Object Localization
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What dimensional information do radiographs typically provide?
Two-dimensional (2D) information
Why is localization in the third dimension important in dentistry?
To identify the position of foreign objects, pathology, impacted teeth, tooth roots/canals, etc
What are the two common approaches to obtaining 3D info from 2D radiographs?
Using two projections at right angles (e.g., periapical and occlusal)
Tube-shift technique (SLOB/Clark’s rule)
What does the right-angle technique use to determine object location?
Two radiographs taken at 90° to each other (e.g., periapical and occlusal)
What does the periapical projection localize?
Mesiodistal and superoinferior dimensions
What does the occlusal projection localize?
Mesiodistal and buccolingual dimensions
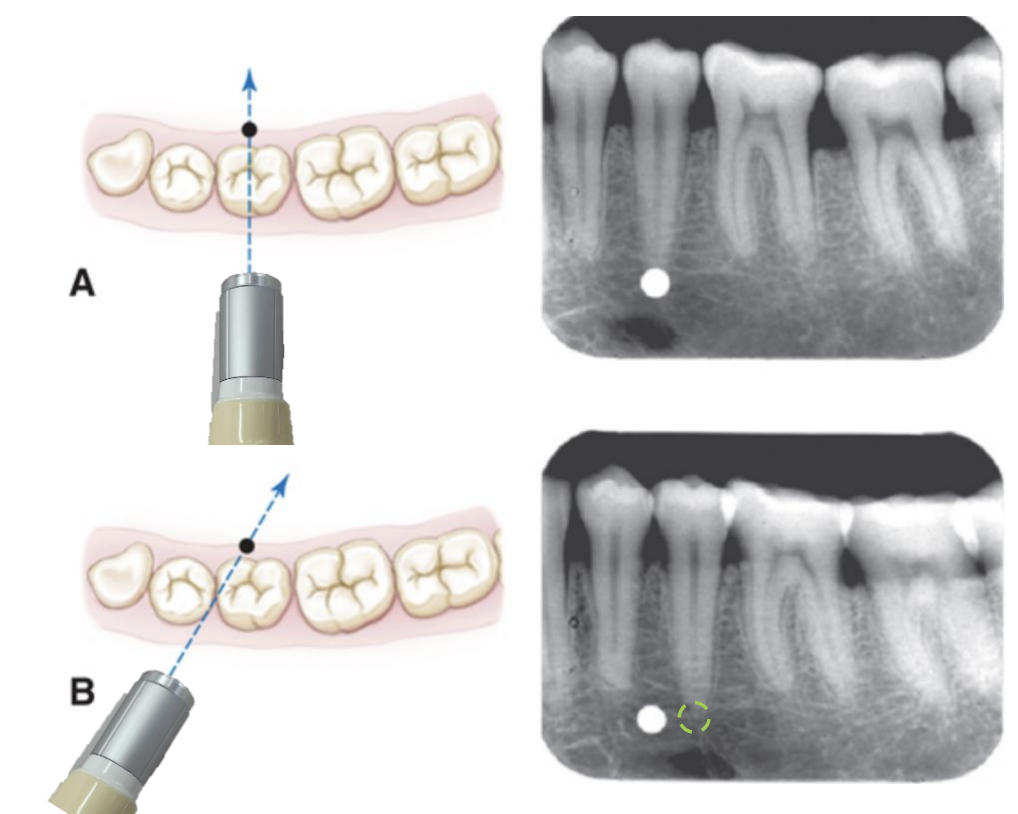
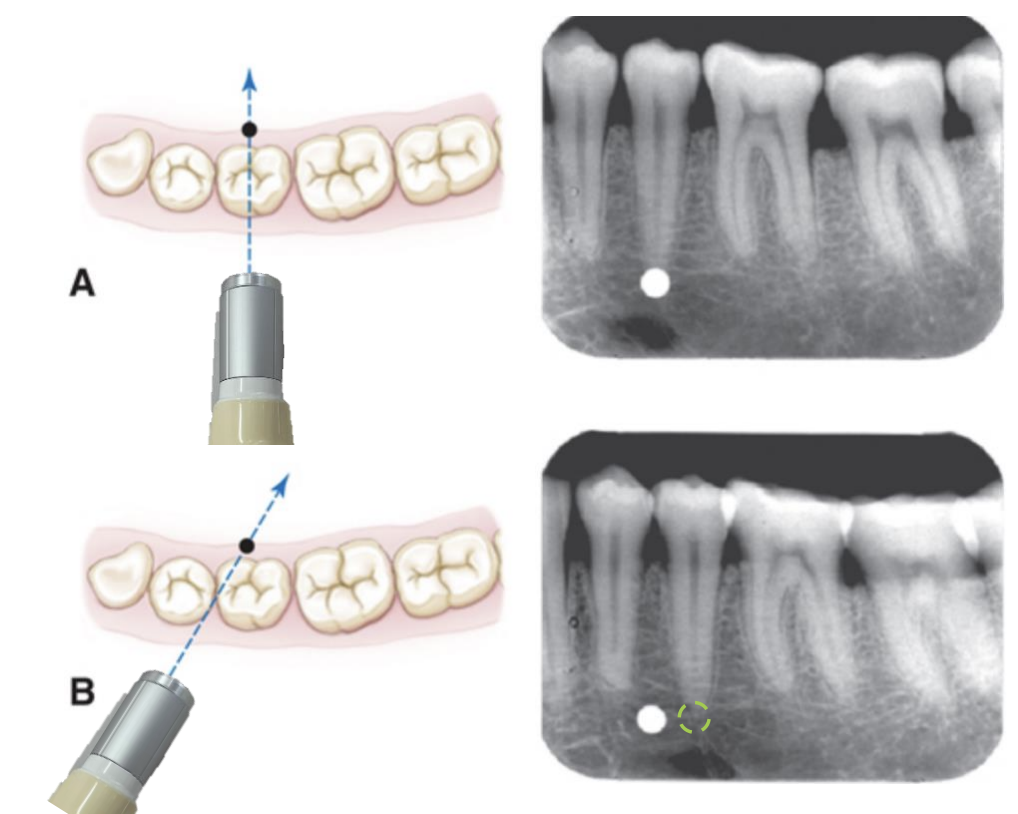
What principle is the tube-shift technique based on?
The change in the relative positions of objects when the x-ray beam angle changes
What does the SLOB rule stand for?
Same direction = Lingual object
Opposite direction = Buccal object
What does it mean if an object doesn't appear to move between radiographs?
It lies in the same vertical plane (depth) as the reference object.
What should be used as a reference when applying SLOB?
A clear, consistent anatomical or structural reference object visible in both images
What anatomical landmarks help identify tube head direction?
Mental foramen, zygomatic process, external oblique ridge, mylohyoid ridge, etc
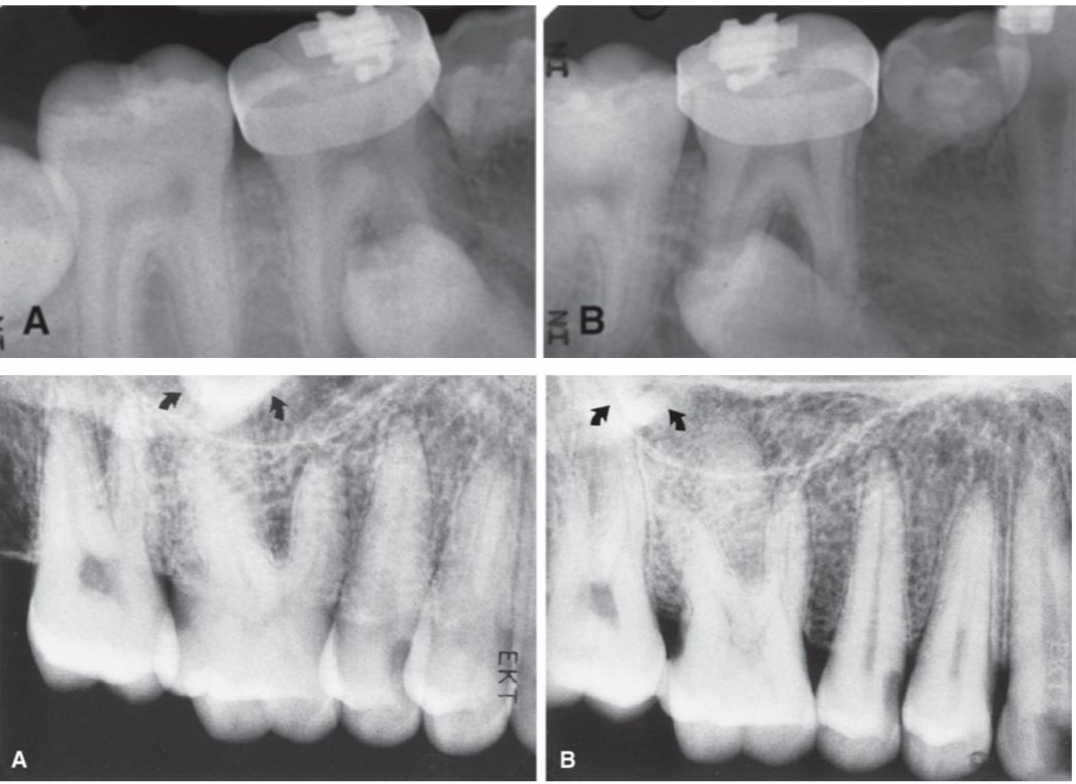
If an orthodontic bracket on tooth #30 shifts distally from image A to B, what was the direction of the tube shift?
Mesially (because buccal objects move in the opposite direction).
What affects the degree of object shift seen between two radiographs?
The degree of tube shift
The object’s distance from the reference point
Why is the tube-shift technique important in endodontics?
To separate and identify root canals, and estimate their lengths during root canal treatment
Tube Shift Technique: Lingual Object
Tube Shift Technique: Buccal Object
Tube Shift Technique: Orthodontic bracket is buccal #30
Buccal objects shift in the opposite direction from the tube
From image A to B, bracket shifts distally, so, the tube must be shifting mesially