Cellular Adaptation- PRELIMS L3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
ADAPTATION
Reversible changes in size, number, phenotype, metabolic activity, or functions of cells in response to changes in their environment.
ABNORMALITIES IN CELL GROWTH
Retrogressive changes
Progressive changes
Degenerative changes
RETROGRESSIVE CHANGES
Organs or tissues are smaller than normal
TWO MAIN TYPES OF RETROGRESSIVE CHANGES
Developmental changes- present at birth
Atrophy- acquired
DEVELOPMENTAL CHANGES
Aplasia
Agenesia
Hypoplasia
Atresia
APLASIA (DC)
Incomplete or defective development of tissue or organ, represented only by a mass of fatty or fibrous tissue, bearing no resemblance to the adult structure
Most commonly seen in one paired structures such as kidneys, gonads, adrenals

AGENESIA (DC)
Complete non-appearance of the organ
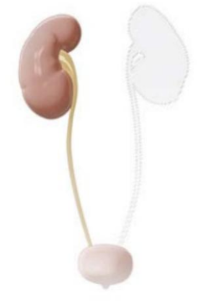
HYPOPLASIA (DC)
Failure of an organ to reach or achieve its full mature or adult size due to incomplete development
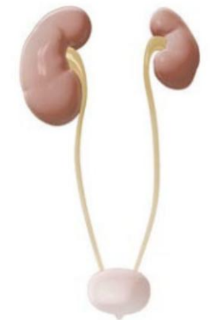
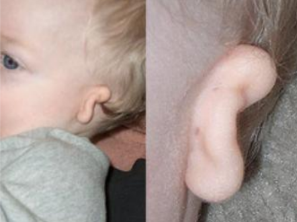
ATRESIA (DC)
Failure of an organ to form an opening
ATROPHY
Decreased cell and organ size, as a result of decreased nutrient supply of disuse
Decreased cell size and total number of cells or both
TYPES OF ATROPHY
Physiologic atrophy
Pathologic atrophy
Starvation atrophy
PHYSIOLOGIC ATROPHY
During normal development
In adult:
⚬ Thymus
⚬ Uterus during parturition
⚬ Breast tissue after lactation
PATHOLOGIC ATROPHY
Depends on the basic cause & maybe generalized or localized
STARVATION ATROPHY
Wasting of muscle
COMMON CAUSE OF ATROPHY
Decreased workload
Loss of innervation
Diminished blood supply
Inadequate nutrition
Loss of endocrine stimulation
Pressure
PROGRESSIVE CHANGES
Organs or tissues are larger than normal
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
HYPERTROPHY
Increased cell size and organ size
No new cells. Just Increased in size due to synthesis of more structural components
TYPES OF HYPERTROPHIES
True hypertrophy
False hypertrophy
Compensatory hypertrophy
TRUE HYPERTROPHY
Due to increased workload and endocrine stimulation
FALSE HYPERTROPHY
Due to edema fluid and connective tissue proliferation
COMPENSATORY HYPERTROPHY
Involves one of the paired organs when the other opposite organ has been removed or suffered functional insufficiency
HYPERLASIA
Increased in size of an organ or tissued due to increase in the number of cells resulting from growth of new cells
Does not always increase the size of an organ
Hypertrophy and Hyperplasia co-exist in many organs
Only if cells is dividing in response to hormones and growth factor
PATHOLOGICAL HYPERPLASIA
Excess hormones & GF
PHYSIOLOGICAL HYPERPLASIA
Growth of normal cells in response to a specific stimulus and remains subject to normal regulatory control mechanisms
DEGENERATIVE CHANGES
Changes due to aberration of cellular growth
Metaplasia
Dysplasia
Anaplasia
Neoplasia
METAPLASIA
Replacement of one type of cell with another type of cell
Often in response or adaptation to chronic injury.
Differentiated cell type is replaced by similarly differentiated cell
Usually induced by altered differentiation pathway of tissue stem cells; may result in reduced functions or increased propensity for malignant transformation.
DYSPLASIA
Literally means “disordered growth”
Regressive alteration in adult cells manifested by variation in size, shape and orientation.
Premalignant change
ANAPLASIA
Differentiation
Marked regressive change in adult cells towards a more embryonic cell type.
Criterion towards malignancy
NEOPLASIA
Continuous abnormal proliferation of cells without control.
Overproduction of cells leads to mass or tumor.