Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Lipids
The one class of biological molecules that do not include true polymers, unified by their poor mixture with water
Consist mostly of hydrocarbon regions
Biologically important types include fats, phospholipids, and steroids
Fats
Type of lipid constructed from glycerol and fatty acid molecules
Glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
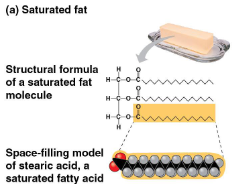
Saturated fats
Fats with the maxiumum number of hydrogen atoms and no double bonds
Solid at room temperature
Includes most animal fats
Can cause cardiovascular disease through plaque deposits
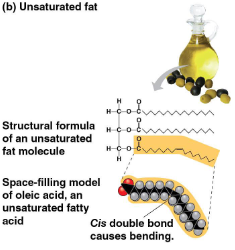
Unsaturated fats
Fats with one or more double bonds and fewer hydrogen atoms
Liquid at room temperature
Includes plant fats and fish fats
Hydrogenation
The process of converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
This leads to trans fats with double bonds in vegetable oils that can contribute to cardiovascular disease
Adipose cells
Cells used for storage in humans and other mammals that cushion the body and organs
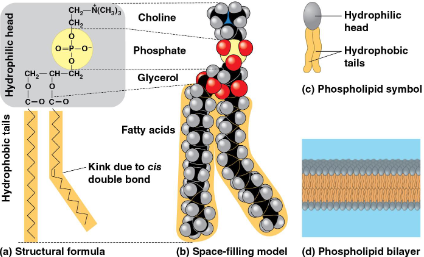
Phospholipid
Type of lipid with two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol
Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, phosphate heads are hydrophilic
In water, they assemble a bilayer with the tails toward the interior as a boundary between cells and their environment
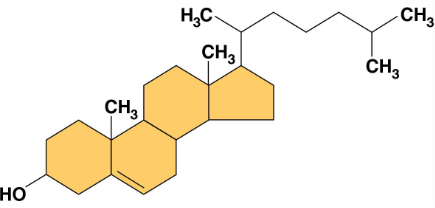
Steroids
Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
Cholesterol
A type of steroid from which animal cell membranes and other steroids are synthesized
High levels of this may contribute to cardiovascular disease