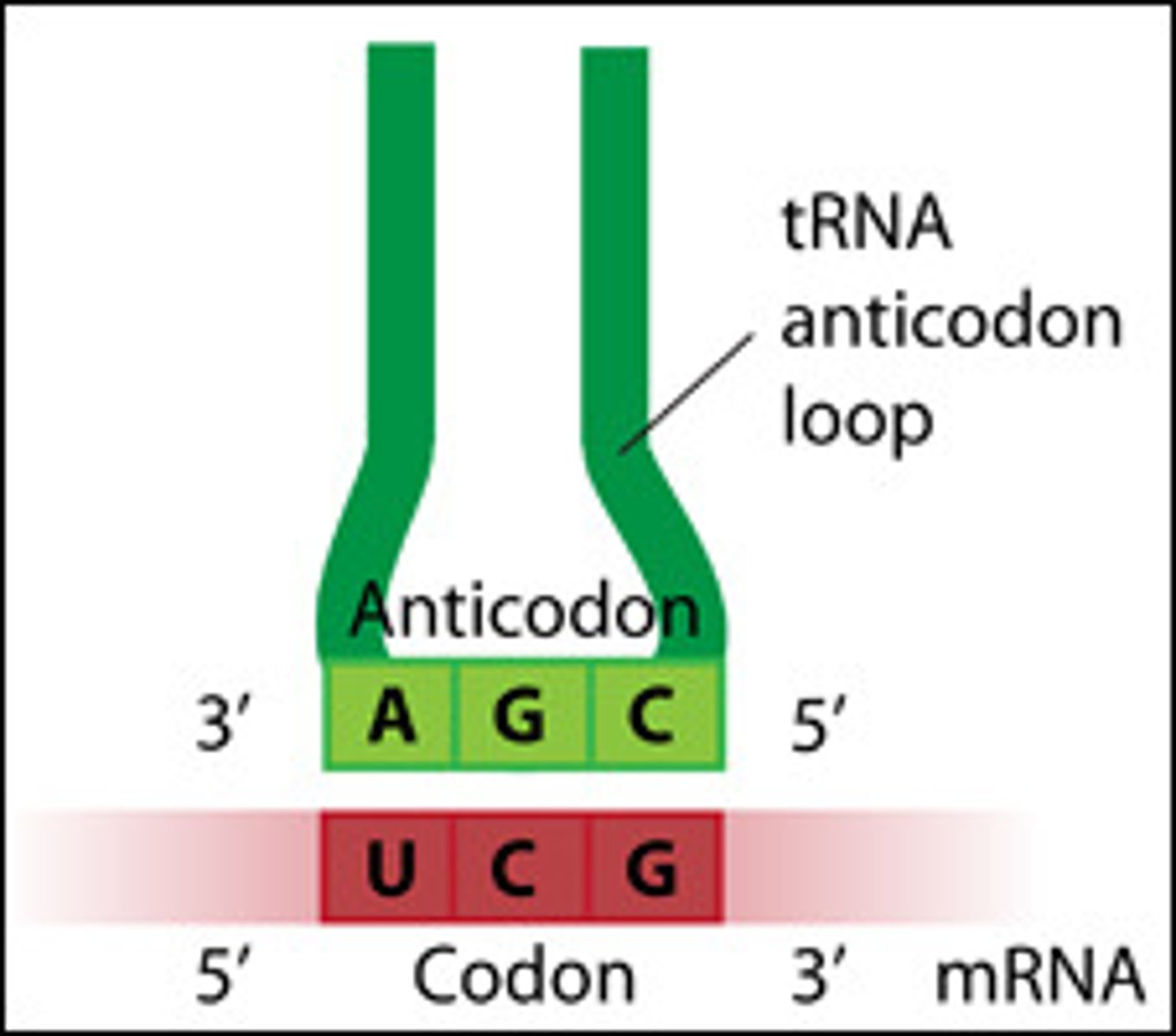
Function of tRNA
carries an amino acid to its correct codon on the ribosome specified by the codon on the mRNA
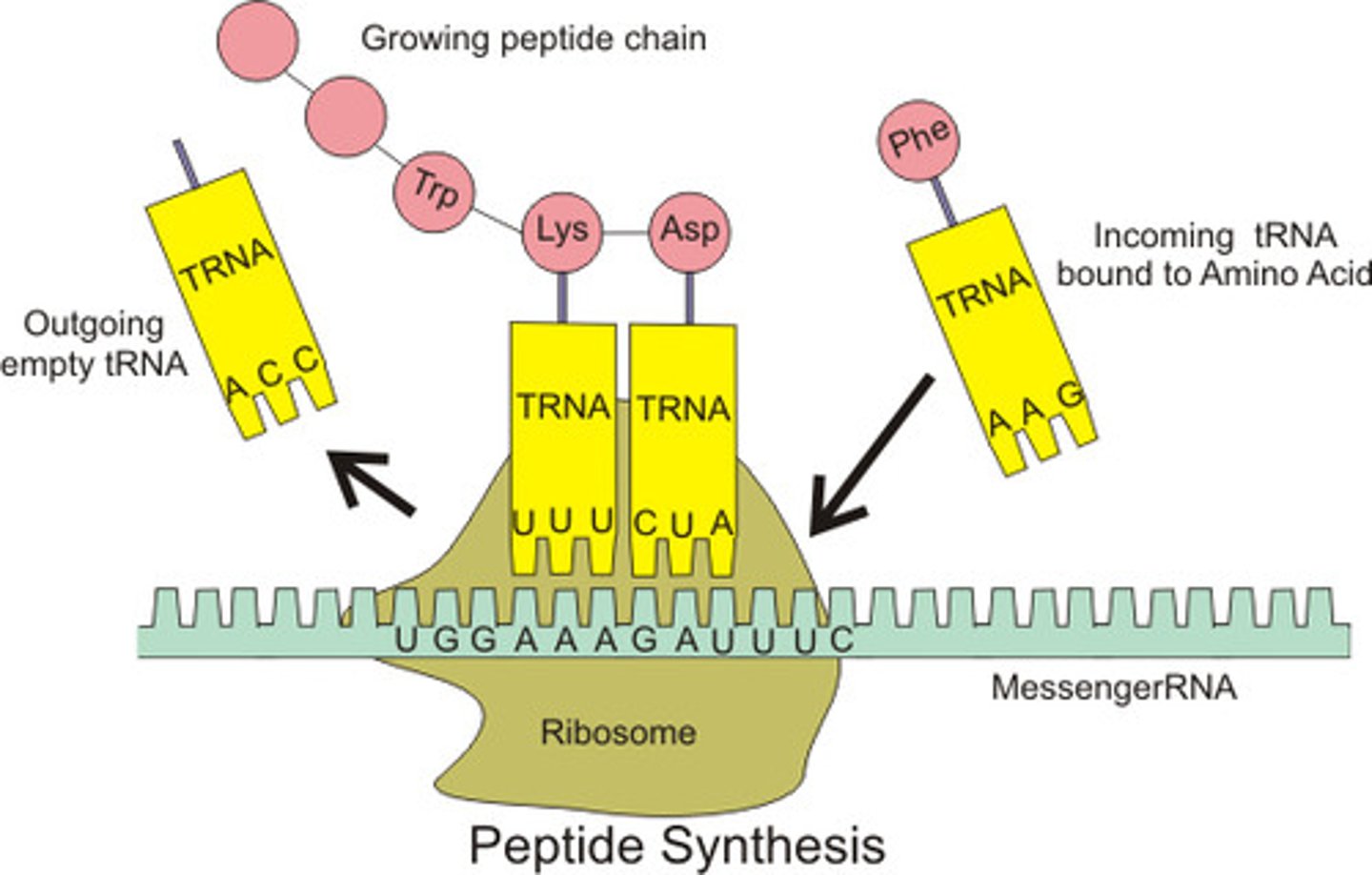
When is translation initiated
when the rRNA in the ribosome interacts with the mRNA at the start codon
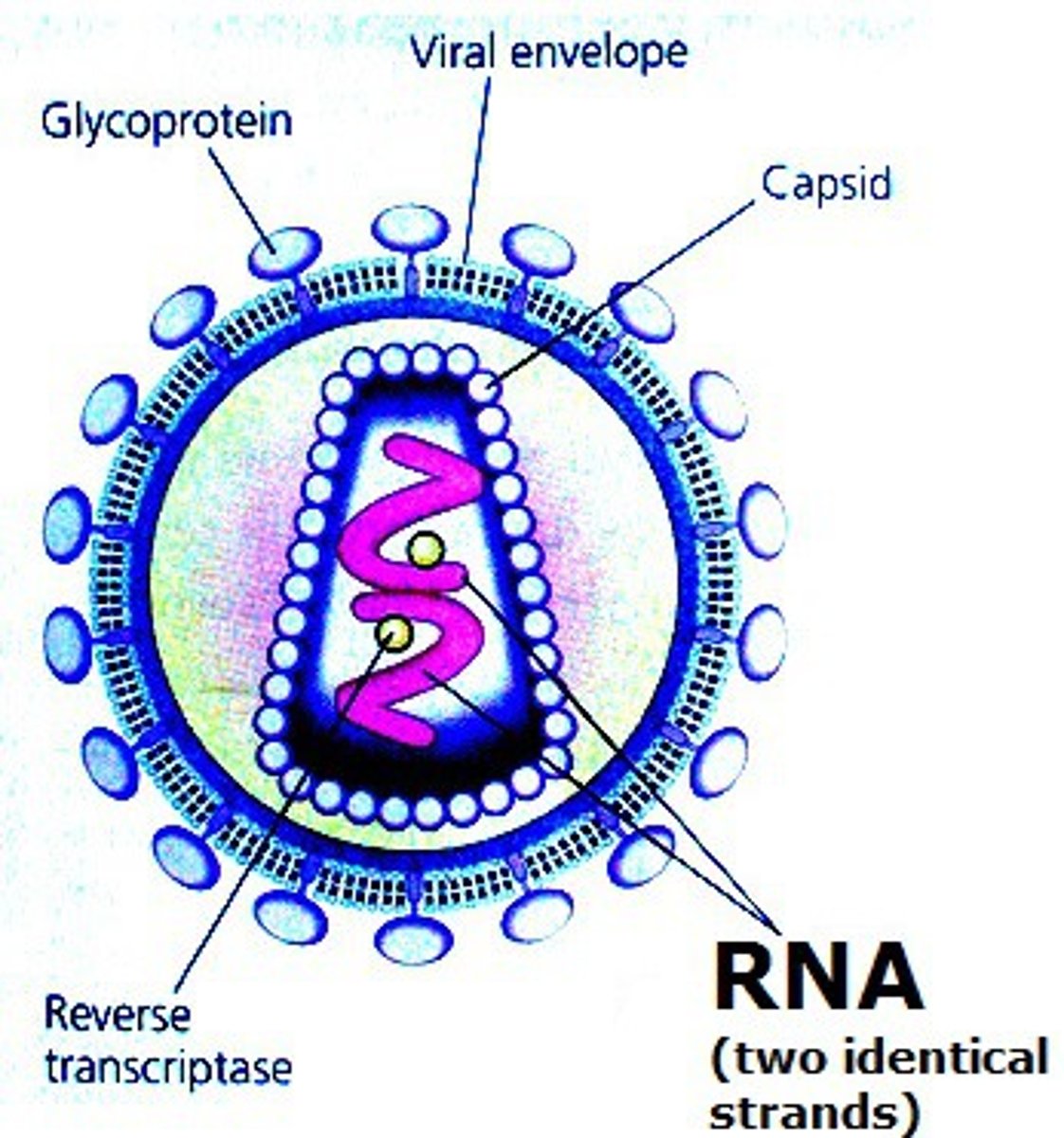
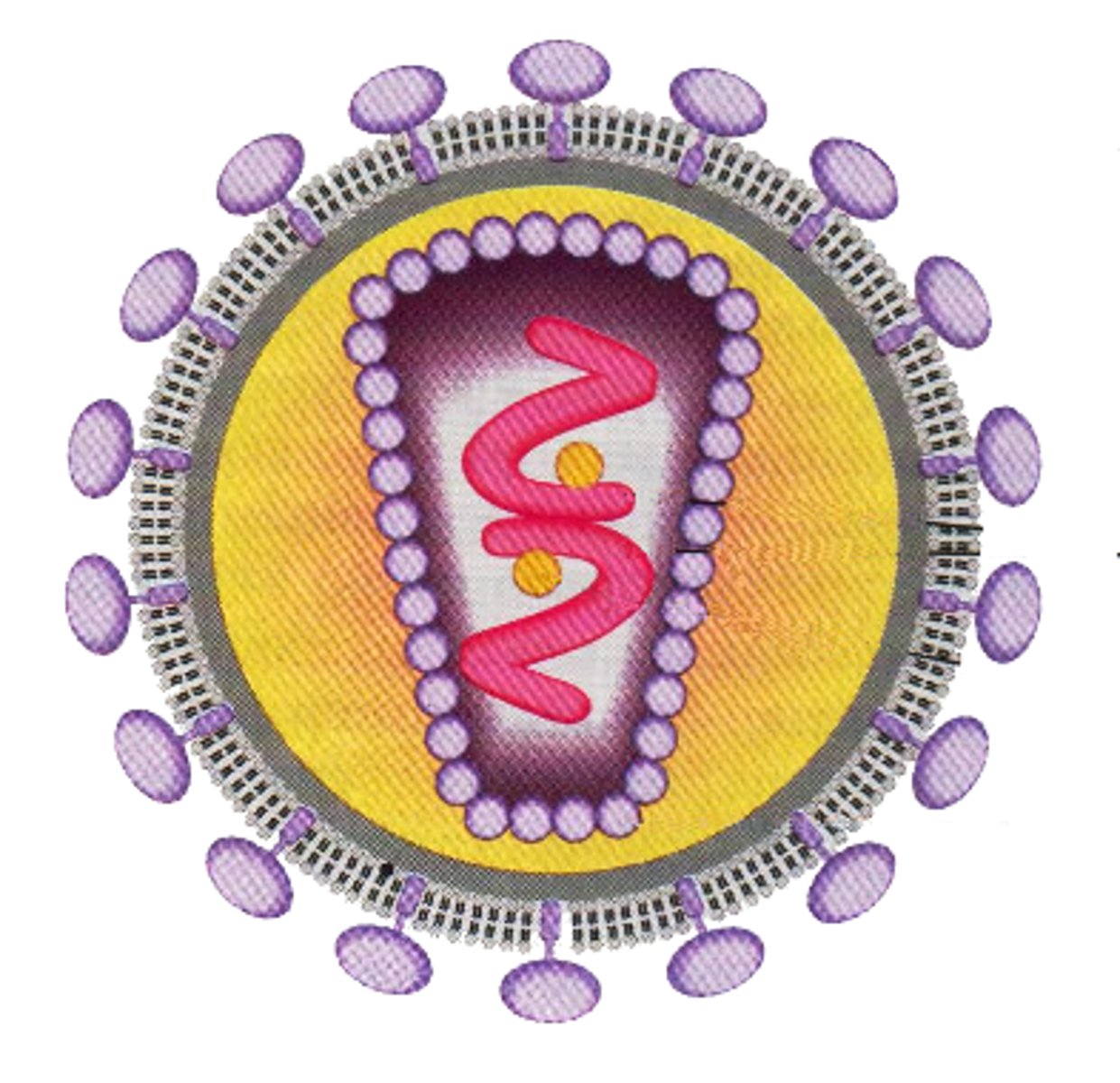
Retroviruses
use reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA genome into DNA
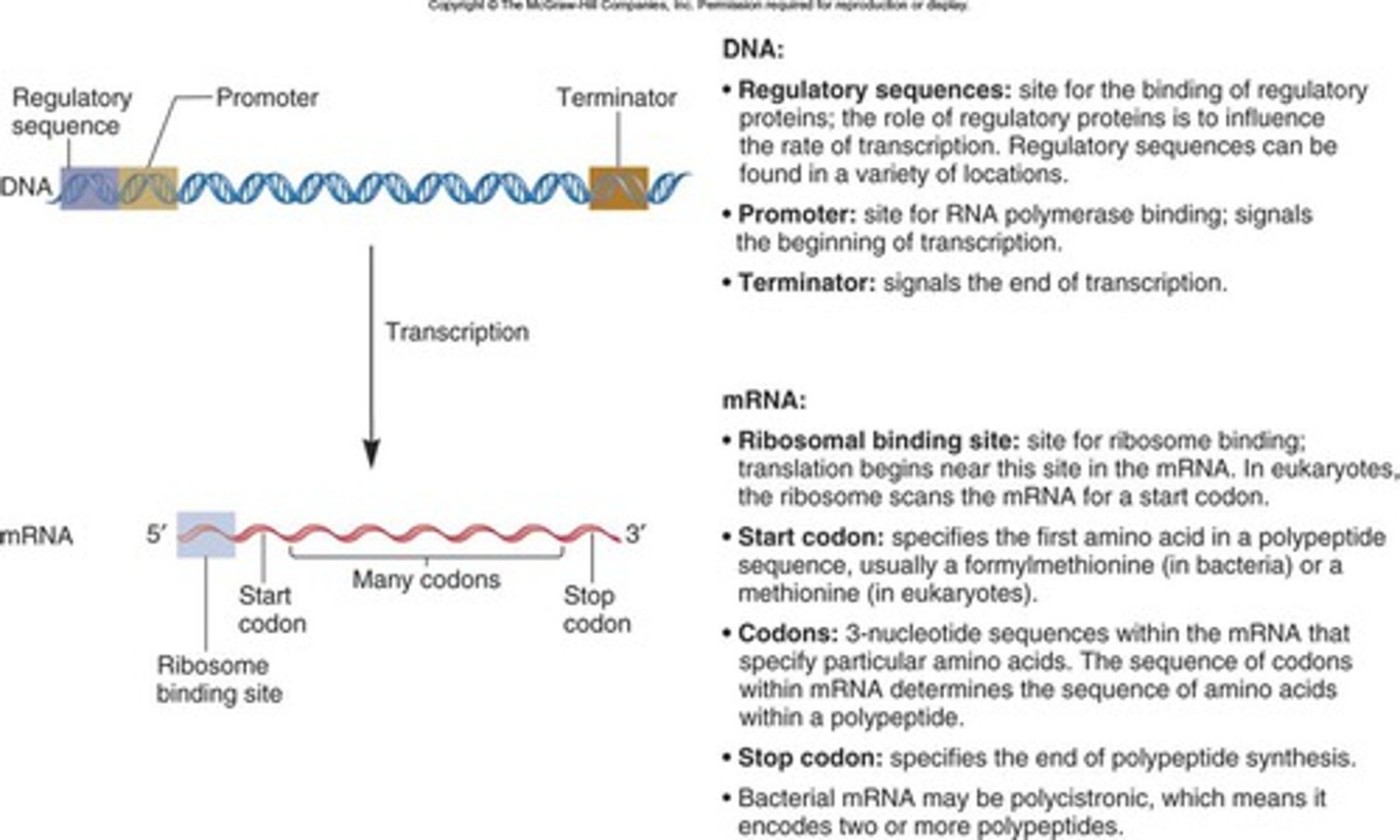
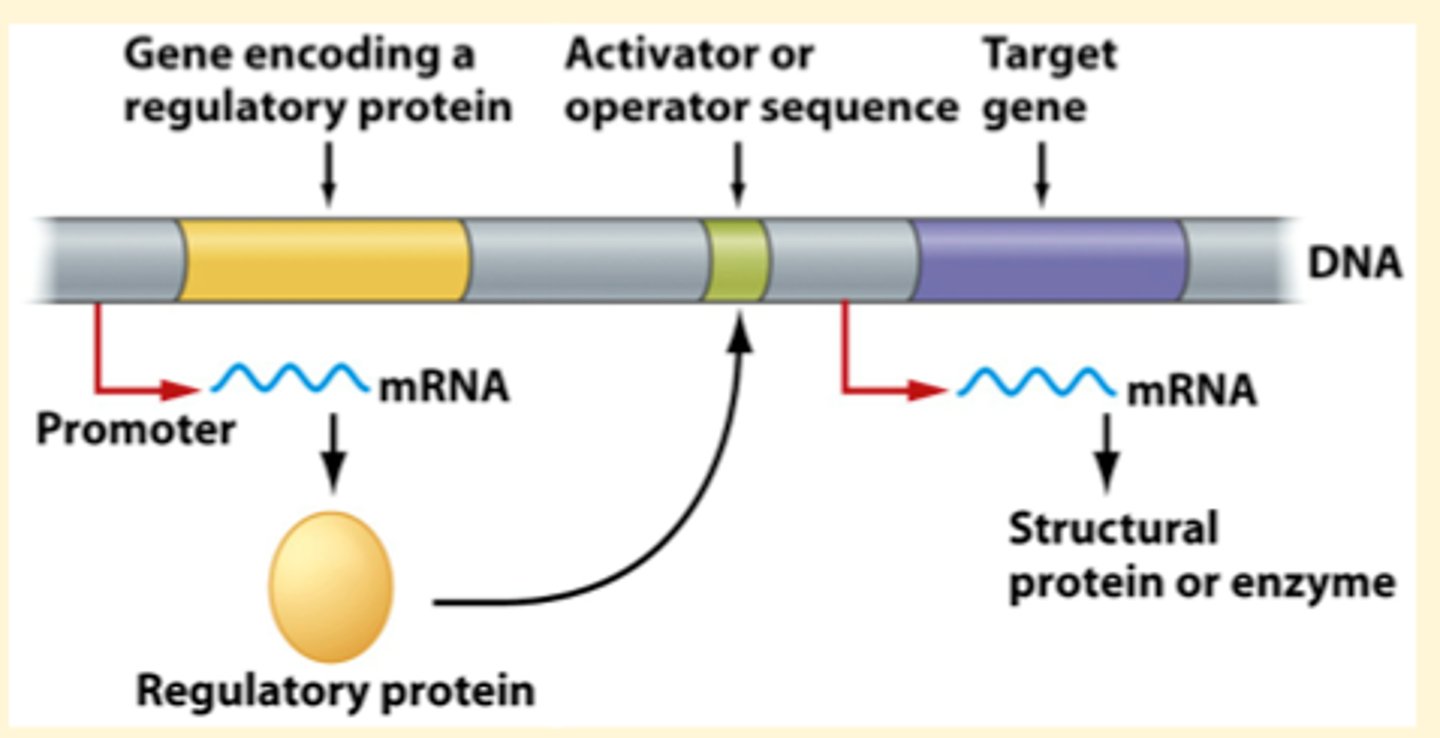
What are regulatory sequences?
Site for the binding of regulatory proteins (e.g. promoter); the role of regulatory proteins is to influence the rate of transcription.
epigenetic changes
stable alterations of chromatin structure that may be passed on to cells or individual organisms. can affect gene expression through reversible modifications or histones
How are different genes expressed in different tissues/cells?
Observable cell differentiation results
from the expression of genes for tissue-
specific proteins.
What are the group of genes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
- In prokaryotes, groups of genes called
operons are transcribed in a single mRNA
molecule. The lac operon is an example of an
inducible system.
- In eukaryotes, groups of genes may be
influenced by the same transcription factors
to coordinately regulate expression.
Why can changes in genotype can result in changes in
phenotype?
- The function and amount of gene products
determine the phenotype of organisms.
- The normal function of the genes and
gene products collectively comprises the
normal function of organisms.
- Disruptions in genes and gene products
cause new phenotypes.
What is the primary source of genetic variation?
Mutations
Central dogma of retrovirus
RNA to DNA to mRNA to protein
coding strand is also known as
non-template strand, sense strand

snRNPs
Recognize introns and snip them out
What are the important models of gene regulation?
The inducible (lac) and repressible (trp) operons.
What is a corepressor?
a molecule that cooperates with a repressor protein to switch an operon off. (essentially binds to repressor. e.g. tryptophan in trp operon).
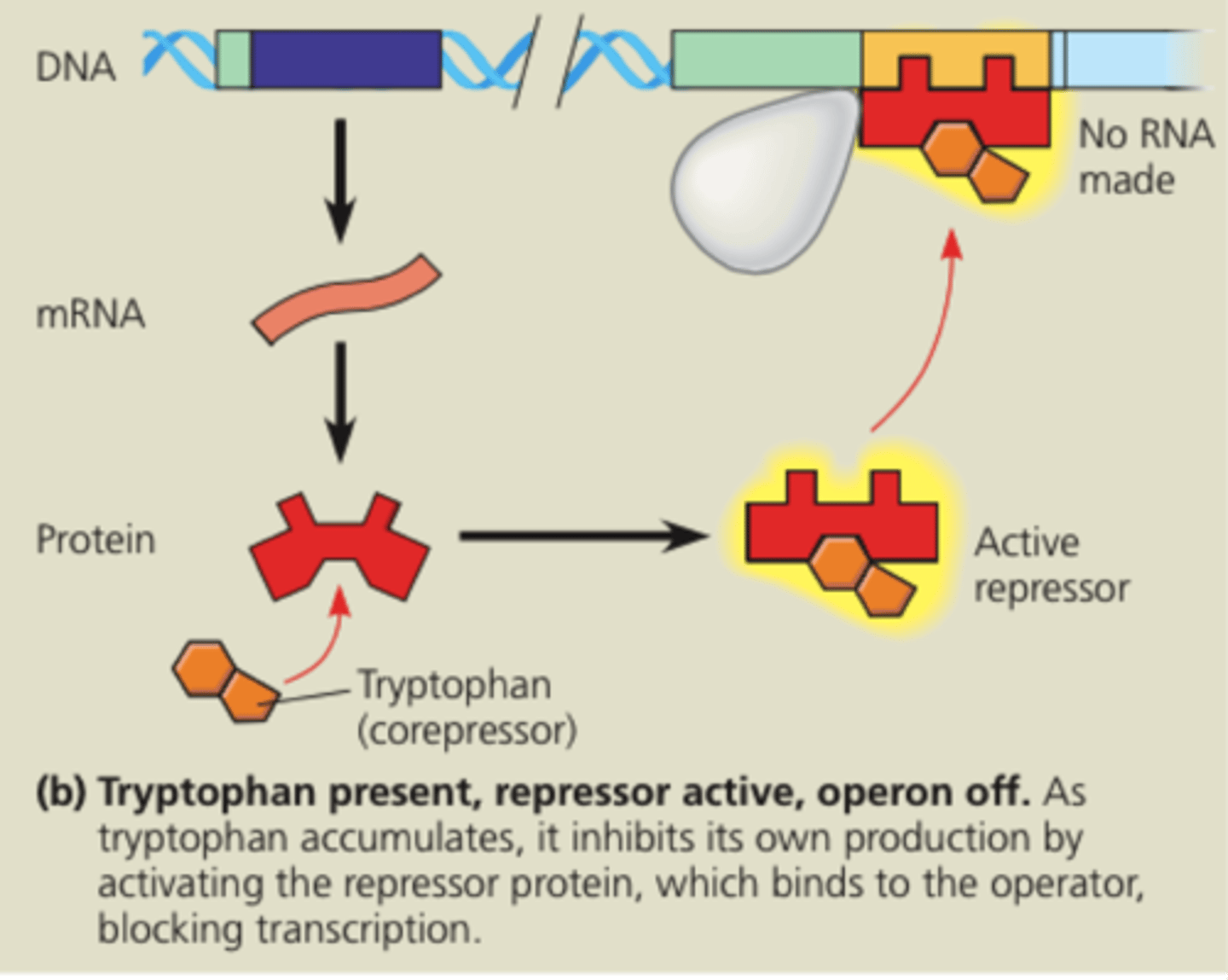
Regulatory gene
codes for repressor protein. located some distance from its operon and has its own promoter.
Regulation at the transcriptional level
- RNA polymerase must bind to the promoter to initiate transcription. This requires transcription factors (whose presence/absence enables/inhibits transcription)
Regulation at the post-transcriptional level
- alternative RNA splicing
- RNA splicing
Regulation of chromatin structure
Chemical modifications to histones and DNA
of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression.
-acetylation
-methylation
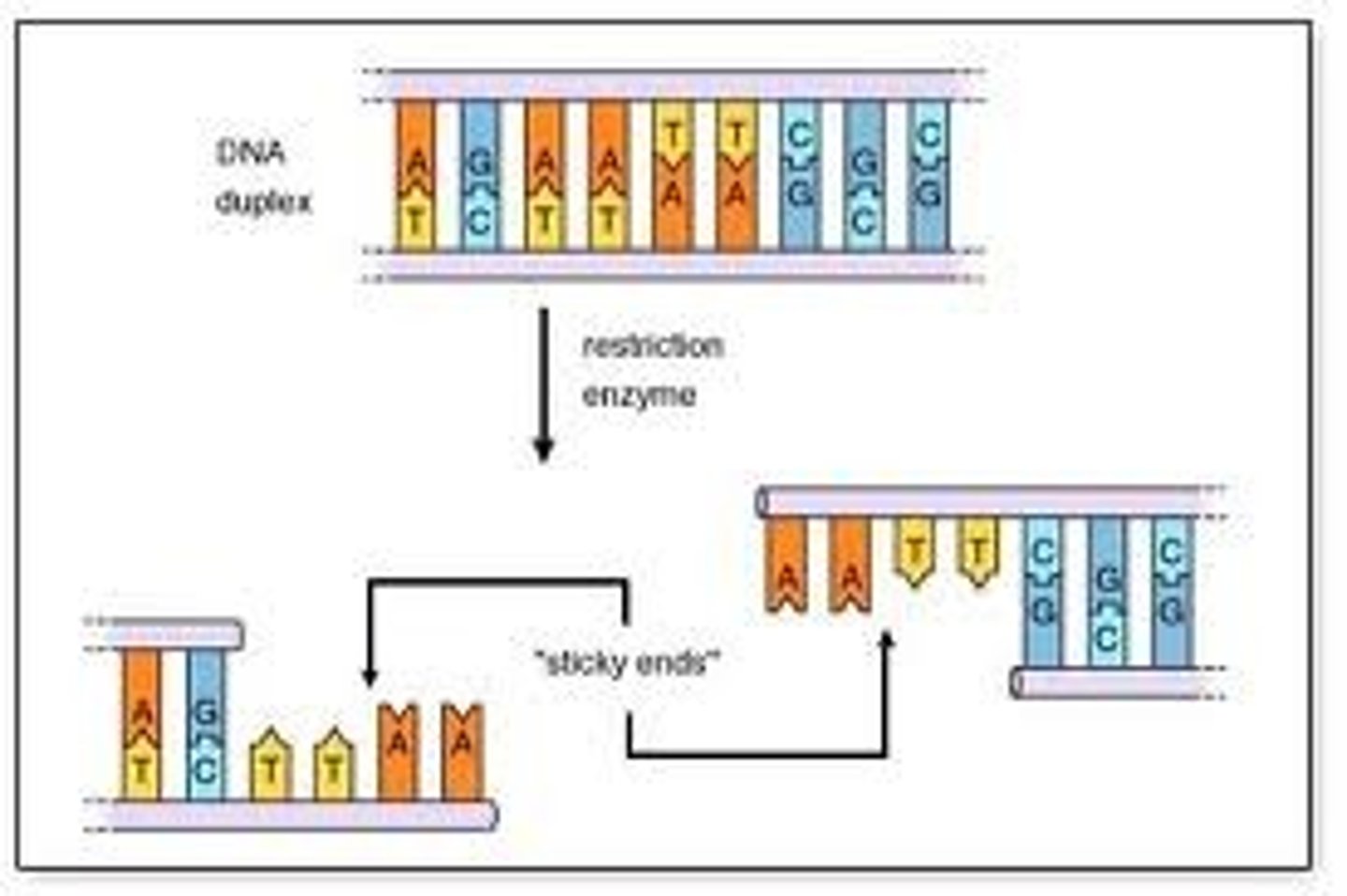
Restriction enzymes
scissors that cut at DNA at recognition sequences/sites that results in restriction fragments
Tip for determining codons:
DNA to codon(mRNA) to anticodon (tRNA).
e.g. DNA triplet = AAA, codon =UUU, anticodon= AAA