DPT 642: Radiology of the Foot & Ankle
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Medial Collateral Ligament
AKA Deltoid Ligament
Fan shape from medial malleolus to the talus, navicular and sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus
Very strong; seldom injured in isolation.
Lateral Collateral Ligament
3 distinct bands extending from lateral malleolus to the talus and calcaneus
Anterior Talofibular (ATFL)
Posterior Talofibular
Calcaneofibular
Tibiofibular Syndesmotic Complex
Considered one of the most important stabilizing structures of the ankle
Consists of 3 structures:
Anterior Tibiofibular ligament
Posterior Tibiofibular ligament
Interosseous Membrane
It's the shortest and weakest of the three lateral ankle ligaments, making it the first to fail during a sprain
why is the anterior talofibular ligamentmost commonly injured ligament
Anteroposterior (AP)
Lateral
Oblique
Basic Recommended Projections for the Foot
Anteroposterior (AP)
AP oblique (mortise)
Lateral
Basic Recommended Projections for the Ankle
Trauma
Osseous changes due to metabolic disease, systemic disease or nutritional deficiency
Neoplasms
Bone pathologies
Infections
Arthopathies (pre-op. post-op, or follow up)
Congenital syndromes or developmental disorders
Vascular lesions
Evaluation of soft tissue
Pain
indication for radiographs of the foot/ankle
Anteroposterior of Ankle (AP)
Demonstrates distal tibia and fibula including the medial and lateral malleoli and dome of talus
AP Oblique (mortise view) of Ankle
Demonstrates the entire ankle mortise.
Achieved by internally rotating the leg 15-20 degrees to place both malleoli in the same plane
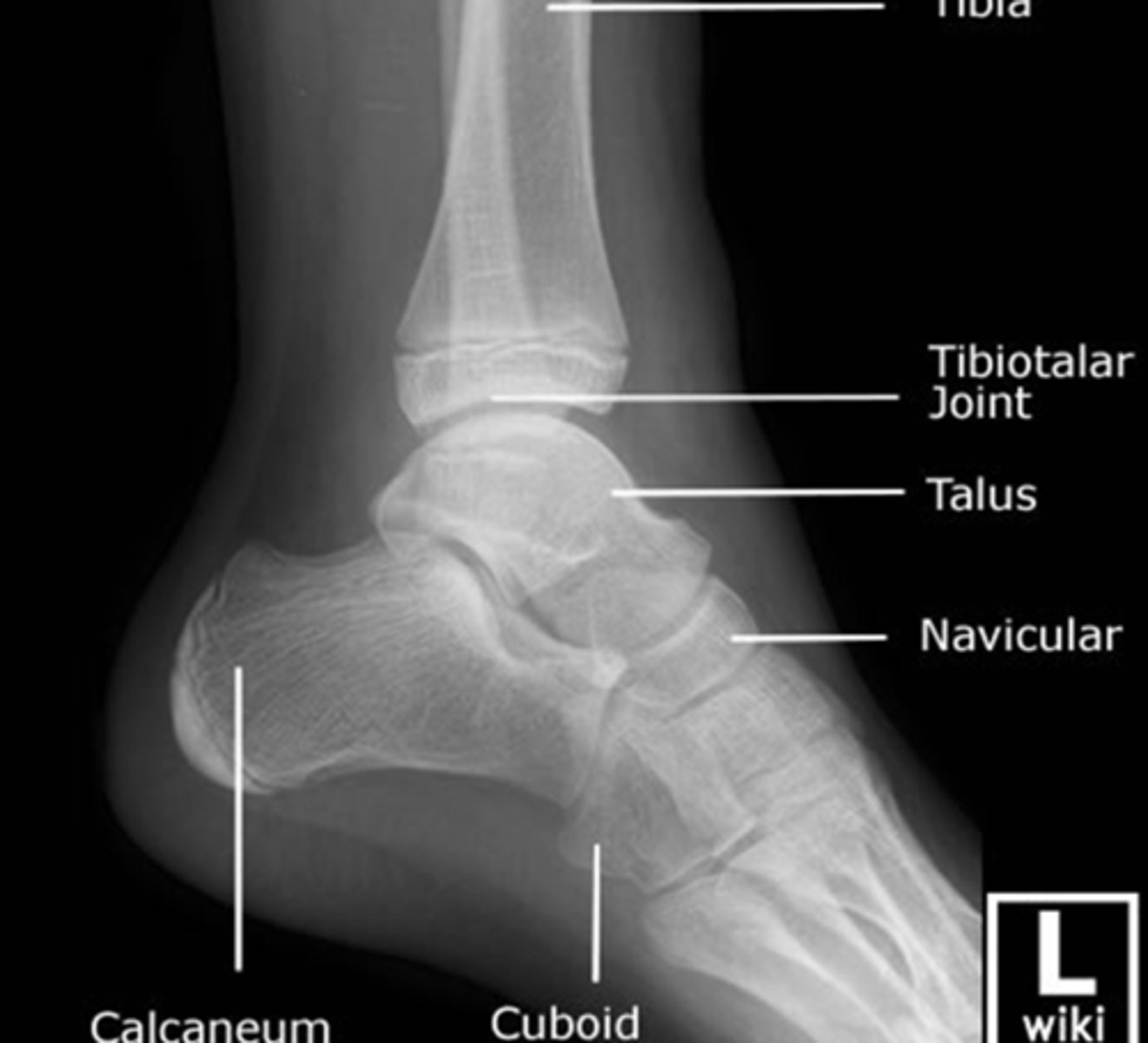
Lateral view of the Ankle
Demonstrates the anterior and posterior aspects of the distal tibia, lateral relationship of the tibiotalar and subtalar articulations, the talus and the calcaneus
Lateral view of the Ankle
Observe:
Fibula is superimposed behind the posterior tibia and talus
Anterior tubercle and posterior rim of the tibia are well demonstrated
Subtalar joint
Talus & Calcaneus seen clearly and their articulations with the navicular and cuboid bones.
Stress views of ankle
consists of AP inversion and eversion and anterior talar drawer
Anteriorposterior view of foot
Demonstrates:
Phalanges
Metatarsals
Cuneiforms
Cuboid
Navicular
Sesamoid Bones?
Possible at Met heads 1-3
First Intermetatarsal Angle
Transverse Tarsal Joint (Chopart)
Tarsometatarsal Joint (Lisfranc)
Lateral view of foot
Demonstrates:
Calcaneus
Talus
Subtalar Joint
Chopart
Lisfranc
Tarsal Sinus
Boehler angle AKA tuberosity or Salient angle
Calcaneal Inclination Angle
Oblique view of foot
Foot and leg are medially rotated as a unit approximately 45 degrees from AP view
Severe Trauma
Complex Fractures & Dislocations
Loose Bodies
OCD lesion
Tarsal Coalition
Pre-op Planning
indications for CT of foot/ankle
Alignment of Anatomy
Bone Density
Cartilage and Joint Spaces
Soft Tissues
ABCDS of CT of foot/ankle
Alignment, bone signal, cartilage or joint spaces, edema, soft tissue
ABCDS of MRI
Achilles tendon disorders
Posterior tibial tendon disorders
Ligamentous tears
Osteochondral or articular cartilage abnormalities
Loose bodies
Plantar fasciitis, rupture or fibromatosis
Sinus tarsi syndrome
Synovial based disorders
Marrow abnormalities
Neoplasms
Infections
Arthritides
Tumors
Fractures
Trauma
Instability
Prolonged or refractory ankle pain
indications for MRI of foot/ankle
Ottawa Ankle and Foot Clinical Prediction Rule
States that x-rays should be ordered after ankle or foot trauma IF:
The patient is unable to weight bear AND
The patient has point tenderness in either the malleolar zone midfoot zone, base of fifth metatarsal or navicular
Is 100% sensitive for detecting fractures
inversion sprains
85% of all ankle sprains
Stress the Lateral Collateral ligaments
Anterior talofibular & Calcaneofibular are most commonly injured components
Typically do not result in bony involvement
eversion sprains
Stress the Medial Collateral Ligaments
Generally associated with bony damage
Avulsion fractures
Instability
Tearing of the distal tibiofibular syndesmotic complex
Sinus tarsi syndrome
Impingement syndrome
Associated Injuries with Severe Sprains may include:
Tendinitis or tendinopathy
partial tears in the tendon
tendinosis
micro tearing within the tendon with subsequent healing by disorganized collagen, which has less tensile strength than a normal tendon.
Fractures at the Ankle
MOI: generally axial or rotational loading
Classification:
Unimalleolar
Bimalleolar
Trimalleolar
Other:
Shaft fractures of fibula and tibia
Comminuted fracture of the distal tibia
Intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond or talar dome
trimalleolar fracture
indication of fracture of BOTH malleoli and the posterior rim of the tibia, sometimes called the third malleolus
bimalleolar fracture
indication of fracture of BOTH the medial and lateral malleolus
unimalleolar fracture
indication of fracture of EITHER the medial or lateral malleolus
hindfoot
most common locations for a fracture in the foot
hindfoot fracture
Calcaneal
MOI: Fall from height
*most fractured tarsal
Classified as intra-articular (three times more common) or extra-articular
Talar
MOI: large force through DF foot
midfoot fracture
Navicular
Most stress fractured tarsal
4 Types:
Dorsal avulsion at deltoid attachment
Tuberosity fractures
Body fractures
Stress fractures
forefoot fracture
MOI: direct trauma like dropping heavy object on them
Classification usually by location
First metatarsal
Second, third or fourth metatarsals
Fifth metatarsal
hallux valgus
Deformity of forefoot in which the first metatarsal is deviated medially and great toe is deviated laterally (greater than 10 degrees)
More common in females
pes cavus
claw foot"
Medial longitudinal arch is abnormally high
Etiology unknown
pes planus
"flat foot"
Classified as:
Rigid (Pathological)
Flexible (Physiological)
Low arch in weight bearing that returns to normal in NWB